Monitoring Gas Emissions in Agricultural Productions through Low-Cost Technologies: The POREM (Poultry-Manure-Based Bio-Activator for Better Soil Management through Bioremediation) Project Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Limits and the Potentialities of LCSs
1.2. The Aim and the Focus of This Work
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Site of the Experiment
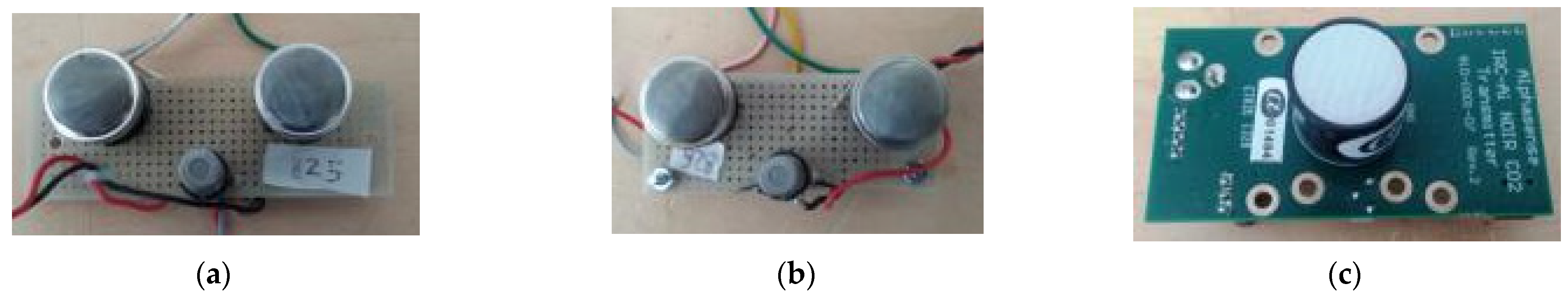
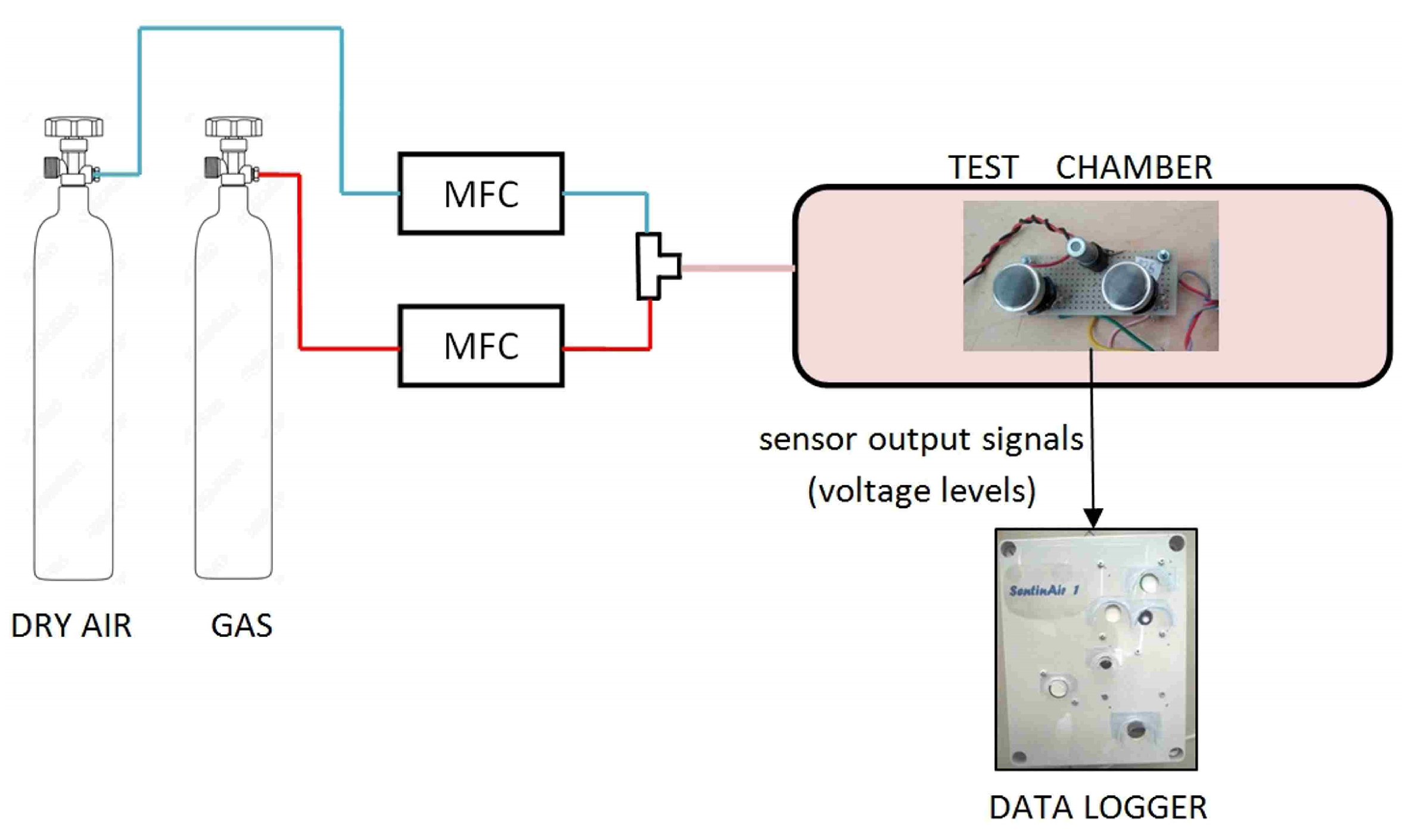
2.2. The LCSs Selected for Gas Monitoring and Their Calibration
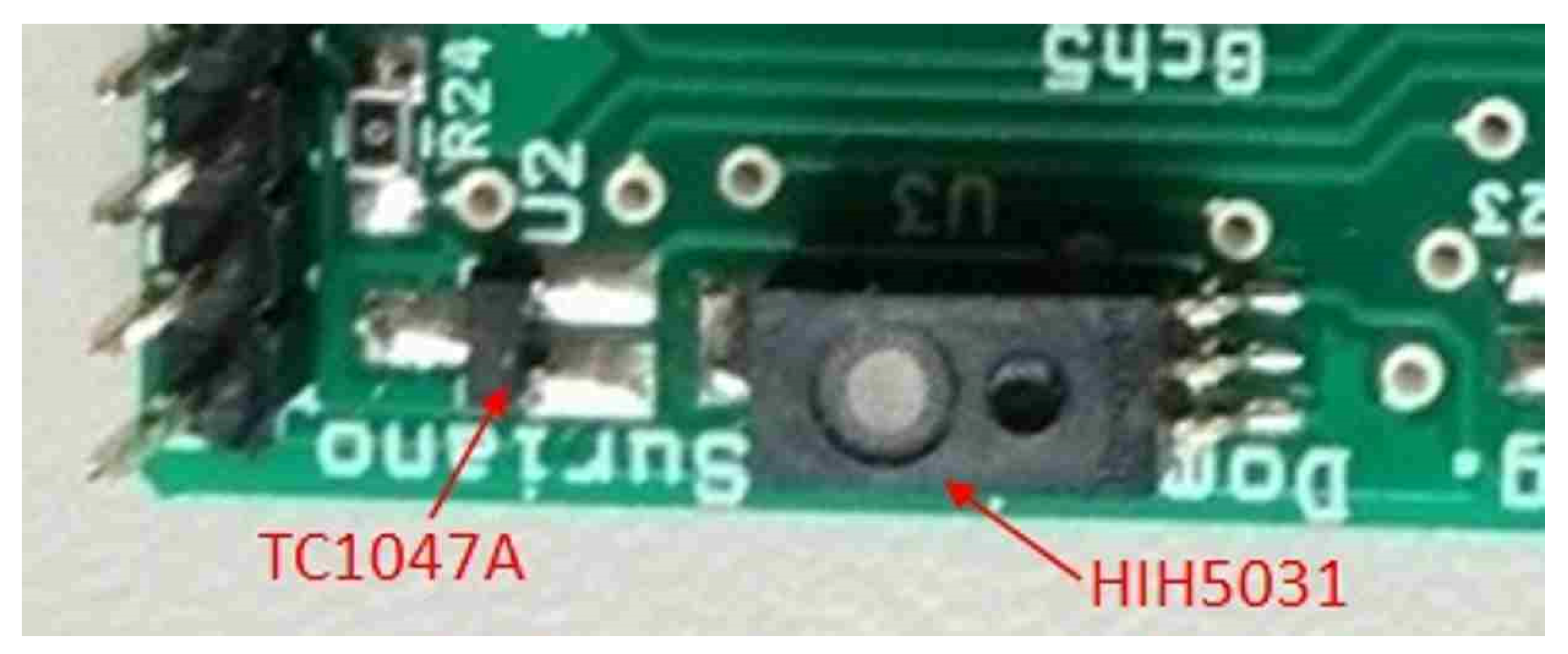
2.3. The Monitoring of the Temperature inside the Manure Heaps and Other Environmental Variables
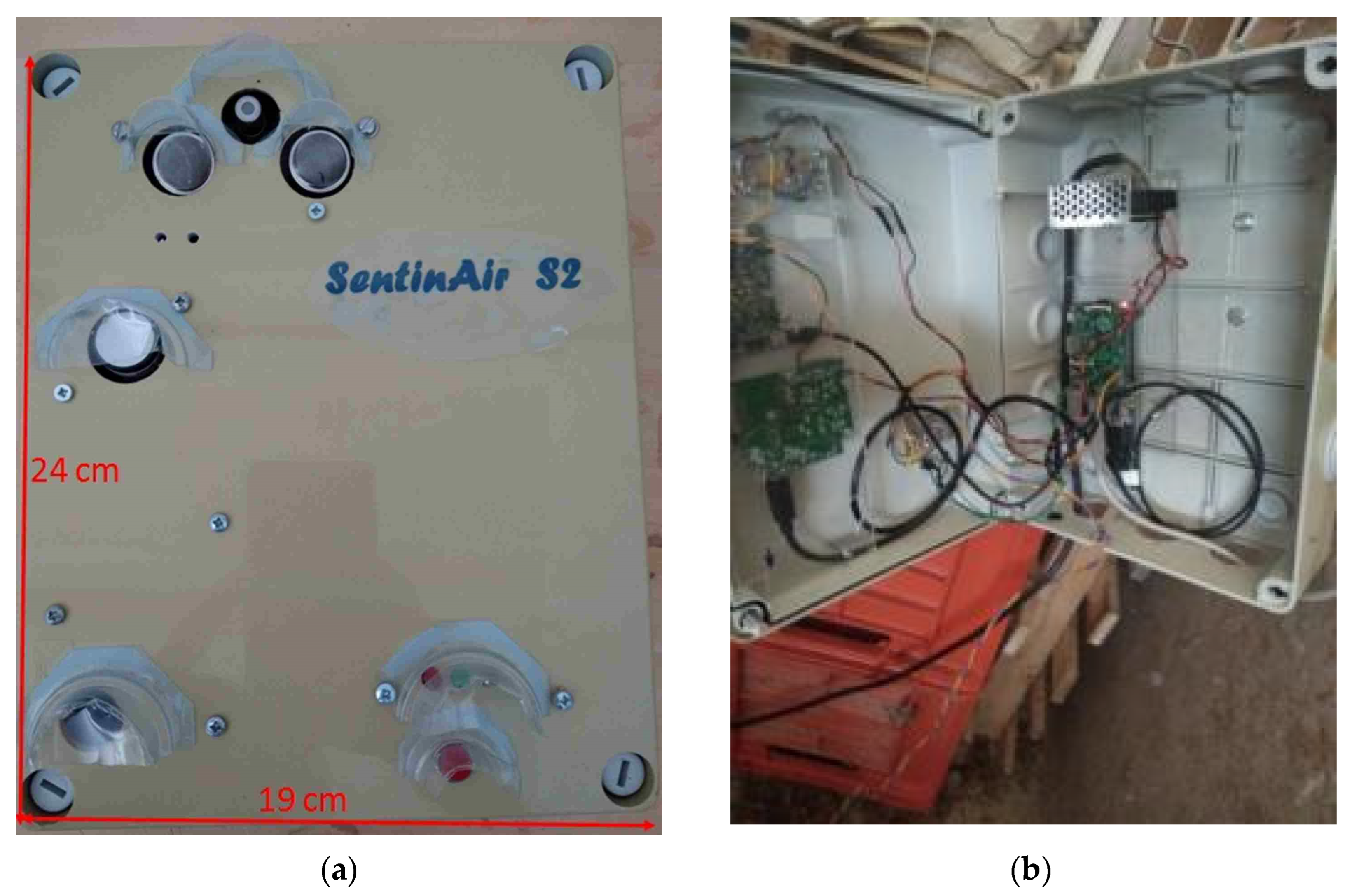
2.4. The Monitoring Unit and the Communication Protocol
3. Results
3.1. The Results of the Calibration of the Resistive Gas Sensors in the Laboratory
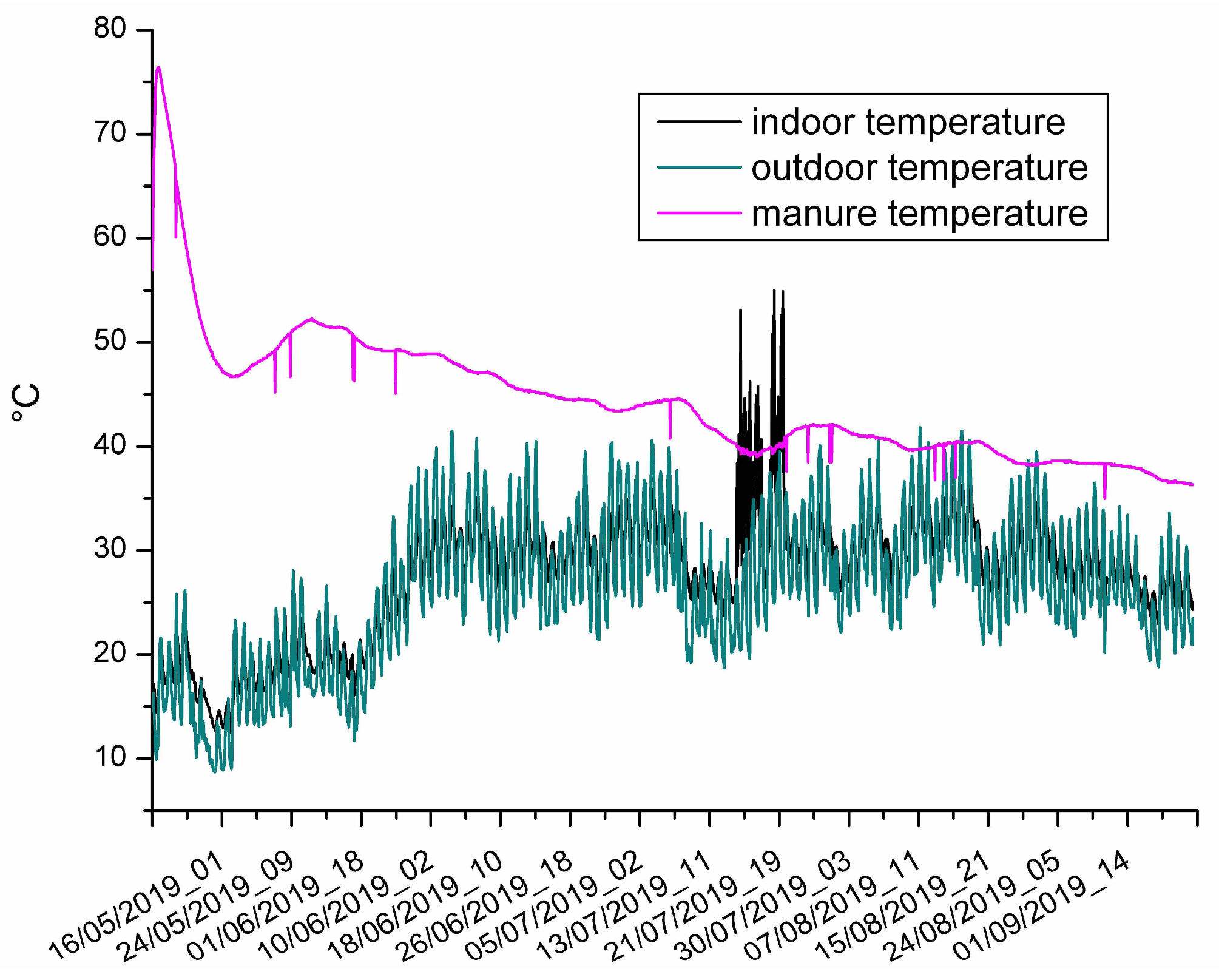
3.2. The Results of the On-Field Monitoring
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, P.; Morawska, L.; Martani, C.; Biskos, G.; Neophytou, M.; Di Sabatino, S.; Bell, M.; Norford, L.; Britter, R. The rise of low-cost sensing for managing air pollution in cities. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, E.G.; Watkins, T.H.; Solomon, P.A.; Thoma, E.D.; Williams, R.W.; Hagler, G.S.; Shelow, D.; Hindin, D.A.; Kilaru, V.J.; Preuss, P.W. The Changing Paradigm of Air Pollution Monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11369–11377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagulian, F.; Barbiere, M.; Kotsev, A.; Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Lagler, F.; Redon, N.; Crunaire, S.; Borowiak, A. Review of the Performance of Low-Cost Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, A.; Ferrero, R.; Gandino, F.; Montrucchio, B.; Rebaudengo, M. A mobile and low-cost system for environmental monitoring: A case study. Sensors 2016, 16, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castell, N.; Dauge, F.R.; Schneider, P.; Vogt, M.; Lerner, U.; Fishbain, B.; Broday, D.; Bartonova, A. Can commercial low-cost sensor platforms contribute to air quality monitoring and exposure estimates? Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Aye, L.; Ngo, T.D.; Zhou, J. Performance evaluation of low-cost air quality sensors: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, I.; Symanski, E.; Stock, T.H. Feasibility of using low-cost portable particle monitors for measurement of fine and coarse particulate matter in urban ambient air. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masic, A.; Bibic, D.; Pikula, B.; Blazevic, A.; Huremovic, J.; Zero, S. Evaluation of optical particulate matter sensors under realistic conditions of strong and mild urban pollution. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 6427–6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, V.; Carotta, M.C.; Fabbri, B.; Gherardi, S.; Giberti, A.; Malagù, C. Array of sensors for detection of gaseous malodors in organic decomposition products. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 174, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriano, D.; Rossi, R.; Alvisi, M.; Cassano, G.; Pfister, V.; Penza, M.; Trizio, L.; Brattoli, M.; Amodio, M.; De Gennaro, G. A Portable Sensor System for Air Pollution Monitoring and Malodours Olfactometric Control. In Sensors and Microsystems: AISEM 2011 Proceedings; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 109. [Google Scholar]
- Abulude, F.O.; Suriano, D.; Oluwagbayide, S.D.; Akinnusotu, A.; Abulude, I.A.; Awogbindin, E. Study on indoor pollutants emission in Akure, Ondo State, Nigeria. Arab. Gulf J. Sci. Res. 2023; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriano, D.; Penza, M. Assessment of the Performance of a Low-Cost Air Quality Monitor in an Indoor Environment through Different Calibration Models. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriano, D.; Prato, M. An Investigation on the Possible Application Areas of Low-Cost PM Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring. Sensors 2023, 23, 3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trizio, L.; Brattoli, M.; De Gennaro, G.; Suriano, D.; Rossi, R.; Alvisi, M.; Cassano, G.; Pfister, V.; Penza, M. Application of artificial neural networks to a gas sensor-array database for environmental monitoring. In Sensors and Microsystems; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Cavaliere, A.; Carotenuto, F.; Di Gennaro, F.; Gioli, B.; Gualtieri, G.; Martelli, F.; Matese, A.; Toscano, P.; Vagnoli, C.; Zaldei, A. Development of Low-Cost Air Quality Stations for Next Generation Monitoring Networks: Calibration and Validation of PM2.5 and PM10 Sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigi, A.; Mueller, M.; Grange, S.K.; Ghermandi, G.; Hueglin, C. Performance of NO, NO2 low cost sensors and three calibration approaches within a real world application. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 3717–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitarma, R.; Marques, G.; Ferreira, B.R. Monitoring Indoor Air Quality for Enhanced Occupational Health. J. Med. Syst. 2017, 41, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Srinivasan, R.; Ganesan, V. Low Cost, Multi-Pollutant Sensing System Using Raspberry Pi for Indoor Air Quality Monitoring. Sustainability 2021, 13, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Jo, B.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Han, W. Development of an IoT-Based Indoor Air Quality Monitoring Platform. J. Sens. 2020, 2020, 8749764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryner, J.; Phillips, M.; Quinn, C.; Neymark, G.; Wilson, A.; Jathar, S.H.; Carter, E.; Volckens, J. Design and testing of a low-cost sensor and sampling platform for indoor air quality. Build. Environ. 2021, 206, 108398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, S.; Li, X. A cost-effective wireless sensor network system for indoor air quality monitoring applications. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 34, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleixandre, M.; Gerboles, M. Review of small commercial sensors for indicative monitoring of ambient gas. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2012, 30, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Kok, G.; Persijn, S.; Sauerwald, T. Review of Portable and Low-Cost Sensors for the Ambient Air Monitoring of Benzene and Other Volatile Organic Compounds. Sensors 2017, 17, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, J.; Ohodnicki, P.R.; Greve, D.W. SAW Sensors for Chemical Vapors and Gases. Sensors 2017, 17, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, D.; Banerjee, S. Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Sensors: Physics, Materials, and Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penza, M.; Rossi, R.M.; Alvisi, M.; Aversa, P.; Cassano, G.B.; Suriano, D.; Benetti, M.; Cannata’, D.; Di Pietrantonio, F.; Verona, E. SAW Gas Sensors with Carbon Nanotubes Films. In Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Beijing, China, 2–5 November 2008; pp. 1850–1853. [Google Scholar]
- Han, T.; Nag, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Xu, Y. Carbon nanotubes and its gas-sensing applications: A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 291, 107–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, E.S.; Williams, L.R.; Lewis, D.K.; Magoon, G.R.; Onasch, T.B.; Kaminsky, M.L.; Worsnop, D.R.; Jayne, J.T. Use of electrochemical sensors for measurement of air pollution: Correcting interference response and validating measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3575–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, M.I.; Popoola, O.A.M.; Stewart, G.B.; Landshoff, P.; Calleja, M.; Hayes, M.; Baldovi, J.J.; McLeod, M.W.; Hodgson, T.F.; Dicks, J.; et al. The use of electrochemical sensors for monitoring urban air quality in low-cost, high-density networks. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 70, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Urso, P.R.; Arcidiacono, C.; Cascone, G. Assessment of a Low-Cost Portable Device for Gas Concentration Monitoring in Livestock Housing. Agronomy 2023, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, D.; Bornwin, M.; Coorevits, K.; Hempel, S.; van Overbeke, P.; Demeyer, P.; Rawat, A.; Declerck, A.; Amon, T.; Amon, B. A Low-Cost Wireless Sensor Network for Barn Climate and Emission Monitoring—Intermediate Results. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woutersen, A.; de Ruiter, H.; Wesseling, J.; Hendricx, W.; Blokhuis, C.; van Ratingen, S.; Vegt, K.; Voogt, M. Farmers and Local Residents Collaborate: Application of a Participatory Citizen Science Approach to Characterising Air Quality in a Rural Area in The Netherlands. Sensors 2022, 22, 8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seesaard, T.; Goel, N.; Kumar, M.; Wongchoosuk, C. Advances in gas sensors and electronic nose technologies for agricultural cycle applications. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 193, 106673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- POREM Project Webpage. Available online: https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/life/publicWebsite/project/LIFE17-ENV-IT-000333/poultry-manure-based-bioactivator-for-better-soil-management-through-bioremediation (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- Von Essen, S.G.; Auvermann, B.W. Health effects from breathing air near CAFOs for feeder cattle or hogs. J. Agromedicine 2005, 10, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Cortus, E.L. Comparison of Hydrogen Sulfide Concentrations and Odor Annoyance Frequency Predic-tions Downwind from Livestock Facilities. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriano, D. A portable air quality monitoring unit and a modular, flexible tool for on-field evaluation and calibration of low-cost gas sensors. HardwareX 2021, 9, e00198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriano, D. SentinAir system software: A flexible tool for data acquisition from heterogeneous sensors and devices. SoftwareX 2020, 12, 100589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SentinAir GitHub Repository. Available online: https://github.com/domenico-suriano/SentinAir (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Figaro Website. Available online: https://www.figarosensor.com/ (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Alphasense Website. Available online: https://www.alphasense.com/ (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Microchip Website. Available online: https://www.microchip.com/ (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Honeywell Website. Available online: https://www.honeywell.com/ (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Raspberrypi Website. Available online: https://www.raspberrypi.com/ (accessed on 7 July 2024).





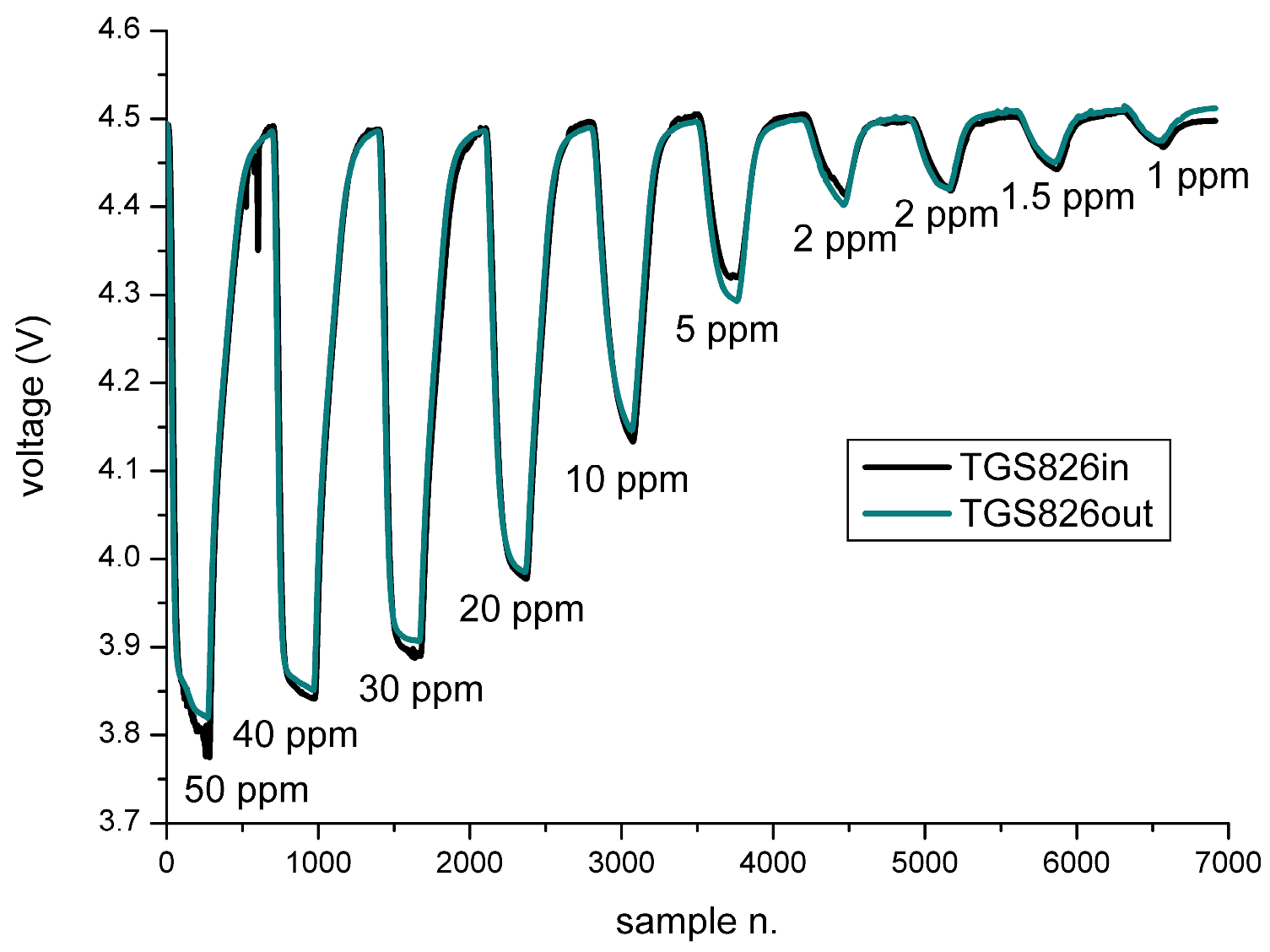
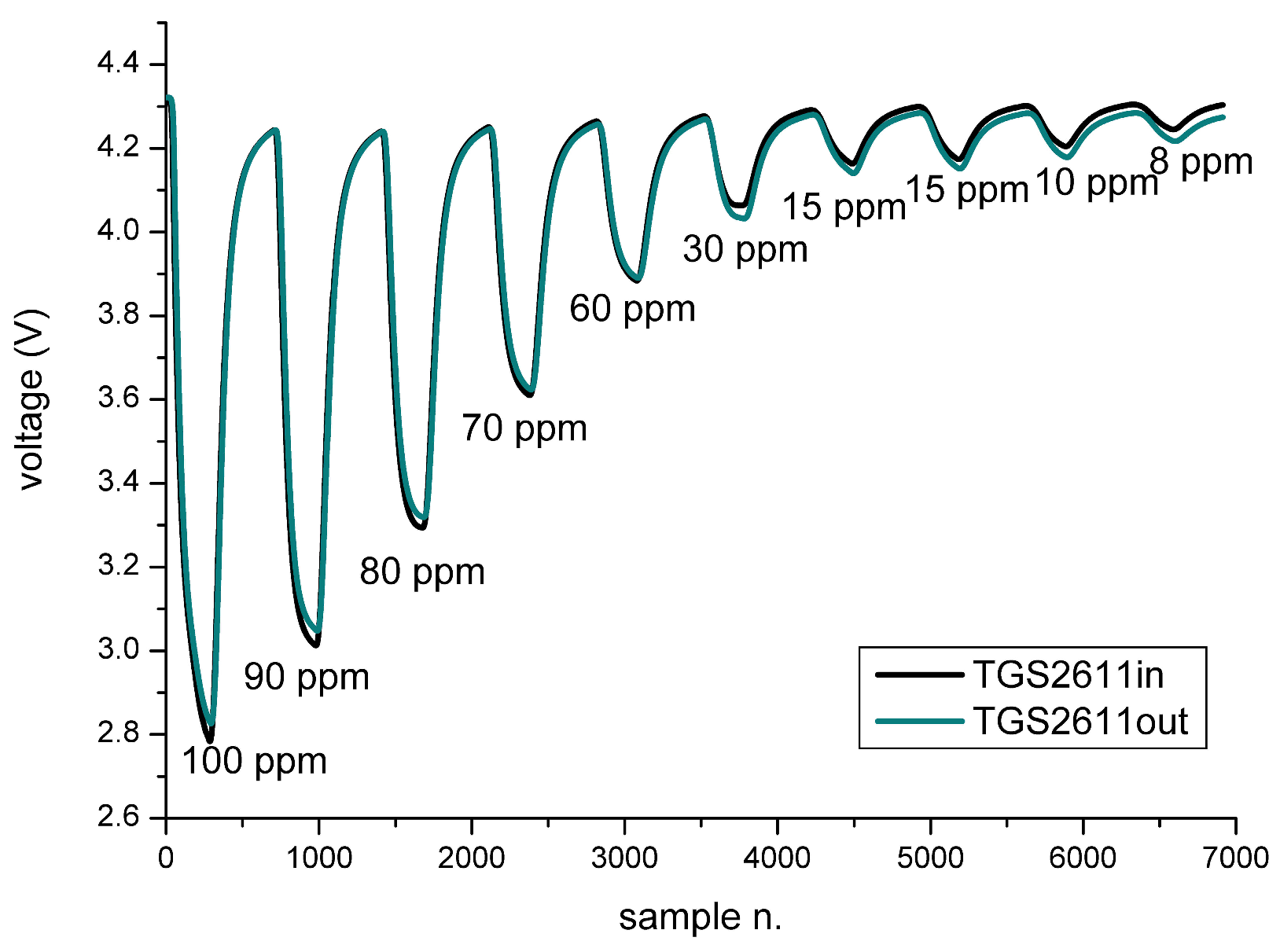



| H2S Concentrations (ppm) | TGS825in (V) | TGS825out (V) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 3.78 | 3.81 |
| 9 | 3.82 | 3.84 |
| 8 | 3.87 | 3.89 |
| 7 | 3.96 | 3.97 |
| 5 | 4.11 | 4.12 |
| 3 | 4.27 | 4.24 |
| 2 | 4.37 | 4.35 |
| 2 | 4.38 | 4.36 |
| 1.5 | 4.41 | 4.4 |
| 1 | 4.45 | 4.44 |
| 0 | 4.48 | 4.47 |
| NH3 Concentrations (ppm) | TGS826in (V) | TGS826out (V) |
|---|---|---|
| 50 | 3.78 | 3.82 |
| 40 | 3.84 | 3.85 |
| 30 | 3.89 | 3.9 |
| 20 | 3.97 | 3.99 |
| 10 | 4.13 | 4.14 |
| 5 | 4.31 | 4.29 |
| 2 | 4.41 | 4.4 |
| 2 | 4.41 | 4.42 |
| 1.5 | 4.44 | 4.45 |
| 1 | 4.46 | 4.47 |
| 0 | 4.49 | 4.49 |
| CH4 Concentrations (ppm) | TGS2611in (V) | TGS2611out (V) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 2.78 | 2.82 |
| 90 | 3.01 | 3.04 |
| 80 | 3.29 | 3.32 |
| 70 | 3.61 | 3.62 |
| 60 | 3.88 | 3.89 |
| 30 | 4.06 | 4.03 |
| 15 | 4.16 | 4.14 |
| 15 | 4.15 | 4.15 |
| 10 | 4.21 | 4.17 |
| 8 | 4.24 | 4.22 |
| 0 | 4.27 | 4.26 |
| Sensor | a (ppm/V) | b (ppm) | R2 | RMSE (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TGS825in | −12.99 | 58.61 | 0.993 | 0.299 |
| TGS825out | −13.85 | 62.19 | 0.992 | 0.331 |
| TGS826in | −61.06 | 270.77 | 0.906 | 5.748 |
| TGS826out | −62.67 | 278.02 | 0.894 | 6.101 |
| TGS2611in | −66.34 | 294.71 | 0.918 | 11.161 |
| TGS2611out | −69.23 | 305.67 | 0.915 | 11.400 |
| Measurement | Min | Max | Mean | Median |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| indoor temperature (°C) | 12.3 | 55 | 27.7 | 29 |
| outdoor temperature (°C) | 8.7 | 41.8 | 26.3 | 26.3 |
| manure temperature (°C) | 35 | 76.4 | 44.4 | 43.5 |
| indoor rh (%) | 27 | 86 | 53 | 51.3 |
| outdoor rh (%) | 19 | 112 | 60 | 57.8 |
| indoor H2S (ppm) | 0 | 34.48 | 0.72 | 0.29 |
| outdoor H2S (ppm) | 0 | 2.8 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| indoor CH4 (ppm) | 0 | 0.64 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| outdoor CH4 (ppm) | 0 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
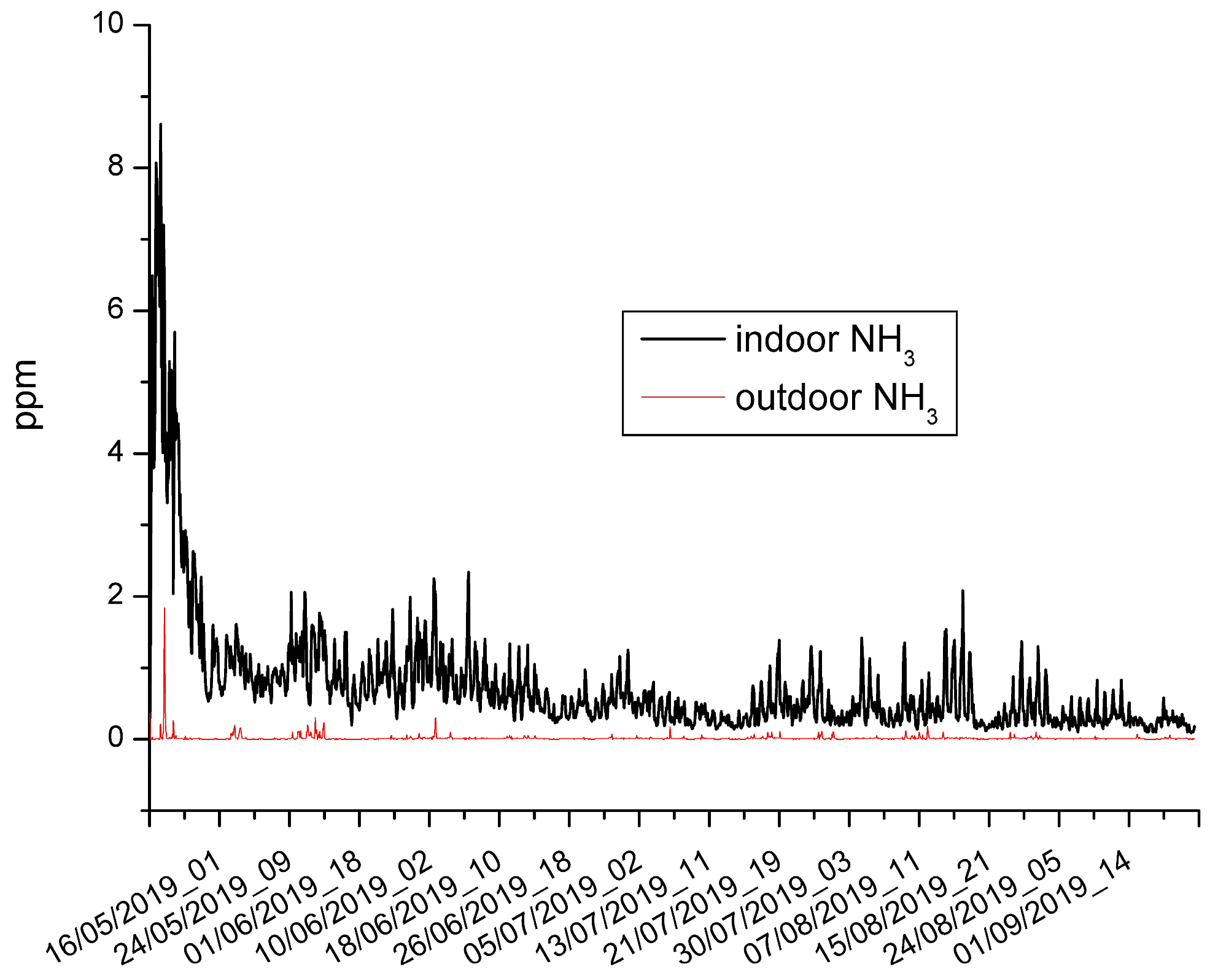
| indoor NH3 (ppm) | 0.09 | 8.61 | 0.74 | 0.5 |
| outdoor NH3 (ppm) | 0 | 1.84 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
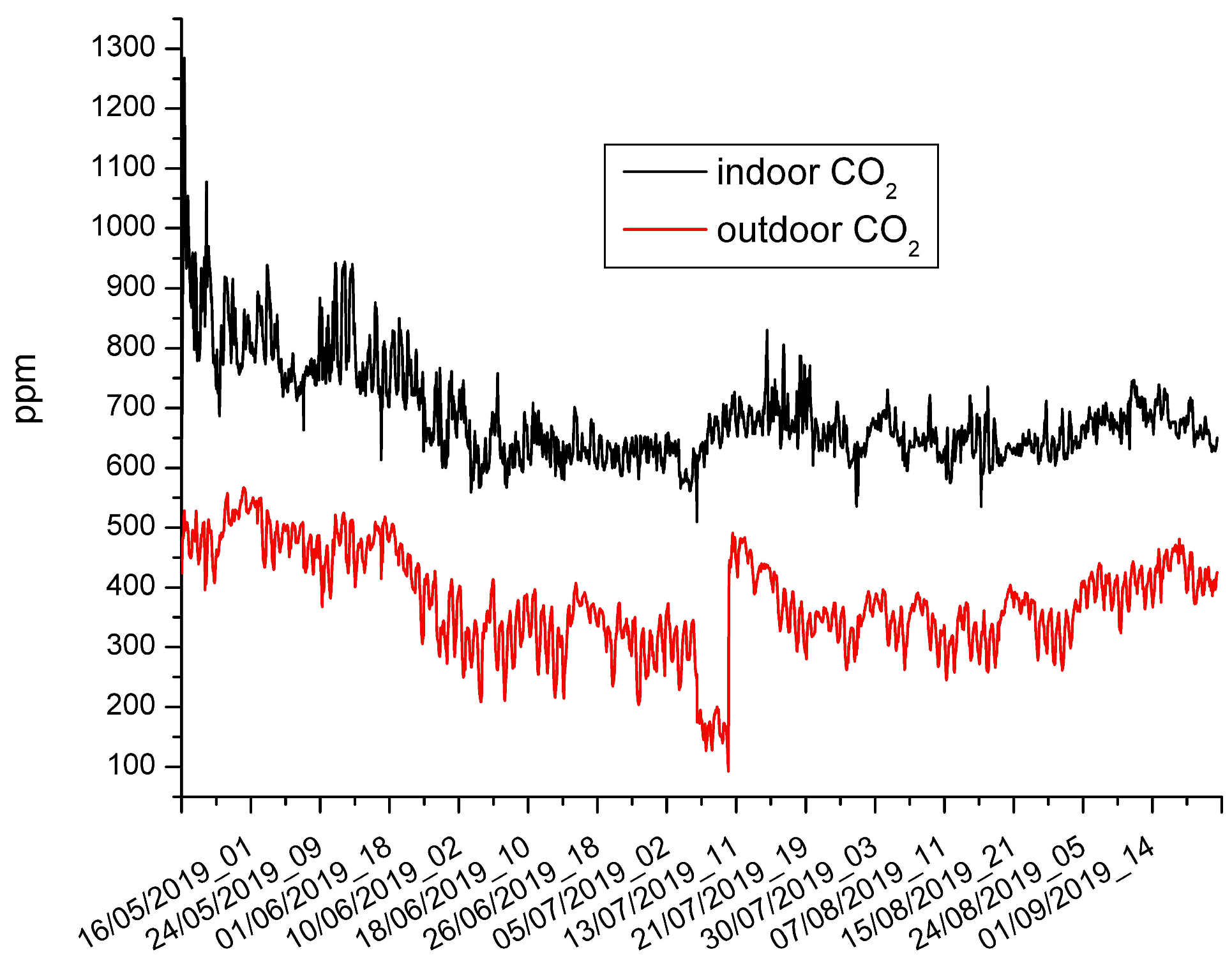
| indoor CO2 (ppm) | 510 | 1285 | 688 | 666 |
| outdoor CO2 (ppm) | 93 | 567 | 377 | 371 |
| Measure | Mean (ppm) | Min (ppm) | Max (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 (indoor study) | 688 | 510 | 1285 |
| CO2 ([30] LCAQM) | 445–780 | 450 | 1400 |
| CO2 ([30] reference) | 559–599 | 480 | 750 |
| NH3 (indoor study) | 0.74 | 0.09 | 8.61 |
| NH3 ([30] LCAQM) | 0.68–3.63 | 0 | 7.1 |
| NH3 ([30] reference) | 1.69–3.51 | 1.4 | 7.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suriano, D.; Abulude, F.O. Monitoring Gas Emissions in Agricultural Productions through Low-Cost Technologies: The POREM (Poultry-Manure-Based Bio-Activator for Better Soil Management through Bioremediation) Project Experience. Earth 2024, 5, 564-582. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth5040029
Suriano D, Abulude FO. Monitoring Gas Emissions in Agricultural Productions through Low-Cost Technologies: The POREM (Poultry-Manure-Based Bio-Activator for Better Soil Management through Bioremediation) Project Experience. Earth. 2024; 5(4):564-582. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth5040029
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuriano, Domenico, and Francis Olawale Abulude. 2024. "Monitoring Gas Emissions in Agricultural Productions through Low-Cost Technologies: The POREM (Poultry-Manure-Based Bio-Activator for Better Soil Management through Bioremediation) Project Experience" Earth 5, no. 4: 564-582. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth5040029
APA StyleSuriano, D., & Abulude, F. O. (2024). Monitoring Gas Emissions in Agricultural Productions through Low-Cost Technologies: The POREM (Poultry-Manure-Based Bio-Activator for Better Soil Management through Bioremediation) Project Experience. Earth, 5(4), 564-582. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth5040029







