Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment—The Occurrence, Sources, Ecological Impacts, Fate, and Remediation Challenges
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
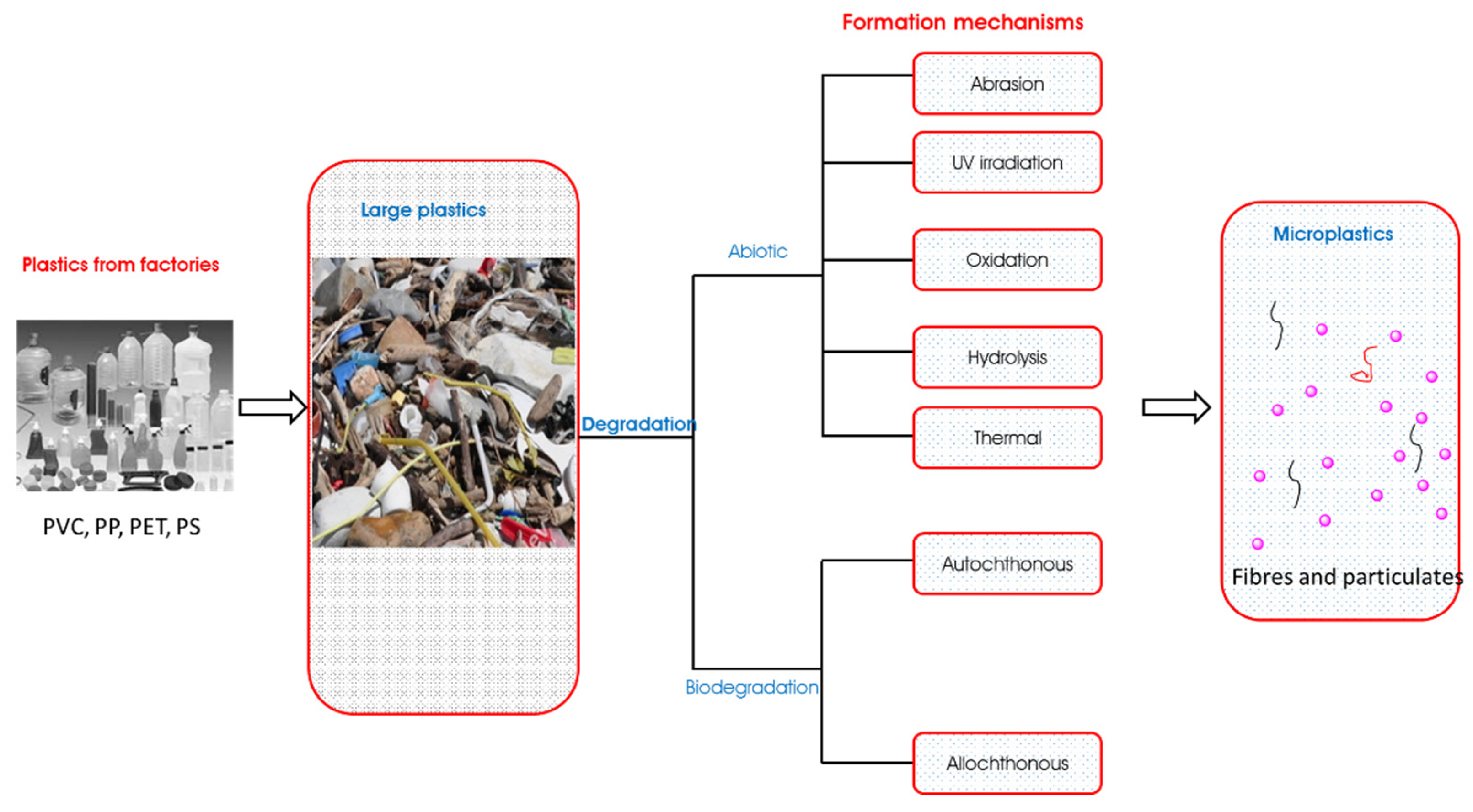
3. Mechanisms of Microplastic Formation
4. Microplastics in Environmental Compartments
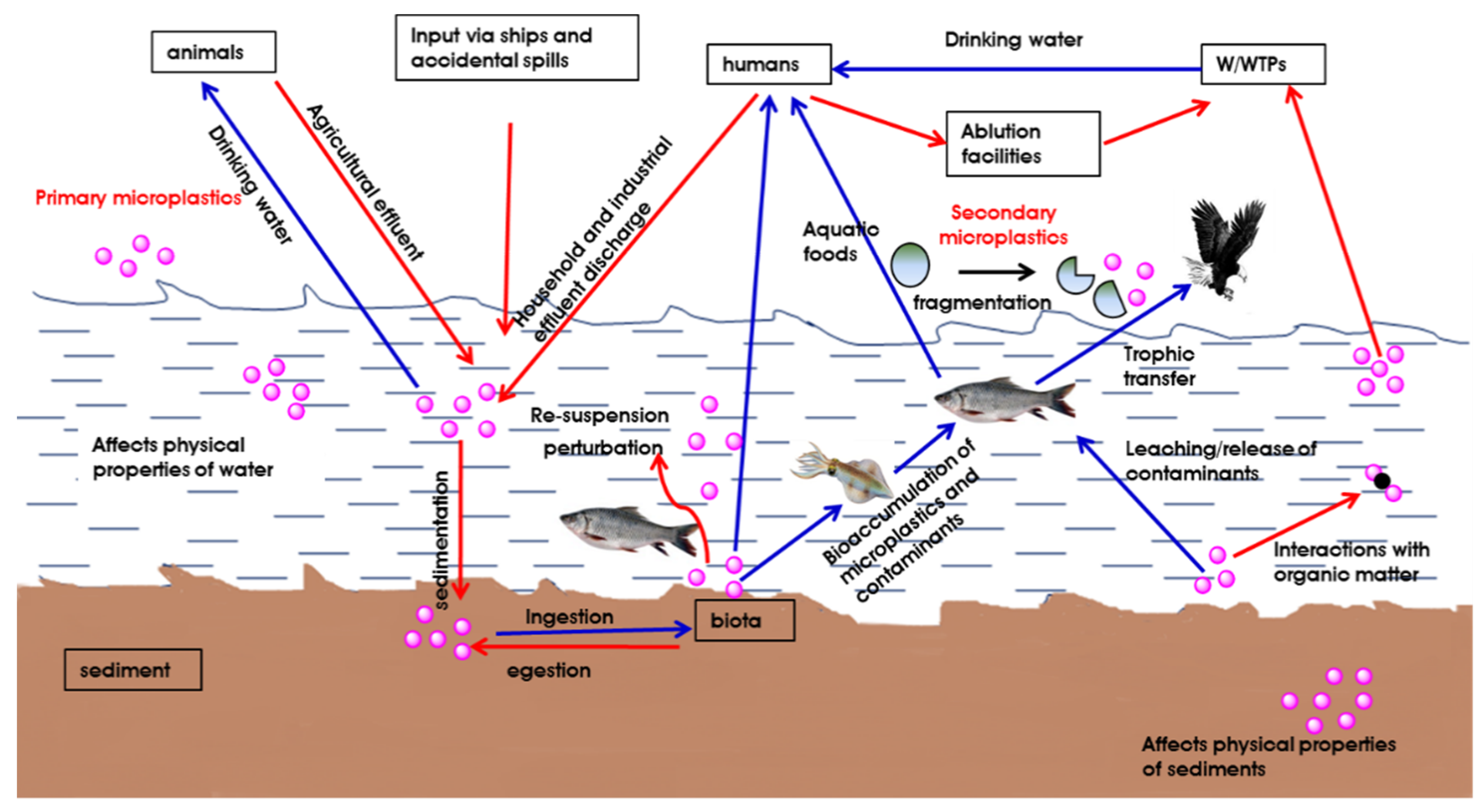
4.1. Aquatic Environment
4.2. Soil and Sediment
5. Interaction of Microplastics with Pollutants
6. Environmental and Health Risk Associated with Microplastics
6.1. Aquatic and Terrestrial Risk/Impacts
6.2. Human Health Risks
6.3. Microplastics in African Aquatic Systems
7. Remediation Strategies
8. Recommendations
9. Conclusion and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Law, K.L.; Thompson, R.C. Oceans. Microplastics in the seas. Science 2014, 345, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastics—The Facts. An Analysis of European Plastics Production, Demand and Waste Data in 2016. Available online: http://www.plasticseurope.org/Document/plastics---the-facts-2016 (accessed on 12 February 2021).
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S. Biological degradation of plastics: A comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of Microplastic on Shorelines Woldwide: Sources and Sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and the fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizzetto, I.; Futter, M.; Langaas, S. Are Agricultural Soils Dumps for Microplastics of Urban Origin? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10777–5010779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNEP. Marine Litter: A Global Challenge; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2009; p. 232. [Google Scholar]
- EIA. Lost at Sea: The Urgent Need to Tackle Marine Litter; EIA: Washigton, DC, USA, 2015.
- Eckert, E.M.; Di Cesare, A.; Kettner, M.T.; Arias-Andres, M.; Fontaneto, D.; Grossart, H.; Corno, G. Microplastics increase the impact of treated wastewater on the freshwater microbial community. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, F.; Quinn, B. The effects of microplastic on freshwater Hydra attenuata feeding, morphology & reproduction. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 487–494. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G.; Xu, P.; Zhu, B.; Bai, M.; Li, D. Microplastics in freshwater river sediments in Shanghai, China: A case study of risk assessment in mega-cities. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Cai, H.; Kolandhasamy, P.; Wu, C.; Rochman, C.M.; Shi, H. Using the Asian clam as an indicator of microplastic pollution in freshwater ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derraik, G.B.J. The pollution of the marine environment by plastic debris: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Busquets, R.; Campos, L.C. Assessment of microplastics in freshwater systems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 707, 135578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwmeester, H.; Hollman, P.C.H.; Peters, R.J.B. Potential Health Impact of Environmentally Released Micro- and Nanoplastics in the Human Food Production Chain: Experiences from Nanotoxicology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8932–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Kwon, O.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Song, Y.K.; Shim, W.J. Marine neustonic microplastics around the south-eastern coast of Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 96, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Yang, J.; Criddle, C.S. Microplastics pollution and reduction strategies. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.G.L.; Nash, R. Microplastics: Finding a consensus on the definition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, M.; Pironti, C.; Motta, O.; Miele, Y.; Proto, A.; Montano, L. Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment: Occurrence, Persistence, Analysis, and Human Exposure. Water 2021, 13, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastics in bivalves cultured for human consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 193, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Chapman, M.G.; Thompson, R.C.; Zettler, L.A.A.; Jambeck, J.; Mallos, N.J. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Stranded Intertidal Marine Debris: Is There a Picture of Global Change? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7082–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, C.; Baker, J.; Bamford, H. Proceedings of the International Research Workshop on the Occurrence, Effects and Fate of Microplastic Marine Debris; NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS-OR&R-30; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administratiom, U.S. Department of Commerce: Washigton, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, M.L.; Gwinnett, C.; Robinson, L.F.; Woodall, L.C. Plastic microfibre ingestion by deep-sea organisms. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajt, O. From plastics to microplastics and organisms. FEBS Open Biol. 2021, 11, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, K.A.; Bootsma, H.A.; Hesslein, A.H. Biomagnification of DDT through the Benthic and Pelagic Food Webs of Lake Malawi, East Africa: Importance of Trophic Level and Carbon Source. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J. Occurrence of microplastics and its pollution in the environment: A review. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2018, 13, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Tahir, A.; Williams, S.L.; Baxa, D.V.; Lam, R.; Miller, J.T.; Teh, F.C.; Werorilangi, S.; Teh, S.J. Anthropogenic debris in seafood: Plastic debris and fibers from textiles in fish and bivalves sold for human consumption. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, A.; Golieskardi, A.; Choo, C.K.; Larat, V.; Galloway, T.S.; Salamatinia, B. The presence of microplastics in commercial salts from different countries. Sci. Rep. 2017, 746173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panti, C.; Giannetti, A.M.; Baini, A.B.M.; Rubegni, A.E.F.; Minutoli, C.R.; Fossi, M.C. Occurrence, relative abundance and spatial distribution of microplastics and zooplankton NW of Sardinia in the Pelagos Sanctuary Protected Area, Mediterranean Sea. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Yang, L.; Xiao, L.; Kehoe, D.K.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Boland, J.J.; Wang, J.J. Microplastic release from the degradation of polypropylene feeding bottles during infant formula preparation. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, J.S. Aquatic Microplastic Research—A Critique and Suggestions for the Future. Water 2020, 12, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Aldridge, D.C. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritization of research needs. Water Res. 2015, 75, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, J.L.; Hutchings, P.; Curley, B.; Hedge, L.; Creese, B.; Johnston, E. Biodiversity conservation in Sydney Harbour. Pac. Conserv. Biol. 2016, 22, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.; Rumi, S.S.; Hu, Y.; Abidi, N. Microfibers from synthetic textiles as a major source of microplastics in the environment: A review. Text. Res. J. 2021, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, M.; Scherer, C.; Alvarez-Muñoz, D.; Brennholt, N.; Bourrain, X.; Buchinger, S.; Fries, E.; Grosbois, C.; Klasmeier, J.; Marti, T.; et al. Microplastics in freshwater ecosystems: What we know and what we need to know. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2014, 26, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xiong, X.; Hu, H.; Wu, C.; Bi, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Lam, P.K.; Liu, J. Occurrence and Characteristics of Microplastic Pollution in Xiangxi Bay of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3794–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Tan, L. Toxic effects of microplastic on marine microalgae Skeletonema costatum: Interactions between microplastic and algae. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Free, C.M.; Jensen, O.P.; Mason, S.A.; Eriksen, M.; Williamson, N.J. High-levels of microplastic pollution in a large, remote, mountain lake. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driedger, A.G.J.; Durr, H.H.; Mitchell, K.; Van Cappellen, P. Plastic debris in the Laurentian Great Lakes: A review. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michielssen, M.R.; Michielssen, E.R.; Ni, J.; Duhaime, M.B. Fate of microplastics and other small anthropogenic litter (SAL) in wastewater treatment plants depends on unit processes employed. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storck, F.; Kools, S.; Rinck-Pfeiffer, S. Microplastics in Fresh Water Resources; GWRC Science Brief September/2015; Global Water Research Coalition: Stirling, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, V.M. Review on the current status of polymer degradation: A microbial approach. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2017, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turra, A.; Manzano, B.; Jasa, R.; Dias, S.; Mahiques, M.M.; Barbosa, L.; Moreira, F.T. Three-dimensional distribution of plastic pellets in sandy beaches: Shifting paradigms. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.C.; Park, B.J.; Palace, V.P. Microplastics in aquatic environments: Implications for Canadian. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cózar, A.; Sanz-Martín, M.; Martí, E.; González-Gordillo, J.I.; Ubeda, B.; Gálvez, J.Á. Plastic Accumulation in the Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaria, G.; Avio, C.G.; Mineo, A.; Lattin, G.L.; Magaldi, M.G.; Belmonte, G.; Moore, C.J.; Regoli, F.; Aliani, S. The Mediterranean Plastic Soup: Synthetic polymers in Mediterranean surface waters. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adomat, Y.; Grischek, T. Sampling and processing methods of microplastics in river sediments—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.E.; Thompson, R.C. Release of synthetic microplastic plastic fibres from domestic washing machines: Effects of fabric type and washing conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 112, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GESAMP. Sources, Fate, and Effects of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Part Two of a Global Assessment; Kershaw, P.J., Rochman, C.M., Eds.; Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection (GESAMP): London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fendall, L.S.; Sewell, M.A. Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: Microplastics in facial cleansers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.E.; Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Characterisation, quantity and sorptive properties of microplastics extracted from cosmetics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Kelly, F.J. Plastic and human health: A micro issue? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P. Microplastics—Occurrence, Fate and Behaviour in the Environment. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2017, 75, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. The impact of polystyrene microplastics on feeding, function, and fecundity in the marine copepod Calanus helgolandicus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehse, S.; Kloas, W.; Zar, C. Short-term exposure with high concentrations of pristine microplastic particles leads to immobilisation of Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Mirande, C.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, V.L.M.; Tassin, B. The first overview of textile fibers, including microplastics, in indoor and outdoor environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 221, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, C.L.; Grif, H.J.; Waluda, C.M.; Thorpe, S.E.; Loaiza, I.; Moreno, B.; Pacherres, C.O.; Hughes, K.A. Microplastics in the Antarctic marine system: An emerging area of research. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzke, D.; Anker-Nilssen, T.; Nost, T.H.; Gotsch, A.; Christensen-Dalsgaard, S.; Langset, M.; Fangel, K.; Albert, A.; Koelmans, A.A. Negligible Impact of Ingested Microplastics on Tissue Concentrations of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Northern Fulmars off Coastal Norway. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1924–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirstein, I.V.; Kirmizi, S.; Wichels, A.; Garin-fernandez, A.; Erler, R.; Martin, L. Dangerous hitchhikers? Evidence for potentially pathogenic Vibrio spp. on microplastic particles. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 120, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akanyange, S.N.; Lyu, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Crittenden, J.C.; Anning, C.; Chen, T.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, H. Does microplastic really represent a threat? A review of the atmospheric contamination sources and potential impact. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remy, F.; Collard, F.; Gilbert, B.; Compère, P.; Eppe, G.; Lepoint, G. When Microplastic Is Not Plastic: The Ingestion of Artificial Cellulose Fibers by Macrofauna Living in Seagrass Macrophyto detritus. Environ. Sci. Technol. Technol. 2015, 49, 11158–11166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouin, T.; Roche, N.; Lohmann, R.; Hodges, G. A Thermodynamic Approach for Assessing the Environmental Exposure of Chemicals Absorbed to Microplastic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, S.A.; Liu, J.; Tesoro, A.G. Transport and fate of microplastic particles in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2016, 91, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, I.A.; Clare, M.A. Dispersion, Accumulation, and the Ultimate Fate of Microplastics in Deep-Marine Environments: A Review and Future Directions. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besseling, E.; Quik, J.T.K.; Sun, M.; Koelmans, A.A. Fate of nano- and microplastic in freshwater systems: A modeling study. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M. Occurrence and Distribution of Microplastics in the Sea Surface Microlayer in Jinhae Bay, South Korea. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.A.; Niven, S.J.; Galloway, T.S.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Microplastic Moves Pollutants and Additives to Worms, Reducing Functions Linked to Health and Biodiversity. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 2388–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.R.; Mayoma, B.S.; Biginagwa, F.J.; Syberg, K. Microplastics in Inland African Waters: Presence, Sources, and Fate. In Freshwater Microplastics: Emerging Environmental Contaminants? Wagner, M., Lambert, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 101–124. [Google Scholar]
- Faure, F.; Corbaz, M.; Baecher, H.; de Alencastro, L. Pollution due to plastics and microplastics in Lake Geneva and in the Mediterranean Sea. Arch. Sci. 2012, 65, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Imhof, H.K.; Ivleva, N.P.; Schmid, J.; Niessner, R.; Laforsch, C. Contamination of beach sediments of a subalpine lake with microplastic particles. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R867–R868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morritt, D.; Stefanoudis, P.V.; Pearce, D.; Crimmen, O.A.; Clark, P.F. Plastic in the Thames: A river runs through it. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 78, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V.; Saad, M.; Renault, N.; Tassin, B. Microplastic contamination in an urban area: A case study in Greater Paris. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, A.; Ramler, D. The discharge of certain amounts of industrial microplastic from a production plant into the River Danube is permitted by the Austrian legislation. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 200, 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blettler, M.C.M.; Ulla, M.A.; Rabuffetti, A.P.; Garello, N. Plastic pollution in freshwater ecosystems: Macro-, meso-, and microplastic debris in floodplain lake. Environ. Monit. Ass. 2017, 189, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubaish, F.; Liebezeit, G. Suspended microplastics and black carbon particles in the Jade system, Southern North Sea. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Worch, E.; Knepper, T.P. Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics in river shore sediments of the Rhine-Main area in Germany. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6070–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, A.; Romano, N.; Galloway, T.; Hamzah, H. Virgin microplastics cause toxicity and modulate the impacts of phenanthrene on biomarker responses in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, S.; Daphi, D.; Lehmann, A.; Rillig, M.C. Transport of microplastics by two collembolan species. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.J.D.; Paco, A.; Santos, P.S.M.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Micro-plastics in soils: Assessment, analytics and risks. Environ. Chem. 2019, 16, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayo, J.; Olmos, S.; López-Castellanos, J.; Alcolea, A. Microplastics And Microfibers In The Sludge Of A Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2016, 11, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziajahromi, S.; Neale, P.; Rintoul, L.; Leusch, F.D.L. Wastewater treatment plants as a pathway 2 for microplastics: Development of a new approach to sample wastewater-based microplastics. Water Res. 2017, 112, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebezeit, G.; Dubaish, F. Microplastics in beaches of the East Frisian Islands Spiekeroog and Kachelotplate. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Vanreusel, A.; Mees, J.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesa, F.S.; Turra, A.; Baruque-ramos, J. Synthetic fibers as microplastics in the marine environment: A review from textile perspective with a focus on domestic washings. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 1116–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, G.; Zhu, B.; Yang, D.; Su, L.; Shi, H.; Li, D. Microplastics in sediments of the Changjiang Estuary, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, R.; Turner, S.D.; Rose, N.L. Microplastics in the sediments of a UK urban lake. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munari, C.; Scoponi, M.; Mistri, M. Plastic debris in the Mediterranean Sea: Types, occurrence and distribution along Adriatic shorelines. Waste Manag. 2017, 67, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, H.A.; Froneman, P.W. A quantitative analysis of microplastic pollution along the south-eastern coastline of South Africa. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, L.A.; Turner, A.; Thompson, R.C. Adsorption of trace metals to plastic resin pellets in the marine environment. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 160, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hentschel, B.T.; Teh, S.J. Long-Term Sorption of Metals Is Similar among Plastic Types: Implications for Plastic Debris in Aquatic Environments. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghilinasrollahabadi, K.; Salehi, M.; Fujiwara, T. Investigate the influence of microplastics weathering on their heavy metals uptake in stormwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L.; Neal, M.A. Applications and societal benefits of plastics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2009, 364, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuten, E.L.; Saquing, J.M.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Barlaz, M.A.; Jonsson, S.; Bjorn, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S.; Yamashita, R.; et al. Transport and release of chemicals from plastics to the environment and to wildlife. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2027–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kefeni, K.K.; Okonkwo, J.O.; Olukunle, O.I.; Botha, B.M. Brominated flame retardants: Sources, distribution, exposure pathways, and toxicity. Environ. Rev. 2011, 19, 238–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermabessiere, L.; Dehaut, A.; Paul-pont, I.; Lacroix, C.; Jezequel, R.; Soudant, P.; Du, G. Occurrence and effects of plastic additives on marine environments and organisms: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-santos, T.; Duarte, A.C. A critical overview of the analytical approaches to the occurrence, the fate and the behaviour of microplastics in the environment. Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 65, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindborg, V.A.; Ledbetter, J.F.; Walat, J.M.; Moffett, C. Plastic consumption and diet of Glaucous-winged Gulls (Larus glaucescens). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2351–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.J.; Lewis, C.; Goodhead, R.M.; Beckett, S.J.; Moger, J.; Tyler, C.R.; Galloway, T.S. Uptake and retention of microplastics by the shore crab Carcinus maenas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8823–8830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosetto, L.C.; Brown, C.; Williamson, J.E. Microplastics on beaches: Ingestion and behavioural consequences for beach hoppers. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.J.; Urbina, M.A.; Goodhead, R.; Moger, J.; Lewis, C.; Galloway, T.S. Effect of microplastic on the gills of the shore crab Carcinus maenas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5364–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sussarellu, R.; Suquet, M.; Thomas, Y.; Lambert, C.; Fabioux, C.; Pernet, M.E.J.; Le Goic, N.; Quillien, V.; Mingant, C.; Epelboin, Y.; et al. Oyster reproduction is affected by exposure to polystyrene microplastics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2430–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidli, S.; Toumi, H.; Lahbib, Y.; El Menif, N.T. The First Evaluation of Microplastics in Sediments from the Complex Lagoon-Channel of Bizerte (Northern Tunisia). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleight, V.A.; Bakir, A.; Thompson, R.C.; Henry, T.B. Assessment of microplastic-sorbed contaminant bioavailability through analysis of biomarker gene expression in larval zebrafish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 116, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngupula, G.W.; Kayanda, R.J.; Mashafi, C.A. Abundance, composition and distribution of solid wastes in the Tanzanian waters of Lake Victoria. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 39, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, T.; Glassom, D.; Smit, A.J. Plastic pollution in five urban estuaries of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biginagwa, F.J.; Mayoma, B.S.; Shashoua, Y.; Syberg, K.; Khan, F.R. First evidence of microplastics in the African Great Lakes: Recovery from Lake Victoria Nile perch and Nile tilapia. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, H.A.; Hean, J.W.; Noundou, X.S.; Froneman, P.W. Do microplastic loads reflect the population demographics along the southern African coastline? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.C.; Perold, V.; Osborne, A.; Moloney, C.L. Consistent patterns of debris on South African beaches indicate that industrial pellets and other mesoplastic items mostly derive from local sources. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Plastics and microplastics in the oceans: From emerging pollutants to emerged threats. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Gimenez, B.C.G. Microplastics in the marine environment: Current trends and future perspectives. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 97, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, E.M.; Shimeta, J.; Nugegoda, D.; Morrison, P.D.; Clarke, B.O. Assimilation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers from microplastics by the marine amphipod, Allorchestes compressa. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8127–8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodson, M.E.; Duffus-Hodson, C.A.; Clark, A.; Prendergast-Miller, M.T.; Thorpe, K.L. Plastic bag derived-microplastics as a vector for metal exposure in terrestrial invertebrates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4714–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellas, J.; Martínez-Armental, J.; Martínez-Cámara, A.; Besada, V.; Martínez-Gómez, C. Ingestion of microplastics by demersal fish from the Spanish Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaposi, K.L.; Mos, B.; Kelaher, B.P.; Dworjanyn, S.A. Ingestion of microplastic has a limited impact on a marine larva. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1638–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobre, C.R.; Santana, M.F.M.; Maluf, A.; Cortez, F.S.; Cesar, A.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Turra, A. Assessment of microplastic toxicity to embryonic development of the sea urchin Lytechinus variegatus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 92, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peda, C.; Caccamo, L.; Fossi, M.C.; Gai, F.; Andaloro, F.; Genovese, L.; Perdichizzi, A.; Romeo, T.; Maricchiolo, G. Intestinal alterations in European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax (Linnaeus, 1758) exposed to microplastics: Preliminary results. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lwanga, E.; Gertsen, H.; Gooren, H.; Peters, P.; Salánki, T.; van der Ploeg, M.; Besseling, E.; Koelmans, A.A.; Geissen, V. Microplastics in the terrestrial ecosystem: Implications for Lumbricus terrestr is (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2685–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keswani, A.; Oliver, D.; Gutierrez, T.; Quilliam, R. Microbial hitchhikers on marine plastic debris: Human exposure risks at bathing waters and beach environments. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 118, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.G.L.; Sobral, P.; Ferreira, A.M. Organic pollutants in microplastics from two beaches of the Portuguese coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1988–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Enhanced desorption of persistent organic pollutants from microplastics under simulated physiological conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusher, A.L.; McHugh, M.; Thompson, R.C. Occurrence of microplastics in the gastrointestinal tract of pelagic and demersal fish from the English Channel. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 67, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarghouei, S.; Hedayati, A.; Raeisi, M.; Hadavand, B.S.; Rezaei, H.; Abed-Elmdoust, A. Size-dependent effects of microplastic on uptake, immune system, related gene expression and histopathology of goldfish (Carassius auratus). Chemosphere 2021, 276, 129977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, J.; Ren, H. Uptake and accumulation of polystyrene microplastics in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and toxic effects in liver. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4054–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Turner, A. Human exposure to microplastics: A study in Iran. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, C.D.; Loder, M.G.; Fricke, N.F.; Lang, T.; Griebeler, E.M.; Janke, M.; Gerdts, G. Plastic ingestion by pelagic and demersal fish from the North Sea and Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, A.; Hoellein, T.J.; Mason, S.A.; Schluep, J.; Kelly, J.J. Microplastic is an abundant and distinct microbial habitat in an urban river. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11863–11871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisser, J.; Shaw, J.; Hallegraeff, G.; Proietti, M.; Barnes, D.K.; Thums, M.; Wilcox, C.; Hardesty, B.D.; Pattiaratchi, C. Millimeter-sized marine plastics: A new pelagic habitat for microorganisms and invertebrates. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, M.C.; Rosenberg, M.; Cheng, L. Increased oceanic microplastic debris enhances oviposition in an endemic pelagic insect. Biol. Lett. 2012, 8, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besseling, E.; Wegner, A.; Foekema, E.M.; Den, H.V.; Greve, M.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Effects of Microplastic on Fitness and PCB Bioaccumulation by the Lugworm Arenicola marina (L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fossi, M.C.; Panti, C.; Guerranti, C.; Coppola, D.; Giannetti, M.; Marsili, L.; Minutoli, R. Are baleen whales exposed to the threat of microplastics? A case study of the Mediterranean fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2374–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, D.; Carvalho-Souza, G. Are we eating plastic-ingesting fish? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 1031–1032, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philipp, C.; Unger, B.; Ehlers, S.M.; Koop, J.H.E.; Siebert, U. First Evidence of Retrospective Findings of Microplastics in Harbour Porpoises (Phocoena phocoena) From German Waters. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 682532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimi, O.S.; Fadare, O.O.; Okiffo, E.D. Microplastics in African ecosystems: Current knowledge, abundance, associated contaminants, techniques, and research needs. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, T.; Glassom, D. Sea-surface microplastic concentrations along the coastal shelf of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weideman, E.A.; Perold, V.; Ryan, P.G. Little evidence that dams in the Orange-Vaal River system trap floating microplastics or microfibres. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahms, H.T.J.; van Rensburg, G.J.; Greenfield, R. The microplastic profile of an urban African stream. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 138893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbogbo, F.; Takyi, J.B.; Billah, M.K.; Ewool, J. Analysis of microplastics in wetland samples from coastal Ghana using the Rose Bengal stain. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adika, S.A.; Mahua, E.; Crane, R.; Marchant, R.; Montford, J.; Folorunsho, R.; Gordon, C. Microplastic ingestion by pelagic and demersal fish species from the Eastern Central Atlantic Ocean, off the Coast of Ghana. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 110998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebere, E.C.; Wirnkor, V.A.; Ngozi, V.E.; Chukwuemeka, I.S. Macrodebris and microplastics pollution in Nigeria: First report on abundance, distribution and composition. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2019, 34, e2019012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oni, B.A.; Ayeni, A.O.; Agboola, O.; Oguntade, T.; Obanla, O. Comparing microplastics contaminants in (dry and raining) seasons for Ox-Bow Lake in Yenagoa, Nigeria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosore, C.; Ojwang, L.; Maghanga, J.; Kamau, J.; Kimeli, A.; Omukoto, J.; Ngisiag’e, N.; Mwaluma, J.; Ong’ada, H.; Magori, C. Occurrence and ingestion of microplastics by zooplankton in Kenya’s marine environment: First documented evidence. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 40, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migwi, F.K.; Ogunah, J.A.; Kiratu, J.M. Occurrence and Spatial Distribution of Microplastics in the Surface Waters of Lake Naivasha, Kenya. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabaka, S.H.; Ghobashy, M.; Marey, R.S. Identification of marine microplastics in Eastern Harbor, Mediterranean Coast of Egypt, using differential scanning calorimetry. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merga, L.B.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; Van den Brink, P.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Distribution of microplastic and small macroplastic particles across four fish species and sediment in an African lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 14052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missawi, O.; Bousserrhine, N.; Belbekhouche, S.; Zitouni, N.; Alphonse, V.; Boughattas, I.; Banni, M. Abundance and distribution of small microplastics (≤3 μm) in sediments and seaworms from the Southern Mediterranean coasts and characterisation of their potential harmful effects. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tata, T.; Belabed, B.E.; Bououdina, M.; Bellucci, S. Occurrence and characterization of surface sediment microplastics and litter from North African coasts of Mediterranean Sea: Preliminary research and first evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.K.H.; Lee, K.K.; Tang, K.H.D.; Yap, P. Microplastics in the freshwater and terrestrial environments: Prevalence, fates, impacts and sustainable solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vethaak, A.D.; Leslie, H.A. Plastic Debris Is a Human Health Issue. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6825–6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venghaus, D.; Barjenbruch, M. Microplastics in urban water management. Tech. Trans. 2017, 1, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Petroody, S.S.A.; Hashemi, S.H.; van Gestel, C.A.M. Transport and accumulation of microplastics through wastewater treatment sludge processes. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Takehana, T.; Taniguchi, I.; Yamaji, H.; Maeda, Y.; Toyohara, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Kimura, Y.; Oda, K.A. A bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly(ethylene terephthalate). Science 2016, 351, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhao, J.; Jian, L. Evidence of Polyethylene Biodegradation by Bacterial Strains from the Guts of Plastic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 48, 13776–13784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombelli, P.; Howe, C.J. Polyethylene bio-degradation by caterpillars of the wax moth Galleria mellonella. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 292–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramila, P.; Ramesh, K.V. Biodegradation of low density polyethylene (LDPE) by fungi isolated from marine water—A SEM analysis. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 5, 5013–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumar, A.; Veerappapillai, S. Biodegradation of Plastics—A Brief Review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2015, 31, 204–209. [Google Scholar]
- FDA. Prohibition against sale or distribution of rinse-off cosmetics containing plastic microbeads. In Microbead-Free Waters Act of 2015; FDA: Washigton, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nhamo, G. Regulating Plastics Waste, Stakeholder Engagement and Sustainability Challenges in South Africa. Urban Forum 2008, 19, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House of Commons Committee. Environmental Impact of Microplastics; House of Commons: Washigton, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, S.C.L.; Paterson, D.M.; Queiros, A.M.; Rees, A.P.; Stephens, N.; Widdicombe, S.; Beaumont, N.J. A conceptual framework for assessing the ecosystem service of waste remediation: In the marine environment. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 20, 2069–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, C.E.; Mineau, M.M.; Rogers, S.H. Examining the ecosystem service of nutrient removal in a coastal watershed. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 20, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrotti, A.A.; Luiza, M. Microplastics in the oceans: The solutions lie on land. J. Field Actions 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar]
- Cammalleri, V.; Marotta, D.; Antonucci, A.; Protano, C.; Fara, G.M. A survey on knowledge and awareness on the issue “mi- croplastics”: A pilot study on a sample of future public health professionals. Annali Di Igiene 2020, 32, 577–589. [Google Scholar]
- Dalu, M.T.B.; Cuthbert, R.N.; Muhali, H.; Chari, L.D.; Manyani, A.; Masunungure, C.; Dalu, T. Is awareness on plastic pollution being raised in schools? Understanding perceptions of primary and secondary school educators. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L.; Green, C. Making sense of microplastics? Public understandings of plastic pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 152, 110908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, S.; Wyer, H.; Leapman, J.C. Addressing the environmental and health impacts of microplastics requires open collaboration between diverse sectors. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3000932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change; IPPC: New York, NY, USA; Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Merkl, A.; Stuchtey, M. Stemming the Tide: Land-based strategies for a plastic-free ocean. In Ocean Conservancy; McKinsey Centre for Business and Environment: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Marine Litter Solutions. Declaration of the Global Plastics Associations for Solutions on Marine Litter Declaration of the Global Plastics Associations for Solutions on Marine Litter. 2017. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiorpqxwJvxAhWJFxQKHbxCDgkQFjABegQIBBAD&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.marinelittersolutions.com%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2018%2F04%2FMarine-Litter-Report-2018.pdf&usg=AOvVaw1e6a9gNP7QDPd43JFpQL-t (accessed on 26 November 2020).
- Eriksen Borgogno, F.; Villarrubia-Gómez, P.; Anderson, E.; Box, C.; Trenholm, N. Mitigation strategies to reverse the rising trend of plastics in Polar Regions. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Risk/Impact Example | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Vector of anthropogenic organic contaminants: | ||
| Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE) congeners | Microplastics contaminated with PBDE congeners mistaken for food by marine Amphipod (Allorchestes compressa) and assimilated | [117] |
| Triclazan (anti- microbial additive to plastics) | Triclazan reported in a marine sediment lug worm. Triclazan causes reduction in immune function and survival, reduction in ability to feed and process sediments | [72] |
| Phthalates | Phthalates are capable of inducing endocrine disruption and dysfunctional reproductive system observed in a laboratory study on fish | [16] |
| Inorganic contaminants e.g., Zn | Microplastics acted as a vector for Zn, by increasing its bioavailability to earthworms, there was no evidence of Zn accumulation, mortality or weight change in earthworms. | [118] |
| (2) Aquatic ecosystems/food webs: | ||
| Ingestion of microplastics by aquatic organisms | Shore crab (Carcinus maenas) take up microplastics via inspiration across the gills and ingestion of pre-exposed food (e.g., mussel Mytilus edulis). | [104] |
| Zooplanktivores confused paint and styrofoam microparticles natural prey. | [17] | |
| Microplastic ingestion was observed in three demersal fish species from the Spanish coasts, the abundance of microplastics (33.3%) occurring stomachs of red mullets followed by dogfish (20.8%) | [119] | |
| Mortality, growth and survival of organisms | Exposure sea urchin (Tripneustes gratilla) to polyethylene microsphere concentrations exceeding those in marine environment a small non-dose dependent effect on larval growth, but there was no significant effect on survival because the microplastics were egested within hours of ingestion. | [120] |
| Acute physiological effects on osmoregulatory and respiratory functions | Acute aqueous exposure of shore crab Carcinus maenas to polystyrene microplastics (diameter: 8 μm) had significant but transient effects on branchial function and ion exchange. Significant dose-dependent effect on oxygen consumption was observed after 1 h of exposure, returning to normal levels after 16 h, while a significant decrease in hemolymph sodium ions and an increase in calcium ions occurred after 24 h post-exposure. | [106] |
| Reproductive effects | Virgin and beach-stranded plastic pellets microplastics increased anomalous embryonic development of sea urchin (Lytechinus variegatus) by 58.1% and 66.5%, respectively, but toxicity of stranded pellets was lower than virgin pellets. Plastic pellets act as a vector of pollutants, especially for plastic additives found on virgin particles. | [121] |
| Chronic alterations in digestive system of aquatic organisms | Microplastics caused histological alterations in distal intestinal of European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax after 60 and 90 days of exposure polyvinylchloride (PVC) microplastics. | [122] |
| Earthworm mortality and growth | Polyethylene microplastics caused significantly higher mortality of earthworm Lumbricus terrestris after 60 days at 28%, 45%, and 60% of microplastics in the litter than at 7% w/w and in the control (0%). Growth rate was also significantly reduced at 28%, 45%, and 60% w/w microplastics, compared to the 7% and control treatments. This has implications on the fate and risk of microplastic once dredged from aquatic systems and disposed of in terrestrial ecosystems. | [123] |
| (3) Human health risks: | ||
| Consumption of microplastic contaminated aquatic foods | Microplastic accumulation in human body, localized particle toxicity, and chemical and microbial contaminants arising from microplastics ingested or inhaled. | Human consumption of bivalves, [56] Consumption of commercial salt, [31] |
| Vector of pathogenic organism and disease vectors | Transmission of pathogens, fecal indicator organisms and harmful algal bloom species (HABs) across beach and bathing environments and potentially promote the spread of infectious diseases | [124] |
| Country | Location | Sample Types | Occurrence | Abundance | Particle Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Africa [140,141] | Estuaries of KwaZulu-Natal River system, South Africa | Fish | Natural microfibres (70.4%), polyethersulphone (10.4%) | 5.54 ± 3.26 p/100 m2 (winter) | 0.02–0.5 |
| Nylon (5.2%) and PVC (3.0%) | 2.96 ± 2.94 p/100 m2 (summer) | ||||
| Water | Fibers: blue (92%) | 2.3 ± 7.2 p/L (wet season), 1.4 ± 2.6 p/L (dry season) | |||
| South Africa [142] | Braamfontein Spruit | Stream sediment | 166.8 p/kg (dw) | 0.053–4 | |
| Johannesburg | |||||
| Ghana [143] | Sakumo II | Water | 0.09 p/mL | 0.1–5 | |
| Ghana [144] | Eastern Central Atlantic Ocean | Marine sediment | 3.2 ± 2.7 dw | ||
| Nigeria [145] | South Eastern Coast | Surface water | 410–1556 p/L | ||
| Nigeria [146] | Yenogoa | Lake sediment | 1004–8329 p/m3 (dry season) | 0.02–0.5 | |
| 201–8369 p/m3 (wet season) | |||||
| Kenya [147] | Centra Kenya | Surface water | 110 p/m3 | 0.25–2.4 | |
| Kenya [148] | Naivasha | Lake surface water | 0.407 ± 0.135 p/m2 | 1–5 | |
| Egypt [149] | Eastern Harbour | Seawater | 83–174 p/100 g (dw) | 0.5–5 | |
| Ethiopia [150] | Lake Ziway | Freshwater | 6.3–115.9 p/kg (dw) | 0.5–5 | |
| Tunisia [151] | Southern Mediterranean | Marine sediment | 129–606 p/kg (dw) | 0.0001–1 | |
| Tunisia [152] | Gulf of Annaba | Marine sediment | 182.66 ± 27.32–649.03 ± 184.02 dw | 0.81–2.16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaukura, N.; Kefeni, K.K.; Chikurunhe, I.; Nyambiya, I.; Gwenzi, W.; Moyo, W.; Nkambule, T.T.I.; Mamba, B.B.; Abulude, F.O. Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment—The Occurrence, Sources, Ecological Impacts, Fate, and Remediation Challenges. Pollutants 2021, 1, 95-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants1020009
Chaukura N, Kefeni KK, Chikurunhe I, Nyambiya I, Gwenzi W, Moyo W, Nkambule TTI, Mamba BB, Abulude FO. Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment—The Occurrence, Sources, Ecological Impacts, Fate, and Remediation Challenges. Pollutants. 2021; 1(2):95-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants1020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaukura, Nhamo, Kebede K. Kefeni, Innocent Chikurunhe, Isaac Nyambiya, Willis Gwenzi, Welldone Moyo, Thabo T. I. Nkambule, Bhekie B. Mamba, and Francis O. Abulude. 2021. "Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment—The Occurrence, Sources, Ecological Impacts, Fate, and Remediation Challenges" Pollutants 1, no. 2: 95-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants1020009
APA StyleChaukura, N., Kefeni, K. K., Chikurunhe, I., Nyambiya, I., Gwenzi, W., Moyo, W., Nkambule, T. T. I., Mamba, B. B., & Abulude, F. O. (2021). Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment—The Occurrence, Sources, Ecological Impacts, Fate, and Remediation Challenges. Pollutants, 1(2), 95-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants1020009








