Design of Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor Encoder/Decoder with Compact Circuit Structure for Booth Multiplier †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Radix-4 Booth Encoding
3. Proposed Radix-4 Booth Encoding Module
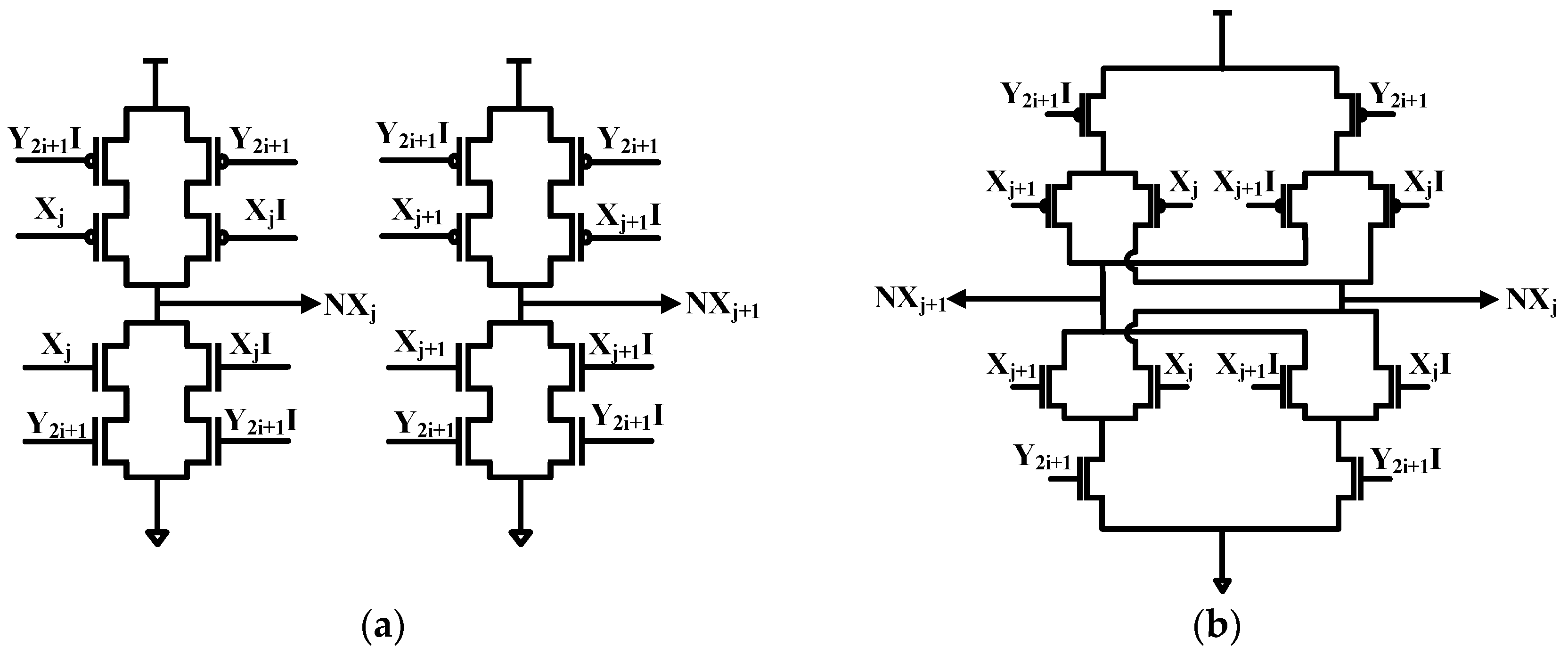
3.1. Encoder
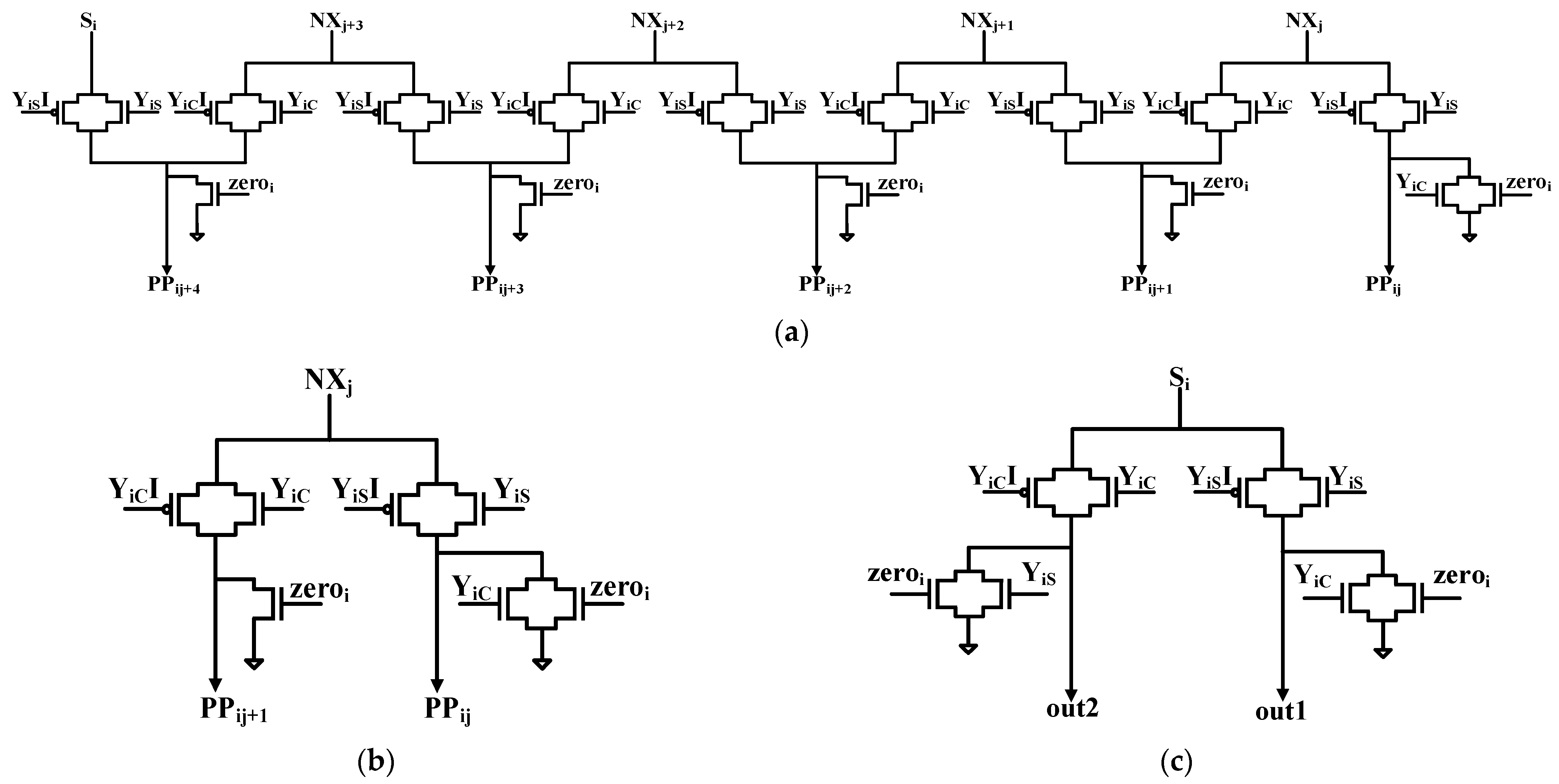
3.2. Decoder
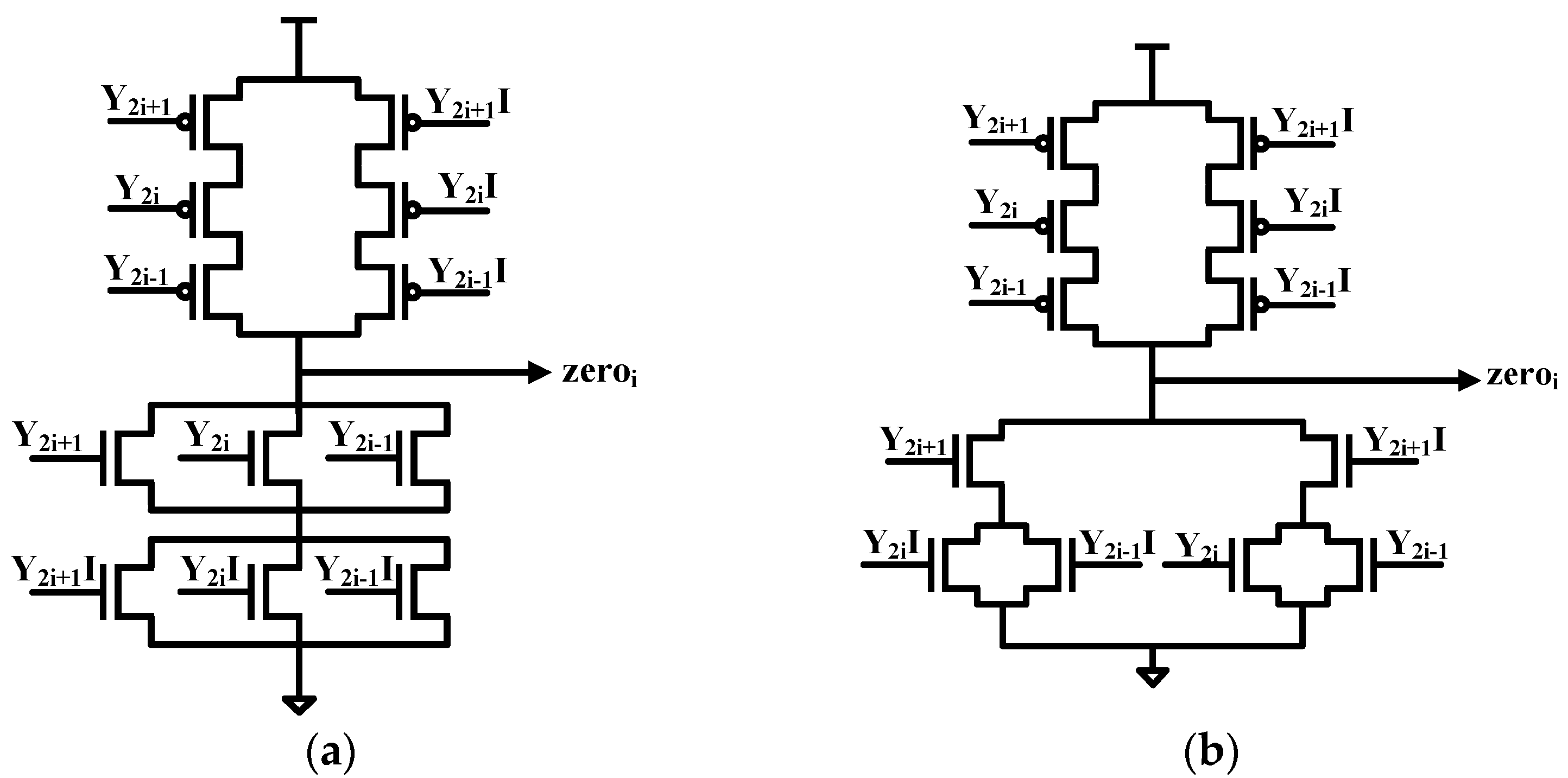
4. Circuit Improvement and Simulation Results
4.1. OAI_zeroi and OAIT_zeroi
4.2. Xj_2 and Xj2
4.3. z_c_s, zc_s, and zcs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MacSorley, O. High-speed arithmetic in binary computers. IRE Proc. 2007, 49, 67–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinfield, L.P. A proof of the modified Booth’s algorithm for multiplication. IEEE Trans. Comput. 1975, 24, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Dai, L.; Huang, M.; Shen, A.; Mao, W.; Hashimoto, M.; Yu, H. A low-power sparse convolutional neural network accelerator with pre-encoding radix-4 Booth multiplier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II: Express Briefs. 2023, 70, 2246–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Han, J. The design of multipliers based on radix-4 Booth coding. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Academic Exchange Conference on Science and Technology Innovation (IAECST), Guangzhou, China, 9–11 December 2022; pp. 1471–1475. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Swartzlander, E.E.; Lombardi, F. A modified partial product generator for redundant binary multipliers. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2016, 65, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y.-S. A low-power booth multiplier using novel data partition method. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Advanced System Integrated Circuits, Fukuoka, Japan, 4–5 August 2004; pp. 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Khater, I.S.; Bellaouar, A.; Elmasry, M.I. Circuit techniques for CMOS low-power high-performance multipliers. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits. 1996, 31, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.D. A signed binary multiplication technique. Quart. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 1951, 4, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercegovac, M.D.; Lang, T. Digital Arithmetic; Morgan Kaufmann: Los Altos, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]


| Y2i+1 | Y2i | Y2i−1 | PP Coef. 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | Xj |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | Xj |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | Xj |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | Xj |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | Xj |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | Xj |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | Xj |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | Xj |
| Y2i+1 | Y2i | Y2i−1 | PP Coef. | negi | YiC | YiS | zeroi | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | Xj | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | Xj | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | Xj | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | Xj | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | Xj | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | Xj | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | Xj | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | Xj | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| OAI_zeroi | OAIT_zeroi | |
|---|---|---|
| Avg. (uW) | 9.2957 | 9.4973 |
| Delay (ps) | 80.8/120 | 91.1/86.4 |
| Y2i+1 | Xj+1 | Xj | NXj+1 | NXj |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Xj_2 | Xj2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Avg. (uW) | 12.1443 | 10.9709 |
| Delay Time (ps) | NXj 66.4/32.7 | NXj 60.7/28.4 |
| NXj+1 66.3/32.8 | NXj+1 45.2/39.2 | |
| Numbers of Transistors | 11 PMOS | 9 PMOS |
| 11 NMOS | 9 NMOS |
| z_c_s (Figure 5a) | zc_s (Figure 5b) | zcs (Figure 5c) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg. (uW) | 23.8827 | 23.0814 | 23.2156 | |
| Delay Time (ps) | YiC | 123/117 | 182/116 | 164/127 |
| YiCI | 141/143 | 199/143 | 180/155 | |
| YiS | 88.5/115 | 79.5/105 | 123/158 | |
| YiSI | 107/142 | 98.8/131 | 95.3/141 | |
| zeroi | 105/86.4 | 102/144 | 113/137 | |
| Numbers of Transistors | 23 PMOS | 19 PMOS | 17 PMOS | |
| 23 NMOS | 19 NMOS | 17 NMOS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-N.; Hung, Y.-C. Design of Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor Encoder/Decoder with Compact Circuit Structure for Booth Multiplier. Eng. Proc. 2025, 103, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025103021
Wang Y-N, Hung Y-C. Design of Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor Encoder/Decoder with Compact Circuit Structure for Booth Multiplier. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 103(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025103021
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yu-Nsin, and Yu-Cherng Hung. 2025. "Design of Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor Encoder/Decoder with Compact Circuit Structure for Booth Multiplier" Engineering Proceedings 103, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025103021
APA StyleWang, Y.-N., & Hung, Y.-C. (2025). Design of Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor Encoder/Decoder with Compact Circuit Structure for Booth Multiplier. Engineering Proceedings, 103(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025103021






