Swarm Drones with QR Code Formation for Real-Time Vehicle Detection and Fusion Using Unreal Engine
Abstract
1. Introduction
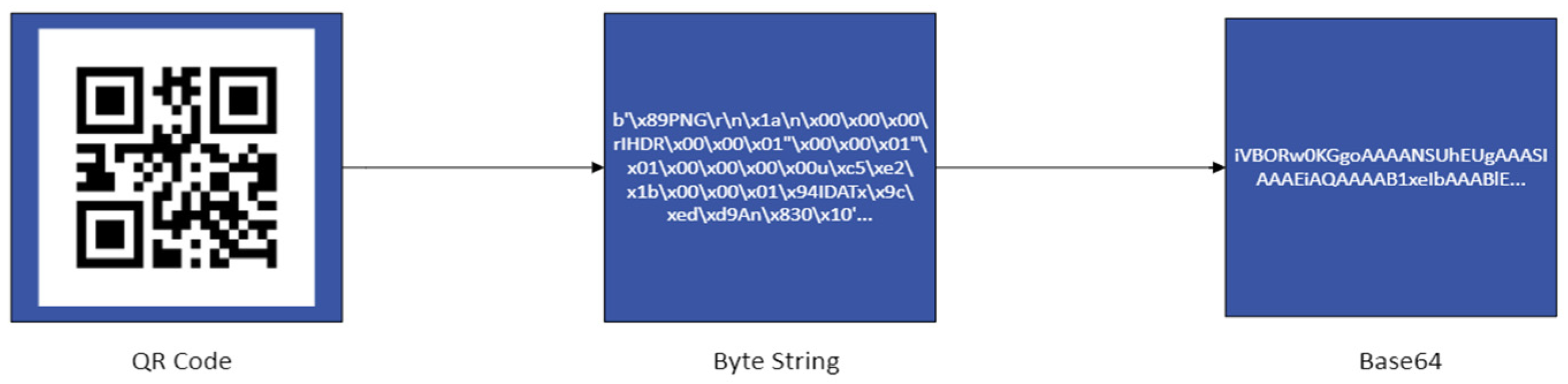
- Implementation of multi-drone formation control strategy, where drones follow each other using a QR code.
- Deployment of onboard cameras coupled with YOLOv8 for real-time vehicle detection using two types of distinct experiments.
- The detection results were fused using a combination of temporal, probabilistic, and geometric fusion methods to obtain more reliable and accurate outputs.
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Unreal Engine
3.2. Microsoft AirSim
4. System Architecture
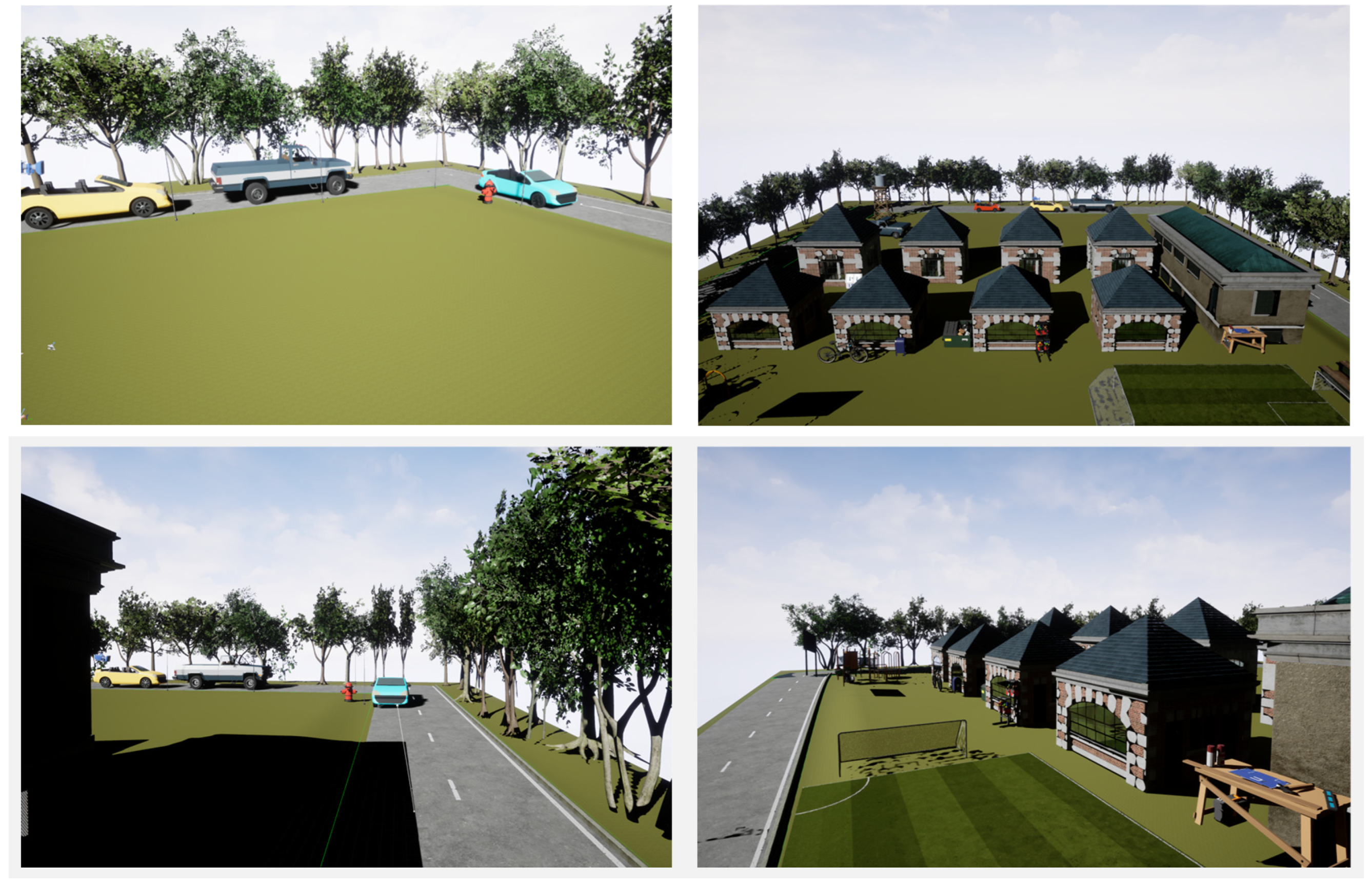
4.1. Environment
4.2. Drone Tracking
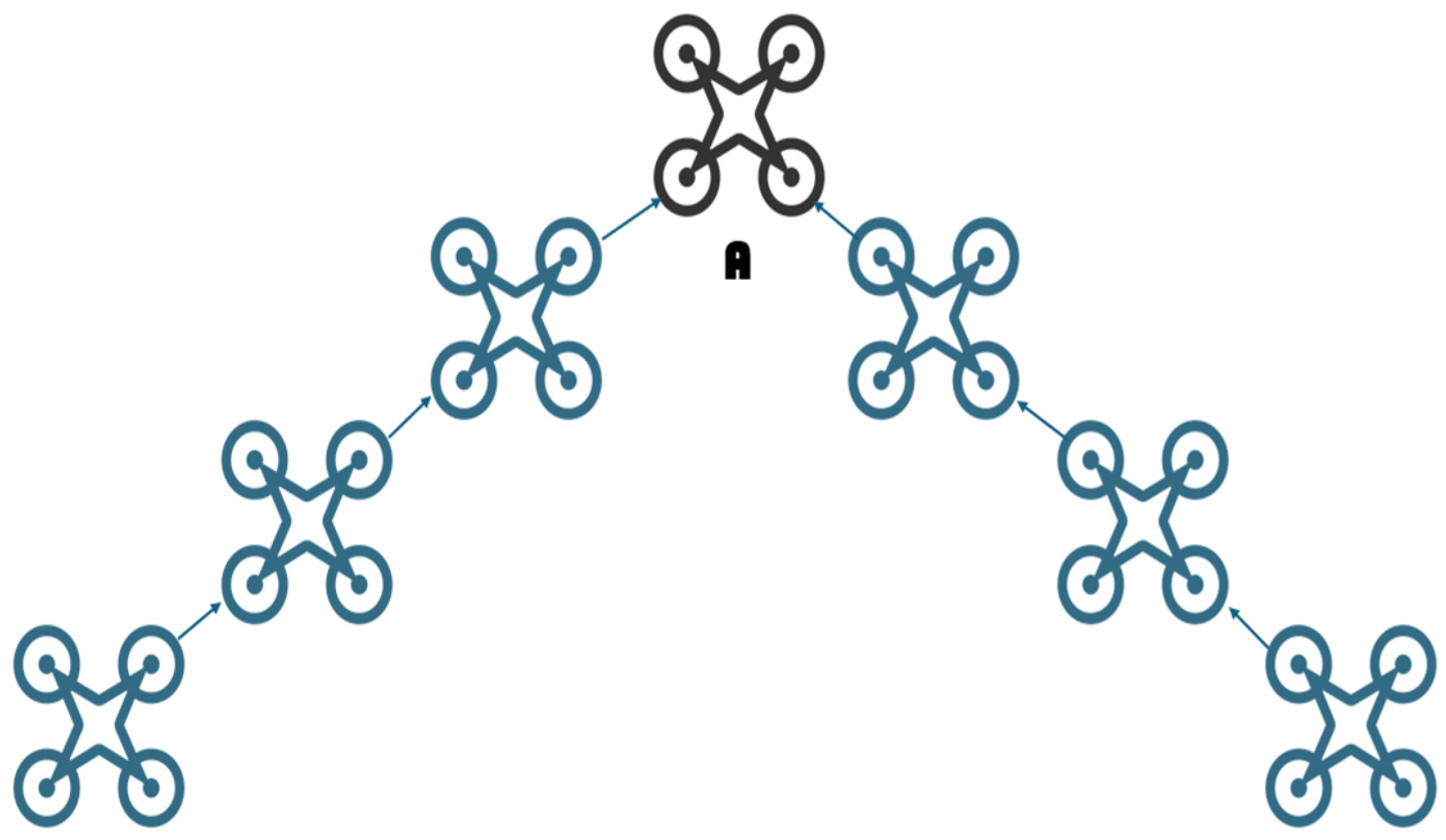
4.3. Drone Formation Strategy
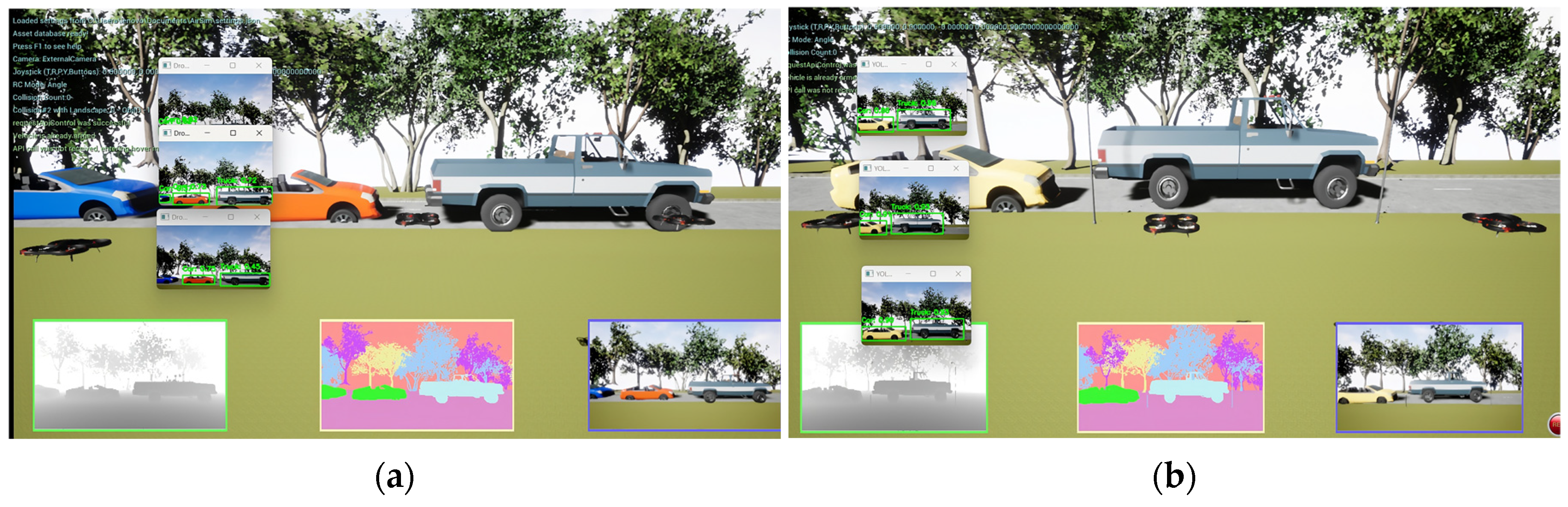
4.4. Vehicle Detection
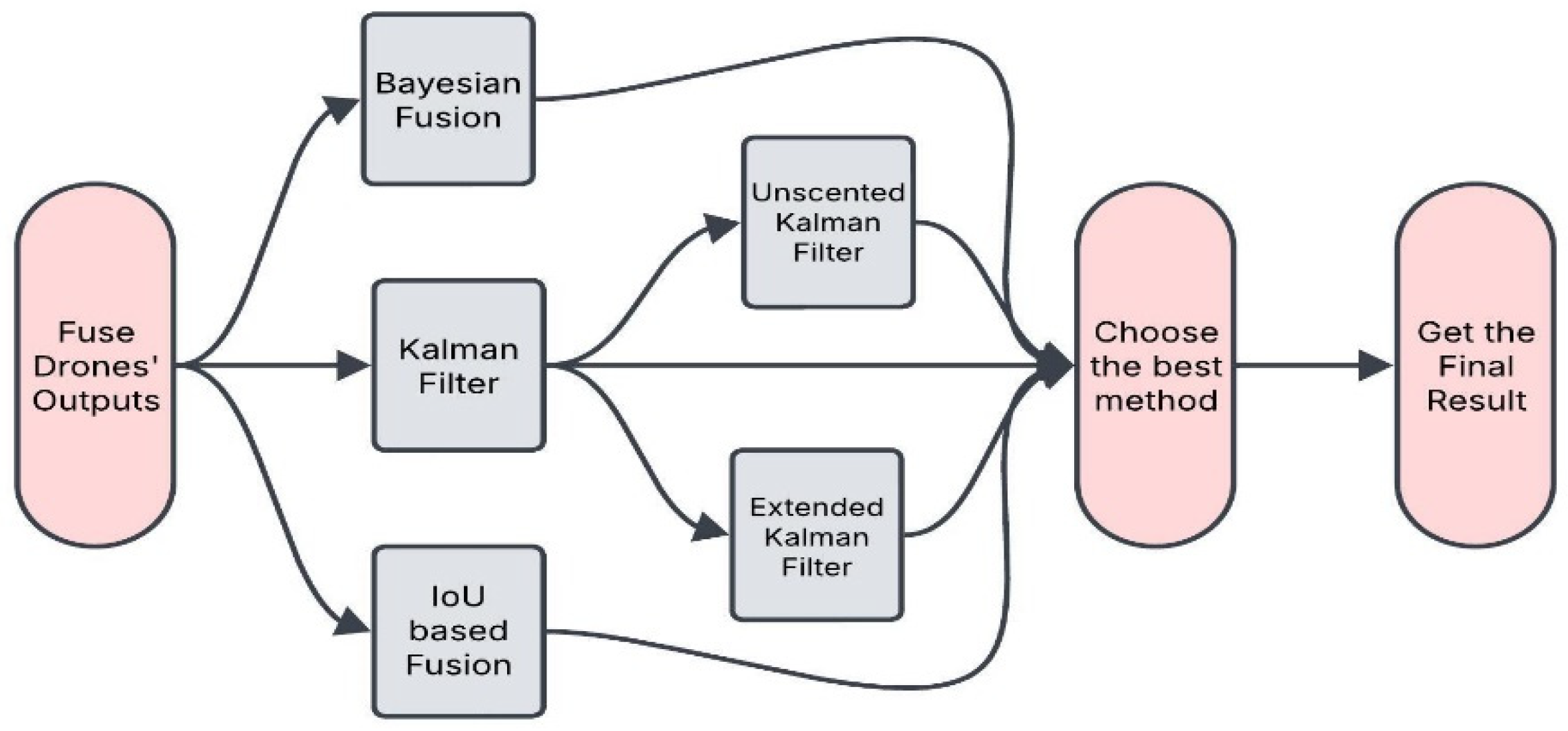
4.5. Fusion Methodology
5. Results and Evaluation Metrics
5.1. Simulation Setup
5.2. Communication Evaluation
- Sent rate is a fraction of the successful transmitted packets to the total number of packets attempted.
- Decode success is a fraction of successful message reconstruction (Follow_Leader_1) to the total number of trails.
- Corruption rate is a fraction of corrupted packets, where bits are flipped by the BER model, relative to the total number of sent packets.
- Latency is the time it takes from the moment the packet is sent until the followers receive and decode it. Both mean and 95th percentile latency was considered.
5.3. Formation Evaluation
- Mean error is the average difference between the correct position and the estimated one. A lower mean error means the system is more accurate.
- Standard deviation (std) is the consistency of the formation error. A lower std value indicates more stable and predictable behaviors.
- Max error is the worst-case deviation observed during the experiments. It shows the extreme mistakes that follower drones make. A lower max error is better for avoiding collision and keeping the format without losing the track.
5.4. Experiments Using Synthetic Drone Dataset
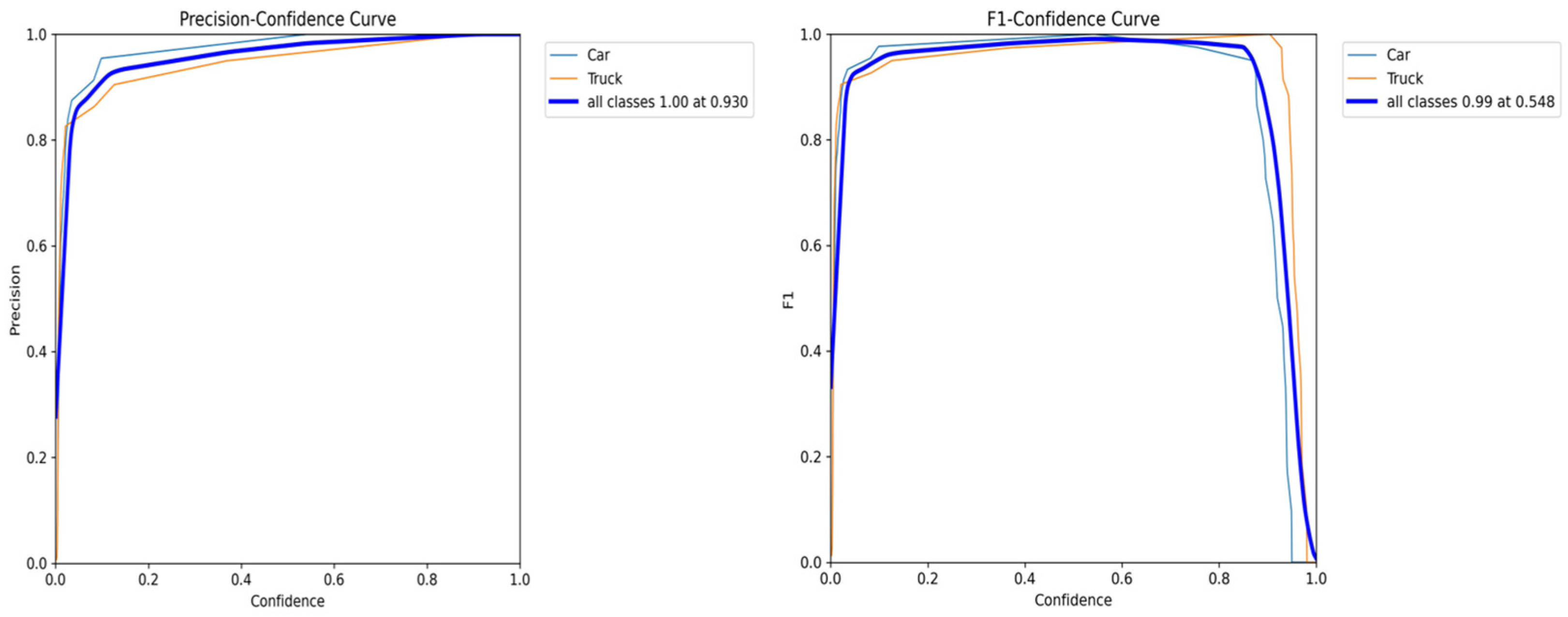
5.5. Detection Evaluation
5.6. Fusion Evaluation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohsan, S.A.H.; Khan, M.A.; Noor, F.; Ullah, I.; Alsharif, M.H. Towards the unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs): A comprehensive review. Drones 2022, 6, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bappy, A.; Asfak-Ur-Rafi, M.; Islam, M.S.; Sajjad, A.; Imran, K.N. Design and Development of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (Drone) for Civil Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, BRAC University, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinov, I.; Petrovsky, A.; Ilin, V.; Pristanskiy, E.; Kurenkov, M.; Ramzhaev, V.; Idrisov, I.; Tsetserukou, D. Warevision: CNN barcode detection-based UAV trajectory optimization for autonomous warehouse stocktaking. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 6647–6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Liang, Q.; Luo, J. Enhanced multi-UAV formation control and obstacle avoidance using IAAPF-SMC. Drones 2024, 8, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enwerem, C.; Baras, J.; Romero, D. Distributed optimal formation control for an uncertain multi-agent system in the plane. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.05841. [Google Scholar]
- Alkouz, B.; Bouguettaya, A.; Mistry, S. Swarm-based Drone-as-a-Service (SDAAS) for delivery. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Web Services (ICWS), Beijing, China, 19–23 October 2020; pp. 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Skobelev, P.; Budaev, D.; Gusev, N.; Voschuk, G. Designing multi-agent swarm of UAV for precise agriculture. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Practical Applications of Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, Toledo, Spain, 20–22 June 2018; pp. 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, C.; Albani, D.; Magistri, F.; Ognibene, D.; Stachniss, C.; Kootstra, G.; Nardi, D.; Trianni, V. Monitoring and mapping of crop fields with UAV swarms based on information gain. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Distributed Autonomous Robotic Systems, Kyoto, Japan, 1–4 June 2021; pp. 306–319. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, H.; Kim, D.; Park, J.; Roh, K.; Hwang, W. 2D barcode detection using images for drone-assisted inventory management. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots (UR 2018), Honolulu, HI, USA, 26–30 June 2018; pp. 461–465. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, L.Y.; Yiu, C.H.; Tang, Y.; Yang, A.S.; Li, B.; Wen, C.Y. Dynamic object tracking on autonomous UAV system for surveillance applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheal, A.A.; Vani, K.; Sanjeevi, S.; Lin, C.H. Object detection and tracking with UAV data using deep learning. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2021, 49, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Har, D.; Kum, D. Drone-assisted disaster management: Finding victims via infrared camera and LiDAR sensor fusion. In Proceedings of the 3rd Asia-Pacific World Congress on Computer Science and Engineering (APWC on CSE), Nadi, Fiji, 5–6 December 2016; pp. 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Catala-Roman, P.; Segura-Garcia, J.; Dura, E.; Navarro-Camba, E.A.; Alcaraz-Calero, J.M.; Garcia-Pineda, M. AI-based autonomous UAV swarm system for weed detection and treatment: Enhancing organic orange orchard efficiency with Agriculture 5.0. Internet Things 2024, 28, 101418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campion, M.; Ranganathan, P.; Faruque, S. UAV swarm communication and control architectures: A review. J. Unmanned Veh. Syst. 2018, 7, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqudsi, Y.; Makaraci, M. UAV swarms: Research, challenges, and future directions. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2025, 72, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrit, O.; Martin, S.; Alagha, K.; Pujolle, G. A new approach to realize drone swarm using ad-hoc network. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual Mediterranean Ad Hoc Networking Workshop (Med-Hoc-Net), Budva, Montenegro, 28–30 June 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chiun, J.; Tan, Y.R.; Cao, Y.; Tan, J.; Sartoretti, G. STAR: Swarm technology for aerial robotics research. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 29 October–1 November 2024; pp. 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, S.; Jeon, J.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y. Swarm reconnaissance drone system for real-time object detection over a large area. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 23505–23516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirkal, J. Drone Simulation Using Unreal Engine. 2020. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Drone-Simulation-Using-Unreal-Engine-Jirkal/969501f3291e182ceda34a5062c7c70a2ef2b130 (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Madaan, R.; Gyde, N.; Vemprala, S.; Brown, M.; Nagami, K.; Taubner, T.; Cristofalo, E.; Scaramuzza, D.; Schwager, M.; Kapoor, A. Airsim drone racing lab. In Proceedings of the NeurIPS 2019 Competition and Demonstration Track, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 177–191. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.; Dey, D.; Lovett, C.; Kapoor, A. Airsim: High-fidelity visual and physical simulation for autonomous vehicles. In Field and Service Robotics: Results of the 11th International Conference; Springer: London, UK, 2017; pp. 621–635. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, Y.; Dillmann, R.; Roennau, A.; Xiong, Z. E-DQN-based path planning method for drones in AirSim simulator under unknown environment. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.H.; Toman, H. Stochastic fusion techniques for state estimation. Computation 2024, 12, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.H.; Sadri, F. Datafusion: Taking source confidence into account. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (ICIST), Istanbul, Turkey, 16–18 March 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]

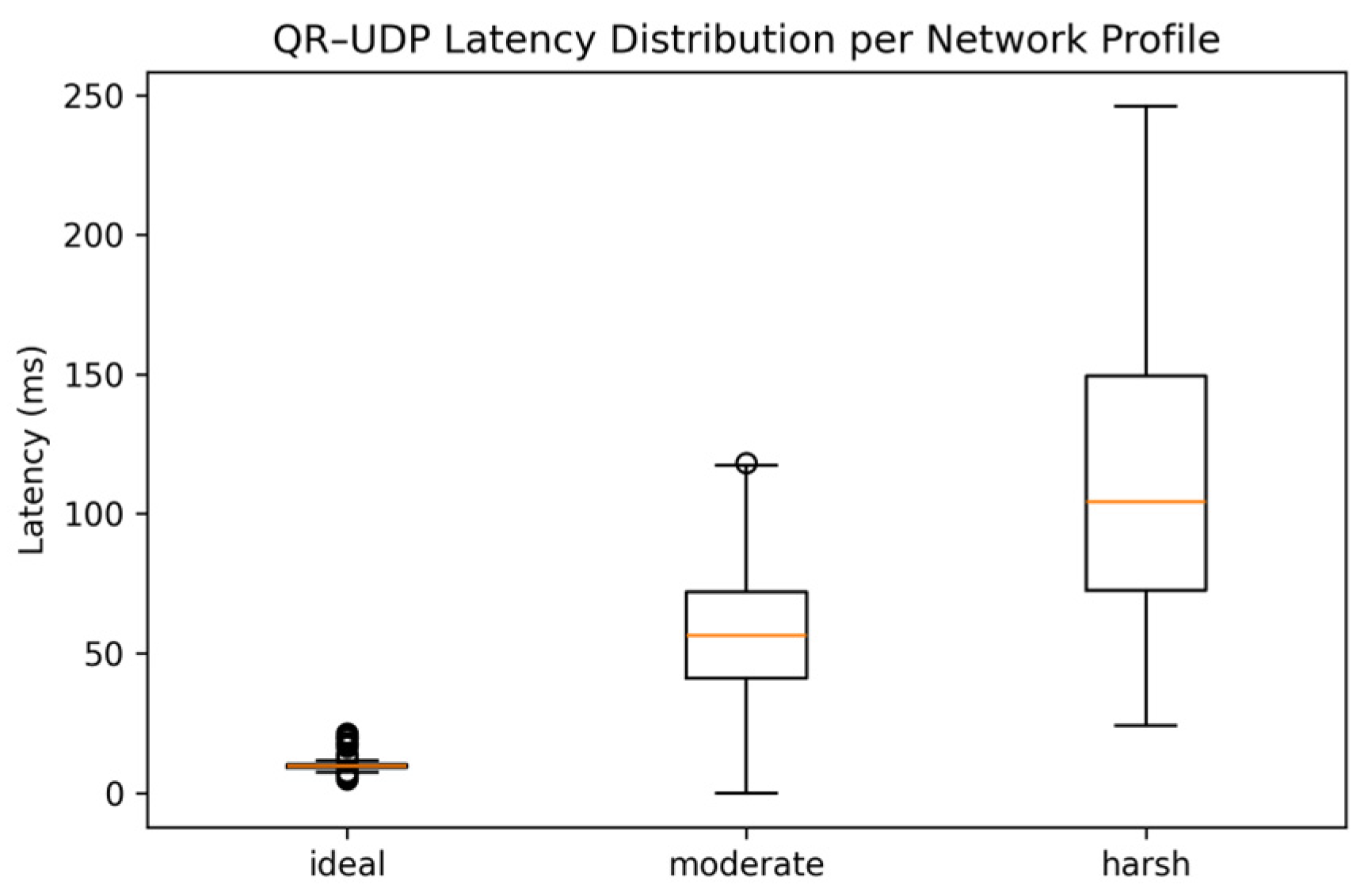

| Profile | Sent Rate | Decode Success | Corruption Rate | Mean Latency (s) | 95th% Latency (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ideal | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.0000 | 0.0100 | 0.0140 |
| Moderate | 0.940 | 0.938 | 0.0025 | 0.0582 | 0.0885 |
| Harsh | 0.818 | 0.795 | 0.0225 | 0.1105 | 0.1979 |
| Profile | Mean Error | Std | Max Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ideal | 0.798 | 0.368 | 1.861 |
| Moderate | 0.906 | 0.950 | 8.645 |
| Harsh | 1.061 | 1.084 | 8.589 |
| Drone ID | Using COCO Model | Using Our Trained Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Confidence Score of Detecting Cars | Confidence Score of Detecting Trucks | Confidence Score of Detecting Cars | Confidence Score of Detecting Trucks | |
| Done1 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.91 | 0.92 |
| Drone2 | 0.61 | 0.66 | 0.90 | 0.91 |
| Drone3 | 0.79 | 0.54 | 0.90 | 0.91 |
| Fusion Techniques | Precision Using COCO Dataset | Precision Using Synthetic Dataset | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Threshold 0.5 | Threshold 0.3 | Threshold 0.5 | Threshold 0.3 | |
| Kalman Filter | 0.7143 | 0.8000 | 0.7500 | 0.8750 |
| Extended Kalman Filter | 0.3571 | 0.4444 | 0.7500 | 0.8750 |
| Unscented Kalman Filter | 0.6154 | 0.7273 | 0.7500 | 0.8750 |
| Bayesian Fusion | 0.6429 | 0.7778 | 0.800 | 0.7500 |
| IoU-Based Fusion | 0.3448 | 0.4091 | 0.800 | 0.6250 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, A.H.; Tomán, H. Swarm Drones with QR Code Formation for Real-Time Vehicle Detection and Fusion Using Unreal Engine. Automation 2025, 6, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation6040087
Ahmed AH, Tomán H. Swarm Drones with QR Code Formation for Real-Time Vehicle Detection and Fusion Using Unreal Engine. Automation. 2025; 6(4):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation6040087
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Alaa H., and Henrietta Tomán. 2025. "Swarm Drones with QR Code Formation for Real-Time Vehicle Detection and Fusion Using Unreal Engine" Automation 6, no. 4: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation6040087
APA StyleAhmed, A. H., & Tomán, H. (2025). Swarm Drones with QR Code Formation for Real-Time Vehicle Detection and Fusion Using Unreal Engine. Automation, 6(4), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation6040087






