Micro-Epidemiological Investigation of Echinococcus multilocularis in Wild Hosts from an Endemic Area of Southwestern Hungary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
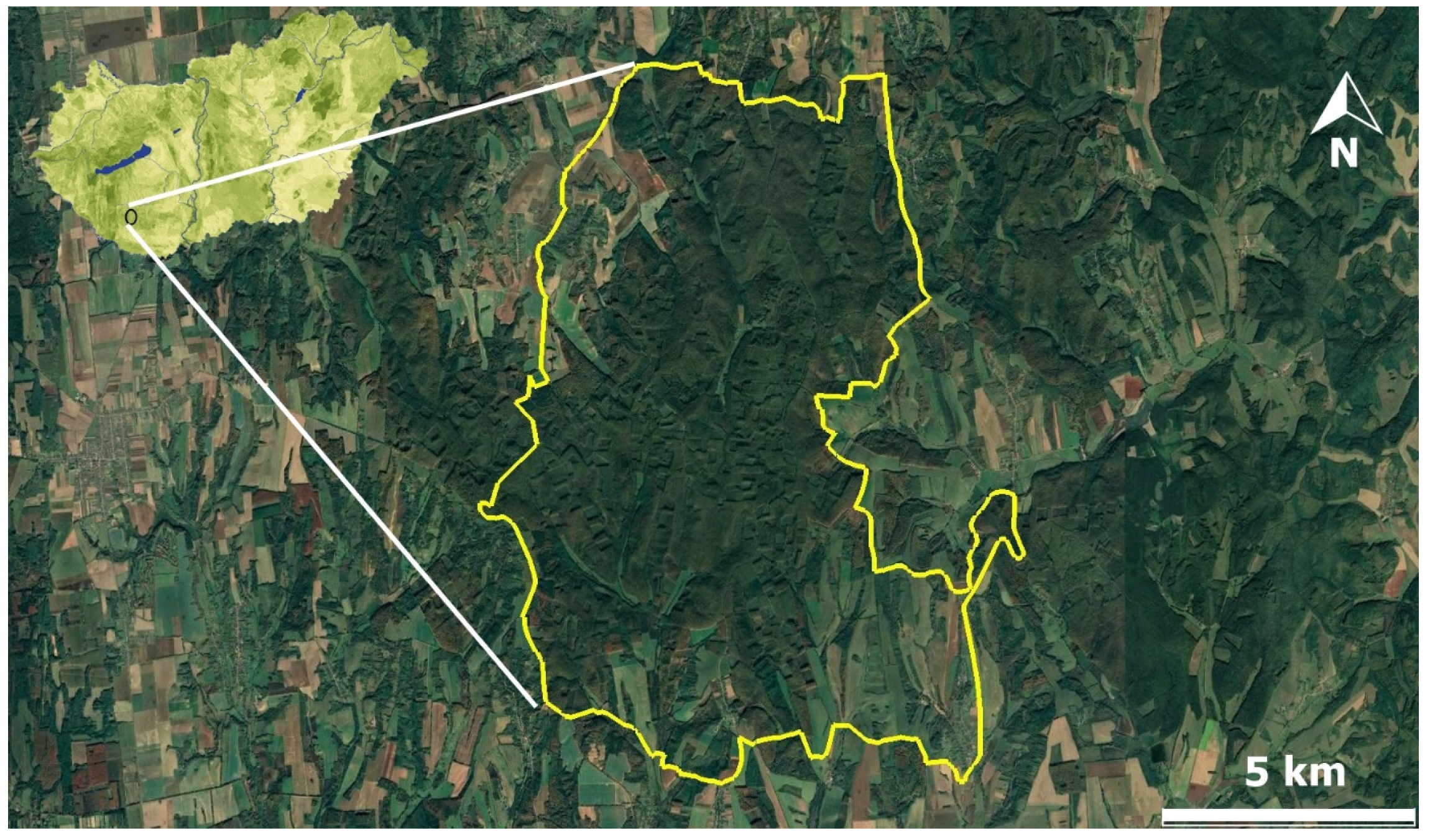
4.1. Study Site
4.2. Parasitological Examination
4.3. Molecular Diagnostic Method
4.4. Spatial Cluster Analysis
4.5. Land Cover Data
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baumann, S.; Shi, R.; Liu, W.; Bao, H.; Schmidberger, J.; Kratzer, W.; Li, W.; Interdisciplinary Echinococcosis Working Group Ulm. Worldwide literature on epidemiology of human alveolar echinococcosis: A systematic review of research published in the twenty-first century. Infection 2019, 47, 703–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2018. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2016. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e05077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezsényi, B.; Dubóczki, Z.; Strausz, T.; Csulak, E.; Czoma, V.; Káposztás, Z.; Fehérvári, M.; Somorácz, Á.; Csilek, A.; Oláh, A.; et al. Emerging human alveolar echinococcosis in Hungary (2003-2018): A retrospective case series analysis from a multi-centre study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, A.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Karamon, J.; Possenti, A.; Conraths, F.J.; Romig, T.; Wysocki, P.; Mannocci, A.; Mipatrini, D.; La Torre, G.; et al. The geographical distribution and prevalence of Echinococcus multilocularis in animals in the European Union and adjacent countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegglin, D.; Bontadina, F.; Deplazes, P. Human-wildlife interactions and zoonotic transmission of Echinococcus multilocularis. Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.C.; Marx, M.; Peyerl-Hoffmann, G.; Kern, W.V. Spatial distribution and incidence trend of human alveolar echinococcosis in southwest Germany: Increased incidence and urbanization of the disease? Infection 2020, 48, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolnai, Z.; Széll, Z.; Sréter, T. Environmental determinants of the spatial distribution of Echinococcus multilocularis in Hungary. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 198, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balog, T.; Nagy, G.; Halász, T.; Csányi, E.; Zomborszky, Z.; Csivincsik, Á. The occurrence of Echinococcus spp. in golden jackal (Canis aureus) in southwestern Hungary: Should we need to rethink its expansion? Parasitol. Int. 2021, 80, 102214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Széll, Z.; Marucci, G.; Pozio, E.; Sréter, T. Echinococcus multilocularis and Trichinella spiralis in golden jackals (Canis aureus) of Hungary. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 197, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalošević, D.; Lalošević, V.; Simin, V.; Miljević, M.; Čabrilo, B.; Bjelić Čabrilo, O. Spreading of multilocular echinococcosis in southern Europe: The first record in foxes and jackals in Serbia. Vojvodina Province. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2016, 62, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindičić, M.; Bujanić, M.; Štimac, M.; Martinković, M.; Tuškan, N.; Špehar, M.; Konjević, D. First identification of Echinococcus multilocularis in golden jackals in Croatia. Acta Parasitol. 2018, 63, 654–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.; Bjørnstad, O.N.; Dobson, A.P.; Merler, S.; Pogalyen, G.; Randolphy, S.E.; Read, A.F.; Skopping, A. The Ecology of Wildlife Diseases, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 6–44. [Google Scholar]
- Lucherini, M.; Lovari, S. Habitat richness affects home range size in the red fox Vulpes vulpes. Behav. Process. 1996, 36, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šálek, M.; Červinka, J.; Banea, O.C.; Krofel, M.; Ćirović, D.; Selanec, I.; Penezić, A.; Grill, S.; Riegert, J. Population densities and habitat use of the golden jackal (Canis aureus) in farmlands across the Balkan Peninsula. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2014, 60, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Tolhurst, B.A.; Zhu, M. Den-site selection at multiple scales by the red fox (Vulpes vulpes subsp. montana) in a patchy human-dominated landscape. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.; Imholt, C.; Caminero-Saldaña, C.; Couval, G.; Giraudoux, P.; Herrero-Cófreces, S.; Horváth, G.; Luque-Larena, J.J.; Tkadlec, E.; Wymenga, E. Europe-wide outbreaks of common voles in 2019. J. Pest. Sci. 2020, 93, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, E.G.; Elmhagen, B.; Glen, A.S.; Letnic, M.; Ludwig, G.; McDonald, R.A. Ecosystem restoration with teeth: What role for predators? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torretta, E.; Riboldi, L.; Costa, E.; Delfoco, C.; Frignani, E.; Meriggi, A. Niche partitioning between sympatric wild canids: The case of the golden jackal (Canis aureus) and the red fox (Vulpes vulpes) in north-eastern Italy. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2021, 21, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamler, J.F.; Stenkewitz, U.; Macdonald, D.W. Lethal and sublethal effects of black-backed jackals on cape foxes and bat-eared foxes. J. Mammal. 2013, 94, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krofel, M.; Giannatos, G.; Ćirović, D.; Stoyanov, S.; Newsome, T.M. Golden jackal expansion in Europe: A case of mesopredator release triggered by continent-wide wolf persecution? Hystrix Ital. J. Mammal. 2017, 28, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, H.; Ito, K.; Peeva, S.; Raichev, E.; Kaneko, Y. Spatial and temporal separation between the golden jackal and three sympatric carnivores in a human-modified landscape in central Bulgaria. Zool. Ecol. 2018, 28, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanszki, J.; Heltai, M. Food preferences of golden jackals and sympatric red foxes in European temperate climate agricultural area (Hungary). Mammalia 2010, 74, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheinin, S.; Yom-Tov, Y.; Motro, U.; Geffen, E. Behavioural responses of red foxes to an increase in the presence of golden jackals: A field experiment. Anim. Behav. 2006, 71, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carricondo-Sanchez, D.; Odden, M.; Kulkarni, A.; Vanak, A.T. Scale-dependent strategies for coexistence of mesocarnivores in human-dominated landscapes. Biotropica 2019, 51, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deplazes, P.; Rinaldi, L.; Alvarez Rojas, C.A.; Torgerson, P.R.; Harandi, M.F.; Romig, T.; Antolova, D.; Schurer, J.M.; Lahmar, S.; Cringoli, G.; et al. Global distribution of alveolar and cystic echinococcosis. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 315–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spassov, N.; Acosta-Pankov, I. Dispersal history of the golden jackal (Canis aureus moreoticus Geoffroy, 1835) in Europe and possible causes of its recent population explosion. Biodivers Data J. 2019, 7, e34825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannister-Tyrrell, M.; Verdonck, K.; Hausmann-Muela, S.; Gryseels, C.; Ribera, J.M.; Grietens, K.P. Defining micro-epidemiology for malaria elimination: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodin, D.G.; Jonsson, C.B.; Allen, L.J.S.; Owen, R.D. integrating landscape hierarchies in the discovery and modelling of ecological drivers of zoonotically transmitted disease from wildlife. In The Connections between Ecology and Infectious Disease, 1st ed.; Hurst, C.J., Ed.; Series Advances in Environmental Microbiology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 5, pp. 299–317. [Google Scholar]
- Hofer, S.; Gloor, S.; Müller, U.; Mathis, A.; Hegglin, D.; Deplazes, P. High prevalence of Echinococcus multilocularis in urban red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) and voles (Arvicola terrestris) in the city of Zürich, Switzerland. Parasitology 2000, 120, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traschel, D.; Deplazes, P.; Mathis, A. Identification of taeniid eggs in the faeces from carnivores based on multiplex PCR using targets in mitochondrial DNA. Parasitology 2007, 134, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulldorff, M.; Huang, L.; Pickle, L.; Duczmal, L. An elliptic spatial scan statistic. Stat. Med. 2006, 25, 3929–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjærulff, T.M.; Ersbøll, A.K.; Gislason, G.; Schipperijn, J. Geographical clustering of incident acute myocardial infarction in Denmark: A spatial analysis approach. Spat. Spatiotemporal Epidemiol. 2016, 19, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreasen, A.M.; Dehlendorff, P.B.; Knudtzen, F.C.; Bødker, R.; Jung Kjær, L.; Skarphedinsson, S. Spatial and temporal patterns of Lyme Neuroborreliosis on Funen, Denmark from 1995–2014. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, M.T.; Davis, R.A.; Blake, D.; Mills, H.; Doherty, T.S. Human impact overrides bioclimatic drivers of red fox home range size globally. Divers. Distrib. 2020, 26, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torretta, E.; Dondina, O.; Delfoco, C.; Riboldi, L.; Orioli, V.; Lapini, L.; Meriggi, A. First assessment of habitat suitability and connectivity for the golden jackal in north-eastern Italy. Mammal. Biol. 2020, 100, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiczigel, J.; Abonyi-Tóth, Z.; Singer, J. An exact confidence set for two binomial proportions and exact unconditional confidence intervals for the difference and ratio of proportions. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2008, 52, 5046–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiczigel, J.; Marozzi, M.; Fabian, I.; Rozsa, L. Biostatistics for parasitologists—A primer to Quantitative Parasitology. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques de Sá, J.P. Applied Statistics Using SPSS, STATISTICA, MATLAB and R, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 303–314. [Google Scholar]
- Swets, J.A. Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science 1988, 240, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziadinov, I.; Deplazes, P.; Mathis, A.; Mutunova, B.; Abdykerimov, K.; Nurgaziev, R.; Torgerson, P.R. Frequency distribution of Echinococcus multilocularis and other helminths of foxes in Kyrgyzstan. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 171, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Valle, D.; Ben Toh, K.; Laporta, G.Z.; Zhao, Q. Ordinal regression models for zero-inflated and/or over-dispersed count data. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 22.0; IBM Corp: Armonk, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
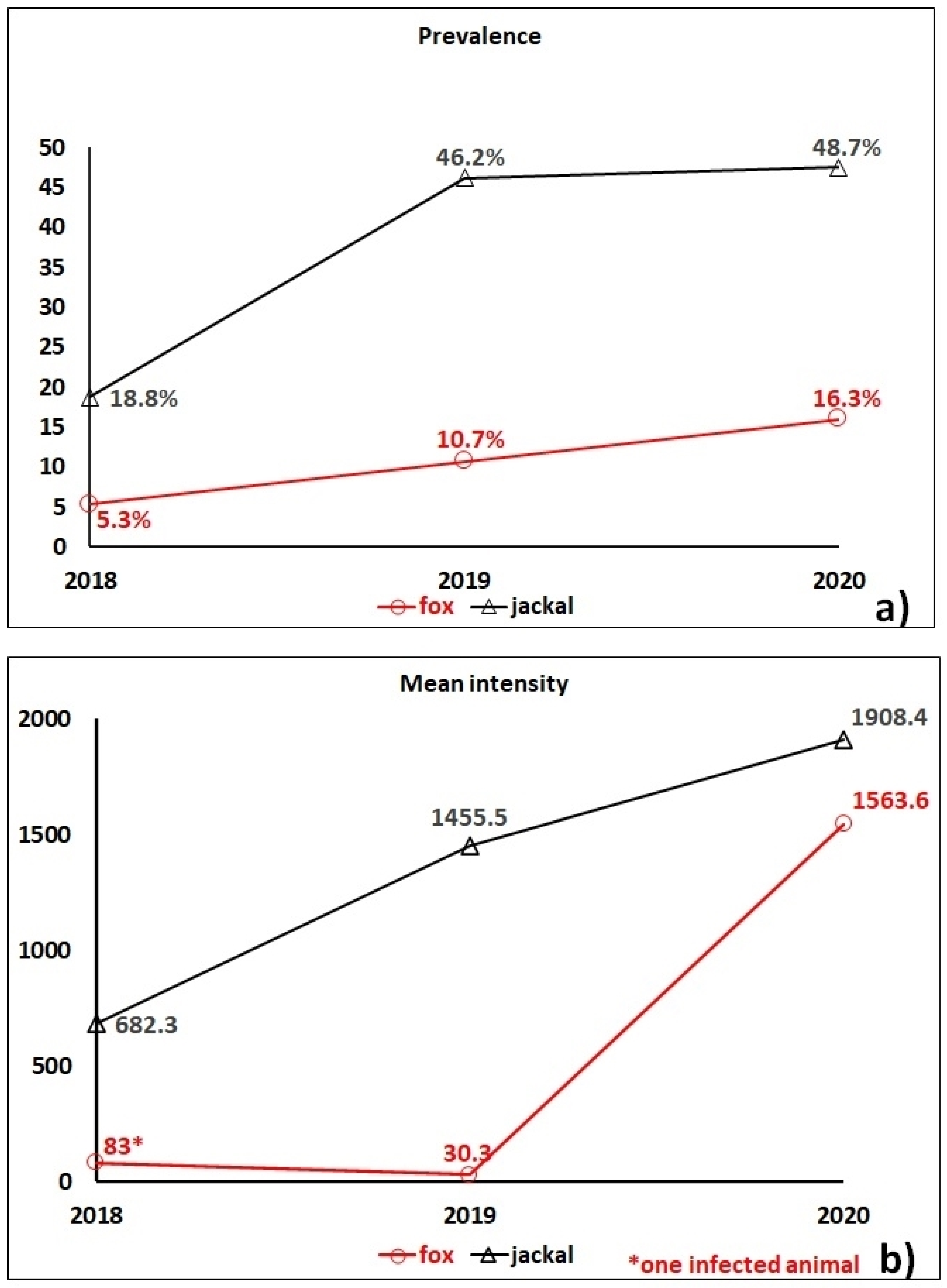
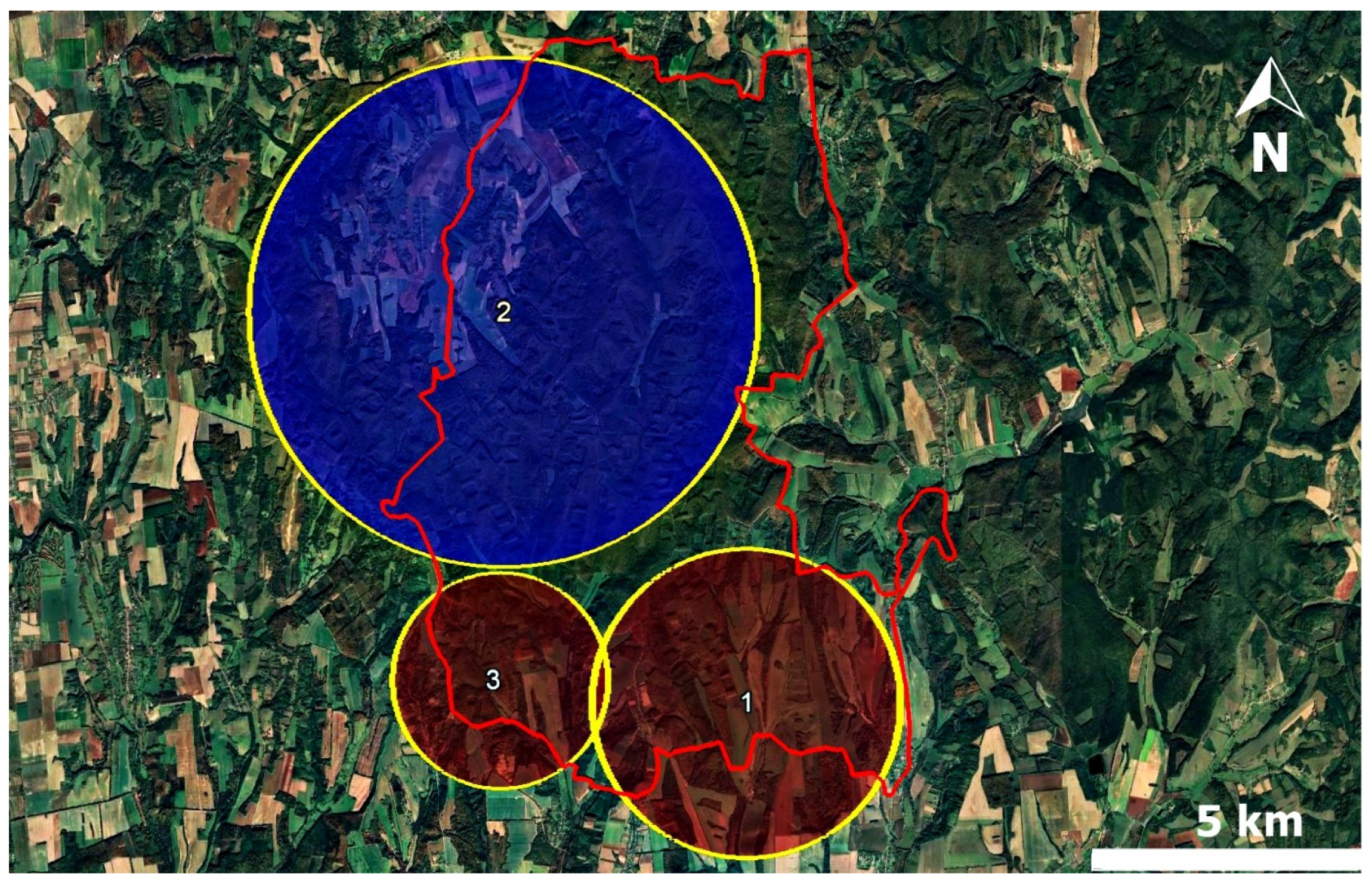
| Cluster | Radius (km) | Infected Animals | Non-Infected Animals | RR * | LLR ** | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 *** | 2.89 | 33 | 38 | 6.18 | 17.32 | <0.0001 |
| 2 | 4.77 | 4 | 77 | 0.13 | 16.38 | <0.0001 |
| 3 | 2.02 | 14 | 8 | 3.48 | 9.09 | 0.001 |
| Predictor | Coefficient | SD * | p-Value | OR ** | OR CI95% *** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| SPEC **** (fox vs. jackal) | 1.59 | ±0.4 | <0.0001 | 4.9 | 2.26 | 10.63 |
| CONSTANT | 0.58 | ±0.73 | 0.43 | 1.78 | ||
| Predictor | Coefficient | SD * | p-Value | OR ** | OR CI95% *** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| SPECfox **** | −1.71 | ±0.45 | <0.0001 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.44 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Halász, T.; Nagy, G.; Nagy, I.; Csivincsik, Á. Micro-Epidemiological Investigation of Echinococcus multilocularis in Wild Hosts from an Endemic Area of Southwestern Hungary. Parasitologia 2021, 1, 158-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia1030017
Halász T, Nagy G, Nagy I, Csivincsik Á. Micro-Epidemiological Investigation of Echinococcus multilocularis in Wild Hosts from an Endemic Area of Southwestern Hungary. Parasitologia. 2021; 1(3):158-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia1030017
Chicago/Turabian StyleHalász, Tibor, Gábor Nagy, István Nagy, and Ágnes Csivincsik. 2021. "Micro-Epidemiological Investigation of Echinococcus multilocularis in Wild Hosts from an Endemic Area of Southwestern Hungary" Parasitologia 1, no. 3: 158-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia1030017
APA StyleHalász, T., Nagy, G., Nagy, I., & Csivincsik, Á. (2021). Micro-Epidemiological Investigation of Echinococcus multilocularis in Wild Hosts from an Endemic Area of Southwestern Hungary. Parasitologia, 1(3), 158-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia1030017





