Welfare Indices in Anurans under Human Care
Abstract
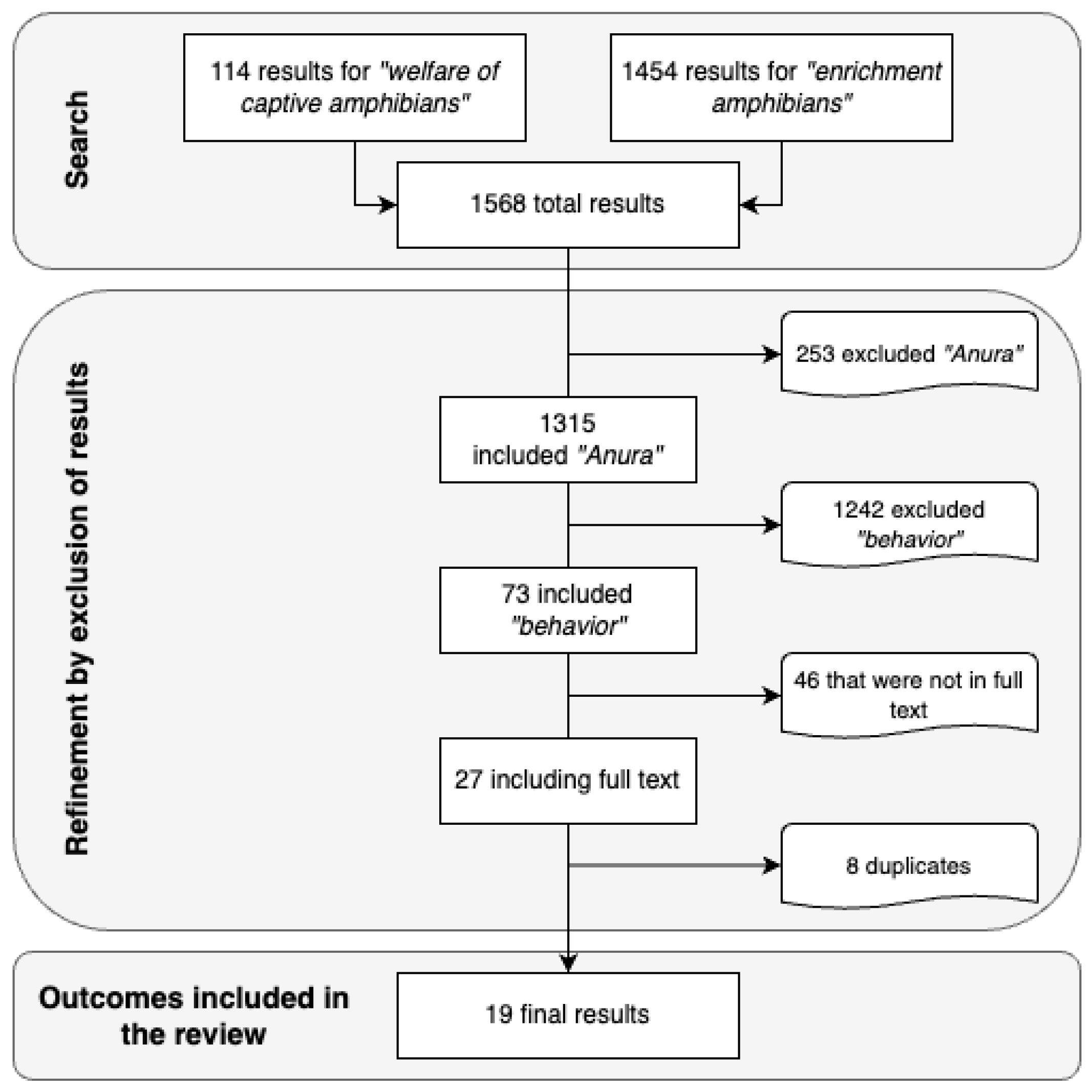
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Knowledge about Behavior in Anurans
4.2. Welfare Indexes
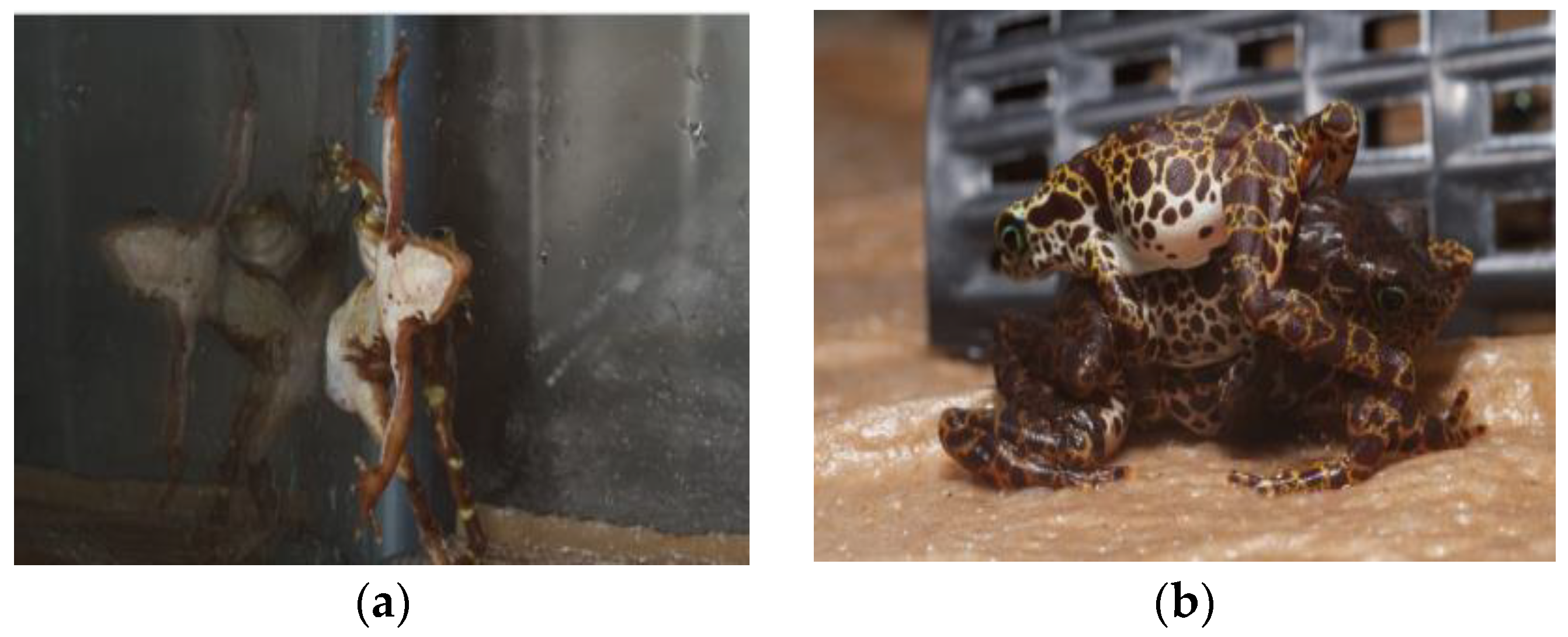
4.3. Environmental Enrichment
- (1)
- Managing a dynamic habitat;
- (2)
- Encouraging social interactions between individuals;
- (3)
- Encouraging foraging behavior;
- (4)
- Introducing new objects;
- (5)
- Species conditioning [11].
4.4. Consequences of Poor Well-Being
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Broom, D.M. Indicators of poor welfare. Br. Vet. J. 1986, 142, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manteca, X.; Salas, M. Concepto de bienestar animal; Zawec Zoo Animal Welfare Education Center: Barcelona, Spain, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Watters, J.V.; Krebs, B.L.; Eschmann, C.L. Assessing animal welfare with behavior: Onward with caution. J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2021, 2, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, N.; Martínez, R.; Perales, J. Guía de Anfibios de Parques Nacionales Españoles. 2015. Available online: https://www.weboryx.com/es/libreria/fauna/anfibios-y-reptiles-de-la-peninsula-iberica-baleares-y-canarias/guia-de-anfibios-de-los-parques-nacionales-espanoles (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Calderón, M.R. Estrategia para el manejo de anfibios sujetos a uso en México. In Temas Sobre Conservación de Vertebrados Silvestres en México, 1st ed.; Sanchéz, O., Peters, E., Moya, H., Eds.; Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales: Orlando, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, M. Frogs in the Household: Pets but not really pets. Qld. Nat. 2017, 55, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- CDMX. Sederec Apoya Proyecto para Producción de Ranas Toro. 2017. Available online: https://www.sepi.cdmx.gob.mx/comunicacion/nota/produccion-ranatoro (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Veterinary Economics Division American Veterinary Medical Association. Avma Pet Ownership and Demographics Sourcebook. 2018. Available online: https://www.avma.org/sites/default/files/resources/AVMA-Pet-Demographics-Executive-Summary.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Ann, L. Keeping the exotic pet mentally healthy. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2015, 18, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, M.P.; Jennings, M.R.; Mellen, J.D. Beyond Mammals. In Second Nature: Environmental Enrichment for Captive Animals, 1st ed.; Shepherdson, J., Ed.; Smithsonian Institution Press y Washington: Orlando, FL, USA, 1998; pp. 205–235. [Google Scholar]
- Hurme, K.; Gonzalez, K.; Halvorsen, M.; Foster, B.; Moore, D.; Diane Chepko-Sade, B. Environmental enrichment for dendrobatid frogs. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2003, 6, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, G.A. Effect of enrichment on the behaviour and growth of juvenile Xenopus laevis. J. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 139, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghardt, G.M. Environmental enrichment and cognitive complexity in reptiles and amphibians: Concepts, review, and implications for captive populations. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2013, 147, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chum, H.; Felt, S.; Garner, J.; Green, S. Biology, behavior, and environmental enrichment for the captive African clawed frog (Xenopus spp.). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 143, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrinton, L.A.; Moerenschlager, A.; Gelling, M.; Atkinson, R.; Hughes, J.; Macdonald, D.W. Conflicting and Complementary Ethics of animal welfare considerations in reintroductions. Conserv. Biol. 2013, 27, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cikanek, S.J.; Nockold, S.; Brown, J.L.; Carpenter, J.W.; Estrada, A.; Guerrel, J.; Hope, K.; Ibañez, R.; Putman, S.B.; Gratwicke, B. Evaluating group housing strategies for the ex-situ conservation of harlequin frogs (Atelopus spp.) Using Behavioral and Physiological Indicators. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaels, C.J.; Antwis, R.E.; Preziosi, R.F. Impact of plant cover on fitness and behavioural traits of captive red-eyed tree Frogs (Agalychnis callidryas). PLoS ONE 2021, 9, e95207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaels, C.J.; Roger Downie, J.; Campbell-Palmer, R. The importance of enrichment for advancing amphibian welfare and conservation goals: A review of a neglected topic. Amphib. Reptile Conserv. 2014, 8, 7–23. [Google Scholar]
- Manteca, X.; Amat, M.; Salas, M.; Temple, D. Animal-based indicators to assess welfare in zoo animals. CABI Digit. Libr. 2016, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.A.; Tamara Montrose, V.; Wills, A.P. Exnotic: Should we be keeping exotic pets? Animals 2021, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasmans, F.; Bogaerts, S.; Braeckman, J.; Cunningham, A.A.; Hellebuyck, T.; Griffiths, R.A.; Sparreboom, M.; Schmidt, B.R.; Martel, A. Future of keeping pet reptiles and amphibians: Towards integrating animal welfare, human health and environmental sustainability. Vet. Rec. 2017, 181, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrell, S.T. Amphibian behavior for the exotic pet practitioner. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2021, 24, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testud, G.; Fauconnier, C.; Labarraque, D.; Lengagne, T.; Le Petitcorps, Q.; Picard, D.; Miaud, C. Acoustic enrichment in wildlife passages under railways improves their use by amphibians. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woody, S.M.; Santymire, R.M.; Cronin, K.A. Posture as a non-invasive indicator of arousal in american toads (Anaxyrus americanus). J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2021, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.; Ortiz-Díez, G. Evaluation of environmental enrichment for Xenopus laevis using a preference test. Lab. Anim. 2021, 55, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, T.J.; Warwick, C.; Bennett, P. Pet management practices of frog and turtle owners in Victoria, Australia. Vet. Rec. 2022, 191, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brod, S.; Brookes, L.; Garner, T.W.J. Discussing the future of amphibians in research. Lab. Anim. 2019, 48, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| References | Taxon | Topic and Main Idea |
|---|---|---|
| Hayes M. et al. Beyond mammals. Second Nature: Environmental Enrichment for Captive Animals. 1998 [10] | N/A | Animal welfare: identify enrichment programs through three requirements:
|
| Hurme K. et al. Environmental enrichment for dendrobatid frogs. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2003 [11] | Dendrobates sp. | Environmental enrichment: identify animal welfare strategies for the development of dendrobate hatchlings |
| Archard G. Effect of enrichment on the behaviour and growth of juvenile Xenopus laevis. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012 [12] | Xenopus laevis | Environmental enrichment: determine if environmental enrichment influences the development of Xenopus laevis |
| Burghardt G. Environmental enrichment and cognitive complexity in reptiles and amphibians: Concepts, review, and implications for captive populations. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012 [13] | N/A | Environmental enrichment: importance of well-being in reptile and amphibian collections |
| Chum H. et al. Biology, behavior, and environmental enrichment for the captive African clawed frog (Xenopus spp). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2013 [14] | Xenopus laevis | Environmental enrichment: strategies for environmental enrichment |
| Harrrington L. et al. Conflicting and complementary ethics of animal welfare considerations in reintroductions. Conserv. Biol. 2013 [15] | N/A | Conservation: animal welfare strategies for species when released |
| Cikanek S. et al. Evaluating group housing strategies for the ex-situ conservation of harlequin frogs (Atelopus spp.) using behavioral and physiological indicators. Plos One. 2014 [16] | Atelopus certus-Atelopus glyphus | Conservation: stress evaluation in a group of frogs through aggressive behaviors and corticosteroids |
| Michaels C. et al. Impact of plant cover on fitness and behavioral traits of captive red-eyed tree frogs. (Agalychnis callidryas). Plos one. 2014 [17] | Agalychnis callidryas | Conservation: implementation of plants in frog enclosures for their conservation |
| Michaels C. et al. The importance of enrichment for advancing amphibian welfare and conservation goals: A review of a neglected topic. Amphib. Reptile Conserv. 2014 [18] | N/A | Environmental enrichment: enrichment for the stimulation of captive amphibians |
| Beltrán N. et al. Guía de anfibios de los parques nacionales españoles. Red de parques nacionales. 2016 [4] | N/A | Conservation: viology of the species |
| Manteca X. et al. Animal-based indicators to assess welfare in zoo animals. CAB Rev. 2016 [19] | N/A | Animal welfare: identify the welfare indicators in zoological collections of reptiles and amphibians |
| Grant R. et al. ExNOTic: Should we be keeping exotic pets?. Anim. 2017 [20] | N/A | Animal welfare: to question whether we should keep exotic animals as pets |
| Pasmans F. et al. Future of keeping pet reptiles and amphibians: towards integrating animal welfare, human health and environmental sustainability. Vet. Rec. 2017 [21] | N/A | Animal welfare: responsible ownership of amphibians and reptiles as pets |
| Brod S. et al. Discussing the future of amphibians in research. Lab. Anim. 2019 [13] | Amphibians | Animal welfare: identify the guidelines for keeping amphibians under human care |
| Ferrel S. et al. Amphibian behavior for the exotic pet practitioner. Vet. Clin. Exot. Anim. 2020 [22] | N/A | Behavior: examine the highlights of amphibian well-being, pain, and behavior |
| Testud G. et al. Acoustic enrichment in wildlife passages under railways improves their use by amphibians. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020 [23] | Triturus spp. | Conservation: evaluation of the impact of transport infrastructure on free-living specimens |
| Woody S. et al. Posture as a non-invasive indicator of arousal in American toads (Anaxyrus americanus). J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2020 [24] | Anaxyrus americanus | Animal welfare: the relationship between the posture of the specimens with the excitement caused by stress in individuals |
| Ramos J. et al. Evaluation of environmental enrichment for Xenopus laevis using a preference test. Lab. Anim. 2021 [25] | Xenopus laevis | Environmental enrichment: examine frog preferences for different items of enrichment |
| Hollew T. et al. Pet management practices of frog and turtle owners in Victoria, Australia. Vet. Record. 2022 [26] | N/A | Animal welfare: to investigate if the owners of frogs and turtles are aware of their welfare needs |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cortés Pérez, E.; Maldonado Reséndiz, R.I. Welfare Indices in Anurans under Human Care. J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2023, 4, 613-622. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg4030043
Cortés Pérez E, Maldonado Reséndiz RI. Welfare Indices in Anurans under Human Care. Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens. 2023; 4(3):613-622. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg4030043
Chicago/Turabian StyleCortés Pérez, Ethel, and Ricardo Itzcóatl Maldonado Reséndiz. 2023. "Welfare Indices in Anurans under Human Care" Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens 4, no. 3: 613-622. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg4030043
APA StyleCortés Pérez, E., & Maldonado Reséndiz, R. I. (2023). Welfare Indices in Anurans under Human Care. Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens, 4(3), 613-622. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg4030043







