Abstract
The possibility of applying biochar in mild torrefaction treatment to improve the thermochemical characteristics of ground biomass was the focus of the study. Camelina straw and switchgrass were torrefied in a reactor using microwave irradiation at torrefaction temperatures of 250 °C and 300 °C with residence times 10, 15 and 20 min, under nitrogen-activated inert conditions. Both biochar addition of more than 10% and residence time significantly affected the product yields, as MW torrefaction temperatures shifted from 250 °C to 300 °C. Overall, the results indicated a slight increase in ash content, mass loss percentage intensification, heating values, and fixed carbon, while moisture content and volatile matter decreased in camelina straw and switchgrass, with or without biochar. Biochar addition with a long residence time (20 min) at 250 °C reduced energy requirement during the microwave torrefaction process. The combustion index values showed that torrefied camelina straw or switchgrass with biochar addition suits co-combustion with coal in a coal-fired plant and is a potential biomaterial for biofuel pellets.
1. Introduction
Sustainable renewable energy sources from biomass can provide energy-dense fuel with lower carbon emissions and a greener environment than fossil fuel and coal [1,2]. Notably, fossil fuel deposits are abundantly found in specific regions of the globe [3]. The increase in energy demand is due to urbanization, technological advancement, and improved living standards [4]. Many energy sources from fossil fuels are utilized to serve the global demand for energy, contributing to substantial environmental pollution. The search for alternative energy in the last two decades has shifted from second-generation (cellulosic biomass from crop/forest residues/dedicated energy crops) to third-generation feedstocks (microalgae and seaweed) [5]. Fossil fuels have been abundant in particular regions, but biomass is scattered globally and is seasonally available, depending on location. Biomass residues and waste are produced globally as by-products of agricultural, forestry, and industrial sectors, as feedstock varieties and alternative biomass, and representing huge resources for the bioeconomy. Biomass is biodegradable, and a significant source of renewable organic matter. Thus, lignocellulosic biomass characteristics have encouraged the research and development of sustainable bioenergy and bioproducts, helping to solve some environmental problems, reduce waste and possibly generate clean and renewable energy [5,6]. Different techniques have been developed for lignocellulosic biomass conversion into bioproducts in the past few years. These various pretreatment techniques depolymerize biomass lignin and disintegrate the recalcitrant structure for conversion into energy or fuel [7]. The raw biomass is structurally heterogeneous and resistant to biological attack and biodegradation, making it challenging to convert into bioenergy and products [8]. Consequently, the physical and chemical properties limit the utilization of agricultural residues and wastes, and woody and other biomass, for energy applications [9].
Microwave (MW) torrefaction is one of the thermo-chemical processes developed over the years. Many studies on MW torrefaction of agricultural/forest residues/wastes and woody biomass have been reported, indicating conversion benefits and successful process results [10,11,12]. MW torrefaction presents many advantages over traditional electric heaters, such as selective and controllable heating without direct contact with the heated biomass [13,14,15]. Agu et al. [16] highlighted the fact that very few studies focused on MW-torrefaction, but more successful studies have been carried out on MW-pyrolysis of wood than on agricultural and forest residues. The torrefaction process removes moisture in biomass, decomposes hemicellulose into volatiles, and dehydrates and partially decomposes cellulose and lignin [17]. Many studies reported that torrefied biomass has superior characteristics compared with raw biomass. The efficacy of MW pyrolysis is dependent upon the operating conditions for product recovery. These factors include temperature, MW power level, and MW absorber addition [15,18]. The current study is anticipated to address the drawbacks of using agricultural wastes or residues as a substitute for coal, and to show how the combination of process/material variables (MW torrefaction) could help improve their fuel properties.
Biochar is a by-product thermo-chemically produced from biomass and forestry residues, and could be used as an MW absorber during biomass torrefaction for low MW energy consumption [16,19]. Biochar application and utilization are essential for agricultural and environmental benefits and for improving the environmental sustainability in thermo-chemical conversions. The anticipated effect of biochar addition during MW torrefaction is the reduction of energy consumption during the process [20]. Many studies reported that MW absorbers could enhance severe torrefaction reaction temperature at very low MW power and improve process energy efficiency and product yields such as bio-oil, solid yield, and bio-gas under different treatment conditions [19,21,22]. Ethaib et al. [15] highlighted the fact that an MW absorber could increase torrefaction temperatures, giving heat to biomass and possibly affecting the quality of the solid yield. Apart from biochar sourced from forest residues and wastes, industrial bio-waste materials (palm kernel shell activated carbon, coconut activated carbon and petroleum coke) could be used as MW absorbers. Thus, the results reported improved heating rate of particles by reducing the drying process [19]. Agu et al. [16] highlighted the fact that torrefied biomass with biochar (250 °C at 15 min) enhanced the fuel properties of wheat and barley straws and could be blended with coal in a coal-fired plant. Ethaib et al. [15] and Li et al. [19] highlighted some advantages of MW absorbers, such as easily mixing with biomass and forming a more uniform mixture, having no after-use problems or disposal challenges, and the ability to be recycled to save costs in the MW torrefaction system. The characterization and properties of biomass with or without MW absorbers differ under various pyrolysis conditions. The analysis depends on feedstock, reactor configurations, and process parameters [19].
Extensive research studies have been carried out, and more are still ongoing with switchgrass and camelina straw for the advancement and sustainability in fuel pellets development, for bioheat and bioethanol production and use as feedstocks for the bio-industry in Canada [23]. Ground camelina straw and switchgrass were torrefied using biochar as an MW absorber to check the suitability; thus, torrefied biomass-biochar as a better quality solid biofuel or blend with coal. The effect of biochar addition and residence time during torrefaction was investigated. The impact on product yields, characterizing physico-chemical properties and energy consumption at two MW power levels (520 W and 650 W) were determined. Furthermore, the torrefied camelina straw and switchgrass with and without biochar were characterized by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and surface morphology examination.
2. Materials and Methods
Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC) Saskatoon Research and Development Centre Farm supplied camelina straw (CS). Switchgrass (SG) of a variety “Cave-in-rock” was harvested from the Nappan farm in Nova Scotia, Canada. Commercial biochar from forest residues collected from soil-matrix was sourced from AirTerra (Calgary, AB, Canada) and ground with a 3 mm screen size. CS and SW were ground using a hammer mill (Serial no. 6M13688; Glen Mills Inc., Maywood, NJ, USA) with a screen size of 6.4 mm, to increase the surface area of the biomass. The ground samples were mixed with biochar (at weight percent), and they were stored in air-tight Ziploc bags. The proximate analysis values of the samples are important for biomass energy application. Remarkably, the as-received samples, CS or SG volatile matter and ash values show evidence of potential higher calorific value and good heating rate (Table 1).

Table 1.
Properties of camelina straw, switchgrass and biochar.
2.1. Microwave Torrefaction Treatment
The experimental plan and analysis are summarized in Figure 1. Batch torrefaction tests were performed using the MW irradiation technique, and all the experiments were replicated three times (Figure 2). Before the MW torrefaction batch process, ground CS or SG was mixed with biochar at different percent (0%, 10% and 20%) weights. A custom-made cylindrical quartz container was used as the reactor. A lip was placed on top of the container, using a close-fitting high-temperature gasket between high-temperature plastic tape to seal the container, making it air-tight. The experimental setup was conducted on a benchtop MW oven with 2.45 GHz (LBM 1.2A/7296, Cober Electronics Inc., Stamford, CT, USA). The temperature sensor was covered with a Teflon tube throughout the experiment and inserted in the middle port to measure the heat distribution in the reactor. The MW temperature and power data were recorded continuously on a laptop computer using real-time graphing and data logging software (OSENSA Innovations Corp. Coquitlam, BC, Canada) [16]. Approximately 100 ± 0.02 g biomass-biochar mixture was placed in the reactor (cylindrical quartz container) for each experiment.
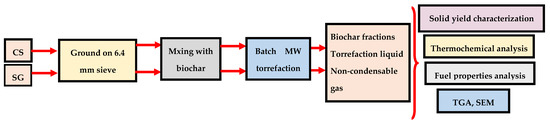
Figure 1.
Experimental plan for microwave (MW) torrefaction of camelina straw (CS) and switchgrass (SG).
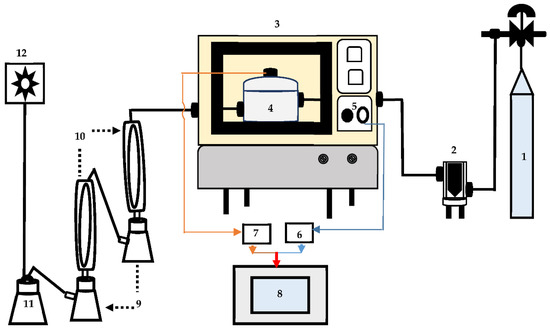
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the microwave torrefaction. (1) Nitrogen gas tank; (2) gas meter; (3) microwave oven; (4) quartz reactor; (5) microwave control panel; (6) power logger; (7) temperature transmitter; (8) recording computer; (9) torrefaction liquor collector; (10) gas condensers; (11) smoke trap; (12) exhaust fan.
The MW oven was turned on, and MW power was varied between 520 to 650 W. Once the biomass-biochar mixture (0%, 10%, and 20% added biochar) reached the desired reaction temperature (250 °C and 300 °C), at residence times of 10, 15, or 20 min, the MW oven was turned off to maintain moderate and mild torrefaction [16]. The process was carried out in triplicate for each sample; the solid fraction was allowed to cool at room temperature and stored in Ziploc bags until needed.
2.2. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
The effect of two independent variables (biochar addition and residence time) on the responses (solid yield, MW energy consumption, and heating value) treated at two MW power levels (520 W and 650 W) was studied using a user-defined design (UDD) of response surface methodology (RSM) of the Minitab software (Version 20.3; eBase Solutions Inc., Vaughan, ON, Canada). The experimental design was a collection of mathematical and statistical techniques for designing experiments, analyzing the effects of variables, building models and optimizing the process variables for optimum response. A polynomial quadratic model was fitted to evaluate the impact of each independent variable on the response shown in Equation (1):
where Y is the response studied by UDD, β0 is the offset term, X1 and X2 are the real variables (biochar addition and residence time, respectively), β1 and β2 are the linear coefficients, β11 and β22 are the quadratic coefficients, and β12 is the interaction effects between X1 and X2 on the response. The UDD technique was used with minimum experimental runs to establish a correlation among independent and response variables. Eighteen experimental runs were performed for each CS or SG sample.
2.3. Product Yield and Thermochemical Analysis
The literature reviews show that increasing torrefaction temperature and residence time decreases solid fraction with increased carbon content causing pore widening and structural ordering on the chars [15]. After each heating cycle, the condensed materials were collected using a water-condenser system, including a five-half-meter-long parallel bulb condenser connected to a conical flask as a torrefaction liquid collector. The torrefaction liquid analysis is not reported in the current paper. However, the weight of noncondensable gas was evaluated based on the mass balance in Equation (2):
Noncondensable gas (% wt.) = 100 − (biochar + torrefaction liquid)
The untorrefied and torrefied CS or SG with and without biochar were analyzed for ash content using the National Renewable Energy Laboratory standard NREL/TP-510-42618 [24], and for moisture content using ASABE standards S358.2 [25]. Elemental composition analysis was carried out using a Vario EL cube CHNS elemental analyzer (Elementar Americas, Inc., Ronkonkoma, NY, USA). The volatile matter was determined according to ASTM D5142, and HHV was calculated based on elemental analysis [16]. The combustion indices (fuel ratio, combustibility index, and volatile ignitability) were calculated [26]:
where SY = solid yield (%), EY = energy yield (%), HHV = higher heating value (MJ/kg), CI = combustibility index (MJ/kg), VI = volatile ignitability (MJ/kg), FC = fixed carbon (% d.b.), MC = moisture content (% d.b.), VM = volatile matter (% d.b.), A = ash content (% d.b.), C = carbon (% d.b. ?), H = hydrogen (%), S = sulfur (%), O = oxygen (%), N = nitrogen (%)
2.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Confocal Microscopy
The TGA of untorrefied and torrefied CS and SG with and without biochar was performed using Q500 equipment (TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA). Each run, approximately 15 mg, was heated from ambient temperature to 600 °C at the constant ramp rate of 10 °C/min under nitrogen flow in the range of 40 mL/min and 60 mL/min throughout the analysis. The difference in the weight of the sample under controlled heating and devolatilization was calculated as the weight loss. A scanning electron microscope (SEM Phenom-World, Eindhoven, Netherlands) was used to observe the physical changes in the raw and torrefied biomass [27]. Laser-scanning confocal microscope ZEN imaging software (Zeiss LSM 880 with AxioObserver; Carl Zeiss Microscopy, LLC, White Plains, NY, USA) was used to visualize and obtain accurate reflectance imaging using a 10x magnifying lens with size x:425.10/y: 425.10 tiles. Since dried samples were used, the excitation and emission wavelengths were set at 405 m and 484 m, respectively [28]. The image examination investigated the degree of heat distortion and damage to the biomass structure due to MW torrefaction. The patterns of surface structural opening during torrefaction at different severity were evaluated using the ZEN 3.5 Lite 2.5D display (Carl Zeiss Microscopy, LLC, White Plains, NY, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Statistical Analysis and Effect of the Response Variables
The statistical significance of the response for the quadratic models of solid yield, MW energy consumption, and HHV from torrefied CS or SG with and without biochar was estimated using the RSM analysis of variance (ANOVA). Effects of the operating and response variables are presented in the supplementary material Tables S1 and S2. The data showed the significant effect of the biomass-biochar mixture and residence time at different MW power levels on the response variables. The coefficient of determination (R2) values ranged between 0.98 and 0.99 and the corresponding R2 adjusted and predicted, indicated that the developed models reliably estimated the relation between the independent and response variables. The coefficient of variation (CV in %) measured the residual variation of data relative to the mean value. The higher the CV, the lower the experiment’s reliability [16]. The response variables indicated low CV values, indicating greater reliability of the experiments. Thus, they could be used for design and scale-up. Overall, the corresponding p-values of A, B, AB, A2, and B2 satisfied the significance, and the two coding factors at different MW power levels affected the responses. Li et al. [19] reported that MW absorbers such as biochar had the potential to improve torrefaction temperature at relatively low MW power. The effectiveness and relationship of coded variables on solid yield, MW energy consumption, and HHV were expressed using RSM three-dimensional (3D) contour plots, to evaluate the interaction between experimental factors and fitness of the obtained model at different MW power levels: Figures S3 and S4a–c.
The 3D contour plots demonstrate the nature of the response surfaces. Each feedstock used in this study displayed different curve plots in response to variable interactions. The results indicated that the torrefied CS or SG with biochar-mix solid yield decreased with increased biochar weight fraction at longer residence time and higher MW power. The curves (Figures S1 and S2 in the Supplementary data) revealed that the extent of mass fraction retained after moderate and severe torrefaction and the mass yield, depended on the type of feedstock used. Biochar addition and longer residence time resulted in less energy usage for the torrefaction of CS or SG (the lighter green color partition) in lower MW power. The combined effect of independent variables reflected in the curved-shaped 3D contour plots on energy consumption indicates higher biochar at the edges, lower energy consumption in the middle, and more energy at the border (zero biochar addition). This implies that biochar addition (>10%) and torrefaction residence time could produce a reliable synergistic effect. However, torrefied CS or SG without biochar increased the MW energy consumption (the intense green color partition). Overall, biochar addition had the most significant effect on the production of the torrefied biochar fraction and as an activator or absorber during biomass thermal conversion. On the other hand, HHV curves reflect the behavior of CS or SG char fractions, showcasing the high HHV values of torrefied CS or SG without biochar. Nanda et al. [29] reported that total energy in biomass was the same, irrespective of the conversion technique. However, to an extent, the form and amount of energy obtained may vary when using different conversion processes.
3.2. Characterization of the Solid Fraction
Physical observations of the torrefied samples revealed tubular-shape changes on the torrefied biomass at different MW power levels, residence times and biochar addition; the yield fractions showed various color variations. The thermal behavior of torrefied biomass is critical in pretreatment process control and torrefaction performance evaluation [30]. Switching the MW power level from 520 W to 650 W at longer residence times caused the volume of the solid biomass fraction to decrease significantly, becoming brittle and fragile and darkening in color (Figure 3). According to Agu et al. [20] and Tumuluru et al. [31], torrefied biomass turns from brown to dark-black at a temperature range of 150 °C to 300 °C; this may be due to chemical compositional changes involving the breakage of hydrogen and carbon bonds in the MW-torrefied biomass. The current study revealed that the color of torrefied biochar fractions darkened with biochar addition and longer residence time. Three products obtained from the MW torrefaction process were char residue fraction, torrefaction liquid, and noncondensable gas. Overall, biochar addition prevailed over residence times and influenced the reaction temperature in the particles during torrefaction.
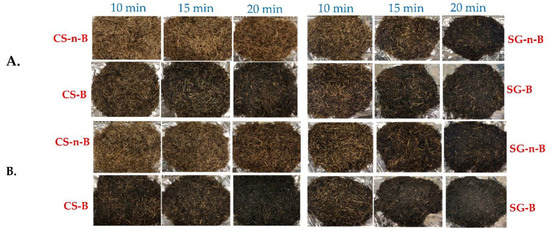
Figure 3.
Microwave torrefied camelina straw and switchgrass with and without biochar (A) 520 W and (B) 650 W. CS-B: camelina straw with biochar; SG-B: switchgrass with biochar; CS-n-B: camelina straw-no-biochar; SG-n-B: switchgrass-no-biochar. The first number after the biomass is % of biomass, and the second number is % of biochar.
The low mass yield may be attributed to higher MW power, extended residence times, and increasing biochar addition, which influenced the activation process. Likewise, the process conditions enhanced the noncondensable gas and torrefaction liquid production. The loss of volatile components and moisture to the surrounding environment resulted from higher MW power and residence times, leaving the material carbonized and lighter [32,33].
Torrefied CS without biochar-mix had a higher solid yield (80.80%) than torrefied SG without biochar (78.28%). Ethaib et al. [15] highlighted the fact that biomass could not be heated up sufficiently when a less than 10% MW absorber was used in the torrefaction process. Torrefied camelina straw and switchgrass biochar-mix recorded the highest solid yield (68.15 and 63.6.%) at a power level of 520 W at 10 min. At 20 min 520 W, CS and SG-biochar fractions, the solid yield values were 51.43% and 47.25%, and at 650 W, solid yield values were 45.18% and 42.48%, respectively. Agu et al. [16] investigated torrefied wheat and barley straw-biochar-mix at 250 °C MW torrefaction temperature and residence time of 15 min. The results indicated that torrefied biochar fraction decreased with the 25% biochar addition (wheat and barley straw with biochar 45.47% and 45.07%). Khelfa et al. [12] investigated MW-assisted pyrolysis of pinewood sawdust mixed with 10% activated carbon addition for bio-oil and bio-char production. The result showed an average of 26.9% solid yields at 20 min with varying MW power. Overall, in our study, the solid yield for CS or SG with biochar addition reduced with increasing MW power level and longer torrefaction residence time.
Mass loss for torrefied CS biochar-mix and SG biochar-mix at MW power levels (520 W and 650 W) and residence times are indicated in Figure 4 and Figure 5. Extended MW heating times and biochar addition increased the mass loss in torrefied camelina straw and switchgrass at different MW power levels. At 520 W and longer residence time, the mass loss was in the range of ≈19–48% for CS and ≈28–52% for SG, while at 650 W and longer residence time, the mass loss was ≈21–54% for CS and ≈29–57% for SW. An MW power of 650 W induced a higher reactivity and more significant degradation of the biomass components. On the other hand, mass loss observed for both samples without biochar was less than 40% at 520 W and 650 W at longer heating times. The effect of biochar addition on solid yield was a little below 50%, and the mass loss was attributed to the thermal decomposition of hemicellulose and some short-chain lignin compounds [16]. Generally, biochar addition improved the torrefaction process reactivity at relatively low MW power, indirectly heating the surrounding CS or SG particles, thereby influencing product yields and quality.
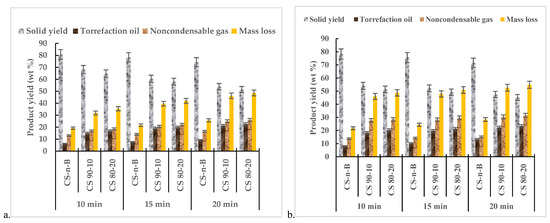
Figure 4.
Fraction yields and mass losses of microwave torrefied camelina straw-biochar-mix at (a) 520 W and (b) 650 W. CS: camelina straw; CS-n-B: camelina straw-no-biochar. The first number after the biomass is % of biomass, and the second number is % of biochar.
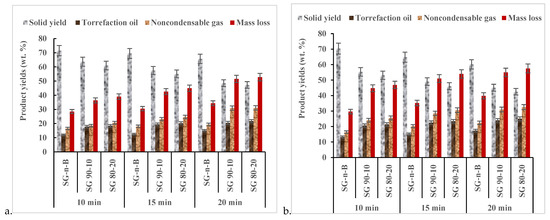
Figure 5.
Fraction yields and mass losses of microwave torrefied switchgrass-biochar-mix at (a) 520 W and (b) 650 W. SG: switchgrass; SG-n-B: switchgrass-no-biochar. The first number after the biomass is % of biomass, and the second number is % of biochar.
The noncondensable gas and torrefaction liquid slightly increased with torrefaction severity. Increasing the MW power level, residence time, and biochar addition affected the noncondensable gas and torrefaction liquid distribution. The highest torrefaction liquid yield (CS-biochar-mix: ≈23.30% and SG-biochar-mix: 25%) was reached at 650 W MW power and 20 min residence time, respectively. Ethaib et al. [15] reported a similar result using a ratio of 1:0.5 biomass to MW absorber at operating MW temperature 273 °C and produced torrefaction oil and gas of approximately 25% and 30%. Recent studies highlighted the fact that biomass thermal cracking and fragmentation could occur as torrefaction heat increases, thus enhancing torrefaction liquid yield [3]. Consequently, the heating rate significantly affects the depolymerization reaction of the biomass, releasing volatile components into the condensate liquid [19,22]. Our study shows that adding biochar (>20%) significantly influenced the increased torrefaction heating rate and torrefaction liquid yield for CS and SG.
3.3. Torrefaction Energy Consumption
Energy consumption is a factor typically linked with MW heating in the torrefaction process [18]. The MW energy consumption during torrefaction was computed using the equation energy (kJ) = power (kW) × residence time (s). Figure 6 shows that the biochar added played a role in the MW torrefaction energy consumption. Biochar addition (>20%) and longer residence time reduced torrefaction energy consumption for torrefied CS or SG, while torrefied CS or SG with no biochar added needed more MW energy input. The highest torrefaction energy consumption (430 kJ and 397 kJ) was recorded with CS and SG with no biochar added at 650 W and 20 min residence time, whereas the lowest MW energy consumption (289 kJ and 308 kJ) was recorded at 520 W and 20 min residence time with 20% biochar added for SG and CS, respectively. Li et al. [19] highlighted the fact that chars produced from biomass as a MW absorber could provide heat and sufficient temperature at a lower MW power than samples without the absorber. Further investigation is ongoing, to determine how environmentally-friendly the biochar fraction is.
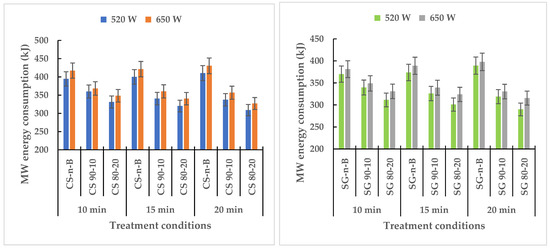
Figure 6.
Microwave torrefaction energy consumption of camelina straw and switchgrass with and without biochar-mix at different power levels and torrefaction residence time. CS: camelina straw; CS-n-B: camelina straw-no-biochar; SG: Switchgrass; SG-n-B: Switchgrass-no-biochar. The first number after the biomass is % of biomass, and the second number is % of biochar.
3.4. Characterizations of the Biochar Fractions
3.4.1. Moisture Content
The product yields (biochar, bio-oil, and bio-gas) obtained from MW torrefaction strongly depended on the feedstock initial moisture content and the biomass species/type used [15]. Moisture removal during torrefaction created internal void spaces in the material, enhancing reactivity to improve heat transfer, and leading to more mass loss [18]. Figure 7 shows that biochar addition significantly affected (p-value = 0.001 and R2 = 0.97) the moisture contents of MW torrefied CS and SG with and without biochar added at different MW power levels. Increasing the MW power level and residence time decreased the moisture content. The moisture content reduction was evident with SG compared to CS for both torrefied samples without biochar-mix. The lowest moisture contents observed for CS without biochar and with biochar added were 1.28% and 1.36% (d.b.), while for SG without biochar and with biochar added, they were 1.09% and 1.12% (d.b.), each at 520 W and 650 W for 20 min residence time. The biochar weight fraction in the biomass mixture resulted in moisture content reduction after the MW torrefaction process and could improve grinding characteristics [16].
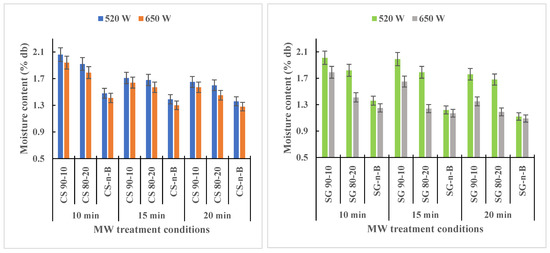
Figure 7.
Moisture content of torrefied camelina straw and switchgrass with or without biochar at various residence times and microwave levels (520 W and 650 W). CS: camelina straw; CS-n-B: camelina straw-no-biochar; SG: Switchgrass; SG-n-B: Switchgrass-no-biochar. The first number after the biomass is % of biomass, and the second number is % of biochar.
3.4.2. Thermochemical Properties Analysis
The results of elemental analyses of biochar, untorrefied and torrefied CS and SG with and without biochar are presented in Table 2. The thermochemical properties data (CHNS values) of coal were compared with the studied samples. In general, oxygen and hydrogen contents decreased, while carbon content increased. Statistical analysis shows that biochar addition, residence time, and the interaction between biochar addition and torrefaction residence time have significant effects (<0.0001 and 0.05, and R2 = 0.99) on the carbon, hydrogen and oxygen contents of torrefied CS and SG. During biomass combustion, the carbon and hydrogen boost energy reactions with oxygen assisting in completing the process, thereby reducing the calorific value of the biomass [34]. At torrefaction, the hydrogen bond is broken down, decreasing the hydrogen and oxygen contents of CS and SG, with or without biochar added. Torrefied CS and SG with and without biochar added had a higher nitrogen content than raw CS and SG. The SG with and without biochar addition had higher carbon with lower oxygen content than CS with and without biochar. The higher carbon content in the samples after torrefaction is responsible for increased HHV in torrefied CS and SG. As observed, CS and SG with or without biochar added, carbonized more under MW heating, and the carbon content varied, depending on the feedstock used. Coal was characterized by a higher sulfur content than biochar, untorrefied and torrefied CS and SG. Overall, biomass can produce sustainable, reliable, and environmentally-friendly alternative energy sources.

Table 2.
Elemental composition of untorrefied and microwave torrefied camelina straw and switchgrass with and without biochar.
3.4.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
Thermogravimetric (TGA and DTG) analyses revealed the microwave effects on torrefaction for raw CS and SG heated in different conditions. The TGA and DTG curves at different residence times are shown in Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10a,b. According to Chen et al. [15], biomass thermal degradation accelerates faster at a residence time of less than 60 min and much more slowly after one hour. Thus, the biomass lignocellulosic components have different thermal decompositions. Thermal decomposition of hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin occurred in the temperature range of 150–350 °C, 275–350 °C, and 250–500 °C, respectively [18]. In the first stage (drying zone), the removal of water molecules and degradation of light organic compounds occurred from 50 °C to 150 °C. In the second stage (devolatilization zone), weight loss occurred in the temperature range 277 °C–296 °C in raw and torrefied CS and SG with or without biochar added, while for biochar alone it occurred at 328 °C. In all the conditions, weight loss occurred between 200 °C and 500 °C. The data showed that weight loss in torrefied CS or SG with biochar-mix was smaller than in torrefied CS or SG without biochar-mix and raw CS or SG. Thus, biochar addition and residence time significantly affected the decomposition and devolatilization of hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin, resulting in the formation of volatiles. With the biochar addition and longer residence time, weight loss from 400 °C to 600 °C revealed the third stage, the residue char formation zone.
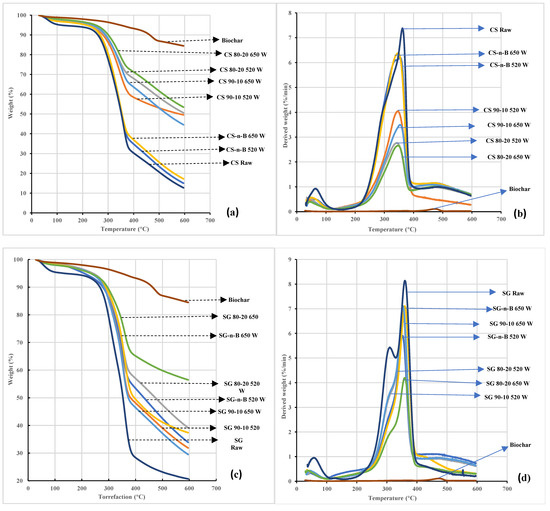
Figure 8.
Thermogravimetric curves of raw and torrefied camelina straw and switchgrass with biochar-mix at 10 min residence time (a) TGA of CS, (b) DTG analyses of CS, (c) TGA of SG, (d) DTG analyses of SG. CS: camelina straw; CS-n-B: camelina straw-no-biochar; SG: Switchgrass; SG-n-B: Switchgrass-no-biochar. the first number after the biomass is % of biomass, and the second number is % of biochar.
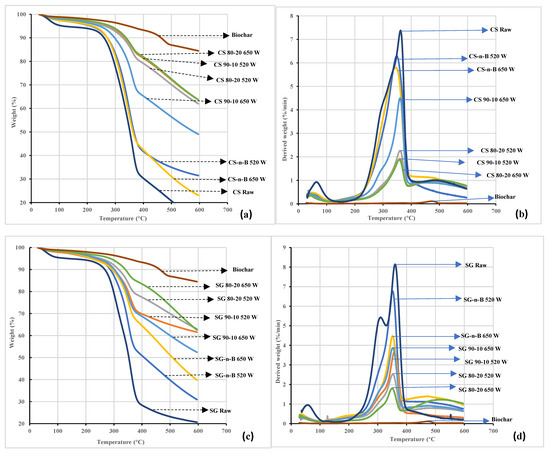
Figure 9.
Thermogravimetric curves of raw and torrefied camelina straw and switchgrass with biochar-mix at 15 min residence time (a) TGA of CS, (b) DTG analyses of CS, (c) TGA of SG, (d) DTG analyses of SG. CS: camelina straw; CS-n-B: camelina straw-no-biochar; SG: Switchgrass; SG-n-B: Switchgrass-no-biochar. The first number after the biomass is % of biomass, and the second number is % of biochar.
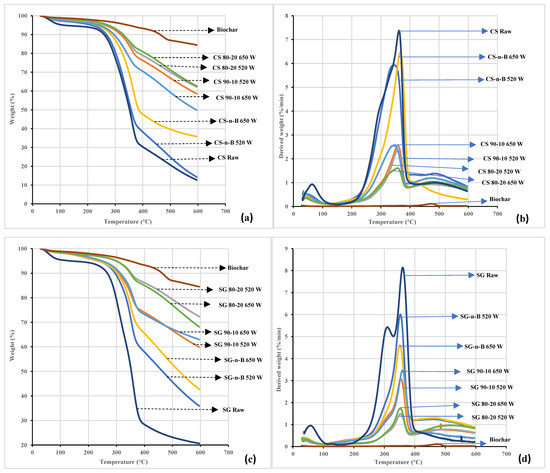
Figure 10.
Thermogravimetric curves of raw and torrefied camelina straw and switchgrass with biochar-mix at 20 min residence time (a) TGA of CS, (b) DTG analyses of CS, (c) TGA of SG, (d) DTG analyses of SG. CS: camelina straw; CS-n-B: camelina straw-no-biochar; SG: Switchgrass; SG-n-B: Switchgrass-no-biochar The first number after the biomass is % of biomass, and the second number is % of biochar.
In this zone, the rate of weight loss declines gradually, forming a residue fraction; this happens due to the decomposition of lignin associated with the phenolic hydroxyl group or decomposition of inorganic carbon in the ash portion [35,36]. Additional investigation is ongoing in analyzing the ash contents of both samples.
The DTG thermographs (Figure 8b, Figure 9b and Figure 10b) show various peaks of the biochar, raw and torrefaction treatment of CS and SG, with or with biochar-mix. The biochar peak was too small and so virtually unnoticed due to the degradation of hemicellulose and cellulose under severe torrefaction conditions. The first peak was observed on each thermograph of the samples but was very visible with raw CS and SG samples. The peak indicated initial moisture removal and light volatile matter heated up to 150 °C. In addition, the succeeding peaks were attributed to the decomposition of hemicellulose and cellulose compounds and lignin forming char residue fractions. In comparison, the thermograph of raw and torrefied CS and SG with or without biochar added, differed in peak positions and heights as the residence time extended. The difference in the curves indicated the presence of organic and inorganic components affected by the torrefaction severity [35]. The DTG shoulder curve of biomass corresponds to hemicellulose degradation at ≈ 300 °C [26]. In the present study, a similar shoulder appeared in raw SG only and was not evident in raw CS. However, in torrefied CS and SG with or without biochar added, the shoulders were not observed, indicating that hemicellulose of raw CS or SG decomposed due to the torrefaction process. Torrefied CS and SG with or without biochar and longer residence time showed DTG peaks representing the degradation of hemicellulose and cellulose range from 290 °C to 315 °C and 322 °C to 367 °C. The hemicellulose peaks disappeared since the degree of torrefaction destroyed the hemicellulose matrix in torrefied CS and SG. In addition, the intensity of cellulose was observed at a minimum of 7.38 and 8.11%/min for raw CS and SG. The intensity peak decreased with biochar addition and higher residence time. At temperatures above 500 °C, the decomposed lignin and the char residue fractions (torrefied CS and SG) can be utilized as solid fuel, bio-absorber/adsorbent, fuel cell, activated carbon, and catalyst.
3.4.4. Fuel Properties Characterization, Energy Yield and Combustibility
The effects of biochar addition and residence time on energy yield, fuel properties and combustibility index of torrefied CS and SG with and without biochar added are shown on Table 3. Notably, the value of energy yield depends upon solid yield and HHV. Increasing the biochar and residence time resulted in a significant energy yield decrease, revealing severe mass loss due to the decline in solid yield. A similar result was observed in our previous work, where the energy yield of wheat and barley straws with biochar decreased substantially with biochar addition [16]. Thus, the severe mass loss at 650 W led to a sharp decrease in energy yield, implying that residence time is crucial for MW torrefaction. The highest energy yields were obtained at CS and SG without biochar at both MW power levels (520 W and 650 W) and shorter residence time (<10 min).

Table 3.
Energy yield and fuel properties of torrefied camelina straw and switchgrass with and without biochar added at different microwave power levels.
The solid yield is an important parameter for quantitively analyzing how much torrefied biomass is converted into solid char for calorific value measurement [18,26]. According to Li et al. [19], MW absorbers in microwave torrefaction at different heating conditions could change the thermodynamic characteristics of the torrefied biomass. Increasing the MW power decreased solid char production, which could be attributed to volatile content reduction during devolatilization of the organic material [12]. As observed, increasing the MW power resulted in a slight increase in ash content, HHV, and fixed carbon, whereas volatile matter decreased. The ash content increased from 3.10% to 5.84% and 3.09% to 7.84% (CS and SG with or without biochar-mix), while the raw CS and SG were 1.41% and 2.67% biochar ash, 7.67% dry basis. The low ash content in raw CS and SG could indicate a promising feedstock for fuel production, notwithstanding the slight increase in ash content due to biochar fractions after torrefaction. However, the slight increase in ash content at different MW power levels could be due to mass loss of the biomass during torrefaction treatment [16].
The HHV increases with biochar addition and longer residence time at different MW power levels in both samples. Chen et al. [30] highlighted the fact that biomass weight fraction loss is due to a higher heating value and saturated moisture uptake. According to Khelfa et al. [12], the HHV after MW-assisted pyrolysis of pinewood sawdust mixed with activated carbon ranged from 17.70 MJ/kg to 30.30 MJ/kg. In our study HHV ranged from 19.55 MJ/kg to 23.35 MJ/kg for CS with and without biochar-mix and 21.47 MJ/kg to 24.93 MJ/kg for SG with and without biochar-mix. Thus, our study results showed a lower HHV than transportation-grade diesel fuels (approximately 36.50 MJ/kg) and natural gas (approximately 42.50 MJ/kg). The results obtained for coal (25 MJ/kg to 35 MJ/kg) showed roughly similar values. In addition, comparing the results obtained from conventional mild torrefaction, a similar HHV of torrefied CS and SG with or without biochar-mix at similar treatment conditions was observed [37].
In addition, at increasing MW power, biochar addition and residence time, the volatile matter decreased while the fixed carbon increased. The decrease in the volatile matter for torrefied CS (75.32% and 58.42%) and SG (74.52% and 49.34%) with and without biochar-mix was relatively minimal for the raw CS and SG values. The impact of biochar (volatile matter 49.83%) addition at different torrefaction MW power significantly affected both samples. Agu et al. [16] and Khelfa et al. [12] reported similar volatile results for torrefied wheat and barley straws with and without biochar (70.69% and 47.41%; and 74.13% and 52.33%) and for pyrolyzed pinewood sawdust with activated carbon (80.90% and 10.8%) at different treatment conditions.
The fixed carbon of torrefied CS and SG with and without biochar increased (from 21.58% to 35.74% for CS and 22.39% to 42.82% for SG). The maximum fixed carbon was observed at 650 W torrefied CS or SG with 20% biochar added and 20 min residence time. Fuel ratio is the ratio of fixed carbon content to volatile matter content. The data could be used to evaluate the co-combustibility of coal and biomass, as an indicator of easy combustion of solid fuels [26,38]. The raw CS and SG fuel ratios were 0.23 and 0.26, respectively, while biochar was 1.16. The fuel ratio of bituminous coal used in coal-fired power plants varies from 0.5 to 3.0. A biomass-coal co-combustion fuel ratio higher than 2.0 could lead to ignition and flammability problems [26]. The results showed that with biochar addition and longer residence time, the fuel ratio of torrefied CS of 0.50–0.61 and torrefied SG of 0.50–0.87 are in the range of coal fuel ratio. Thus, the feedstock used in the study could be considered for co-combustion with coal.
The combustion indices are used to determine the quality of torrefied biomass for fuel compatibility in a combustion process [39,40]. The reported values for the combustibility index range from 20–35 MJ/kg. The volatile ignitability values are above 14 MJ/kg [26,41]. The raw CS and SG values of CI are 89.58 MJ/kg and 74.84 MJ/kg, meaning they are unsuitable for co-combustion with coal unless torrefied. Singh et al. [26] highlighted the fact that high CI, low fuel ratio, and a high volatile value are undesirable for coal co-combustion. Table 3 shows that the torrefied CS and SG without biochar fall into the samples unsuitable for co-combustion with coal. Biochar addition with longer residence time gave close CI values for CS and SG with biochar at 520 W and 650 W, but the CI values were evident in SG with biochar (650 W 15 min and 20 min). The sharp decrease in CI values was due to the impact of biochar addition, torrefied at a higher MW power and longer residence time, thus indicating that camelina straw and switchgrass are potential blends with coal in a coal-fired plant. The VI was calculated using the total fuel energy of the volatile matter with fixed carbon present, mainly pure carbon [26]. The VI values are within the recommended values (≈ 15.79 MJ/kg to 20.70 MJ/kg), as indicated in Table 3. The samples treated at 650 W showed higher values and were closer to the fuel compatibility value compared to samples treated in 520 W as the residence time increased.
3.5. Surface Characterization of Raw and Torrefied Biomass
The surface of raw and torrefied CS and SG with and without biochar added were examined, to understand the morphological changes before and after the MW torrefaction process with varying severity. The effect of the torrefaction can be seen in Figures S3 and S4a–i. Significant changes can be observed in comparing the raw images to the torrefied CS and SG, especially at the different MW power levels. The raw CS and SG showed cracks resulting from grinding before the MW torrefaction heat treatment. The pores and cracks found on the torrefied samples may be related to the hemicellulose degradation during the torrefaction process, and some volatile compounds are released, such as methoxyl groups [26].In addition, the surfaces of the samples heated at 520 W and 650 W showed honeycomb-like pore structures due to the catalytic effect of biochar addition after torrefaction of CS and SG. Figures S3 and S4f–i show the 2.5D plots of torrefied CS and SG surface deformation intensity. In contrast, raw CS and SG show the lowest intensity, revealing the internal tissues of the biomass before heat treatment. Irrespective of the feedstock used, biochar addition and residence time contributed to the surface deformation and disintegration, due to increased heat. The branch structure began to break due to varying degrees of MW irradiation, resulting in cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin collapses.
4. Conclusions
Torrefaction improves many physico-chemical properties of biomass for conversion into bioenergy. The efficiency and impact of biochar addition during the microwave torrefaction of camelina straw and switchgrass were investigated at two microwave power levels. Biochar addition allowed unifying biomass particle heating to play a catalytic role in microwave torrefied camelina straw and switchgrass. The addition of biochar and the increase in the MW power level and residence time improved the physicochemical and fuel properties of camelina straw and switchgrass. Reduced MW energy consumption was achieved at 520 W, 20 min residence time at 20% biochar added to camelina straw and switchgrass, making biochar an MW absorber. The combustion index values indicated that camelina straw or switchgrass mixed with biochar and torrefied in a microwave oven, can convert biomass into energy fuel and improve the quality for blending with coal for co-combustion purposes in a coal-fired plant.
This research shows that biochar can add value to heat combustion and address concerns associated with agricultural and forestry wastes. Additionally, torrefaction is feedstock dependent; hence, results may vary with the biomass used depending on the torrefaction process conditions. A combination of microwave torrefaction technologies has shown strong potential in biomass conversion to solid fuels. More investigation is still ongoing to ascertain the biochar environmental sustainability of the process and the possible economic benefit to the bioenergy industry.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fuels3040036/s1, Figure S1 and Figure S2: Contour plots solid yield (%), MW energy consumption and HHV as a function of residence time (min) and biochar at 520 W and 650 W torrefied camelina straw and torrefied switchgrass; Figure S3 and Figure S4: Scanning electron microscope and confocal laser scanning 2.5D imagery plots for raw and torrefied camelina straw and switchgrass; Table S1 and Table S2: Analysis of variance response variables (solid yield (%), microwave energy consumption (KJ), higher heating value (MJ/kg)) to experimental variables (biochar (%), residence time (min), microwave power (W)) for torrefied camelina straw with and without biochar and switchgrass with and without biochar.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.S.A., L.G.T. and B.E.; methodology, O.S.A., L.G.T. and E.M.; software, O.S.A. and L.G.T.; validation, O.S.A., L.G.T. and E.M.; formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, and visualization, O.S.A.; resources, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition, L.G.T., E.M. and T.D.; writing–review and editing, L.G.T., B.E., E.M. and T.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding support of this project was provided by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) (RGPIN-2017-05287) and BioFuelNet (ASC-16).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the technical support of Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada-Saskatoon Research and Development Centre (AAFC-SRDC).
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflict of interest.
References
- Whalen, J.; Xu, C.C.; Shen, F.; Kumar, A.; Eklund, M.; Yan, J. Sustainable Biofuel Production from Forestry, Agricultural and Waste Biomass Feedstocks. Appl. Energ. 2017, 198, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; McConkey, B.; Huffman, T.; Smith, S.; MacGregor, B.; Yemshanov, D.; Kulshreshtha, S. Potential and Impacts of Renewable Energy Production from Agricultural Biomass in Canada. Appl. Energ. 2014, 130, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; JChakraborty, P.; Mondal, M.K. Pyrolysis of torrefied biomass: Optimization of process parameters using response surface methodology, characterization, and comparison of properties of pyrolysis oil from raw biomass. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 272, 122517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlimatti, H.M.; Mohan, B.R.; Saidutta, M.B. Bio-oil from microwave-assisted pyrolysis of food waste-optimization using response surface methodology. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 123, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usamni, Z.; Sharma, M.; Awasthi, A.K.; Lukk, T.; Tuohu, M.G.; Gong, L.; Nguyen-Tri, P.; Goggard, A.D.; Bill, R.M.; Nayak, C.S.; et al. Lignocellulosic biorefineries: The current state of challenges and strategies for efficient commercialization. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2021, 148, 111258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapalo, S.Y.; Zainuddin, M.F.; Abd Manaf, L.; Roslan, A.M. A review of technical and economic aspects of biomass briquetting. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H. Torrefaction. In Pretreatment of Biomass–Processes and Technologies; Pandey, A., Negi, S., Binod, P., Larroche, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 173–192. [Google Scholar]
- Sokhansanj, S.; Mani, S.; Turhollow, A.; Kumar, A.; Barnsby, D.; Lynd, L.; Laser, M. Large-scale production, harvest and logistics of switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) current technology and envisioning a mature technology. Biof. Bioprod. Bioref. 2009, 3, 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumuluru, J.S. Comparison of chemical composition and energy properties of torrefied switchgrass and corn stover. Front. Energy Res. 2015, 3, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, O.S.; Tabil, L.G.; Venkatesh, V.; Dumonceaux, T.; Mupondwa, E. Pretreatment of crop residues by application of microwave heating and alkaline solution for biofuel processing: A review. In Renewable Resources and Biorefineries; Jacob-Lopes, E., Ed.; IntechOpen Ltd.: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J. Microwave pretreatment. In Pretreatment of Biomass: Processes and Technologies; Pandey, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 157–172. [Google Scholar]
- Khelfa, A.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Koubaa, M.; Vorobiev, E. Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Pine Wood Sawdust Mixed with Activated Carbon for Bio-Oil and Bio-Char Production. Processes 2020, 8, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadi, B.; Iroba, K.L.; Tabil, L.G. Effect of polymer plastic binder on mechanical, storage and combustion characteristics of torrefied and pelletized herbaceous biomass. Appl. Energy 2017, 198, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.F.; Sung, H.T.; Chiueh, P.T.; Lo, S. Microwave torrefaction of sewage sludge and Leucaena. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 70, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethaib, S.; Omar, R.; Kamal, S.M.M.; Biak, D.R.A.; Zubaidi, S.L. Microwave-assisted pyrolysis of biomass waste: A mini review. Processes 2020, 8, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, O.S.; Tabil, L.; Emadi, E.; Mupondwa, E. Torrefaction and pelleting wheat and barley straw for biofuel and energy application. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 699657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Lei, H.; Wang, L.; Bu, Q.; Wei, Y.; Liang, J.; Liu, Y.; Julson, J.; Chen, S.; Wu, J.; et al. Microwave torrefaction of douglas fir sawdust pellets. Energy 2012, 26, 5936–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Jiao, L.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Ahmed, S.; Chen, G. Investigation on microwave torrefaction influence, TG-MS-FTIR analysis, and gasification performance. Energy 2021, 220, 119794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dia, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H.; Goa, Z.; Fu, J.; He, Y. Biochar from microwave pyrolysis of biomass: A review. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 94, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, O.S.; Tabil, L.; Emadi, E.; Mupondwa, E.; Duncan, C. Effect of biochar additive in torrefied biomass: Energy consumption, mass yield, grinding performance, and thermochemical properties. In 2021 ASABE Annual International Virtual Meeting; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Lei, H.; Wang, L.; Yadavalli, G.; Lui, Y.; Julson, Y. The integrated process of microwave torrefaction and pyrolysis of corn stover for biofuel production. J. Analy. Appl. Pyrol. 2014, 108, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liang, J.; Morgan, H., Jr.; Yan, L.; Xu, F.; Mao, H. Microwave-assisted co-pyrolysis of microwave torrefied biomass with waste plastic using ZSM-5 as a catalyst for high quality bio-oil. J. Analy. App. Pyro. 2018, 134, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mupondwa, E.; Li, X.; Tabil, L.G.; Falk, K.; Gugel, R. Technoeconomic analysis of camelina oil extraction as feedstock for biojet fuel in the Canadian Prairies. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 95, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D.; Crocker, D. Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass; Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2008; NREL/TP-510-42618. [Google Scholar]
- ASABE Standard S358.2; Moisture Measurement–Forages. American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2006.
- Singh, S.; Chakraborty, J.P.; Mondal, M.K. Torrefaction of woody biomass (Acacia nilotica): Investigation of fuel and flow properties to study its suitability as a good quality solid fuel. Renew. Energy 2020, 153, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, O.S.; Tabil, L.G.; Dumonceaux, T. Microwave-Assisted Alkali Pre-treatment, Densification and Enzymatic Saccharification of Canola Straw and Oat Hull. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbe, A.M.; Chandra, R.P.; Dogu, D.; van Velzen, S.T.J. Analytical staining of Cellulosic materials: A review. BioResources 2019, 14, 7387–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S.; Mohanty, P.; Pant, K.K.; Naik, S.; Kozinski, J.A.; Dalai, A.K. Characterization of North American lignocellulosic biomass and biochars in terms of their candidacy for alternate renewable fuels. Bioenerg Res 2013, 6, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Peng, J.; Bi, X.T. A state-of-the-art review of biomass torrefaction, densification and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 847–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumuluru, J.S.; Shahab, S.; Hess, J.R.; Wright, C.T.; Boardman, R.D. A review on biomass torrefaction process and product properties for energy applications. Ind. Biotechnol. 2011, 7, 384–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumuluru, J.S. Effect of deep drying and torrefaction temperature on proximate, ultimate composition, and heating value of 2-mm lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta) grind. J. Bioeng. 2016, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iroba, K.L.; Baik, O.D.; Tabil, L.G. Torrefaction of biomass from municipal solid waste fractions I: Temperature profiles, moisture content, energy consumption, mass yield, and thermochemical properties. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 105, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Gao, A.; Ma, Z.; Fei, D.; Chang, Y.; Shen, C. In-depth study of rice husk torrefaction: Characterization of solid, liquid and gaseous products, oxygen migration and energy yield. Biores. Tech. 2018, 253, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Mohanty, K. Pyrolysis kinetics and thermal behaviour of waste sawdust biomass using thermogravimetric analysis. Biores. Tech. 2018, 251, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Guo, F.; Li, X.; Peng, K.; Jiang, X.; Guo, C. Characterization of herb residue and high ash-containing paper sludge blends from fixed bed pyrolysis. Waste Mgt. 2018, 76, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bhownick, G.; Sarmah, A.K.; Sen, R. Production and characterization of a value-added biochar mix using seaweed, rice husk and pine sawdust: A parametric study. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 200, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, H.; Fermoso, J.; Moreno, I.; Coronado, J.M.; Serrano, D.P.; Pizarro, P. Thermochemical valorization of camelina straw waste via fast pyrolysis. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2017, 7, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlu, O.; Kocar, G. Upgrading lignocellulosic waste to fuel by torrefaction: Characterization and process optimization by response surface methodology. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 15, 4746–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manouchehrinejad, Y.; Yue, Y.; de Morais, R.A.L.; Souza, L.M.O.; Singh, H.; Mani, S. Densification of thermally treated energy cane and napier grass. Bio. Energy Res. 2018, 11, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohm, T.I.; Chae, J.S.; Kim, J.K.; Oh, S.C. Study on the characteristics of biomass for co-combustion in coal power plant. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Mgt. 2015, 17, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).