Abstract
Dry Turkish oak (Quercus cerris) sawdust, untreated and treated with three activators, (H3PO4, NaOH and H2O2) was pyrolyzed under limited-oxygen conditions to obtain biochar samples. The electrochemical properties of these samples were tested and compared to the properties of several commercial carbon blacks. The electrochemical characterization was performed via cyclic voltammetry, analyzing the response toward two commonly used redox probes, [Fe(CN)6]3−/−4− and [Ru(NH3)6]2+/3+. The influence of the scan rate on this response was investigated, and the resulting data were used to obtain the values of the heterogenous charge transfer constant, k0. Higher k0 values were observed for carbon blacks than for investigated biochar samples. The detection of 4-nitrophenol and heavy metal ions was used to assess the applicability of biochars for electroanalytical purposes. The response of untreated biochar was comparable with the response of Vulcan carbon black, which showed the best response of all analyzed carbon blacks.
1. Introduction
The preparation of an electrode for electroanalytical application usually involves the usage of some carbonaceous materials. Different carbon materials have been used over the years, starting from graphite and carbon blacks and then moving to more advanced such as nanotubes [1], nanofibers [2], nanorods [3], sheaths [4] or graphene [5,6]. Among them, the most commonly used is carbon black due to its high electrical conductivity, large surface area, chemical stability and cost-effectiveness. In recent years, several articles addressing the response of various carbon blacks toward redox probes and their application in electrochemical sensors were published [7,8].
Carbon blacks are petroleum-based products, obtained via the thermal decomposition of different petroleum derivatives. The production process is constantly improved and optimized to allow control of the particle size distribution and surface functional group distribution [9]. Even so, the process of carbon black production strongly depends on fossil fuels. In order to answer the demand for more sustainable material, alternatives are explored.
Biochar is currently being investigated as a replacement for carbon black in various industrial applications, such as a reinforcing filler in rubber production [8], plastic composites [9] and anode materials in batteries [10]. Biochar is a solid material obtained via the pyrolysis of biomass under limited-oxygen conditions or in an inert atmosphere. Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that has several important parameters that can significantly affect the properties of the resulting biochar: temperature, heating rate and residence time. Among these, the pyrolysis temperature is the factor that has the greatest influence on the final characteristics of the biochar [11]. Pyrolysis is performed over a wide temperature range (300–1100 °C). Moisture and light volatiles are removed at temperatures up to 200 °C, while the decomposition of hemicelluloses and cellulose occurs at temperatures up to 500 °C [12]. The degradation of lignin commences at temperatures above 500 °C [13]. Biochar for biochar-based electrodes is usually produced at high temperatures (800–1100 °C) [14] to ensure full carbonization of the biomass.
When pyrolysis is performed at a heating rate in the range of 0.01–2 °C s−1, it is considered slow pyrolysis, while fast pyrolysis is carried out at higher heating rates (>2 °C s−1) and shorter residence times. Biochar produced via fast pyrolysis has a higher specific surface area and a lower average particle size [15].
By applying appropriate treatments, such as activation or doping, the physicochemical properties of biochar can be modified. These treatments can be applied either as a post-treatment of biochar or as a pre-treatment of biomass so that the activator acts during pyrolysis in a one-pot process [16]. Pre-activation requires less energy and time and is therefore often preferred over post-treatment [17].
Biochar was initially utilized for soil enhancement and carbon sequestration due to its ability to improve soil fertility, retain moisture and stabilize organic matter [18]. Over time, its applications have expanded to include use as an adsorbent for pollutants in water and air treatment, as well as a component in construction materials, energy storage systems and composite materials [19].
The renewable origin and lower environmental footprint of biochar [20] make it an attractive alternative to carbon black. The traditional production of carbon black from fossil fuels emits approximately 1.90–2.25 kg of CO2 per kilogram produced [21]. Biochar produced from biomass residues can be generated with net negative carbon emissions [22], depending on the feedstock and pyrolysis conditions. Moreover, utilizing agricultural or forestry waste as feedstock reduces landfill use and promotes circular economy principles, further enhancing its environmental benefits [23,24].
Conductive carbon inks are a cost-effective and attractive means of producing electrodes for various applications. There are several commercial conductive carbon inks, but the precise ink formulations are often unavailable. The conductive phase in these inks consists of some form of carbon: carbon black, graphite, carbon fiber, graphene, nanotubes [25]. Carbon blacks are often used in conductive ink formulations due to their good conductivity, high surface area, and relatively low cost compared to other conductive materials [26].
This paper explores the usage of biochar as a substitute for carbon black in the production of conductive carbon inks. The biochar was produced at a medium pyrolysis temperature, in an air-limited atmosphere, promoting sustainability of the biochar-production process. Furthermore, this approach preserves the surface functional groups that may significantly affect its electronalytical application. In this study, the electrochemical response of biochar was compared to the electrochemical properties of several carbon blacks. This work provides a novel contribution to understanding the influence of biochar treatment on its electrochemical response. Furthermore, examining carbon blacks under the same experimental conditions allows for a direct and meaningful comparison with biochar, highlighting differences relative to commercially available materials. It is possible to tune the electrochemical properties of biochar to the level comparable to those of the commercial carbon blacks. This paper aims to contribute to the green substituent for production of the various electrodes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biochar Poduction and Treatment
Dry Turkish oak (Quercus cerris) sawdust was collected from the production site and dried at 110 °C for 2 h.
Dry Turkish oak (Quercus cerris) sawdust was activated with chemical agents, H3PO4, NaOH and H2O2, in mass ratios of activator to sawdust of 4:1 for 2 h at 50 °C with constant stirring on a magnetic stirrer. A measured amount of sawdust was mixed in the given ratio with a dry activator (NaOH), and 50 mL of distilled water was added so that the NaOH concentration was 6 M. For activators in solution (H3PO4 and H2O2), the volume corresponding to the required mass fraction was calculated and then topped up to 50 mL with distilled water. The final concentrations were 2.45 M for H3PO4 and 7.06 M for H2O2. After activation, the obtained samples were filtered using a Buchner funnel and dried to a constant mass at 60 °C. Untreated sawdust and activated samples were carbonized during 60 min at 400 °C, with a ramp of 5 °C/min, in air-limited conditions (in a sealed ceramic vessel placed in a muffle furnace). After the carbonization process was completed, each of the obtained samples was powdered and washed with distilled water until the filtrate reached a neutral pH. The biochar obtained from untreated sample was designated as BC, activated with H3PO4 as BC-P, activated with NaOH as BC-N, and activated with H2O2 as BC-H.
Carbon blacks Vulcan XC72R, Black Pearls 1100 and Regal 330 were obtained from Cabot Corporation (Boston, MA, USA). The samples were designated as Vulcan, Pearls and Regal, respectively. Graphite fine powder was purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany).
2.2. Ink Formulation
In order to investigate the contribution of various carbonaceous species, conductive inks were prepared according to a previously published procedure [27]. For the investigation of carbon blacks and biochar, the composition of conductive ink involved the following: 130 mg of graphite powder, 50 mg of carbon black or biochar, 0.2 g of nail polish and 0.45 mL of acetone. The resulting inks were designated using the same name as the carbon black or biochar used in their preparation (Vulcan, Pearls, Regal, BC, BC-H, BC-N and BC-P).
The prepared ink was coated on the surface of a plastic foil with a doctor blade coater, while aluminum foil served as the current collector. Strips measuring 0.5 cm × 1 cm were cut from the coated layer to serve as a working electrode.
2.3. Electrochemical Investigation
Electrochemical experiments were performed using an Autolab electrochemical work station (Autolab PGSTAT302N, Metrohm-Autolab BV, Utrecht, The Netherlands) and a three-electrode cell composed of an Ag/AgCl in 3 M KCl as the reference electrode, a platinum rod as the counter electrode and a conductive ink strip as the working electrode.
The electrochemical properties were tested via cyclic voltammetry (CV) in 5 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/−4 + 0.1 M KCl and 1 mM [Ru(NH3)6]2+/3+ + 0.1M KCl. The electrode activity toward 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) was investigated in 1 mM 4-NP in 0.1 M Britton–Robinson (BR) buffer, pH 5.
Square wave voltammetry (SWV) was used to investigate the electrode response toward heavy metals using two procedures. The first procedure included the accumulation step of Pb on the electrodes from a magnetically stirred solution of 10 μM Pb2+ in BR, pH 5, followed by a striping step in 1.0 M HCl. After the reduction of the accumulated metal ions at a potential of −1.3 V for 40 s, the determination of metal ions was performed via square wave voltammetry (potential range of −0.8 V to −0.2 V, potential step of 10 mV, frequency of 10 Hz and modulation amplitude of 20 mV). The second procedure was performed directly using 1.0 M HCl containing an equimolar concentration (10 μM) of Pb2+ and Cu2+.
3. Results
3.1. Electrochemical Characterization: Response Toward Redox Probes [Fe(CN)6]3−/−4− and [Ru(NH3)6]2+/3+
The first insight into the electrochemical properties of different surfaces can be obtained based on their response to redox probes. The redox probes are species with well-defined redox reactions, and the most often used are the [Fe(CN)6]3−/−4− and [Ru(NH3)6]2+/3+ redox pairs. The response of the investigated electrodes to these redox probes is presented in Figure 1.
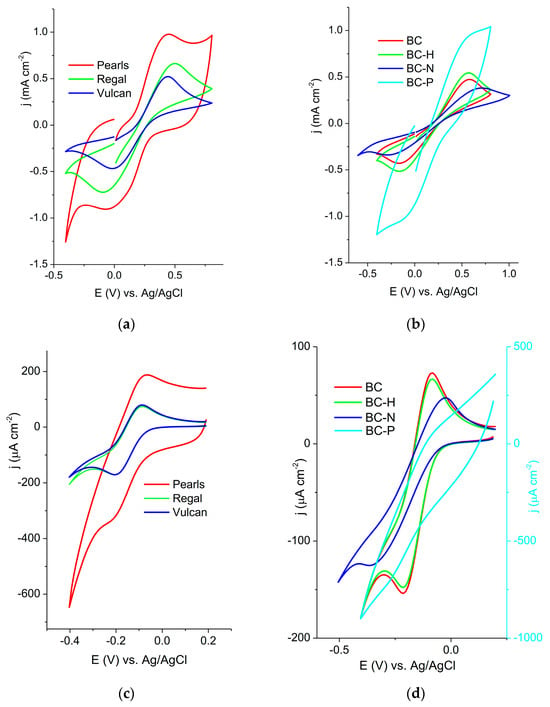
Figure 1.
Cyclic voltammograms of conductive ink electrodes containing (a) carbon blacks and (b) biochars recorded in 5 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/−4− + 0.1 M KCl at a scan rate of 20 mV s−1; (c) carbon blacks and (d) biochars recorded in 1 mM [Ru(NH3)6]2+/3+ + 0.1 M KCl at a scan rate of 20 mV s−1; the BC-P sample is referred to in a secondary axis.
The cyclic voltammograms are presented in two groups—carbon blacks and biochars—for clarity.
The investigated electrodes exhibited the expected pair of peaks for both redox probes. Scan rate studies were performed to investigate the dependence of the peak current and peak potential on the scan rate (Figures S1a–S14a, Supplementary data). All electrodes showed a linear relationship between the peak current and the square root of the scan rate, indicating a diffusion-controlled process (Figures S1b–S14b, Supplementary data). The values of the correlation coefficient (R2) ranged from 0.982 to 0.999, indicating an excellent linear relationship between the measured variables. The only exception was the response of the BC-N electrode toward the [Fe(CN)6]3−/−4− redox probe, where the faradic current was not clearly resolved form the background current at higher scan rates. The deviation of the Ia/Ic ratio from unity and the peak-to-peak separation value being higher than the expected value of 59 mV (Table 1) indicated that the process is not reversible. The electrochemically active surface area was calculated using the Randles–Ševćik equation for irreversible systems (1) based on data obtained for the [Fe(CN)6]3−/−4− redox probe, since ΔEp was >200 mV [28]:
where n is the total number of electrons transferred per molecule in the electrochemical process, n′ is the number of electrons transferred per molecule in the rate-determining step, α is the transfer coefficient, A is the area of the working electrode in cm2, C is the concentration in mmol/cm3, D is the diffusion constant in cm2/s and ν is the scan rate in V/s. The electrochemically active surface area was calculated using the Randles–Ševćik equation for quasi-reversible systems (2) based on data obtained for the [Ru(NH3)6]2+/3+ redox probe, since ΔEp was <200 mV.

Table 1.
The parameters obtained from cyclic voltammograms recorded as the response to redox probes.
The Epa of the oxidation process shifted to more positive values with an increasing scan rate, confirming that the charge-transfer process was not reversible, for both redox probes. However, due to the different peak-to-peak separation values, different methods were applied for the calculation of the value of the standard heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant (k0). The k0 value for the [Fe(CN)6]3−/−4− redox probe was calculated using Equation (3):
where R, T and F are the universal gas constant, absolute temperature and Faraday constant, respectively, DR is the diffusion coefficient of the reduced species, k0 is the heterogeneous standard rate constant, α is the energy transfer coefficient and n is the number of electrons transferred during the heterogeneous reaction.
The value of αn can be calculated from the slope of Ep vs. lnυ, and the value of the heterogeneous standard rate constant can be obtained from the intercept (Figures S1c–S7c, Supplementary data).
The calculation of the heterogeneous standard rate constant (k0) for the [Ru(NH3)6]2+/3+ redox probe was calculated using Lavagnini et al.’s [29] modification of the Nicholson method (4), by calculating ψ from the ΔEp:
Plotting ψ vs. [πDnF/RT]-1/2v-1/2, the values of k0 can be obtained as the slope of the straight line (Figures S8c–S14c, Supplementary data).
The electrochemical response of redox probes at carbon-based electrodes has been extensively discussed in the literature. Redox probes are commonly classified as inner-sphere or outer-sphere, based on the mechanism by which electron transfer occurs [30]. The hexacyanoferrate couple, [Fe(CN)6]3−/4−, is typically considered an inner-sphere redox probe, whereas [Ru(NH3)6]2+/3+ is generally regarded as an outer-sphere redox probe. Inner-sphere probes require specific interactions with the electrode surface—such as coordination or chemical bonding—to facilitate charge transfer. Consequently, their electrochemical response is highly sensitive to the surface chemistry and composition of the electrode [31]. In contrast, electron transfer for outer-sphere probes like [Ru(NH3)6]2+/3+ occurs without the formation of chemical bonds or adsorption on the electrode surface [31]. Therefore, their response is largely independent of surface functional groups and reflects the intrinsic kinetics of electron transfer. However, the classification of [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− has been debated. Several studies have reported that this redox couple may exhibit characteristics of both inner- and outer-sphere behavior, depending on the electrode material and surface modifications. This ambiguity has led to questioning the utility and precision of the inner-/outer-sphere classification [32], particularly in the case of [Fe(CN)6]3−/4−. In this work, we focus exclusively on the electrochemical responses observed at the investigated electrodes, without assigning or discussing the mechanistic classification of the redox probes used.
Building on the discussion of redox probe interactions with carbon-based electrodes, the behavior of graphene synthesized using a radiofrequency thermal plasma jet from six compounds from four classes of organic precursors (alkanes, alcohols, carboxylic acids and aldehydes) illustrates how surface chemistry significantly influences electron transfer. Specifically, the electrochemical response of graphene toward redox probes was found to correlate with both the total oxygen content and the nature of oxygen-containing functional groups [6]. Hydroxyl groups were shown to impede charge-transfer kinetics, whereas other oxygen functionalities—excluding ester-type C–O–C bonds—tended to enhance electron transfer.
The treatment used in this study alters the surface properties. FTIR studies of biochar subjected to various chemical treatments demonstrate that surface functionalization plays a critical role in modulating their properties. Biochar treated with H2O2 exhibited minimal changes in surface chemistry compared to the untreated material [33]. In contrast, alkali-treated biochar showed an increased presence of hydrogen-bonded –OH groups, indicative of alcohols and phenols. Treatment with H3PO4 led to the formation of amino-phosphonic acid functionalities and P–OH bonds, alongside an enhancement of the aromatic structure [34,35]. The activation of biochar did not lead to increased k0 values, which may be attributed to one or a combination of the following effects: (i) surface functionalization introducing insulating groups (e.g., excess oxygen-containing moieties), (ii) pore collapse or blockage caused by aggressive activation and (iii) disruption of conductive graphitic domains.
Electrochemical measurements revealed that biochar-based electrodes exhibit slower charge-transfer kinetics compared to commercial carbon blacks (i.e., lower k0 values for both redox probes). The similar electrochemical behavior observed between Pearl 1100 and phosphoric acid-treated biochar (BC-P) is primarily attributed to their high surface area, evident in high capacitive contributions that dominate over faradaic processes. These findings underscore the importance of both the specific surface chemistry and morphological properties of carbon materials in determining their electrochemical performance.
3.2. The Application of 4-Nitrophenol Oxidation
The investigated electrodes were applied for the oxidation and reduction of 4-NP. Cyclic voltammograms were recorded in 0.1 M BR buffer, pH 5, containing 50 μM 4-NP, first toward positive potentials—where oxidation of the 4-NP phenolic group is expected—and then in the cathodic direction, toward potentials where reduction of the nitro-group is expected. Cyclic voltammograms of Pearl and BC-P were dominated by high-capacitive currents (Figure 2a). A slight oxidation peak at approximately 1.1 V is observed for the Pearl electrode. Reduction of the nitro-group is not distinct at any of the recorded CVs.
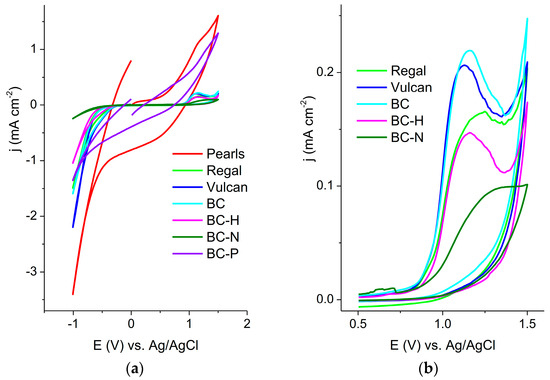
Figure 2.
Cyclic voltammograms of investigated electrodes in 50 μM 4-NP in 0.1 M BR buffer, pH 5, recorded at 20 mVs−1: (a) full potential range; (b) potential range for oxidation of 4-NP.
The enlarged area of the recorded CV in the potential range of the oxidation of 4-NP is presented in Figure 2b. The highest current was recorded at the BC electrode.
The oxidation mechanism of 4-nitrophenol involves proton–electron-coupled electron transfer [36], as presented in Equation (5):
The highest oxidation current was obtained for the BC sample, while the current response of BC-H was comparable with the that of Regal. According to the literature, the interaction of 4-NP with carbon surfaces can include several possible mechanisms: π-π interaction (interaction of the π electrons of the aromatic ring of phenols with electron-rich regions located in graphene layers of carbons) [37,38], hydrogen bonding between the hydroxyl group of 4-NP and various groups on the adsorbent surface [39], electrostatic repulsion and basic carbonyl surface groups forming a bond with the aromatic ring of phenol (donor–acceptor interaction) [40]. The dominant type of interaction depends on the properties of the electrode surface, as well as the pH of the solution and the presence of the other ions. Supong et al. [41] used the DFT calculation to estimate the interaction of 4-NP with variously activated biochar. They concluded that among the different functional groups on biochar (-OH, -CHO, -COOH), the -COOH group interacted most strongly with 4-NP. However, the influence of pH on the interaction between 4-NP and the surface group should be taken into account. The pKa of 4-NP is 7.15, and at pH 5 (the pH at which the experiments were performed), 4-NP exists primarily in its molecular form. On the other hand, the pKa of –COOH groups in biochar is between 4 and 6 [42]. At pH 5, most of the –COOH groups would be deprotonated, and electrostatic repulsion between –COO- and the benzene ring of 4-NP would greatly affect other attractive interactions.
Activation processes with NaOH, H2O2 and H3PO4 are expected to increase the presence of oxygenated species on the biochar surface, particularly –COOH groups. The lower peak currents recorded for the activated biochars are likely a consequence of the increased presence of –COOH groups. The shift of the peak potential for 4-NP oxidation toward more positive values observed for BC-N might indicate strong structural disorder that affects the conductivity of biochar, further hindering the charge-transfer process.
Untreated biochar may retain redox-active quinone-like moieties and a more intact microporous structure, both of which can facilitate electron transfer and enhance the electrochemical response. In contrast, chemical activation might disrupt these beneficial features or introduce excessive functional groups that reduce conductivity.
3.3. The Application for Heavy Metal Ion Detection
The applicability of conductive ink electrodes for the detection of heavy metals was tested using square wave voltammetry. Two methods were applied: (1) accumulation from a buffer solution at pH 5, followed by striping determination in 0.1 M HCl, and (2) direct determination in 1.0 M HCl containing heavy metal ions. In the first method, ion accumulation on the electrode surface was carried out from a 0.1 M (BR) buffer solution at pH 5 containing 10 μM Pb2+ ions. A well-defined peak of Pb2+ around −0.50 V vs. Ag/AgCl was observed in the SWV curves of most of the investigated electrodes (Figure 3a).
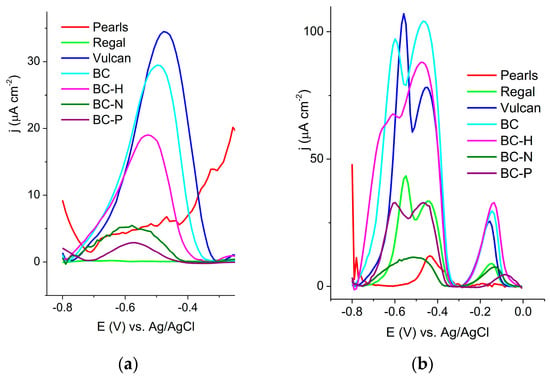
Figure 3.
Square wave voltammogram recorded on investigated electrodes (a) in 1.0 M HCl after accumulation of Pb2+ from 0.1 M BR buffer, pH 5, containing 10 μM Pb2+; (b) in 1.0 M HCl containing an equimolar concentration 10 μM of Pb2+and Cu2+.
The current response of different electrodes reflected the availability of binding sites for Pb2+ adsorption on the electrode surface of various carbons at pH 5. The best response was obtained with the Vulcan electrode, while the response of the BC electrode was comparable. The Pearls and Regal electrodes did not provide a measurable response. The BC-H electrode exhibited a good response, while the responses of BC-N and BC-P were measurable but low.
In the second approach, the SWV was recorded in 1.0 M HCl containing an equimolar concentration of Pb2+ and Cu2+ ions (Figure 3b). In this procedure, the adsorption of cations is governed by the applied potential. At a potential of −1.3 V vs. Ag/AgCl, water electrolysis commences (6):
creating a local alkaline environment. This resulting increase in pH might induce the deprotonation of surface groups, forming adsorption sites for positively charged metal cations [43,44].
The expected peaks corresponding to the oxidation of lead and copper can be observed at around −0.5 V and −0.15 V, respectively. An additional peak at approximately −0.45 V is visible for some electrodes; this peak originates from Cu2+ ions, accumulated through inter-metallic assemblies with lead [45]. The BC-N and Pearls electrodes showed a very low response. The response of BC was comparable to that of Vulcan, while BC-H showed the highest current for Cu2+.
4. Conclusions
Carbon black is an essential component of many electrochemical systems particularly battery and supercapacitor electrodes. Its function is to increase electrical conductivity and boost efficiency. In electrode material, carbon black facilitates effective electron transfer by acting as a conductive agent. However, carbon blacks are produced through the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, which poses challenges for sustainable chemistry. One of the sustainable alternatives is bio-based carbon blacks. In this study, biochar produced at 400 °C under moderate conditions—chosen to promote sustainability—from oak sawdust, either untreated or treated with activators, was tested as an electrode material. The results presented in this paper demonstrate that biochar can be a suitable alternative to carbon black, while good performance can be obtained through the proper choice of production procedure and electrode working conditions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/suschem6030021/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.M.; methodology, Z.M.; investigation, G.S., J.P., V.R. and Z.M.; data curation, M.A., N.J.-J. and Z.M.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.M.; writing—review and editing, M.A. and N.J.-J.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been financially supported by the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation of the Republic of Serbia (Contract No: 451-03-136/2025-03/200026). This work is correlated with the following UN Sustainable Development Goals: SDS 3, SDG 6 and SDG 12.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CV | Cyclic Voltammetry |
| SWV | Square Wave Voltammetry |
References
- Leppänen, E.; Etula, J.; Engelhardt, P.; Sainiod, S.; Jiang, H.; Mikladal, B.; Peltonen, A.; Varjos, I.; Lauril, T. Rapid industrial scale synthesis of robust carbon nanotube network electrodes for electroanalysis. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 896, 115255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, M.A.; Pérez-Ràfols, C.; Oliveira, F.M.; Sofer, Z.; Díaz-Cru, J.M.; Gusmão, R.; Serrano, N. Antimonene-Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Nanofibers Electrode for Enhanced Electroanalytical Response of Metal Ions. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, K.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ji, H. An ultrathin carbon layer activated CeO2 heterojunction nanorods for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 259, 118085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Liu, K.; Ye, K.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Hong, L. Constructing Fe-MOF-Derived Z-Scheme Photocatalysts with Enhanced Charge Transport: Nanointerface and Carbon Sheath Synergistic Effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 25494–25502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzyka, K.; Xu, G. Laser-induced Graphene in Facts, Numbers, and Notes in View of Electroanalytical Applications: A Review. Electroanalysis 2022, 34, 574–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fronczak, M.; Karoly, Z.; Bankovic, P.; Mojovic, Z. The influence of precursor selection on electrochemical properties of radiofrequency thermal plasma synthesized graphene. Microchem. J. 2024, 199, 110079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.; Fogel, R.; Purcarea, C.; Necula-Petrareanu, G.; Fanjul-Bolado, P.; Ibanez, D.; Vasilescu, A.; Maria Banciu, R.; Limson, J. Electrochemical characterization of carbon black in different redox probes and their application in electro-chemical sensing. Carbon Trends 2024, 17, 100408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicentini, F.C.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A.; Janegitz, B.C.; Machado, S.A.S.; Fatibello-Filho, O. Nanostructured carbon black for simultaneous sensing in biological fluids. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 227, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicentini, F.C.; Silva, T.A.; Fatibello-Filho, O. Carbon black electrodes applied in electroanalysis. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2024, 43, 101415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubura, J.; Kojić, P.; Ikonić, B.; Pavličević, J.; Govedarica, D.; Bera, O. Influence of biochar and carbon black on natural rubber mixture properties. Polym. Int. 2022, 71, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniyi, A.G.; Iwuozor, K.O.; Emenike, E.C.; Amoloye, M.A.; Aransiola, E.S.; Motolani, F.O.; Kayode, S.H. Prospects and problems in the development of biochar-filled plastic composites: A review. Funct. Compos. Struct. 2023, 5, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seroka, N.S.; Luo, H.; Khotseng, L. Biochar-Derived Anode Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Review. Batteries 2024, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinke, C.; de Oliveira, P.R.; Bonacin, J.A.; Janegitz, B.C.; Mangrich, A.S.; Marcolino-Junior, L.H.; Bergamini, M.F. State-of-the-art and perspectives in the use of biochar for electrochemical and electroanalytical applications. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Dong, X.; Ime, I.M.; Gao, B.; Ma, L.Q. Pyrolytic temperatures impact lead sorption mechanisms by bagasse biochars. Chemosphere 2014, 105, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas-Aguiar, E.; Gascó, G.; Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Méndez, A. The effect of biochar and compost from urban organic waste on plant biomass and properties of an artificially copper polluted soil. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 124, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Tian, W.; Zhao, J.; Zou, M.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, J. A comprehensive review of capacitive deionization technology with biochar-based electrodes: Biochar-based electrode preparation, deionization mechanism and applications. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.; Sokołowska, Z.; Boguta, P. Biochar physicochemical properties: Pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2020, 19, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, B.; Zubatiuk, T.; Leszczynska, D.; Leszczynski, J.; Chen, W.Y. Chemical activation of biochar for energy and environmental applications: A comprehensive review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2019, 35, 777–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Xiong, Q.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, S.; Li, H.; Huang, H. An overview on engineering the surface area and porosity of biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 144204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.; da Silva, L.P.; Rodrigues, P.M.S.M.; Esteves da Silva, J. Sustainable Technological Applications of Green Carbon Materials. Sustain. Chem. 2024, 5, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.C.B.D.; Evaristo, R.B.W.; Dutra, R.C.; Suarez, P.A.Z.; Silveira, E.A.; Ghesti, G.F. Advancing Biochar Applications: A Review of Production Processes, Analytical Methods, Decision Criteria, and Pathways for Scalability and Certification. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu El Haija, K.; Santos, R.M. Rethinking Biochar’s MRV Systems: A Perspective on Incorporating Agronomic and Organic Chemistry Indicators. Sustain. Chem. 2024, 5, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, F.; Bhagde, T.; Slaughter, D.S.; Zorba, V.; Stokes-Draut, J. Techno-economic and carbon dioxide emission assessment of carbon black production. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 436, 140224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Teng, F.; Chen, M.; Du, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, R.; Wang, P. Exploring negative emission potential of biochar to achieve carbon neutrality goal in China. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Ouyang, X.; Lv, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S. A Review of Carbon-Based Conductive Inks and Their Printing Technologies for Integrated Circuits. Coatings 2023, 13, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.; Al-Ahmadi, A.; Potts, S.J.; Claypole, T.; Deganello, D. The effect of graphite and carbon black ratios on conductive ink performance. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 9520–9530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cândido, T.C.d.O.; Pereira, A.C.; da Silva, D.N. Development and Characterization of Conductive Ink Composed of Graphite and Carbon Black for Application in Printed Electrodes. Analytica 2023, 4, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachioti, M.G.; Lazanas, A.C.; Prodromidis, M.I. Shedding light on the calculation of electrode electroactive area and heterogeneous electron transfer rate constants at graphite screen-printed electrode. Microchim. Acta 2023, 7, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavagnini, I.; Antiochia, R.; Magno, F. An Extended Method for the Practical Evaluation of the Standard Rate Constant from Cyclic Voltammetric Data. Electroanalysis 2004, 16, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCreery, R.L. Advanced carbon electrode materials for molecular electrochemistry. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2646–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, T.J.; Hyde, M.E.; Compton, R.G. Nanotrench arrays reveal insight into graphite electrochemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5121–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, J.F.; de Carvalho, R.C.; Betts, A.J. Use of Inner/Outer Sphere Terminology in Electrochemistry—A Hexacyanoferrate II/III Case Study. Electrochem 2023, 4, 313–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakout, S.M. Monitoring the Changes of Chemical Properties of Rice Straw–Derived Biochars Modified by Different Oxidizing Agents and Their Adsorptive Performance for Organics. Bioremediation J. 2015, 19, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Fan, S. Preparation of KOH and H3PO4 Modified Biochar and Its Application in Methylene Blue Removal from Aqueous Solution. Processes 2019, 7, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, C.; Xing, X.; Chen, L.; Yao, B.; Chao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Dong, J.; Liu, C.; et al. Interconnected pyrolysis and activation with in-situ H3PO4 activation of biochar from pear wood chips in a pilot scale dual fluidized bed. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žunić, M.J.; Milutinović-Nikolić, A.D.; Stanković, D.M.; Manojlović, D.D.; Jović-Jovičić, N.P.; Banković, P.T.; Mojović, Z.D.; Jovanović, D.M. Electrooxidation of p-nitrophenol using a composite organo-smectite clay glassy carbon electrode. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 313, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.; Arafat, H.A.; Pinto, N.G. Effect of chemical heterogeneity on the adsorption mechanism of dissolved aromatics on activated carbon. Carbon 2000, 38, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xuan, F.; Guo, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Wu, L. Rapid and efficient adsorption of p-nitrophenol over biomass-derived vertically aligned graphene nanosheets fabricated by hydrothermal/molten salt-assisted pyrolysis method. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 129368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Gou, X.; Fanga, S.; Chang, C.; Li, H.; Han, X. Adsorption of p-nitrophenol on activated carbon derived from the lignin of cellulosic ethanol by-product. Rev. Roum. de Chim. 2018, 63, 1135–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Haydar, S.; Ferro-García, M.A.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Joly, J.P. Adsorption of p-nitrophenol on an activated carbon with dif-ferent oxidations. Carbon 2003, 41, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supong, A.; Bhomick, P.C.; Sinha, U.B.; Sinha, D. A combined experimental and theo-retical investigation of the adsorption of 4-Nitrophenol on activated biocarbon using DFT method. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 2023–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, B. Proton uptake behaviors of organic and inorganic matters in biochars prepared under different pyrolytic temperatures. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 140853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.P.; White, H.S. Voltammetry of molecular films containing acid/base groups. Langmuir 1993, 9, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, I.; Seivewright, B.; Bruce Lennox, R. Electric field driven protonation/deproton ation of self-assembled monolay-ers of acid-terminated thiols. Langmuir 2006, 22, 4420–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Ali, A.; Jamal, R.; Simayi, R.; Xiang, L.; Ding, S.; Abdiryim, T. Poly(EDOT-pyri dine-EDOT) and poly(EDOT-pyridazine-EDOT) hollow nanosphere materials for the electrochemical detection of Pb2+ and Cu2+. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 822, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).