A Comprehensive Examination of Key Characteristics Influencing the Micro-Extrusion Process for Pure Copper Cross-Shaped Couplings
Abstract
1. Introduction
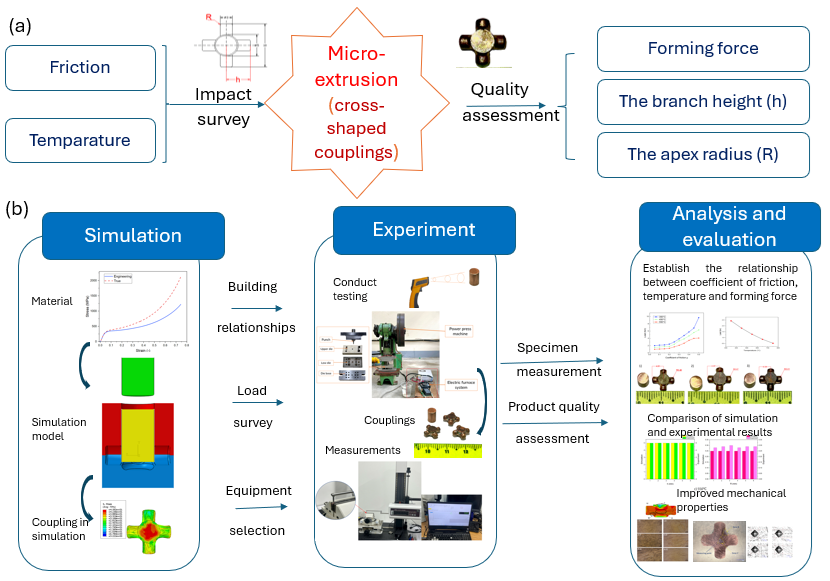
2. Materials and Methods
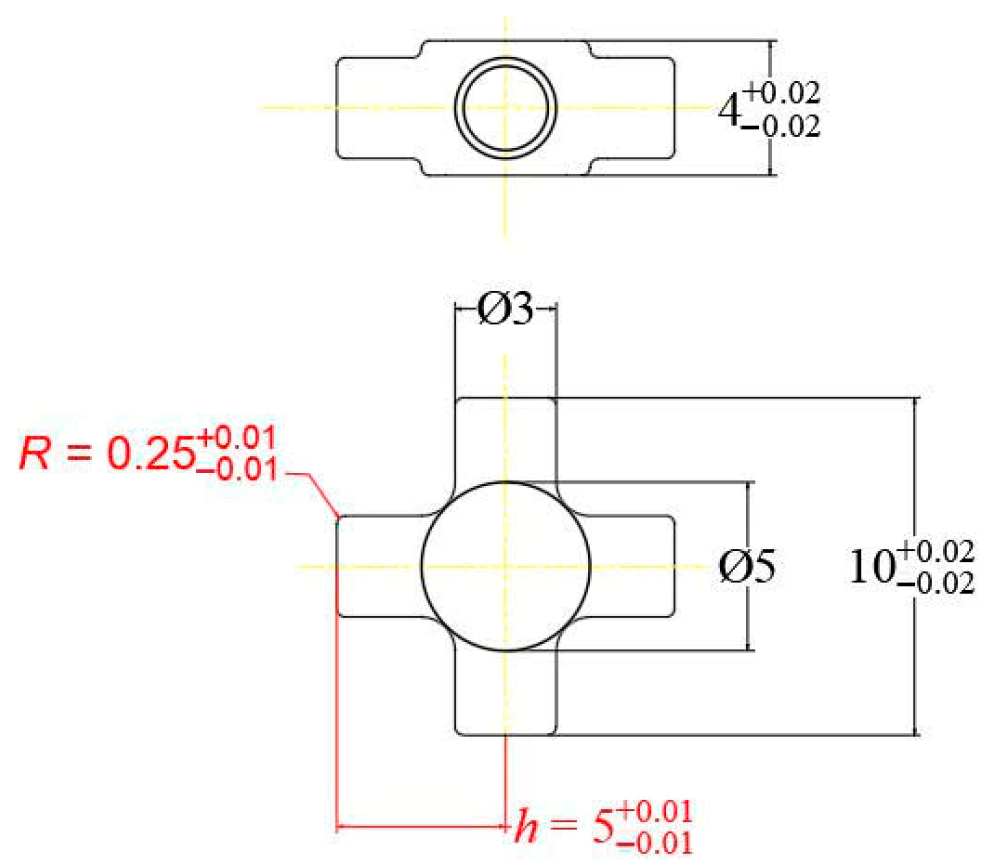
2.1. Objective
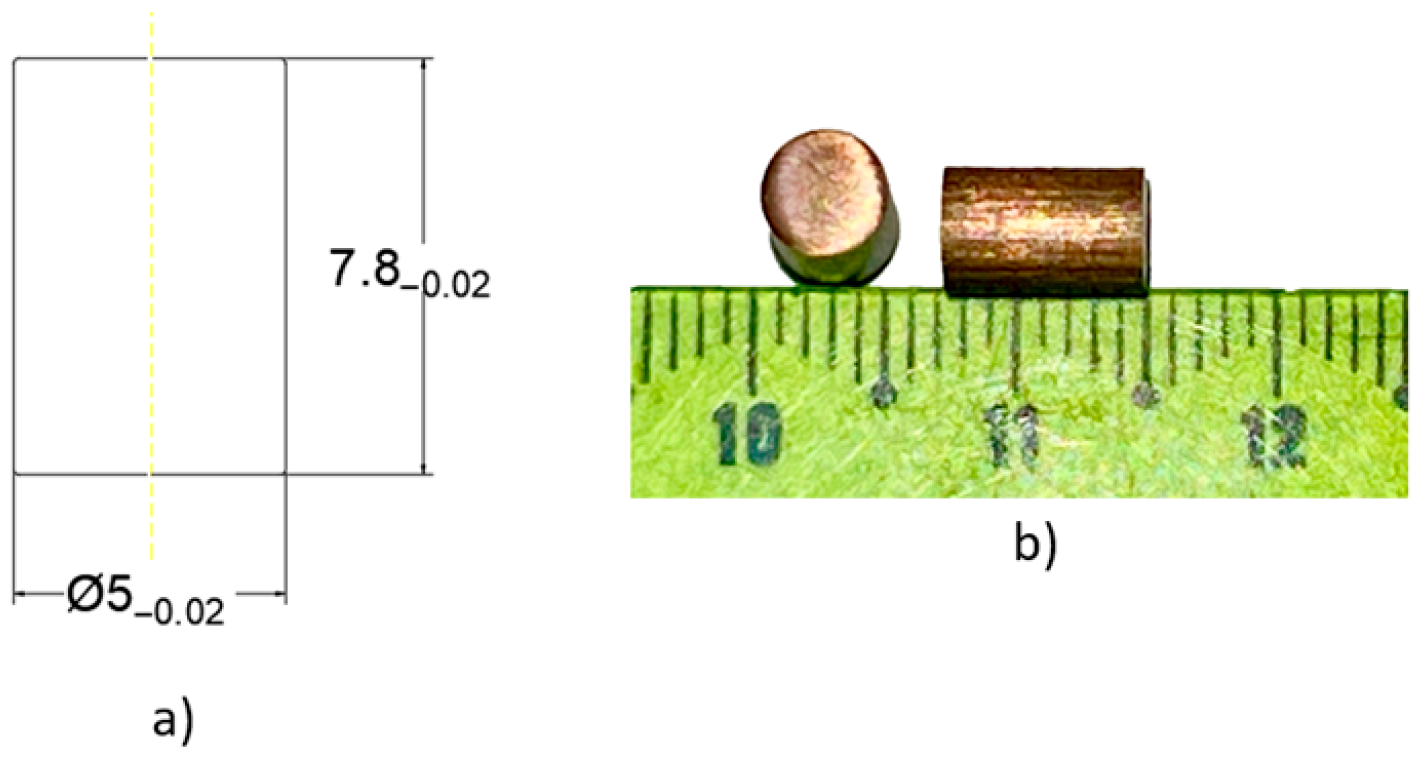
2.2. Material
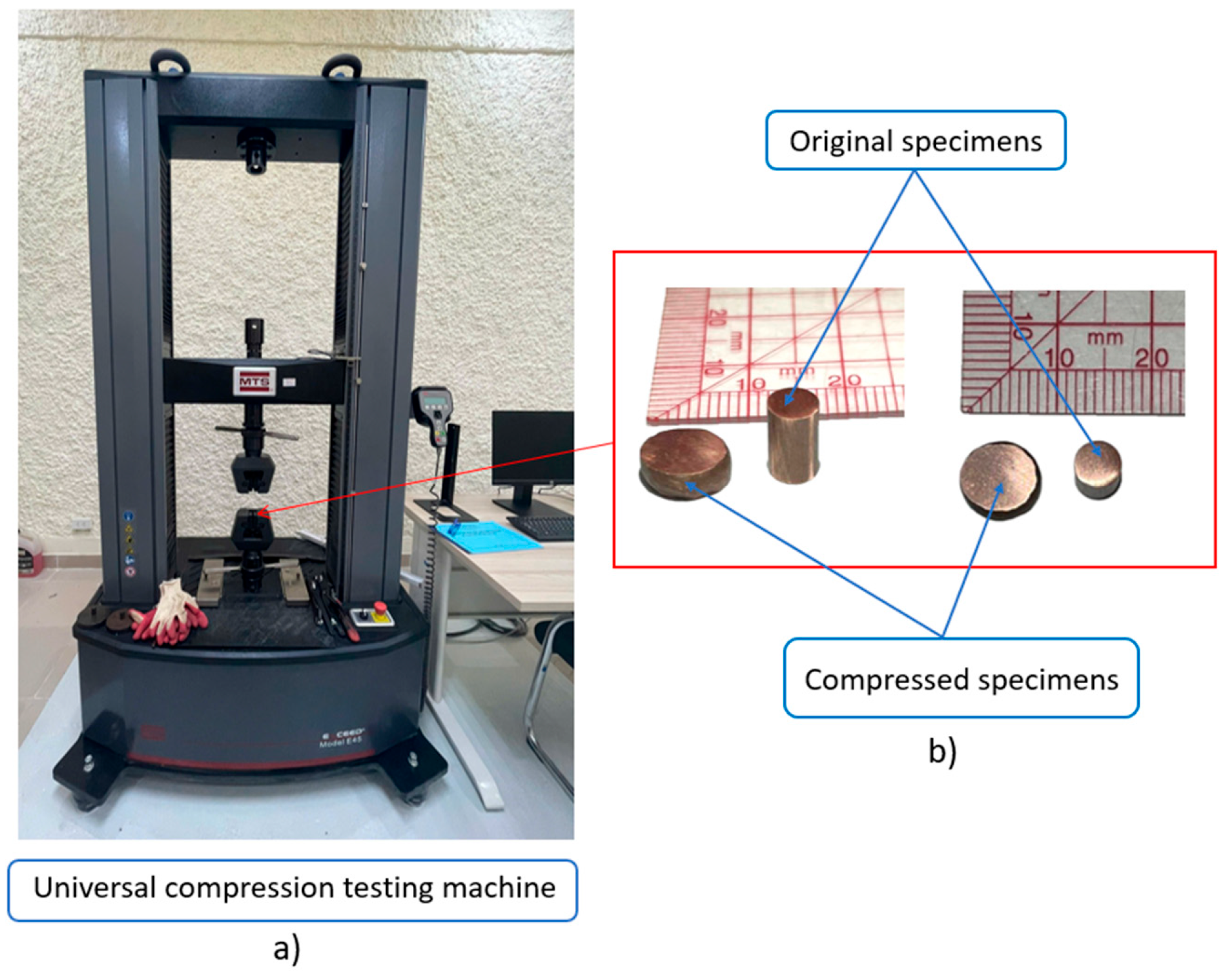
2.3. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Numerical Simulation
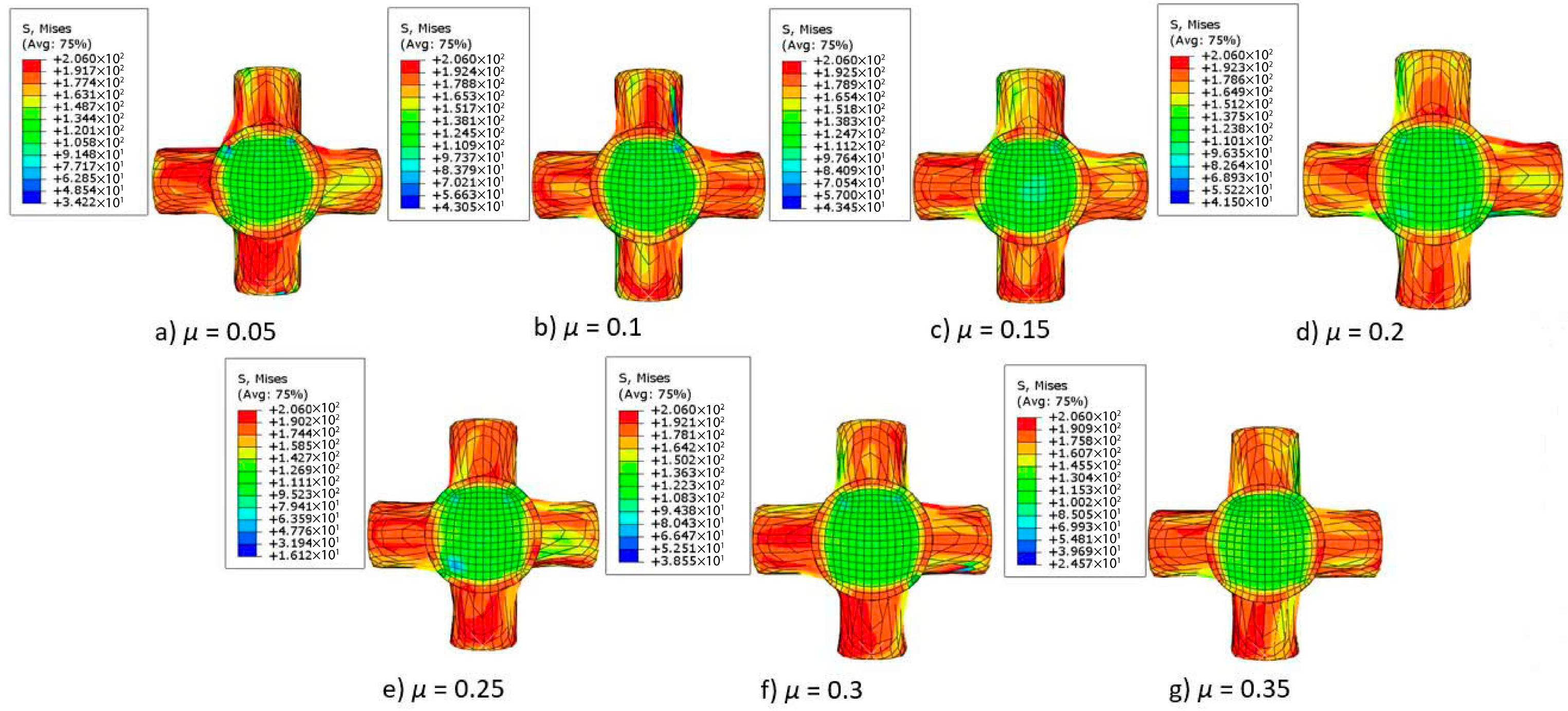
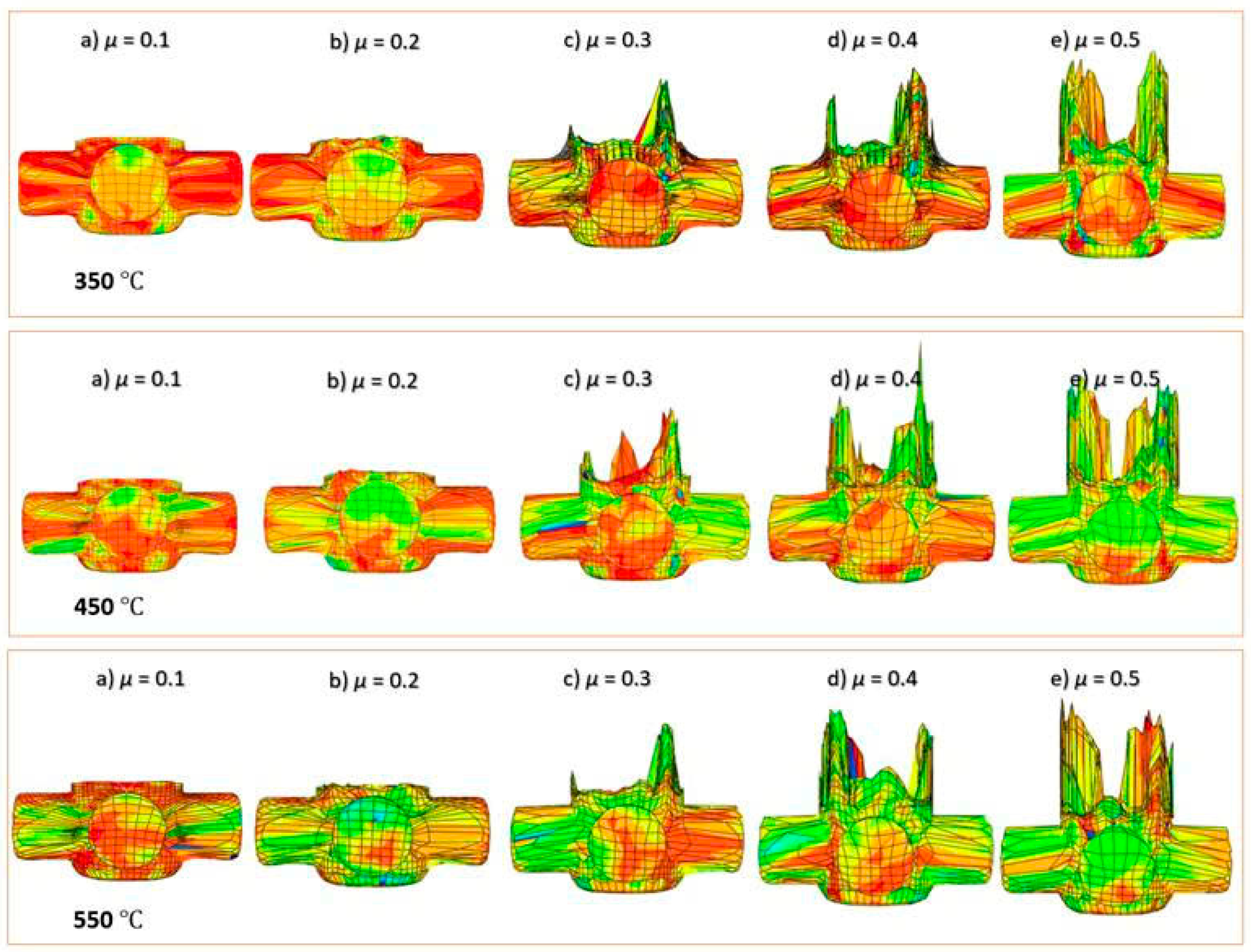
3.1.1. Effects of Friction on the Forming Process and Product Quality
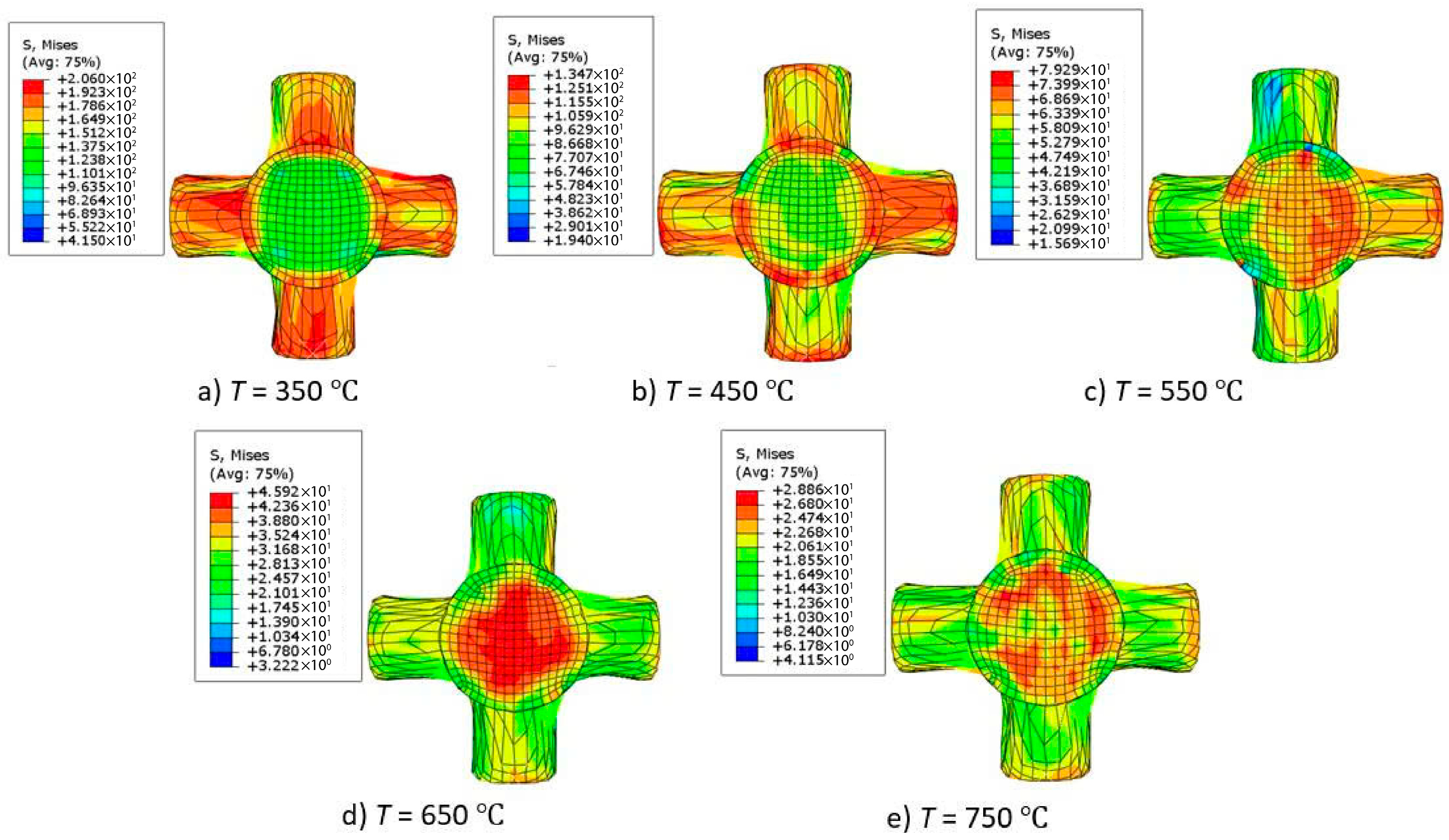
3.1.2. Effects of Temperature on the Forming Process and Product Quality
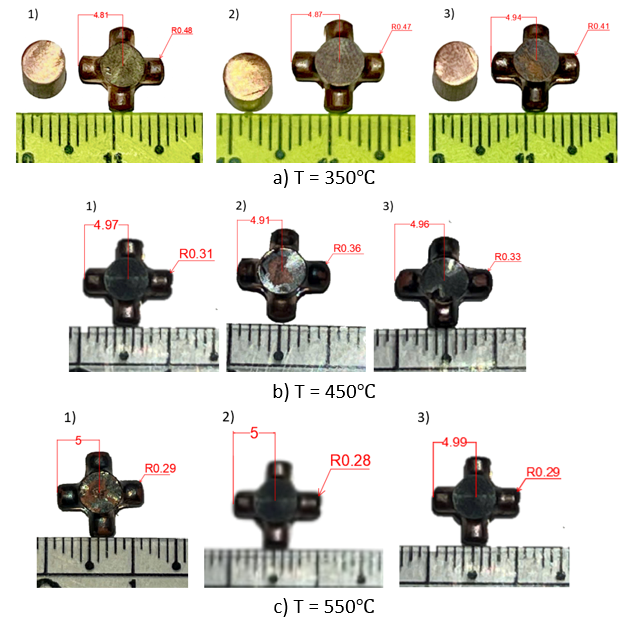
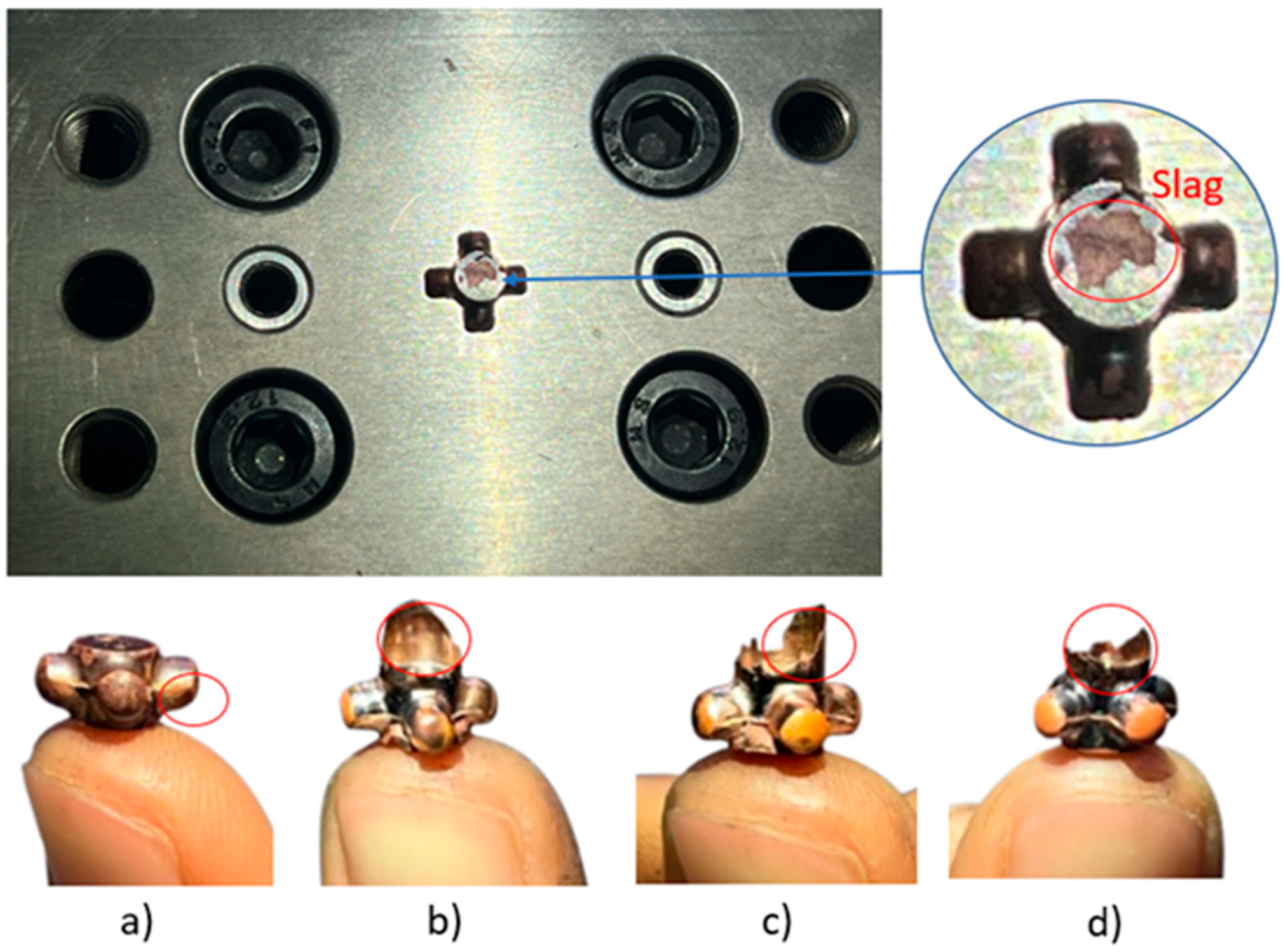
3.2. Experimental Result of Cross-Shaped Coupling
4. Conclusions
- •
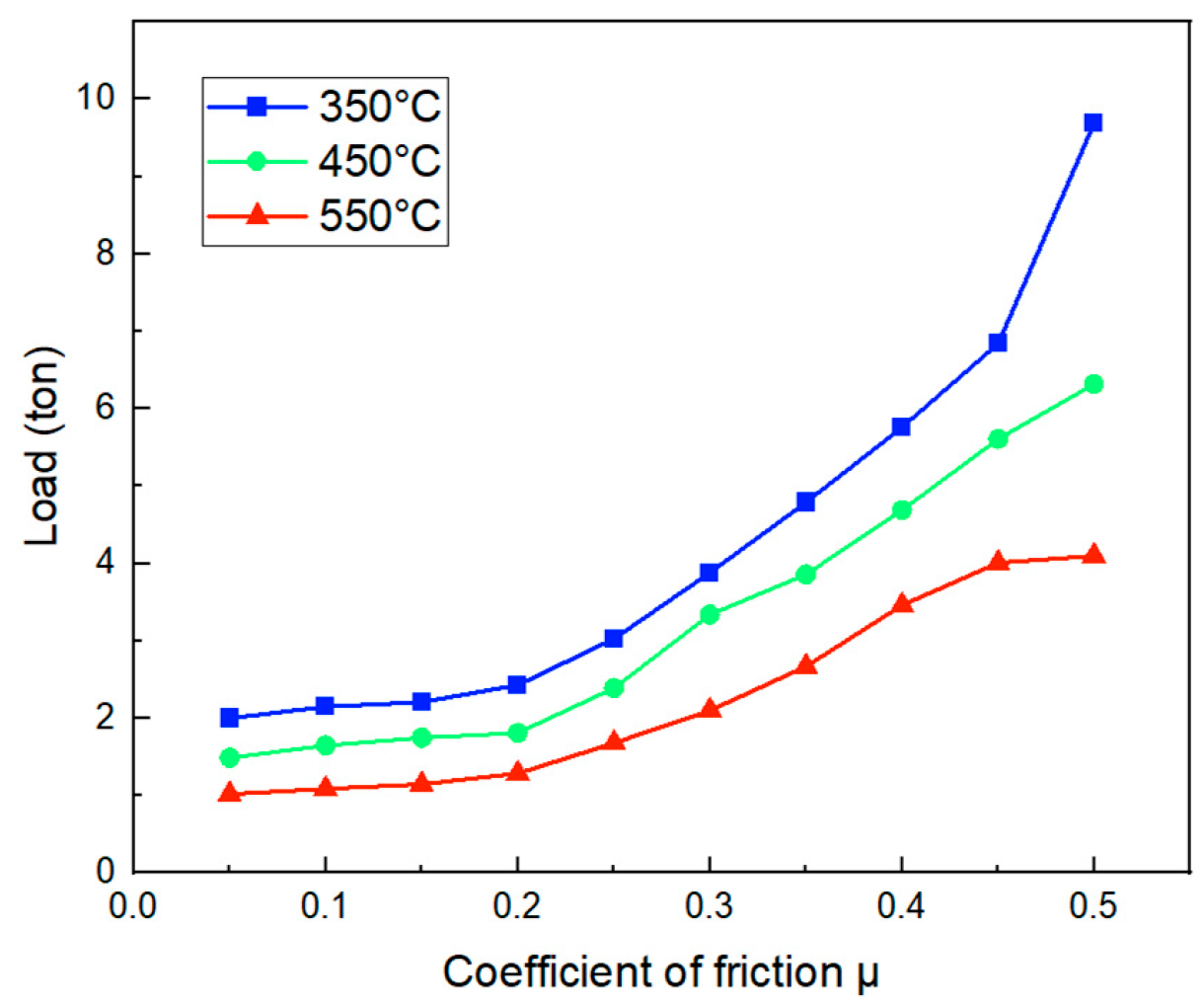
- The effects of friction and temperature on the forming force are clearly demonstrated. Specifically, when the friction coefficient increases from 0.05 to 0.5 at billet temperatures of 350 °C, 450 °C, and 550 °C, the forming force increases by 384.5%, 324.16%, and 301.96%, respectively. Meanwhile, raising the billet temperature from 350 °C to 750 °C results in a reduction of the forming force by up to 78.6%.
- •
- Numerical simulations successfully predict the most critical regions in terms of formability on the cross-shaped coupling, particularly at the apex radius R—the area subject to the highest internal pressure. In this zone, the material tends to flow backward toward the punch-die clearance before completely filling the die cavity, thus posing challenges to achieving full shape.
- •
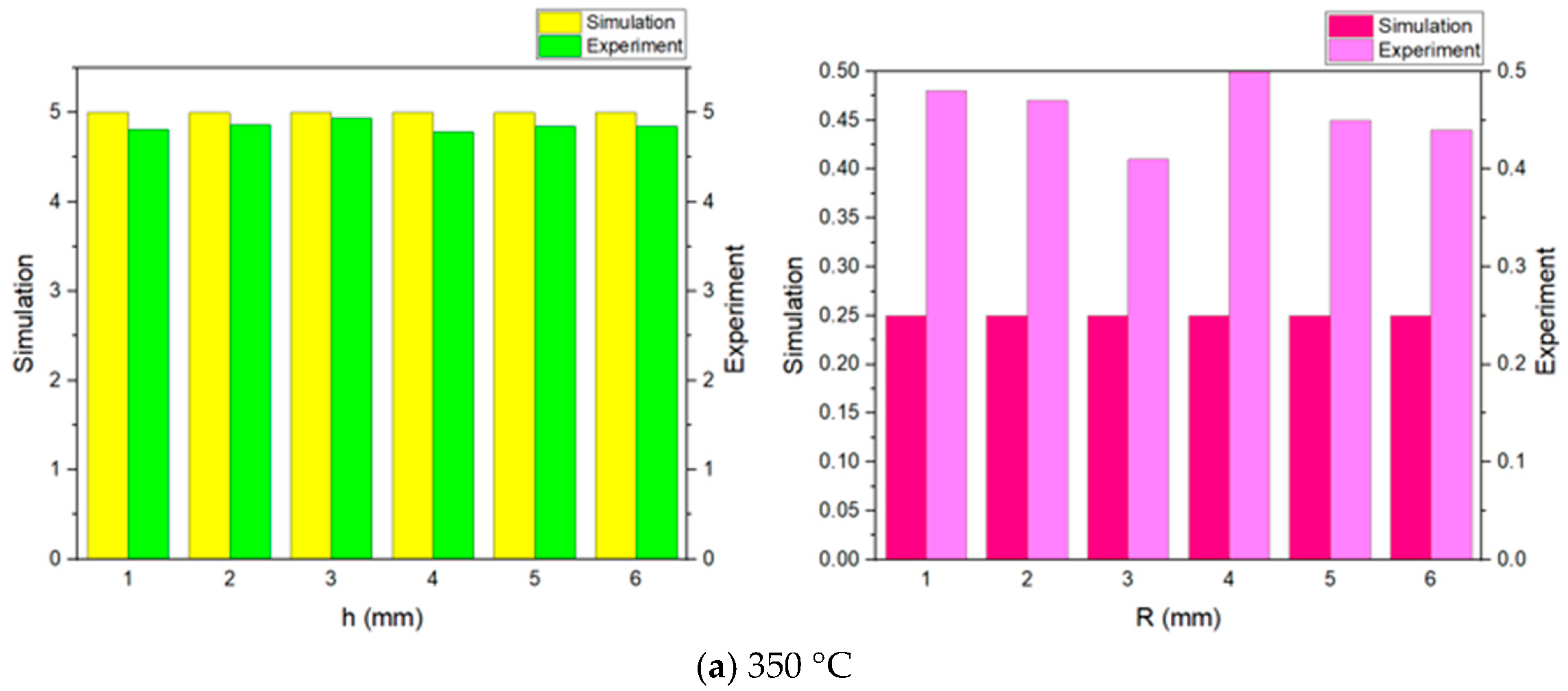
- Experimental results reveal that the branch height h is reproduced with high accuracy, maintaining an error below 5%. However, the targeted radius R at the apex is not fully attained under the current experimental conditions. Additionally, the study identifies a billet temperature of approximately 550 °C as the optimal processing window for micro-extrusion.
- •
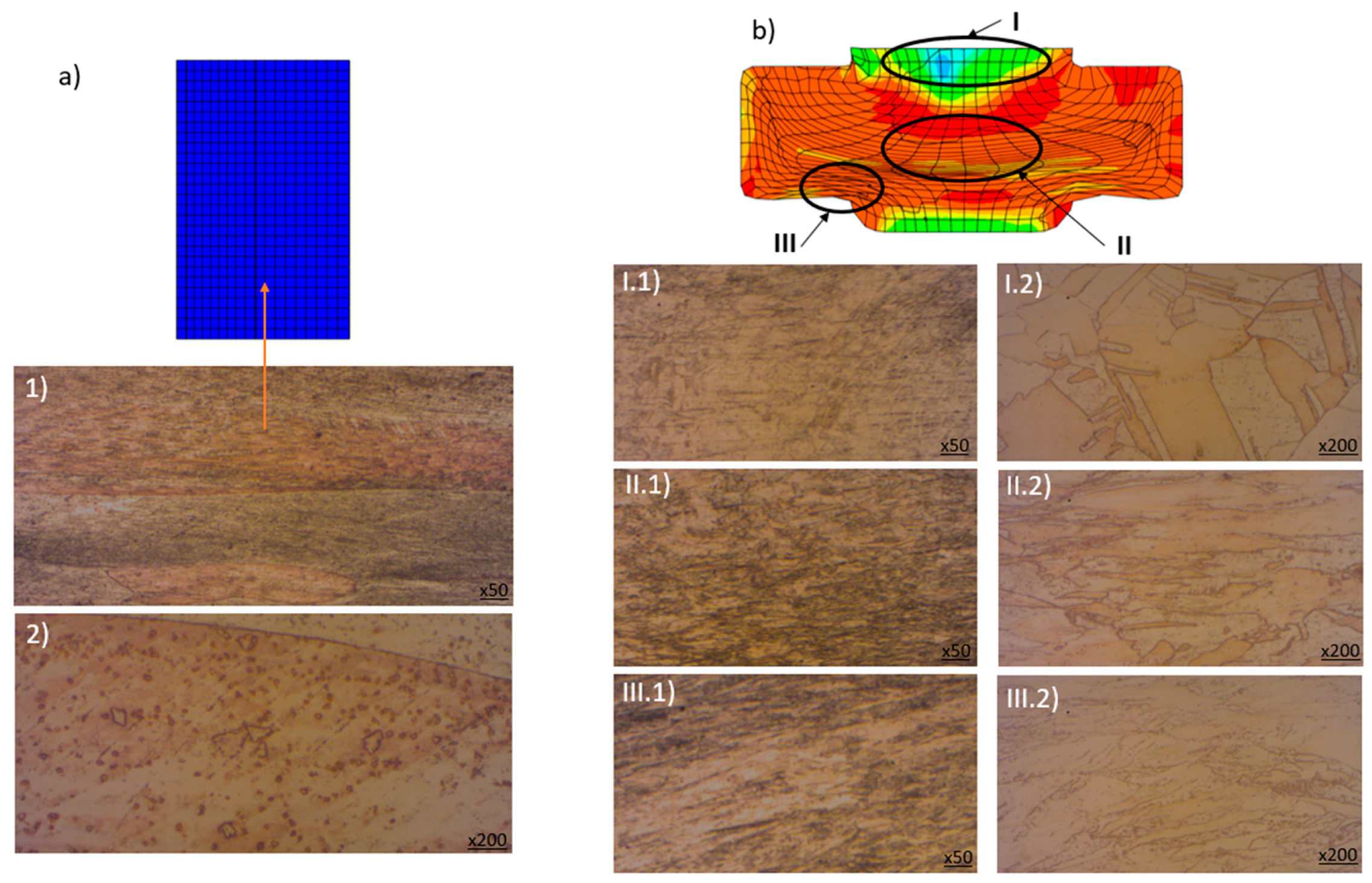
- Microstructural evaluation indicates that under the influence of elevated temperature, the mechanical properties of the material are enhanced due to strain hardening. In Zone III, the grains exhibit significant deformation and are oriented along the curvature, whereas in Zone I, the grains undergo minimal deformation and are distributed equixially.
- •
- The XRD results reveal that while the phase composition remains unchanged, the crystal structure (texture and dislocation density) was modified by plastic deformation and strain-hardening mechanisms, leading to a significant improvement in the mechanical properties, particularly hardness. In Region B—the fillet area where the product branch is formed—the grains exhibit elongated orientation and the highest hardness values, reflecting the effectiveness of the micro-extrusion process.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manabe, K.-i. Metal Micro-Forming. Metals 2020, 10, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pasquale, G. Additive Manufacturing of Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS). Micromachines 2021, 12, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar-Cunha, A.; Covas, J.A.; Sikora, J. Optimization of Polymer Processing: A Review (Part I—Extrusion). Materials 2022, 15, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pricci, A.; de Tullio, M.D.; Percoco, G. Analytical and Numerical Models of Thermoplastics: A Review Aimed to Pellet Extrusion-Based Additive Manufacturing. Polymers 2021, 13, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Yuan, L.; Chen, W.; Bao, J.; Su, Q.; Xu, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; et al. A Review on Micro/Nanoforming to Fabricate 3D Metallic Structures. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2000893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Feng, L.; Kang, F.; Du, H.; Chen, Z. Recent research and advances in extrusion forming of magnesium alloys: A review. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 953, 170080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preedawiphat, P.; Mahayotsanun, N.; Sucharitpwatskul, S.; Funazuka, T.; Takatsuji, N.; Bureerat, S.; Dohda, K. Finite Element Analysis of Grain Size Effects on Curvature in Micro-Extrusion. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, J.; Quodbach, J. Versatility on demand—The case for semi-solid micro-extrusion in pharmaceutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 172, 104–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, M.; Naniz, M.A.; Kouhi, M.; Saberi, A.; Zolfagharian, A.; Bodaghi, M. Recent progress in extrusion 3D bioprinting of hydrogel biomaterials for tissue regeneration: A comprehensive review with focus on advanced fabrication techniques. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 9, 535–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strano, M.; Rane, K.; Farid, M.A.; Mussi, V.; Zaragoza, V.; Monno, M. Extrusion-based additive manufacturing of forming and molding tools. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 117, 2059–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhou, H. Current and Future Trends for Polymer Micro/nano Processing in Industrial Applications. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2200903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabaa, M.; Monteiro, F.; Bensag, H.; Dandache, A. Green Industrial Internet of Things from a smart industry perspectives. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 430–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollertsen, F. (Ed.) Introduction. In Micro Metal Forming; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.-Y.; Shi, S.Q.; Fu, M.W. Progressive microforming of pin-shaped plunger parts and the grain size effect on its forming quality. Mater. Des. 2020, 187, 108–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Dodaran, M.; Ahmed, S.; Shao, S.; Meng, W.J.; Juul, K.J.; Nielsen, K.L. Grain-size affected mechanical response and deformation behavior in microscale reverse extrusion. Materialia 2019, 6, 100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajenthirakumar, D.; Srinivasan, N.; Sridhar, R. Kumar, R., Chauhan, V.S., Talha, M., Pathak, H., Eds.; Development of a Micro-forming System for Micro-extrusion Process of Micro-pin in AZ80 Alloy. In Machines, Mechanism and Robotics. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering 2022; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Shan, D.; Zhang, L.; Guo, B. Micro-Extrusion Process and Microstructure Evolution of Miniature Heat Pipe in 6063 Aluminum Alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 6463–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiswanto, G.; Supriadi, S.; Dwiyati, S. Challenge in magnesium microforming. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1070, 012121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elaziem, W.; Hamada, A.; Makino, T.; Hassan, M.A. Microstructural evolution during extrusion of equal channel angular-pressed AA1070 alloy in micro/mesoscale. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 36, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanthakumar, S.; Rajenthirakumar, D.; Avinashkumar, S. Influence of temperature on deformation behavior of copper during microextrusion process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2020, 234, 095440621989911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.-q.; Li, F.; Huo, P.-d.; Wang, Y. Microstructure evolution and ductility improvement mechanisms of magnesium alloy in interactive alternating forward extrusion. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 2557–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, K.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, M. Effect of Holding Time on the Extrusion Force and Microstructure Evolution during the Plastic Forming of Ti-6Al-4V Micro-Gears. Materials 2022, 15, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, B.; Sahoo, S.K.; Panigrahi, S.K. Micro-extrusion: A potential approach to micro-manufacture miniaturize magnesium metal matrix composite components. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 131, 2473–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Lv, P.; Liu, F.; Xu, L.; Bai, W.; Han, G. Evaluation of interfacial friction characteristics in multi-mode ultrasonic vibration assisted micro-extrusion process. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 88, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, B.; Panigrahi, S.K. A superplastic micro-extrusion technology to develop engineered magnesium micro-components. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 327, 118350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slámečka, K.; Drotárová, L.; Oliver-Urrutia, C.; Tkachenko, S.; Remešová, M.; Gejdoš, P.; Čelko, L.; Montufar, E.B. Low-temperature gas nitriding effects on mechanical and biological properties of open-porous pure titanium produced by robotic micro-extrusion. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 505, 132084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Li, M.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, B.; Zhao, D.; Zhai, W. Porous polyetherimide fiber fabricated by a facile micro-extrusion foaming for high temperature thermal insulation. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 65, 102247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Han, G.; Liu, F.; Hu, J.; Xu, L.; Bai, W.; Chen, H. Surface and volume effects in multimodal ultrasonic vibration assisted micro-extrusion forming: Experiments and modelling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2023, 322, 118185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Han, K.; Gao, F.; Shi, H.; Song, H.; Zhang, Y.; An, C. Research on the performance of high-strength explosive ink and application of direct writing technology in micro-explosive network. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrmann, G.; Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Magnetic 3D-Printed Composites—Production and Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trzepieciński, T.; Najm, S.M.; Sbayti, M.; Belhadjsalah, H.; Szpunar, M.; Lemu, H.G. New Advances and Future Possibilities in Forming Technology of Hybrid Metal–Polymer Composites Used in Aerospace Applications. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kodli, B.; Saxena, K. Micro Forming and its Applications: An Overview. Key Eng. Mater. 2022, 924, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Wan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, H. Experimental investigation into effects of different ultrasonic vibration modes in micro-extrusion process. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 67, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, Y. A micro-coupling for micro mechanical systems. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2016, 29, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, G.; Kumar, R.; Shelare, S.; Pachpor, A.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, S.; Bisht, Y.; Abbas, M. Unravelling the Dynamics of Misalignment-Induced Vibrations in Two Jaw Elastomeric Couplings for Enhanced Industrial Reliability: A Comprehensive Analysis of Dynamics and Diagnostic Approaches. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2024, 12, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloy, J.; Mounier, E. Status of the MEMS industry. In Proceedings of the MEMS/MOEMS Components and Their Applications II, San Jose, CA, USA, 24–25 January 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wen, M.; Cui, H.; Guo, J.; Wang, C. Hot Deformation Behavior and Processing Maps of Pure Copper during Isothermal Compression. Materials 2023, 16, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhfuss, B. Bulk Metal Forming. In Micro Metal Forming; Vollertsen, F., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; p. 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucharitpwatskul, S.; Mahayotsanun, N.; Bureerat, S.; Dohda, K. Effects of Tool Coatings on Energy Consumption in Micro-Extrusion of Aluminum Alloy 6063. Coatings 2020, 10, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Cheng, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, H.; Han, G. Investigation on friction characteristics of micro double cup extrusion assisted by different ultrasonic vibration modes. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 123, 2549–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruchamy, K.; Rajenthirakumar, D.; Arunkumar, M. Microforming: Exploring the role of temperature and forming die in deformation behavior of AL6063 in forward microextrusion. J. Alloys Compd. Commun. 2025, 7, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, Q. Recrystallization Behavior of a Pure Cu Connection Interface with Ultrasonic Welding. Metals 2020, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosford, W.; Caddell, R. Metal Forming Mechanics and Metallurgy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- William, D.; Callister, D.G.R. Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction, 10th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nanthakumar, S.; Thangaraju, D.; Avinash Kumar, R.K. Experimental investigation of 2D-SnS 2 hexagonal nanosheets as lubricating additive in the microextrusion process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2022, 237, 095440622211236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
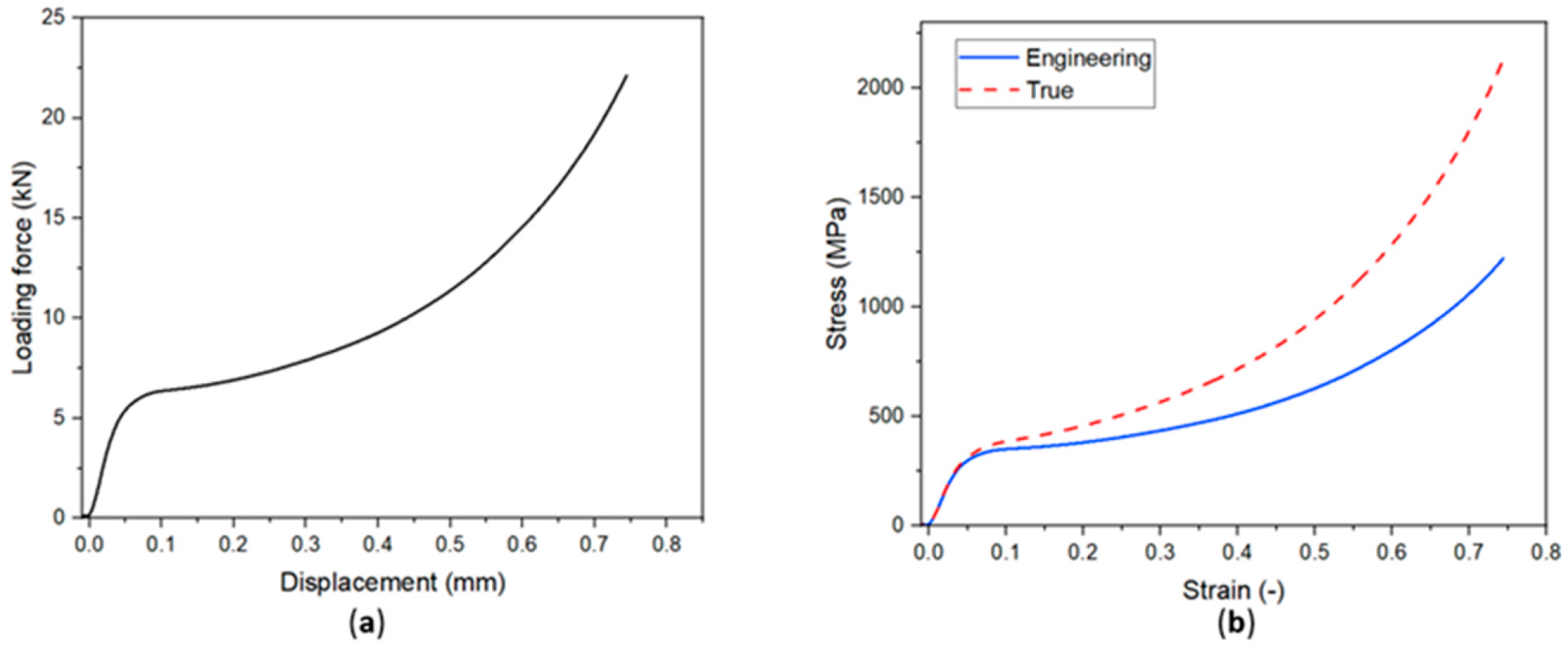
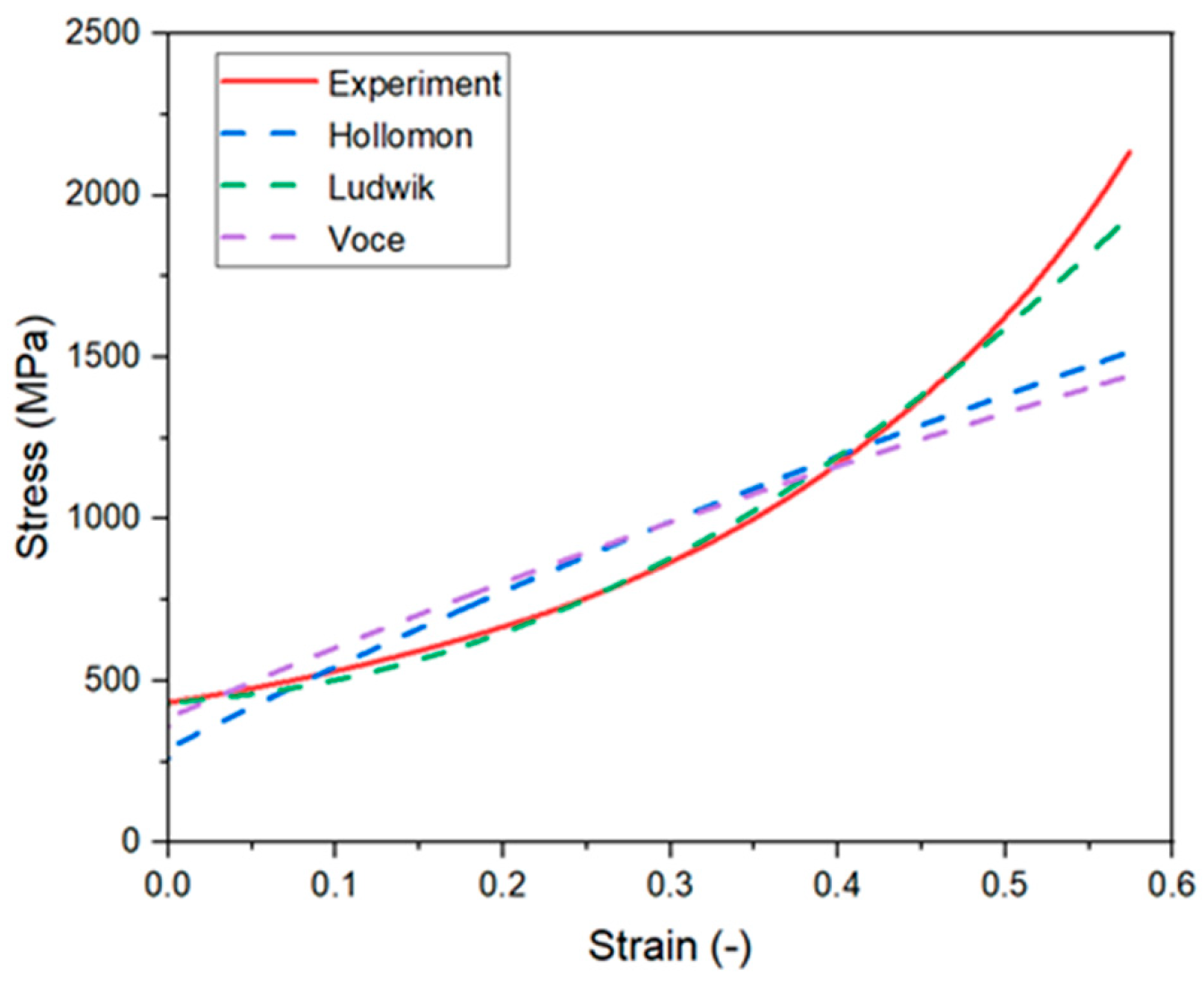

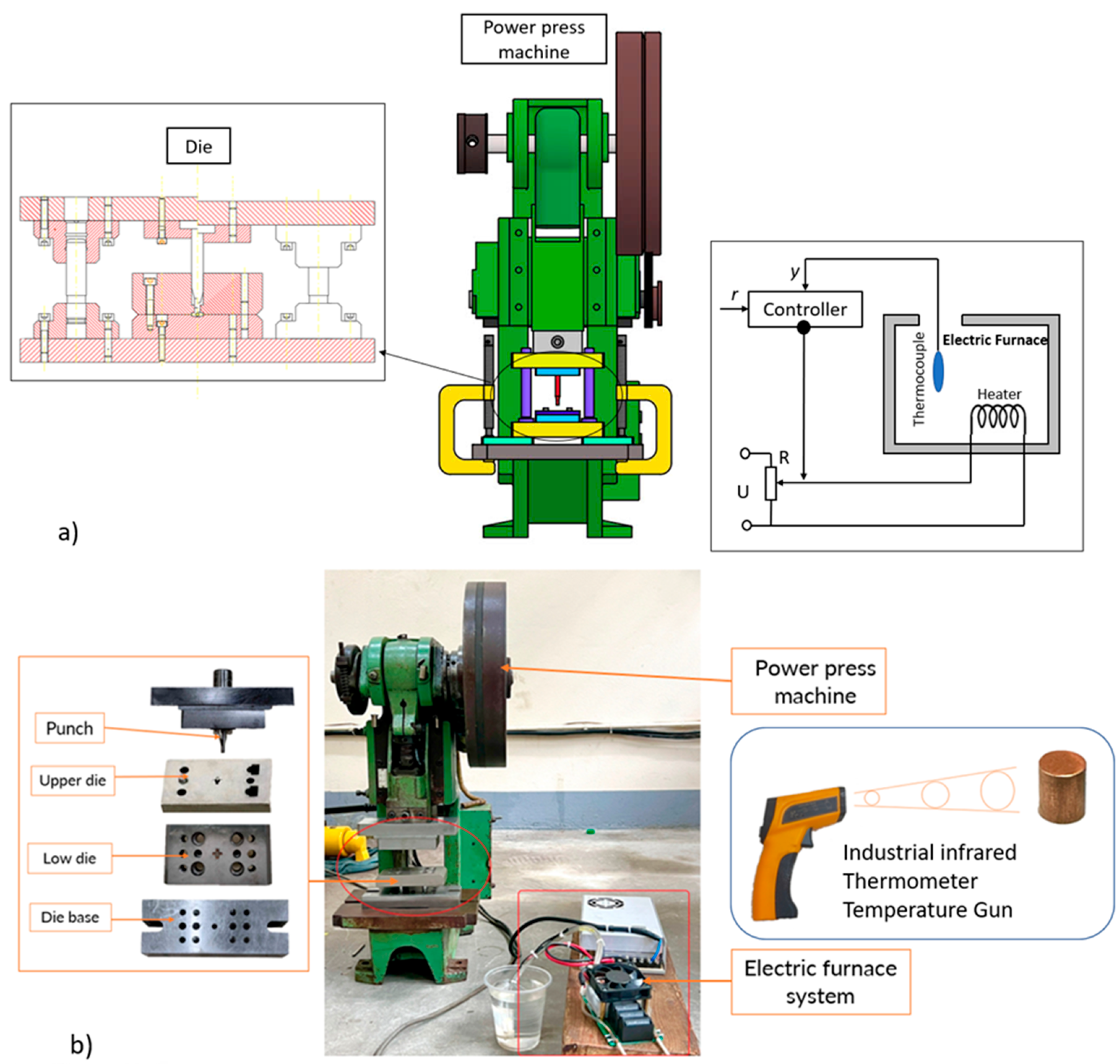



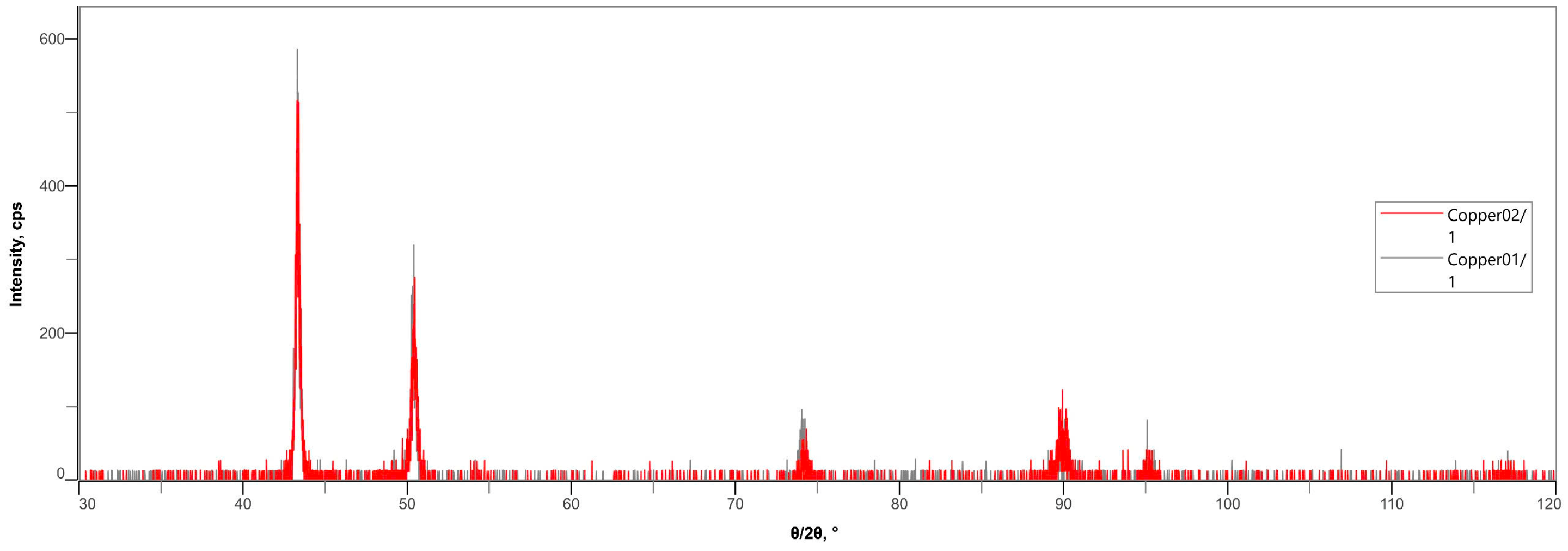
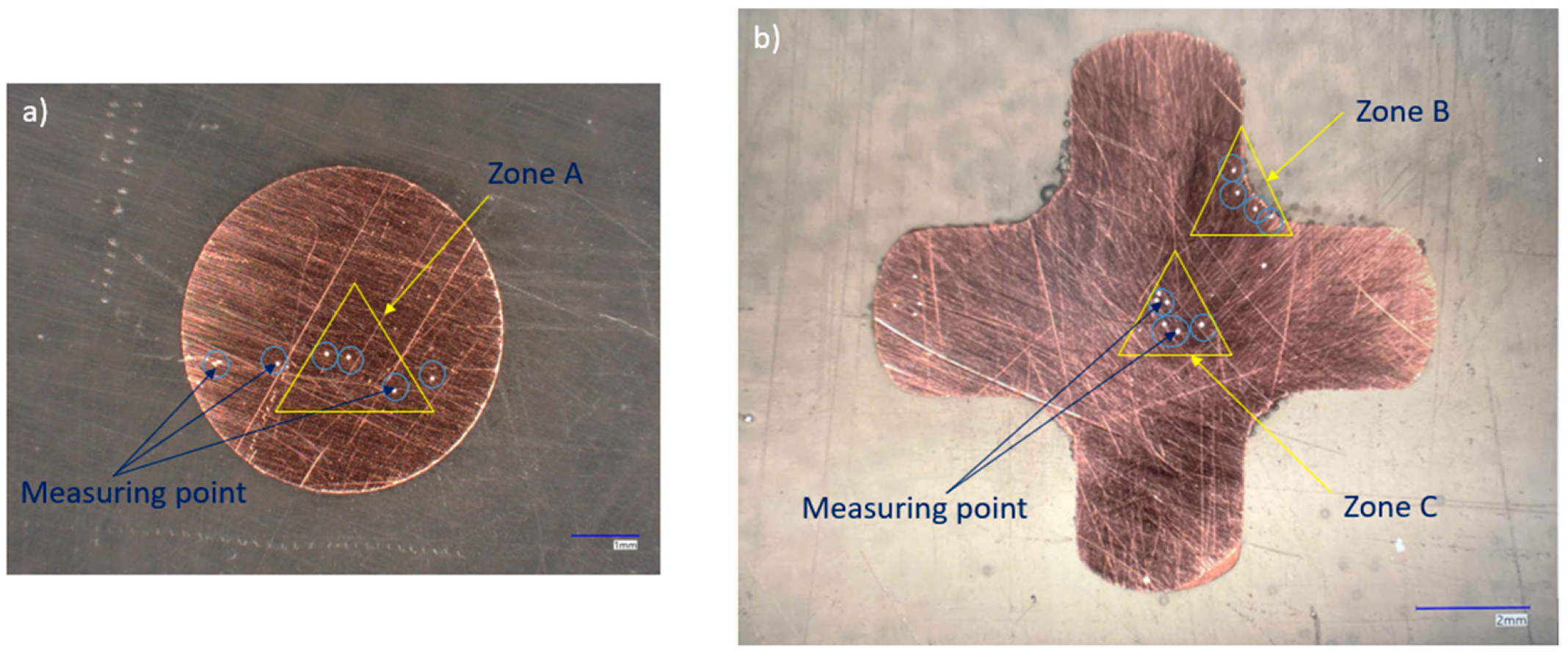
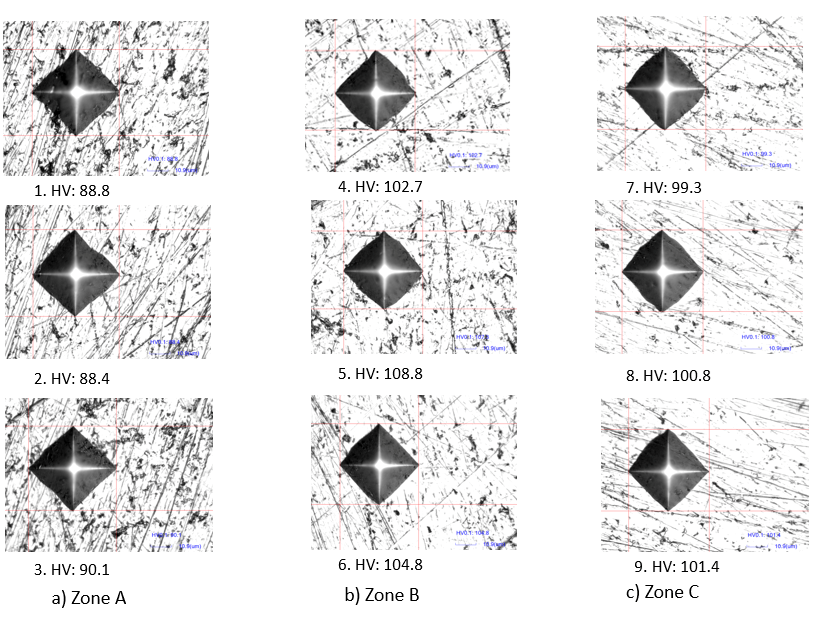
| Material | Composition (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C11000 | Cu > 99.8 | Mn < 0.001 | Bi < 0.001 | As < 0.001 | Fe < 0.001 | Ni < 0.001 |
| Hardening Law | Hollomon | Ludwik | Voce | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | K (MPa) | n | K (MPa) | (MPa) | n | (MPa) | (MPa) | b |
| Value | 3064 | 0.998 | 10,961 | 418.5 | 2.804 | 743,891 | 134.99 | 0.00356 |
| Material | C11000 |
|---|---|
| , kg/m3) | 8.96 × 10−6 |
| Elastic modulus (E, kN/mm2) | 69 |
| Poisson coefficient | 0.34 |
| 385 | |
| Thermal conductivity (W/mK) | 379 (at 550 °C) |
| Linear coefficient of expansion | 17.1 × 10−6/°C |
| No. | Hardness Value (HV) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Zone A | Zone B | Zone C | |
| 1 | 88.8 | 102.7 | 99.3 |
| 2 | 88.4 | 107.3 | 100.8 |
| 3 | 90.1 | 104.8 | 101.4 |
| AVG. | 89.1 | 104.9 | 100.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen Thi, T.; Mai Thi, T.; Nguyen, M.-Q. A Comprehensive Examination of Key Characteristics Influencing the Micro-Extrusion Process for Pure Copper Cross-Shaped Couplings. Eng 2025, 6, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6100250
Nguyen Thi T, Mai Thi T, Nguyen M-Q. A Comprehensive Examination of Key Characteristics Influencing the Micro-Extrusion Process for Pure Copper Cross-Shaped Couplings. Eng. 2025; 6(10):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6100250
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen Thi, Thu, Thuy Mai Thi, and Minh-Quan Nguyen. 2025. "A Comprehensive Examination of Key Characteristics Influencing the Micro-Extrusion Process for Pure Copper Cross-Shaped Couplings" Eng 6, no. 10: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6100250
APA StyleNguyen Thi, T., Mai Thi, T., & Nguyen, M.-Q. (2025). A Comprehensive Examination of Key Characteristics Influencing the Micro-Extrusion Process for Pure Copper Cross-Shaped Couplings. Eng, 6(10), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6100250








