Optimization of the Spinning Parameters for Wire-Based Electrospinning of Casein–PEO Nanofiber Mats †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
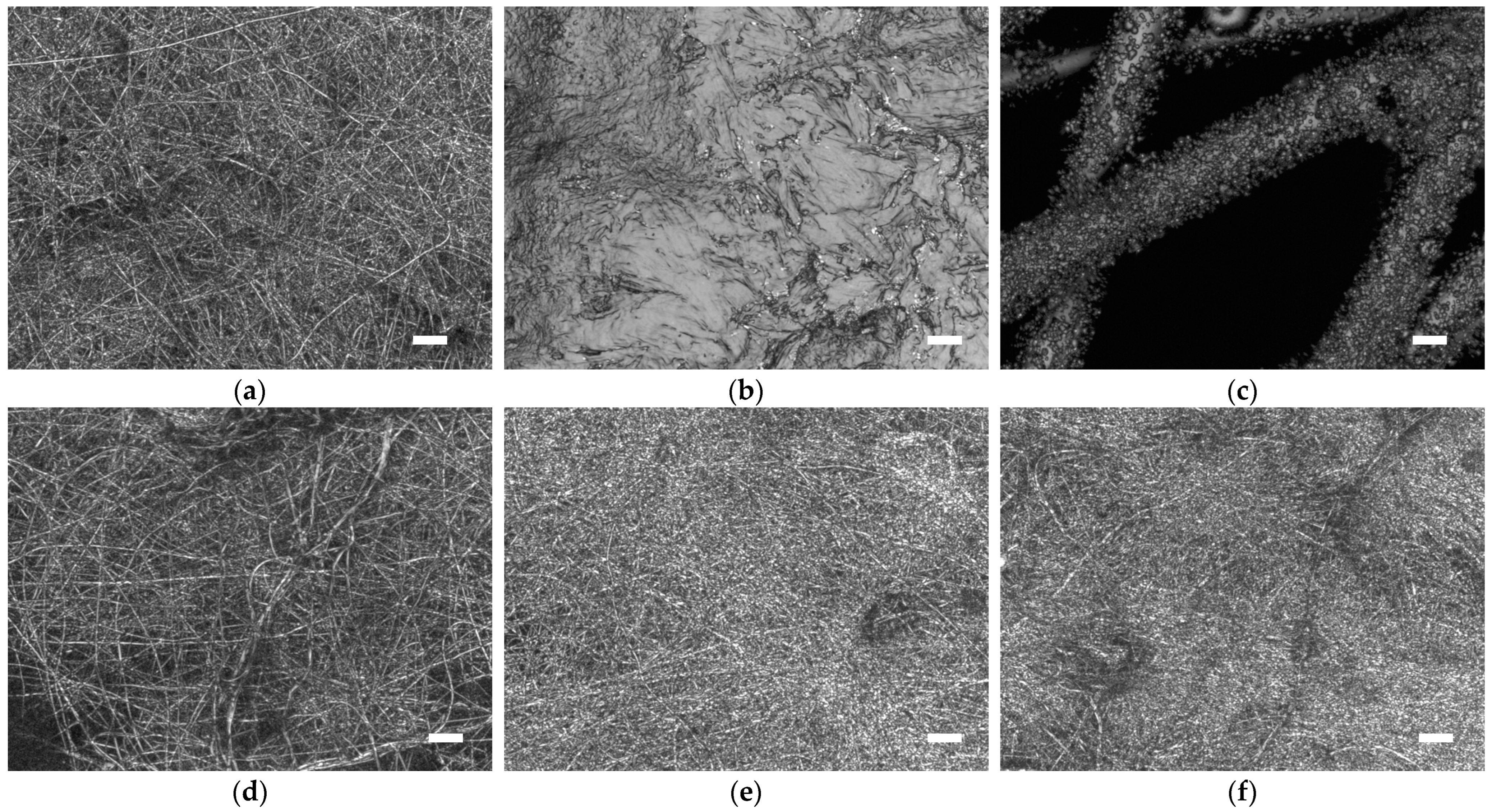
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gandhi, S.; Roy, I. Drug delivery applications of casein nanostructures: A minireview. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biranje, S.S.; Sun, J.Z.; Cheng, L.; Cheng, Y.; Shi, Y.F.; Yu, S.J.; Jiao, H.X.; Zhang, M.; Lu, X.C.; Han, W.J.; et al. Development of Cellulose Nanofibril/Casein-Based 3D Composite Hemostasis Scaffold for Potential Wound-Healing Application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 3792–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.C.; Hu, Q.Y.; Liang, X.R.; Fang, S. Fabrication of colloidal stable gliadin-casein nanoparticles for the encapsulation of natamycin: Molecular interactions and antifungal application on cherry tomato. Food Chem. 2022, 391, 133288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Movahedi, M.; Salehi, A.O.M.; Hajipour, F.P.; Eternad, S. Casein release and characterization of electrospun nanofibres for cartilage tissue engineering. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2022, 45, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendil, Ö.; Yilmaz, S.S.; Ozcelik, E.Y.; Uzuner, H.; Aytac, A. Cross-linked electrospun polyvinyl alcohol/sodium caseinate nanofibers for antibacterial applications. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2023, 29, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, N.; Chakraborty, S.; Mary, N.L.; Suguna, L. Incorporating silver nanoparticles into electrospun nanofibers of casein/polyvinyl alcohol to develop scaffolds for tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, N. Electrospinning of Biofibers and their Applications. In Electrospun Nanofibers from Bioresources for High-Performance Applications, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 29–48. [Google Scholar]
- Golba, B.; Kalaoglu-Altan, O.I.; Sanyal, R.; Sanyal, A. Hydrophilic Cross-Linked Polymeric Nanofibers Using Electrospinning: Imparting Aqueous Stability to Enable Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, S.; Thangam, R.; Fathima, N.N. Electrospinning of casein nanofibers with silver nanoparticles for potential biomedical applications. Electrospinning of casein nanofibers with silver nanoparticles for potential biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.M.; Hu, W.; Yang, H.Y.; Li, C.Z.; Cui, H.Y.; Li, X.Z.; Lin, L. Controlled release and antibacterial properties of PEO/casein nanofibers loaded with Thymol/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes in beef preservation. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasula, P.M.; Sousa, A.M.M.; Liou, S.-C.; Li, R.; Bonnaillie, L.M.; Liu, L.S. Electrospinning of casein/pullulan blends for food-grade applications. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Ziegler, G.R.; Harte, F.M. Ethanol-mediated electrospinning of casein-only bead-free nanofibers. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 148, 109503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diestelhorst, E.; Mance, F.; Mamun, A.; Ehrmann, A. Chemical and Morphological Modification of PAN Nanofibrous Mats with Addition of Casein after Electrospinning, Stabilisation and Carbonisation. Tekstilec 2020, 63, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothe, T.; Großerhode, C.; Hauser, T.; Kern, P.; Stute, K.; Ehrmann, A. Needleless electrospinning of PEO nanofiber mats. Adv. Eng. Res. 2017, 102, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wehlage, D.; Blattner, H.; Sabantina, L.; Böttjer, R.; Grothe, T.; Rattenholl, A.; Gudermann, F.; Lütkemeyer, D.; Ehrmann, A. Sterilization of PAN/Gelatine Nanofi brous Mats for Cell Growth. Tekstilec 2019, 62, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianfar, P.; Vitale, A.; Dalle Vacche, S.; Bongiovanni, R. Enhancing properties and water resistance of PEO-based electrospun nanofibrous membranes by photo-crosslinking. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 1879–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, E.; Güth, U.; Brockhagen, B.; Döpke, C.; Ehrmann, A. Examination of Polymer Blends by AFM Phase Images. Technologies 2023, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripatanasuwan, S.; Zhong, Z.X.; Reneker, D.H. Effect of evaporation and solidification of the charged jet in electrospinning of poly(ethylene oxide) aqueous solution. Polymer 2007, 48, 5742–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelipenko, J.; Kristl, J.; Jankovic, B.; Baumgartner, S.; Kocbek, P. The impact of relative humidity during electrospinning on the morphology and mechanical properties of nanofibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample No. | Mol. Weight PEO (kDa) | Mass PEO/g | Mass Casein/g | Mass Water/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 300 | 3.2 | 1.5 | 36.8 |
| 2 | 1000 | 3.2 | 3.0 | 36.8 |
| 3 | 40 | 10.0 | 3.0 | 30.0 |
| 4 | 17 | 34.4 | 3.0 | 5.6 |
| 5 | 10 | 32.0 | 3.0 | 8.0 |
| 6 | 6 | 38.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 |
| 7 | 300 | 3.2 | 3.0 | 36.8 |
| 8 | 300 | 3.2 | 3.0 | 36.8 |
| 9 | 300 | 3.2 | 3.0 | 36.8 |
| 10 | 300 | 3.2 | 4.0 | 36.8 |
| 11 | 300 | 3.2 | 3.0 | 36.8 |
| 12 | 300 | 3.2 | 1.0 | 36.8 |
| 13 | 1000 | 3.2 | 3.0 | 36.8 |
| 14 | 300 | 3.2 | 3.0 | 36.8 |
| 15 | 600 | 2.8 | 1.5 | 37.2 |
| 16 | 300 | 3.2 | 1.0 | 36.8 |
| 17 | 300 | 3.2 | 2.0 | 36.8 |
| Sample No. | Electrode–Electrode Distance (mm) | Carriage Speed (mm/s) | Rel. Humidity (%) | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 240 | 100 | 32–33 | |
| 2 | 240 | 100 | 32–33 | |
| 3 | 120 | 100 | 32–33 | |
| 4 | 120 | 100 | 32–33 | |
| 5 | 120 | 100 | 32–33 | |
| 6 | 120 | 100 | 32–33 | |
| 7 | 240 | 100 | 34–37 | |
| 8 | 240 | 100 | 37–40 | |
| 9 | 240 | 100 | 36–39 | |
| 10 | 240 | 50 | 32–33 | |
| 11 | 240 | 100 | 32–33 | +10 g beeswax (Lembcke, Faulenrost, Germany) |
| 12 | 240 | 100 | 32–33 | 4 days stirring |
| 13 | 240 | 50 | 32–33 | |
| 14 | 240 | 100 | 32–33 | 7 days at 40 °C |
| 15 | 240 | 100 | 32–33 | |
| 16 | 240 | 100 | 32–33 | 1 day at 40 °C |
| 17 | 240 | 100 | 32–33 | 7 days at 40 °C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramirez Candia, H.G.; Güth, U.; Grothe, T.; Ehrmann, A. Optimization of the Spinning Parameters for Wire-Based Electrospinning of Casein–PEO Nanofiber Mats. Eng. Proc. 2024, 81, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024081007
Ramirez Candia HG, Güth U, Grothe T, Ehrmann A. Optimization of the Spinning Parameters for Wire-Based Electrospinning of Casein–PEO Nanofiber Mats. Engineering Proceedings. 2024; 81(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024081007
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamirez Candia, Hiram Gyrad, Uwe Güth, Timo Grothe, and Andrea Ehrmann. 2024. "Optimization of the Spinning Parameters for Wire-Based Electrospinning of Casein–PEO Nanofiber Mats" Engineering Proceedings 81, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024081007
APA StyleRamirez Candia, H. G., Güth, U., Grothe, T., & Ehrmann, A. (2024). Optimization of the Spinning Parameters for Wire-Based Electrospinning of Casein–PEO Nanofiber Mats. Engineering Proceedings, 81(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024081007










