Abstract
With the interest aroused by the development of modern concretes such as printable or self-compacting concretes, a better understanding of the rheological behavior, directly linked to fresh state properties, seems essential. This paper aims to provide a phenomenological description of the rheological behavior of cement paste. The first part is devoted to the most common testing procedures that can be performed to characterize the rheological properties of cement suspensions. The second one deals with the complexities of the rheological behavior of cement paste including the non-linearity of flow behavior, the viscoelasticity and yielding, and the structural build-up over time.
1. Introduction
The development of modern cementitious materials, such as 3D-printable cementitious materials [1,2,3], low-carbon cement [4,5], or self-compacting concrete [6,7], requires a deep understanding of the rheological behavior at the fresh state. Other types of concretes including recycled aggregates or plastic fiber pose challenges with respect to their fresh state behavior [8,9]. In addition, several processes, such as pumping or casting, are strongly conditioned by the rheological behavior. For instance, the development of 3D-printable concretes based on extrusion generates several challenges that directly concern the rheology of cementitious materials. Indeed, 3D concrete formulations must be pumpable but stable in shape once placed without formwork. In addition, the sequential layers put in place by extrusion must adhere and structure themselves quickly. Finally, the geometry of the printed parts must be controlled within the appropriate geometric tolerances [3,10].
At the fresh cement paste scale, the rheological behavior is dictated by the cement particles’ organization and the interparticle forces [11]. Several methods and procedures were developed to characterize this behavior and to examine the effect of influencing factors such as superplasticizers [12,13,14], supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) [15,16], or formulation parameters [17]. Moreover, the rheological behavior of cement paste exhibits different complexities such as non-linearity (shear thinning/shear thickening), viscoelasticity, yielding, structural build-up at rest, and chemical evolution. In general, the rheograms of cement paste are not linear and can present a shear-thinning phenomenon leading to the decrease in viscosity with an increasing shear rate. This behavior is characteristic of flocculated suspensions [15,18] and is attenuated with the incorporation of a dispersant (superplasticizer). In fact, the flow behavior becomes linear with viscosity independent from the shear rate due to the enhanced dispersion by the addition of the superplasticizer.
Furthermore, cementitious materials cannot be described as thixotropic materials [19,20,21,22,23], since the evolution of rheological properties at rest is not fully reversible. At rest, a structural build-up due to flocculation and chemical evolution occurs and allows for evaluating the loss of workability during the dormant period of cement hydration. An irreversible part due to chemical hydration remains despite the application of a strong shearing which theoretically can erase the structural build-up [20]. The addition of dispersants or retarders induces a decrease in the structural build-up, and the behavior of the cement paste tends towards a thixotropic behavior [20].
It thus appears that the rheological behavior of cement paste is complex due to several factors such as the polydispersity of cement particles, their morphology, the interaction between particles, and the chemical evolution (dissolution/precipitation). In this paper, the testing procedures commonly used to characterize the rheological behavior of cement paste are presented first. Then, the rheological behavior of cement paste is described through flow behavior including steady and transient modes, as well as dynamic rheology. Finally, the structural build-up of cement paste during the dormant period of cement hydration is described.
2. Testing Procedures
Rheological measurements can be carried out using rotational rheometers with different types of geometries. It has to be kept in mind that several artifacts could occur and lead to misinterpretations of results [24]. In this section, only the most relevant testing procedures that can be performed for cement paste are presented.
2.1. Flow Tests
Flow tests are usually performed using rotational rheometers by applying an imposed shear rate or shear stress. The most relevant procedure for cement paste consists of the application of a strong preshear in order to induce a structural breakdown and ensure a same initial state for the tested samples, followed by a flow sweep (or stepped flow) with a decreasing shear rate, as shown in Figure 1. The applied time at each step must be greater than the characteristic time, which depends on the shear rate. In fact, the characteristic time is inversely proportional to the shear rate. So, for a high shear rate, the required time to reach the steady state flow is negligible, while for a very low shear rate, this time increases and is of the order of 10 to 50 s. It should be noted that most modern rheometers are equipped with steady state sensors that allow the equilibrium state to be detected at each applied shear rate.
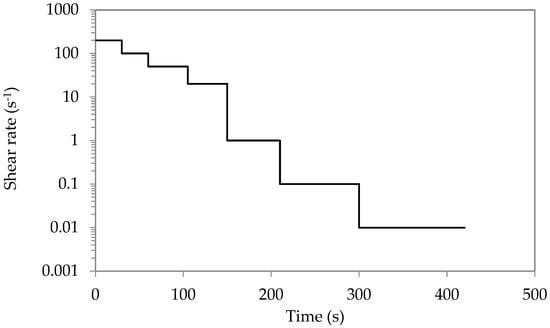
Figure 1.
Flow sweep test with a decreasing shear rate.
The response given by such flow test in terms of shear stress and viscosity is presented in Figure 2. The flow curve is non-linear and displays shear-thinning behavior. In fact, the viscosity decreases with an increasing shear rate, which characterizes the breakdown of agglomerated particles. For a low shear rate, the shear stress remains almost constant, which describes the flow stoppage of freshly mixed cement paste. This shear stress is defined as the dynamic yield stress and corresponds to the minimum stress required to initiate the flow onset.
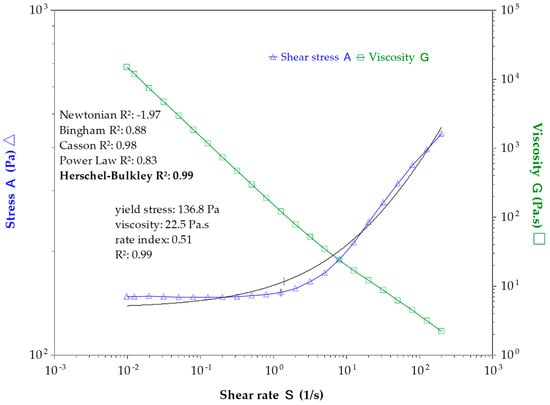
Figure 2.
Shear stress and viscosity as a function of the shear rate for cement paste with a w/c ratio of 0.4 after 20 min of hydration (test performed with Rheometer AR2000Ex from TA Instruments equipped with Vane geometry).
As presented in Figure 2, several laws allow for fitting the flow curve. However, for non-Newtonian and yield stress fluid such as cement paste, the flow behavior can be described by the Casson law as well as by the Herschel–Bulkley model. This latter is widely used for cement paste behavior and is defined as follows:
where is the shear stress (Pa), is the yield stress (Pa), is the shear rate (s−1), is the viscosity (Pa·s), and is the rate index. and are the fitting parameters. A thinning behavior is represented by a rate index n inferior to 1, as shown in Figure 2. When the rate index is equal to 1, the Herschel–Bulkley law is equivalent to the Bingham law and represents a linear behavior for which the viscosity remains constant with the shear rate. A shear-thickening phenomenon is represented by a rate index superior to 1.
The Casson model can also describe a non-linear flow behavior (shear-thinning) with a yield stress term. It is defined as follows:
where is the yield stress (Pa) and is a model constant (Pa·s).
2.2. Oscillation Metods
Dynamic rheology consists of small-amplitude oscillation shear (SAOS) [17,21,25] and large-amplitude oscillation shear (LAOS) [26]. These procedures seem to be more appropriate for examining the microstructure of cement paste. The LAOS procedure appears to be relevant to investigating the evolution of non-linear viscoelastic properties at different frequencies and amplitudes represented by the Pipkin diagram [26]. The SAOS procedure is more appropriate for examining the structural build-up during the dormant period of cement hydration [21,22,27,28,29].
Oscillation procedures include strain sweep, frequency sweep, and time sweep tests. They consist of the measurement of the viscoelastic properties such as the storage (or elastic) modulus G′, the loss (viscous) modulus G″, critical strains, and other parameters (phase angle, oscillation stress …). The frequency sweep mode is generally performed to investigate the cement paste stability [30]. The time sweep procedure is appropriate for examining the structural build-up and thixotropy [19,21,22]. Strain (or stress) sweep tests can be carried out to probe the microstructure of cement paste and can give information concerning the network of cement particles and the forces acting inside this network.
The amplitude sweep can be performed by applying an increasing stress (or strain) at a frequency of 1 Hz [17,19,23]. The typical response of amplitude sweep is presented in Figure 3. It is worth noting that this kind of non-destructive test allows the microstructure of fresh cement paste to be probed [17,27,31]. As shown in Figure 3, the evolution of storage and loss moduli during an amplitude sweep follows three phases. The first phase in which the moduli remain almost constant is defined as the linear viscoelastic domain (LVED). In this domain, the microstructure of cement paste is maintained [27]. The SAOS procedure allowing the structural build-up to be characterized is commonly performed in this strain region. In addition, cement paste will behave like a solid if the storage modulus G′ is greater than the loss modulus G″. The liquid-like behavior corresponds to G′ < G″. The end of the LVED is characterized by a significant drop of the moduli. The strain associated with this decrease onset is of the order of 10−2% and can be interpreted as a signature of the breakage of the links between cement particles (C-S-H links and attractive colloidal forces) [17,23,27,29,32].
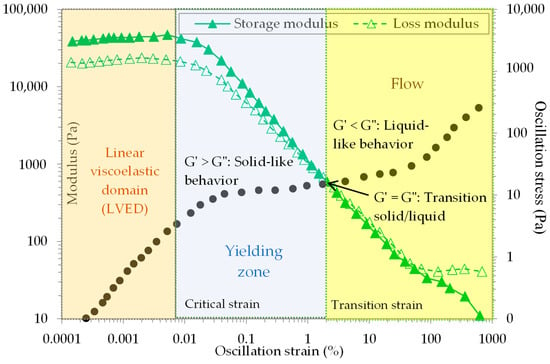
Figure 3.
Example of an amplitude (strain or stress) oscillation test (test performed with Rheometer AR2000Ex from TA Instruments equipped with Vane geometry).
The second phase corresponds to the yielding zone. The oscillation stress remains almost constant in this region, and the moduli (G′ and G″) decrease significantly. In addition, there is a transition point corresponding to the intersection of the storage modulus and the loss modulus curves (G′ = G″) which defines a solid/liquid transition, i.e., the flow onset. This transition point is associated with a large strain (transition strain). The yield stress can be determined at this point.
The last phase is associated with a large strain and describes the flow behavior (liquid-like behavior G′ < G″).
2.3. Transient Mode
The transient mode includes stress growth, stress relaxation, and creep/recovery procedures. This paper focuses on the stress growth procedure widely used to measure the static yield stress.
The stress growth procedure consists of the application of a very low shear rate in the range of 10−3 s−1–10−2 s−1, depending on the rheometer sensitivity. In fact, the yield stress corresponds to the minimum stress required to initiate flow. Theoretically, it corresponds to the shear stress at rest, i.e., for a shear rate equal to 0. Since rheometers cannot apply a shear rate of zero, this shear rate must be as low as possible. The correct measurement of the yield stress consists of the application of a strong pre-shearing phase, followed by a sufficient resting time to allow the structure to be rebuilt [23,33,34,35,36]. Then, a very low shear rate in the range of 10−3 s−1–10−2 s−1 is applied to the cement paste during a sufficient time to reach the steady state flow. This time has to be greater than the characteristic time of flocculation, which is of the order of 10 s [23]. Vane geometry appears to be the most suitable for such a test. However, it is important to determine beforehand the geometric constants making it possible to calculate, respectively, the shear stress and the shear rate from the applied torque and the rotational velocity. This can be accomplished using the Couette analogy method described by Aît-Kadi et al. [37].
The typical curve given by the stress growth procedure is presented in Figure 4. It can be observed that the evolution of shear stress as a function of shear strain follows at least two steps. First, the shear stress increases almost linearly with the strain until it reaches a peak followed by a plateau. The linear increase for a low strain is consistent with elasticity (solid regime) and can be represented as follows:
where is the shear stress (Pa), G is the instantaneous shear modulus (Pa), and is the shear strain.
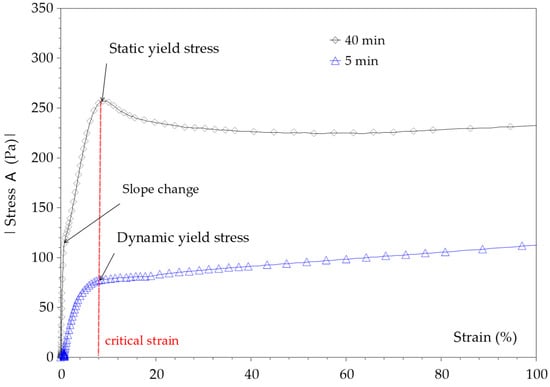
Figure 4.
Shear stress as a function of shear strain during the stress growth procedure (cement paste with w/c = 0.4) performed after 5 min and 40 min of hydration with AR2000Ex equipped with Vane geometry.
The peak defines the static yield stress corresponding to the flow onset, i.e., the shear stress where the suspension just starts to flow. In cement suspensions, the yield stress originates from the network of interacting particles due to direct contacts and colloidal attractive forces [11]. This peak is not always observed. Its observation depends on several factors such as the particle properties (shape, particle size distribution), solid volume fraction, and time of hydration. In cement pastes, this peak becomes more visible with the progress of the hydration, as shown in Figure 4 [20]. Moreover, one can simply observe a plateau defining the steady state flow under a low shear rate. This plateau defines the dynamic yield stress (Figure 4). In the plateau, the shear stress is related to the shear rate through the Newton law as follows:
where is the viscosity (Pa·s), and is the shear rate (s−1).
The transition point between the linear regime and the plateau which defines the yield stress can be associated with a characteristic time required to reach the steady state flow. This characteristic time is inversely proportional to the shear rate as follows:
where is the critical strain of the order of few %. For a shear rate of 10−2 s−1 and a critical strain of about 10%, the characteristic time is of the order of 10s, which is close to the characteristic time of flocculation [23].
Furthermore, as reported by Roussel et al. [23], in the very first stages of the shearing process, the shear stress–shear strain curve can exhibit an abrupt change in the slope (Figure 4 and Figure 5). Fourmentin et al. [38] reported the same trend. In fact, at a very low shear strain, there is a quick increase in the shear stress associated with a high instantaneous shear modulus, which could characterize a very stiff material [23,38]. This slope change is associated with a very low strain which cannot be associated with the flow onset. According to Roussel et al. [23], this low strain could be associated with the breakage of the contacts between cement particles formed by C-S-H links. The critical strain of the order of few % at the flow onset describes large structural changes in the suspension [11,23].
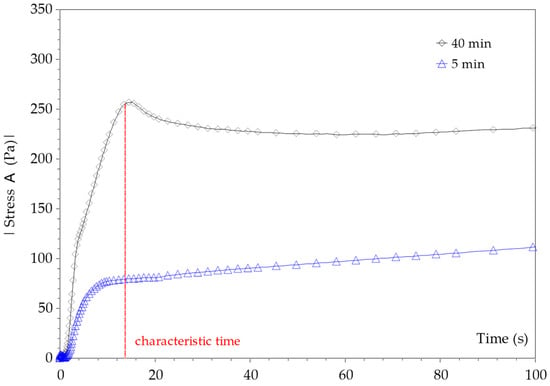
Figure 5.
Evolution of shear stress as a function of time during the stress growth procedure (cement paste with w/c = 0.4) performed after 5 min and 40 min of hydration.
3. Rheological Behavior of Cement Paste
3.1. Flow Behavior
The cementitious suspensions generally display a shear-thinning behavior with a continuous decrease in viscosity with the shear rate. This behavior, characteristic of flocculated suspensions, describes the deflocculation under shearing. For simplification, the rheological behavior of cement paste is often assimilated to a Binghamian behavior under certain conditions. In addition, cement pastes (without dispersant) exhibit a yield stress that has to be overcome to initiate flow. Viscoplastic models such as the Herschel–Bulkley model or Bingham model seem to be relevant and are widely used to describe the flow behavior of cement pastes. The flow curve obtained by a stress (or shear rate) sweep is fitted with such models to determine the dynamic yield stress at a very low shear rate.
The effect of several parameters such as the properties of cement, water-to-cement ratio (w/c), admixtures, and supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) on the flow behavior has been widely studied [15,23,32,39,40,41,42,43,44,45]. The effect of w/c on rheological parameters can be described by the dependence on the solid volume fraction through the Krieger–Dougherty law for viscosity [46] or yield stress [47] or by the yield stress model (YODEL) developed by Flatt and Bowen [48]. The effect of admixtures (especially superplasticizers) and SCMs has been the subject of a large number of publications.
Although it is often assumed, by simplification, that cement pastes behave like a Bingham fluid, it turns out that many experimental results reveal behaviors marked by nonlinear flow curves, especially with shear-thinning behavior. However, cement pastes can also display a shear-thickening behavior, particularly in the presence of superplasticizers and/or certain mineral additions [15,49,50]. The shear-thickening behavior refers to the abrupt or continuous increase in viscosity with the shear rate. This behavior can be described with the Herschel–Bulkley model with a rate index n > 1. Different assumptions have been proposed to explain the origins of this behavior.
By carrying out dynamic simulations, Bossis and Brady [51] proposed a mechanism based on particle clustering to explain the shear thickening. The cluster formation results from the lubrication forces. In a suspension with short-range repulsive interparticle forces (electro-steric effect; Brownian motion) such as cement paste with a superplasticizer, the cluster formation could be avoided, especially at low or moderate shear rates. With an increasing shear rate, the hydrodynamic forces increase until their intensity exceeds that of the repulsive forces, thus inducing the formation of particle clusters.
Another mechanism based on the order–disorder transition has been proposed to explain the shear thickening [15,52,53,54]. According to this theory, the shear-thickening behavior would be the consequence of the transition from a layered flow, where the particles are ordered in successive layers, to a locally disordered state, where the particles are dislodged from the layer structure. In fact, the hydrodynamic forces cause this instability, which breaks up the layered flow. This local instability induces particle jamming, which probably involves cluster formation, leading to an increase in viscosity.
In the case of cement paste, Roussel et al. suggest that these mechanisms do not seem relevant. Indeed, according to the authors, the macroscopic flow behavior of cement pastes can be characterized by two transitions: macroscopic shear thinning resulting from the transition between a colloidal and viscous regime, and shear thickening corresponding to the transition between a viscous and inertial regime. At a high shear rate, particle inertia dominates hydrodynamic effects, which may lead to shear thickening.
3.2. Linear Visco-Elastic Domain
The linear visco-elastic domain (LVED) can be determined by oscillation rheology (Section 2.2). In this domain, the storage and loss moduli remain constant. Generally, fresh cement pastes (without a superplasticizer) exhibit a solid-like behavior in this domain with a storage modulus greater than the loss modulus (G′ > G″). The end of this domain is associated with a shear strain of the order of 10−2%. This shear strain can be attributed to the breakage of the links between particles due to early hydrates nucleation [23] and/or the attractive colloidal forces [29,32]. It has to be kept in mind that this critical strain remains identical from fresh cement paste to hardened cement paste [29]. In addition, it is of the same order of magnitude as the critical strain for which cracks propagate in hardened concrete [23].
The effect of several factors (w/c ratio, SP dosage, SCMs …) on the LVED of fresh cement paste has been investigated, but the number of studies remains relatively limited [17,19,27,29,55,56]. Recently, an interesting study dealing with the effect of the w/c ratio and superplasticizer (SP) on the viscoelastic properties of fresh cement pastes has been carried out [17]. The results show that both the storage modulus and viscoelastic stress increase with the decreasing w/c ratio, which is consistent with the fact that the stiffness of cement paste increases with the solid volume fraction. In fact, the storage modulus could follow a Krieger–Dougherty law [47].
Furthermore, it appears that the critical strain at the end of the LVED is strongly affected by the superplasticizer dosage, while the effect of the w/c ratio is less significant. Only a high w/c ratio leads to an increase in this critical strain [17]. The effect of the SP dosage thus appears to be more significant than that of the w/c ratio (Figure 6). The interpretation of this phenomenon remains complex, and some ambiguities remain in the literature. First, the critical strain at the end of the LVED is attributed to the breakage of C-S-H bridges between cement particles [17,23]. However, in a calcite suspension (chemically inert), which has granular properties close to those of cement paste and is sometimes used to mimic the fresh behavior of cement paste [57,58], the end of the LVED is characterized by a critical strain of the same order of magnitude [59].
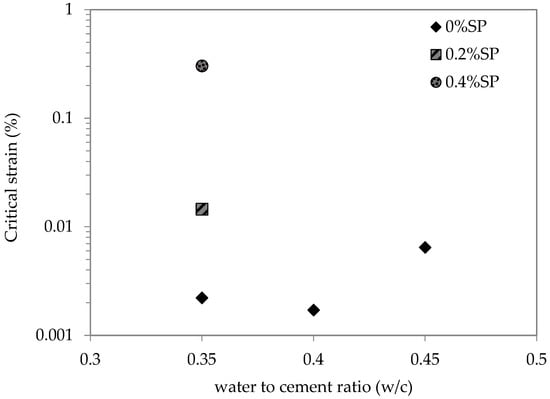
Figure 6.
Effect of water-to-cement ratio (w/c) and superplasticizer dosage on the critical strain (data from [17]).
Concerning the effect of w/c on the critical strain, Jiao and De Schutter [17] explain it by the increase in the dissolution rate, leading to the increase in early hydrates formation. In addition, these early hydrates could be more fragile when w/c increases. The effect of the superplasticizer on the critical strain is explained by the entanglement of superplasticizer molecules with each other and the possible enhancement of the C-S-H bridges. According to these authors, the cohesive bonding between cement particles is improved, which increases the deformation capacity of the connections. The oscillatory shear strain required to initiate the relative movement between particles thus increases. However, some ambiguities could be pointed out. First, there is no consensus on the formation of early hydrates, which can form links between cement particles. According to Sujata and Jennings [60], alite (C3S) particles get covered by C-S-H after 10 min of hydration, while Gauffinet et al. [61] reported 1 h after the contact between alite and lime solution. In addition, Zingg et al. [62] found that, in the presence of a superplasticizer (dispersed cement paste), the early hydrates precipitate mainly in the pore solution.
In calcite suspensions, the dependence of the critical strain on the solid volume fraction has been investigated by Liberto et al. [59]. It was found that the critical strain varies in a non-monotonic way with the solid volume fraction and displays a minimum for a volume fraction of 20% of about 10−2%. The authors attributed this critical strain to the inter-floc rupture associated with a weak-link structure. The second critical strain (where G′ = G″) of the order of few % is associated with the fragmentation of flocs.
It thus appears that the interpretation of the viscoelastic properties of fresh cement pastes is complex. Further investigations are required to deepen the comprehension of the origins of each transition in the microstructure of fresh cement paste.
3.3. Structural Build-Up
The term thixotropy reflects the fact that the rheological properties (viscosity) are time-dependent. Thixotropic materials thus become more fluid with an increasing shear time (at a constant shear rate) or more viscous when kept at rest. Therefore, the viscosity of thixotropic material gradually increases with the resting time (build-up), and when it is sheared, it must recover its initial state (break-down). Thixotropy therefore assumes that the evolution of rheological properties over time is reversible. Thus, the application of a shear makes it possible to erase the history of the structuration at rest. This reversible phenomenon is often attributed to reversible physico-chemical phenomena such as flocculation/deflocculation in colloidal suspensions [23].
The term “thixotropy” is often used for cementitious materials to describe the reversible evolution at the macroscopic scale, e.g., the maintenance of workability [35,44,63,64]. However, due to cement hydration, the initial state cannot be completely recovered. This is referred to as workability loss (or slump loss). In fact, during the low-activity period of cement hydration, also called the dormant period, chemical changes occur in the cementitious material, leading to the formation of hydrates bridges between cement particles [23]. Despite a strong shear, the history of the structuration is not fully erased. This is why the term “structural build-up” seems to be relevant to describing the time-dependence of the rheological behavior of cementitious materials. It can be noted that the addition of admixtures such as superplasticizers allows for approaching an ideal thixotropic behavior due to the retarding/dispersive effect [20].
Various testing procedures and approaches have been reported in the literature. The first procedure, called the hysteresis loop, consists of applying an increasing and decreasing shear rate. The area between the ascending and descending curve is an indicator of the thixotropy. This method can be used as a preliminary attempt to assess the thixotropy [65,66]. In fact, the hysteresis area depends not only on time but also on shear history (shear rate, test condition, step duration). The most common test consists of the measurement of the static yield stress (using the stress growth procedure) after different resting periods [20,21,67,68]. The slope of the yield stress–resting time curve (Athix) is a strong indicator of the structural build-up. Another interesting method is based on time sweep measurements using small-amplitude oscillatory shear (SAOS). It consists of the determination of the evolution of both the storage and loss moduli with rest time [21,22].
The contribution of physical and chemical parts to the structural build-up is an interesting challenge. In fact, a deep understanding of the structuration of fresh cementitious materials during the dormant period is essential to controlling the placement of modern concretes such as 3D-printable concretes, low-carbon concretes, or self-compacting concretes.
Mostafa and Yahia [21] found that the physical structural changes at rest can be described by the percolation time. This latter corresponds to the time needed to form a colloidal percolated network, where the phase angle (determined by SAOS measurements) reaches its lowest and steady value. In addition, the linear increase at rest of the storage modulus within the dormant period can describe the chemical rigidification rate of a formed network. The authors suggested that these parameters can be used in combination to describe the physical and chemical structuration of cement suspensions with different water-to-cement ratios, superplasticizer dosages, and SCMs replacements.
Another interesting study, performed by Zhang et al. [22] through SAOS measurements, allowed the chemical and thixotropic part to be quantified. The authors suggested that the structural build-up is the sum of the chemical and thixotropic parts. Moreover, it appears that the thixotropic part dominates the chemical contribution until the beginning of the acceleration period of hydration, where the chemical contribution dramatically increases. The addition of a superplasticizer (SP) allows for reducing the thixotropic part, while the chemical contribution is comparable with and without SP.
Another study based on a succession of stress growth procedures (with or without the pre-shear phase) has been carried out to assess the contribution of reversible and irreversible parts of the structural build-up. It was found that the structural build-up of a chemically inert material (calcite) is completely reversible. The structural build-up in such colloidal suspension is due to flocculation induced by attractive colloidal forces. Furthermore, for cement paste without a superplasticizer, there is a significant increase in the static yield stress despite the strong pre-shear which is supposed to erase the structural build-up (irreversible part) (Figure 7). The evolution of the static yield stress with hydration time showed two stages. The first one is characterized by a linear increase in the static yield stress with time until 40 min of hydration, and the second one is characterized by a significant increase from 40 min (slope change) (Figure 7). The irreversible part (after the pre-shear phase) showed linear evolution without a slope change. This suggests that the physical part (flocculation) is not necessarily reversible in cement suspensions and/or that the chemical changes probably contain a reversible part. The addition of a superplasticizer strongly affects the structural build-up due to the retarding and dispersive effects. In the presence of a superplasticizer, the contribution of the cement hydration to the structural build-up could be neglected. The cement paste thus behaves like a thixotropic material with reversible changes. The use of a superplasticizer allows for reducing the workability loss during the dormant period [20].
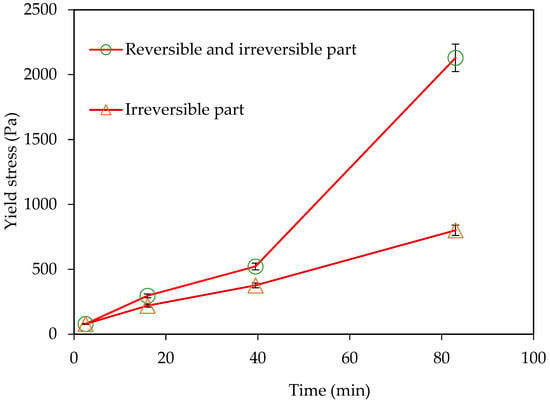
Figure 7.
Evolution of the static yield stress with and without a pre-shear phase [20].
Recently, an interesting study was performed by Zhang et al. [68] to clarify and quantify the contribution of colloidal forces and C-S-H formation to the structural build-up. It was shown that the evolution of the static yield stress during the dormant period follows three stages (Figure 8). The initial stage, in the first 30 min, corresponds to the rapid linear growth of the static yield stress. In the induction period (30–60 min), the static yield stress increases slowly. Finally, the acceleration stage (>60 min) is marked by an exponential growth of the static yield stress. This evolution is almost comparable to that presented in Figure 7.
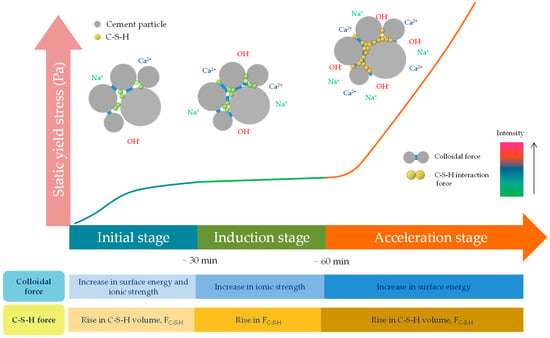
Figure 8.
Schematic illustration of the static yield stress and interaction force evolution of fresh cement paste [68].
Zhang et al. [68] showed that the interparticle force, which is the combination of the colloidal force and interaction force between C-S-H particles, is the driving force for the evolution of static yield stress. The contribution of colloidal force appears to be greater in the early period (the initial and induction period), while the C-S-H force determines the evolution trend of the static yield stress since the induction period.
4. Conclusions
This paper presented a phenomenological description of the rheological behavior of cement paste. In fact, this rheological behavior displays several complexities such as non-linearity, yielding, time-dependence and chemical changes.
The most common testing procedures allowing for the characterization of this behavior have been reported. For flow behavior, the most relevant protocol consists of the application of a ramp sweep (shear rate or shear stress) so that the flow curve (shear stress as a function of the shear rate) is at steady state flow. The structural build-up can be characterized by static yield stress measurements or the SAOS protocol for various resting times.
The non-linearity of flow behavior corresponds to a shear-thinning/shear-thickening phenomenon that can be represented by the Herschel–Bulkley model. If the shear-thinning phenomenon can be related to the flocculation state, the origins of shear thickening are not clearly elucidated. Theories based on order–disorder transition, particle clustering, or viscous/inertial regime transition have been developed to explain the appearance of shear thickening.
Furthermore, oscillation rheology allows for determining the linear viscoelastic domain (LVED) in which both storage and loss moduli remain constant. The end of this linear domain is associated with a critical strain of the order of 10−2%. This critical strain could be the signature of the breakage of interparticle bonds formed by early hydrates (C-S-H) and/or attractive colloidal forces, especially for cements with supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) and alternative cements such as calcium sulfoaluminates cements or belite ye’elimite ferrite (BYF) cements.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Nicolas, R.; Richard, B.; Nicolas, D.; Irina, I.; Temitope, K.J.; Dirk, L.; Viktor, M.; Romain, M.; Arnaud, P.; Ursula, P.; et al. Assessing the fresh properties of printable cement-based materials: High potential tests for quality control. Cem. Concr. Res. 2022, 158, 106836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biricik, Ö.; Mardani, A. Parameters affecting thixotropic behavior of self compacting concrete and 3D printable concrete; a state-of-the-art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 339, 127688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N. Rheological requirements for printable concretes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 112, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Lei, L.; Plank, J. Influence of PCE superplasticizers on the fresh properties of low carbon cements containing calcined clays: A comparative study of calcined clays from three different sources. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 139, 105072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayati, B.; Newport, D.; Wong, H.; Cheeseman, C. Low-carbon cements: Potential for low-grade calcined clays to form supplementary cementitious materials. Clean. Mater. 2022, 5, 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaimster, R.; Dixon, N. Self-compacting concrete. In Advanced Concrete Technology; Japan Concrete Institute: Tokyo, Japan, 2003; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Brouwers, H.J.H.; Radix, H.J. Self-compacting concrete: Theoretical and experimental study. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 2116–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hu, R.; Yang, D.; Ma, Z. Micro-macro characterizations of mortar containing construction waste fines as replacement of cement and sand: A comparative study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 383, 131328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Deng, Q.; Liang, C.; Ma, Z.; Wu, H. Upcycling of recycled plastic fiber for sustainable cementitious composites: A critical review and new perspective. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 142, 105192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N.; Bessaies-Bey, H.; Kawashima, S.; Marchon, D.; Vasilic, K.; Wolfs, R. Recent advances on yield stress and elasticity of fresh cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N.; Lemaître, A.; Flatt, R.J.; Coussot, P. Steady state flow of cement suspensions: A micromechanical state of the art. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.C.; Chiu, J.J.; Da Chen, S.; Tseng, Y.C. Effect of addition time of a superplasticizer on cement adsorption and on concrete workability. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1999, 21, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiocchio, G.; Paolini, A.E. Optimum time for adding superplasticizer to Portland cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1985, 15, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houst, Y.F.; Flatt, R.J.; Bowen, P.; Hofmann, H.; Mäder, U.; Widmer, J.; Sulser, U.; Bürge, T.A. Influence of Superplasticizer Adsorption on the Rheology of Cement Paste. In Proceedings of the International RILEM Conference on “The Role of Admixtures in High Performance Concrete”, Monterrey, Mexico, 21–26 March 1999; pp. 387–402. [Google Scholar]
- Cyr, M.; Legrand, C.; Mouret, M. Study of the shear thickening effect of superplasticizers on the rheological behaviour of cement pastes containing or not mineral additives. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayat, K.H.; Yahia, A.; Sayed, M. Effect of supplementary cementitious materials on rheological properties, bleeding, and strength of structural grout. ACI Mater. J. 2008, 105, 585–593. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, D.; De Schutter, G. Insights into the viscoelastic properties of cement paste based on SAOS technique. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 357, 129320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, C. Contribution à l’étude de la rhéologie du béton frais. Matér. Constr. 1972, 5, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhou, D.; Khayat, K.H.; Feys, D.; Shi, C. On the measurement of evolution of structural build-up of cement paste with time by static yield stress test vs. small amplitude oscillatory shear test. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 99, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bitouri, Y.; Azéma, N. On the “Thixotropic” Behavior of Fresh Cement Pastes. Eng 2022, 3, 677–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.M.; Yahia, A. New approach to assess build-up of cement-based suspensions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 85, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Mezhov, A.; Schmidt, W. Chemical and thixotropic contribution to the structural build-up of cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N.; Ovarlez, G.; Garrault, S.; Brumaud, C. The origins of thixotropy of fresh cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewoldt, R.H.; Johnston, M.T.; Caretta, L.M. Experimental Challenges of Shear Rheology: How to Avoid Bad Data BT—Complex Fluids in Biological Systems: Experiment, Theory, and Computation; Spagnolie, S.E., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 207–241. ISBN 978-1-4939-2065-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ukrainczyk, N.; Thiedeitz, M.; Kränkel, T.; Koenders, E.; Gehlen, C. Modeling SAOS Yield Stress of Cement Suspensions: Microstructure-Based Computational Approach. Materials 2020, 13, 2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, T.; Chaouche, M. Rheological behavior of cement pastes under Large Amplitude Oscillatory Shear. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 89, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.A.; Struble, L.J. Use of oscillatory shear to study flow behavior of fresh cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 1993, 23, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, S.; Chaouche, M.; Corr, D.J.; Shah, S.P. Rate of thixotropic rebuilding of cement pastes modified with highly purified attapulgite clays. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 53, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachbaur, L.; Mutin, J.C.; Nonat, A.; Choplin, L. Dynamic mode rheology of cement and tricalcium silicate pastes from mixing to setting. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, J.T.; Combrinck, R.; Boshoff, W.P. Rheo-viscoelastic behaviour of fresh cement-based materials: Cement paste, mortar and concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 248, 118667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiedeitz, M.; Kränkel, T.; Gehlen, C. Viscoelastoplastic classification of cementitious suspensions: Transient and non-linear flow analysis in rotational and oscillatory shear flows. Rheol. Acta 2022, 61, 549–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.-G.; Struble, L.J. Microstructure and Flow Behavior of Fresh Cement Paste. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1997, 80, 2021–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaut, F.; Mokéddem, S.; Chateau, X.; Roussel, N.; Ovarlez, G. Effect of coarse particle volume fraction on the yield stress and thixotropy of cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot, A.; Lecompte, T.; Khelifi, H.; Brumaud, C.; Hot, J.; Roussel, N. Yield stress and bleeding of fresh cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N. Steady and transient flow behaviour of fresh cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bitouri, Y.; Azéma, N. Contribution of turbidimetry on the characterization of cement pastes bleeding. Adv. Cem. Res. 2023, 35, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aït-Kadi, A.; Marchal, P.; Choplin, L.; Chrissemant, A.S.; Bousmina, M. Quantitative analysis of mixer-type rheometers using the couette analogy. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2002, 80, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourmentin, M.; Ovarlez, G.; Faure, P.; Peter, U.; Lesueur, D.; Daviller, D.; Coussot, P. Rheology of lime paste—A comparison with cement paste. Rheol. Acta 2015, 54, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papo, A.; Piani, L. Flow Behavior of Fresh Portland Cement Pastes. Part. Sci. Technol. 2004, 22, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, Y.P.; Roshavelov, T.T. Flow behaviour of modified cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1993, 23, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, A.; Geiker, M.R.; Justnes, H.; Lauten, R.A.; De Weerdt, K. On the effect of calcium lignosulfonate on the rheology and setting time of cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 100, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, J.; Sakai, E.; Miao, C.W.; Yu, C.; Hong, J.X. Chemical admixtures—Chemistry, applications and their impact on concrete microstructure and durability. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barneoud-Chapelier, A.; Le Saout, G.; Azéma, N.; El Bitouri, Y. Effect of polycarboxylate superplasticizer on hydration and properties of belite ye’elimite ferrite cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 322, 126483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsubo, Y.; Miyai, S.; Umeya, K. Time-dependent flow of cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1980, 10, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emoto, T.; Bier, T.A. Rheological behavior as influenced by plasticizers and hydration kinetics. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, I.M.; Dougherty, T.J. A Mechanism for Non-Newtonian Flow in Suspensions of Rigid Spheres. Trans. Soc. Rheol. 1959, 3, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaut, F.; Chateau, X.; Coussot, P.; Ovarlez, G. Yield stress and elastic modulus of suspensions of noncolloidal particles in yield stress fluids. J. Rheol. 2008, 52, 287–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, R.J.; Bowen, P. Yodel: A yield stress model for suspensions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 1244–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odler, I.; Duckstein, U.; Becker, T. On the combined effect of water solubles lignosulfonates and carbonates on portland cement and clinker pastes 1. Physical properties. Cem. Concr. Res. 1978, 8, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.M.; Asaga, K. Rheological properties of cement mixes: III. The effects of mixing procedures on viscometric properties of mixes containing superplasticizers. Cem. Concr. Res. 1979, 9, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, J.F.; Bossis, G. The rheology of concentrated suspensions of spheres in simple shear flow by numerical simulation. J. Fluid Mech. 1985, 155, 105–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.L. Explanations for the cause of shear thickening in concentrated colloidal suspensions. J. Rheol. 1998, 42, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovarlez, G.; Bertrand, F.; Rodts, S. Local determination of the constitutive law of a dense suspension of noncolloidal particles through magnetic resonance imaging. J. Rheol. 2006, 50, 259–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.A. Shear-Thickening (“Dilatancy”) in Suspensions of Nonaggregating Solid Particles Dispersed in Newtonian Liquids. J. Rheol. 1989, 33, 329–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; Lesage, K.; Yardimci, M.Y.; El Cheikh, K.; Shi, C.; De Schutter, G. Rheological behavior of cement paste with nano-Fe3O4 under magnetic field: Magneto-rheological responses and conceptual calculations. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 120, 104035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; Shi, C.; De Schutter, G. Magneto-responsive structural build-up of highly flowable cementitious paste in the presence of PCE superplasticizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 327, 126925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikanovic, N.; Jolicoeur, C. Influence of superplasticizers on the rheology and stability of limestone and cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramaux, A.; Azéma, N.; El Bitouri, Y.; David, G.; Negrell, C.; Poulesquen, A.; Haas, J.; Remond, S. Synthesis of phosphonated comb-like copolymers and evaluation of their dispersion efficiency on CaCO3 suspensions part II: Effect of macromolecular structure and ionic strength. Powder Technol. 2018, 334, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberto, T.; Le Merrer, M.; Barentin, C.; Bellotto, M.; Colombani, J. Elasticity and yielding of calcite paste: Scaling laws in a dense colloidal suspension. Soft Matter 2017, 13, C6SM02607A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sujata, K.; Jennings, H.M. Formation of a Protective Layer During the Hydration of Cement. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1992, 75, 1669–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauffinet, S.; Finot, É.; Lesniewska, E.; Nonat, A. Direct observation of the growth of calcium silicate hydrate on alite and silica surfaces by atomic force microscopy; [Observation directe de la croissance d’hydrosilicate de calcium sur des surfaces d’alite et de silice par microscopie a force atomique]. C. R. l’Acad. Sci. Ser. IIa Sci. Terre Planet. 1998, 327, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Zingg, A.; Holzer, L.; Kaech, A.; Winnefeld, F.; Pakusch, J.; Becker, S.; Gauckler, L. The microstructure of dispersed and non-dispersed fresh cement pastes—New insight by cryo-microscopy. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.A. Thixotropy—A review. J. Nonnewton. Fluid Mech. 1997, 70, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapasin, R.; Longo, V.; Rajgelj, S. Thixotropic behaviour of cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1979, 9, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N. A thixotropy model for fresh fluid concretes: Theory, validation and applications. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkova, V.; Samichkov, V. Some influences on the thixotropy of composite slag Portland cement suspensions with secondary industrial waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billberg, P. Form Pressure Generated by Self-Compacting Concrete: Influence of Thixotropy and Structural Behaviour at Rest. Ph.D. Thesis, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Shi, J.; Jiang, Y.; Banthia, N.; Zhang, Y. Clarifying and quantifying the driving force for the evolution of static yield stress of cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 167, 107129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).