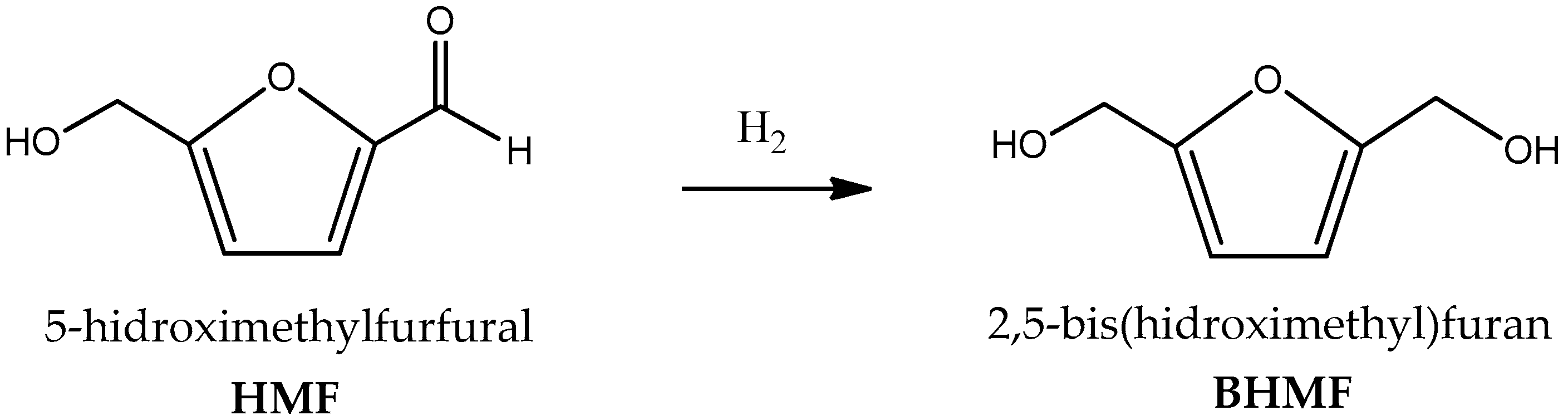
Liquid-Phase Hydrogenation over a Cu/SiO2 Catalyst of 5-hydroximethylfurfural to 2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)furan Used in Sustainable Production of Biopolymers: Kinetic Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Catalyst Preparation and Characterization
2.2. Catalytic Tests
2.3. Procedure for Numerical Calculus and Fittings
3. Results
3.1. Textural and Physicochemical Properties of Cu/SiO2-PD Catalyst
3.2. Catalytic Test
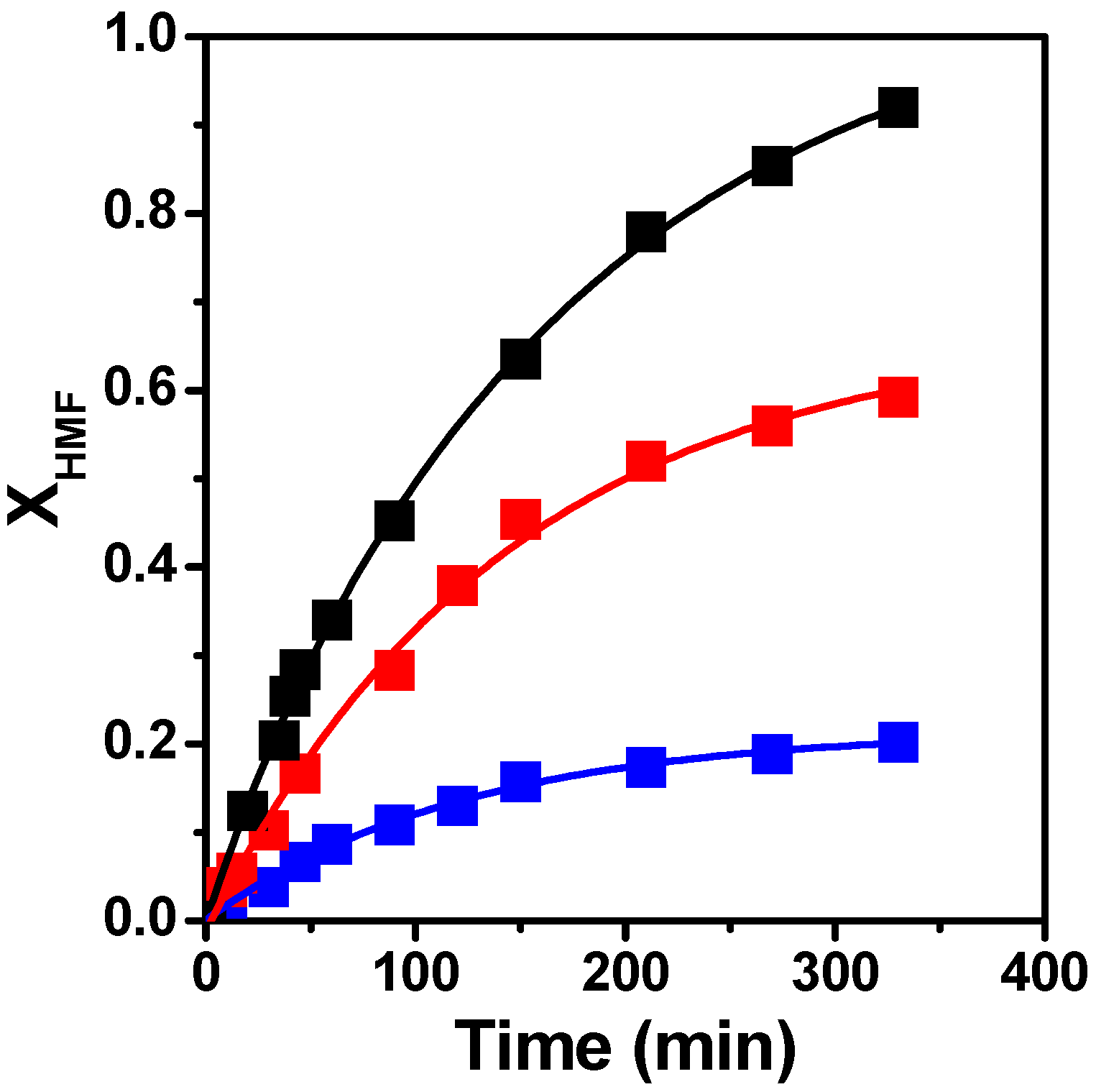
3.2.1. Solvent Influence on Catalytic Performance
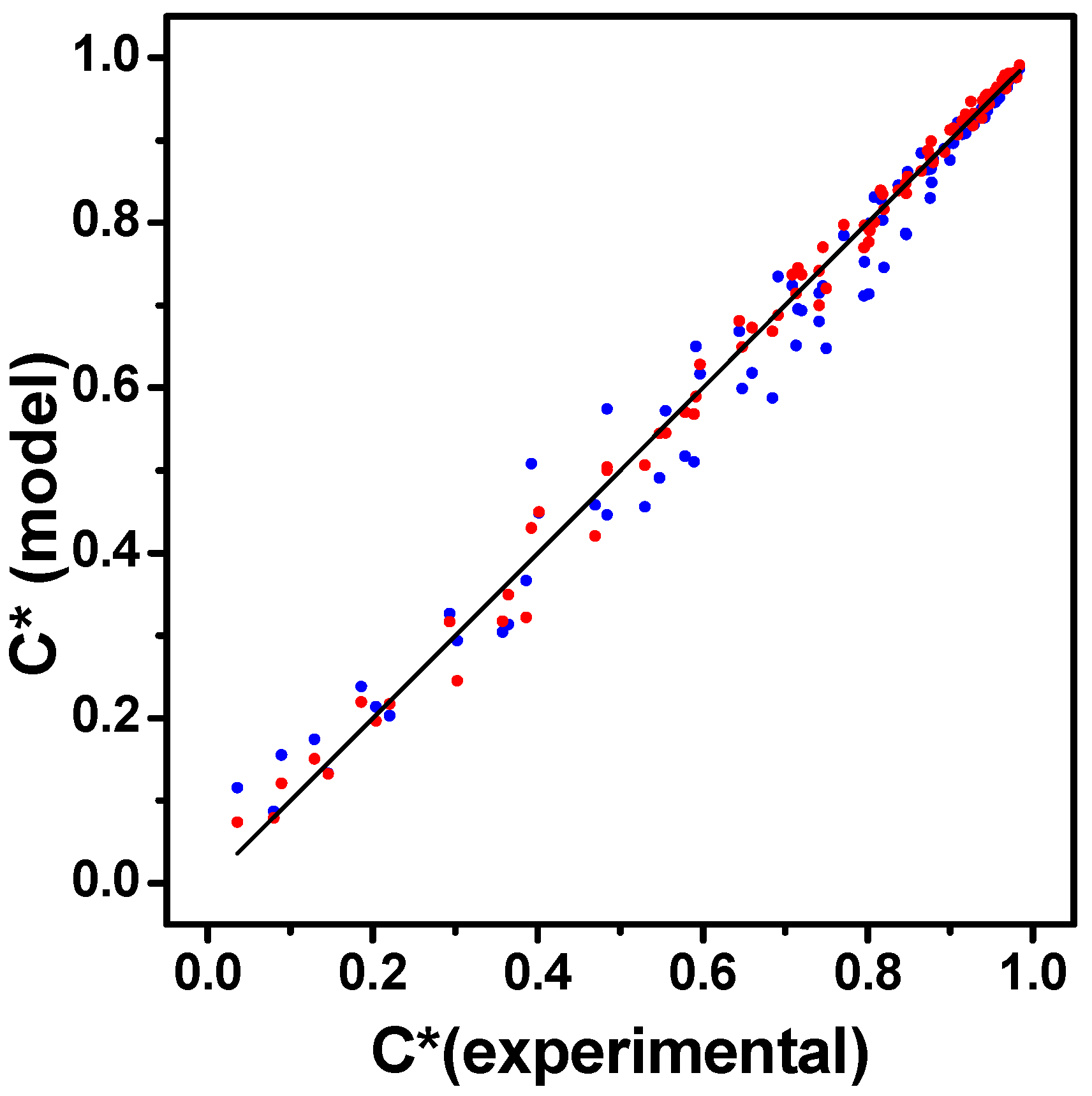
3.2.2. Kinetic Modeling of HMF Hydrogenation with the Cu/SiO2-PD Catalyst
Hypothesis and Principal Model Rate Equations Used
- The reactants, namely H2 and HMF, can be adsorbed on the adsorption sites (S, or S1 and S2) with 1:1 stoichiometry;
- The H2 chemisorption is non-dissociative;
- The reaction product, BHMF, can be adsorbed on the adsorption sites (S, or S1 and S2) with 1:1 stoichiometry;
- The surface irreversible reaction between adsorbed H2 and HMF is the controlling step of the reaction;
- The adsorptions of H2, HMF, and BHMF on the catalyst sites are reversible steps in equilibrium;
- According to the experimental conditions, for each catalytic run, the H2 concentration in the liquid phase is constant and determined by the H2 pressure and the Henry constant in THF.
| H2(g) ⇌ H2(l) | ⋯ | H = PH2(g)/CH2(l) |
| H2(l) + S1 ⇌ H2S1 | ⋯ | KH = CH2S1/(CH2(l)·CS1) |
| HMF + S2 ⇌ HMFS2 | ⋯ | KA = CHMFS2/(CHMF·CS2) |
| HMFS2 + H2S1 ⇀ BHMFS2 + S1 | ⋯ | rHMF = ksr·CHMFS2·CH2S1 |
| BHMFS2 ⇌ BHMF + S2 | ⋯ | KB = CBHMFS2/(CBHMF·CS2) |
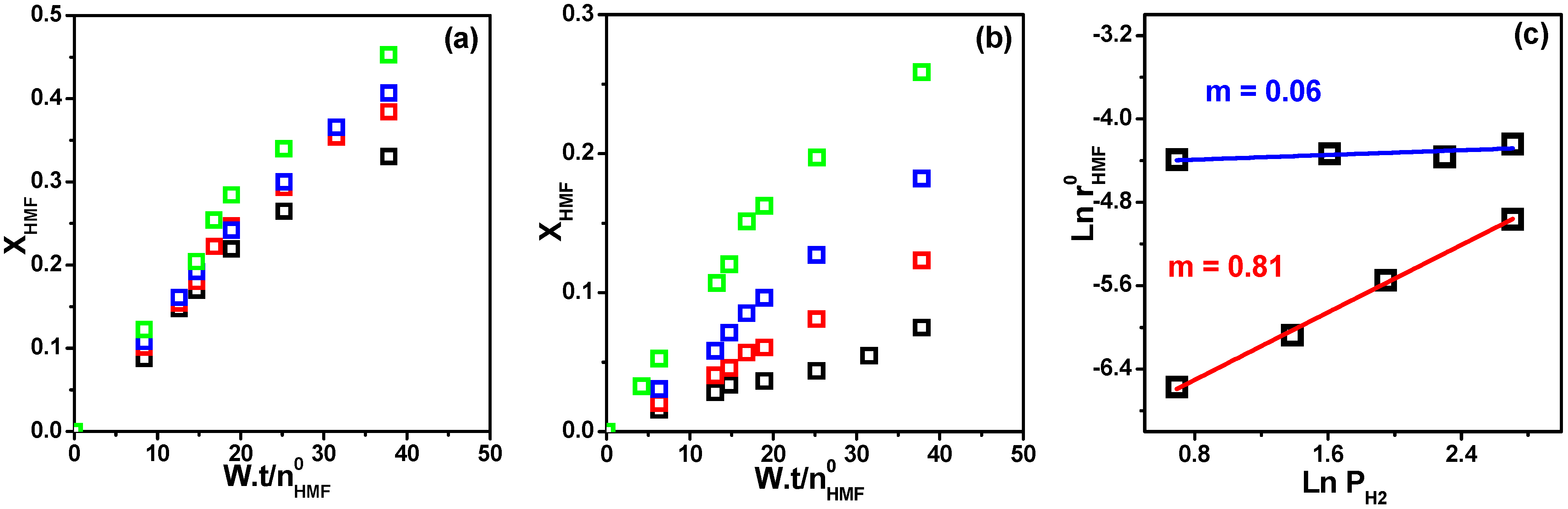
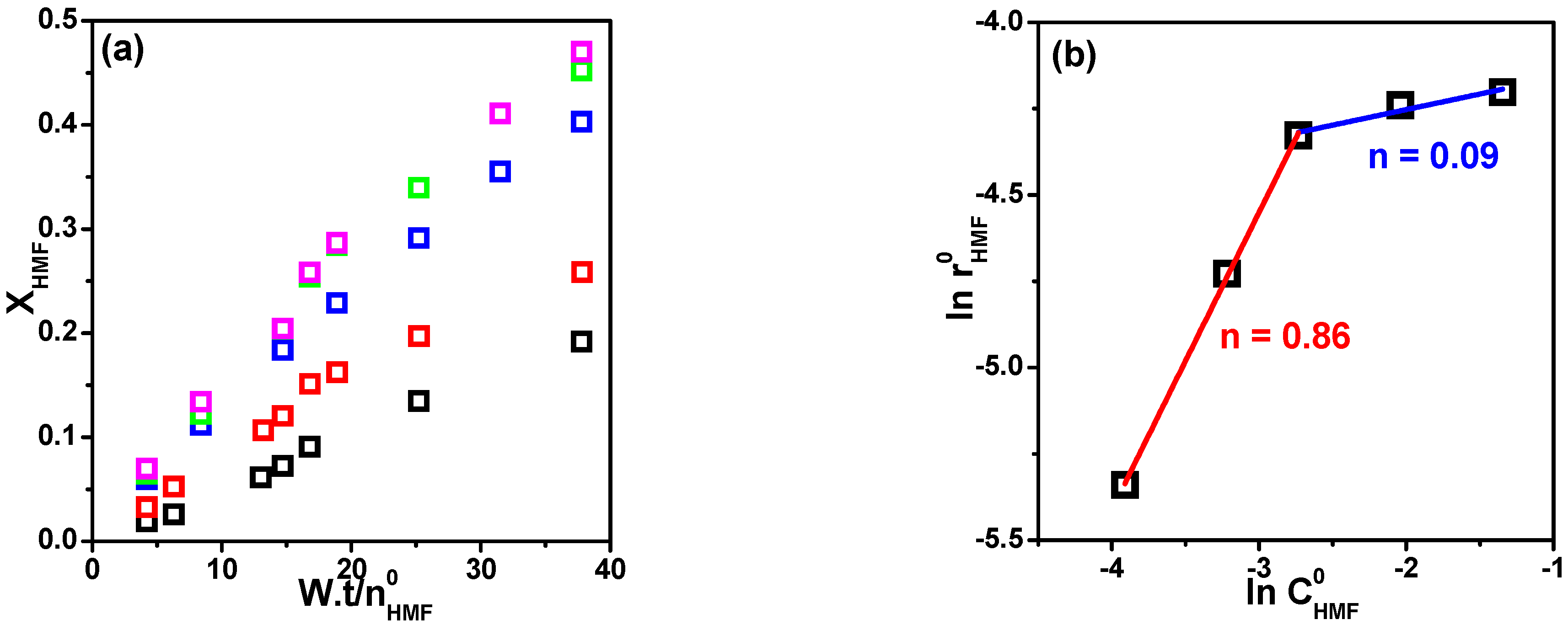
Influence of Hydrogen Pressure
Influence of HMF Concentration
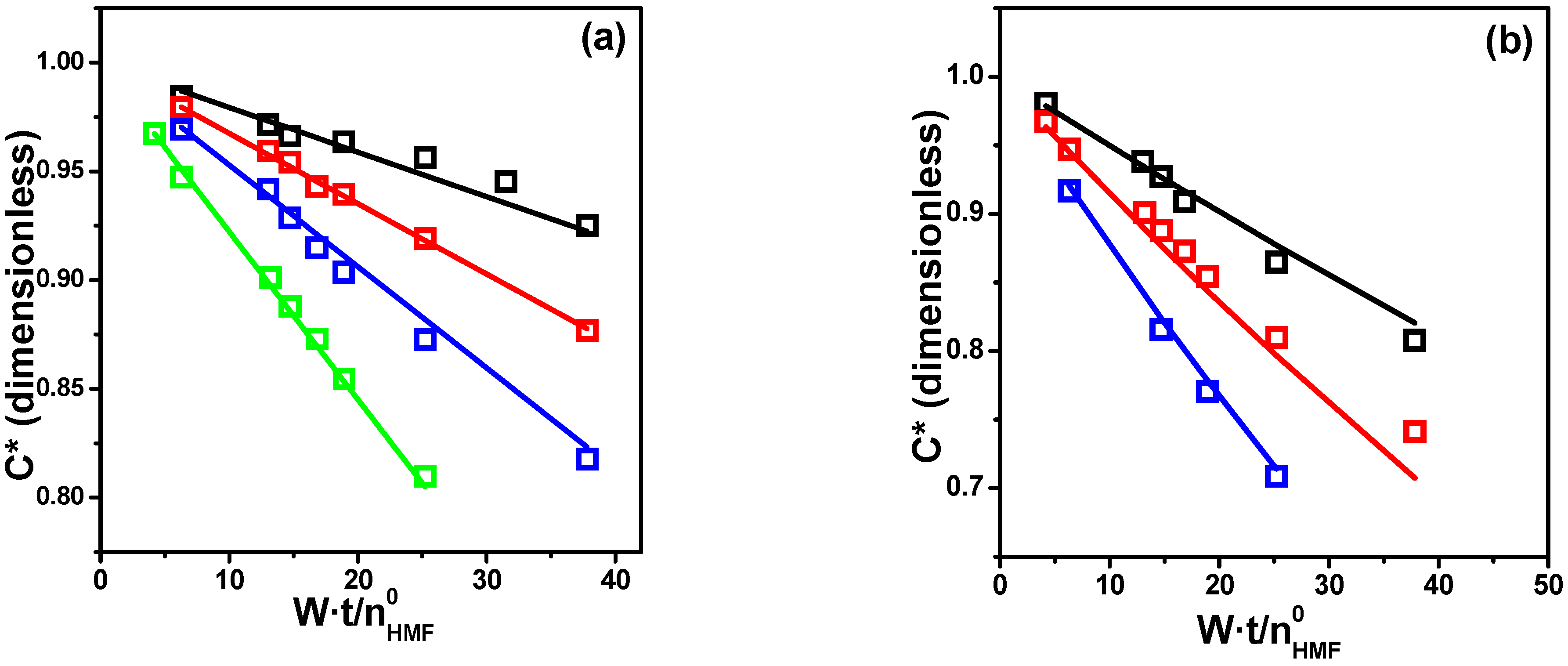
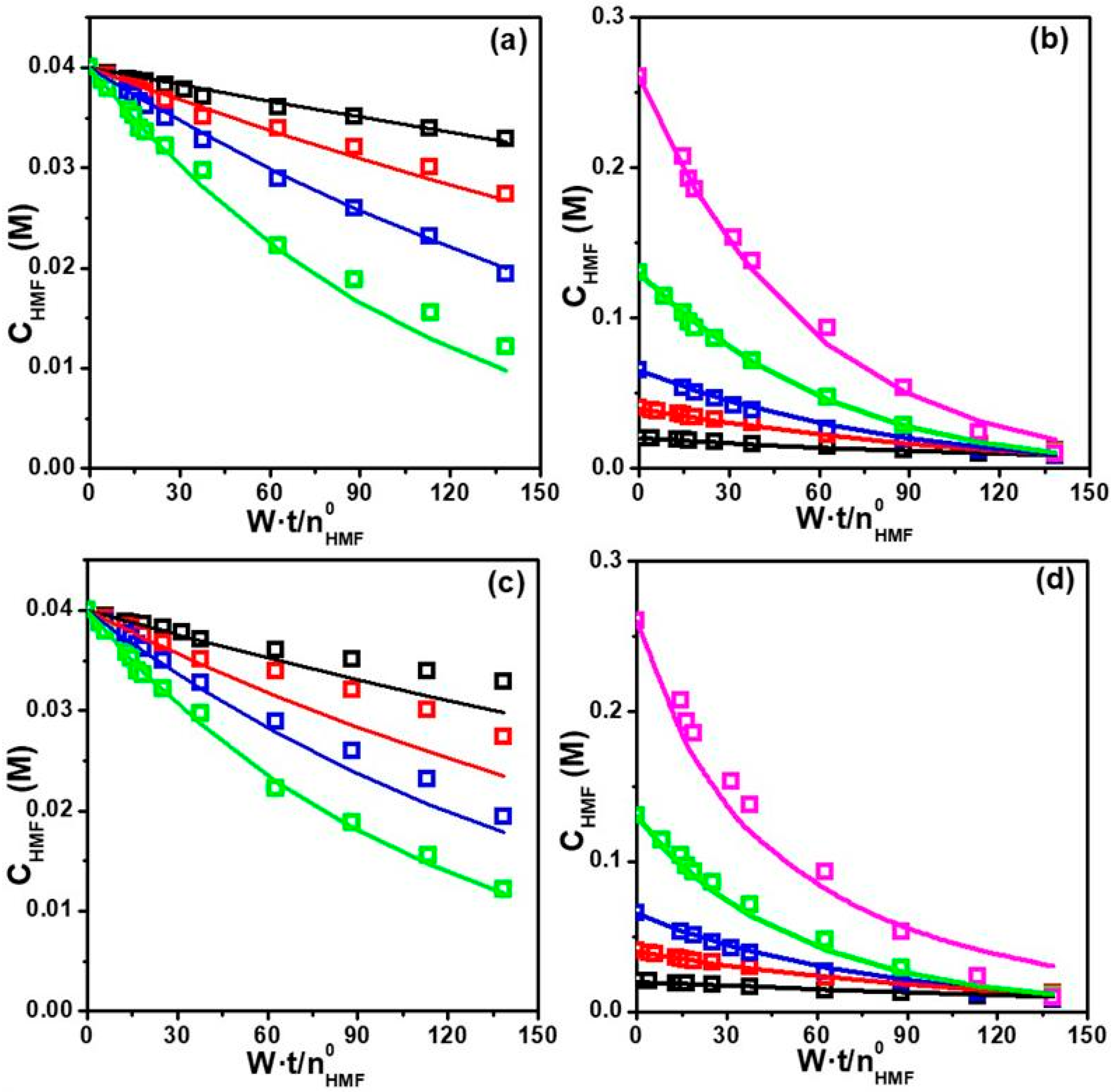
Pseudo-Homogeneous Modeling
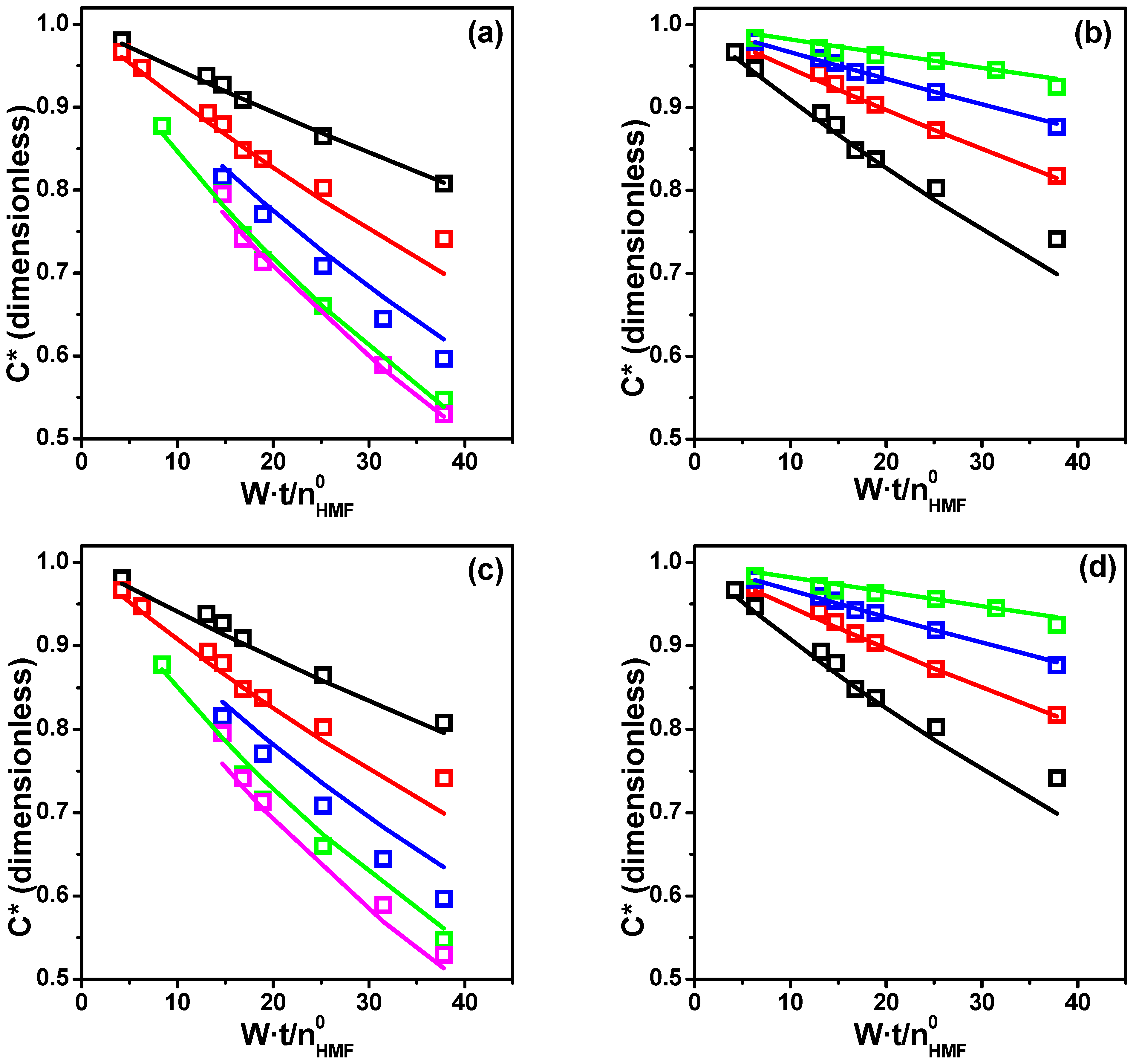
LHHW Heterogeneous Modeling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations and Nomenclature
| HMF | 5-hydroxymethylfurfural |
| BHMF | 2,5-bis-(hydroxymethyl)furan |
| H2O | Water |
| 2-POH | 2-propanol |
| THF | Tetrahydrofuran |
| LHHW | Langmuir–Hinshelwood–Hougen–Watson |
| W | Mass of Cu/SiO2 catalyst charged in the reactor (g) |
| t | Time of reaction (h) |
| nj | Moles of species j (mol) |
| n0HMF | Initial moles of HMF charged in the reactor (mol) |
| XHMF | Fractional conversion of HMF |
| yj | Fractional yield of reaction product j |
| Sj | Selectivity to reaction product j |
| CB | Carbon balance of reaction |
| r0HMF | Initial HMF reaction rate (mol/g·h) |
| rHMF | HMF reaction rate (mol/g·h) |
| CHMF | HMF concentration in the liquid phase (mol/L) |
| CBHMF | BHMF concentration in the liquid phase (mol/L) |
| CH2 | Hydrogen concentration in the liquid phase (mol/L) |
| PH2 | Hydrogen pressure in the gas phase (kPa) |
| C* | Experimental or model-calculated dimensionless HMF concentration (CHMF/C0HMF) |
| m | Apparent order of reaction for H2 |
| n | Apparent order of reaction for HMF |
| H | Henry constant of H2 in the liquid solvent (kPa·L/mol)) |
| kph | Forward rate constant for pseudo-homogeneous model (mol1−n·Ln/(h·g·kPam)) |
| ksr | Forward rate constant for solid surface elemental reaction (g/h·mol) |
| KH | Adsorption equilibrium constant for H2 on the catalytic site (L/mol) |
| KA | Adsorption equilibrium constant for HMF on the catalytic site (L/mol) |
| KB | Adsorption equilibrium constant for BHMF on the catalytic site (L/mol) |
| CTSi | Total surface concentration of site Si (S1 or S2) (mol/g) |
| CjSi | Surface concentration of species j adsorbed on site Si (S1 or S2) (mol/g) |
| k | Lumped kinetic constant for LHHW model ((L/(h·g·kPa)) |
| KBS | Parameter considering the irreversible adsorption of BHMF on the S or S2 sites (L/mol) |
| SSE | Squared sum of errors |
| DC | Determination coefficient |
| IC | 95% confidence interval |
Appendix A
References
- Mülhaupt, R. Green Polymer Chemistry and Bio-based Plastics: Dreams and Reality. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Ogunseitan, O.A.; Wong, M.H.; Tang, Y. Sustainable materials alternative to petrochemical plastics pollution: A review analysis. Sustain. Horiz. 2022, 2, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Verma, A.; Shome, A.; Sinha, R.; Sinha, S.; Jha, P.K.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Shubham; Das, S.; et al. Impacts of Plastic Pollution on Ecosystem Services, Sustainable Development Goals, and Need to Focus on Circular Economy and Policy Interventions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, A.Z.; Deiab, I.; Darras, B.M. Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), green alternatives to petroleum-based plastics: A review. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 17151–17196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrha, H.; Cabrera, J.; Dai, Y.; Irfan, M.; Toma, A.; Jiao, S.; Liu, X. Bio-Based Plastics Production, Impact and End of Life: A Literature Review and Content Analysis. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Lee, J.M. Recent Advances in Reductive Upgrading of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural via Heterogeneous Thermocatalysis. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, 1864–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoonsap, S.; Buengkitcharoen, L.; Amnuaypanich, S.; Thongnoppakhun, N.; Patdhanagul, N.; Suthirakun, S.; Sukpattanacharoen, C.; Amnuaypanich, S. Synergistic effect of silanols in mesopores leading to unexpected catalysis of dendritic mesoporous silica particles in the aqueous-phase synthesis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from fructose. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Huete, F.; Messina, C.; Cigana, B.; Forgione, P. Diverse applications of biomass-derived 5-hydroxymethyl furfural and derivatives as renewable starting materials. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Tang, X.; Peng, L.; Wei, J.; Lin, L. Methods in the synthesis and conversion of 2,5-Bis-(hydroxymethyl)furan from bio-derived 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and its great potential in polymerization. Bioresources 2018, 13, 7137–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Z.; Chen, E.Y. Polyesters and Poly(ester-urethane)s from Biobased Difuranic Polyols. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 7118–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friend, C.M.; Xu, B. Heterogeneous Catalysis: A Central Science for a Sustainable Future. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Ishizaka, T.; Kawanami, H. Selective hydrogenation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-bis-(hydroxymethyl)furan using Pt/MCM-41 in an aqueous medium: A simple approach. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4734–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikanova, K.; Redina, E.; Kapustin, G.; Chernova, M.; Tkachenko, O.; Nissenbaum, V.; Kustov, L. Advanced Room-Temperature Synthesis of 2,5-Bis(hydroxymethyl)furan-A Monomer for Biopolymers-From 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, J.; Esaki, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Arai, S.; Satsuma, A. Selective hydrogenation of 2-hydroxymethyl-5-furfural to 2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)furan over gold sub-nano clusters. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Li, C.; Wang, A.; Zhang, T. Biomass into chemicals: One-pot production of furan-based diols from carbohydrates via tandem reactions. Catal. Today 2014, 234, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhen, H.; Dong, F.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.W. Switchable synthesis of 2,5-dimethylfuran and 2,5-dihydroxymethyltetrahydrofuran from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural over Raney Ni catalyst. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 60467–60472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, S.; Chadwick, D.; Hellgardt, K. Towards sustainable hydrogenation of 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural: A two-stage continuous process in aqueous media over RANEY® catalysts. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 31401–31407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandi, F.; Bäumel, M.; Shekova, I.; Molinari, V.; Al-Naj, M. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Hydrodeoxygenation to 2,5-Dimethylfuran in Continuous-Flow System over Ni on Nitrogen-Doped Carbon. Sustain. Chem. 2020, 1, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deussen, P.; Galvanin, F. A model-based experimental design approach toassess the identifiability of kinetic models ofhydroxymethylfurfural hydrogenation in batchreaction systems. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 178, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, C. Selective Hydrogenation of the Carbonyls in Furfural and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Catalyzed by PtNi Alloy Supported on SBA-15 in Aqueous Solution Under Mild Conditions. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 759512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Rezayan, A.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Xu, C.C.; Nie, R. On-demand, highly tunable, and selective 5-hydroxymethylfurfural hydrogenation to furan diols enabled by Ni and Ni3Ga alloy catalysts. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Dong, L.; Wang, Z.; Han, X.; Daemen, L.; Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; et al. A unique Co@CoO catalyst for hydrogenolysis of biomass-derived 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-dimethylfuran. Nat. Comm. 2022, 13, 3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srifa, A.; Kalong, M.; Praikaew, W.; Ratchahat, S.; Chaiwat, W.; Koo-Amornpattana, W.; Klysubun, W.; Limphirat, W.; Assabumrungrat, S.; Kaw, S. Regulation of Pt Loading on Co/Al2O3 Catalysts for Selective Hydrogenation and Hydrogenolysis of 5- Hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-Bis(hydroxymethyl)furan and 2,5-Dimethylfuran. ChemCatChem 2024, 16, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Kong, X.; Zheng, H.; Ding, G.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.W. Efficient synthesis of 2,5-dihydroxymethylfuran and 2,5-dimethylfuran from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural using mineral-derived Cu catalysts as versatile catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 8, 4208–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upare, P.P.; Hwang, Y.K.; Hwang, D.W. An integrated process for the production of 2,5-dihydroxymethylfuran and its polymer from fructose. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 875–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, F.; Yang, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, K.; Liu, X.; Xu, Q.; Yin, D.; Yu, N. Silica-supported non-precious copper catalyst for catalytic hydrogenation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)furan. Mol. Catal. 2024, 553, 113794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Feng, J.; Zheng, L.; Wang, B.; Bi, R.; He, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, D. Interfacial Structure-Determined Reaction Pathway and Selectivity for 5-(Hydroxymethyl)furfural Hydrogenation over Cu-Based Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Chen, Z.; Yang, J.; Hongli He, M.L.; Chen, G.; Huai, L.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J. Boosting hydrogenation properties of supported Cu-based catalysts by replacing Cu0 active sites. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2025, 361, 124563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayan, A.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Nie, R.; Wang, J.; Lu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Si, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Efficient and switchable production of bio-diol/triol chemicals from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Green Chem. 2025, 2578–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.B.; Vaidya, P.D. Kinetics of Catalytic Hydrogenation of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-bis-Hydroxymethylfuran in Aqueous Solution over Ru/C. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2015, 848, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelin, J.; Meyer, C.I.; Duarte, H.A.; Marchi, A. A Stable and Reusable Supported Copper Catalyst for the Selective Liquid-Phase Hydrogenation of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-Bis(hydroxymethyl)furan. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Levie, R. Advanced Excel for Scientific Data Analysis; Oxford University Press: Oxford, MS, USA, 2004; pp. 423–512. [Google Scholar]
- Zelin, J.; Meyer, C.I.; Duarte, H.A.; Marchi, A.A. Selective liquid-phase hydrogenation of fructose to D-mannitol over copper-supported metallic nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 319, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yan, P.; Xu, W.; Liu, X.; Xia, Z.; Chung, B.; Jia, S.; Zhang, Z.C. Hydrogenation/Hydrolytic Ring Opening of 5-HMF by Cp*-Iridium(III) Half-Sandwich Complexes for Bioketones Synthesis. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, B.; Arias, K.S.; Climent, M.J.; Concepción, P.; Corma, A.; Iborra, S. Selective Conversion of HMF into 3-Hydroxymethylcyclopentylamine through a One-Pot Cascade Process in Aqueous Phase over Bimetallic NiCo Nanoparticles as Catalyst. ChemSusChem 2015, 5, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Yang, D.; Cao, O.; Dai, J.; Yang, R.; Gu, X.; Li, F. Recent advances in catalytic synthesis of 2,5-furandimethanol from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and carbohydrates. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2023, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragno, D.; Di Carmine, G.; Brandolese, A.; Bortolini, O.; Giovannini, P.; Fantin, G.; Bertoldo, M.; Mass, A. Oxidative NHC-Catalysis as Organocatalytic Platform for the Synthesis of Polyester Oligomers by Step-Growth Polymerization. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 14701–14710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasarti, A.F.; Bertero, N.M.; Apesteguía, C.R.; Marchi, A.J. Liquid-phase hydrogenation of acetophenone over silica-supported Ni, Co and Cu catalysts: Influence of metal and solvent. Appl. Catal. A 2014, 475, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, D. An accurate model for estimating H2 solubility in pure water and aqueous NaCl solutions. Energies 2022, 15, 5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertero, N.; Trasarti, A.; Apesteguía, C.; Marchi, A. Solvent effect in the liquid-phase hydrogenation of acetophenone over Ni/SiO2: A comprehensive study of the phenomenon. Appl. Catal. A 2011, 394, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, H.A.; Luggren, P.J.; Zelin, J.; Sad, M.E.; Diez, V.K.; Di Cosimo, J.I. Selective aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol on inexpensive and reusable ZnO/MnCO3 catalyst. Catal. Today 2022, 394, 178–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertero, N.; Trasarti, A.; Acevedo, M.; Apesteguía, C.; Marchi, A. Solvent effects in solid acid-catalyzed reactions: The case of the liquid-phase isomerization/cyclization of citronellal over SiO2-Al2O3. Mol. Catal. A 2020, 481, 110192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamlet, M.J.; Abboud, J.L.; Abraham, M.H.; Taft, R.W. Linear Solvation Energy Relationships. 23. A Comprehensive Collection of the Solvatochromic Parameters, π*, α, and β, and Some Methods for Simplifying the Generalized Solvatochromic Equation. Jor. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.I.; Regenhardt, S.A.; Zelin, J.; Sebastian, V.; Marchi, A.J.; Garetto, T.F. A kinetic modelling of the liquid-phase oxidation of lactose over Pt- and Au- Supported catalysts. Top. Catal. 2016, 59, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, G.S.; Meyer, C.I.; Duarte, H.; Sanz, O.; Montes, M.; Marchi, A.J.; Regenhardt, S.A. Catalytic and kinetic study of the liquid-phase oxidation of lactose over Au/Al2O3 nanostructured catalyst in a monolithic stirrer reactor. Cat. Today 2022, 383, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
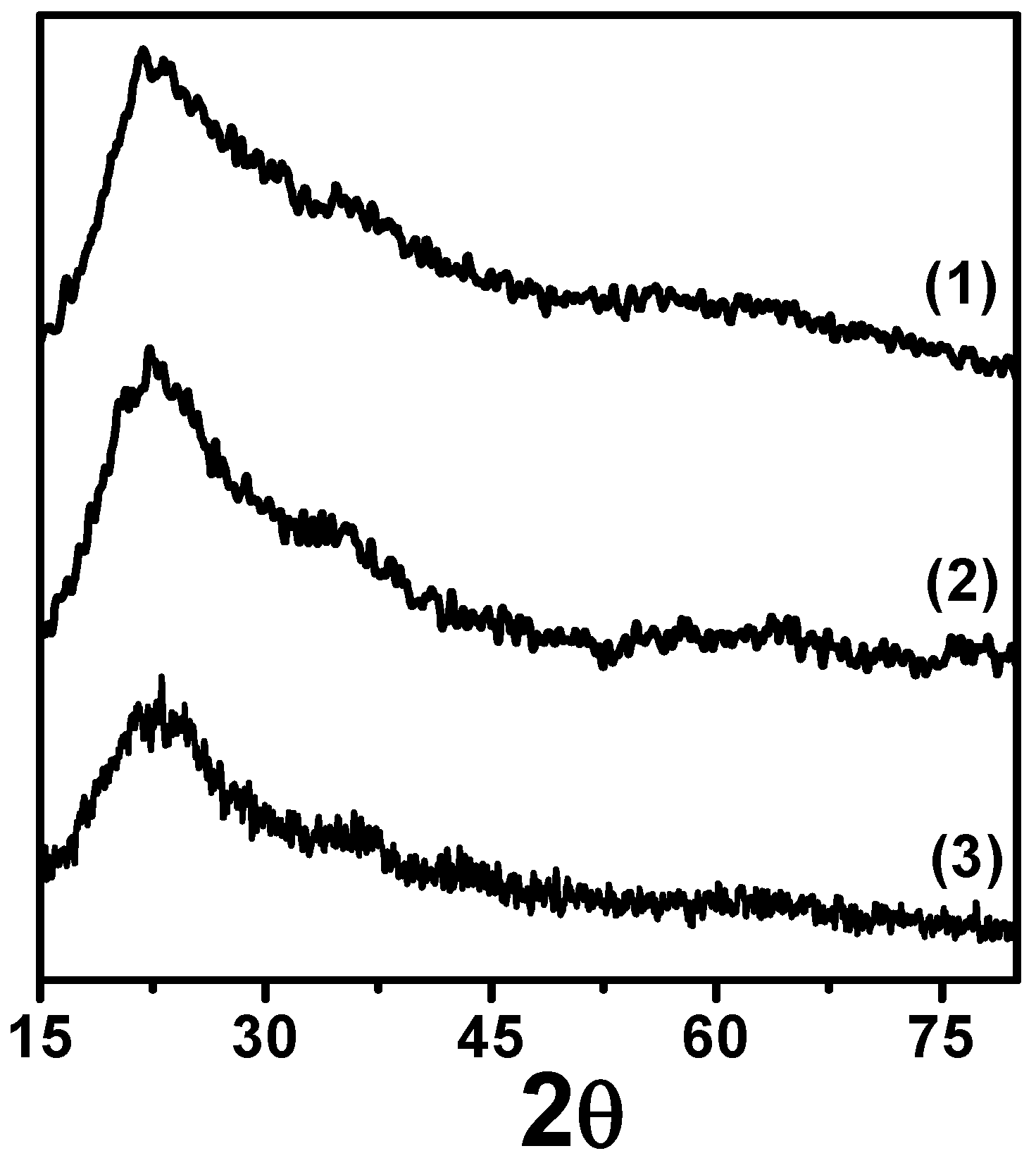
| Samples | Cu(a) (%w/t) | Sg (m2/g) | Vp (cm3/g) | dp (nm) | TPR(b) (K) | (c) (%) | (d) (nm) | dTEM(e) (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | - | 296 | 1.06 | 14.3 | - | - | - | - |
| Cu/SiO2-PD | 8.0 | 270 | 0.94 | 12.7 | 566 | 21 | 3.6 | 4.7 |
| Solvent | 102 a (mol/h.g) | XHMF b (%) | c (%) | SBHMF d (%) | CB e (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THF | 1.44 | 91 | 90 | 98 | 99 |
| 2-POH | 0.94 | 59 | 58 | 98 | 98 |
| H2O | 0.35 | 20 | 9 | 45 | 98 |
| Run | (M) | PH2 (kPa) | T (K) | ·102 (mol/h.g) | TOF (1/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.020 | 1500 | 393 | 0.48 | 227 |
| 2 | 0.040 | 1500 | 393 | 0.70 | 333 |
| 3 | 0.065 | 1500 | 393 | 1.32 | 624 |
| 4 | 0.130 | 1500 | 393 | 1.44 | 680 |
| 5 | 0.260 | 1500 | 393 | 1.50 | 707 |
| 6 | 0.040 | 700 | 393 | 0.39 | 185 |
| 7 | 0.040 | 400 | 393 | 0.23 | 110 |
| 8 | 0.040 | 200 | 393 | 0.14 | 64 |
| 9 | 0.130 | 1000 | 393 | 1.27 | 601 |
| 10 | 0.130 | 500 | 393 | 1.31 | 620 |
| 11 | 0.130 | 200 | 393 | 1.24 | 586 |
| Runs | From Model 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m a | n a | m a | n a | DC b | |
| 2, 6–8 | 0.81 ± 0.07 | n.a. | 0.66 ± 0.04 | −0.09 ± 0.90 | 0.9916 |
| 4, 9–11 | 0.06 ± 0.08 | n.a. | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.80 ± 0.93 | 0.9803 |
| 1–3 (4–5) | n.a. | 0.86 ± 0.07 | n.a. | 0.78 ± 0.11 | 0.9782 |
| Parameter | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | CI a | Estimate | CI a | |
| k | 0.036 | 0.006 | 0.040 | 0.008 |
| KH | 0.018 | 0.007 | 0.031 | 0.019 |
| KA | 5.93 | 0.94 | 16.8 | 5.2 |
| KB | 7.01 | 2.29 | 26.5 | 11.7 |
| DC b | 0.9920 | 0.9849 | ||
| Parameter | Modified Model 2 | Modified Model 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | CI a | Estimate | CI a | |
| k | 0.039 | 0.010 | 0.032 | 0.003 |
| KH | 0.031 | 0.012 | 0.015 | 0.008 |
| KA | 3.77 | 1.57 | 18.8 | 3.0 |
| KB | 0.022 | 7.91 | 6.24 | 5.44 |
| KBS | 2.46 | 2.57 | 1.90 | 1.08 |
| CD | 0.9744 | 0.9936 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zelin, J.; Duarte, H.A.; Marchi, A.J.; Meyer, C.I. Liquid-Phase Hydrogenation over a Cu/SiO2 Catalyst of 5-hydroximethylfurfural to 2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)furan Used in Sustainable Production of Biopolymers: Kinetic Modeling. Sustain. Chem. 2025, 6, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem6030022
Zelin J, Duarte HA, Marchi AJ, Meyer CI. Liquid-Phase Hydrogenation over a Cu/SiO2 Catalyst of 5-hydroximethylfurfural to 2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)furan Used in Sustainable Production of Biopolymers: Kinetic Modeling. Sustainable Chemistry. 2025; 6(3):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem6030022
Chicago/Turabian StyleZelin, Juan, Hernán Antonio Duarte, Alberto Julio Marchi, and Camilo Ignacio Meyer. 2025. "Liquid-Phase Hydrogenation over a Cu/SiO2 Catalyst of 5-hydroximethylfurfural to 2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)furan Used in Sustainable Production of Biopolymers: Kinetic Modeling" Sustainable Chemistry 6, no. 3: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem6030022
APA StyleZelin, J., Duarte, H. A., Marchi, A. J., & Meyer, C. I. (2025). Liquid-Phase Hydrogenation over a Cu/SiO2 Catalyst of 5-hydroximethylfurfural to 2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)furan Used in Sustainable Production of Biopolymers: Kinetic Modeling. Sustainable Chemistry, 6(3), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem6030022








