Synthesis and Crystal and Electronic Structures of the Zintl Phase Sr21Cd4Sb18
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Crystallographic Studies
2.3. Electronic Band Structure Calculations
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis
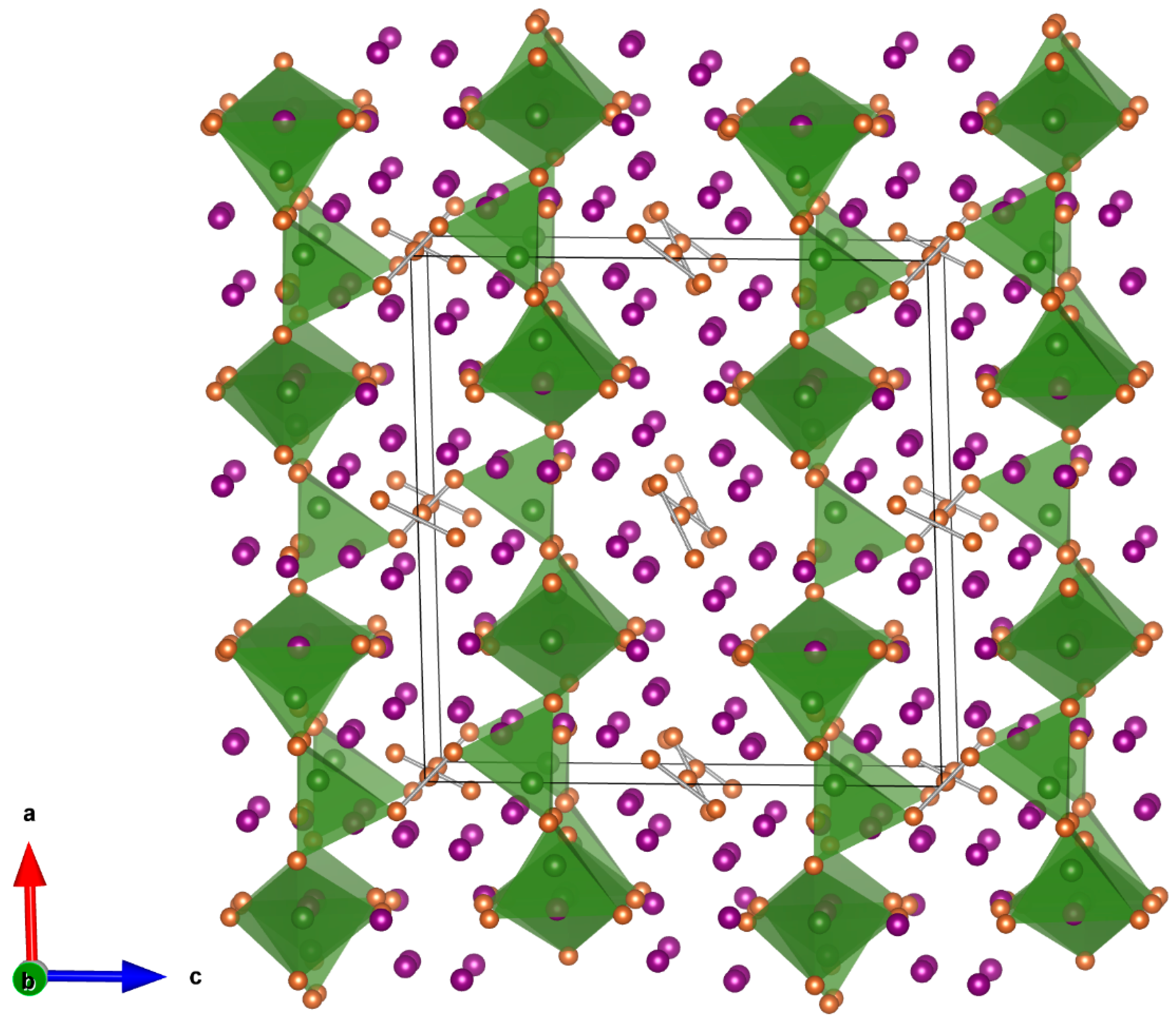
3.2. Structure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corbett, J.D. Polyanionic Clusters and Networks of the Early p-Element Metals in the Solid State: Beyond the Zintl Boundary. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janka, O.; Kauzlarich, S.M. Zintl Compounds, Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, H.; Eisenmann, B.; Müller, W. Zintl Phases: Transitions between Metallic and Ionic Bonding. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1973, 12, 694–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, H. On the problem of polar intermetallic compounds: The simulation of E. Zintl’s work for the modern chemistry of intermetallics. Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1985, 15, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guloy, A.M. Polar Intermetallics and Zintl Phases along the Zintl Border. In Inorganic Chemistry in Focus III; Meyer, G., Naumann, D., Wesemann, L., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; pp. 157–171. [Google Scholar]
- Papoian, G.A.; Hoffmann, R. Hypervalent bonding in one, two, and three dimensions: Extending the Zintl-Klemm concept to nonclassical electron-rich networks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 2408–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevov, S.C. Intermetallic Compounds—Principles and Practice; Westbrook, J.H., Fleischer, R.L., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 113–132. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-J.; Kanatzidis, M.G. A unique framework in BaGa2Sb2: A new Zintl phase with large tunnels. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 3781–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.R.; Kauzlarich, S.M.; Gascoin, F.; Snyder, G.J. Yb14MnSb11: New high efficiency thermoelectric material for power generation. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 1873–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbunmi, M.O.; Bobev, S. Exploiting the fraternal twin nature of thermoelectrics and topological insulators in Zintl phases as a tool for engineering new efficient thermoelectric generators. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2023, 11, 8337–8357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saparov, B.; Bobev, S.; Ozbay, A.; Nowak, E.R. Synthesis, structure and physical properties of the new Zintl phases Eu11Zn6Sb12 and Eu11Cd6Sb12. J. Solid State Chem. 2008, 181, 2690–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascoin, F.; Ottensmann, S.; Stark, D.; Haïle, S.M.; Snyder, G.J. Zintl phases as thermoelectric materials: Tuned transport properties of the compounds CaxYb1–xZn2Sb2. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1860–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauzlarich, S.M.; Brown, S.R.; Snyder, G.J. Zintl phases for thermoelectric devices. Dalton Trans. 2007, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, G.J.; Toberer, E.S. Complex thermoelectric meterials. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Condron, C.L.; Holm, A.P.; Kauzlarich, S.M. Synthesis, structure, and magnetic properties of a new ternary Zintl phase: Sr21Mn4Sb18. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 10720–10721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauzlarich, S.M. Chemistry, Structure and Bonding of Zintl Phases and Ions; VCH: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Nesper, R. The Zintl-Klemm concept–a historical survey. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2014, 640, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saparov, B.; Bobev, S. Isolated [ZnPn2]4– chains in the Zintl phases Ba2ZnPn2 (Pn = As, Sb, Bi): Synthesis, structure, and bonding. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 5173–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.; Saparov, B.; Bobev, S. Synthesis, crystal structures and properties of the Zintl phases Sr2ZnP2, Sr2ZnAs2, A2ZnSb2 and A2ZnBi2 (A = Sr and Eu). Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2011, 637, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xue, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Sui, J.; Liu, X.; Cao, F.; et al. Zintl-phase Eu2ZnSb2: A promising thermoelectric material with ultralow thermal conductivity. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2831–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikov, A.; Bobev, S. Zintl phases with group 15 elements and the transition metals: A brief overview of pnictides with diverse and complex structures. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 270, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, M.; Wu, K.; Tao, X.; Huang, B.-B.; Xia, S.-Q. Tuning the thermoelectric properties of Ca9Zn4+xSb9 by controlled doping on the interstitial structure. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 6917–6924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Liu, K.F.; Wang, Q.Q.; Wang, M.Y.; Pan, Y.M.; Xia, S.-Q. Exploring new Zintl phases in the 9-4-9 family via Al substitution. Synthesis, structure, and physical properties of Ae9Mn4–xAlxSb9 (Ae = Ca, Yb, Eu). Inorg. Chem. 2020, 56, 3709–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobev, S.; Thompson, J.D.; Sarrao, J.L.; Olmstead, M.M.; Hope, H.; Kauzlarich, S.M. Probing the limits of the Zintl concept: Structure and bonding in rare-earth and alkaline-earth zinc-antimonides Yb9Zn4+xSb9 and Ca9Zn4.5Sb9. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 5044–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbunmi, M.O.; Baranets, S.; Bobev, S. Enhanced thermoelectric performance in the Zintl antimonides (Ca,RE)9Cd4Sb9 (RE = rare-earth metal). Synergy between increased structural complexity and drive towards optimized chemical bonding. Mater. Today Adv. 2022, 16, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, K.-F.; Tan, W.-J.; Liu, X.-C.; Xia, S.-Q. Sr9Mg4.45(1)Bi9 and Sr9Mg4.42(1)Sb9: Mg-containing Zintl phases with low thermal conductivity. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 4026–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazem, N.; Hurtado, A.; Klobes, B.; Hermann, R.P.; Kauzlarich, S.M. Eu9Cd4–xCM2+x–y□ySb9: Ca9Mn4Bi9-type structure stuffed with coinage metals (Cu, Ag, and Au) and the challenges with classical valence theory in describing these possible Zintl phase. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranets, S.; Voss, L.; Stoyko, S.; Bobev, S. Synthesis, crystal structure and physical properties of the solid solutions Ca14–xRExCdSb11 (RE = La–Nd, Sm, Gd–Yb, x ≈ 0.85 ± 0.15). J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 245101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.-J.; Liu, Y.T.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, T.-J.; Zhao, X.-B.; Tao, X.T.; Xia, S.-Q. Structure, magnetism, and thermoelectric properties of magnesium-containing antimonide Zintl phases Sr14MgSb11 and Eu14MgSb11. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toberer, E.S.; Cox, C.A.; Brown, S.R.; Ikeda, T.; May, A.F.; Kauzlarich, S.M.; Snyder, G.J. Traversing the metal-insulator transition in a Zintl phase: Rational enhancement of thermoelectric efficiency in Yb14Mn1–xAlxSb11. Adv. Func. Mater. 2008, 18, 2795–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, M.; Shen, J.; Zhu, T.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Tao, X.-T.; Xia, S.-Q. A14MgBi11 (A = Ca, Sr, Eu): Magnesium Bismuth Based Zintl Phases as Potential Thermoelectric Materials. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 10576–10583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.; von Allmen, P.; Cheikh, D.; Bux, S.; Fleurial, J.P. Impact of Anionic Substitution in Yb14MgSb11–xAsx Compounds on the Electronic and Thermoelectric Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 18490–18504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastbjerg, S.; Uvarov, C.A.; Kauzlarich, S.M.; Nishibori, E.; Spackman, M.A.; Iversen, B.B. Multi-temperature Synchrotron Powder X-ray Diffraction Study and Hirshfeld Surface Analysis of Chemical Bonding in the Thermoelectric Zintl Phase Yb14MnSb11. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 3723–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; He, A.; Wille, E.L.K.; Jo, N.-H.; Fettinger, J.C.; Canfield, P.C.; Kauzlarich, S.M. Tuning the Intermediate Valence Behavior in the Zintl Compound Yb14ZnSb11 by Incorporation of RE3+[Yb14–xRExZnSb11 (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.7), RE = Sc, Y, La, Lu and Gd]. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 2694–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, A.K.; Gupta, S.; Corbett, J.D. New tetragonal structure type for A2Ca10Sb9 (A = Li, Mg). Electronic variability around a Zintl phase. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovchinnikov, A.; Chanakian, S.; Zevalkink, A.; Bobev, S. Ultralow Thermal Conductivity and High Thermopower in a New Family of Zintl Antimonides Ca10MSb9 (M = Ga, In, Mn, Zn) with Complex Structures and Heavy Disorder. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 3172–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgsmiller, L.; Li, Q.; Toriyama, M.Y.; Snyder, G.J. New Zintl Phase Yb10MgSb9 with High Thermoelectric Performance. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2300393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobev, S.; Fritsch, V.; Thompson, J.D.; Sarrao, J.L.; Eck, B.; Dronskowski, R.; Kauzlarich, S.M. Synthesis, structure and properties of the new rare-earth Zintl phase Yb11GaSb9. J. Solid State Chem. 2005, 178, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.-Q.; Hullmann, J.; Bobev, S.; Ozbay, A.; Nowak, E.R.; Fritsch, V. Synthesis, crystal structures, magnetic and electric transport properties of Eu11InSb9 and Yb11InSb9. J. Solid State Chem. 2007, 180, 2088–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordier, G.; Schäfer, H.; Stelter, M. Ca11InSb9, eine Zintlphase mit diskreten InSb49– Anionen. Z. Naturforsch. B 1985, 40, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suen, N.-T.; Wang, Y.; Bobev, S. Synthesis, crystal structures, and physical properties of the new Zintl phases A21Zn4Pn18 (A = Ca, Eu; Pn = As, Sb)—Versatile arrangements of [ZnPn4] tetrahedra. J. Solid State Chem. 2015, 227, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Darone, G.M.; Bobev, S. The new Zintl phases Eu21Cd4Sb18 and Eu21Mn4Sb18. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 238, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.-Q.; Bobev, S. Zintl phase variations through cation selection. Synthesis and structure of A21Cd4Pn18 (A = Eu, Sr, Ba; Pn = Sb, Bi). Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 1919–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.-Q.; Bobev, S. Diverse polyanions based on MnBi4 and MnSb4 tetrahedra: Polymorphism, structure, and bonding in Ca21Mn4Bi18 and Ca21Mn4Sb18. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, A.P.; Olmstead, M.M.; Kauzlarich, S.M. The crystal structure and magnetic properties of a new ferrimagnetic semiconductor: Ca21Mn4Sb18. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Cryst. 2015, A71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. 2015, C71, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelato, L.M.; Parthé, E. STRUCTURE TIDY– a computer program to standardize crystal structure data. J. Appl. Cryst. 1987, 20, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, O.K. Linear methods in band theory. Phys. Rev. B. 1975, 12, 3060–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, O.K.; Jepsen, O. Explicit, first-principles tight-binding theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 53, 2571–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Barth, U.; Hedin, L. A local exchange-correlation potential for the spin polarized case. I. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1972, 5, 1629–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; Ovchinnikov, A.; Baitinger, M.; Krnel, M.; Burkhardt, U.; Grin, Y.; Bobev, S. Lithium metal atoms fill vacancies in the germanium network of a type-I clathrate: Synthesis and structural characterization of Ba8Li5Ge41. Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 10310–10322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Kim, S.J. Sr11Cd6Sb12: A new Zintl compound with infinite chains of pentagonal tubes, J. Solid State Chem. 2004, 177, 3418–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauling, L. The Nature of the Chemical Bonding, 3rd ed.; Cornell Univ. Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1960; p. 403. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg, S.; Dronskowski, R. The Crystal Orbital Hamilton Population (COHP) Method as a Tool to Visualize and Analyze Chemical Bonding in Intermetallic Compounds. Crystals 2018, 8, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Compound | Pearson Symbol | Space Group | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sr21Mn4Sb18 | mS172 | C2/m (No. 12) | [15] |
| β-Ca21Mn4Sb18 | mS172 | C2/m (No. 12) | [44] |
| Ca21Zn4Sb18 | mS172 | C2/m (No. 12) | [41] |
| Ca21Zn4As18 | mS172 | C2/m (No. 12) | [41] |
| Eu21Zn4Sb18 | mS172 | C2/m (No. 12) | [41] |
| Eu21Zn4As18 | mS172 | C2/m (No. 12) | [41] |
| Eu21Mn4Sb18 | mS172 | C2/m (No. 12) | [42] |
| Eu21Cd4Sb18 | mS172 | C2/m (No. 12) | [42] |
| Eu21Cd4Bi18 | mS172 | C2/m (No. 12) | [42] |
| Sr21Cd4Sb18 | mS172 | C2/m (No. 12) | [43] |
| Sr21Cd4Bi18 | mS172 | C2/m (No. 12) | This work |
| Ca21Mn4Bi18 | mS172 | C2/c (No. 15) | [44] |
| α–Ca21Mn4Sb18 | mS172 | C2/c (No. 15) | [45] |
| Eu21Zn4Sb18 | oS344 | Cmce (No. 64) | [41] |
| Ba21Cd4Sb18 | oS344 | Cmce (No. 64) | [43] |
| Chemical Formula | Sr21Cd4Sb18 |
|---|---|
| Formula weight | 4481.12 |
| a/Å | 18.2536(6) |
| b/Å | 17.4018(5) |
| c/Å | 17.8979(6) |
| β/° | 92.024(1) |
| V/Å3 | 5681.6(3) |
| ρcalc./g cm−3 | 5.24 |
| μ(Mo-Kα)/cm−1 | 293.6 |
| Collected reflections | 43,869 |
| Independent reflections | 8507 [Rint = 0.0579] |
| Goodness-of-fit | 1.11 |
| R1 (I > 2σ(I)) a | 0.0322 |
| wR2 (I > 2σ (I)) a | 0.0499 |
| R1 (all data) a | 0.0430 |
| wR2 (all data) a | 0.0534 |
| Δρmax,min/e−·Å−3 | 1.58, –2.05 |
| Sr21Cd4Sb18 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atom | Wyckoff Site | x | y | z | Ueq/Å2 |
| Sr1 | 8j | 0.0834(1) | 0.1547(1) | 0.3506(1) | 0.010(1) |
| Sr2 | 8j | 0.0863(1) | 0.1628(1) | 0.1454(1) | 0.009(1) |
| Sr3 | 8j | 0.1119(1) | 0.1205(1) | 0.5767(1) | 0.011(1) |
| Sr4 | 8j | 0.1190(1) | 0.3719(1) | 0.0567(1) | 0.012(1) |
| Sr5 | 8j | 0.1567(1) | 0.3380(1) | 0.4359(1) | 0.010(1) |
| Sr6 | 8j | 0.2533(1) | 0.3247(1) | 0.2431(1) | 0.010(1) |
| Sr7 | 8j | 0.3660(1) | 0.3694(1) | 0.0601(1) | 0.011(1) |
| Sr8 | 8j | 0.4290(1) | 0.1685(1) | 0.1569(1) | 0.010(1) |
| Sr9 | 8j | 0.4458(1) | 0.1260(1) | 0.3804(1) | 0.010(1) |
| Sr10 | 4i | 0.2533(1) | 0 | 0.4182(1) | 0.011(1) |
| Sr11 | 4i | 0.2636(1) | 0 | 0.0925(1) | 0.011(1) |
| Sr12 | 4i | 0.5931(1) | 0 | 0. 2548(1) | 0.012(1) |
| Cd1 | 8j | 0.2656(1) | 0.1201(1) | 0.2480(1) | 0.011(1) |
| Cd2 | 4i | 0.0006(1) | 0 | 0.7929(1) | 0.012(1) |
| Cd3 | 4i | 0.1572(1) | 0 | 0.7535(1) | 0.011(1) |
| Sb1 | 8j | 0.0794(1) | 0.3179(1) | 0.2563(1) | 0.009(1) |
| Sb2 | 8j | 0.2571(1) | 0.1980(1) | 0.0971(1) | 0.009(1) |
| Sb3 | 8j | 0.2686(1) | 0.1961(1) | 0.3909(1) | 0.010(1) |
| Sb4 | 8j | 0.4294(1) | 0.3564(1) | 0.2413(1) | 0.009(1) |
| Sb5 | 4i | 0.0465(1) | 0 | 0.4380(1) | 0.010(1) |
| Sb6 | 4i | 0.0570(1) | 0 | 0.0565(1) | 0.010(1) |
| Sb7 | 4i | 0.1523(1) | 0 | 0.2522(1) | 0.009(1) |
| Sb8 | 4i | 0.2499(1) | 0 | 0.6244(1) | 0.010(1) |
| Sb9 | 4i | 0.3805(1) | 0 | 0.2564(1) | 0.009(1) |
| Sb10 | 4i | 0.4291(1) | 0 | 0.5334(1) | 0.009(1) |
| Sb11 | 4i | 0.4653(1) | 0 | 0.0723(1) | 0.010(1) |
| Sb12 | 4i | 0.7400(1) | 0 | 0.1170(1) | 0.009(1) |
| Sb13 | 4h | 0 | 0.2451(1) | 1/2 | 0.009(1) |
| Sb14 | 4g | 0 | 0.2444(1) | 0 | 0.009(1) |
| Atom Pair | Distance/Å | Atom Pair | Distance/Å |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cd1—Sb3 | 2.8789(7) | Cd3—Sb8 | 2.9113(9) |
| Cd1—Sb7 | 2.9433(6) | Cd3—Sb12 | 2.9307(9) |
| Cd1—Sb9 | 2.9618(6) | Cd3—Sb4 × 2 | 2.9612(6) |
| Cd1—Sb2 | 3.0208(7) | Sb5—Sb5 | 2.841(1) |
| Cd2—Sb7 | 2.8767(9) | Sb10—Sb10 | 2.889(1) |
| Cd2—Sb4 × 2 | 2.8821(6) | Sb11—Sb11 | 2.923(1) |
| Cd2—Sb3 | 2.929(1) | Sb5—Sb5 | 2.841(1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghosh, K.; Bobev, S. Synthesis and Crystal and Electronic Structures of the Zintl Phase Sr21Cd4Sb18. Solids 2023, 4, 344-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids4040022
Ghosh K, Bobev S. Synthesis and Crystal and Electronic Structures of the Zintl Phase Sr21Cd4Sb18. Solids. 2023; 4(4):344-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids4040022
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhosh, Kowsik, and Svilen Bobev. 2023. "Synthesis and Crystal and Electronic Structures of the Zintl Phase Sr21Cd4Sb18" Solids 4, no. 4: 344-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids4040022
APA StyleGhosh, K., & Bobev, S. (2023). Synthesis and Crystal and Electronic Structures of the Zintl Phase Sr21Cd4Sb18. Solids, 4(4), 344-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids4040022






