Optimized DSP Framework for 112 Gb/s PM-QPSK Systems with Benchmarking and Complexity–Performance Trade-Off Analysis
Abstract
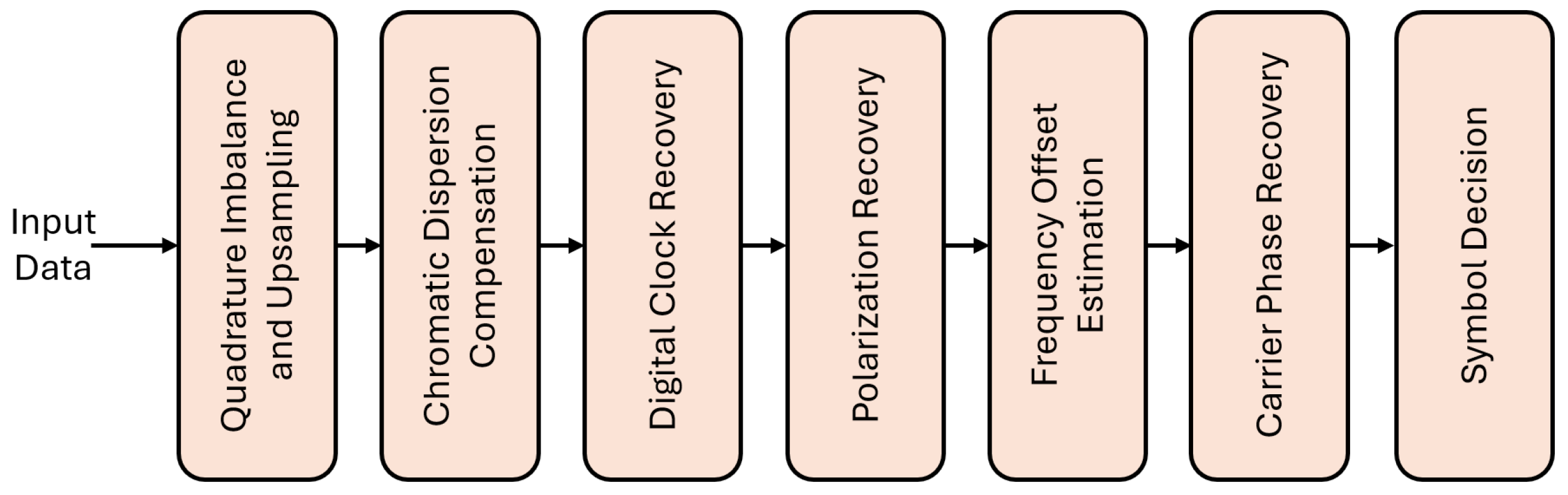
1. Introduction
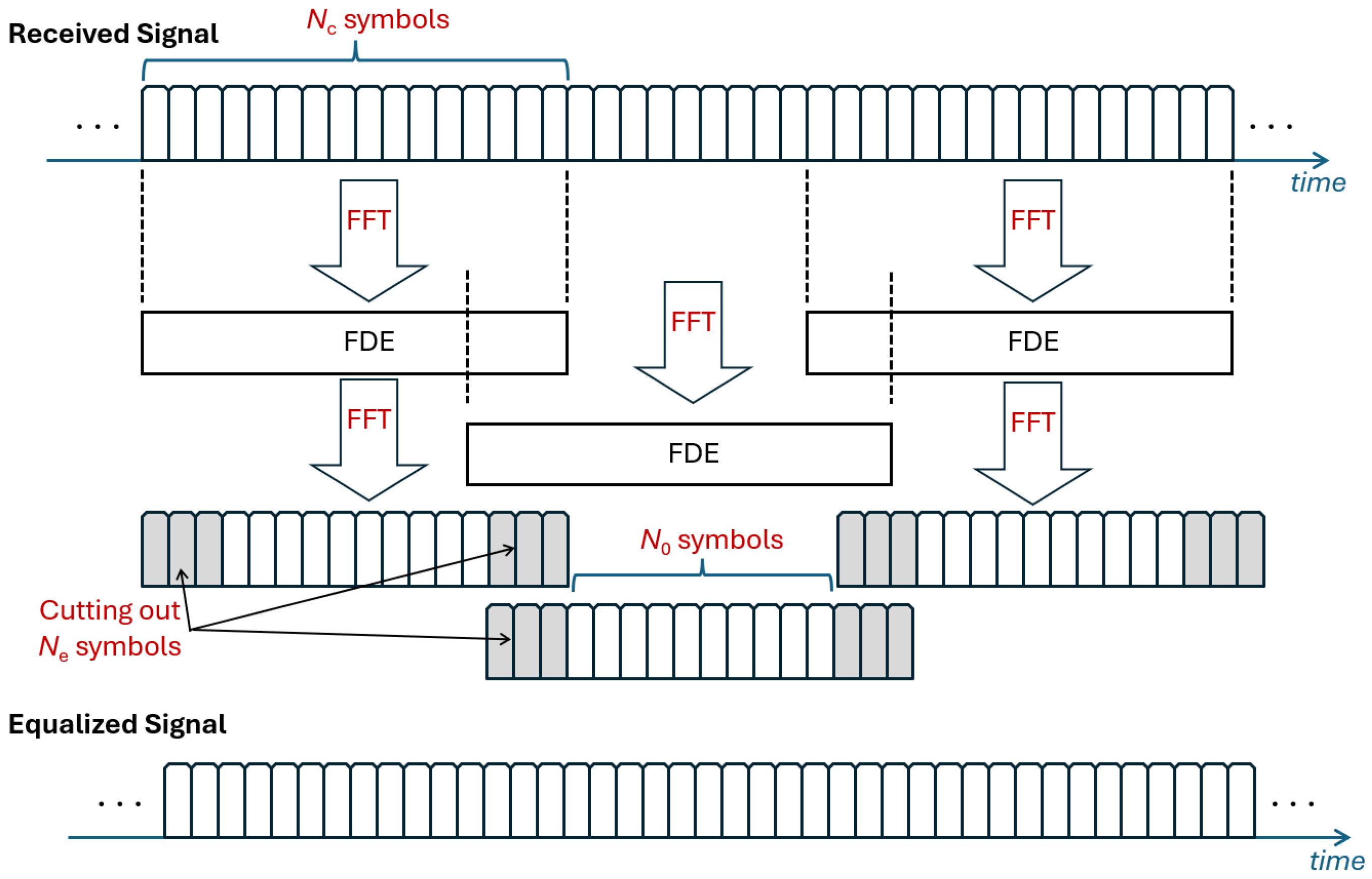
2. Efficient Chromatic Dispersion Compensation
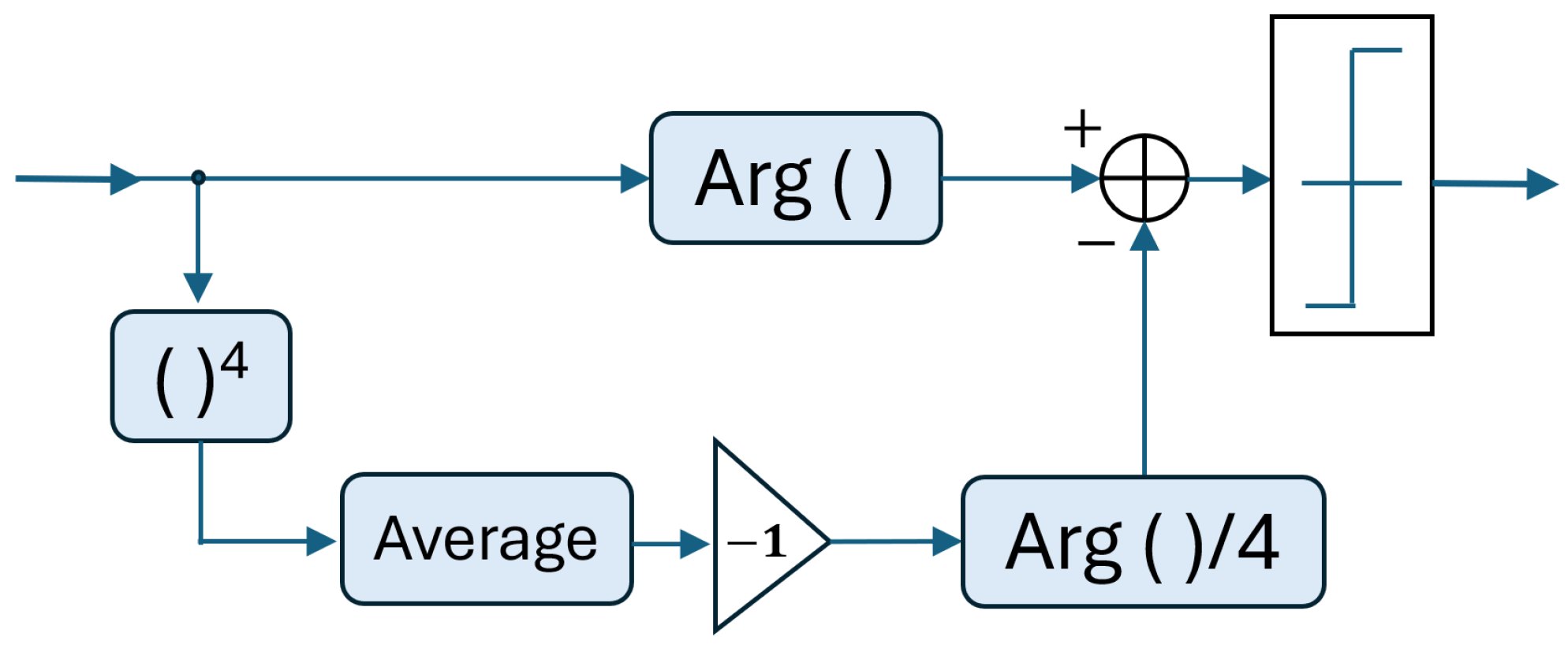
3. Improvements to Digital Phase Carrier Recovery
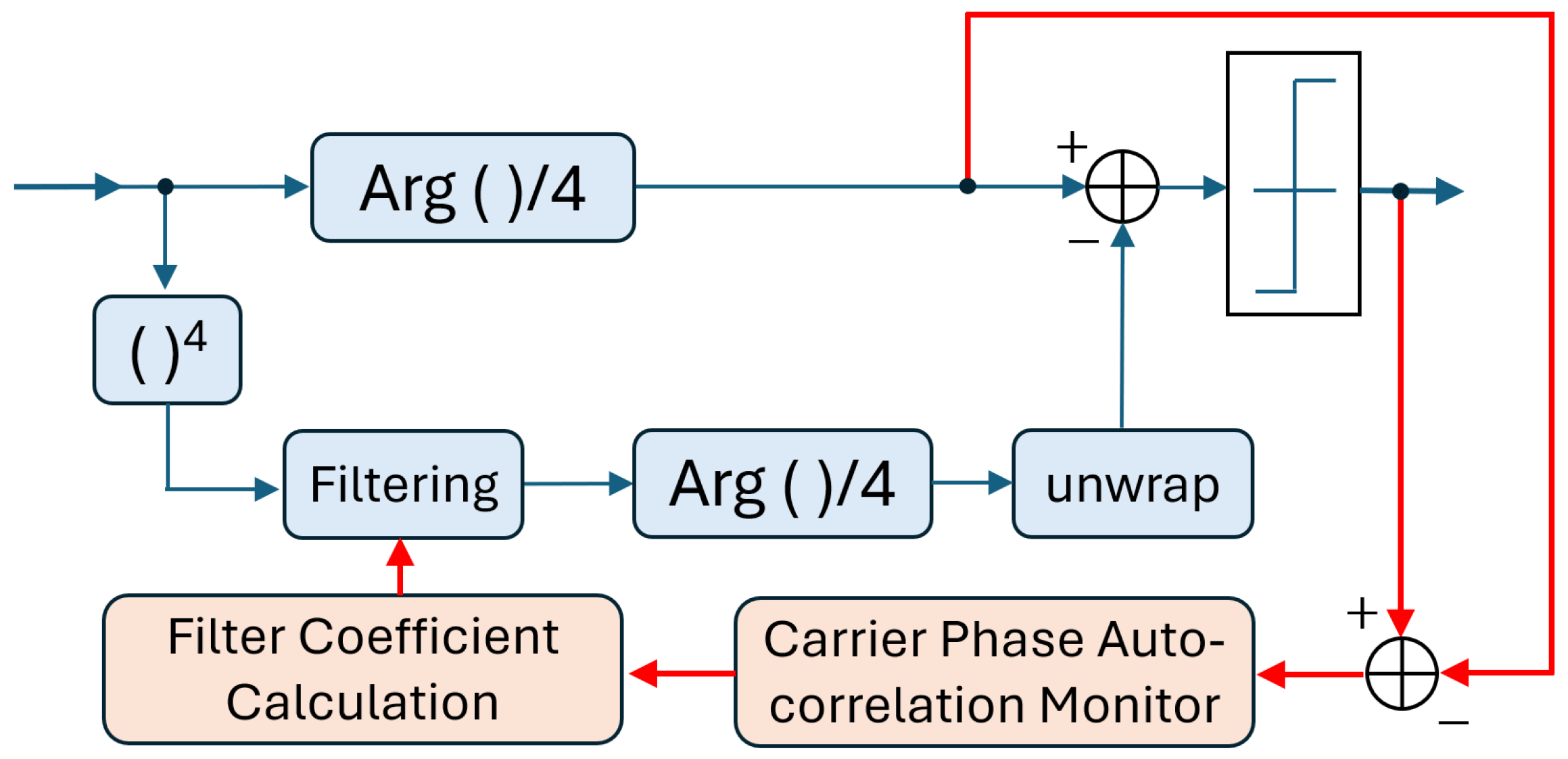
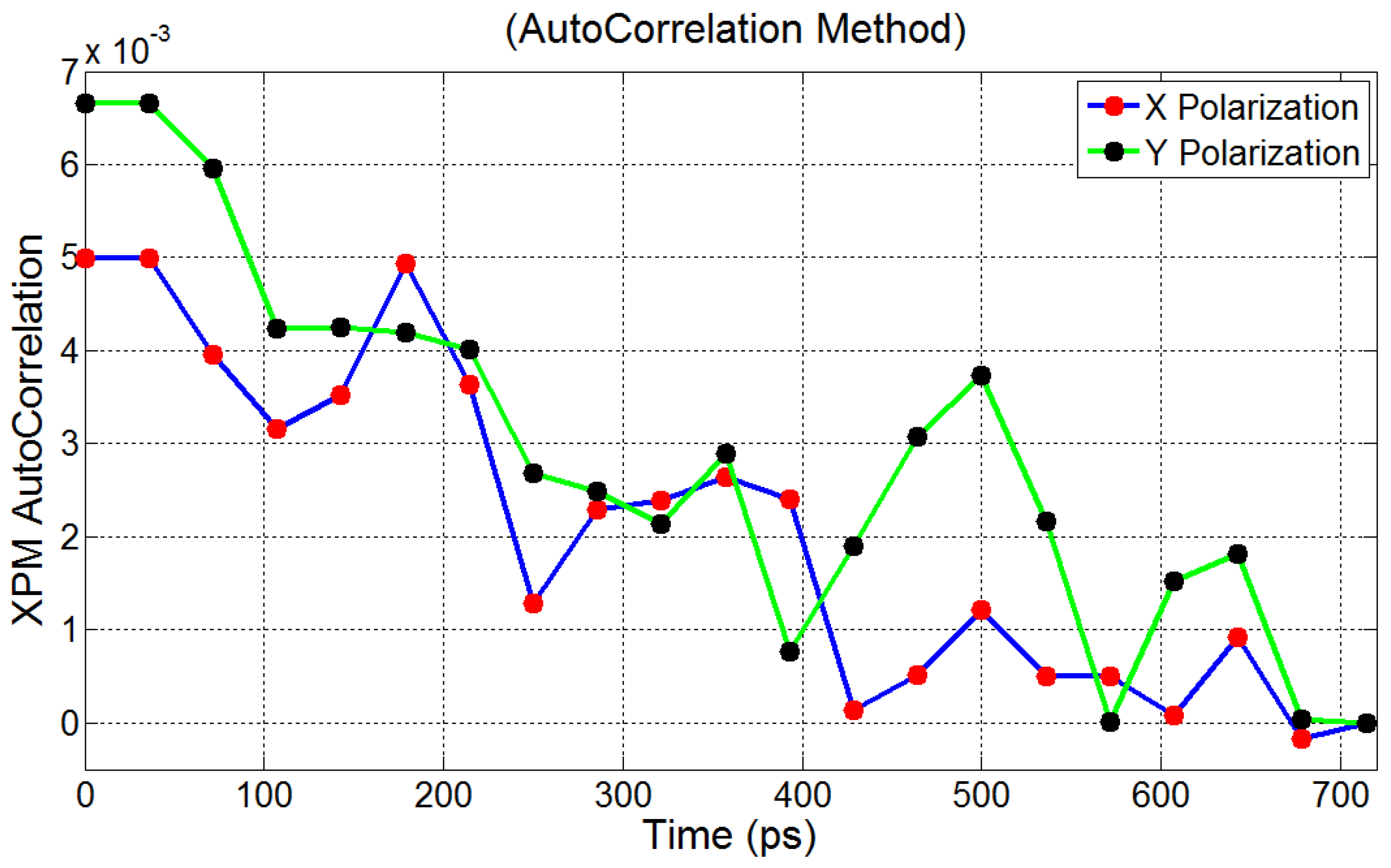
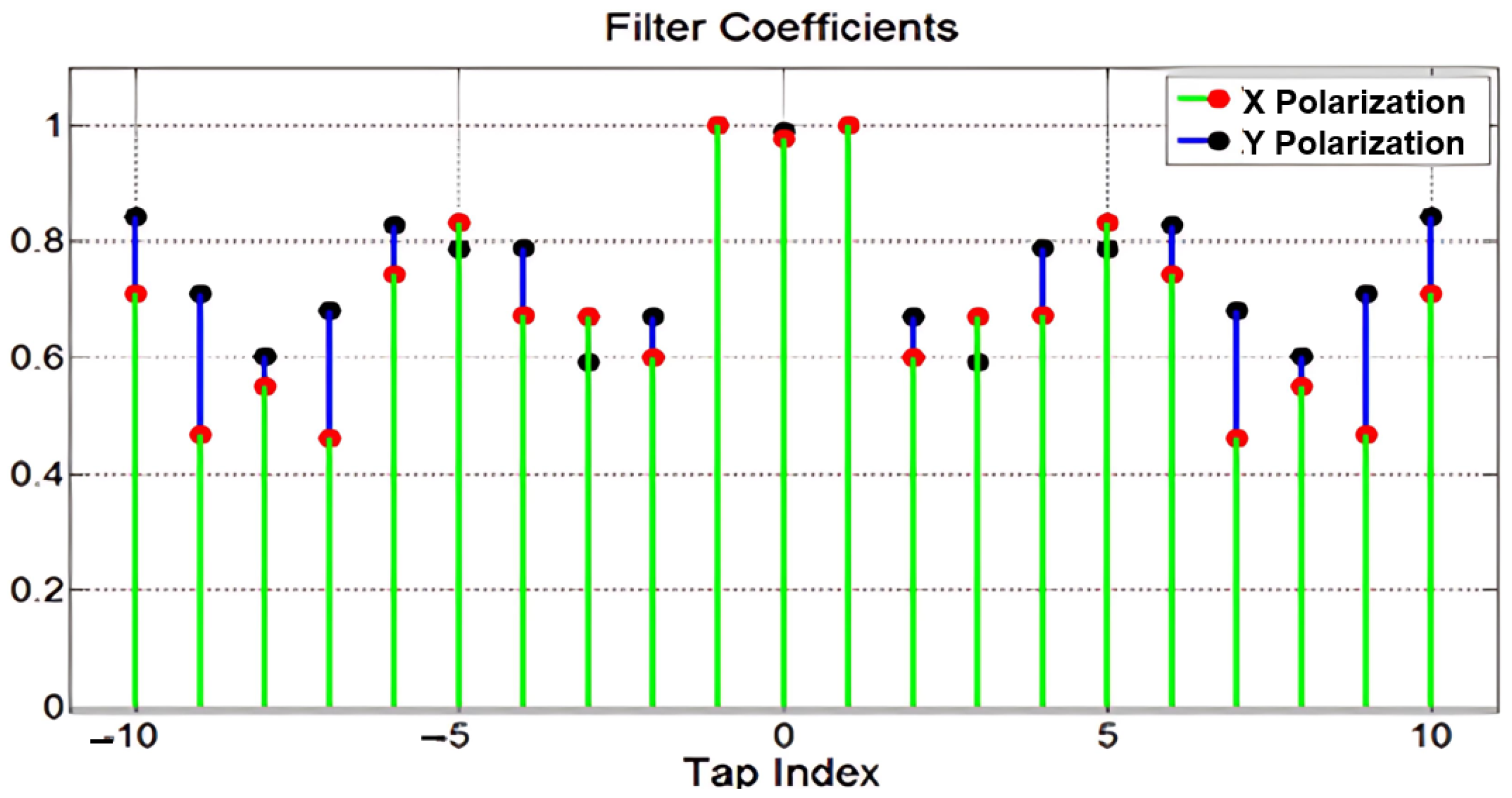
3.1. Optimal Filtering Using XPM and ASE Noise Correlation
3.2. System Parameter Sensitivity and Physical Layer Considerations
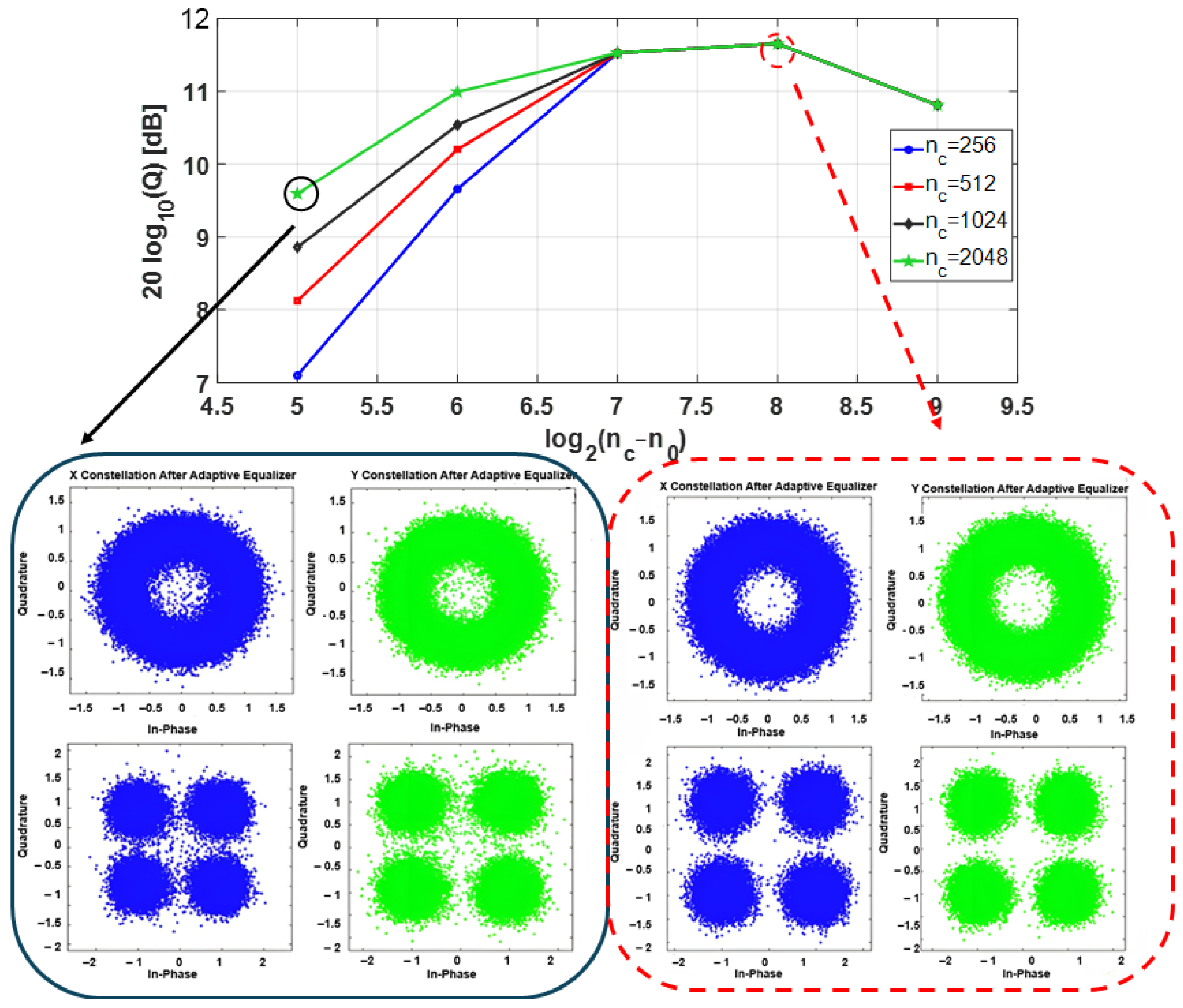
3.2.1. Sensitivity to FFT Block Length and Overlap Factor
3.2.2. Impact of Nonlinear Dispersion
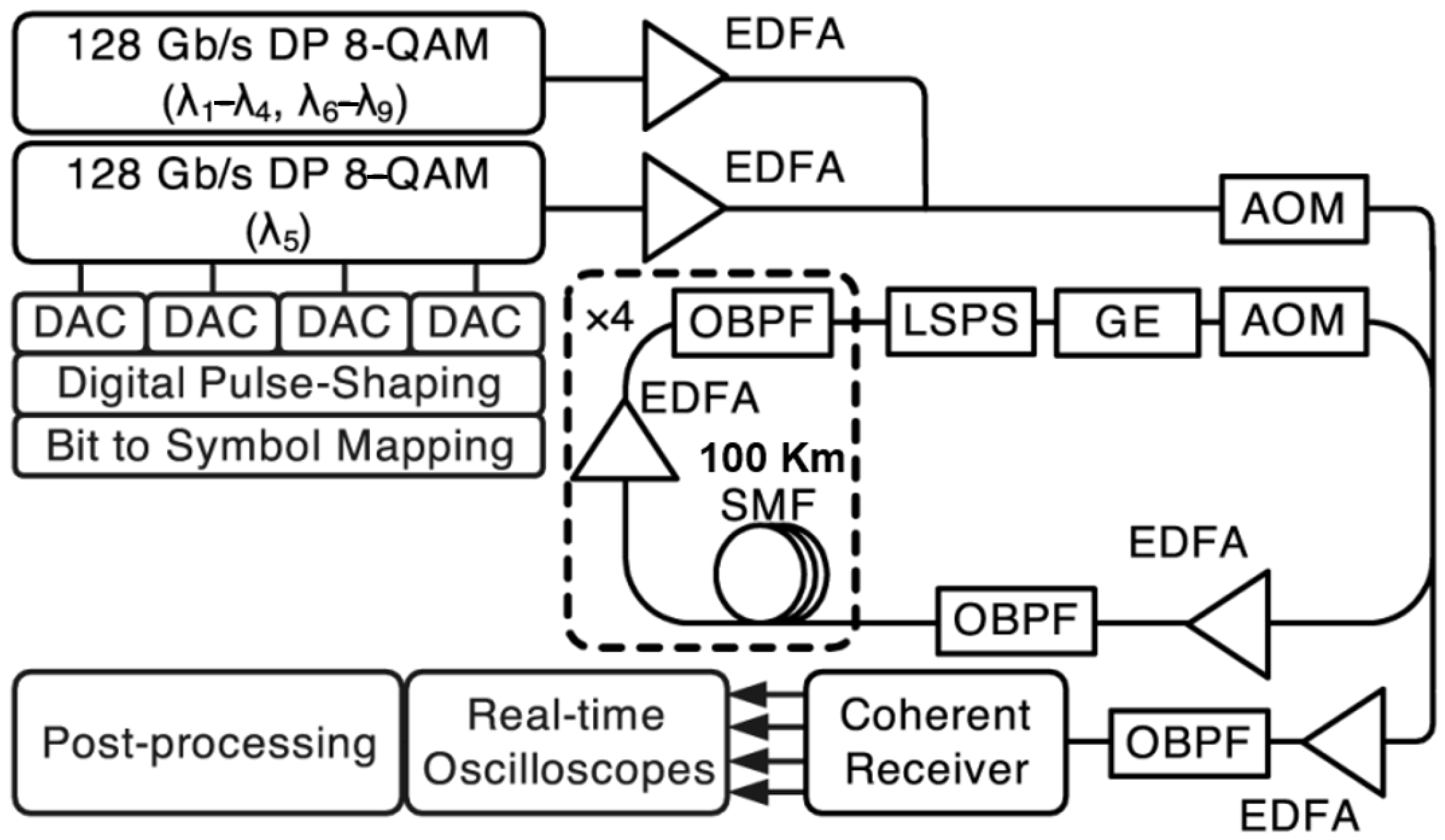
4. Comparative Benchmarking and Complexity–Performance Trade-Off Analysis
4.1. Comparative Benchmarking with Latest Results
4.2. Complexity Versus Performance Trade-Off Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hazzouri, S.M. The Applications of Digital Signal Processing Techniques for Enhancing the Performance of High Speed Optical Communication Systems. Galoitica J. Math. Struct. Appl. 2023, 8, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhan, Y.; Pan, H.; Peng, H. An unsupervised coherent receiver digital signal processing algorithm based on spectral clustering with no data preamble. IET Optoelectron. 2024, 18, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Grewal, N.S.; Kaur, B. Performance investigation and development of 112 gbit/s dual polarization 16 QAM transmission system using differential encoding. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2022, 55, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Chow, C.; Kuo, P.C.; Chen, G.H.; Yeh, C.; Chen, J.; Lai, Y. DP-QPSK Coherent Detection Using 2D Grating Coupled Silicon Based Receiver. IEEE Photonics J. 2021, 13, 7900105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Song, J.; Li, Y.; Qiu, J.; Zuo, Y.; Li, W.; Hong, X.; Guo, H.; Wu, J. Real-time 15GBaud QPSK and 16QAM Flexible Coherent Optical Receiver Implemented on a Single FPGA Chip with Low Complexity DSP. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th Information Communication Technologies Conference (ICTC), Nanjing, China, 17–19 May 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadamin, J.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Saleem, S.M. Performance Evaluation of 100 Gb/s WDM DP-QPSK Lightwave System with Reduced PMD Effects. Int. J. Commun. Antenna Propag. (IRECAP) 2019, 9, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, T.; Fujiwara, M.; Igarashi, R.; Iiyama, N.; Koma, R.; Kani, J.; Yoshida, T. Symmetric 10 Gbit/s 40-km reach DSP-based TDM-PON with a power budget over 50 dB. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 17499–17509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, P.; Singh, M.; Malhotra, J.; Dhasarathan, V. Performance analysis of 160 Gbit/s single-channel PDM-QPSK based inter-satellite optical wireless communication (IsOWC) system. Wirel. Netw. 2020, 26, 3579–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kani, J.; Yoshida, T. Carrier Phase Estimation Softwarized on GPU Using Decision-Aided Phase Unwrapping for Flexible Optical Coherent Access Systems. J. Light. Technol. 2021, 39, 1706–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidan, R.L.; Méric, H.; Sommer, J. Frame format and DSP receiver design for a 56-GBaud GEO DP-QPSK coherent optical feeder link. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications (ICSOS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 11–13 October 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.; O’Sullivan, M.; Wu, K.T.; Sun, H.; Awadalla, A.; Krause, D.J.; Laperle, C. Performance of Dual-Polarization QPSK for Optical Transport Systems. J. Light. Technol. 2009, 27, 3546–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, E.; Lau, A.P.T.; Barros, D.J.F.; Kahn, J.M. Coherent Detection in Optical Fiber Systems. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 753–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downie, J.D.; Hurley, J.; Cartledge, J.; Ten, S.; Bickham, S.; Mishra, S.; Zhu, X.; Kobyakov, A. 40 × 112 Gb/s transmission over an unrepeatered 365 km effective area-managed span comprised of ultra-low loss optical fibre. In Proceedings of the 36th European Conference and Exhibition on Optical Communication, Turin, Italy, 19–23 September 2010; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casasco, M.; Rizzelli, G.; Pagano, A.; Riccardi, E.; Ferrero, V.; Gaudino, R. Metro-Passive Optical Network Convergence: 400 Gbps Fully Coherent Transmission Using Pre-Commercial Transceivers. Electronics 2024, 13, 2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, Z.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Su, X.; Ko, W.; Zuo, Y.; Lian, H.; Zeng, R.; Wang, Y.; et al. Demonstration of an 8-Gbit/s quadrature-phase-shift-keying coherent underwater wireless optical communication link using coherent heterodyne detection under scattering conditions. Opt. Lett. 2024, 49, 4397–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Xu, M.; Pu, M.; Ding, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; et al. Demonstration of 120 Gbit/s turbulence-resilient coherent optical communication employing cylindrical vector beam multiplexing. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 42165–42175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, R.; Kobayashi, T.; Ishihara, K.; Takatori, Y.; Sano, A.; Miyamoto, Y. Coherent Optical Single Carrier Transmission Using Overlap Frequency Domain Equalization for Long-Haul Optical Systems. J. Light. Technol. 2009, 27, 3721–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, J.C.; Fludger, C.R.S.; Duthel, T.; Schulien, C.; Schmauss, B. Efficient frequency domain chromatic dispersion compensation in a coherent Polmux QPSK-receiver. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC) and National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference (NFOEC), San Diego, CA, USA, 21–25 March 2010; Volume 2010, pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherici, C.; Kandouci, M. Coherent optical-OFDM system’s contribution to the management of chromatic and polarization mode dispersion using DSP. J. Opt. Commun. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X. Density-matrix-formalism based scheme for polarization mode dispersion monitoring and compensation in optical fiber communication systems. Optoelectron. Lett. 2023, 19, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frunza, A.; Choqueuse, V.; Morel, P.; Azou, S. A Parametric Network for the Global Compensation of Physical Layer Linear Impairments in Coherent Optical Communications. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2022, 3, 1428–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, L.; Yan, W.; Nakashima, H.; Tanimura, T.; Oda, S.; Hoshida, T.; Rasmussen, J.C. Improvements to Digital Carrier Phase Recovery Algorithm for High-Performance Optical Coherent Receivers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2010, 16, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Tao, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, L.; Oda, S.; Hoshida, T.; Rasmussen, J.C. A Linear Model for Nonlinear Phase Noise Induced by Cross-phase Modulation. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC) and National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference (NFOEC), San Diego, CA, USA, 24–26 March 2009; Volume 2009, p. OTuD5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Cai, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. A Low-Complexity Joint Compensation Scheme of Carrier Recovery for Coherent Free-Space Optical Communication. Photonics 2023, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, J.; Zeng, X. A Low-latency Carrier Phase Recovery Hardware for Coherent Optical Communication. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Austin, TX, USA, 27 May–1 June 2022; pp. 2506–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.; Boscolo, S.K.; Sygletos, S. Online Kernel-Based Phase Recovery for Parametrically Amplified Optical Transmission. In Proceedings of the 2024 14th International Symposium on Communication Systems, Networks and Digital Signal Processing (CSNDSP), Rome, Italy, 17–19 July 2024; pp. 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, M.; Lorences-Riesgo, A.; Martins, C.; Mumtaz, S.; Charlet, G.; Monteiro, P.; Guiomar, F. Carrier-Phase Recovery for Coherent Optical Systems: Algorithms, Challenges and Solutions. J. Light. Technol. 2024, 42, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, J.M.H.; Falou, A.R.E.; Gürkan, Z.N.; Alboon, S.A.; Karar, A.S. Enhanced Performance of Intensity Modulation With Direct Detection Using Golay Encoded Nyquist Pulses and Electronic Dispersion Compensation. IEEE Photonics J. 2024, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Luk, R.W.; Sanka, A.I.; Ye, Z.; Chen, D.; Yan, H.; Cheung, R.C.C. Low-Complexity Chromatic Dispersion Compensation Using High-Radix Fermat Number Transform. J. Light. Technol. 2024, 42, 5190–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Lauinger, V.; Häger, C.; Schröder, J.; i Amat, A.G.; Schmalen, L.; Wymeersch, H. Blind frequency-domain equalization using vector-quantized variational autoencoders. In Proceedings of the 49th European Conference on Optical Communications (ECOC 2023), Glasgow, UK, 1–5 October 2023; Volume 2023, pp. 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Romoh, M.; Costa, N.; Jaouën, Y.; Napoli, A.; Pedro, J.; Spinnler, B.; Yousefi, M. Equalization in dispersion-managed systems using learned digital back-propagation. Opt. Contin. 2023, 2, 2088–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartledge, J.C.; Downie, J.; Hurley, J.E.; Zhu, X.; Roudas, I. Bit Error Ratio Performance of 112 Gb/s PM-QPSK Transmission Systems. J. Light. Technol. 2012, 30, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karar, A.S.; Gazor, S.; Gao, Y.; Cartledge, J.C.; O’Sullivan, M.; Laperle, C.; Borowiec, A.; Roberts, K. Polynomial Pulses for Mitigating Fiber Nonlinearity in Coherent Optical Fiber Communications. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2015, 27, 1653–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gómez, F.J.; Kramer, G. Mismatched Models to Lower Bound the Capacity of Dual-Polarization Optical Fiber Channels. J. Light. Technol. 2021, 39, 3390–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Yang, J.; Zeng, J.; Liu, W.; Yu, C.; Li, F.; Li, Z. Non-integer Oversampling for Coherent PON Systems at 400 Gb/s. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2024, 16, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, N.; Pendem, S.V.; Lall, B.; Choudhary, A. Transformer-Based Nonlinear Equalization for DP-16QAM Coherent Optical Communication Systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2024, 28, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, L.; Dai, X.; Mei, L.; Du, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, T.; Yang, Q.; Liu, D. Penalty mitigation for OSC-induced XPM in long-haul WDM coherent systems by digital up-conversion coding. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 8875–8883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
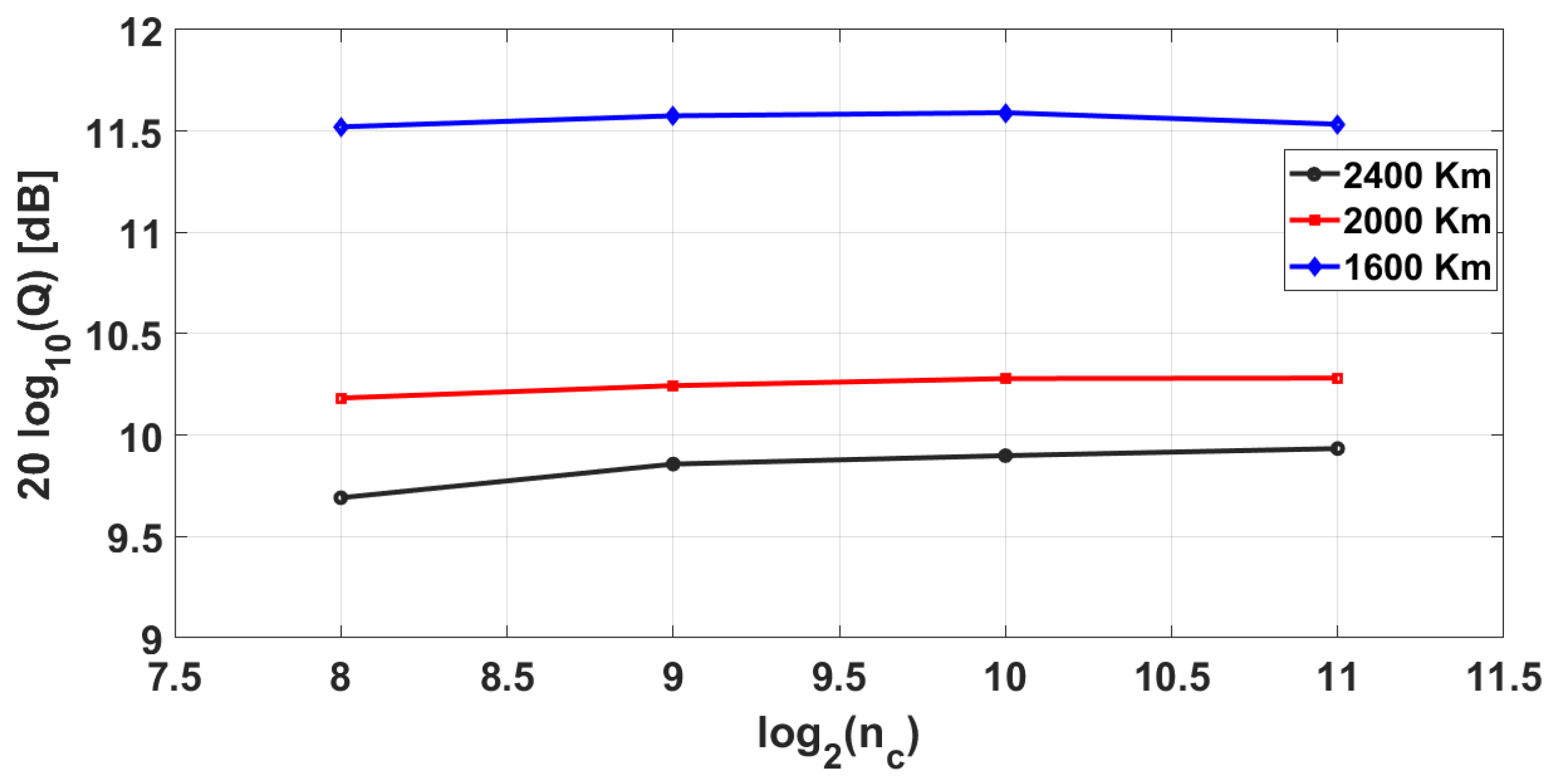
| Distance (km) | V-V Algorithm (Q, dB) | Optimal Filtering (AutoCorr) | Optimal Filtering (MSDP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1600 | 11.60 | 11.68 | 11.53 |
| 2000 | 10.36 | 10.33 | 10.32 |
| 2400 | 9.93 | 9.92 | 9.83 |
| Launch Power (dBm/ch) | V-V Algorithm (Q, dB) | Optimal Filtering (AutoCorr) | Optimal Filtering (MSDP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 11.76 | 11.76 | 11.72 |
| 7 | 11.14 | 11.08 | 11.04 |
| 9 | 9.49 | 9.47 | 9.45 |
| Study and Year | Rate/Modulation | Max Distance | DSP Method | Q Factor (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our study | 112 Gb/s PM-QPSK | 2400 km | OFDE + MSDP-CPR (adaptive) | 9.9–11.7 |
| Wang [35] | 400 Gb/s coherent PON via SCM | Metro (<100 km) | Non-integer oversampling DSP | N/A (maintained) |
| Gautam [36] | DP-16QAM (long-haul) | ≥2000 km | Transformer-based nonlinear equalizer | >DBP baseline |
| Kherici [19] | 112 Gb/s CO-OFDM QPSK | 2000 km | CO-OFDM + adaptive CD/PMD/CPR | 10.2–11.3 |
| Neves [27] | 100–400 Gb/s DP-QPSK/16QAM | 3000 km | ML-based CPR | 11–12.8 |
| Lin [25] | 200 Gb/s DP-QPSK | 1600 km | Low-latency FPGA-based CPR hardware | 11.5–12.5 |
| Chen [37] | 200 Gb/s DP-16QAM | 1618 km | Dual-OSC coding XPM mitigation | +1.3 dB gain |
| Karar [33] | 112 Gb/s PM-QPSK | 2000 km | Polynomial pulse shaping for NL mitigation | ∼11.0 |
| Study and Year | Q Factor (dB) | DSP Complexity | Scalability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our study | 9.9–11.7 | Low | Excellent | FFT-based CD compensation + adaptive CPR |
| Wang [35] | N/A (maintained) | Very Low | Limited (metro only) | Non-integer oversampling DSP for PON |
| Gautam [36] | >DBP baseline | High | Moderate | Transformer-based nonlinear equalizer |
| Kherici [19] | 10.2–11.3 | Moderate | Good | CO-OFDM with adaptive CD/PMD/CPR |
| Neves [27] | 11–12.8 | Very High | Moderate | ML-based CPR, data- and computation-heavy |
| Nguyen [26] | 11.5–12.5 | High | Good | Kernel-based online phase recovery |
| Chen [37] | +1.3 dB gain | Low | Good | OSC-based XPM suppression without DSP overhead |
| Karar [33] | ∼11.0 | Low | Good | Polynomial pulse shaping for nonlinear mitigation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barakat, J.M.H.; Karar, A.S.; Neji, B. Optimized DSP Framework for 112 Gb/s PM-QPSK Systems with Benchmarking and Complexity–Performance Trade-Off Analysis. Eng 2025, 6, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6090218
Barakat JMH, Karar AS, Neji B. Optimized DSP Framework for 112 Gb/s PM-QPSK Systems with Benchmarking and Complexity–Performance Trade-Off Analysis. Eng. 2025; 6(9):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6090218
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarakat, Julien Moussa H., Abdullah S. Karar, and Bilel Neji. 2025. "Optimized DSP Framework for 112 Gb/s PM-QPSK Systems with Benchmarking and Complexity–Performance Trade-Off Analysis" Eng 6, no. 9: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6090218
APA StyleBarakat, J. M. H., Karar, A. S., & Neji, B. (2025). Optimized DSP Framework for 112 Gb/s PM-QPSK Systems with Benchmarking and Complexity–Performance Trade-Off Analysis. Eng, 6(9), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6090218









