Homogenization Method to Calculate the Stiffness Matrix of Laminated Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Problematic
1.2. State of Art
1.3. Paper Organization
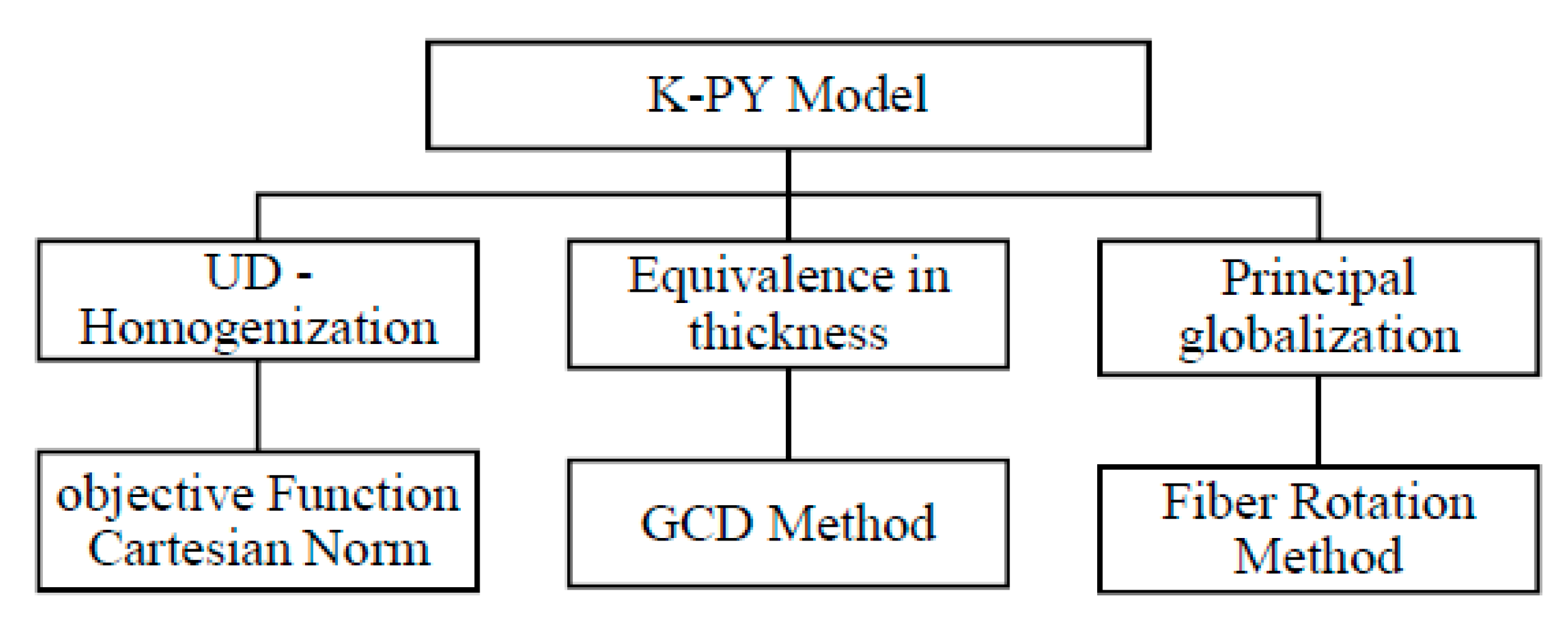
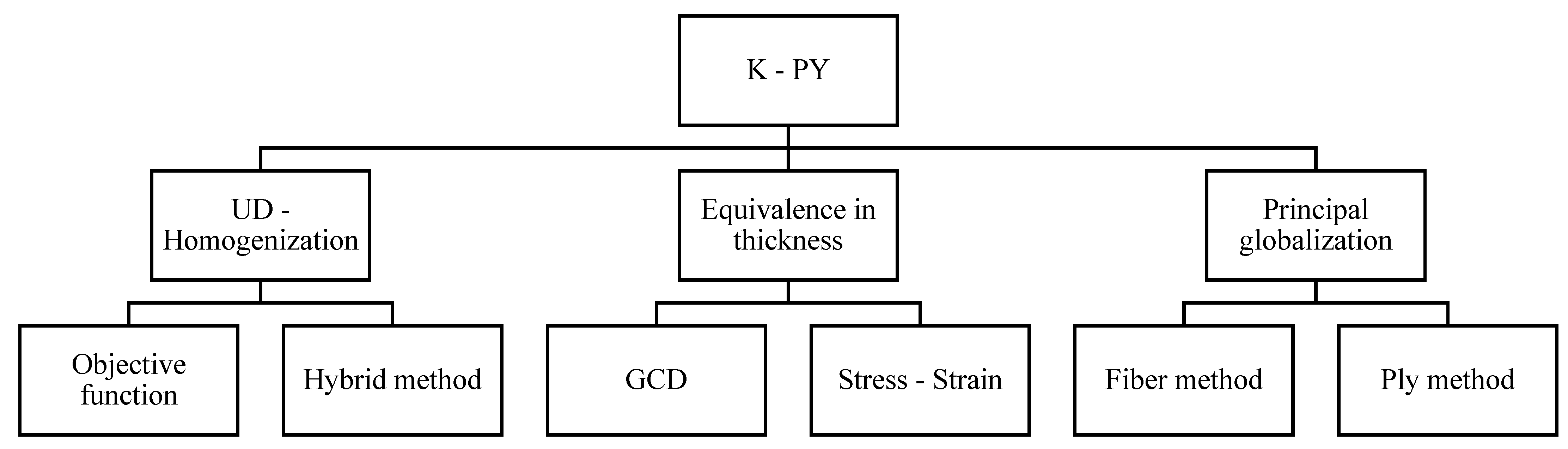
2. Methodology
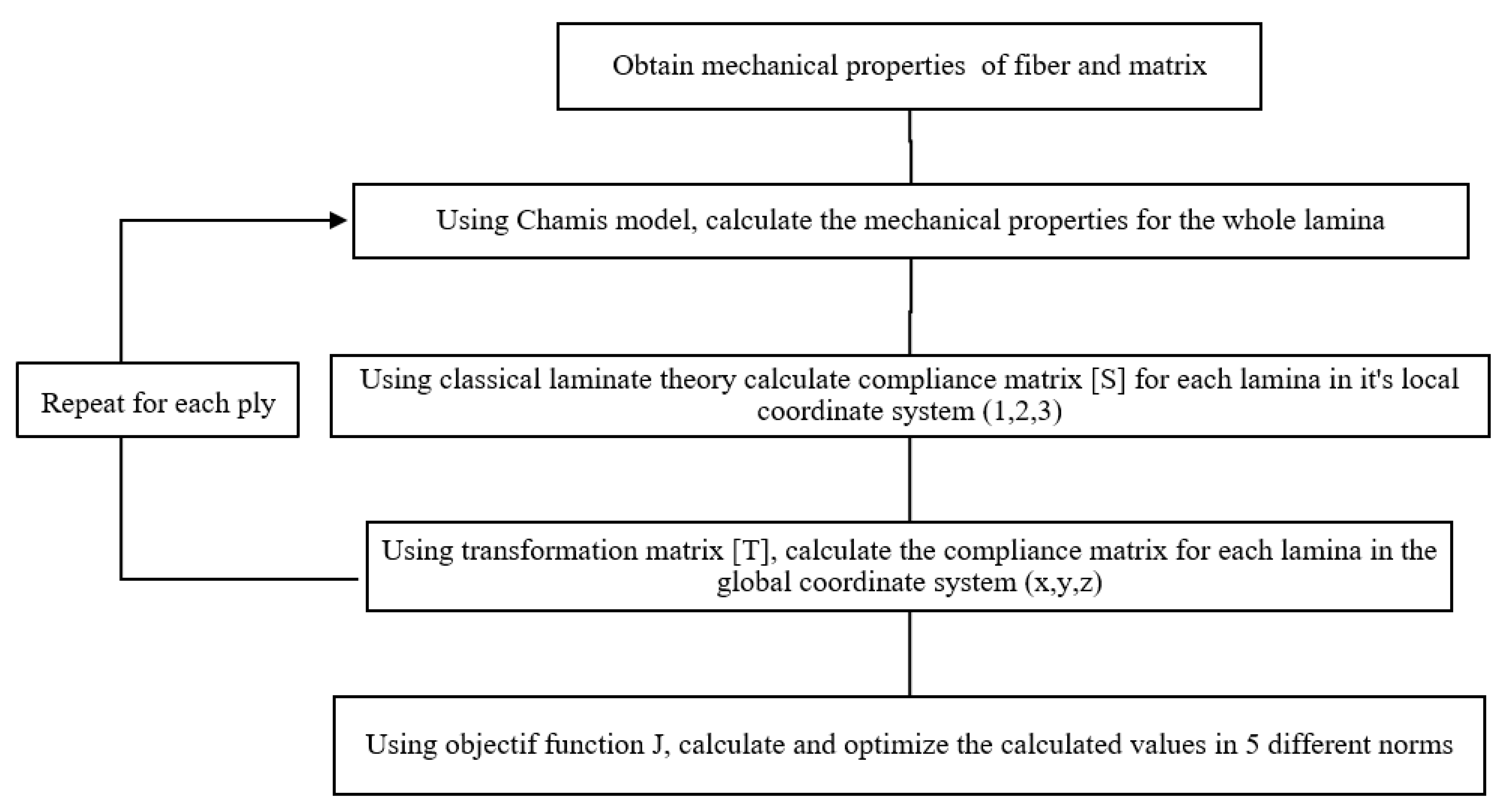
2.1. UD (Unidirectional)—Homogenization:
2.1.1. Algorithm Objectif Function
- Objective function
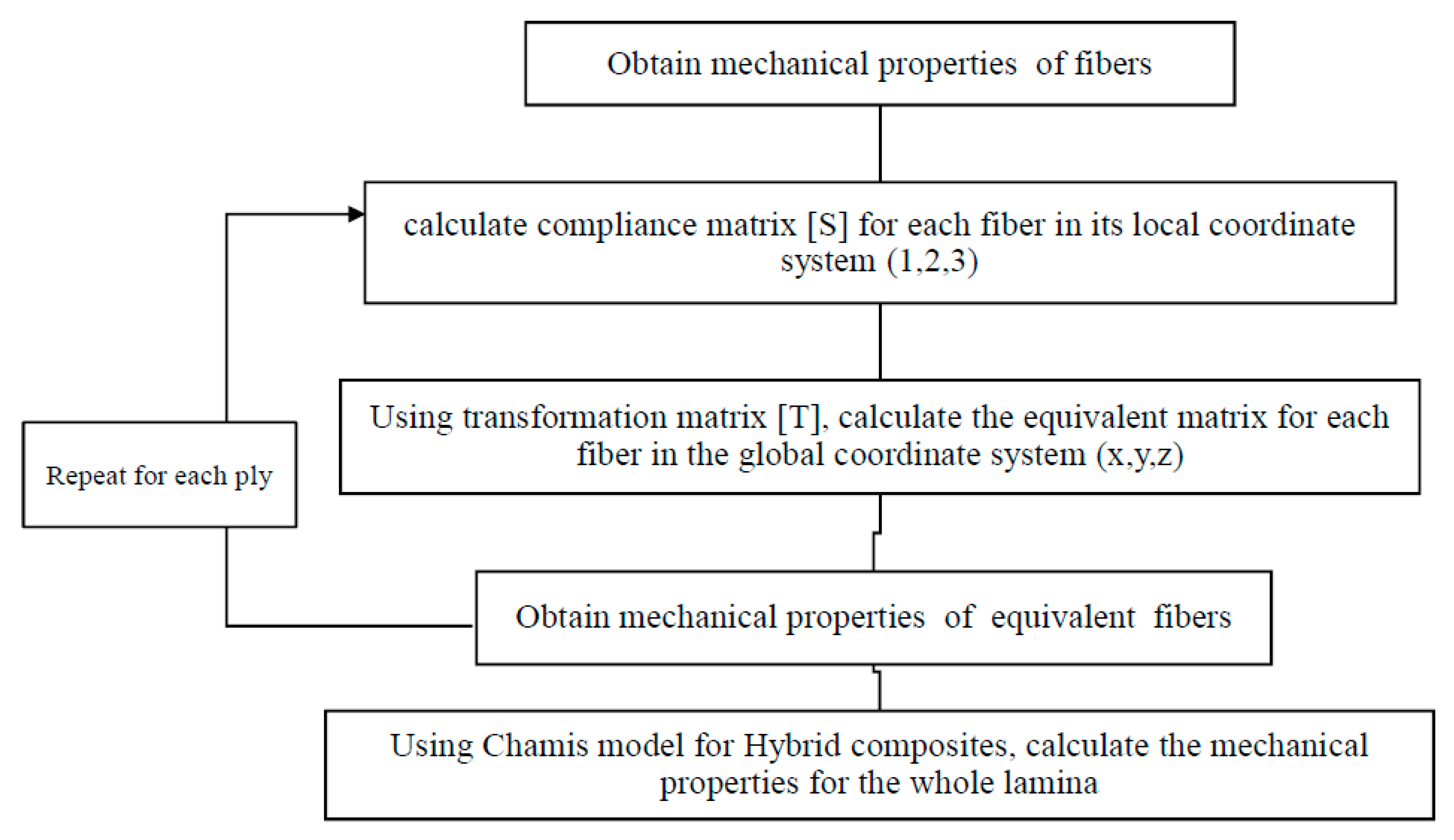
2.1.2. Hybrid Method
- Chamis model for Hybrid Composites:
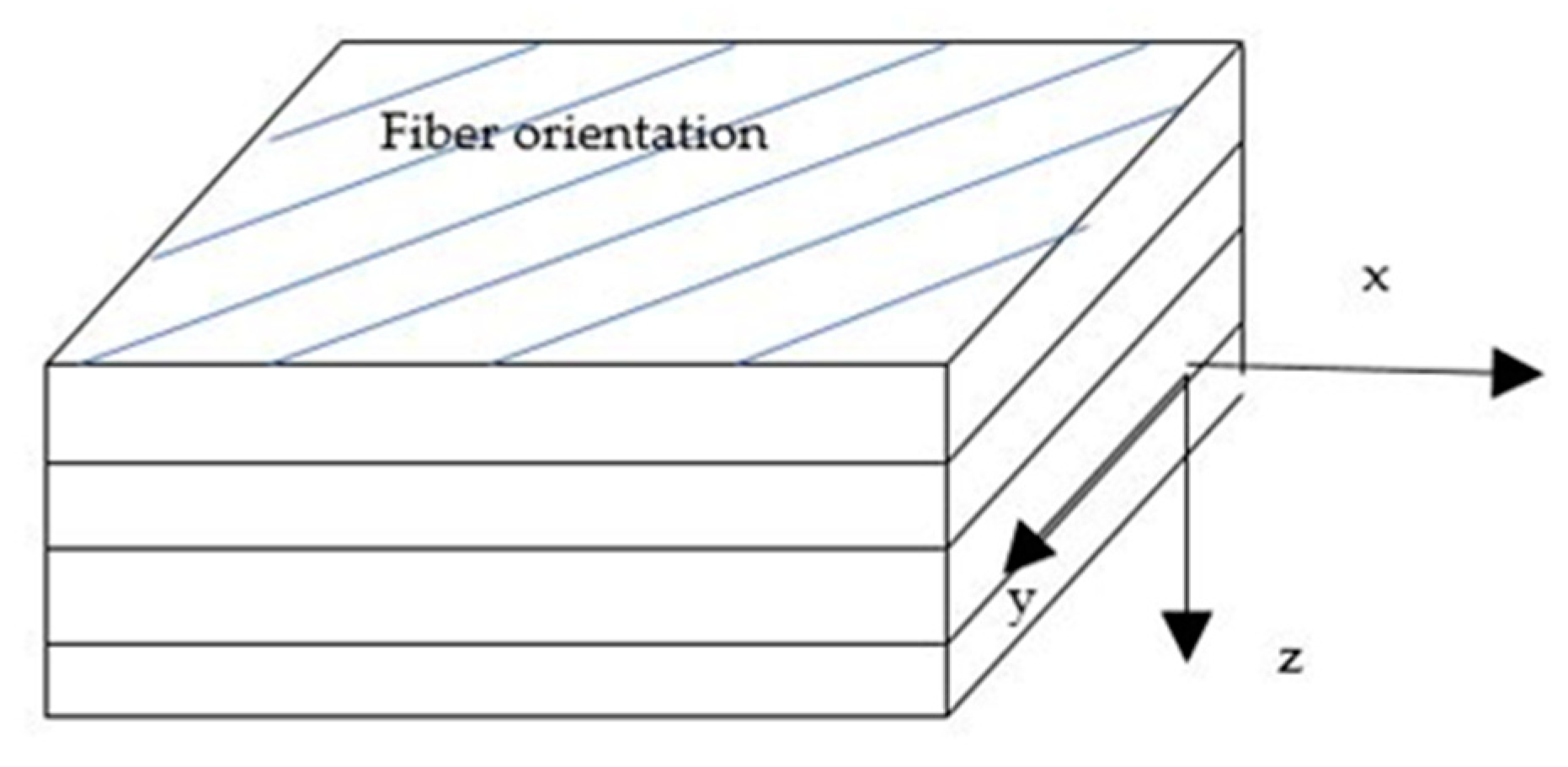
2.2. Principal Globalization
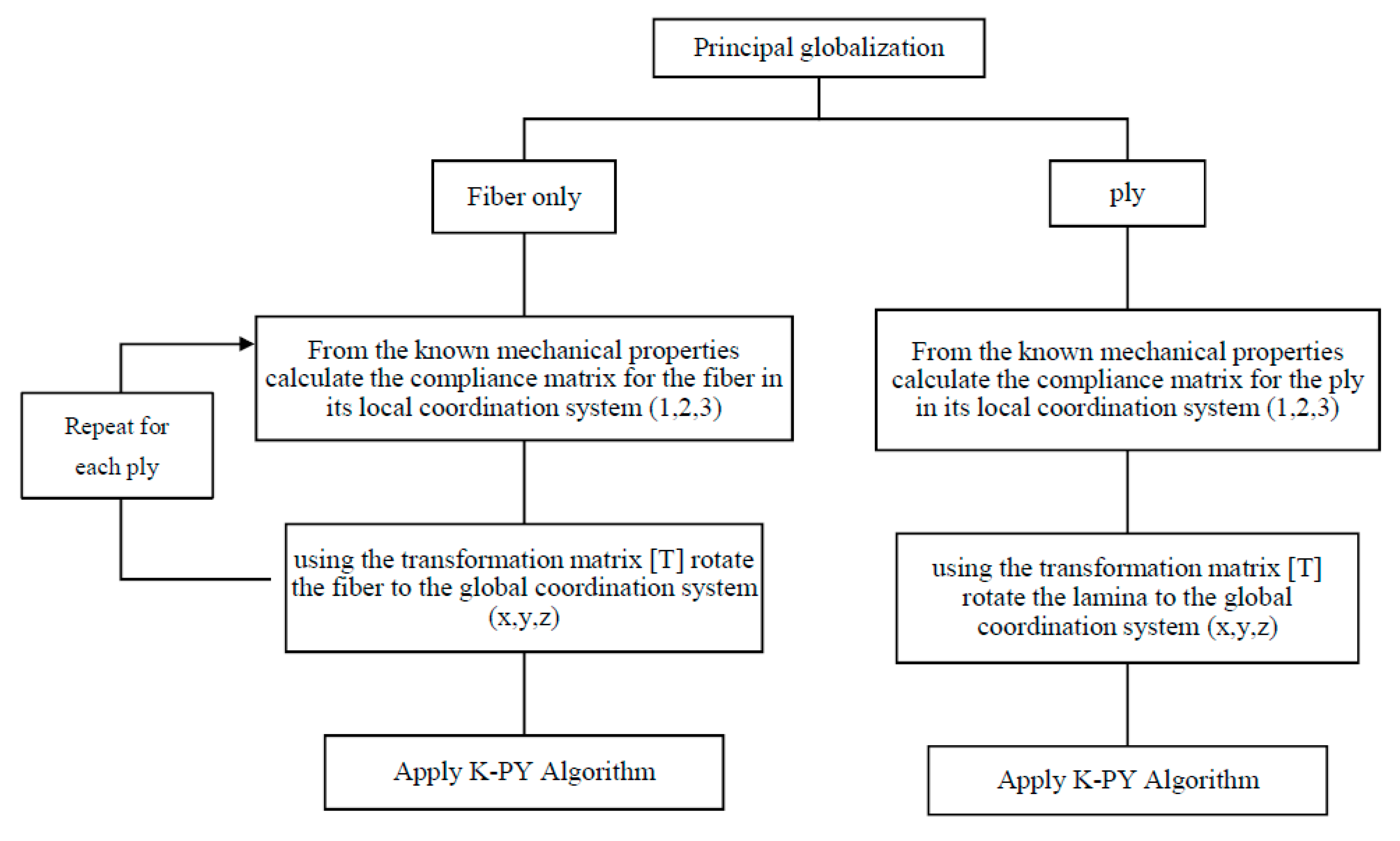
2.3. Thickness
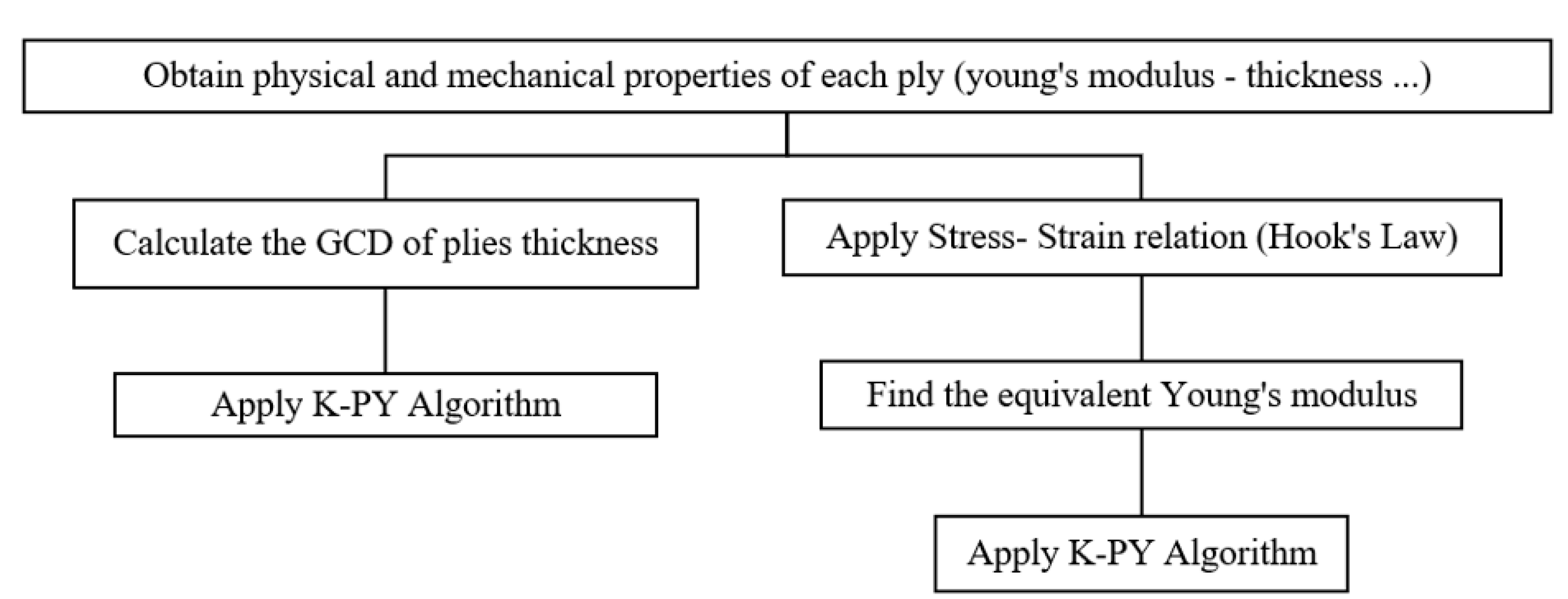
2.3.1. GCD of Plies
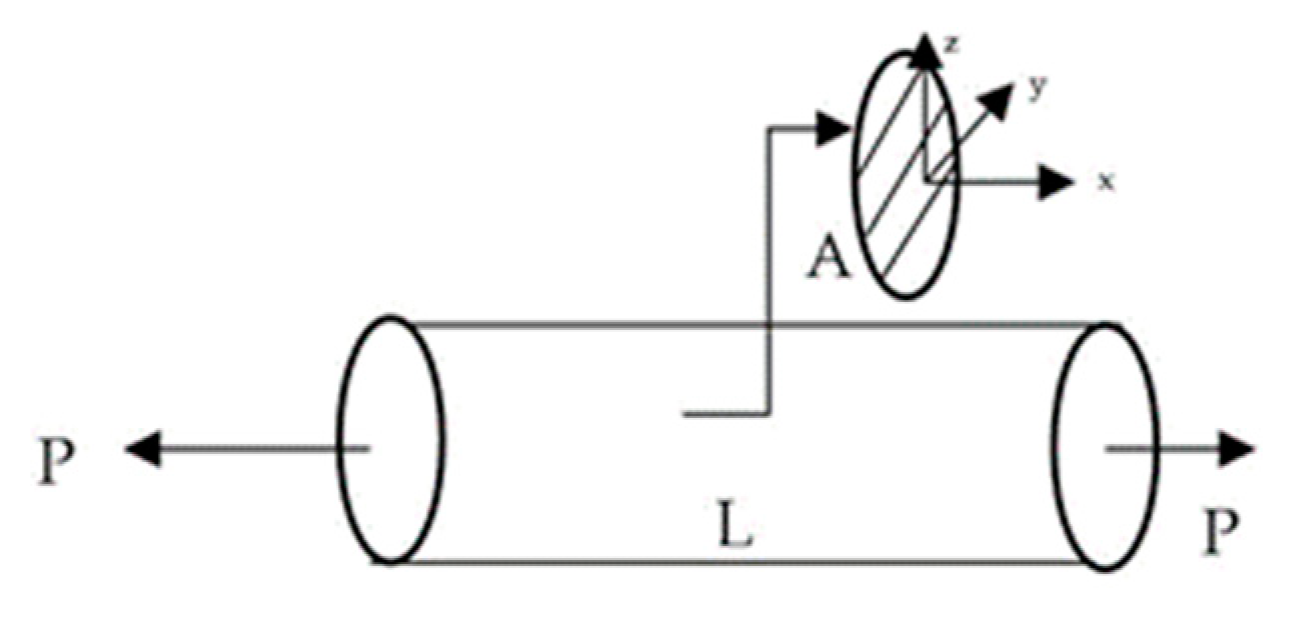
2.3.2. Stress–Strain Relation (Hook’s Law Method)
3. Materials
3.1. UD—Homogenization
- Glass/epoxy [0/0] laminate;
- Silenka E-Glass 1200 tex MY750/HY917/DY063 epoxy [0/90]s laminate;
- Silenka E-Glass 1200 tex/MY750/HY917/DY063 epoxy [+45/−45]s laminate;
- E-Glass 21xK43 Gevetex/LY556/HT907/DY063 [+90/+30/−30]s laminate.
3.2. Principal Globalization
3.3. Equivalence in Thickness
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. UD—Homogenization
4.2. Principal Globalization
4.3. Equivalence in Thickness
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daniel, G.; Suong, V.H.; Tsai, W.S. Composite Materials: Design and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chamis, C.C. Mechanics of composite materials: Past, present, and future. J. Compos. Technol. Res. 1989, 11, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjay, K.M. Composites Manufacturing: Materials, Product and Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ogin, S.L.; Brøndsted, P.; Zangenberg, J. Composite Materials: Constituents, Architecture, and Generic Damage Modeling Damage, Fatigue and Failure of Composite Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016; pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, D. The Fundamental Principles of Composite Material Stiffness Predictions; University of the West England: Bristol, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lydzba, D. Effective Properties of Composites, Introduction to Micromechanics; Wroclaw University of Technology: Wrocław, Poland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, W.S. Equivalent thermal expansion coefficients of lumped layer in laminated composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 2402–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Shapiro, V. Efficient 3D analysis of laminate structures using ABD-equivalentmaterial models. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2015, 106, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, Y. Introduction to the Micromechanics of Composite Materials, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, A.; Mali, H.S.; Misra, R.K. Unit cell model of woven fabric textile composite for multiscale analysis. Procedia Eng. 2013, 68, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuksenko, D.; Böhm, H.J.; Drach, B. Effect of micromechanical parameters of composites with wavy fibers on their effective response under large deformations. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2018, 121, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarenko, L.; Stolarski, H.; Altenbach, H. Thermo-elastic properties of random composites with unidirectional anisotropic short-fibers and interphases. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 2018, 70, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Sankar, B.V. Mechanical properties of hybrid composites using finite element method based micromechanics. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 58, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamis, C.C.; Sinclair, J.H. Mechanics of intraply hybrid composites—Properties, analysis, and design. Polym. Compos. 1980, 1, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-W. Microstructural Design of Fiber Composites; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Halpin, J.C.; Kardos, J.L. The Halpin-Tsai equations: A review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1976, 16, 344–352. [Google Scholar]
- Swolfs, Y.; Gorbatikh, L.; Verpoest, I. Fibre hybridisation in polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 67, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.; Pimenta, S. Modelling hybrid effects on the stiffness of aligned discontinuous composites with hybrid fibre-types. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 152, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minculete, N.; Moradi, H.R. Some Improvements of the Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality Using the Tapia Semi-Inner-Product. Mathematics 2020, 8, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante-Solís, M.A.; Valadez-González, A.; Herrera-Franco, P.J. A note on the effect of the fiber curvature on the micromechanical behavior of natural fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites. Express Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh-Aghdam, M.K.; Ansari, R.; Mahmoodi, M.J. Micromechanical estimation of biaxial thermomechanical responses of hybrid fiber-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites containing carbon nanotubes. Mech. Mater. 2018, 119, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisnom, M.R.; Khan, B.; Hallett, S.R. Size effects in unnotched tensile strength of unidirectional and quasi-isotropic carbon/epoxy composites. Compos. Struct. 2008, 84, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anto, A.D.; Mia, S.; Hasib, M.A. The influence of number and orientation of ply on tensile properties of hybrid composites. J. Phys. Mater. 2019, 2, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobah, Y.; Ghazzawi, Y.; Bourchak, M. Mechanical properties of hybrid carbon fibre reinforced polyethene and epoxy composites. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2015, 10, 7053–7057. [Google Scholar]
- Parvanesh, V.; Shariati, M.; Nezakati, A. Statistical analysis of the parameters influencing the mechanical properties of layered MWCNTs/PVA nano composites. Int. J. Nano Dimens. 2015, 6, 509–516. [Google Scholar]
- Kaw, A.K. Mechanics of Composite Materials, Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Series; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bufler, H. Theory of elasticity of a multilayered medium. J. Elast. 1971, 1, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.K.; Booker, J.R. Finite layer analysis of nonhomogeneous soils. J. Eng. Mech. Div. 1982, 108, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.N.; Pindera, M.-J.; Pipes, R.B.; Dick, B. Composite Defect Significance; MSC TFR 1312/1108 (NADC Report No. 81034-60); Spring Hottse: Montgomery County, PA, USA, 1982; Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.895.3671&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Aboudi, J. Micromechanical analysis of thermo-inelastic multiphase short-fiber composites. Compos. Eng. 1995, 5, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Babu, P.E.J.; Savithri, S.; Pillai, U.T.S.; Pai, B.C. Micromechanical modeling of hybrid composites. Polymer 2005, 46, 7478–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, R.; Hallal, A.; Fardoun, F.; Chehade, F.H. Comparative Review Study on Elastic Properties Modeling for Unidirectional Composite Materials. Compos. Prop. 2012, 17, 391–408. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, M.W.E.; Nallim, L.G.; Luccioni, B.M. A micro-macromechanical approach for composite laminates. Mech. Mater. 2008, 40, 885–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Menezes, E.A.W.; Eggers, F.; Marczak, R.J.; Iturrioz, I.; Amico, S.C. Hybrid composites: Experimental, numerical and analytical assessment aided by online software. Mech. Mater. 2020, 148, 103533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soden, P.D.; Hinton, M.J.; Kaddour, A.S. Lamina properties, lay-up configurations and loading conditions for a range of fiber-reinforced composite laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1998, 58, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisnom, M.R. Size effects in the testing of fibre-composite materials. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1999, 59, 1937–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Fibers (GPa) |
|---|
| E-Glass Ef11 = Ef22 = 72.4; Gf12 = 30.2; νf23 = 0.2 |
| Silenka E-Glass 1200 tex Ef11 = Ef22 = 74; Gf12 = 30.2; νf23 = 0.2 |
| E-Glass 21xK43 Gevetex Ef11 = Ef22 = 80; Gf12 = 30.2; νf23 = 0.2 |
| Matrices |
|---|
| Epoxy Em = 2.76; Gm = 1.567; νm = 0.35 |
| MY750/HY917/DY063 epoxy Em = 3.35; Gm = 1.24; νm = 0.35 |
| LY556/HT907/DY063 Em = 3.35; Gm = 1.24; νm = 0.35 |
| Graphite/Epoxy Laminate Properties |
|---|
| Vf = 0.7 |
| E1 = 181 |
| E2 = E3 = 10.3 |
| G12 = G13 = 7.17 |
| G23 = 5.79 |
| ν12 = ν13 = 0.28 |
| Property | E-Glass/Epoxy Laminate | Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Laminate |
|---|---|---|
| Vf | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| E1 | 45.6 | 126 |
| E2 = E3 | 16.2 | 11 |
| G12 = G13 | 5.83 | 6.6 |
| G23 | 5.79 | 3.93 |
| ν12 = ν13 | 0.278 | 0.28 |
| ν23 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Type of Composite | Orientation | Experimental | Norm 0 | Norm ∞ | Norm Cart. | Norm 3 | Norm 4 | Hybrid Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass/epoxy | [0/0] | 56 | 55.14 | 55.14 | 55.14 | 55.14 | 32.39 | 50 |
| E-Glass 1200 tex MY750/HY917/DY063 epoxy | [0/90]s | 29.2 | 12.564 | 45.74 | 29.152 | 29.152 ± 16.58i | 24.14 | 31.19 |
| E-Glass 1200 tex MY750/HY917/DY063 epoxy | [+45/−45]s | 14.4 | 12.72 | 12.72 | 12.72 | 12.72 | 7.471 | 16.511 |
| E-Glass/LY556/HT907/DY063 | [+90/+30/−30]s | 27.4 | 12.52 | 29.12 | 28.8766 | 28.8766 ± 13.085i | 21.71 | 30.633 |
| Type of Composite | Orientation | Experimental | Norm 0 | Norm ∞ | Norm Cart. | Norm 3 | Norm 4 | Hybrid Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass/epoxy | [0/0] | 15 | 18.18 | 18.18 | 18.18 | 18.18 | 10.679 | 13 |
| E-Glass 1200 tex MY750/HY917/DY063 epoxy | [0/90]s | 17.2 | 12.86 | 21.673 | 17.2665 | 17.2 ± 4.4064i | 11.155 | 21.476 |
| E-Glass 1200 tex MY750/HY917/DY063 epoxy | [+45/−45]s | 17.1 | 18.67 | 18.67 | 18.67 | 18.67 | 10.966 | 21.281 |
| E-Glass/LY556/HT907/DY063 | [+90/+30/−30]s | 22.3 | 12.55 | 39.154 | 24.401 | 24.401 ± 11.05i | 18.623 | 27.374 |
| Type of Composite | Orientation | Experimental | Norm 0 | Norm ∞ | Norm Cart. | Norm 3 | Norm 4 | Hybrid Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass/epoxy | [0/0] | 3 | 2.57 | 2.57 | 2.57 | 2.57 | 1.5 | 5.5 |
| E-Glass 1200 tex MY750/HY917/DY063 epoxy | [0/90]s | 5.83 | 4.832 | 6.464 | 5.648 | 5.648 ± 0.816i | 3.428 | 3.7876 |
| E-Glass 1200 tex MY750/HY917/DY063 epoxy | [+45/−45]s | 10.6 | 7.047 | 7.047 | 7.047 | 7.047 | 4.14 | 5.6186 |
| E-Glass/LY556/HT907/DY063 | [+90/+30/−30]s | 5.79 | 5 | 6.43 | 5.66 | 5.66 ± 0.588i | 3.383 | 3.924 |
| Engineering Constants (GPa) | Kaw | Fiber Method | PLY Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ex | 124.5 | 124.728 | 126.828 |
| Ey | 67.43 | 68.27 | 69.25 |
| Gxy | 7.17 | 7.55 | 7.64 |
| Type of Composite | Thickness (mm) | CLT Experimental | GCD Method | Hook’s Law Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G–G–G–G–G–G | 0.05–0.03 | 46.875 | 46.54 | 44.1 |
| C–C–C–C–C–C | 0.05–0.03 | 126.857 | 127.104 | 122.458 |
| G–G–C–C–G–G | 0.05–0.03 | 65.346 | 73.39 | 61.56 |
| C–C–G–G–C–C | 0.05–0.03 | 108.42 | 100.25 | 101.75 |
| Type of Composite | Thickness (mm) | CLT Experimental | GCD Method | Hook’s Law Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G–G–G–G–G–G | 0.05–0.03 | 16.658 | 18.2 | 17.674 |
| C–C–C–C–C–C | 0.05–0.03 | 11.07 | 10.29 | 11.358 |
| G–G–C–C–G–G | 0.05–0.03 | 15.369 | 15.563 | 15.90 |
| C–C–G–G–C–C | 0.05–0.03 | 12.365 | 12.92 | 12.983 |
| Type of Composite | Thickness (mm) | CLT Experimental | GCD Method | Hook’s Law Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G–G–G–G–G–G | 0.05–0.03 | 5.83 | 5.89 | 6.72 |
| C–C–C–C–C–C | 0.05–0.03 | 6.6 | 6.81 | 7.61 |
| G–G–C–C–G–G | 0.05–0.03 | 6 | 6.19 | 7.55 |
| C–C–G–G–C–C | 0.05–0.03 | 6.423 | 6.5 | 7.63 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaddaha, M.A.; Younes, R.; Lafon, P. Homogenization Method to Calculate the Stiffness Matrix of Laminated Composites. Eng 2021, 2, 416-434. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng2040026
Kaddaha MA, Younes R, Lafon P. Homogenization Method to Calculate the Stiffness Matrix of Laminated Composites. Eng. 2021; 2(4):416-434. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng2040026
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaddaha, Mohamad Abbas, Rafic Younes, and Pascal Lafon. 2021. "Homogenization Method to Calculate the Stiffness Matrix of Laminated Composites" Eng 2, no. 4: 416-434. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng2040026
APA StyleKaddaha, M. A., Younes, R., & Lafon, P. (2021). Homogenization Method to Calculate the Stiffness Matrix of Laminated Composites. Eng, 2(4), 416-434. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng2040026






