Abstract
Surrogate fuels are composed of a few pure components, mixed together in order to imitate a real fuel’s characteristics regarding its combustion and emission. In this study, four surrogate feeds were synthesized, corresponding to petroleum middle distillates. The desulfurization of the surrogate blends was performed using the hydrogen peroxide–acetic acid oxidative system. Consequently, extractive desulfurization was carried out using imidazolium-based ionic liquids, namely 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide [BMIM][Br] and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulfate [BMIM][HSO4], in a multiple extraction cycle procedure. Both ionic liquids were synthesized and characterized with spectroscopic techniques. The influence of the extraction temperature process was studied. In each extraction cycle, the sulfur concentration and the physical properties of the surrogate extraction products were estimated. The used ionic liquids were regenerated with a reasonably effective method. The synthesized and recycled ionic liquids showed high desulfurization efficiency, while [BMIM][Br] prevailed. Additionally, extractive desulfurization in oxidized surrogate LCO using ionic liquids is comparable with that using acetonitrile, since it has an advantage in terms of mass yield.
1. Introduction
Hydrodesulfurization (HDS) is the main conventional method for the removal of detrimental sulfur-containing compounds from middle petroleum distillates. Due to the steric hindrance of the refractory thiophenic compounds, more intensive conditions are needed for the implementation of HDS, including more active catalysts, a high temperature and high hydrogen pressure, leading to the elevated investment and operating costs [1] of the whole project.
In order to remove the organic sulfur compounds efficiently, new methods [2,3] have been implemented, such as selective extraction [4], adsorption [5], oxidation [6] and biodesulfurization [7,8]. Oxidative desulfurization (ODS) is an alternative and especially attractive method. Its main advantages are the following: it can be performed in the liquid phase, under mild conditions of temperature and pressure, and no hydrogen is required. As a result, the operating cost of the process is low. Moreover, the refractory organic sulfur compounds show high reactivity during the ODS process. The ODS procedure takes place in the presence of an oxidant agent and a catalyst. Different oxidation systems have been used. Among them, the hydrogen peroxide–carboxylic acids system [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20] has major advantages, such as low environmental impact, safety and high-quality products. Oil-soluble oxidants such as tert-butyl hydroperoxide [21,22,23] have also been proposed and found to be efficient for ODS.
Complementary and assisting methods have been implemented in the oxidative desulfurization process in order to enhance its effectiveness, such as heterogeneous catalysis [24,25] ultrasound irradiation [26,27,28] and ionic liquids.
Ionic liquids are characterized as “green” solvents, due to their notably low vapor pressure. They are organic salts that are liquids at temperatures below 100 °C. Their exclusive properties—for example, their chemical and thermal stability, their non-flammability and high ionic conductivity [29]—have aroused interest in their implementation in oxidative and extractive desulfurization procedures [30,31,32,33]. Nevertheless, studies in real petroleum feeds are scarce, since the desulfurization yields are not so efficient; therefore, the research is focused on surrogate diesel fuels, usually with a low sulfur concentration [34,35,36,37,38,39]. Organic sulfur compounds are more soluble in ionic liquids than in hydrocarbons. Extractive desulfurization using ionic liquids is based on this fact [40,41]. Ionic liquids can be easily recycled and reused. The economic benefit of this process is an important perspective for their future implementation on an industrial scale [42,43].
In current engines, the performance and the emissions are mainly affected by the fuels’ characteristics and composition. Real fuels are blends of hundreds of hydrocarbons and other compounds. Simplified surrogate fuels are used to represent them [44]. It is currently impossible to imitate a petroleum distillate, since it is too complicated to be simulated. Therefore, it is of great interest to create a surrogate of a simpler mixture that captures the essential characteristics of the original petroleum distillate and contains fewer than ten compounds, the selection of which depends on the specific properties required and the conclusions necessary.
Taking into consideration the above-mentioned aspects, the present study focuses on the synthesis of model sulfur compound surrogate blends that imitate real petroleum fractions. The selected sulfur compounds and the hydrocarbons are representative of those found in petroleum middle distillates. The widely applied method of oxidative desulfurization using the hydrogen peroxide–acetic acid system was combined with “green” extractive desulfurization using ionic liquids. Our goal was to develop a desulfurization procedure that would be simple, flexible and economically affordable, in order to investigate the behavior of surrogate blends corresponding to petroleum middle distillates. Moreover, the ionic liquids applied were synthesized, purified, identified and recycled in an effective procedure.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The LCO, HGO, LGO and kerosene petroleum fractions were supplied by the Hellenic Petroleum Elefsis and Aspropyrgos refineries. The properties of the four fractions are presented in Table 1 [45].

Table 1.
Properties of the petroleum middle distillates [45].
Sulfur compounds, typical of those contained in middle petroleum fractions, were used for the synthesis of the surrogate feeds corresponding to petroleum distillates. These compounds were: 1-dodecanethiol, representing mercaptans, n-butyl sulfide representing sulfides, tert-butyl disulfide representing disulfides, benzothiophene and dibenzothiophene as one- and two-ring aromatic sulfur compounds, respectively. For this study, 1-dodecanethiol >95% was purchased from TCI, benzothiophene (BT) 98% was obtained from Flurochem (Glossop, UK), and n-butyl sulfide 99%, tert-butyl disulfide 98% and dibenzothiophene (DBT) 98% were supplied by Acros Organics (Geel, Belgium).
Additionally, the following hydrocarbons were used for the synthesis of the surrogate matrixes. Decahydronaphthalene 98%, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene 98%, 1-methylnaphthalene 96%, naphthalene 99% and dodecane 99% were purchased from Acros Organics and n-hexadecane 95% from Alfa Aesar (Heysham, UK).
Acetic acid 99% was obtained from Fluka (Munich, Germany). Hydrogen peroxide 30% w/v was purchased from PSR Panreac (Barcelona, Spain). Acetonitrile HPLC Gradient Grade was obtained from Carlo Erba (Milano, Italy). Methanol ≥99.8%, ethyl acetate ≥99.5% and dichloromethane ≥99.9% were supplied by Honeywell/Riedel-de Haën (Seelze, Germany). Cyclohexane 99.5% was obtained from Lab-Scan(Tokyo, Japan). Meanwhile, 1-methylimidazole 99% and 1-bromobutane ≥98% were obtained from Alfa Aesar. Sodium bisulfate monohydrate 99% was obtained from AcrosOrganics (Geel, Belgium), and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulfate ≥95% (HPLC) was purchased from Aldrich (St. Louis, MI, USA). All of the reagents and solvents were used as received.
2.2. Apparatus
A Velp Scientifica reactor apparatus was used for the synthesis of the ionic liquid [BMIM][Br], the regeneration of both used ionic liquids, [BMIM][Br] and [BMIM][HSO4], as well as the oxidative desulfurization of the surrogate feeds. The main parts of the apparatus consisted of a ceramic heater, 1000 and 500 mL heating mantles and 1000 and 500 mL three-necked round bottom flasks. The apparatus was also equipped with a condenser, a magnetic stirrer and a temperature sensor digital thermoregulator, for the continuous control and adjustment of the desired temperature.
A microwave apparatus, StarSYNTH Milestone, was used for the synthesis of the ionic liquid [BMIM][HSO4].
2.3. Analysis
The infrared spectra of the liquid samples were recorded using an IRAffinity-1 Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer (Shimadzu). The number of scans was 20 and the resolution 4.0 cm−1. The spectrometer was equipped with a horizontal attenuated total reflectance sample cell made from zinc selenide (ZnSe) crystal.
The infrared spectra of the ionic liquids and the solid samples were acquired on a Jasco FT-IR-4200 spectrometer. Dried KBr was used for the formation of the sample pellets. The spectrometer was equipped with a TGR detector with an accumulation of 32 and a resolution of 4.0 cm−1.
The 1H NMR spectra of the ionic liquids and the solid samples were acquired on a Varian V600 MHz. The 1H NMR chemical shifts were referenced to the peak at 7.26 ppm corresponding to the dilution solvent CDCl3 [46].
The density and the kinematic viscosity of the ionic liquids, the petroleum fractions, the surrogate mixtures, the oxidized and the extracted surrogate products were measured with the SVM 300 Stabinger (Anton Paar) viscometer, as provided in the ASTM D7042 method.
The sulfur content (% w/w) of the samples was measured by X-ray fluorescence as provided in the ISO 8754 method using a SpectroXepos (Ametek) unit.
The cloud points and the pour points were estimated according to the ISO 3015 and ISO 3016 methods, respectively, in a G.G.T. unit. The measurements of the cold filter plugging points (CFPP) were obtained using an ISL (FPP 5GS) unit, according to the EN 116 method.
The freezing point of kerosene was measured as provided in the ASTMD5972 and ASTMD7153 methods, in the Hellenic Petroleum SA Laboratories.
The aromatics concentration (% w/w) of the petroleum fractions was measured via the chromatographic technique as provided in the EN 12916 test method, also in the Hellenic Petroleum SA Laboratories.
The sulfur speciation of the petroleum feeds was analyzed with GC/SCD in the Chemical Process and Energy Resources Institute of the Centre for Research and Technology Hellas.
2.4. Synthesis of Ionic Liquids
The chemical structures of the ionic liquids [BMIM][Br] and [BMIM][HSO4] are shown in Figure 1 [45].
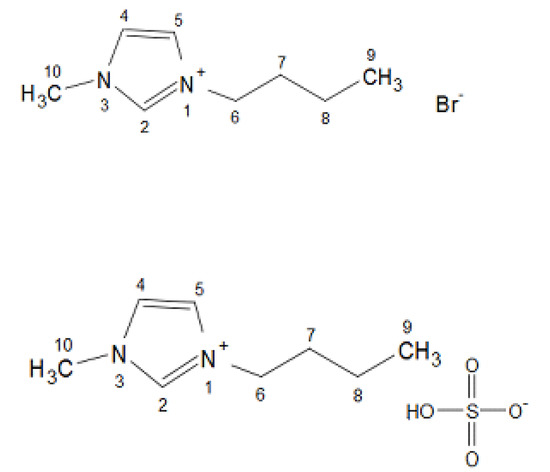
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of the ionic liquids [BMIM][Br] and [BMIM][HSO4] [45].
2.4.1. Synthesis of [BMIM][Br]
The primary experimental tests for the synthesis of [BMIM][Br] were performed on a small scale of 20 g. Afterwards, the ionic liquid was synthesized on a larger scale of 100 and 200 g [47,48].
The reaction mixture was prepared using the required amounts of 1-methylimidazole and 1-bromobutane, in a molar ratio of n1-methylimidazole to n1-bromobutane, equal to 0.95. First, 1-methylimidazole was transferred to a round-bottomed flask, which was embedded in an ice bath. The apparatus was equipped with a reflux condenser. Then, 1-bromobutane was added dropwise, under an inert atmosphere. In order to avoid phase separation at the initial stages of the reaction, the mixture was stirred at 400 rpm. The ice bath was removed as soon as the addition of 1-bromobutane was completed. Then, the mixture was heated at 70 °C, with the same stirring rate, under an inert atmosphere, for 24 h. The two-phased reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature. The upper phase, which contained the unreacted substances, was decanted. Ethyl acetate was added at a ratio of 1:1 to the synthesized ionic liquid, followed by vigorous mixing. Ethyl acetate was decanted. This procedure was repeated twice, adding fresh ethyl acetate, in order to remove all of the residual reactants. The ionic liquid was dried under high vacuum at 70 °C, until no weight loss was observed.
The reaction yield varied from 90 to 99% in all production batches. The ionic liquid [BMIM][Br] was identified using solid-state FT-IR and 1H NMR techniques.
2.4.2. Synthesis of [BMIM][HSO4]
The synthesis of [BMIM][HSO4] with the method of concentrated sulfuric acid [49] has a number of disadvantages. Most importantly, the caustic sulfuric acid is evolved, the corrosive hydrogen bromide is released and the reaction time is 48 h. Using sodium bisulfate instead of sulfuric acid and a microwave irradiation apparatus [50] is a simplified method for the synthesis of [BMIM][HSO4], while the reaction time is decreased to 34 min. An amount of approximately 18 g [BMIM][Br] with an equal molar amount of sodium bisulfate were transferred to a 50 mL microwave testing tube made of quartz. A magnetic stirrer was added and the tube inserted into the microwave apparatus. The mixture was exposed to microwave irradiation at the power level of 70 Watt. The reaction time was 34 min, the reaction temperature 75 °C and the pressure 35 bar. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature. Then, the mixture was extracted 10 times with dichloromethane at a ratio of 1:1 and afterwards filtered. Solid sodium bromide remained on the filter. The filtrate was composed of the ionic liquid and dichloromethane. In order to remove dichloromethane, the filtrate was transferred to a rotary evaporator. Then, the ionic liquid was dried under vacuum at 70 °C.
The ionic liquid [BMIM][HSO4] was identified using solid-state FT-IR and 1H NMR techniques.
The reaction yield reached 77%. Since the reaction yield was relatively low, it was decided to purchase the rest of the required amount of [BMIM][HSO4] that was used in the extractions.
2.5. Synthesis of the Surrogate Feeds
Taking into account the sulfur speciation of the petroleum fractions, the contained sulfur compounds were grouped so that they would correspond to one of the five following model compounds: 1-dodecanethiol, n-butyl sulfide, tert-butyl disulfide, benzothiophene and dibenzothiophene. Then, the total partial concentration of each one of the five model sulfur compounds was calculated for each surrogate blend.
The selection of the five model sulfur compounds was made so that they could be found in petroleum middle distillates and they represent various kinds of sulfur compounds, such as thiols, sulfides, disulfides and sulfur-containing aromatic compounds. In addition, they should be commercially available and economically feasible to purchase.
Similarly, taking into consideration the aromatics concentrations as shown in Table 1 [45], and the typical hydrocarbon concentration of the respective petroleum distillates, a number of hydrocarbons and their combinations were tested for the synthesis of the surrogate blends’ matrixes. Their choice was based on the fact that the model feeds should be as simple as possible and stable during their stay for a reasonable period of time.
The synthesis of the surrogate blends resulted in the following concentrations.
The surrogate kerosene consisted of 60% w/w dodecane, 25% w/w decahydronaphthalene, 15% w/w 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene, 10% w/w sulfur from 1-dodecanethiol, 15% w/w sulfur from n-butyl sulfide, 15% w/w sulfur from tert-butyl disulfide and 60% w/w sulfur from benzothiophene.
The surrogate LGO contained 35% w/w n-hexadecane, 35% w/w decahydronaphthalene, 20% w/w 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene, 10% w/w naphthalene, 10% w/w sulfur from 1-dodecanethiol, 10% w/w sulfur from n-butyl sulfide, 10% w/w sulfur from tert-butyl disulfide, 45% w/w sulfur from benzothiophene and 25% w/w sulfur from dibenzothiophene.
The surrogate LCO consisted of 15% w/w n-hexadecane, 15% w/w decahydronaphthalene, 20% w/w 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene, 50% w/w 1-methylnaphthalene, 20% w/w sulfur from benzothiophene and 80% w/w sulfur from dibenzothiophene.
The surrogate HGO contained 35% w/w n-hexadecane, 35% w/w decahydronaphthalene, 20% w/w 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene, 10% w/w naphthalene, 5% w/w sulfur from 1-dodecanethiol, 5% w/w sulfur from n-butyl sulfide, 5% w/w sulfur from tert-butyl disulfide, 25% w/w sulfur from benzothiophene and 60% w/w sulfur from dibenzothiophene.
The properties of the surrogate feeds are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Properties of the surrogate feeds corresponding to petroleum middle distillates.
2.6. Oxidative Desulfurization
The reaction mixtures were prepared using 300 g of the specific surrogate blend and the required amount of acetic acid. The molar ratio of nCH3COOH to nS was equal to 17. Each reaction mixture was transferred to a round-bottomed flask, stirred continuously at 400 rpm and heated to the desired reaction temperature. The apparatus was equipped with a reflux condenser. Initial studies of the oxidative desulfurization of the four petroleum fractions were performed using three different oxidation temperatures: 50, 70 and 90 °C [20]. It was concluded that, under the specific conditions, the optimum minimum oxidation temperature for kerosene and LGO was 70 °C, while that for LCO and HGO was 90 °C. The same optimum minimum temperatures were maintained during the oxidative desulfurization of the surrogate blends corresponding to petroleum distillates.
The required amount of oxidant was estimated so that the molar ratio of nH2O2 to nS was equal to 3. The aqueous solution 30% w/v of the hydrogen peroxide was added to the reaction mixture in three steps, as soon as the system reached the specific optimum reaction temperature. When the addition was complete, the mixture was stirred for a further 1.5 hours. Since the reaction mixture consisted of two phases, intense mixing was required to ensure the homogeneous composition of the bulk liquids. The progress of the oxidation procedure was monitored from the FT-IR spectra of the liquid samples, which were withdrawn from the reaction mixture every 30 min. At the end of the oxidation, the system was cooled to room temperature and settled. Two phases were invariably formed: the upper organic phase and the bottom aqueous phase.
In every oxidized mixture, white solid sediment was formed and separated from the liquid supernatant. The sediment was filtered under vacuum, washed with deionized water 100 °C and dried in a desiccator under vacuum. The precipitates were identified using solid-state FT-IR and 1H NMR techniques.
The remaining liquid supernatant from the oxidized mixture was transferred to a separation funnel to settle. Subsequently, the organic phase and the aqueous phase were separated. The organic phase was washed with deionized water 100 °C, so as to remove the acetic acid. The traces of the water were removed using a rotary evaporator. The oxidized organic phases were analyzed for their sulfur content and their physical properties. The characteristics of the intermediate oxidized surrogate products are shown in Table 3. The liquid FT-IR spectra of the oxidized surrogate products were acquired.

Table 3.
Properties of the intermediate oxidized surrogate feeds.
2.7. Extractive Desulfurization
2.7.1. Extraction with Solvents
Acetonitrile and methanol were used for the extractive desulfurization of the oxidized surrogate products. Appropriate amounts of each solvent and oxidized product were mixed according to the feed-to-solvent ratio (S/F). The two-phased mixtures were vigorously shaken and centrifuged. Afterwards, they were placed in small separation funnels to settle overnight. The extracted surrogate products were separated from the solvent phases. Their weights were measured. The extracted surrogate products were analyzed for their sulfur content and their physical properties (kinematic viscosity and density). Subsequently, the liquid FT-IR spectra were acquired.
2.7.2. Extraction with Ionic Liquids
Primary tests were conducted at three different temperatures, i.e., at an ambient temperature of approximately 25 °C, at 50 and at 70 °C, in order to ascertain the desulfurization capability of [BMIM][Br] and [BMIM][HSO4]. The two fresh ionic liquids were tested for each oxidized surrogate blend. In a conical flask, 10 g of each oxidized surrogate feed was added and the respective amount of each ionic liquid was weighed at a mass ratio of 1.0:1.0. The two-phased mixtures were stirred continuously at 400 rpm for 30 min, and then placed in separation funnels to settle overnight. The two phases were separated and their weights were measured. Subsequently, the upper phases corresponding to the extracted surrogate products were analyzed for their sulfur content and their physical properties (kinematic viscosity and density).
It was concluded that the extraction temperature did not seem to affect the desulfurization capability of the two ionic liquids. Therefore, the ambient temperature was chosen for the subsequent extraction cycles, in order to keep the energy consumption as low as possible.
A similar procedure was performed for a number of extraction cycles. When no reduction in the sulfur content of the extracted surrogate product was observed, the sequential extraction cycle was not repeated. In every cycle, the sulfur content, the density and the viscosity were analyzed, and the mass yield was estimated.
The liquid FT-IR spectra of the final extraction cycle surrogate products were acquired.
The same multiple extraction cycle procedure was followed in the recycled ionic liquids [BMIM][Br] and [BMIM][HSO4] at ambient temperature. Similarly, in every cycle, the sulfur content, the density and the viscosity were analyzed, and the mass yield was estimated, while the liquid FT-IR spectra of the final extracted surrogate products were acquired.
2.8. Regeneration of Ionic Liquids
The sulfur concentrations of the used [BMIM][Br]and [BMIM][HSO4] were 0.025% w/w and 7.730% w/w, respectively. Each used ionic liquid was transferred to a 1000 mL flask and dried under vacuum using the reactor apparatus at 70 °C for 5 h.
Initial experimental tests using conventional solvents such as ethyl acetate, cyclohexane and dichloromethane took place for the regeneration process of the used ionic liquids. Ethyl acetate proved to be more efficient in reducing the sulfur content of the regenerated ionic liquids.
Consequently, the following regeneration procedure was performed. At first, the mass ratio of ionic liquid to ethyl acetate was equal to 1.0:1.0. The mixture was stirred at 60 °C for 120 min [51] using the reactor apparatus. Then, ethyl acetate was removed by decantation, and the extraction was repeated two more times. Subsequently, the mass ratio of ionic liquid to ethyl acetate changed to 1.0:0.5, and the same procedure was performed three more times. Both of the regenerated ionic liquids were heated at 70 °C for 12 h under vacuum in order to remove all volatile residues.
The sulfur content of the recycled [BMIM][Br] decreased to 0.009% w/w while the mass loss was 6.6% w/w. The sulfur content of the recycled [BMIM][HSO4] was reduced to 7.409% w/w while the mass loss was 4.5% w/w.
The recycled ionic liquids were identified using solid-state FT-IR and 1H NMR spectroscopy.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties and Characterization of the Synthesized Ionic Liquids
The physical properties of the synthesized [BMIM][Br] and [BMIM][HSO4], namely the density, the dynamic viscosity and the kinematic viscosity, at two different temperatures, 40 and 100 °C, are shown in Table 4 [45]. In both ionic liquids, the increase in temperature reduced their density and their dynamic and kinematic viscosity [52,53].

Table 4.
Physical properties of the synthesized and recycled ionic liquids [45].
3.1.1. Solid-State FT-IR Spectroscopy
In the FT-IR spectrum of [BMIM][Br], the quaternary anine salt formation can be attributed to the broad band at 3436 cm−1 [48,51]. The aromatic C-H stretch in cyclic imidazolium is represented by both peaks at 3147 and 3086 cm−1 [51]. The bands at 2961 and 2873 cm−1 are due to the aliphatic asymmetric and symmetric C-H stretching vibrations of the methyl groups [54]. The peaks at 1632 and 1572 cm−1 can be attributed to the C=C and C=N stretching vibrations [48]. The bands at 1466 and 1384 cm−1 are due to the aliphatic asymmetric and symmetric C-H bending vibrations of the methyl groups [54]. The peaks at 1337 and 1169 cm−1 can be attributed to aromatic and non-aromatic, respectively, tertiary amine C-N stretch [54]. The band at 849 cm−1 corresponds to the C-N stretching vibration [48,51]. The out-of-plane (“oop”) bending of the C-H aromatic ring bonds is presented in the low-frequency range of the spectrum between 900 and 675 cm−1 [55].
In the FT-IR spectrum of [BMIM][HSO4], the quaternary amine salt formation can be attributed to the broad band at 3446 cm−1, while the aromatic C-H stretch in cyclic imidazolium can be attributed to both peaks at 3151 and 3104 cm−1. The bands at 2962 and 2874 cm−1 are due to the aliphatic asymmetric and symmetric C-H stretching vibrations of the methyl groups, while the bands at 1466 and 1384 cm−1 are due to the aliphatic asymmetric and symmetric C-H bending vibrations of the methyl groups. The peaks at 1633 and 1573 cm−1 correspond to the C=C and C=N stretching vibrations, while the peaks at 1338 cm−1 can be attributed to the aromatic tertiary amine C-N stretch. The band at 887 cm−1 corresponds to the C-N stretching vibration. The broad band at 1220 cm−1 is due to the asymmetric and symmetric S=O stretching frequency of sulfates [55]. The in-plane bending bands of the C-H aromatic ring bonds emerge in the 1300–1000 cm−1 region, while out-of-plane (“oop”) bending bands appear in the low-frequency range of the spectrum between 900 and 675 cm−1 [55].
The FT-IR spectra of the two new ionic liquids, [BMIM][Br] and [BMIM][HSO4], are shown in Figure 2 [45] and Figure 3 [45], respectively.
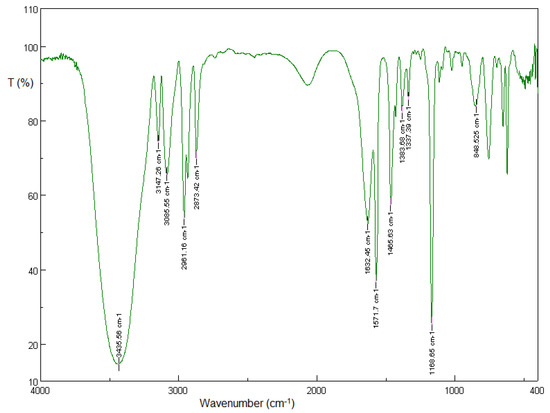
Figure 2.
Solid-state FT-IR spectrum of the fresh [BMIM][Br]. Sample pellet with KBr, number of scans: 32, resolution: 4.0 cm−1 [45].
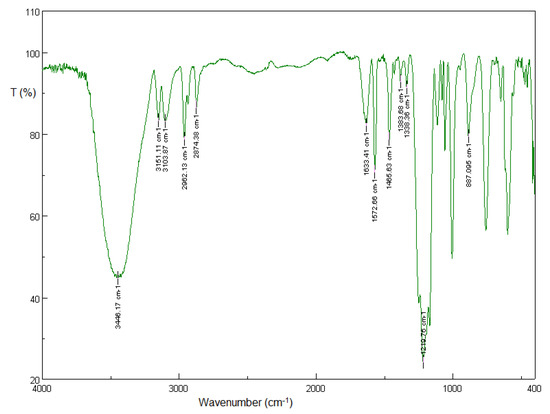
Figure 3.
Solid-state FT-IR spectrum of the fresh [BMIM][HSO4]. Sample pellet with KBr, number of scans: 32, resolution: 4.0 cm−1 [45].
3.1.2. 1H NMR Spectroscopy
The fresh ionic liquids were identified using 1H NMR spectroscopy. The concentration of the analyte was approximately 10 mg of the fresh ionic liquid, in 0.7 mL of the solvent CDCl3. In Figure 1, the chemical structure and the atom numbering of both ionic liquids are presented [45].
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide ([BMIM][Br]). 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm): 10.50 (s, 1H, H-2 methine proton), 7.47 (s, 1H, H-4 methine proton), 7.37 (s, 1H, H-5 methine proton), 4.32 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H, H-6 methylene protons), 4.12 (s, 3H, H-10 methyl protons), 1.93–1.86 (m, 2H, H-7 methylene protons), 1.42–1.34 (m, 2H, H-8 methylene protons), 0.95 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H, H-9 methyl protons). The 1H NMR spectrum of the fresh [BMIM][Br] is shown in Figure 4 [45].
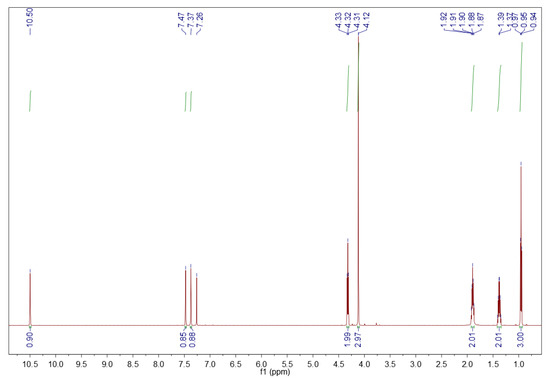
Figure 4.
1H NMR spectrum of the fresh [BMIM][Br]. Sample of 10 mg in 0.7 mL deuterated chloroform, 600 MHz [45].
The 1H NMR spectrum of the purchased [BMIM][HSO4] is depicted in Figure 5 [45]. Since its purity is ≥95%, some traces of impurities appear. The peaks corresponding to [BMIM][HSO4] are shown below.
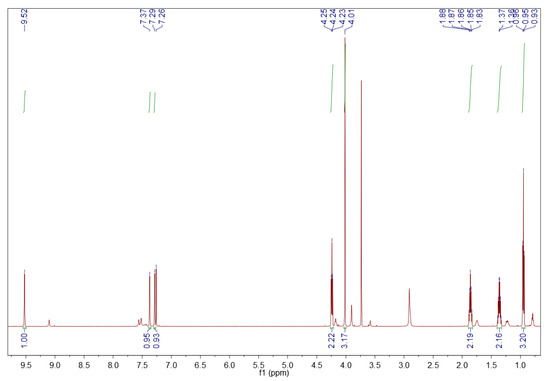
Figure 5.
1H NMR spectrum of the fresh [BMIM][HSO4]. Sample of 10 mg in 0.7 mL deuterated chloroform, 600 MHz [45].
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulfate ([BMIM][HSO4]). 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm): 9.52 (s, 1H, H-2 methine proton), 7.37 (s, 1H, H-4 methine proton), 7.29 (s, 1H, H-5 methine proton), 4.24 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H, H-6 methylene protons), 4.01 (s, 3H, H-10 methyl protons), 1.89–1.82 (m, 2H, H-7 methylene protons), 1.40–1.32 (m, 2H, H-8 methylene protons), 0.95 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H, H-9 methyl protons).
3.2. Characterization of the Precipitated Sediments
The identification of the solid sediments that were precipitated during the oxidation of the surrogate blends was performed using solid-state FT-IR and 1H NMR techniques. The relationship between the electron densities of the sulfur atoms in the model sulfur compounds and their reactivities during oxidation is well-described in the literature. The electron densities of the model sulfur compounds were investigated during their oxidation with hydrogen peroxide and formic acid [12]. The electron density of dibenzothiophene (DBT) was 5758, while the electron density of benzothiophene (BT) was 5739. During the oxidation of BT and the other sulfur substances with higher electron densities than BT, the corresponding sulfones were formed. When the electron density on the sulfur atom was higher, the rate constant of oxidation was higher. This result indicated initially and proved eventually that the apparent rate constants are reduced in the order: DBT > BT [12]. The above-mentioned literature data were confirmed and extended later [14,56], pointing out the oxidation path of heterocyclic sulfur substances such as benzothiophene and dibenzothiophene. In particular, the corresponding sulfones of benzothiophene, dibenzothiophene and diphenyl sulfide are synthesized, and are present as solid residues, at the end of all oxidation reactions performed [57]. It has been reported that the sulfoxide of benzothiophene cannot be isolated using various oxidants [58,59]. The electron density of dibenzothiophene is higher than that of benzothiophene [12]; consequently, its reactivity is also higher [58], and the oxides of benzothiophene are less stable than the oxides of dibenzothiophene [60]. From the above, it can be concluded that, under the applied experimental conditions, the formation of dibenzothiophene sulfone is expected to prevail.
3.2.1. Solid-State FT-IR Spectroscopy
The FT-IR spectra of the sulfones show strong absorption bands at 1350–1300 and 1160–1120 cm−1, due to the asymmetric and symmetric of the SO2 group, respectively. The presence of hydrogen bonds results in absorption near 1300 and 1125 cm−1. In addition, the sulfoxides show strong absorption in the 1070–1030 cm−1 region. The sulfoxide group is also susceptible to hydrogen bonding; therefore, the absorption shifts to slightly lower frequencies [55].
The solid-state FT-IR spectrum of the sediment resulting from the oxidation of surrogate kerosene showed that sulfone was formed, since two absorbance bands appeared at 1286 and 1150 cm−1, attributed to asymmetric and symmetric SO2 stretching. The absorption band due to sulfoxides was minor.
The characterization of the residual substances produced from both surrogate LGO and surrogate LCO oxidation indicated that sulfone was synthesized because of the strong absorption at 1288 and 1166 cm−1 and the weak absorption at 1046 cm−1. Similarly, the FT-IR spectrum of the precipitate from surrogate HGO oxidation showed that the characteristic sulfone bands were present at 1289 cm−1 νas(S=O) and 1166 cm−1 νs(S=O), while a weak sulfoxide peak appeared at 1047 cm−1.
Nevertheless, the verification of the oxidized sulfur species that were formed was to be clarified by the 1H NMR spectra of the corresponding compounds.
3.2.2. 1H NMR Spectroscopy
The 1H NMR data of the surrogate kerosene’s oxidized precipitate are consistent with the literature [61] and confirm the results from the solid-state FT-IR spectrum, namely that the oxidized product is the sulfone. As depicted in Figure 6, 1H NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz) δ (ppm): 7.72 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.59–7.49 (m, 2H), 7.36 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.22 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H), 6.72 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H).
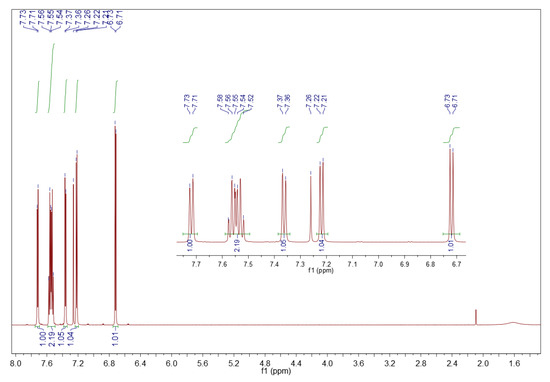
Figure 6.
1H NMR spectrum of sediment precipitated from the surrogate kerosene. Sample of 10 mg in 0.7 mL deuterated chloroform, 600 MHz.
The other sediments resulting from the oxidation of the surrogates LGO, LCO and HGO consist of dibenzothiophene sulfones exclusively. This fact supports the above-mentioned studies, according to which dibenzothiophene oxidation prevails over benzothiophene oxidation.
The 1H NMR spectra of the formed dibenzothiophene sulfone are consistent with the literature [62]. Therefore, the precipitate from surrogate LGO oxidation is dibenzothiophene sulfone, 1H NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz) δ (ppm): 7.85–7.76 (m, 4H), 7.64 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 7.53 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H). Its spectrum is depicted in Figure 7.
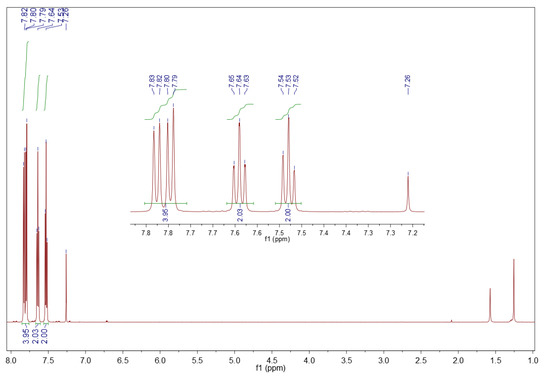
Figure 7.
1H NMR spectrum of sediment precipitated from the surrogate LGO. Sample of 10 mg in 0.7 mL deuterated chloroform, 600 MHz.
The sediment from surrogate LCO oxidation is dibenzothiophene sulfone, 1H NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz) δ (ppm): 7.85–7.75 (m, 4H), 7.63 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.52 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H). Its spectrum is shown in Figure 8.
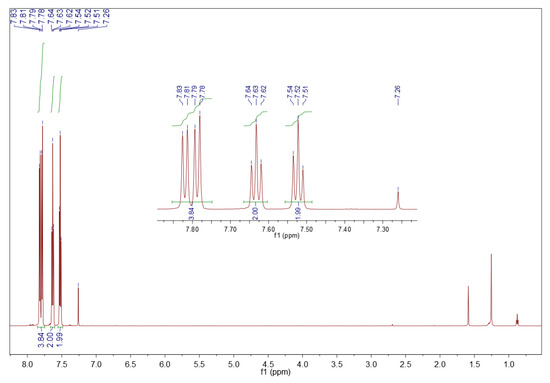
Figure 8.
1H NMR spectrum of sediment precipitated from the surrogate LCO. Sample of 10 mg in 0.7 mL deuterated chloroform, 600 MHz.
The precipitate from surrogate HGO oxidation is dibenzothiophene sulfone, 1H NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz) δ (ppm): 7.85–7.77 (m, 4H), 7.64 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.53 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H). Its spectrum is presented in Figure 9.
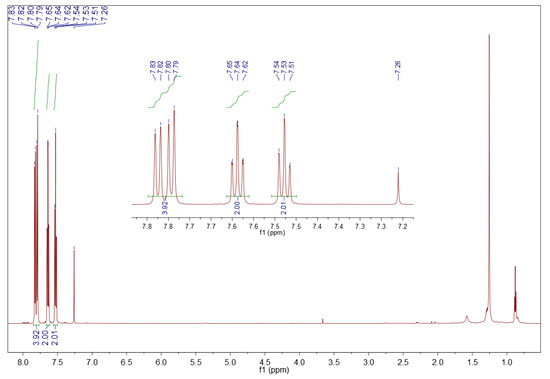
Figure 9.
1H NMR spectrum of sediment precipitated from the surrogate HGO. Sample of 10 mg in 0.7 mL deuterated chloroform, 600 MHz.
3.3. Desulfurization of the Surrogate Blends Using Conventional Solvents
3.3.1. Properties of the Raffinate Surrogate Products
The properties of the raffinate surrogate products using acetonitrile and methanol are shown in Table 5. In every case, the sulfur content is lower when the extraction solvent is acetonitrile, and the solvent to feed ratio (S/F) is 2.0:1.0. The desulfurization yields during the extractions of the oxidized surrogates, kerosene, LGO, LCO and HGO, using acetonitrile with an S/F ratio equal to 2.0:1.0 are 97, 99, 96, and 96%, respectively. In the case of methanol, the desulfurization yields of the oxidized surrogates, kerosene, LGO, LCO and HGO, are 95, 99, 92, and 93%, respectively. It is worth mentioning that, in the case of the oxidized surrogate LCO, a great mass loss of the raffinate surrogate product occurred. More specifically, the mass yield of the extracted surrogate LCO decreased to 23% when acetonitrile was used, while the mass yield was higher than 28% when methanol was used. Nevertheless, the tendency of the results encountered with methanol is very similar to acetonitrile. Conclusively, methanol’s performance is better for lighter surrogates (kerosene and LGO) and slightly lower for LCO and HGO surrogates.

Table 5.
Properties of the oxidized surrogates’ supernatants after their treatment with conventional solvents.
During the extractions for a specific oxidized feed and extraction solvent, as the S/F ratio increases, the density decreases, while the kinematic viscosity increases. In every surrogate feed, the density of the surrogate raffinates is lower when the extraction solvent is acetonitrile rather than methanol. This fact can be justified since acetonitrile’s desulfurization capability is better than methanol’s in removing sulfones, unsaturated hydrocarbons and aromatics, resulting in a more refined extract.
3.3.2. Liquid FT-IR Spectroscopy
During the oxidative desulfurization of surrogate kerosene, the peak at 760 cm−1, which can be attributed to benzothiophene, disappears, since its oxidized form, benzothiophene sulfone, precipitates from the reaction mixture as a solid [57]. The most prominent and most informative bands in the spectra of aromatic compounds result from the out-of-plane (“oop”) bending of the ring bonds. These strong absorption bands occur in the low-frequency range between 900 and 675 cm−1 [55]. In the FT-IR spectra of surrogate kerosene’s extracted products, the absorption bands decrease and mainly the peaks at 741, 804, 864 and 944 cm−1. Similarly, the peak at 1494 cm−1, which is ascribed to skeletal vibrations (involving carbon–carbon stretching within the aromatic ring), is reduced. As the S/F ratio increases, the intensity of the peaks decreases. The spectra of the extracted products of surrogate kerosene, using acetonitrile and methanol, are almost identical, even though acetonitrile prevails in the effectiveness of removing different kinds of compounds.
In the FT-IR spectrum of the oxidized surrogate LGO, two peaks disappear, in comparison with the spectrum of the crude surrogate blend. The first one at 761 cm−1 is due to the out-of-plane bending of the aromatics, and the second at 1716 cm−1 could be characterized as a weak combination and overtone band. During the extractions with the two conventional solvents, acetonitrile seems to be a more efficient extractant than methanol in the removal of aromatic compounds and other species from the extraction mixture. When the proportion S/F rises, the intensities of the absorption bands are lessened. This phenomenon influences mostly the following peaks at 741, 781 and 804 cm−1 due to the out-of-plane bending of the aromatic bonds C-H: 1494, 1509, 1598 cm−1 attributed to skeletal vibrations of aromatics and heteroaromatics, 3016, 3054 cm−1 due to aromatic C-H stretching. The FT-IR spectra of the extracted surrogate LGO products are almost identical when the extraction solvent is methanol and the S/F ratio is 1.5:1.0 or 2.0:1.0.
During the oxidation of the surrogate LCO, the peak at 1228 cm−1 due to the in-plane bending of the aromatics, and the peak at 1716 cm−1 attributed to the skeletal stretching vibration within the aromatic ring, vanish. On the contrary, a peak emerges at 1313 cm−1 that characterizes the asymmetric SO2 stretching of the sulfone formation. When the oxidized surrogate LCO is extracted with acetonitrile and methanol, the shape of the FT-IR spectra changes dramatically in the low- as well as in the high-frequency region. This fact confirms the previous observations regarding the great mass loss of the surrogate LCO raffinate products.
In the case of surrogate HGO, the peaks that diminish or disappear from the spectrum of the oxidized surrogate product are those at 721, 741, 761 cm−1 and at 1026, 1069, 1074, 1159, 1228 cm−1 due to the out-of-plane and the in-plane bending of the ring C-H bonds, respectively. During the extractions with acetonitrile and methanol, the FT-IR spectra of the extracted surrogate HGO products are greatly changed, as inferred from the intensities of the absorption peaks, which are reduced throughout the whole spectrum. The spectra of the raffinate surrogate HGO products are almost identical when acetonitrile is used as an extractant. Similarly, the spectra of the extracted surrogate HGO products are very much alike when methanol is used as an extractant and the S/F ratio is 1.0:1.0 or 1.0:1.5. In every case, acetonitrile is more effective than methanol in removing sulfur compounds and aromatics.
3.4. Desulfurization of the Oxidized Surrogate Blends Using Ionic Liquids
3.4.1. Influence of Temperature Extraction
The examination of the extraction temperature’s influence on the desulfurization efficiency of the ionic liquids is of great importance in order to implement a low-energy-consumption procedure. Initial extraction tests using the fresh ionic liquids took place at three different temperatures, i.e., at an ambient temperature of approximately 25 °C, at 50 and at 70 °C, in all four oxidized surrogate mixtures. In every extracted product, the sulfur content (% w/w), the density and the kinematic viscosity were measured and the mass yield (% w/w) was estimated.
The results of the extractions are shown in Figure 10 for the fresh [BMIM][Br] and in Figure 11 for the fresh [BMIM][HSO4]. It is obvious that the desulfurization capabilities of both fresh ionic liquids do not change significantly with the increase of the extraction temperature. Moreover, in some cases, the desulfurization capabilities of the fresh ionic liquids are even lower at the higher temperatures of 50 and 70 °C.
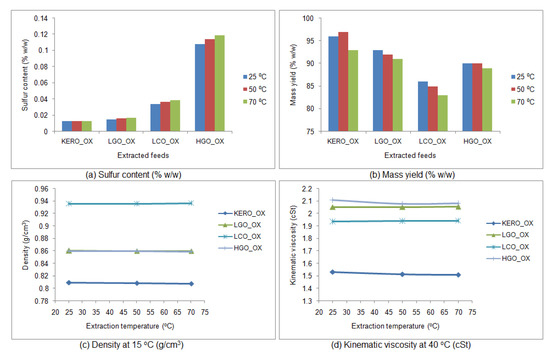
Figure 10.
Influence of temperature on the desulfurization capability of the fresh [BMIM][Br]: (a) sulfur content of the surrogate raffinates (% w/w), (b) mass yield of the surrogate raffinates (% w/w), (c) density of the surrogate raffinates at 15 °C (g/cm3), (d) kinematic viscosity of the surrogate raffinates at 40 °C (cSt). (KERO_ OX: oxidized surrogate kerosene, LGO_OX: oxidized surrogate LGO, LCO_OX: oxidized surrogate LCO, HGO_OX: oxidized surrogate HGO).
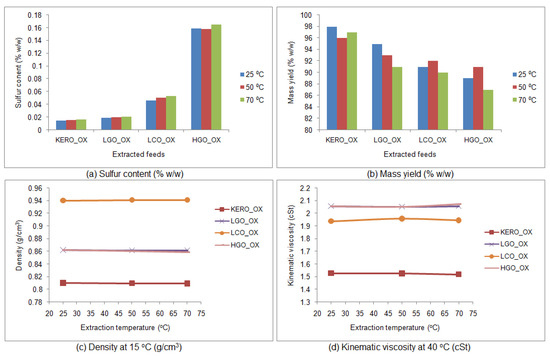
Figure 11.
Influence of temperature on the desulfurization capability of the fresh [BMIM][HSO4]: (a) sulfur content of the surrogate raffinates (% w/w), (b) mass yield of the surrogate raffinates (% w/w), (c) density of the surrogate raffinates at 15 °C (g/cm3), (d) kinematic viscosity of the surrogate raffinates at 40 °C (cSt). (KERO_ OX: oxidized surrogate kerosene, LGO_OX: oxidized surrogate LGO, LCO_OX: oxidized surrogate LCO, HGO_OX: oxidized surrogate HGO).
The FT-IR spectra of the raffinate surrogate blends were acquired. It was concluded that, regardless of the extraction temperature, the FT-IR spectra of the extracted products are completely identical. This observation reinforced the fact that, under the specific extraction conditions, the influence of temperature is negligible, while its increase may decrease the desulfurization capability of the fresh ionic liquids.
Therefore, the ambient temperature was selected for the multiple-stage extraction procedure of the surrogate blends.
3.4.2. Properties of the Raffinate Surrogate Products
The oxidized products of the surrogate kerosene, LGO, LCO and HGO were subjected to sequential extractions using the fresh ionic liquids. In every cycle of the extractions, the sulfur content (% w/w), the density at 15 °C (g/cm3) and the kinematic viscosity at 40 °C (cSt) were measured, and the desulfurization yield and the mass yield (% w/w) were estimated. The results of the extractions using the fresh [BMIM][Br] are presented in Table 6 and Table 7, while the results of the extractions using the fresh [BMIM][HSO4] are summarized in Table 8 and Table 9.

Table 6.
Sulfur content, desulfurization yield and mass yield of the surrogate raffinates during the multiple-stage extractions with fresh [BMIM][Br].

Table 7.
Density and kinematic viscosity of the surrogate raffinates during the multiple-stage extractions with fresh [BMIM][Br].

Table 8.
Sulfur content, desulfurization yield and mass yield of the surrogate raffinates during the multiple-stage extractions with fresh [BMIM][HSO4].

Table 9.
Density and kinematic viscosity of the surrogate raffinates during the multiple-stage extractions with fresh [BMIM][HSO4].
The final desulfurization yields of the raffinate surrogates of kerosene and LGO are 94 and 98%, respectively. It is evident that the desulfurization capability of the fresh [BMIM][Br] is higher than the desulfurization capability of the fresh [BMIM][HSO4], especially in the heavier surrogate blends of LCO and HGO. The final desulfurization yields of the raffinate surrogates of LCO and HGO are 97 and 98% when the extraction ionic liquid is the fresh [BMIM][Br], and 94 and 97% in the case of the fresh [BMIM][HSO4]. The density of the surrogate raffinates decreases during the successive extractions, caused by the removal of sulfur compounds, aromatics and other species from the extraction mixture. On the contrary, the viscosity of the surrogate raffinates increases. These variations are higher when the extraction ionic liquid is the fresh [BMIM][Br] because of its higher desulfurization capability. The mass yields of the raffinates using both ionic liquids usually show an increasing tendency.
During the extractive desulfurization procedure, the electrophilic cation [BMIM]+ acts as a Lewis acid. The pKa of H2SO4 is −14, while the pKa of HBr is −9; hence, H2SO4 is a stronger acid compared to HBr. Therefore, [Br]−, the conjugate base of HBr, is a stronger base compared to [HSO4]−, the conjugate base of H2SO4. Consequently, it could be assumed that the stronger base [Br]− induces greater polarization to the imidazolium cation, enhancing its electrophilicity in the removal of susceptible sulfur compounds and other species.
It is important to mention that significant partial discoloration of the surrogate raffinates takes place during the successive extractions of the oxidized surrogate products, using both fresh ionic liquids.
The sequential extractions for all oxidized surrogate blends stopped at the point where no change in the sulfur concentration of the extracted surrogate product was observed.
The use of conventional solvents, acetonitrile and methanol, leads usually to lower densities and viscosities, for almost all surrogate raffinates compared to ionic liquid extracts. Moreover, the desulfurization rates of these extractants are higher in the light surrogate oxidized blends, namely kerosene and LGO. Nevertheless, in the heavy surrogate oxidized blends the extraction procedure using ionic liquids and especially [BMIM][Br] can be comparable or even competitive with that carried out with conventional solvents. This fact is more interesting in the case of LCO’s surrogate raffinate products, since there is a great mass loss, ranging from 72 to 77%, when conventional solvents are used.
3.4.3. Liquid FT-IR Spectroscopy
The liquid FT-IR spectra of the final extraction cycle of the surrogate raffinates were acquired and compared to those of the oxidized surrogate products.
The FT-IR spectra of the surrogate kerosene’s raffinates coming from the final extraction cycle, using [BMIM][Br] and [BMIM][HSO4], and the spectrum of the oxidized surrogate kerosene are almost identical.
The FT-IR spectra of the final extraction cycle surrogate LGOs, using the two fresh ionic liquids, are completely identical. In comparison with the spectrum of the oxidized surrogate LGO, the intensities of specific peaks are reduced. The peaks most affected are the ones at 781 cm−1 due to the out-of-plane and 1011, 1128, 1266 cm−1 due to the in-plane bending of the aromatic bonds C-H, 1509, 1598 cm−1 attributed to skeletal vibrations of aromatics and heteroaromatics and 3054 cm−1 due to aromatic C-H stretching.
Similarly, the FT-IR spectra of the surrogate LCO’s raffinates coming from the final extraction cycle, using the fresh [BMIM][Br] and [BMIM][HSO4], are very much alike. The absorbance bands that are changed during the extractions of the oxidized surrogate LCO appear mainly at 1020, 1165, 1213, 1266 cm−1 due to the in-plane bending of the aromatic bonds C-H, 1313 cm−1 due to asymmetric sulfone stretching, 1397, 1508, 1597 cm−1 attributed to skeletal vibrations of aromatics and heteroaromatics and the region between 3025 and 3085 cm−1 due to aromatic C-H stretching.
In the case of surrogate HGO, the FT-IR spectra of the extracted products do not match since there a significant difference in the intensity of the peak at 781 cm−1 attributed to the out-of-plane bending of the ring C-H bonds. These spectroscopic data indicate that the fresh [BMIM][Br] seems to be a more efficient extractant than [BMIM][HSO4], and are in accordance with the above-mentioned desulfurization results. Comparatively with the spectrum of the oxidized surrogate HGO, the peaks affected most are the following, shown at 761, 781 cm−1 due to the out-of-plane and 1010, 1128, 1138, 1209, 1267 cm−1 due to the in-plane bending of the aromatic bonds C-H, 1494, 1509, 1597 cm−1 attributed to skeletal vibrations of aromatics and heteroaromatics and 3017, 3053 cm−1 due to aromatic C-H stretching.
3.5. Properties and Characterization of the Recycled Ionic Liquids
The sulfur content and the physical properties of the recycled ionic liquids are shown in Table 4 [45], in comparison with the respective properties of the new ionic liquids.
The implemented regeneration procedure decreases the sulfur concentration of the recycled [BMIM][HSO4] to an even lower level than its initial one. The physical properties of the recycled [BMIM][HSO4], namely the density and the dynamic and kinematic viscosity, are increased.
The physical properties of the recycled [BMIM][Br], i.e., the density, the dynamic viscosity and the kinematic viscosity, were reduced during the regeneration procedure. The sulfur concentration of the recycled [BMIM][Br] was not zeroed but reduced by 64%.
From the above, it is assumed that the applied regeneration procedure is quite effective in removing the sulfur substances that remain in both used ionic liquids.
3.5.1. Solid-State FT-IR Spectroscopy
The study of the FT-IR spectra of the recycled ionic liquids showed that their characteristic groups remain intact. This observation supports the assumption that both ionic liquids retain their main chemical structure during the recycling procedure.
In the FT-IR spectrum of the recycled [BMIM][Br], the quaternary anine salt formation can be attributed to the broad band at 3444 cm−1 [48,51]. The aromatic C-H stretch in cyclic imidazolium is represented by both peaks at 3147 and 3087 cm−1 [51]. The bands at 2961 and 2873 cm−1 are due to the aliphatic asymmetric and symmetric C-H stretching vibrations of the methyl groups [54]. The peaks at 1632 and 1571 cm−1 can be attributed to the C=C and C=N stretching vibrations [48]. The bands at 1465 and 1384 cm−1 are due to the aliphatic asymmetric and symmetric C-H bending vibrations of the methyl groups [54]. The peaks at 1337 and 1169 cm−1 can be attributed to aromatic and non-aromatic, respectively, tertiary amine C-N stretch [54]. The band at 850 cm−1 corresponds to the C-N stretching vibration [48,51].
In the FT-IR spectrum of the recycled [BMIM][HSO4], the quaternary amine salt formation can be attributed to the broad band at 3446 cm−1, while the aromatic C-H stretch in cyclic imidazolium can be attributed to both peaks at 3150 and 3091 cm−1. The bands at 2962 and 2874 cm−1 are due to the aliphatic asymmetric and symmetric C-H stretching vibrations of the methyl groups, while the bands at 1466 and 1385 cm−1 are due to the aliphatic asymmetric and symmetric C-H bending vibrations of the methyl groups. The peaks at 1633 and 1573 cm−1 correspond to the C=C and C=N stretching vibrations, while the peaks at 1337 cm−1 can be attributed to the aromatic tertiary amine C-N stretch. The band at 888 cm−1 corresponds to the C-N stretching vibration. The broad band at 1221 cm−1 is due to the asymmetric and symmetric S=O stretching frequency of sulfates [55].
In both FT-IR spectra of the recycled ionic liquids, the in-plane bending bands of the C-H aromatic ring bonds emerge in the region of 1300–1000 cm−1. Similarly, the bands in the low-frequency range of the spectrum between 900 and 675 cm−1 represent the out-of-plane (“oop”) bending of the C-H aromatic ring bonds [55].
The FT-IR spectra of the two recycled ionic liquids [BMIM][Br] and [BMIM][HSO4] are depicted in Figure 12 and Figure 13, respectively.
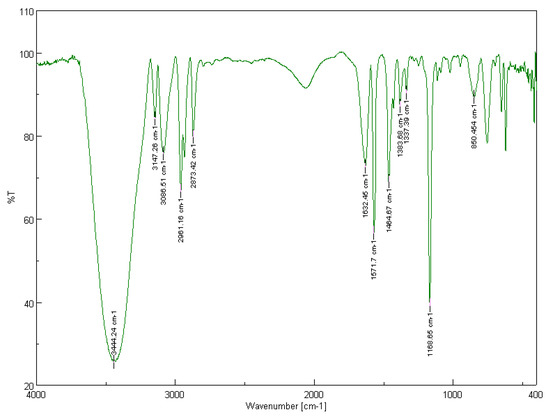
Figure 12.
Solid-state FT-IR spectrum of the recycled [BMIM][Br]. Sample pellet with KBr, number of scans: 32, resolution: 4.0 cm−1.
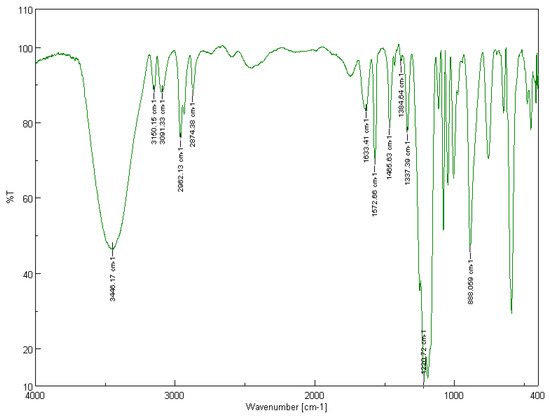
Figure 13.
Solid-state FT-IR spectrum of the recycled [BMIM][HSO4]. Sample pellet with KBr, number of scans: 32, resolution: 4.0 cm−1.
3.5.2. 1H NMR Spectroscopy
The recycled ionic liquids were identified using 1H NMR spectroscopy. The concentration of the analyte was approximately 10 mg of the recycled ionic liquid, in 0.7 mL of the solvent CDCl3. The 1H NMR spectrum of the recycled [BMIM][Br] was more or less similar to that of the new ionic liquid. This observation suggests that the regeneration procedure is quite effective in the case of [BMIM][Br]. In the 1H NMR spectrum of the recycled [BMIM][HSO4], the main peaks remain. Therefore, it is assumed that the ionic liquid retains its fundamental chemical structure. However, some new peaks emerge, which can be attributed to impurities, meaning the remaining organic sulfur compounds and other species. Therefore, it is concluded that the regeneration of [BMIM][HSO4] is adequate but not complete. The peaks that correspond to the ionic liquids [BMIM][Br] and [BMIM][HSO4] are the following.
Recycled 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide ([BMIM][Br]). 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm): 10.36 (s, 1H, H-2 methine proton), 7.55 (s, 1H, H-4 methine proton), 7.43 (s, 1H, H-5 methine proton), 4.31 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H, H-6 methylene protons), 4.10 (s, 3H, H-10 methyl protons), 1.91–1.85 (m, 2H, H-7 methylene protons), 1.40–1.31 (m, 2H, H-8 methylene protons), 0.93 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H, H-9 methyl protons). The 1H NMR spectrum of the recycled [BMIM][Br] is depicted in Figure 14.
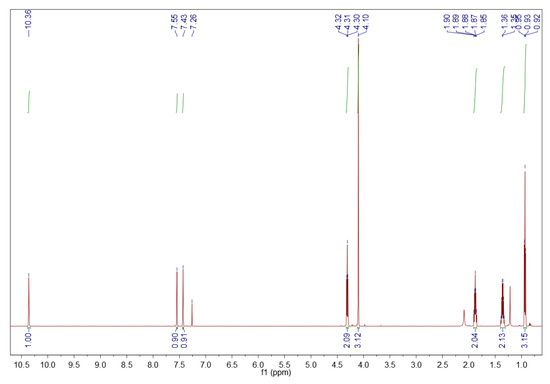
Figure 14.
1H NMR spectrum of the recycled [BMIM][Br]. Sample of 10 mg in 0.7 mL deuterated chloroform, 600 MHz.
Recycled 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulfate ([BMIM][HSO4]). 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm): 9.69 (s, 1H, H-2 methine proton), 7.32 (s, 1H, H-4 methine proton), 7.30 (s, 1H, H-5 methine proton), 4.30 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H, H-6 methylene protons), 4.07 (s, 3H, H-10 methyl protons), 1.95–1.86 (m, 2H, H-7 methylene protons), 1.46–1.37 (m, 2H, H-8 methylene protons), 1.00 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H, H-9 methyl protons). The 1H NMR spectrum of the recycled [BMIM][HSO4] is depicted in Figure 15.
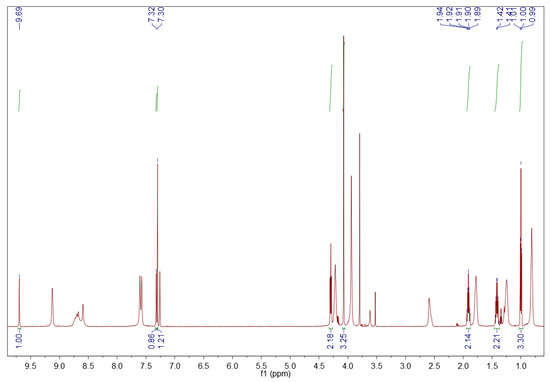
Figure 15.
1H NMR spectrum of the recycled [BMIM][HSO4]. Sample of 10 mg in 0.7 mL deuterated chloroform, 600 MHz.
3.6. Desulfurization of the Oxidized Surrogate Blends Using Recycled Ionic Liquids
3.6.1. Properties of the Raffinate Surrogate Products
A similar extraction procedure was implemented using the two recycled ionic liquids. The oxidized products of the surrogate kerosene, LGO, LCO and HGO were extracted in a multiple-cycle procedure that continued until no change in the sulfur concentration of the extracted surrogate products was observed. In every extraction cycle, the sulfur content, the density and the kinematic viscosity were measured, and the desulfurization yield and the mass yield were calculated. The results of the extractions using the recycled [BMIM][Br] are presented in Table 10 and Table 11. The results of the extractions using the recycled [BMIM][HSO4] are shown in Table 12 and Table 13. A comparison of the desulfurization capability of the two fresh and the two recycled ionic liquids is presented in Figure 16.

Table 10.
Sulfur content, desulfurization yield and mass yield of the surrogate raffinates during the multiple-stage extractions with recycled [BMIM][Br].

Table 11.
Density and kinematic viscosity of the surrogate raffinates during the multiple-stage extractions with recycled [BMIM][Br].

Table 12.
Sulfur content, desulfurization yield and mass yield of the surrogate raffinates during the multiple-stage extractions with recycled [BMIM][HSO4].

Table 13.
Density and kinematic viscosity of the surrogate raffinates during the multiple-stage extractions with recycled [BMIM][HSO4].
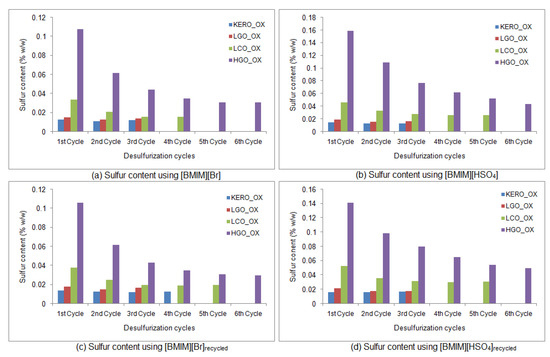
Figure 16.
Desulfurization capability of the two fresh and the two recycled ionic liquids. Sulfur content (% w/w) of the surrogate raffinates during the extractions using: (a) [BMIM][Br], (b) [BMIM][HSO4], (c) recycled [BMIM][Br], (d) recycled [BMIM][HSO4]. (KERO_ OX: oxidized surrogate kerosene, LGO_OX: oxidized surrogate LGO, LCO_OX: oxidized surrogate LCO, HGO_OX: oxidized surrogate HGO).
It is worth mentioning that both recycled ionic liquids during the successive extractions retain their ability to decolorize the surrogate products.
The final desulfurization yield of the raffinate surrogate LGO is 98%, for both recycled ionic liquids. Moreover, the final desulfurization yields of the raffinate surrogate kerosene, LCO and HGO are 94, 96 and 98% when the extraction ionic liquid is the recycled [BMIM][Br], and 92, 94 and 96% when the extraction ionic liquid is the recycled [BMIM][HSO4]. These results indicate that both recycled ionic liquids retain their desulfurization capabilities at the same levels as the fresh ones.
In Figure 16, the fresh and the recycled ionic liquids are compared for their desulfurization effectiveness, in each oxidized surrogate feed. It is obvious that the efficiency of both fresh and recycled [BMIM][Br] is almost the same. Similarly, the effectiveness of fresh and recycled [BMIM][HSO4] is very much alike. Nevertheless, [BMIM][Br] seems to be slightly superior to [BMIM][HSO4] in the extractive desulfurization procedure of surrogate blends. Conclusively, the desulfurization capability of the ionic liquids follows the order: [BMIM][Br] ≥ [BMIM][Br]recycled ≥ [BMIM][HSO4] ≥ [BMIM][HSO4]recycled.
As in the case of the fresh ionic liquids, in the recycled ionic liquids, the kinematic viscosity increases, while the density of the surrogate raffinates, in most cases, decreases during the extractions. The differences in the values of these physical parameters are higher when the extractant is the recycled [BMIM][Br], due to its better desulfurization capability in removing of sulfur substances and other species. The mass yield values of the surrogate raffinates follow an upward trend during the extractions, for both recycled ionic liquids.
Moreover, in the heavy oxidized surrogate blends, the extraction procedure using the recycled ionic liquids, as with the fresh ones, can be comparable to the procedure using the conventional solvents acetonitrile and methanol.
3.6.2. Liquid FT-IR Spectroscopy
The FT-IR spectra of the final surrogate raffinates that were extracted using the recycled ionic liquids were acquired and studied. Afterwards, they were compared to the respective spectra using the fresh ionic liquids.
It is concluded that the FT-IR spectra of the surrogate raffinates that were extracted using the recycled ionic liquids are similar and, in some cases, completely identical to the ones using the fresh ionic liquids.
The FT-IR spectra of the extracted surrogate kerosene are almost the same using both fresh and recycled ionic liquids.
In the case of the surrogate LGO, the FT-IR spectra of the extracted products using fresh and recycled [BMIM][Br] are similar, as well as the spectra of the surrogate raffinates using fresh and recycled [BMIM][HSO4]. Nevertheless, [BMIM][Br] prevails over [BMIM][HSO4] in terms of the extractive efficiency, as can be concluded from the intensity of the peak at 781 cm−1 attributed to the out-of-plane bending of the aromatics.
The FT-IR spectra of the surrogate LCO’s raffinates with fresh and recycled [BMIM][HSO4] are almost the same. The monitoring of the intensity of the absorbance band in the region 3025–3087 cm−1, due to aromatic C-H stretching, shows that the effectiveness of the ionic liquids follows the order: [BMIM][Br]recycled ≥ [BMIM][Br] ≥ [BMIM][HSO4] = [BMIM][HSO4]recycled.
Finally, the FT-IR spectra of the surrogate HGO’s raffinates with fresh and recycled [BMIM][Br] are nearly identical. The observation of the peak’s intensity at 781 cm−1, attributed to the out-of-plane absorption bands of the aromatics, results in the below sequence indicating their extractive efficiency: [BMIM][Br]recycled = [BMIM][Br] ≥ [BMIM][HSO4] ≥ [BMIM][HSO4]recycled.
From the above-mentioned spectroscopic data, it can be concluded that the differences in the FT-IR spectra of the surrogate raffinates are minor; therefore, the desulfurization and extractive capability of the ionic liquids is in agreement with the above-mentioned sequence: [BMIM][Br] ≥ [BMIM][Br]recycled ≥ [BMIM][HSO4] ≥ [BMIM][HSO4]recycled.
4. Conclusions
In the present study, four surrogate blends that correspond to petroleum fractions were synthesized using different kinds of model sulfur compounds and hydrocarbons typical of those present in petroleum middle fractions. Our focus was to utilize the surrogate blends to imitate their petroleum analogs, and to be as simple and stable as possible, during their stay for a reasonable period of time.
The implemented desulfurization procedure combined both oxidative and extractive desulfurization, using conventional solvents and ionic liquids. The process resulted in high desulfurization efficiency for all surrogate blends. When ionic liquids were used as extractants, the maximum desulfurization yields achieved were as follows: 94% for surrogate kerosene, 98% for surrogate LGO, 97% for surrogate LCO and 98% for surrogate HGO.
The raffinate surrogate products were discolored, and their density decreased, during the multiple extraction cycle procedure using both fresh and recycled ionic liquids. The data obtained from the processing of the FT-IR spectra match and correspond to the characteristics and properties of the extracted surrogate products.
In the case of surrogate LCO, the procedure carried out with the fresh and recycled [BMIM][Br] can be competitive with the respective one performed with acetonitrile. The desulfurization capability of the applied ionic liquids follows the order: [BMIM][Br] ≥ [BMIM][Br]recycled ≥ [BMIM][HSO4] ≥ [BMIM][HSO4]recycled.
Conclusively, the regeneration process seems to be significantly efficient. The sulfur content of the recycled [BMIM][Br] was reduced by 64%. In the case of the recycled [BMIM][HSO4], the sulfur content reached its initial concentration. The desulfurization capabilities of both ionic liquids remain intact after their recovery and regeneration.
Author Contributions
The authors listed contributed substantially to the work reported in this research article. E.S. prepared the original draft. D.K. reviewed and edited the manuscript before submission. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Hellenic Petroleum Elefsis and Aspropyrgos refineries for the petroleum feeds’ supply and also the Hellenic Petroleum SA Laboratories for the technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Babich, I.V.; Moulijn, J.A. Science and Technology of Novel Processes for Deep Desulfurization of Oil Refinery Streams: A Review. Fuel 2003, 82, 607–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, E.; van Veen, J.A.R. On Novel Processes for Removing Sulfur from Refinery Stream. Catal. Today 2006, 116, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A. Characterization, Determination and Elimination Technologies for Sulfur from Petroleum: Toward Cleaner Fuel and a Safe Environment. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 25, e00080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Srivastava, V.C.; Nanoti, S.M. Extractive Desulfurization of Gas Oils: A Perspective Review for Use in Petroleum Refineries. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2017, 46, 319–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, R.; Anbia, M. Zeolites for Adsorptive Desulfurization from Fuels: A Review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 167, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; He, H.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, C.; Zeng, G.; Qiu, L. Performances, Kinetics and Mechanisms of Catalytic Oxidative Desulfurization from Oils. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 103253–103269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boniek, D.; Figueiredo, D.; Dos Santos, A.F.B.; Stoianoff, M.A.D.R. Biodesulfurization: A Mini Review about the Immediate Search for the Future Technology. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2015, 17, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebali, G.; Ball, A.S. Biodesulfurization of Diesel Fuels: Past, Present and Future Perspectives. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 110, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimlich, B.N.; Wallace, T.J. Kinetics and Mechanism of the Oxidation of Dibenzothiophene in Hydrocarbon Solution. Tetrahedron 1966, 22, 3571–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aida, T.; Yamamoto, D. Oxidative desulfurization of liquid fuels. In Proceedings of the American Chemical Society (ACS) National Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 21–26 August 1994; Volume 39, pp. 623–626. [Google Scholar]
- Zannikos, F.; Lois, E.; Stournas, S. Desulfurization of Petroleum Fractions by Oxidation and Solvent Extraction. Fuel Process. Technol. 1995, 42, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, S.; Nonaka, T.; Takashima, N.; Qian, W.; Ishihara, A.; Imai, A.T.; Kabe, T. Oxidative Desulfurization of Light Gas Oil and Vacuum Gas Oil by Oxidation and Solvent Extraction. Energy Fuels 2000, 14, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, Y.; Tachibana, K.; Hirai, T.; Komasawa, I. Desulfurization and Denitrogenation Process for Light Oils Based on Chemical Oxidation Followed by Liquid-Liquid Extraction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 4362–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, P.; Scarsella, M. Oxidative Desulfurization: Oxidation Reactivity of Sulfur Compounds in Different Organic Matrixes. Energy Fuels 2003, 17, 1452–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, Y.; Hirai, T. Desulfurization of Vacum Gas Based on Chemical Oxidation Followed by Liquid-Liquid Extraction. Energy Fuels 2004, 18, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.F.; Al-Malki, A.; El-Ali, B.; Martinie, G.; Siddiqui, M.N. Deep Desulfurization of Gasoline and Diesel Fuels Using Non-Hydrogen Consuming Techniques. Fuel 2006, 85, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkordi, A.M.; Sobati, M.A.; Nazem, M.A. Oxidative Desulfurization of Non-hydrotreated Kerosene Using Hydrogen Peroxide and Acetic Acid. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 17, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedzeki, N.S.; Ibrahem, B.J. Reduction of Sulfur Compounds from Petroleum Fraction Using Oxidation-Adsorption Technique. Iraqi J. Chem. Pet. Eng. 2015, 16, 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Rakhmanov, E.V.; Domashkin, A.A.; Myltykbaeva, Z.K.; Kairbekov, Z.; Shigapova, A.A.; Akopyan, A.V.; Anisimov, A.V. Peroxide Oxidative Desulfurization of a Mixture of Nonhydrotreated Vacuum Gas Oil and Diesel Fraction. Pet. Chem. 2016, 56, 742–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karonis, D.; Syntyhaki, E. Oxidative desulfurization of petroleum middle distillates using hydrogen peroxide/acetic acid and solvent extraction. In Proceedings of the 12th International Colloquium, Fuels—Conventional and Future Energy for Automobiles, Stuttgart, Germany, 25–26 June 2019; pp. 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Qian, E.W.; Amano, H.; Okata, K.; Ishihara, A.; Kabe, T. Oxidative desulfurization of fuel oil Part I. Oxidation of dibenzothiophenes using tert-butyl hydroperoxide. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 253, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, A.; Wang, D.; Dumeignil, F.; Amano, H.; Qian, E.W.; Kabe, T. Oxidative desulfurization and denitrogenation of a light gas oil using an oxidation/adsorption continuous flow process. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 279, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chica, A.; Corma, A.; Dómine, M.E. Catalytic oxidative desulfurization (ODS) of diesel fuel on a continuous fixed-bed reactor. J. Catal. 2006, 242, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, B.N.; Jhung, S.H. Oxidative Desulfurization and Denitrogenation of Fuels Using Metal-Organic Framework-Based/-Derived Catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 259, 118021–118045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliao, D.; Mirante, F.; Ribeiro, S.O.; Gomes, A.C.; Valenca, R.; Ribeiro, J.C.; Pillinger, M.; de Castro, B.; Goncalves, I.S.; Balula, S.S. Deep Oxidative Desulfurization of Diesel Fuels Using Homogeneous and SBA-15-Supported Peroxophosphotungstate Catalysts. Fuel 2019, 241, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, F.A.; Mello, P.D.A.; Bizzi, C.A.; Nunes, M.A.; Moreira, E.M.; Alencar, M.S.; Motta, H.N.; Dressler, V.L.; Flores, É.M. Sulfur Removal from Hydrotreated Petroleum Fractions Using Ultrasound-Assisted Oxidative Desulfurization Process. Fuel 2011, 90, 2158–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ja’fari, M.; Ebrahimi, S.L.; Khosravi-Nikou, M.R. Ultrasound-Assisted Oxidative Desulfurization and Denitrogenation of Liquid Hydrocarbon Fuels: A Critical Review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, N.S.; Gogate, P.R. Intensified Approach for Desulfurization of Simulated Fuel Containing Thiophene Based on Ultrasonic Flow Cell and Oxidizing Agents. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 51, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, T.; Ramalingam, A. Desulfurization and Denitrification of Diesel Oil Using Ionic Liquids. Experiments and Quantum Chemical Predictions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; p. 342. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Xia, S.; Ma, P. Use of ionic liquids as ‘green’ solvents for extractions. Review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A. Oxidative desulfurization of fuels using ionic liquids: A review. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2015, 9, 262–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.H.; Hayyan, M.; Hashim, M.A.; Hayyan, A. The role of ionic liquids in desulfurization of fuels: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 1534–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Abdeltawab, A.A.; Yakout, S.M.; Yu, G. A combination desulfurization method for diesel fuel: Oxidation by ionic liquid with extraction by solvent. Fuel 2018, 224, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Sun, Z.; Li, F. Optimization of oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene using acidic ionic liquid as catalytic solvent. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2009, 37, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Guo, C.; Xing, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H. Extraction and oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuel catalyzed by a Brønsted acidic ionic liquid at room temperature. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1220–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Song, D.; Asumana, C.; Yu, G. Deep oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuels by Lewis acidic ionic liquids based on 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium metal chloride. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2012, 359, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Dong, Y.; Bai, L.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X. Fast oxidative desulfurization of fuel oil using dialkylpyridinium. Fuel 2013, 103, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Guan, Y.; Abdeltawab, A.A.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Yuan, X.; Wang, C.; Yu, G. Using functional acidic ionic liquids as both extractant and catalyst in oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuel: An investigation of real feedstock. Fuel 2015, 146, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Guo, H.; Abdeltawab, A.A.; Guan, Y.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Yu, G.; Yu, L. Brønsted–Lewis Acidic Ionic Liquids and Application in Oxidative Desulfurization of Diesel Fuel. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 2998–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bösmann, A.; Datsevich, L.; Jess, A.; Lauter, A.; Schmitz, C.; Wasserscheid, P. Deep desulfurization of diesel fuel by extraction with ionic liquids. Chem. Comm. 2001, 23, 2494–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eßer, J.; Wasserscheid, P.; Jess, A. Deep desulfurization of oil refinery streams by extraction with ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2004, 6, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, N.L.; Ahn, K.; Koo, Y.-M. Methods for recovery of ionic liquids—A review. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmina, O.; Hallett, J.P. (Eds.) Application, Purification, and Recovery of Ionic Liquids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; p. 286. [Google Scholar]
- Sarathy, S.M.; Farooq, A.; Kalghatgi, G.T. Recent progress in gasoline surrogate fuels. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2018, 65, 67–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syntyhaki, E.; Karonis, D. Oxidative and extractive desulfurization of petroleum middle distillates, using imidazole ionic liquids. Fuel Comm. 2021, 7, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, H.E.; Kotlyar, V.; Nudelman, A. NMR Chemical Shifts of Common Laboratory Solvents as Trace Impurities. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 7512–7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsanas, C.; Tzani, A.; Papadopoulos, A.; Detsi, A.; Voutsas, E. Ionic liquids as entrainers for the separation of the ethanol/water system. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2014, 379, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharaskar, S.A.; Wasewar, K.L.; Varma, M.N.; Shende, D.Z. Imidazolium ionic liquid as energy efficient solvent for desulfurization of liquid fuel. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 155, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajika, H.; Niknam, K.; Parsa, F. Using Acidic Ionic Liquid 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium Hydrogen Sulfate in Selective Nitration of Phenols under Mild Conditions. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2009, 6, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Kaur, S.; Sapehiyia, V.; Singh, J.; Kad, G. Microwave accelerated preparation of [bmim][HSO4] ionic liquid: An acid catalyst for improved synthesis of coumarins. Catal. Commun. 2005, 6, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bui, T.T.; Nguyen, D.D.; Van Ho, S.; Nguyen, B.T.; Uong, H.T.N. Synthesis, characterization and application of some non-halogen ionic liquids as green solvents for deep desulfurization of diesel oil. Fuel 2017, 191, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, K.R.; Stark, A.; Torre, M.-J. Viscosity and Density of 1-Alkyl-3-methylimidazolium Ionic Liquids. In Clean Solvents; (ACS Symposium Series); American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; Volume 819, pp. 34–49. [Google Scholar]
- Tshibangu, P.N.; Ndwandwe, S.N.; Dikio, E.D. Density, Viscosity and Conductivity Study of 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium Bromide. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of Infrared Spectra, A Practical Approach. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: West Essex, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Webster, F.X.; Kiemle, D.J. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- De Filippis, P.; Scarsella, M.; Verdone, N. Oxidative Desulfurization I: Peroxyformic Acid Oxidation of Benzothiophene and Dibenzothiophene. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 4594–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syntyhaki, E.; Karonis, D. Evaluation of Oxidative Desulfurization and Solvent Extraction of Model Sulfur Compounds, Present in Petroleum Middle Distillates, with Infrared and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Anal. Lett. 2020, 54, 1470–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.N.; Espenson, J.H. Stepwise Oxidation of Thiophene and Its Derivatives by Hydrogen Peroxide Catalyzed by Methyltrioxorhenium(VII). Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 7211–7216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geneste, P.; Olive, J.L.; Ung, S.N.; Faghi, M.E.A.E.; Easton, J.W.; Beierbeck, H.; Saunders, J.K. Carbon-13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study of Benzo[b]thiophenes and Benzo[b]thiophene S-Oxides and S,S-Dioxides. J. Org. Chem. 1979, 44, 2887–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiemann, T.; Arima, K.; Kumazoe, K.; Mataka, S. Benzothiophene-S-Oxides—An Overview. Rep. Inst. Adv. Mater. Study 2000, 14, 139–142. [Google Scholar]
- Madec, D.; Mingoia, F.; Macovei, C.; Maitro, G.; Giambastiani, G.; Poli, G. New Enantiopure Bis(thioether) and Bis(sulfoxide) Ligands from Benzothiophene. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 2005, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Liu, A.-H.; He, L.-N.; Li, B.; Diao, Z.-F.; Li, Y.-N. Catalyst-free approach for solvent-dependent selective oxidation of organic sulfides with oxone. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).