Gastrointestinal Helminths of Suliformes Birds from the Southern Coast of São Paulo, Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sigrist, T. The Avis Brasilis Field Guide to the Birds of Brazil: Plates and Maps; Avis Brasilis Editora: Vinhedo, Brazil, 2009; pp. 1–480. [Google Scholar]
- Sick, H. Ordem Sphenisciformes. In Ornitologia Brasileira; Nova Fronteira: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1997; pp. 186–188. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber, E.A.; Burger, J. Biology of Marine Birds; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; 722p. [Google Scholar]
- Croxall, J.P.; Prince, P.A. Cephalopods as prey I. Seabirds. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1996, 351, 1023–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Sibley, D.; Elphick, C.; Dunning, J.B. National Audubon Society. In The Sibley Guide to Bird, Life, Behavior; Alfred, A., Ed.; Knopf: New York, NY, USA, 2001; 588p. [Google Scholar]
- Del Hoyo, J.; Collar, N.J. HBW and Bird Life International Illustrated Checklist of the Birds of the World. Volume 1: Non-Passerines, 1st ed.; Lynx Edicions: Barcelona, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Furness, R.W.; Camphuysen, K.C.J. Seabirds as monitors of the marine environment. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1997, 54, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappole, J.H.; Huba’lek, Z. Birds and influenza H5N1 virus movement to and within North America. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1486–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente, J.J.; Rodrigues, H.O.; Gomes, D.C.; Pinto, R.M. Nematóides do Brasil. Parte IV. Nematóides De Aves. Rev. Bras. Zool. 1995, 12 (Suppl. 1), 1–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, J.F.R.; Monteiro, C.M.; Amato, S.B. Contracaecum rudolphii Hartwich (Nematoda, Anisakidae) from the Neotropical cormorant, Phalacrocorax brasilianus (Gmelin) (Aves, Phalacrocoracidae) in southern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Zool. 2006, 23, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, C.M.; Amato, J.F.R.; Amato, S.B. Primeiro registro de Syncuaria squamata (Linstow) (Nematoda, Acuariidae) em biguás, Phalacrocorax brasilianus (Gmelin) (Aves, Phalacrocoracidae) no Brasil. Rev. Bras. Zool. 2006, 23, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, C.M.; Amato, J.F.R.; Amato, S.B. A new species of Andracantha Schmidt (Acantocephala, Polymorphidae) parasite of Neotropical cormorants, Phalacrocorax brasilianus (Gmelin) (Aves, Phalacrocoracidae) from southern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Zool. 2006, 23, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, E.L.; Santana, R.L.S.; Mangas, T.P.; Gisele, E.G. Diversity of helminths parasitizing Phalacrocorax brasilianus (Gmelin, 1789) in the Brazilian Amazon. Braz. J. Vet. Parasitol. 2024, 33, e011824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lignon, J.S.; Cárdenas, M.Q.; Martins, N.S.; Santos, T.S.; Martins, K.R.; Silva, E.A.; Soares, M.P.; Cunha, R.C.; Monteiro, S.G.; França, R.T.; et al. First record of Contracaecum australe (Nematoda: Anisakidae) infecting Neotropic cormorant (Phalacrocorax brasilianus) (Aves: Phalacrocoracidae) in southern Brazil with a phylogenetic analysis. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2024, 55, 101106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoff, M.; Gomes, D.C. Metodologia básica para coleta e processamento de helmintos parasitos. In Conceitos e Métodos para Formação de Profissionais em Laboratórios de Saúde, Volume 5, 1st ed.; Molinaro, E.M., Caputo, L.F.G., Amendoeira, M.R.R., Eds.; EPSJV, IOC: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2012; Capítulo 3; pp. 251–281. [Google Scholar]
- De Ley, P.; Blaxter, M.L. Systematic position and phylogeny. In The Biology of Nematodes, 1st ed.; Lee, D.L., Ed.; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 2002; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.L.; Anderson, R.C.; Bartlett, C.M. Revision of the genus Syncuaria Gilbert, 1927 (Nematoda: Acuarioidea). Can. J. Zool. 1986, 64, 1186–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, J.J.; Pinto, R.M.; Noronha, D.; Carvalho, P.G. Nematode parasites of Brazilian Pelecaniformes and Trogoniformes birds: A general survey with new records for the species. Rev. Bras. Zool. 1996, 13, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbin, L.; Mattiucci, S.; Paoletti, M.; González-Acuña, D.; Nascetti, G. Genetic and Morphological Evidences for the Existence of a New Species of Contracaecum (Nematoda: Anisakidae) Parasite of Phalacrocorax brasilianus (Gmelin) from Chile and its Genetic Relationships with Congeners from Fish-eating Birds. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 476–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, O.M. Classification of the Acanthocephala. Folia Parasitol. 2013, 60, 273–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.O.; Lafferty, J.M.; Shostak, A. Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, D.R.; Luque, J.L. Community ecology of the metazoan parasites of white croaker, Micropogonias furnieri (Osteichthyes: Sciaenidae), from the coastal zone of the State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2001, 96, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque, J.L.; Alves, D.R.; Ribeiro, R.S. Community ecology of the metazoan parasites of banded croaker, Paralonchurus brasiliensis (Osteichthyes: Sciaenidae), from the coastal zone of the State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2003, 25, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.J.; Raso, T.F.; Faria, P.J.; Campos, F.P. Occurrence of Contracaecum pelagicum Johnston & Mawson 1942 (Nematoda, Anisakidae) in Sula leucogaster Boddaert 1783 (Pelecaniformes, Sulidae). Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2005, 57, 565–567. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, R.H.S.; Furtado, A.; Santos, J.N.; Giese, E.G. Contracaecum larvae: Morphological and morphometric retrospective analysis, biogeography and zoonotic risk in the Amazon. Braz. J. Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 28, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vooren, C.M.; Brusque, L.F. As Aves do Ambiente Costeiro do Brasil: Biodiversidade e Conservação; FUNBIO: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1999; 58p. [Google Scholar]
- Martini, R.; Mangini, P.R.; Lange, R.R. Seabirds health and conservation medicine in Brazil. J. Nat. Conserv. 2022, 69, 126238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, P.P.; Lugarini, C. Procellariformes e outras Aves de Ambientes Marinhos (Albatroz, Petrel, Fragata, Atobá, Biguá e Gaivota). In Tratado de Animais Selvagens, 2nd ed.; Cubas, Z.S., Silva, J.C.R., Catão-Dias, J.L., Eds.; Roca: São Paulo, Brazil, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 900–948. [Google Scholar]
- Branco, J.O.; Fracasso, H.A.A.; Machado, I.F.; Evangelista, C.L.; Hillesheim, J.C. Alimentação natural de Fregata magnificens (Fregatidae, Aves), nas Ilhas Moleques do Sul, Santa Catarina, Brasil. Rev. Bras. Ornitol. 2007, 15, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, S.D.E.; Pereira, B.B.N.; Siciliano, S.; Costa, C.H.C.; Almosny, N.R.P.; Brener, B. Contracaecum pelagicum and C. plagiaticium (Nematoda: Anisakidae) infection in Magellanic penguins (Sphenisciformes: Spheniscidae) on the coast of Rio de Janeiro State. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2013, 33, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ederlil, N.B.; Oliveira, F.C.R.; Monteiro, C.M.; Silveira, L.S.; Rodrigues, M.L.A. Ocorrência de Contracaecum pelagicum Johnston & Mawson, 1942 (Nematoda, Anisakidae) em pinguim-de-magalhães (Spheniscus magellanicus Foster, 1781) (Aves, Spheniscidae) no litoral do Espírito Santo. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2009, 61, 1006–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente, J.J.; Pinto, R.M.; Noronha, D.; Gonçalves, L. Nematode Parasites of Brazilian Ciconiiformes Birds: A General Survey with New Records for the Species. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1995, 90, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, K.R.; Correa, L.L.C.; Petry, M.V. Dieta de Nannopterum brasilianus (Aves: Phalacrocoracidae), no Sul do Brasil. Oecol. Aust. 2019, 23, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, P.; Ortega, J.; Schlatter, R. Nematode parasites of the digestive tract in Neotropic cormorant chicks (Phalacrocorax brasilianus) from the River Cruces Ramsar site in southern Chile. Parasitol. Res. 2005, 97, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Threlfall, W. Endoparasites of the Double-crested Cormorant (Phalacrocorax auritus) in Florida. Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1982, 49, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Abollo, E.; Gestal, C.; Pascual, S. Anisakid infection in the European Shag Phalacrocorax aristotelis aristotelis. J. Helminthol. 2001, 75, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Moussawi, A.A. Insights at morphological features of Contracaecum rudolphii Hartwich, 1964 (Nematoda: Anisakidae) as revealed by scanning electron microscope (SEM). J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 116–119. [Google Scholar]
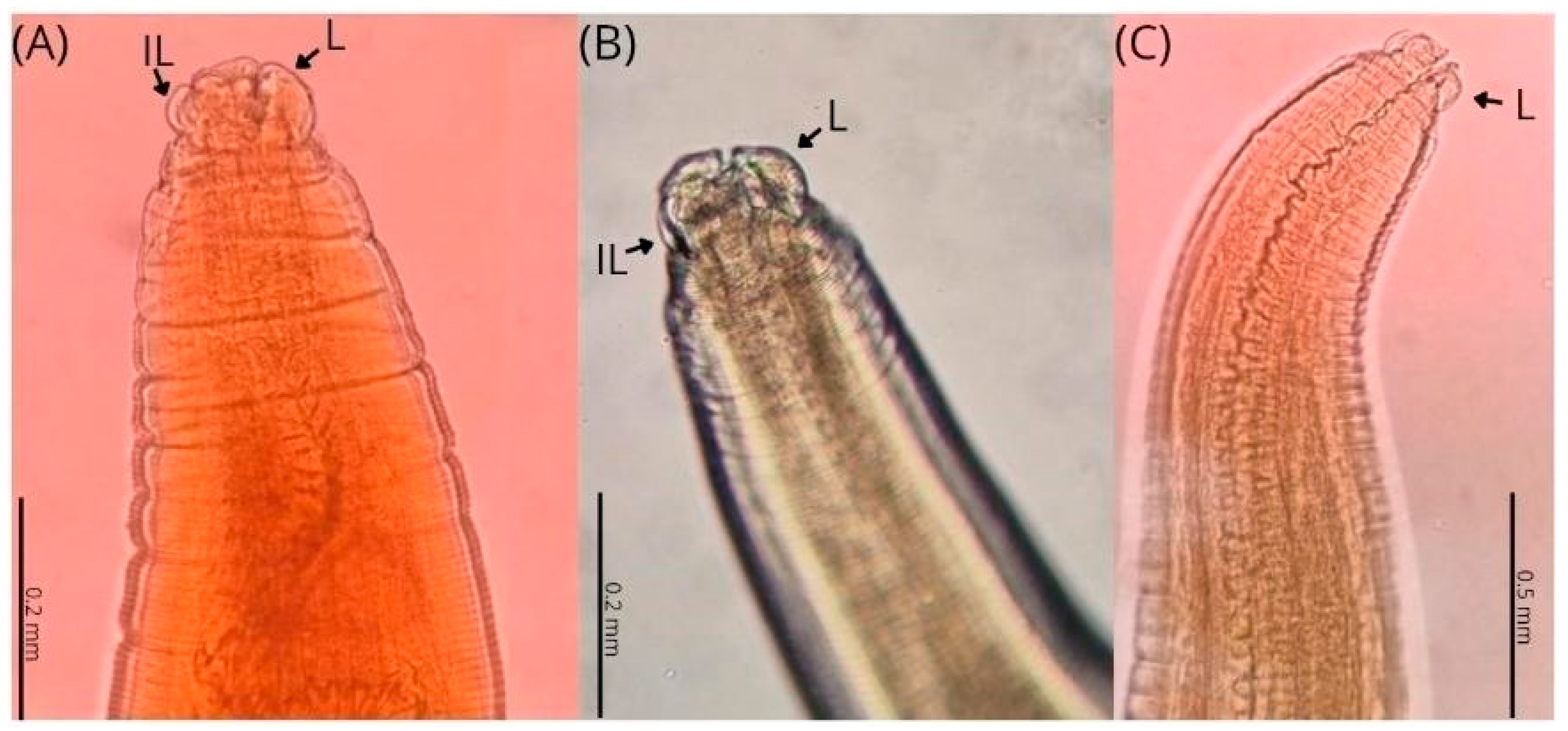
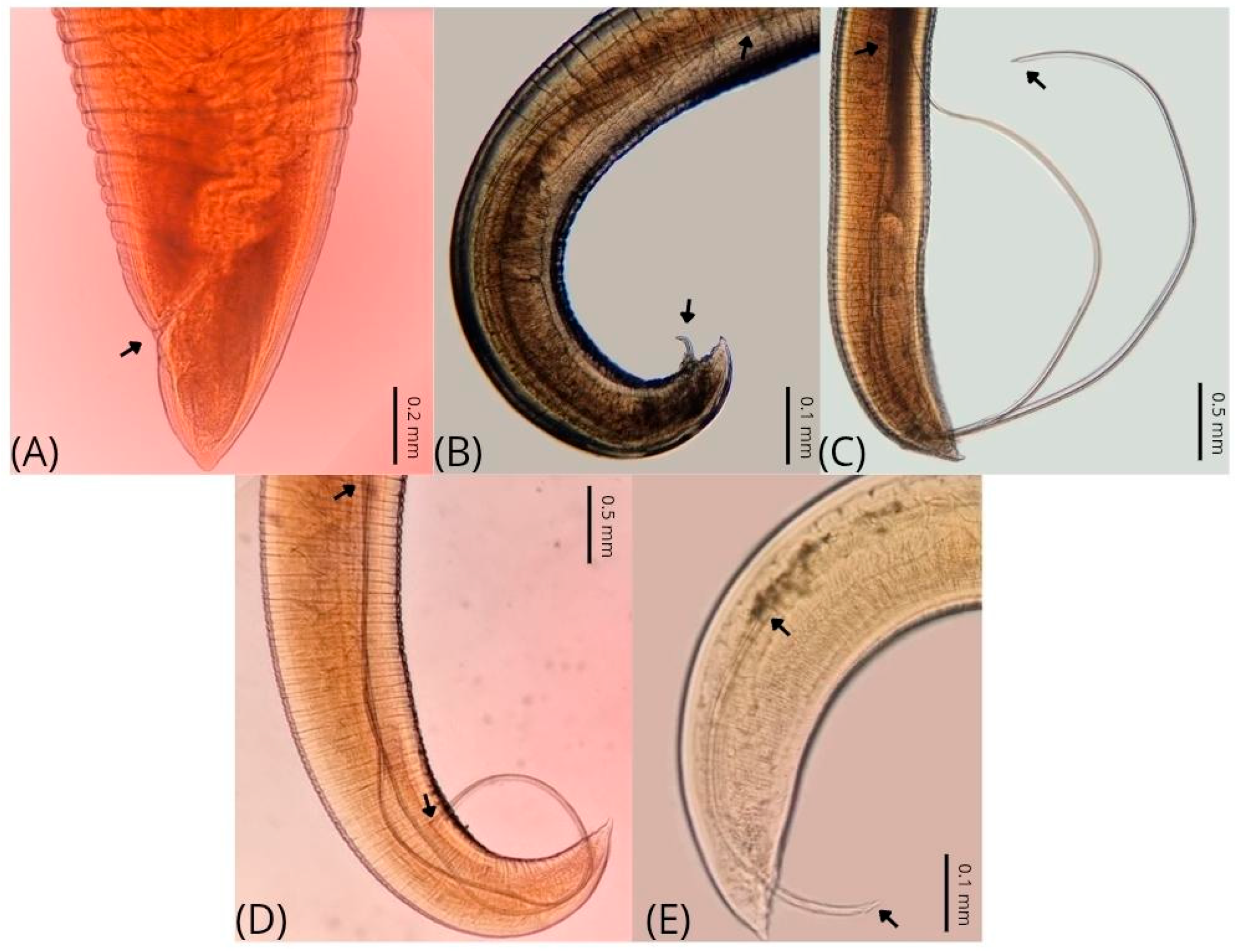
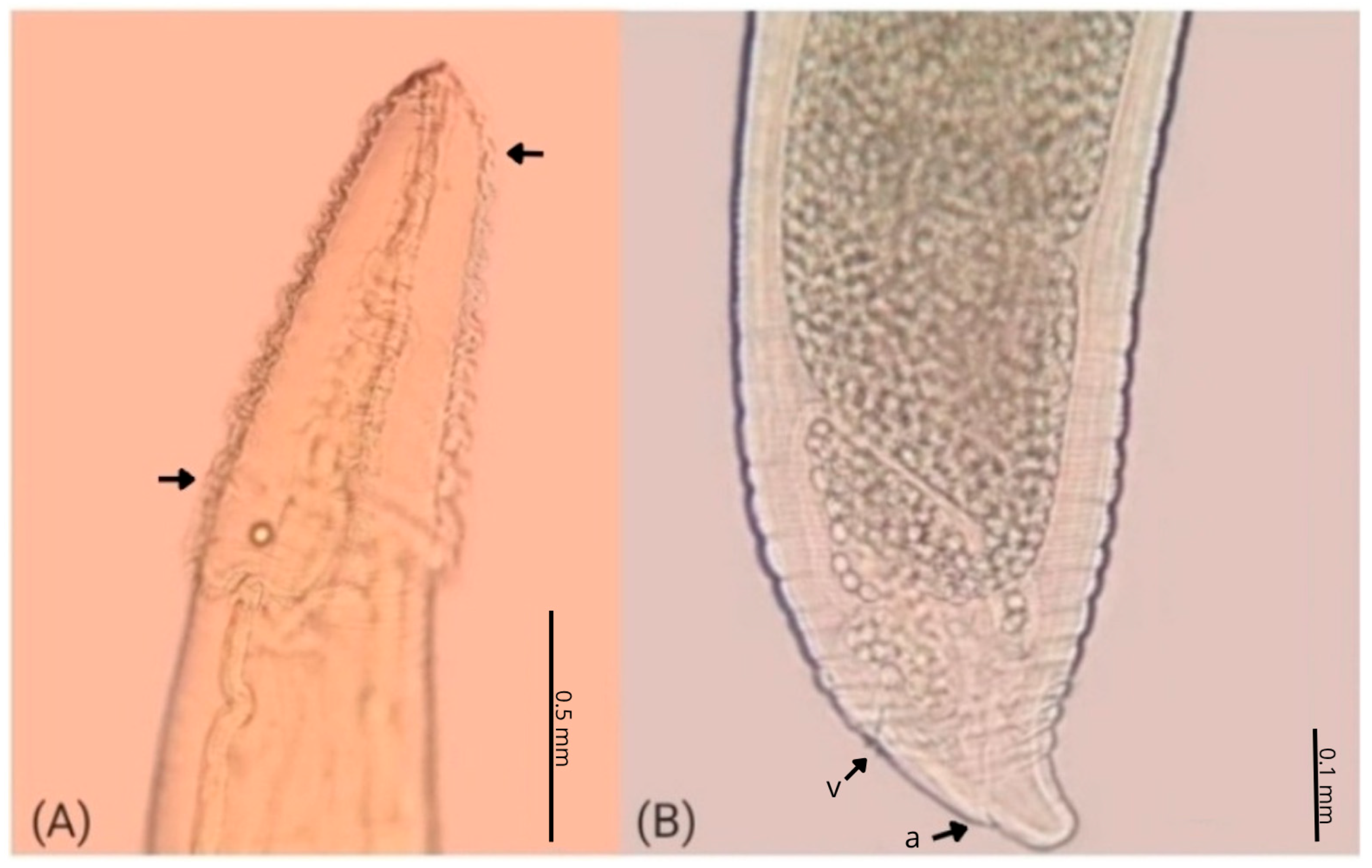
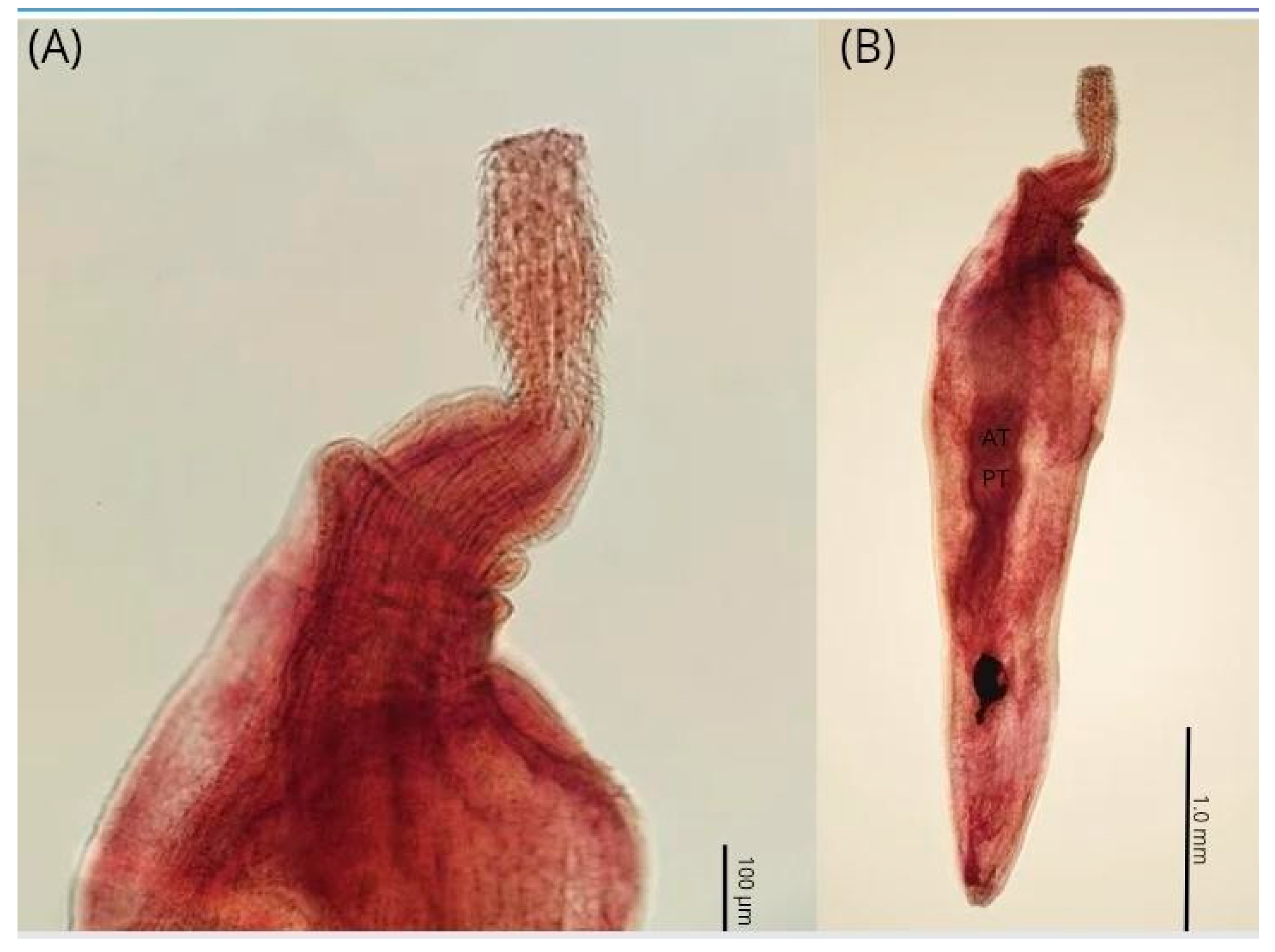
| Parameters | C. plagiaticium Male | C. plagiaticium Female |
|---|---|---|
| Total Length (mm)—Range | 16.54–17.74 | 21.66–31.60 |
| Total Length (mm)—Mean | 17.14 | 26.63 |
| Total Width (mm)—Range | 0.51–0.65 | 0.65–1.26 |
| Total Width (mm)—Mean | 0.58 | 0.95 |
| Spicules (mm)—Range | 4.09–4.27 | - |
| Spicules (mm)—Mean | 4.18 | - |
| Eggs (mm)—Range | - | 0.048 |
| Eggs (mm)—Mean | - | 0.048 |
| Vulva–Anterior End Distance (mm)—Range | - | 6.86–15.69 |
| Vulva–Anterior End Distance (mm)—Mean | - | 11.27 |
| Anus–Caudal Apex Distance (mm)—Range | - | 0.37–0.47 |
| Anus–Caudal Apex Distance (mm)—Mean | - | 0.42 |
| Parameters | C. plagiaticium Male | C. plagiaticium Female | C. pelagicum Male | C. pelagicum Female |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Length (mm)—Range | 14.80–19.90 | 16.84–30.15 | - | 36.0 |
| Total Length (mm)—Mean | 17.31 | 21.03 | - | - |
| Total Width (mm)—Range | 0.47–1.05 | 0.56–1.69 | - | 1.33 |
| Total Width (mm)—Mean | 0.67 | 1.03 | - | - |
| Spicules (mm)—Range | 2.04–3.80 | - | - | - |
| Spicules (mm)—Mean | 3.03 | - | - | - |
| Eggs (mm)—Range | - | 0.048–0.057 | - | - |
| Eggs (mm)—Mean | - | 0.050 | - | - |
| Vulva–Anterior End Distance (mm)—Range | - | 10.10–16.68 | - | 9.28 |
| Vulva–Anterior End Distance (mm)—Mean | - | 12.01 | - | - |
| Anus–Caudal Apex Distance (mm)—Range | - | 0.28–0.32 | - | 0.30 |
| Anus–Caudal Apex Distance (mm)—Mean | - | 0.29 | - | - |
| Species | Prevalence | Range of Infection | Mean Intensity/Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contracaecum australe | 40% | 19–33 | 24 |
| Contracaecum rudolphii | 50% | 4–32 | 14.4 |
| Contracaecum multipapillatum | 10% | - | 1 |
| Syncuaria squamata | 30% | 5–6 | 5.3 |
| Andracantha tandemtesticulata | 10% | - | 271 |
| Parameters | C. australe Male | C. australe Female | C. rudolphii Male | C. rudolphii Female | C. multipapillatum Male |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Length (mm)—Range | 13.20–26.27 | 18.80–46.36 | 11.04–19.74 | 15.27–36.66 | 12.52 |
| Total Length (mm)—Mean | 19.43 | 26.53 | 16.46 | 24.50 | - |
| Total Width (mm)—Range | 0.51–0.94 | 0.58–1.17 | 0.30–0.82 | 0.61–1.31 | 0.50 |
| Total Width (mm)—Mean | 0.75 | 0.91 | 0.62 | 0.94 | - |
| Spicules (mm)—Range | 7.87–16.88 | - | 8.27–11.58 | - | 1.18 |
| Spicules (mm)—Mean | 13.22 | - | 9.81 | - | - |
| Eggs (mm)—Range | - | 0.048 | - | 0.048 | - |
| Eggs (mm)—Mean | - | 0.048 | - | 0.048 | - |
| Vulva–Anterior End Distance (mm)—Range | - | 5.28–11.15 | - | 5.87–10.81 | - |
| Vulva–Anterior End Distance (mm)—Mean | - | 7.93 | - | 8.09 | - |
| Anus–Caudal Apex Distance (mm)—Range | - | 0.19–0.37 | - | 0.11–0.35 | - |
| Anus–Caudal Apex Distance (mm)—Mean | - | 0.33 | - | 0.28 | - |
| Parameters | S. squamata Female |
|---|---|
| Total Length (mm)—Range | 21.15–27.49 |
| Total Length (mm)—Mean | 23.89 |
| Total Width (mm)—Range | 0.47–0.70 |
| Total Width (mm)—Mean | 0.63 |
| Cordon Length (mm)—Range | 0.82–1.20 |
| Cordon Length (mm)—Mean | 0.98 |
| Cordon Width (mm)—Range | 0.28–0.58 |
| Cordon Width (mm)—Mean | 0.38 |
| Eggs (mm)—Range | 0.028 × 0.019 |
| Eggs (mm)—Mean | 0.028 × 0.019 |
| Anus–Caudal Apex Distance (mm)—Range | 0.07–0.09 |
| Anus–Caudal Apex Distance (mm)—Mean | 0.09 |
| Vulva–Caudal Apex Distance (mm)—Range | 0.28–0.30 |
| Vulva–Caudal Apex Distance (mm)—Mean | 0.28 |
| Parameters | A. tandemtesticulata Male |
|---|---|
| Total Length (mm)—Range | 1.65–5.05 |
| Total Length (mm)—Mean | 3.59 |
| Total Width (mm)—Range | 0.47–0.98 |
| Total Width (mm)—Mean | 0.83 |
| Proboscis Length (mm)—Range | 0.45–0.63 |
| Proboscis Length (mm)—Mean | 0.52 |
| Proboscis Width (mm)—Range | 0.12–0.19 |
| Proboscis Width (mm)—Mean | 0.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brener, B.; Sena, G.; Antonello, M.; Piolla, J.; Fonseca, M.; Knoff, M. Gastrointestinal Helminths of Suliformes Birds from the Southern Coast of São Paulo, Brazil. Parasitologia 2025, 5, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5030032
Brener B, Sena G, Antonello M, Piolla J, Fonseca M, Knoff M. Gastrointestinal Helminths of Suliformes Birds from the Southern Coast of São Paulo, Brazil. Parasitologia. 2025; 5(3):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5030032
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrener, Beatriz, Guilherme Sena, Magda Antonello, Júlia Piolla, Michelle Fonseca, and Marcelo Knoff. 2025. "Gastrointestinal Helminths of Suliformes Birds from the Southern Coast of São Paulo, Brazil" Parasitologia 5, no. 3: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5030032
APA StyleBrener, B., Sena, G., Antonello, M., Piolla, J., Fonseca, M., & Knoff, M. (2025). Gastrointestinal Helminths of Suliformes Birds from the Southern Coast of São Paulo, Brazil. Parasitologia, 5(3), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5030032







