The Mechanical Properties of Brass Alloys: A Review †
Abstract
1. Introduction
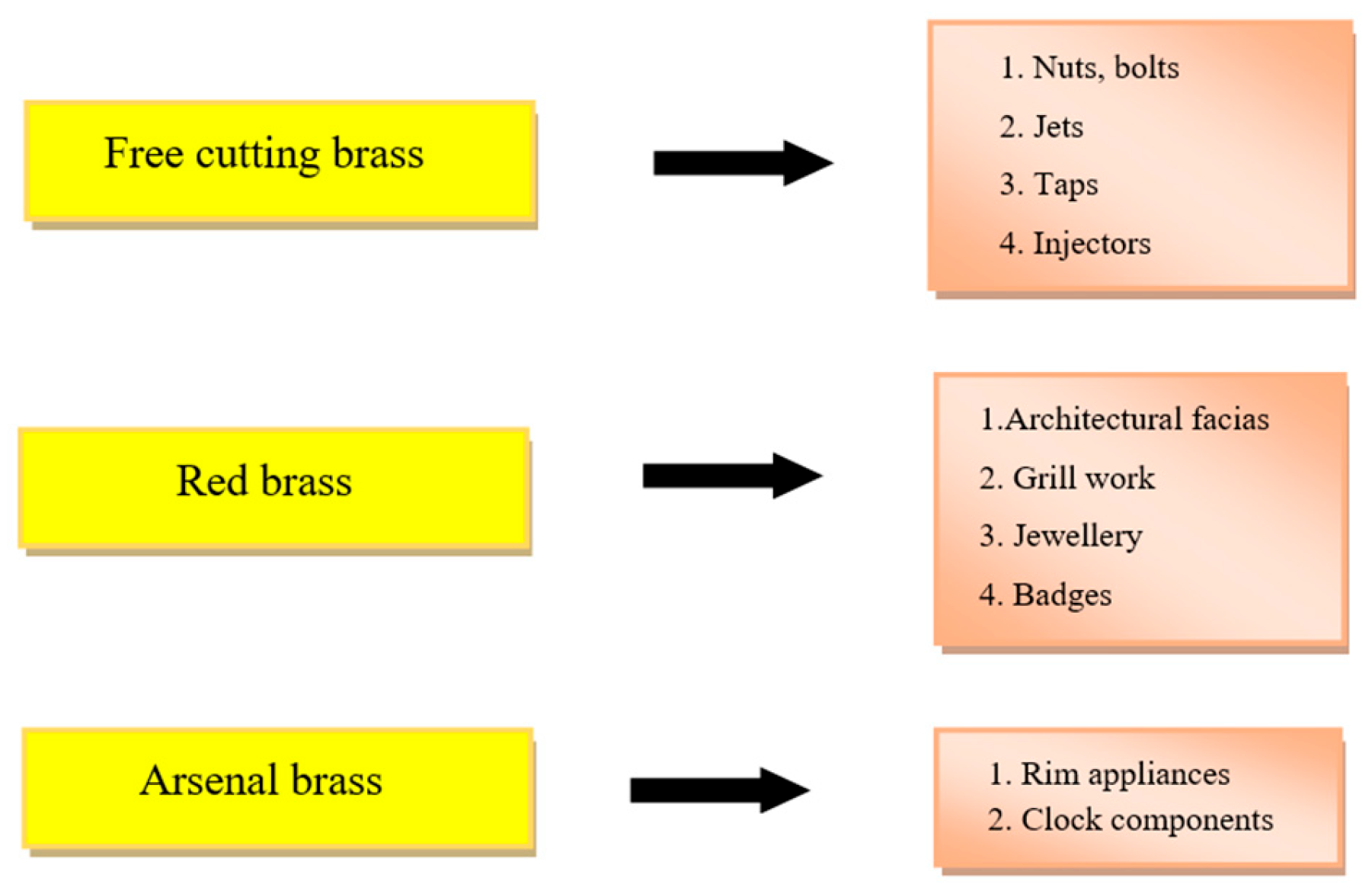
2. Brass and Alloys
3. Production Process
4. Mechanical Properties of Brass Alloys
5. Corrosion Properties of Brass Alloys
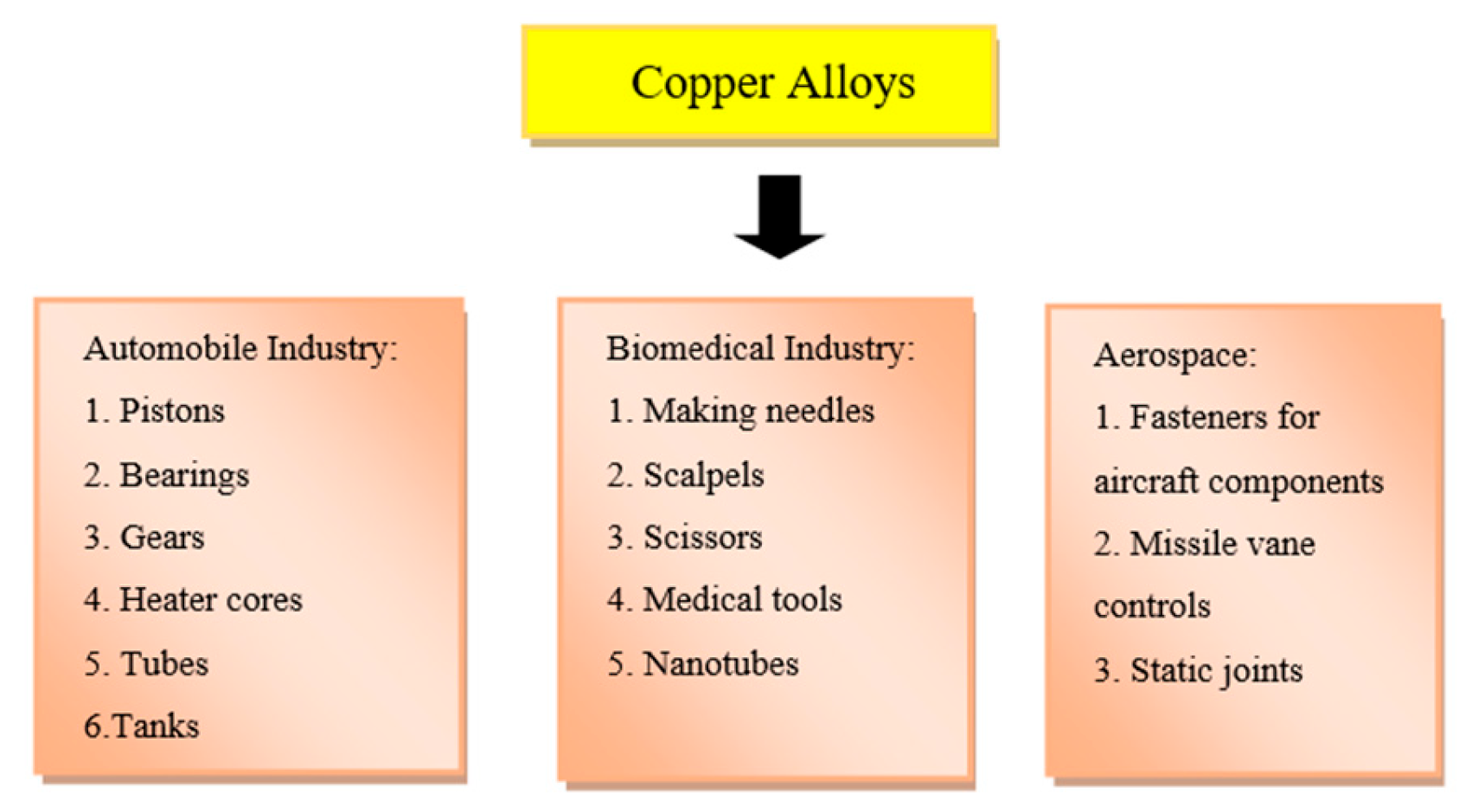
6. Applications
6.1. Mechanical Fasteners
6.2. Adhesive Bonding
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Imai, H.; Kosaka, Y.; Kojima, A.; Li, S.; Kondoh, K.; Umeda, J.; Atsumi, H. Characteristics and machinability of lead-free P/M Cu60–Zn40 brass alloys dispersed with graphite. Powder Technol. 2010, 198, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, A.K.; Spretnak, J.W. The effect of solute (Zn) concentration on the plastic deformation properties of α and α + β Cu-Zn alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1976, 24, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, C.N.; Georgiou, E.P.; Simeonidis, K. Lubricated wear behavior of leaded α + β brass. Tribol. Int. 2012, 50, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achiţei, D.C.; Minciună, M.G.; Vizureanu, P.; Sandu, A.V.; Cimpoeşu, R.; Istrate, B. Study on structure and properties of CuZnPb alloy. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 133, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Fontaine, A.; Keast, V.J. Compositional distributions in classical and lead-free brasses. Mater. Charact. 2006, 57, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfenden, A.; Wright, P.K. Role of lead in free-machining brass. Met. Technol. 1979, 6, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddart, C.T.H.; Lea, C.; Dench, W.A.; Green, P.; Pettit, H.R. Relationship between lead content of Cu-40Zn, machinability, and swarf surface composition determined by auger electron spectroscopy. Met. Technol. 1979, 6, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazopoulos, G. Leaded brass rods C 38500 for automatic machining operations: A technical report. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2002, 11, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaded Brasses, Copper Development Association Inc. Available online: https://www.copper.org/resources/properties/microstructure/lead_brasses.html (accessed on 17 January 2022).
- Siu, K.W.; Kwok, J.C.M.; Ngan, A.H.W. Thermo-mechanical processing of brass components for potable-water usage increases risks of Pb leaching. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshin, G.V.; Ferguson, J.F.; Lancaster, A.N. Influence of natural organic matter on the corrosion of leaded brass in potable water. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllidou, S.; Parks, J.; Edwards, M. Lead particles in potable water. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2007, 99, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Sinsheimer, P.; Sarver, E.; Parks, J.; Edwards, M. Evaluating “lead-free” brass performance in potable water. Corrosion 2019, 75, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfland, C.; Scardina, P.; Edwards, M. Lead-contaminated water from brass plumbing devices in new buildings. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2010, 102, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllidou, S.; Nguyen, C.K.; Zhang, Y.; Edwards, M.A. Lead (Pb) quantification in potable water samples: Implications for regulatory compliance and assessment of human exposure. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 185, 1355–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estelle, A.A. Drinking water lead regulations: Impact on the brass value chain. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kondoh, K.; Imai, H.; Atsumi, H. Fabrication and properties of lead-free machinable brass with Ti additive by powder metallurgy. Powder Technol. 2011, 205, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sdwa/use-lead-free-pipes-fittings-fixtures-solder-and-flux-drinking-water (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Schultheiss, F.; Windmark, C.; Sjöstrand, S.; Rasmusson, M.; Ståhl, J.E. Machinability and manufacturing cost in low-lead brass. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 99, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuyucak, S.; Sahoo, M. A review of the machinability of copper-base alloys. Can. Metall. Q. 1996, 35, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksongkarm, P.; Rojananan, S.; Rojananan, S. Bismuth formation in lead-free Cu-Zn-Si yellow brass with various bismuth-tin alloy additions. Mater. Trans. 2018, 59, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adineh, M.; Doostmohammadi, H. Microstructure, mechanical properties and machinability of Cu-Zn-Mg and Cu-Zn-Sb brass alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1504–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsumi, H.; Imai, H.; Li, S.; Kondoh, K.; Kousaka, Y.; Kojima, A. The effect of solid solutionizing Ti element on microstructural and mechanical properties of extruded Cu-40Zn-Ti ternary alloy. Trans. JWRI 2011, 40, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Ding, Z.; Tao, Q.C.; Liang, L.; Ding, Y.F.; Zhang, W.W.; Zhu, Q.L. High-strength and free-cutting silicon brasses designed via the zinc equivalent rule. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 723, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulfatzis, A.; Pantazopoulos, G.; David, C.; Sagris, S.; Paipetis, A. Final heat treatment as a possible solution for the improvement of machinability of Pb-free brass alloys. Metals 2018, 8, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulfatzis, A.I.; Pantazopoulos, G.A.; Paipetis, A.S. Microstructure and properties of lead-free brasses using post-processing heat treatment cycles. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazopoulos, G.; Vazdirvanidis, A. Characterization of the microstructural aspects of machinable α–β phase brass. Microsc. Anal. 2008, 22, 13–16. [Google Scholar]

| S. No. | Properties | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Density | 8.49 g/cm3 |
| 2 | Elastic modulus | 97 Gpa |
| 3 | Yield strength | 124–310 Mpa |
| 4 | Ultimate strength | 338–469 Mpa |
| S. No. | Properties | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Solubility | Insoluble in water |
| 2 | Melting temperature | 930 °C |
| 3 | Explosive properties | Low explosive point properties and ductility |
| 4 | Oxidising properties | Will react exothermically if mixed with strong oxidising substance |
| S. No. | Materials | Properties | Methodology |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cu | Highly Malleable and Ductile | Powder Metallurgy |
| 2 | UNSC26000 | High Tensile Strength | Machine Rolling and Thread Knurling |
| 3 | CZ106 | Superior Drawing Properties and Ductility | Powder Metallurgy |
| 4 | CZ108 | Good Cold Heading and Bending Properties | Cold Working |
| 5 | CZ112 | Harder and Stronger Duplex Structure | Powder Metallurgy |
| 6 | CZ132 | Good Machinability and Formability | Hot Forging |
| 7 | CZ126 | High Ductility and Formable Characteristics | Powder Metallurgy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jasper, S.; Subash, R.; Muthuneelakandan, K.; Vijayakumar, D.; Jhansi Ida, S. The Mechanical Properties of Brass Alloys: A Review. Eng. Proc. 2025, 93, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025093011
Jasper S, Subash R, Muthuneelakandan K, Vijayakumar D, Jhansi Ida S. The Mechanical Properties of Brass Alloys: A Review. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 93(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025093011
Chicago/Turabian StyleJasper, S., R. Subash, K. Muthuneelakandan, D. Vijayakumar, and S. Jhansi Ida. 2025. "The Mechanical Properties of Brass Alloys: A Review" Engineering Proceedings 93, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025093011
APA StyleJasper, S., Subash, R., Muthuneelakandan, K., Vijayakumar, D., & Jhansi Ida, S. (2025). The Mechanical Properties of Brass Alloys: A Review. Engineering Proceedings, 93(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025093011





