- Article
Adaptive Thermostat Setpoint Prediction Using IoT and Machine Learning in Smart Buildings
- Fatemeh Mosleh,
- Ali A. Hamidi and
- Md Atiqur Rahman Ahad
- + 1 author
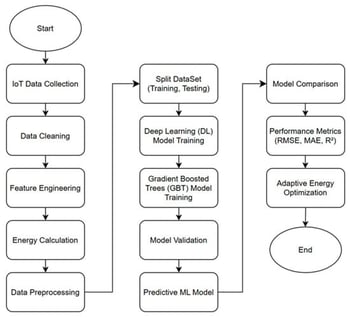
Increased global energy consumption contributes to higher operational costs in the energy sector and results in environmental deterioration. This study evaluates the effectiveness of integrating Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and machine learning techniques to predict adaptive thermostat setpoints to support behavior-aware Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) operation in residential buildings. The dataset was collected over two years from 2080 IoT devices installed in 370 zones in two buildings in Halifax, Canada. Specific categories of real-time information, including indoor and outdoor temperature, humidity, thermostat setpoints, and window/door status, shaped the dataset of the study. Data preprocessing included retrieving data from the MySQL database and converting the data into an analytical format suitable for visualization and processing. In the machine learning phase, deep learning (DL) was employed to predict adaptive threshold settings (“from” and “to”) for the thermostats, and a gradient boosted trees (GBT) approach was used to predict heating and cooling thresholds. Standard metrics (RMSE, MAE, and R2) were used to evaluate effective prediction for adaptive thermostat setpoints. A comparative analysis between GBT ”from” and “to” models and the deep learning (DL) model was performed to assess the accuracy of prediction. Deep learning achieved the highest performance, reducing the MAE value by about 9% in comparison to the strongest GBT model (1.12 vs. 1.23) and reaching an R2 value of up to 0.60, indicating improved predictive accuracy under real-world building conditions. The results indicate that IoT-driven setpoint prediction provides a practical foundation for behavior-aware thermostat modeling and future adaptive HVAC control strategies in smart buildings. This study focuses on setpoint prediction under real operational conditions and does not evaluate automated HVAC control or assess actual energy savings.
5 February 2026