Waiting Times for Surgery and Radiotherapy Among Breast Cancer Patients in Switzerland: A Cancer Registry-Based Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Analysis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Outcomes
- (a)
- Time to diagnosis: time between needle/core biopsy and pathology results.
- (b)
- Time to surgery: time between pathology results and the time of surgery.
- (c)
- Time from biopsy to surgery: the time between needle/core biopsy and the time of surgery.
- (d)
- Time to radiotherapy: the time between surgery and start of radiotherapy.
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Waiting Times in 2003–2005
3.2. Trends in Waiting Times from 2003–2005 to 2015–2017
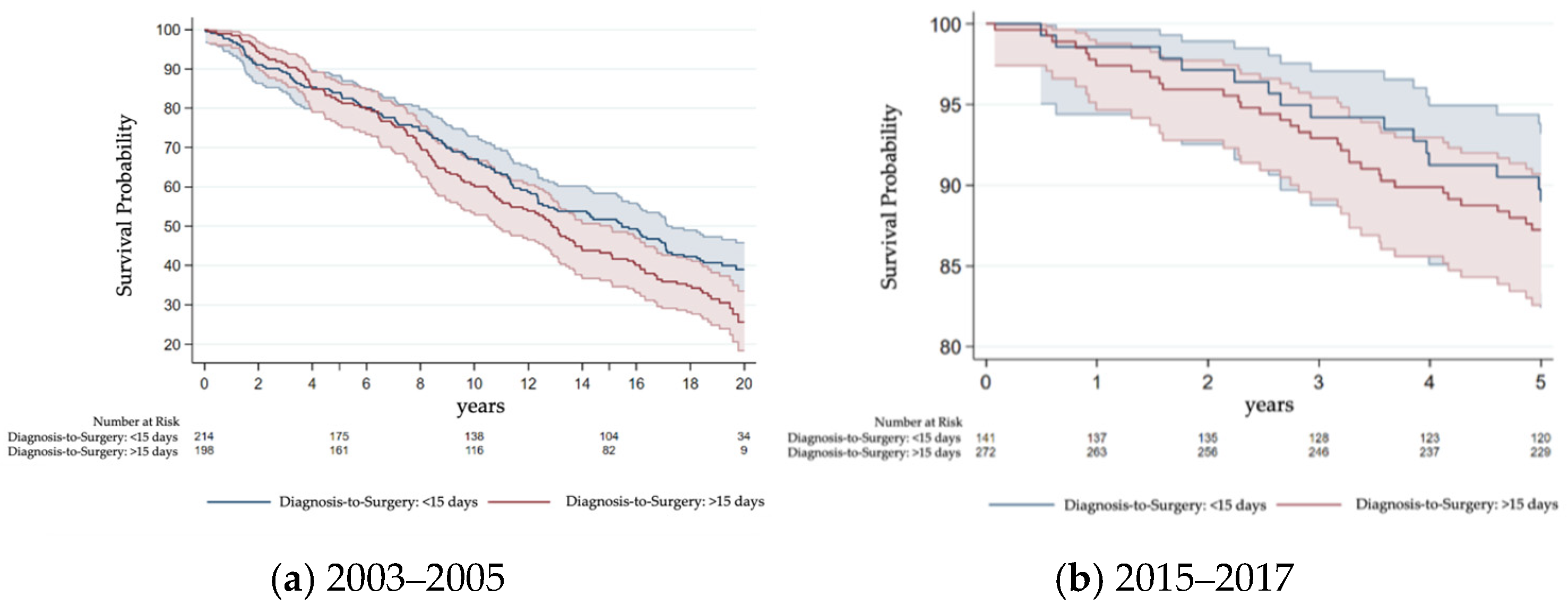
3.3. Survival Differences Due to Waiting Time
4. Discussion
4.1. Timeliness of Surgery in Switzerland in 2003–2005
4.2. Disparities in Waiting Times Until Surgery in Switzerland in 2003–2005
4.3. Waiting Time Until Surgery over Time
4.4. Timeliness of Radiotherapy in Switzerland in 2003–2005
4.5. Disparities in Waiting Times Until Radiotherapy in Switzerland in 2003–2005
4.6. Waiting Time Until Radiotherapy over Time
4.7. Survival Impact of Delays
4.8. Strengths and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Y | Years |
| TTS | Time to surgery |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
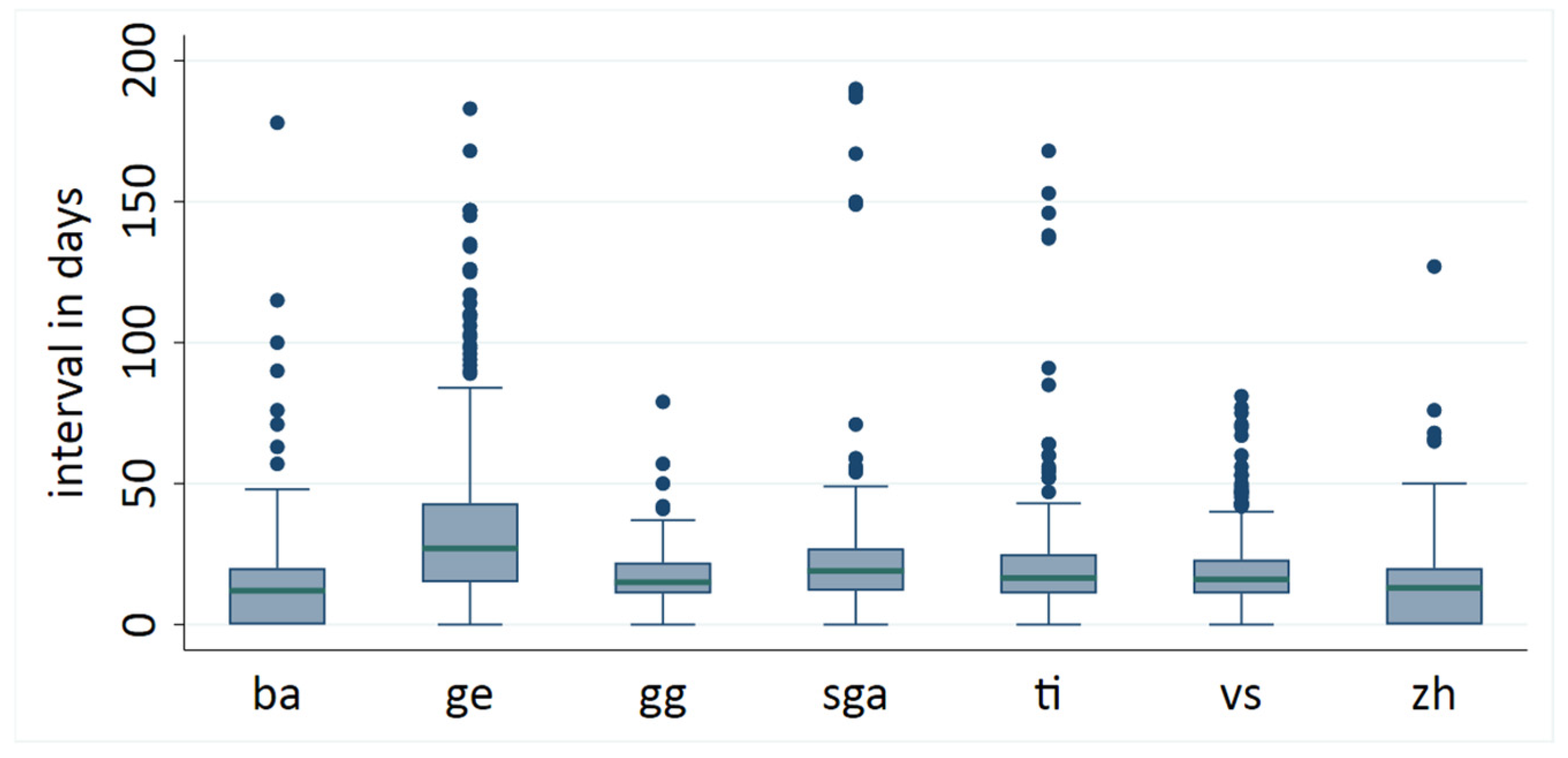
| ba | Basel |
| ge | Genf |
| gg | Grison |
| sga | East Switzerland |
| ti | Ticino |
| vs | Valais |
| zh | Zurich |
| BS | Basel Stadt |
| BL | Basel Land |
| AI | Appenzell Innerrhoden |
| AR | Appenzell Ausserrhoden |
| SG | St. Gallen |
| GR | Graubuenden |
| GL | Glarus |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| EUSOMA | European Society of Breast Cancer Specialists |
| OS | Overall survival |
| BC | Breast cancer |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| SGS | Swiss Society of Senology |
References
- Chavez-MacGregor, M.; Clarke, C.A.; Lichtensztajn, D.Y.; Giordano, S.H. Delayed Initiation of Adjuvant Chemotherapy Among Patients With Breast Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleicher, R.J.; Ruth, K.; Sigurdson, E.R.; Beck, J.R.; Ross, E.; Wong, Y.N.; Patel, S.A.; Boraas, M.; Chang, E.I.; Topham, N.S.; et al. Time to Surgery and Breast Cancer Survival in the United States. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassem, J.; Ozmen, V.; Bacanu, F.; Drobniene, M.; Eglitis, J.; Lakshmaiah, K.C.; Kahan, Z.; Mardiak, J.; Pieńkowski, T.; Semiglazova, T.; et al. Delays in diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer: A multinational analysis. Eur. J. Public Health 2014, 24, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleicher, R.J.; Ruth, K.; Sigurdson, E.R.; Ross, E.; Wong, Y.N.; Patel, S.A.; Boraas, M.; Topham, N.S.; Egleston, B.L. Preoperative delays in the US Medicare population with breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 4485–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.M.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Nguyen, L.M.; Pham, A.T.; Luu, H.N.; Tran, H.T.T.; Tran, T.V.; Shu, X.O. Delay in the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer in Vietnam. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 7683–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, R.; Ray, R.M.; Roth, J.; Johnson, L.; Warnick, G.; Anderson, G.L.; Kroenke, C.H.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Simon, M.S.; Fung, C.; et al. The association of delay in curative intent treatment with survival among breast cancer patients: Findings from the Women’s Health Initiative. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 180, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, P.J.; Cook, A.R.; Binte Mohamed Ri, N.K.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Hartman, M. Impact of delayed treatment in women diagnosed with breast cancer: A population-based study. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.C.; Ziogas, A.; Anton-Culver, H. Delay in surgical treatment and survival after breast cancer diagnosis in young women by race/ethnicity. JAMA Surg. 2013, 148, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, L.; Bergh, J.; Humphreys, K.; Wärnberg, F.; Törnberg, S.; Czene, K. Time from breast cancer diagnosis to therapeutic surgery and breast cancer prognosis: A population-based cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Zheng, X.; Ouyang, Z. The Relationship between Time to Surgery (TTS) and Survival in Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Iran. J. Public Health 2021, 50, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, T.P.; King, W.D.; Thibodeau, S.; Jalink, M.; Paulin, G.A.; Harvey-Jones, E.; O’Sullivan, D.E.; Booth, C.M.; Sullivan, R.; Aggarwal, A. Mortality due to cancer treatment delay: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2020, 371, m4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; King, W.D.; Korzeniowski, M.; Wallace, D.L.; Mackillop, W.J. The Effect of Waiting Times for Postoperative Radiotherapy on Outcomes for Women Receiving Partial Mastectomy for Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Oncol. (R. Coll. Radiol.) 2016, 28, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hébert-Croteau, N.; Freeman, C.R.; Latreille, J.; Rivard, M.; Brisson, J. A population-based study of the impact of delaying radiotherapy after conservative surgery for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2004, 88, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Barbera, L.; Brouwers, M.; Browman, G.; Mackillop, W.J. Does delay in starting treatment affect the outcomes of radiotherapy? A systematic review. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Sun, G.Y.; Tang, Y.; Jing, H.; Song, Y.W.; Jin, J.; Liu, Y.P.; Zhao, X.R.; Song, Y.C.; Chen, B.; et al. Timing of postmastectomy radiotherapy following adjuvant chemotherapy for high-risk breast cancer: A post hoc analysis of a randomised controlled clinical trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 174, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Mujar, N.M.; Dahlui, M.; Emran, N.A.; Hadi, I.A.; Yan, Y.W.; Arulanantham, S.; Chea, C.H.; Mohd Taib, N.A. Breast Cancer Care Timeliness Framework: A Quality Framework for Cancer Control. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2022, 8, e2100250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bommel, A.C.; Spronk, P.E.; Vrancken Peeters, M.T.; Jager, A.; Lobbes, M.; Maduro, J.H.; Mureau, M.A.; Schreuder, K.; Smorenburg, C.H.; Verloop, J.; et al. Clinical auditing as an instrument for quality improvement in breast cancer care in the Netherlands: The national NABON Breast Cancer Audit. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 115, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrua, M.; Couralet, M.; Nitenberg, G.; Morin, S.; Serin, D.; Minvielle, E. Development and feasibility of a set of quality indicators relative to the timeliness and organisation of care for new breast cancer patients undergoing surgery. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2012, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiss Society of Senology. SGS Kriterien Brustzentren. 2019. Available online: https://www.senologie.ch/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/SGS_Kriterien_Brustzentren.pdf (accessed on 2 August 2015).
- Tomatis, M.; Mano, M.P.; Baiocchi, D.; Barca, A.; Bordon, R.; Casella, D.; Donati, G.; Berti, R.; Filippini, L.; Frigerio, A.; et al. Audit system on Quality of breast cancer diagnosis and Treatment (QT): Results of quality indicators on screen-detected lesions in Italy for 2006 and preliminary results for 2007. Epidemiol. Prev. 2009, 33 (Suppl. 2), 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Bundesamt für Statistik. Taschenstatistik der Schweiz; Bundesamt für Statistik: Neuchatel, Switzerland, 2008; Available online: https://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/de/home/statistiken/kataloge-datenbanken/publikationen/uebersichtsdarstellungen/taschenstatistik-schweiz.html (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Biganzoli, L.; Marotti, L.; Hart, C.D.; Cataliotti, L.; Cutuli, B.; Kühn, T.; Mansel, R.E.; Ponti, A.; Poortmans, P.; Regitnig, P.; et al. Quality indicators in breast cancer care: An update from the EUSOMA working group. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 86, 59–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUSOMA. The requirements of a specialist breast unit. Eur. J. Cancer 2000, 36, 2288–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKevitt, E.C.; Dingee, C.K.; Warburton, R.; Pao, J.S.; Brown, C.J.; Wilson, C.; Kuusk, U. Coordination of radiologic and clinical care reduces the wait time to breast cancer diagnosis. Curr. Oncol. 2017, 24, e388–e393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NHS. Delivering Cancer Waiting Times. A Good Practice Guide; NHS: London, UK, 2015; Available online: https://www.england.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/delivering-cancer-wait-times.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Kaufman, C.S.; Shockney, L.; Rabinowitz, B.; Coleman, C.; Beard, C.; Landercasper, J.; Askew, J.B.; Wiggins, D.; Committee, Q.I. National Quality Measures for Breast Centers (NQMBC): A robust quality tool: Breast center quality measures. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, C.; Whitehead, M.; Eisen, A.; Holloway, C.M.B.; Groome, P.A. Factors associated with waiting time to breast cancer diagnosis among symptomatic breast cancer patients: A population-based study from Ontario, Canada. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 187, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinié, F.; Leux, C.; Delafosse, P.; Ayrault-Piault, S.; Arveux, P.; Woronoff, A.S.; Guizard, A.V.; Velten, M.; Ganry, O.; Bara, S.; et al. Waiting time disparities in breast cancer diagnosis and treatment: A population-based study in France. Breast 2013, 22, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjoe, J.A.; Heslin, K.; Perez Moreno, A.C.; Thomas, S.; Kram, J.J.F. Factors Associated with Breast Cancer Surgery Delay Within a Coordinated Multihospital Community Health System: When Does Surgical Delay Impact Outcome? Clin. Breast Cancer 2022, 22, e91–e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotogea, A.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Mirea, L.; Prummel, M.V.; Chong, N.; Shumak, R.S.; O’Malley, F.P.; Holloway, C.M.; Group, B.S.S. Factors associated with wait times across the breast cancer treatment pathway in Ontario. Springerplus 2013, 2, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nessim, C.; Winocour, J.; Holloway, D.P.; Saskin, R.; Holloway, C.M. Wait times for breast cancer surgery: Effect of magnetic resonance imaging and preoperative investigations on the diagnostic pathway. J. Oncol. Pract. 2015, 11, e131–e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortorello, G.N.; Shafique, N.; Keele, L.; Susman, C.G.; Dheer, A.; Fayanju, O.M.; Tchou, J.; Miura, J.T.; Karakousis, G.C. Longitudinal Increases in Time to Surgery for Patients with Breast Cancer: A National Cohort Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 31, 6804–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.; Parker, Q.; Horkoff, M.; Humphreys, M.; Hardy, E.; McClellan, K.; Brierley, Y.; Brosseau, L.; Rempel, H. Deteriorating wait times for breast cancer patients at a regional hospital in BC, 2013 versus 2023. BC Med. J. 2024, 66, 240–247. [Google Scholar]
- Bleicher, R.J. Timing and Delays in Breast Cancer Evaluation and Treatment. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 2829–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutch Institute for Clinical Auditing (DICA). Factsheet Indicatoren NABON Breast Cancer Audit; Dutch Institute for Clinical Auditing (DICA): Leiden, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bouche, G.; Ingrand, I.; Mathoulin-Pelissier, S.; Ingrand, P.; Breton-Callu, C.; Migeot, V. Determinants of variability in waiting times for radiotherapy in the treatment of breast cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2010, 97, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikeljevic, J.S.; Haward, R.; Johnston, C.; Crellin, A.; Dodwell, D.; Jones, A.; Pisani, P.; Forman, D. Trends in postoperative radiotherapy delay and the effect on survival in breast cancer patients treated with conservation surgery. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, B.; Goldberg, M.S.; Mayo, N.E.; Valois, M.F.; Scott, S.C.; Hanley, J. Waiting time for radiation therapy in breast cancer patients in Quebec from 1992 to 1998: A study of surgically treated breast cancer patients in Quebec documents and helps to explain increased waiting times for radiation therapy. Healthc. Policy 2006, 1, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jack, R.H.; Davies, E.A.; Robinson, D.; Sainsbury, R.; Møller, H. Radiotherapy waiting times for women with breast cancer: A population-based cohort study. BMC Cancer 2007, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobsen, J.J.; van der Palen, J.; Baum, M.; Brinkhuis, M.; Struikmans, H. Timing of radiotherapy in breast-conserving therapy: A large prospective cohort study of node-negative breast cancer patients without adjuvant systemic therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katik, S.; Gort, M.; Jobsen, J.J.; Maduro, J.H.; Struikmans, H.; Siesling, S. Factors influencing time between surgery and radiotherapy: A population based study of breast cancer patients. Breast 2015, 24, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benk, V.; Ho, V.; Fortin, P.R.; Zhang, G.; Levinton, C.; Freeman, C.R. Predictors of delay in starting radiation treatment for patients with early stage breast cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1998, 41, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chen, J.; Ma, D.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yu, X.; Yang, Z.; et al. Delayed initiation of radiation therapy is associated with inferior outcomes for breast cancer patients with hormone receptor-negative tumors after breast-conserving surgery. Gland. Surg. 2021, 10, 2631–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, A.M.; Mazor, A.M.; Obeid, E.; Daly, J.M.; Sigurdson, E.R.; Handorf, E.A.; DeMora, L.; Aggon, A.A.; Bleicher, R.J. Time to Surgery and the Impact of Delay in the Non-Neoadjuvant Setting on Triple-Negative Breast Cancers and Other Phenotypes. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 1679–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polverini, A.C.; Nelson, R.A.; Marcinkowski, E.; Jones, V.C.; Lai, L.; Mortimer, J.E.; Taylor, L.; Vito, C.; Yim, J.; Kruper, L. Time to Treatment: Measuring Quality Breast Cancer Care. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 3392–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, A.A.; Hanlon, B.M.; Schumacher, J.R.; Vande Walle, K.A.; Wilke, L.G.; Neuman, H.B. Reexamining Time From Breast Cancer Diagnosis to Primary Breast Surgery. JAMA Surg. 2023, 158, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Choi, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kwon, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Jeon, S.; Lee, C.; Woo, H. Time to surgery and survival in breast cancer. BMC Surg. 2022, 22, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaglehouse, Y.L.; Georg, M.W.; Shriver, C.D.; Zhu, K. Time-to-surgery and overall survival after breast cancer diagnosis in a universal health system. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 178, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Li, S.; Huang, J.; Fei, X.; Shen, K.; Chen, X. Time interval between breast cancer diagnosis and surgery is associated with disease outcome. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardin, S.; Mora, E.; Varughese, F.M.; D’Avanzo, F.; Vachanaram, A.R.; Rossi, V.; Saggia, C.; Rubinelli, S.; Gennari, A. Breast Cancer Survivorship, Quality of Life, and Late Toxicities. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recht, A.; Come, S.E.; Henderson, I.C.; Gelman, R.S.; Silver, B.; Hayes, D.F.; Shulman, L.N.; Harris, J.R. The sequencing of chemotherapy and radiation therapy after conservative surgery for early-stage breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, M.J.; Saskin, R.; Singh, S. Association between waiting time for radiotherapy after surgery for early-stage breast cancer and survival outcomes in Ontario: A population-based outcomes study. Curr. Oncol. 2020, 27, e216–e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Switzerland (7 Registries) 2003–2005 (2628 Patients) | Eastern Switzerland (1 Registry) 2003–2005 (434 Patients) | Eastern Switzerland (1 Registry) 2015–2017 (421 Patients) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geography | |||
| Rural | 1445 (55%) | 434 (100%) | 421 (100%) |
| Metropolitan | 1183 (45%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Missing | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Age | |||
| <60 | 760 (29%) | 103 (24%) | 135 (32%) |
| 60–69 | 699 (26.5%) | 97 (22%) | 108 (25%) |
| 70–79 | 648 (24.5%) | 120 (28%) | 96 (23%) |
| 80+ | 521 (20%) | 114 (26%) | 82 (20%) |
| Missing | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Mean | 67.10 ±13.36 | 69.45 ±13.84 | 66.66 ± 13.04 |
| Median | 67 (58–77) | 71 (60–80) | 67 (56–77) |
| Tumor board | |||
| Yes | 1518 (58%) | 148 (34%) | 258 (61%) |
| No | 492 (19%) | 72 (17%) | 5 (1%) |
| Missing | 618 (23%) | 214 (49%) | 158 (38%) |
| Clinical trial | |||
| Yes | 51 (2%) | 25 (6%) | NA |
| No | 1170 (44.5%) | 317 (73%) | |
| Missing | 1407 (53.5%) | 92 (21%) | |
| Health insurance | |||
| Private | 470 (18%) | 31 (7%) | 33 (8%) |
| Semi-private | 245 (9%) | 107 (25%) | 0 (NA) |
| Public | 1240 (47%) | 214 (49%) | 365 (86.55) |
| Missing | 673 (26%) | 82 (19%) | 23 (5.5%) |
| Hospital facility | |||
| Private | 582 (22%) | 96 (22%) | 133 (31.5%) |
| Public | 1392 (53%) | 309 (71%) | 278 (66%) |
| Missing | 654 (25%) | 29 (7%) | 10 (2.5%) |
| Nationality | |||
| Swiss | 2292 (87%) | 410 (94%) | 345 (82%) |
| Non-Swiss | 336 (13%) | 24 (6%) | 46 (11%) |
| Missing | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 30 (7%) |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) | |||
| <25 | 376 (14.5%) | 72 (16.5%) | NA |
| 25–29 | 194 (7.5%) | 46 (10.5%) | |
| >30 | 130 (5%) | 25 (6%) | |
| Missing | 1928 (73%) | 291 (67%) | |
| Mean | 25.51 ±5.54 | 25.82 ± 4.89 | |
| Median | 24.38 (21.63–28.40) | 24.92 (22.23–28.58) | |
| Type of surgery | |||
| Mastectomy | 528 (20%) | 149 (34%) | 70 (16.5%) |
| Breast-conserving surgery | 1309 (50%) | 256 (59%) | 341 (81%) |
| Missing | 791 (30%) | 29 (7%) | 10 (2.5%) |
| Radiotherapy | |||
| Yes | 1548 (59%) | 214 (49.5%) | 281 (67%) |
| No | 1055 (40%) | 218 (50%) | 114 (27%) |
| Missing | 25 (1%) | 2 (0.5%) | 26 (6%) |
| T classification | |||
| T1 | 1672 (64%) | 233 (54%) | 258 (61%) |
| T2 | 731 (28%) | 170 (39%) | 135 (32%) |
| T3 | 81 (3%) | 19 (4%) | 17 (4%) |
| T4 | 89 (3%) | 12 (3%) | 6 (1%) |
| Missing | 55 (2%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (1%) |
| N Classification | |||
| N0 | 1895 (72%) | 315 (73%) | 324 (77%) |
| N1 | 456 (17%) | 92 (21%) | 82 (19%) |
| N2 | 79 (3%) | 16 (4%) | 11 (3%) |
| N3 | 38 (1%) | 5 (1%) | 1 (0%) |
| Missing | 160 (6%) | 6 (1%) | 3 (1%) |
| Tumor grade | |||
| Low | 728 (28%) | 94 (22%) | 106 (25%) |
| Intermediate | 1430 (54%) | 255 (59%) | 263 (62%) |
| High | 334 (13%) | 52 (12%) | 48 (11%) |
| Missing | 136 (5%) | 33 (8%) | 4 (1%) |
| Estrogen receptor | |||
| Less than 10% | 193 (7%) | 30 (7%) | 20 (5%) |
| 10–50% | 167 (6%) | 26 (6%) | 5 (1%) |
| More than 50% | 2154 (82%) | 355 (82%) | 391 (93%) |
| Missing | 114 (4%) | 23 (5%) | 5 (1%) |
| Progesteron receptor | |||
| Less than 10% | 631 (24%) | 102 (24%) | 77 (18%) |
| 10–50% | 602 (23%) | 86 (20%) | 60 (14%) |
| More than 50% | 1281 (49%) | 223 (51%) | 279 (66%) |
| Missing | 114 (4%) | 23 (5%) | 5 (1%) |
| HER2 receptor status | |||
| Overexpressed or gen amplified | 218 (8%) | 29 (7%) | 23 (5%) |
| Not overexpressed or gen not amplified | 1616 (61%) | 211 (49%) | 392 (93%) |
| Missing | 794 (30%) | 194 (45%) | 6 (1%) |
| Received hormonal therapy | |||
| Yes | 1927 (73%) | 316 (73%) | 294 (70%) |
| No | 592 (23%) | 115 (26%) | 120 (28%) |
| Missing | 109 (4%) | 3 (1%) | 7 (2%) |
| Time Intervals in Days | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biopsy-to-Diagnosis | Diagnosis-to-Surgery | Biopsy-to-Surgery | Surgery-to-Radiotherapy | |||||
| Geography | N | Mean | N | Mean | N | Mean | N | Mean |
| Metropolitan | 1164 | 6.01 | 1097 | 22.39 | 1087 | 28.90 | 750 | 59.23 |
| Rural | 1042 | 2.47 | 1346 | 15.87 | 972 | 24.34 | 767 | 54.24 |
| Total | 2206 | p = 0.018 | 2443 | p = 0.0001 | 2059 | p = 0.0649 | 1517 | p = 0.0003 |
| Missing | 422 | 185 | 569 | 1111 | ||||
| Tumor board | ||||||||
| Yes | 1251 | 5.37 | 1454 | 20.78 | 1194 | 30.75 | 916 | 55.70 |
| No | 420 | 0.68 | 421 | 19.31 | 373 | 22.32 | 261 | 58.42 |
| Total | 1671 | p = 0.0354 | 1875 | p = 0.5455 | 1567 | p = 0.0185 | 1177 | p = 0.1365 |
| Missing | 957 | 753 | 1061 | 1451 | ||||
| Age | ||||||||
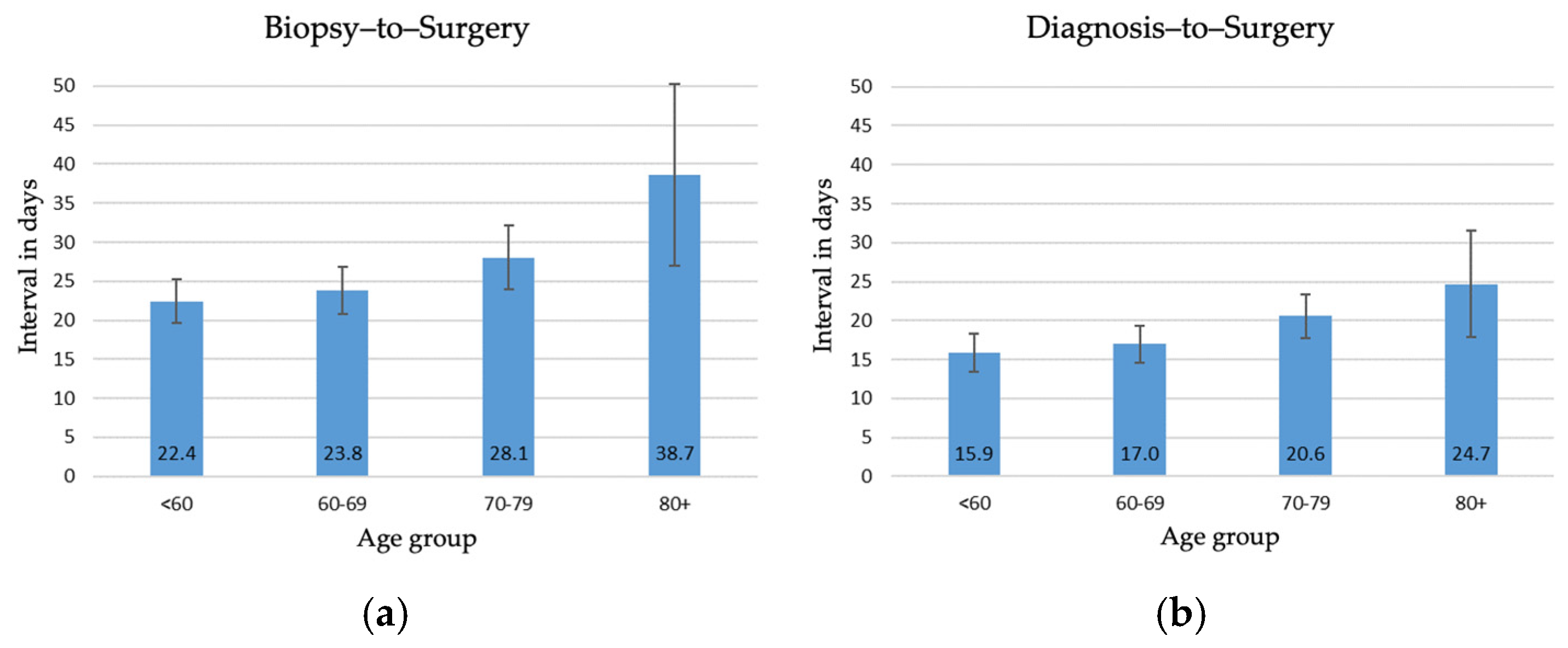
| <60 | 636 | 3.55 | 750 | 15.93 | 627 | 22.41 | 549 | 55.56 |
| 60–69 | 600 | 4.18 | 686 | 16.96 | 589 | 23.75 | 522 | 56.80 |
| 70–79 | 557 | 3.92 | 613 | 20.57 | 524 | 28.05 | 371 | 57.60 |
| 80+ | 413 | 6.31 | 394 | 24.70 | 319 | 38.66 | 75 | 60.07 |
| Total | 2206 | p = 0.6332 | 2443 | p = 0.0029 | 2059 | p = 0.0002 | 1517 | p = 0.4519 |
| Missing | 422 | 185 | 569 | 1111 | ||||
| Insurance | ||||||||
| Private | 439 | 4.43 | 443 | 18.20 | 414 | 24.04 | 320 | 59.00 |
| Semi-private | 218 | 4.29 | 243 | 11.00 | 216 | 16.15 | 163 | 55.82 |
| Public | 1777 | 5.39 | 1156 | 22.41 | 1054 | 30.14 | 708 | 54.72 |
| Total | 1777 | p = 0.8692 | 1842 | p = 0.0001 | 1684 | p = 0.0013 | 1191 | p = 0.471 |
| Missing | 851 | 786 | 944 | 1437 | ||||
| Facility | ||||||||
| Private | 538 | 3.20 | 579 | 14.89 | 536 | 19.01 | 429 | 59.55 |
| Public | 1245 | 6.19 | 1391 | 21.36 | 1244 | 29.95 | 814 | 54.52 |
| Total | 1783 | p = 0.1359 | 1970 | p = 0.0005 | 1780 | p = 0.0001 | 1243 | p = 0.0010 |
| Missing | 845 | 658 | 848 | 1385 | ||||
| Clinical trial | ||||||||
| Participant | 47 | 0.74 | 51 | 23.82 | 47 | 26.60 | 43 | 55.09 |
| Non-participant | 1064 | 1.60 | 1086 | 27.63 | 987 | 31.91 | 707 | 54.44 |
| Total | 1111 | p = 0.8182 | 1137 | p = 0.5188 | 1034 | p = 0.4700 | 750 | p = 0.8481 |
| Missing | 1517 | 1491 | 1594 | 1878 | ||||
| Nationality | ||||||||
| Swiss | 1913 | 4.49 | 2121 | 18.48 | 1779 | 26.65 | 1296 | 56.48 |
| Foreign | 293 | 3.33 | 322 | 20.92 | 280 | 27.39 | 221 | 58.06 |
| Total | 2206 | p = 0.5996 | 2443 | p = 0.3260 | 2059 | p = 0.8364 | 1517 | p = 0.4136 |
| Missing | 422 | 185 | 569 | 1111 | ||||
| BMI | ||||||||
| <25 | 325 | 5.50 | 363 | 23.31 | 312 | 32.56 | 228 | 54.03 |
| 25–30 | 175 | 2.31 | 190 | 24.46 | 172 | 28.98 | 128 | 53.06 |
| 30+ | 120 | 2.51 | 124 | 24.92 | 114 | 29.45 | 92 | 50.91 |
| Total | 620 | p = 0.5149 | 677 | p = 0.8771 | 598 | p = 0.6934 | 448 | p = 0.6794 |
| Missing | 2008 | 1951 | 2030 | 2180 | ||||
| Surgery | ||||||||
| Mastectomy | 474 | 7.36 | 527 | 24.02 | 474 | 33.96 | 63 | 72.98 |
| Breast-conserving | 1222 | 4.61 | 1308 | 18.61 | 1221 | 24.42 | 1102 | 56.33 |
| Total | 1696 | p = 0.2022 | 1835 | p = 0.0065 | 1695 | p = 0.0013 | 1165 | p < 0.0001 |
| Missing | 932 | 793 | 933 | 1463 | ||||
| Coeff. | Std. Err. | t | p > t | 95% Confidence Interval | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 20.227 | 3.668 | 5.51 | 0 | 13.032 | 27.422 | *** |
| Urban | 9.455 | 2.121 | 4.46 | 0 | 5.295 | 13.617 | *** |
| Tumor board | −4.297 | 2.961 | −1.45 | 0.147 | −10.107 | 1.512 | |
| Age 70+ | 3.856 | 2.052 | 1.88 | 0.06 | −0.169 | 7.882 | * |
| Private insurance | −5.818 | 2.667 | −2.18 | 0.029 | −11.05 | −0.587 | ** |
| Private hospital | −7.376 | 2.969 | −2.48 | 0.013 | −13.2 | −1.553 | ** |
| Mastectomy | 4.408 | 2.25 | 1.96 | 0.05 | −0.005 | 8.822 | * |
| Coeff. | Std. Err. | t | p > t | 95% Confidence Interval | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 52.212 | 2.898 | 18.02 | 0 | 46.526 | 57.898 | *** |
| Urban | 6.304 | 1.647 | 3.83 | 0 | 3.072 | 9.535 | *** |
| Tumor board | −1.792 | 2.343 | −0.76 | 0.445 | −6.390 | 2.807 | |
| Age 70+ | −0.328 | 1.639 | −0.2 | 0.841 | −3.545 | 2.888 | |
| Private insurance | 1.356 | 2.067 | 0.66 | 0.512 | −2.700 | 5.412 | |
| Private hospital | 0.518 | 2.227 | 0.23 | 0.816 | −3.852 | 4.889 | |
| Mastectomy | 18.426 | 3.313 | 5.56 | 0 | 11.926 | 24.927 | *** |
| Time Intervals in Days | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis-to-Surgery | Surgery-to-Radiotherapy | |||||||
| 2003–2005 | 2015–2017 | 2003–2005 | 2015–2017 | |||||
| Tumor board | N | Mean | N | Mean | N | Mean | N | Mean |
| Yes | 147 | 21.68 | 255 | 23.44 | 83 | 50.72 | 155 | 49.10 |
| No | 51 | 11.18 | 5 | 30.75 | 18 | 54.50 | 2 | 41.00 |
| Total | 198 | p = 0.0115 | 260 | p = 0.4699 | 101 | p = 0.4450 | 157 | p = 0.4975 |
| Missing | 236 | 161 | 333 | 264 | ||||
| Age | ||||||||
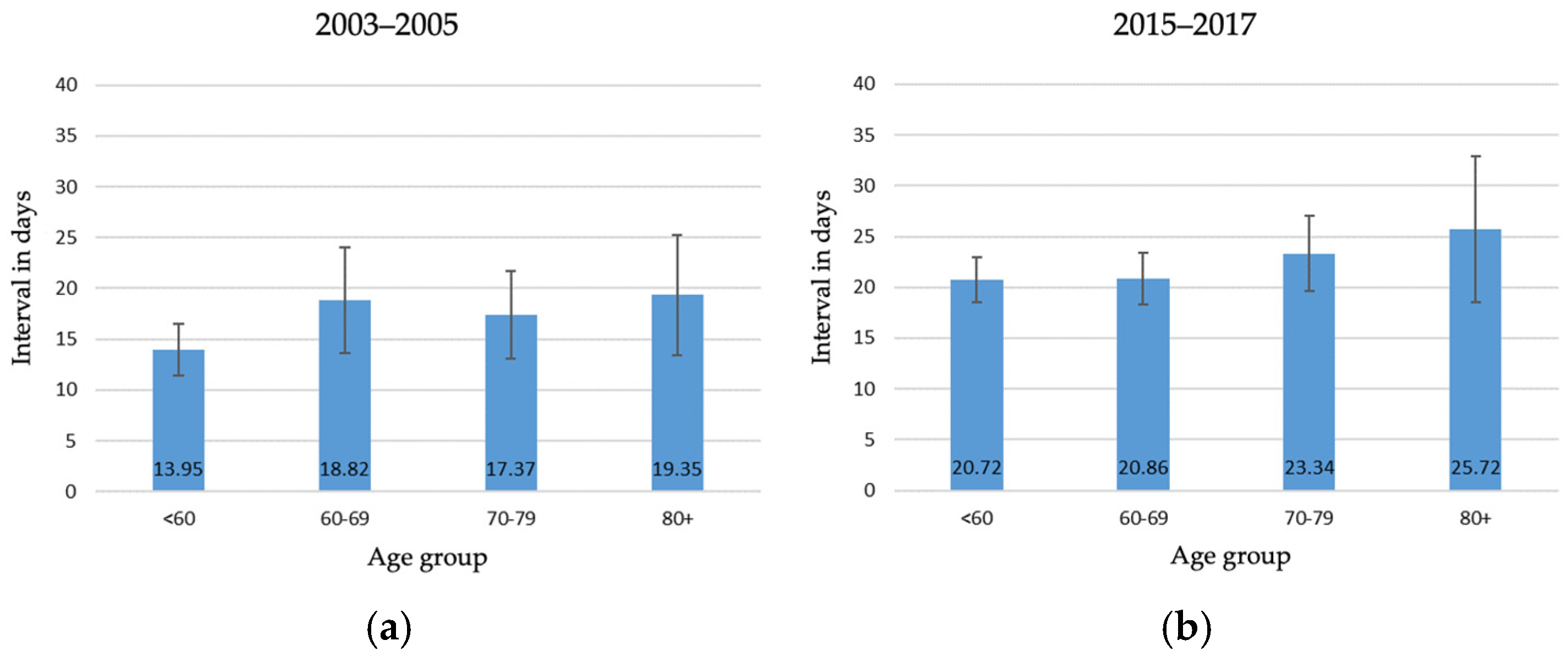
| <60 | 103 | 13.95 | 135 | 20.72 | 74 | 49.45 | 86 | 47.17 |
| 60–69 | 97 | 18.82 | 107 | 20.86 | 66 | 55.15 | 66 | 53.02 |
| 70–79 | 118 | 17.37 | 94 | 23.34 | 65 | 53.31 | 54 | 43.67 |
| 80+ | 87 | 19.35 | 75 | 25.72 | 7 | 54.29 | 22 | 50.19 |
| Total | 405 | p = 0.3546 | 411 | p = 0.2240 | 212 | p = 0.2615 | 228 | p = 0.0264 |
| Missing | 29 | 10 | 222 | 193 | ||||
| Insurance | ||||||||
| Private | 135 | 15.89 | 33 | 21.82 | 88 | 53.28 | 23 | 50.09 |
| Public | 197 | 18.10 | 356 | 22.40 | 102 | 50.15 | 195 | 48.11 |
| Total | 332 | p = 3573 | 389 | p = 0.8631 | 190 | p = 0.2053 | 218 | p = 0.6107 |
| Missing | 102 | 32 | 244 | 203 | ||||
| Facility | ||||||||
| Private | 96 | 12.96 | 132 | 21.12 | 64 | 55.41 | 72 | 47.18 |
| Public | 309 | 18.58 | 276 | 22.72 | 148 | 51.34 | 155 | 48.88 |
| Total | 405 | p = 0.0387 | 408 | p = 0.4102 | 212 | p = 0.1190 | 227 | p = 0.5010 |
| Missing | 29 | 13 | 222 | 194 | ||||
| Clinical trial | Not available | Not available | ||||||
| Participant | 25 | 18.20 | 21 | 51.19 | ||||
| Non-participant | 303 | 18.50 | 175 | 52.92 | ||||
| Total | 328 | p = 0.9538 | 196 | p = 0.6642 | ||||
| Missing | 106 | 238 | ||||||
| Nationality | ||||||||
| Swiss | 381 | 17.22 | 337 | 22.31 | 192 | 52.58 | 189 | 49.13 |
| Foreign | 24 | 17.83 | 46 | 21.29 | 20 | 52.45 | 26 | 44.15 |
| Total | 405 | p = 0.9003 | 383 | p = 0.7200 | 212 | p = 0.9751 | 215 | p = 0.1713 |
| Missing | 29 | 38 | 222 | 206 | ||||
| BMI | Not available | Not available | ||||||
| <25 | 72 | 16.49 | 44 | 50.59 | ||||
| 26–30 | 46 | 18.93 | 29 | 47.31 | ||||
| 30+ | 25 | 23.00 | 20 | 52.00 | ||||
| Total | 143 | p = 0.3986 | 93 | p = 0.5433 | ||||
| Missing | 291 | 341 | ||||||
| Surgery | ||||||||
| Mastectomy | 149 | 22.07 | 69 | 25.55 | 8 | 62.25 | 3 | 58.33 |
| Breast-conserving | 256 | 14.53 | 339 | 21.58 | 204 | 52.19 | 225 | 48.16 |
| Total | 405 | p = 0.0016 | 408 | p = 0.1037 | 212 | p = 0.1094 | 228 | p = 0.3175 |
| Missing | 29 | 13 | 222 | 193 | ||||
| Hazard Ratio | Std. Err. | z | p < z | 95% Confidence Interval | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis-to-Surgery ≥ 15 days | 1.002 | 0.195 | 0.01 | 0.992 | 0.685 | 1.466 | |
| Tumor board | 1.100 | 0.277 | 0.38 | 0.705 | 0.671 | 1.801 | |
| Age 70+ | 2.491 | 0.301 | 7.54 | 0.000 | 1.965 | 3.158 | *** |
| Private insurance | 0.816 | 0.165 | −1.01 | 0.314 | 0.549 | 1.213 | |
| Private hospital | 1.286 | 0.557 | 0.58 | 0.561 | 0.550 | 3.006 | |
| Mastectomy | 1.570 | 0.303 | 2.33 | 0.020 | 1.075 | 2.291 | ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oehler, C.; Zimmermann, M.E.N.; Mousavi, M.; Joorawon, K.R.; Blum, M.; Herrmann, C.; Zwahlen, D.R. Waiting Times for Surgery and Radiotherapy Among Breast Cancer Patients in Switzerland: A Cancer Registry-Based Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Analysis. Radiation 2025, 5, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation5030023
Oehler C, Zimmermann MEN, Mousavi M, Joorawon KR, Blum M, Herrmann C, Zwahlen DR. Waiting Times for Surgery and Radiotherapy Among Breast Cancer Patients in Switzerland: A Cancer Registry-Based Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Analysis. Radiation. 2025; 5(3):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation5030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleOehler, Christoph, Michel Eric Nicolas Zimmermann, Mohsen Mousavi, Kattic Ram Joorawon, Marcel Blum, Christian Herrmann, and Daniel Rudolf Zwahlen. 2025. "Waiting Times for Surgery and Radiotherapy Among Breast Cancer Patients in Switzerland: A Cancer Registry-Based Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Analysis" Radiation 5, no. 3: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation5030023
APA StyleOehler, C., Zimmermann, M. E. N., Mousavi, M., Joorawon, K. R., Blum, M., Herrmann, C., & Zwahlen, D. R. (2025). Waiting Times for Surgery and Radiotherapy Among Breast Cancer Patients in Switzerland: A Cancer Registry-Based Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Analysis. Radiation, 5(3), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation5030023






