Abstract
The association between type 1 diabetes (T1D) and coeliac disease (CD) is well known. Metabolic control of thirty-seven patients aged between 1 and 18 years, with coexisting T1D and CD were evaluated. The control group includes 37 patients affected only by diabetes. All data relating to the metabolic control of all patients were acquired through examination of medical records and CMG reports available on dedicated online platforms. Glucose variability was expressed as Coefficient of Variation (CV) and Standard Deviation of blood glucose values (SD). The formula used for CV computation is: CV (%) = 100 × SD (daily glycemia)/Mean (daily glycemia). Patients with T1D and CD showed a significant reduction in rapid pre-prandial insulin. The same reduction was present if we consider only patients using CGM. In patients without CGM, there was no difference in the doses of basal, pre-prandial and total insulin. Indicators of metabolic control were overlapping between the two groups in patients who used CGM. On the contrary, diabetic and coeliac patients without CGM had increased levels of glycaemic variability indicators and HbA1c. Finally, the percentage of target glycaemic values and >250 mg/dL glycaemic values were significantly decreased and increased, respectively in T1D and CD patients without CGM. With this study we wanted to demonstrate if CGM could improve metabolic control of patients with coexisting T1D and CD. Our data show a worse metabolic control in patients with T1D and CD who did not use CGM. Instead, patients who use CGM, regardless of the concomitant CD, manage to achieve the same glycaemic targets through an adjustment of titration of pre-prandial insulin doses.
1. Introduction
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is one of the most common chronic diseases of childhood [1]. It is characterized by a deficit or absence of insulin resulting from T-cell-mediated destruction of beta cells of the pancreas, and the development of islet-specific autoantibodies [2,3]. Coeliac disease (CD) is an autoimmune disorder caused by “gluten”, the alcohol-soluble protein fraction of the wheat, in individuals with genetic predisposition [4]. The first association between type 1 diabetes and coeliac disease was suggested in 1969 [5]. This association is linked to the genetic risk factors of both diseases which include human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genes and non-HLA genes [6,7]. CD is observed in about 10% of patients with T1D, and the prevalence of CD among children with T1D is significantly higher than in non-diabetic children [8,9]. Most children are asymptomatic or only mildly symptomatic for CD, so screening for CD is recommended for children with T1D at the onset and during follow-up [10].
T1D management was radically changed after the publication of the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) [11]. Insulin therapy became the standard of care for T1D treatment with the aim of adjusting blood glucose and glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c) levels in order to prevent future complications [12,13]. A lot of new therapeutics have been created in the last two decades (insulin pump or continuous glucose monitoring—CGM), especially in children, but T1D treatment remains a big challenge for the patients and their families [14]. A multidisciplinary team approach is necessary to provide guidance and help in the use of new technologies [15].
CGM was introduced in 1999 and consists of a disposable sensor that measures glucose concentration in the interstitial fluid, and a transmitter that sends and stores the sensor values to a receiver and other mobile devices (smartphone, smart watch, cloud—with the possibility of sharing the data with the family members and health professionals) [16].
The use of CGM, which includes both real-time CGM (rtCGM) and intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM), has grown rapidly over the past few years thanks to the improvements in sensor accuracy, greater convenience and ease of use, and expanding reimbursement [17].
Although the association between T1D and CD has been known for some time, how much this really affects the patient’s metabolic control has not yet been fully clarified.
Specifically, studies have analysed the metabolic control in this particular condition. However, very few take into consideration the use of CGM, which could instead be useful to reduce the discomfort of these patients deriving from all the dietary restrictions and nutritional characteristics of gluten-free products. In fact, the gluten-free diet (GFD) currently represents the standard treatment of CD and the only one needed in more than 70% of patients [18].
Recent studies show that patients with CD seem to have similar lifestyle and similar total daily energy intake compared to control groups. GFD is usually characterised by higher intake of fat and a lower intake of fibre and carbohydrates. The principle concern is the high consumption of total and saturated fats in GFD, which exceeds the nutritional goal recommended by the current reference intake levels for the Italian population (LARN) [19]. Furthermore, a lot of gluten-free foods have a high glycaemic index and so they could have an impact on glycaemic values, HbA1c, insulin doses, lipid profile, and risk of complications [20].
Evidence indicates long-term negative outcomes for patients suffering from both T1D and CD, including an increased risk of retinopathy, nephropathy, and subclinical atherosclerosis [21].
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the metabolic control of patients with coexisting T1D and CD in paediatric age (1–18 years), considering in particular the management of diabetes using CGM, the data it provides to the patient, and the benefit it can bring to the patient. The hypothesis is that CGM may improve metabolic control in patients who follow a GFD.
2. Materials and Methods
Metabolic control was evaluated in 37 patients, with coexisting T1D and CD. All enrolled patients had diabetes onset for at least 12 months and had been on a GFD for at least 6 months. For all patients, the diagnosis of T1D was made at the regional centre of Diabetology of the “SS. Annunziata” Hospital in Chieti. The diagnosis of T1D was based on one or more diabetes-associated autoantibodies (glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 autoantibodies—GAD, tyrosine phosphatase-like insulinoma antigen 2—IA2, insulin autoantibodies—IAA, and beta-cell specific zinc transporter 8 autoantibodies—ZnT8). The diagnosis of CD was made according to the 2012 guidelines of ESPGHAN (European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition). No distinction was made for the type of T1D onset (whether with DKA or not), nor for the type of clinical presentation of CD.
The age range of patients was from 1 to 18 years; the median age was 13.44 years. There were 20 females and 17 male patients; the median of the age of female patients was 15.9; the median of the age for male patients was 13.1. Twenty-eight patients followed multiple daily injections (MDI) therapy schedule while nine patients used continuous subcutaneous insulin injection (CSII); 20 patients used CGM and 17 used subcutaneous blood glucose monitoring (SBGM). CGM systems used by patients involved in our study were FreeStyle Libre 2 and Dexcom G5.
All the data considered in this study were collected during the last quarterly clinical checkup carried out (period considered: from September 2020 up to September 2021) in a state of clinical well-being of the patient. Written informed consent was obtained for all patients after the visit.
Apart from T1D and CD, only 2 of the 37 patients presented further comorbidities: one male patient was affected by trisomy 21 and one female patient by Turner syndrome.
Exclusion criteria were other diabetes type, age < 1 year or ≥18 years, use of systemic glucocorticoids for seven or more consecutive days during the last 3 months, known hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism not adequately controlled, poor adherence to GFD, treatment with oral glucose-lowering drugs at any time after diagnosis. Furthermore, all patients who, at the time of the last clinical checkup, reported recent signs and/or symptoms probably attributable to intercurrent pathologies were excluded. The adherence to GFD was monitored periodically with dosage of coeliac antibodies and absence of signs or symptoms suggestive of re-exposure to gluten.
Metabolic control—HbA1c, insulin requirement, percentage of time in range (TIR), time above range (TAR), time below range (TBR), average of blood glucose values, glycaemic variability (%CV or SD—coefficient of variation and standard deviation of blood glucose values)—of these patients with T1D and CD was compared with a group of patients affected only by T1D.
The control group was made of 37 patients with the same personal characteristics: 20 females and 17 male patients; age range from 1 to 18 years; the median of the age was 13.45; the median age of female patients was 16; the median age for male patients was 13.1.
All personal and anamnestic data of both the intervention group and the control group were acquired from medical records.
All data relating to the metabolic control of all patients were acquired through an examination of medical records and through the data available on dedicated online platforms, in particular Diasend® Personal and Libreview®, free services for diabetic patients used for monitoring their blood sugar, CGM, and insulin from home.
Demographic and clinical characteristics collected were sex, age at the time of the clinical check-up, age at diabetes diagnosis, T1D duration, mode of diabetes management (CSII or MDI), insulin dose (U/kg/day), use or not of CGM, age at coeliac disease diagnosis, coeliac disease duration, anthropometric measurements at the time of the clinical check-up (height, weight, and body mass index [BMI]), with z-scores computed using Cacciari and Milani data [22,23].
All patients were managed according to standard care. Specifically, in our centre, carbohydrate counting and education on glycaemic index or insulin coverage of high-fat, high-protein meals are commonly introduced at onset of disease. Metabolic control data documented were insulin sensitivity factor, insulin-carbohydrate ratio, HbA1c levels, percentage of time above range (TAR—% of readings and time > 250 mg/dL—Level 2), time above range (TAR—% of readings and time 181–250 mg/dL—Level 1), time in range (TIR—% of readings and time 70–180 mg/dL, time below range (TBR—% of readings and time 54–69 mg/dL—Level 1, time below range (TBR—% of readings and time < 54 mg/dL—Level 2), mean glucose, glycaemic variability (standard deviation—DS—and coefficient of variability—CV).
The data relating to metabolic control were calculated by evaluating the glycaemic trend (with the CGM) or the daily blood sugar levels for a period of one month earlier than the clinical control considered.
Baseline variables included age, sex, duration of diabetes, bodyweight, body mass index (BMI), insulin regimen, HbA1c; I:CHO ratio. Follow-up variables included daily blood glucose levels (BGL) and blood glucose variability. Self-monitoring blood glucose measurements were downloaded on the physician computers using the Diasend® system. Data from the 30 days before clinical check-up were extracted. Baseline characteristics were expressed as mean and standard deviation (SD) or percentage for continuous and categorical variables, respectively. All data were compared using Student’s t test for paired data, and when appropriate, Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test. Mean glycaemic levels were computed by day by insulin regimen. Glucose variability was expressed as Coefficient of Variation (CV) [24] and Standard Deviation of blood glucose values (SD). The formula used for CV computation was CV (%) = 100 × SD (daily glycemia)/Mean (daily glycemia).
Results were expressed as the estimated mean with their 95% confidence intervals (CIs). p-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
The t-test (also known as Student’s t-test) is a tool for evaluating the means of one or two populations by hypothesis testing. The t-test can be used to determine whether a single group differs from a known value (one-sample t-test), whether two groups differ from each other (t-test two independent samples), or whether there is a significant difference in paired measurements (test t with dependent samples or paired). In this study t-test two independent samples and test t with paired samples have been used.
All analyses were performed using SAS software release 24 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA).
The study protocol was approved by the local Ethics Committee for Biomedical Research (Comitato Etico per la Ricerca Biomedica delle Province di Chieti e di Pescara e dell’Università degli Studi “G.d’Annunzio” di Chieti e Pescara; reporting of ethics approval n. 6 of 31 March 2016).
3. Results
Statistical analyses were carried out on all data of 37 patients, of whom 28 patients (75.7%) followed MDI therapy schedule; 9 patients (24.3%) used CSII; 20 (54%) of 37 patients used CGM. All patients had good compliance to GFD. Statistical analyses were carried out in the control group of 37 patients, of whom 28 patients (75.7%) followed multiple daily injections (MDI) therapy schedule; 9 patients (24.3%) used CSII; 20 (54%) patients used CGM (See Table 1).

Table 1.
Statistical results for paired data between the two group of patients.
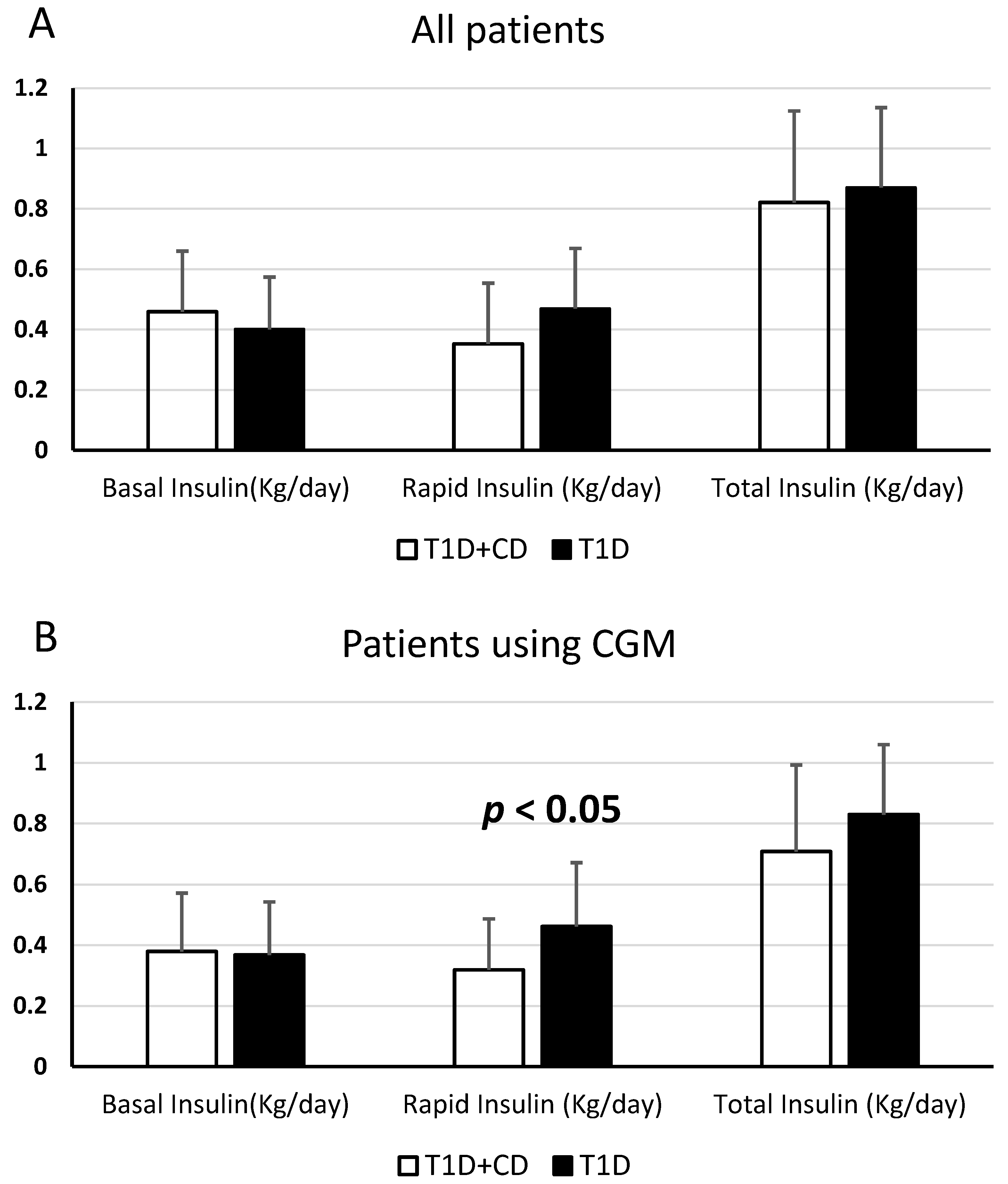
In the comparison between patients with coexisting T1D and CD and only T1D patients, a statistically significant difference was found in the mean of daily doses of rapid insulin/kg. In particular, the mean in patients affected by both diseases was 0.35 ± 0.2 U/Kg/day, and the mean of doses of rapid insulin/kg in patients affected by only diabetes was 0.47 ± 0.2 U/Kg/day—(p < 0.05), so patients with T1D + CD use less doses of rapid insulin than only T1D patients.
These data were confirmed in the analysis of all patients who used CGM (20 patients with T1D and CD and 20 patients with only T1D). The difference about the mean of daily doses of rapid insulin/kg was found statistically significant. In patients affected by both diseases, the mean of daily doses of rapid insulin/kg was 0.32 ± 0.17 U/Kg/day, the mean of doses of rapid insulin/kg in patients affected by only diabetes was 0.46 ± 0.21 U/Kg/day—(p < 0.05).
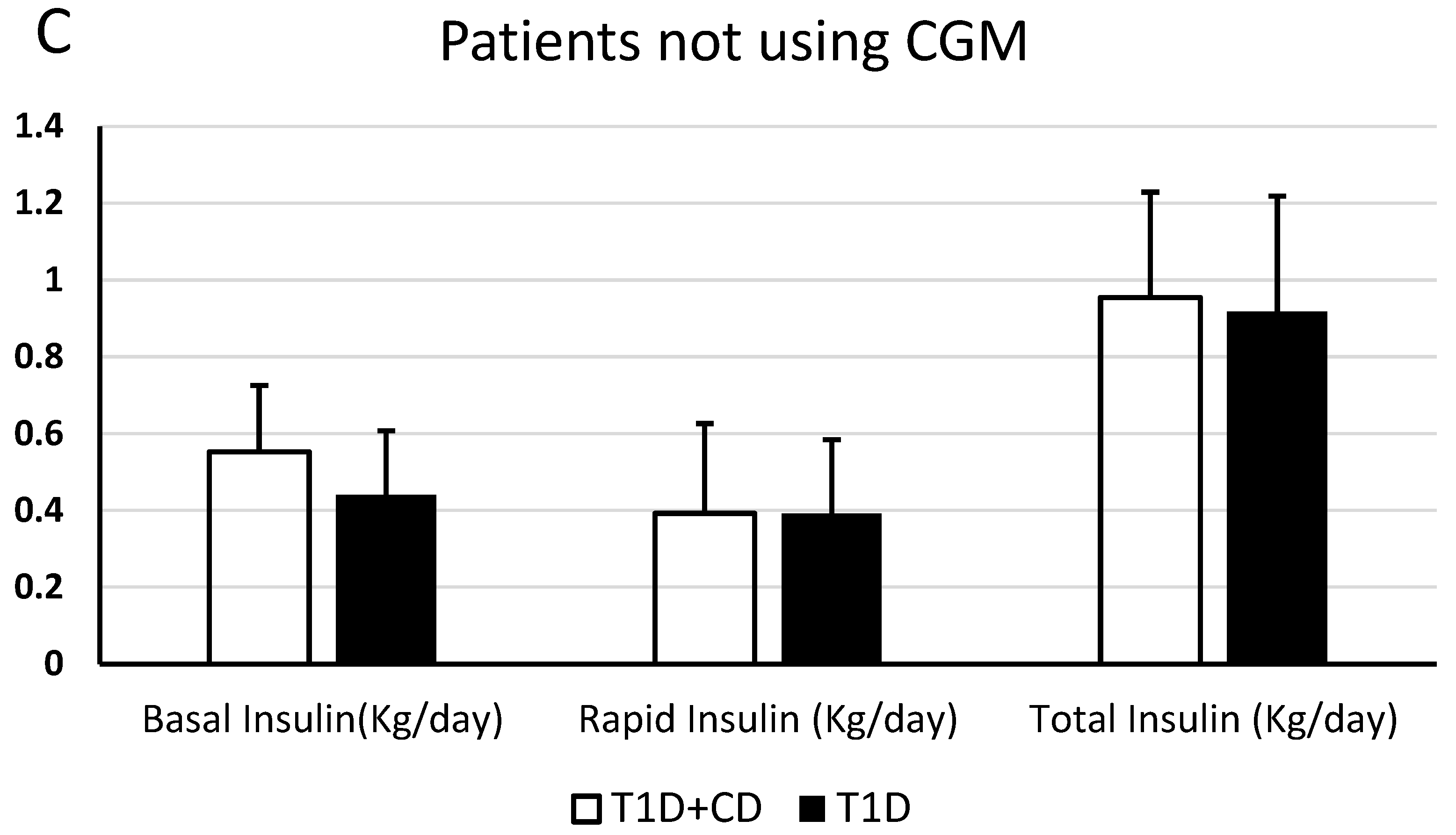
In patients who did not use CGM, there was no statistically significant difference in the doses of basal, pre-prandial or total insulin/kg.
In patients affected by both diseases, not using CGM, the mean doses of rapid insulin/kg was 0.39 ± 0.23 U/Kg/day, the mean doses of rapid insulin/kg in patients affected by only diabetes was 0.48 ± 0.19 U/Kg/day—(p > 0.05) (Figure 1).
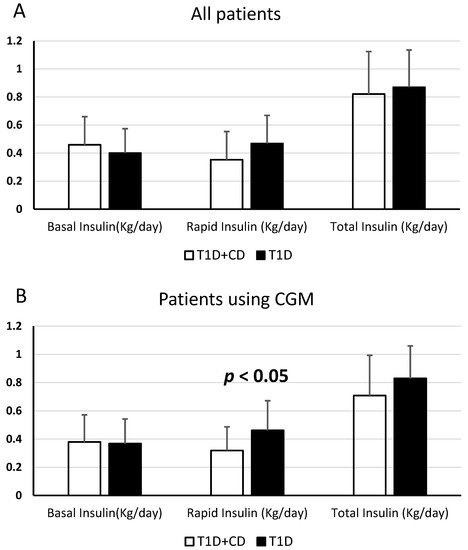
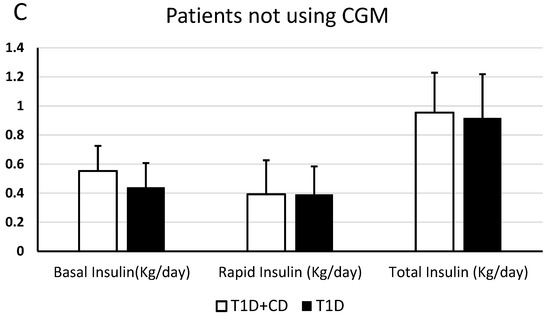
Figure 1.
Difference between patients with T1D + CD and only T1D patients, concerning the mean of daily doses of basal insulin, rapid insulin and total insulin (U/kg/day). (A): statistically significant difference considering all patients; (B): statistically significant difference comparing patients who use CGM; (C): no statistically significant difference comparing patients who do not use CGM.
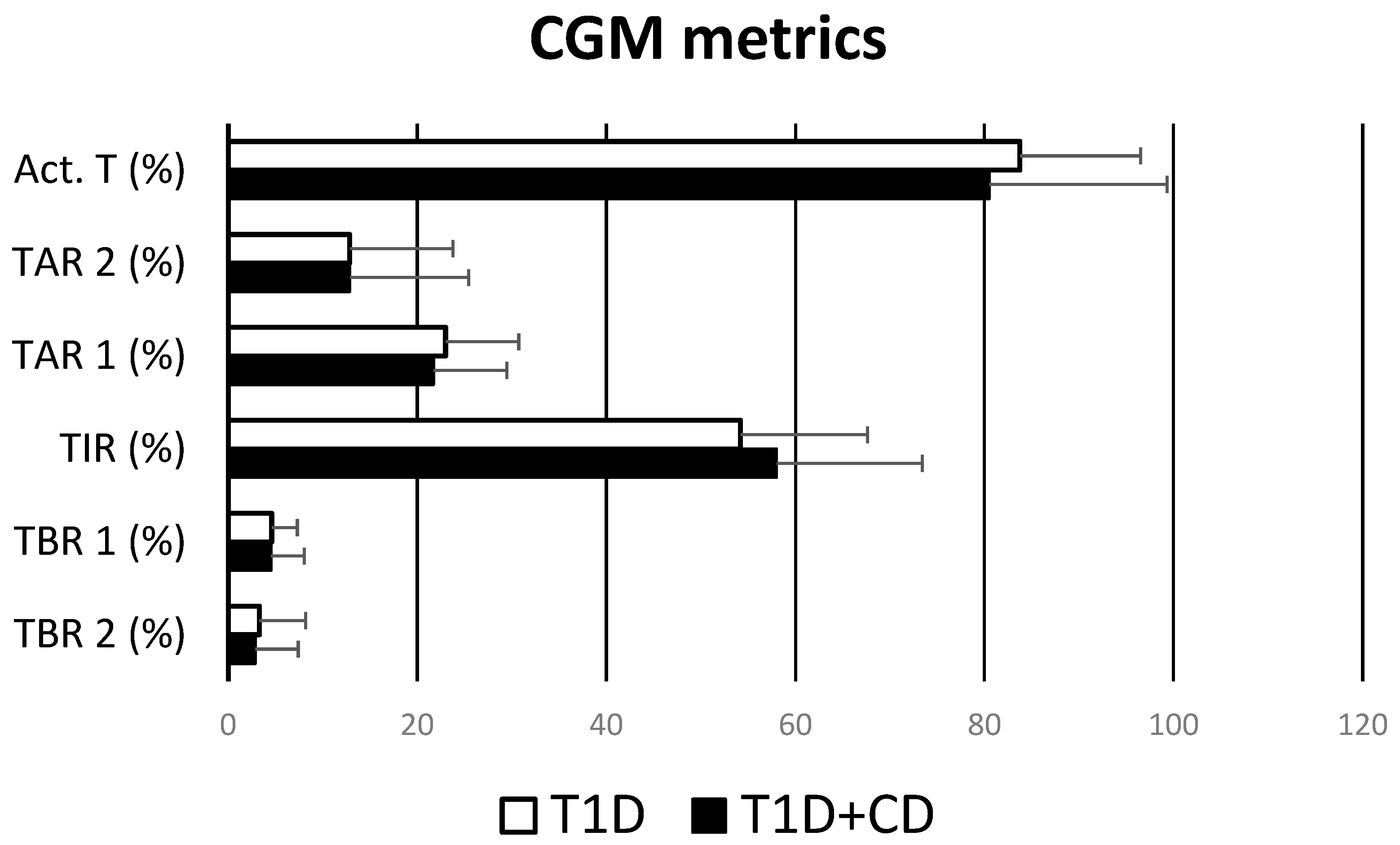
In addition, CGM metrics about metabolic control in all patients were found to overlap between the two groups of patients: no statistically significant differences were detected between % activity time, % TAR 2, % TAR 1, % TIR, % TBR 2, % TBR 1 (Figure 2).
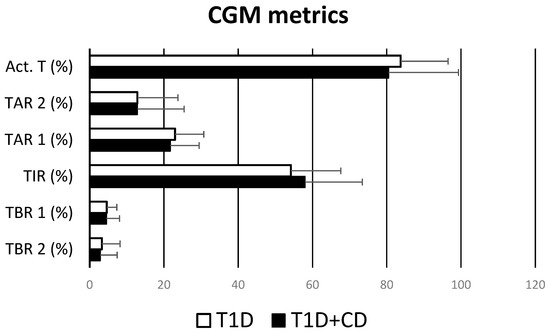
Figure 2.
Comparison between CGM metrics between patients with T1D + CD and only T1D.
All statistical results of patients using CGM are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Statistical results for paired data between patients (T1D + CD and only T1D) who use CGM.
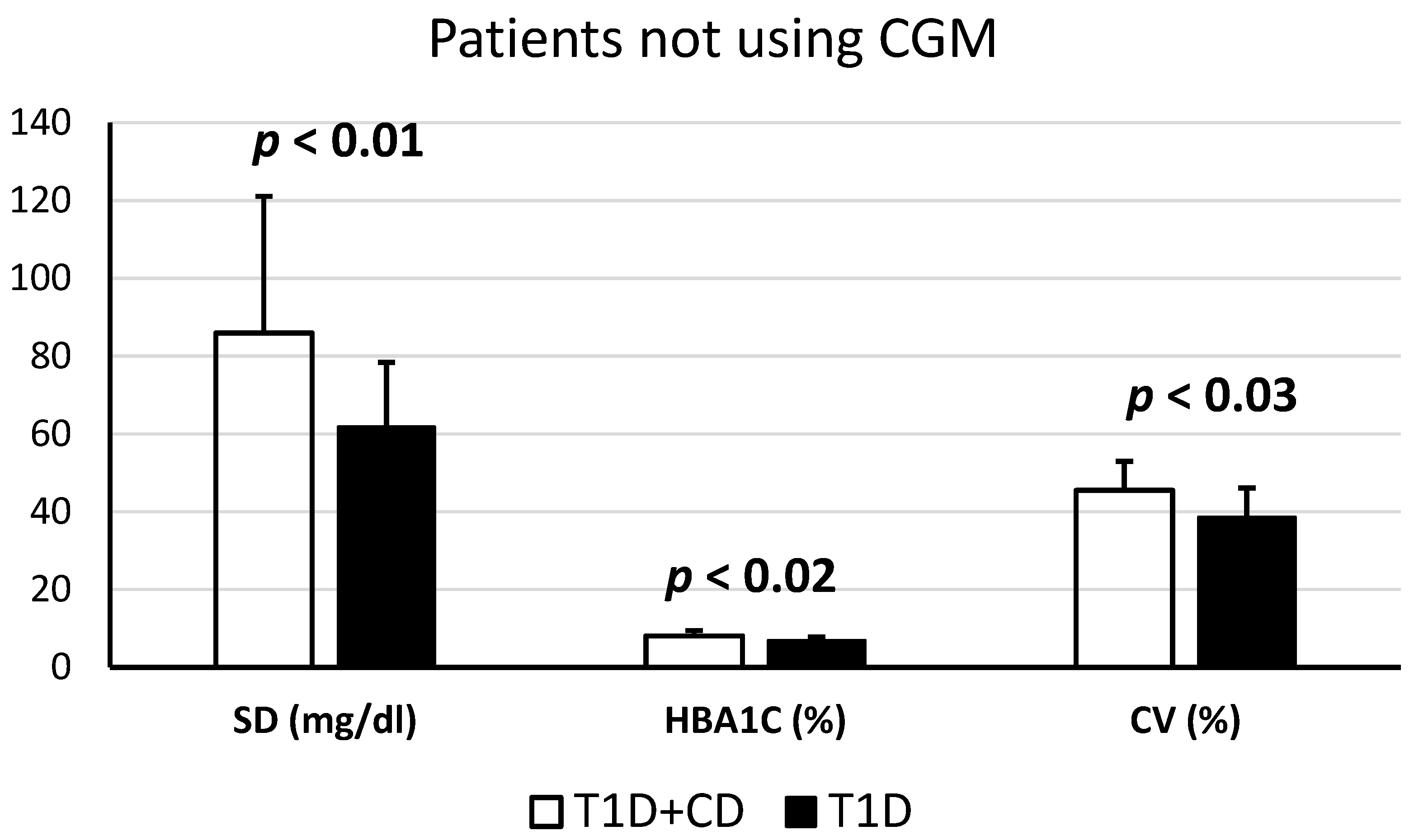
Concerning glucose variability, in all patients not using CGM, a statistically significant difference was found between SD, CV, and HbA1c levels (%), comparing patients affected by T1D and CD and patients with only T1D.
In particular, the SD value in T1D + CD patients not using CGM was 85.95 ± 35.18 mg/dL, the SD value in T1D patients not using CGM was 61.82 ± 16.59 mg/dL—(p < 0.05). The mean of CV in T1D + CD patients not using CGM was 45.5 ± 9.67%. The mean of CV in T1D patients not using CGM was 38.65 ± 7.47%—(p < 0.05) The mean of HbA1c in T1D + CD patients not using CGM was 8.05 ± 1.46%. The mean of HbA1c in T1D patients not using CGM was 6.91 ± 0.86%—(p < 0.05). These data express a worse metabolic control in patients who in addition to diabetes mellitus are also affected by coeliac disease and who do not use CGM (Figure 3).

Figure 3.
Statistically significant differences concerning glucose variability between patients T1D and CD.
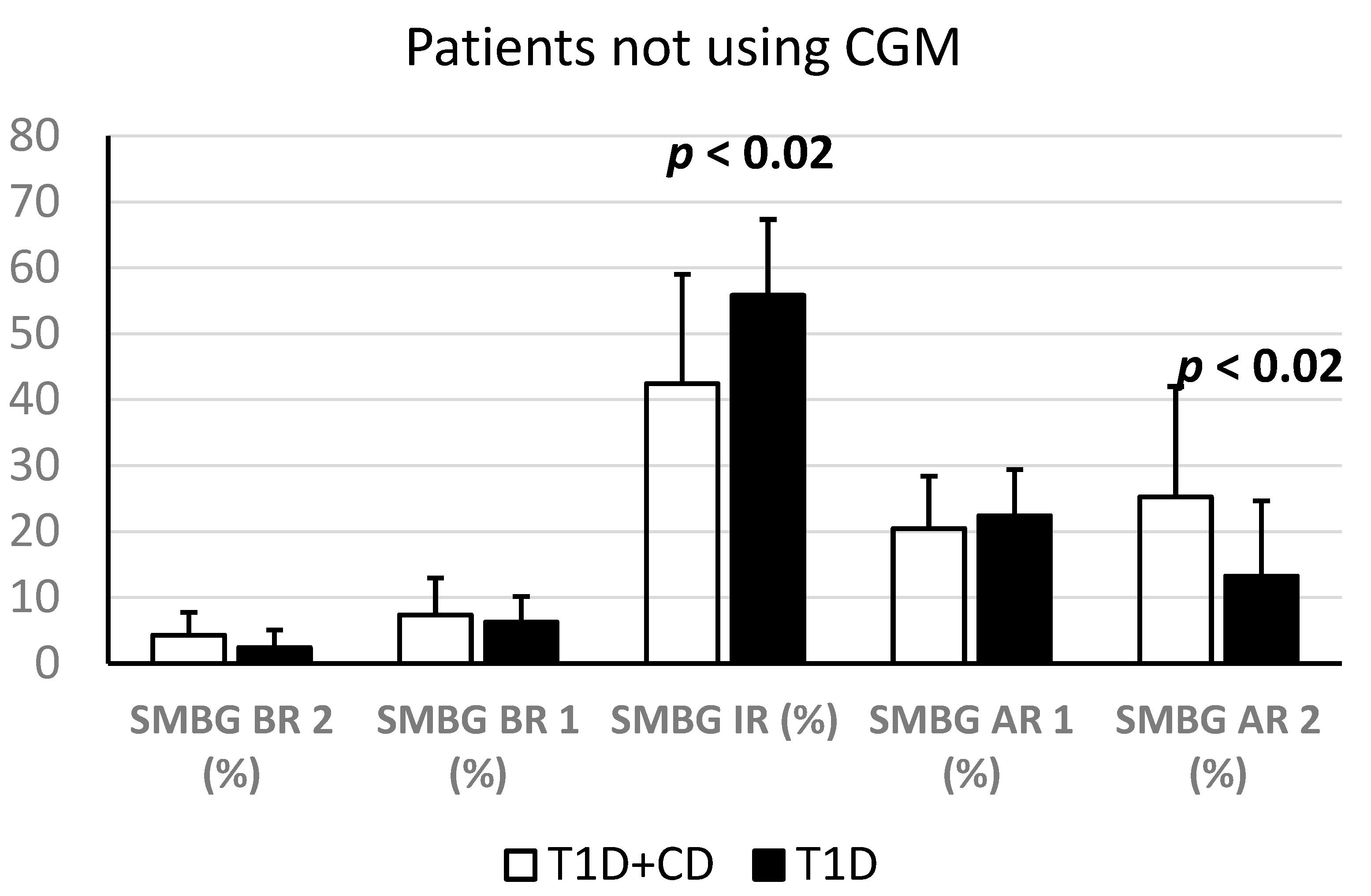
Using self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG), the percentage of target glycaemic values (In Range—IR) and >250 mg/dL glycaemic values (Above Range Level 2—AR2) are, respectively, significantly decreased and increased in patients affected by T1D and CD patients who do not use CGM. In particular, the mean of % SMBG IR was 42.41 ± 16.59% in T1D + CD patients; instead, this value was 55.82 ± 11.5% in patients suffering only from T1D—(p < 0.05); the mean of % SMBG AR 2 was 25.23 ± 16.78% in T1D + CD patients; comparatively, this value was 13.24 ± 11.44% in patients living only with T1D—(p < 0.05) (Figure 4).

Figure 4.
Statistically significant differences concerning SMBG values (%) between patients T1D + CD and only T1D patients. % SMBG Below Range 2 = values < 54 mg/dL; % SMBG Below Range 1 = values between 54 and 69 mg/dL; % SMBG In Range = values 70–180 mg/dL; % SMBG Above Range 1 = values between 181 and 250 mg/dL; % SMBG Above Range 2 = values > 250 mg/dL.
All statistical results of patients not using CGM are shown in Table 3. In this group, age, weight, weight-SDS, height, height-SDS, BMI, and BMI-SDS were not statistically different.

Table 3.
Statistical result test for paired data between patients (T1D + CD and only T1D) who do not use CGM. % SMBG Below Range 2 = values < 54 mg/dL; % SMBG Below Range 1 = values between 54 and 69 mg/dL; % SMBG In Range = values 70–180 mg/dL; % SMBG Above Range 1 = values between 181 and 250 mg/dL; % SMBG Above Range 2 = values > 250 mg/dL.
4. Discussion
The association between type 1 diabetes and coeliac disease is mainly based on genetic risk factors which include human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genes and non-HLA genes, in particular HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8 [25,26,27].
These two pathologies have other potential risk factors in common in addition to genetics: environment, viral infections, characteristics of the intestinal microbiome, possible biological dysregulation (both innate and adaptive) [28].
CD is observed in about 10% of patients with T1D, with a prevalence between 0.6 and 16.4%, according to different studies [29]. In Italy, in children with T1D, the CD prevalence is around 7% [9].
T1D forces patients (and their families) to pay greater attention to the daily diet, especially for children. However, coeliac disease requires a strict gluten-free diet.
These pathologies greatly influence everyday life, the lifestyle of patients (and of their families), and often together impact upon metabolic control and complications.
In this study we analysed the metabolic control of patients with diabetes and coeliac disease. We compared them with patients living only with diabetes. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to evaluate the effect of use of the CGM on the metabolic control of patients living with both conditions.
In the first part of our study, through a case–control analysis, we compared 37 patients living with both T1D and CD and all 37 patients living only with T1D. In this analysis, a statistically significant difference was found between the mean of daily doses of rapid insulin/kg. Patients with both T1D and CD used fewer doses of rapid insulin/kg than patients with only T1D. These data have been confirmed in the second analysis between the 20 subjects who used CGM living with both T1D and CD and 20 subjects using CGM with T1D only. In fact, also in this case, patients using CGM and on a GFD diet used fewer doses of rapid insulin/kg than patients using CGM with only T1D.
This could be explained by the gluten-free diet and its lower carbohydrate content [19].
In fact, the daily intake of carbohydrates and their energy intake in GFD are usually lower than a normal diet. In the study of Lionetti et al., a group of patients on a GFD diet was compared with a control group. The result was that the daily intake of simple sugars and their contribution to the daily energy intake were significantly different between the two groups, with a higher intake in the control group [19].
All this may be in contrast to previous evidence of a high glycaemic index in a lot of gluten-free foods [30]. However, it could suggest a tendency of patients living with the two pathologies to change their diet to achieve better metabolic control and a lower use of insulin. This does not consider any nutritional imbalances and could increase the risk of complications, in particular cardiovascular ones. Nutritional support of these patients would be essential to make them (and their family) aware that the GFD diet must be free of gluten, but also healthy (i.e., avoiding nutrient, vitamins and minerals deficiency or excess, and should include a combination of naturally gluten-free foods and certified manufactured gluten-free products) in patients living with T1D [30].
This is the first known study to assess the impact of CGM use in patients with both diabetes and coeliac disease. The effectiveness and usefulness of CGM for diabetic subjects to improve their metabolic control are well known: among adolescents and young adults with T1D, CGM compared with standard blood glucose monitoring resulted in a greater improvement in metabolic control [31,32,33,34].
Our data suggest that CGM can have the same impact and benefit for those living with both diabetes and coeliac disease. In fact, comparing all CGM metrics (Figure 2 and Table 2) between subjects affected by both diseases and only diabetics, it emerges that there are no statistically significant differences. Coeliac patients can therefore have metabolic control that is comparable to patients who are not on a GFD. They probably manage to achieve this result thanks to a better titration of the pre-prandial insulin with the use of CGM. This hypothesis was confirmed by the analysis between the 17 patients who do not use CGM affected by both diseases and 17 patients who do not use CGM affected by only T1D: in this case, there were no statistically significant differences in the daily doses of basal, pre-prandial, and total insulin/kg.
In addition, the important role that CGM can play in patients on a GFD could be demonstrated by other results of our study, i.e., those with T1D and CD who do not use CGM had a worse metabolic control, expressed by increased levels of HbA1c, SD, and CV, as well as lower % SMBG values to target, and higher % SMBG values >250 mg/dL, compared to those with only T1D (Table 3).
Previous studies tended to analyse the impact of GFD on metabolic control but not the use of CGM. Moreover, these studies were not focused on children. For example, the CD DIET study evaluates CD screening rates and glycaemic outcomes of GFD in patients with T1D who are asymptomatic for CD. Biopsy-confirmed CD patients were randomized to GFD or gluten-containing diet to assess changes in HbA1c and CGM over 12 months. This study concluded that CD was frequently observed in asymptomatic patients with T1D and clinical vigilance was favoured from GFD [35]. Another recent study published in 2020 was a randomized controlled trial that evaluated the effect of GFD on hypoglycaemia, height, weight, HbA1c, insulin dose requirement, and bone mineral homeostasis in T1D patients with subclinical disease (patients >5 years old). A decrease in hypoglycaemic episodes and better glycaemic control were found in patients on a GFD (not statistically significant difference) [36].
5. Conclusions
This study evaluated metabolic control in patients affected by both type 1 diabetes and coeliac disease compared to patients affected only by T1D. The aim was to understand the possible impact of CGM on metabolic control of patients on a GFD.
It is well known that optimizing metabolic control in diabetic patients is critical to reduce the risk of complications in the medium and long term; even more so in patients who also live with coeliac disease. In fact, the gluten-free diet has an impact on the daily life of the patient and therefore a high probability of poor adherence to healthy habits. This represents an additional risk of nutritional imbalance and the appearance of cardio-vascular complications.
It is therefore essential to assess the support that CGM can bring to these patients and its impact on metabolic control and their quality of life. This study showed that CGM seems to be very useful and promising. It would also be interesting to assess the impact of other technologies, such as CSII.
Our study was limited by sample size. However, it lays the foundations for future research that will be necessary to evaluate this issue further. Our study showed for the first time that CGM represents a valid support to the achievement of an optimal metabolic control in patients living with both T1D and CD. Implementing the use of this technology in patients living with both T1D and CD may allow targeted adjustments of insulin therapy in children who follow the GFD. In particular, CGM was important in optimizing pre-prandial insulin in coeliac children.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.T., M.C. and F.A.; methodology, S.T.; formal analysis, S.T. and F.A.; investigation, F.A.; resources, S.T. and M.C.; data curation, F.A. and S.T.; writing—original draft preparation, F.A.; writing—review and editing, M.A.S. and M.P.; supervision, S.T. and M.A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the local Ethics Committee for Biomedical Research (Comitato Etico per la Ricerca Biomedica delle Province di Chieti e di Pescara e dell’Università degli Studi “G.d’Annunzio” di Chieti e Pescara; reporting of ethics approval n. 6 of 31 March 2016).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patients to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Anonymized individual-participant data that support the findings of this study will be made available 12 months from the corresponding author (S.T.) upon reasonable request. Data will be shared according to the EU General Data Protection Regulation, national legislation and hospital data protection regulations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gale, E.A.M. Type 1 diabetes in the young: The harvest of sorrow goes on. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 1435–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschou, S.A.; Papadopoulou-Marketou, N.; Chrousos, G.P.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C. On type 1 diabetes mellitus pathogenesis. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, R38–R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, W.; Gyenesei, A.; Krętowski, A. The Multifactorial Progression from the Islet Autoimmunity to Type 1 Diabetes in Children. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, B.P.; Williams, E.; Clarke, K. A Comprehensive Review of Celiac Disease/Gluten-Sensitive Enteropathies. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 57, 226–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker-Smith, J.A.; Grigor, W. COELIAC DISEASE IN A DIABETIC CHILD. Lancet 1969, 293, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.; Wilming, L.; Rand, V.; Lovering, R.C.; Bruford, E.A.; Khodiyar, V.K.; Lush, M.J.; Povey, S.; Talbot, C.C.; Wright, M.W.; et al. Gene map of the extended human MHC. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Rewers, M.; Eisenbarth, G.S. Genetic testing: Who should do the testing and what is the role of genetic testing in the setting of celiac disease? Gastroenterology 2005, 128, S33–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barera, G.; Bonfanti, R.; Viscardi, M.; Bazzigaluppi, E.; Calori, G.; Meschi, F.; Bianchi, C.; Chiumello, G. Occurrence of Celiac Disease After Onset of Type 1 Diabetes: A 6-Year Prospective Longitudinal Study. Pediatrics 2002, 109, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti, F.; Bruno, G.; Chiarelli, F.; Lorini, R.; Meschi, F.; Sacchetti, C.; The Diabetes Study Group of Italian Society of Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology. Younger Age at Onset and Sex Predict Celiac Disease in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes: An Italian multicenter study. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sud, S.; Marcon, M.; Assor, E.; Palmert, M.R.; Daneman, D.; Mahmud, F.H. Celiac Disease and Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes: Diagnostic and Treatment Dilemmas. Int. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2010, 2010, 161285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group; Nathan, D.M.; Genuth, S.; Lachin, J.; Cleary, P.; Crofford, O.; Davis, M.; Rand, L.; Siebert, C. The Effect of Intensive Treatment of Diabetes on the Development and Progression of Long-Term Complications in Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Writing Team for the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Research Group. Effect of Intensive Therapy on the Microvascular Complications of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2002, 287, 2563–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, M.A.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Michels, A.W. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2014, 383, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, J.E.; Shivers, J.P.; Zisser, H. Continuous glucose monitors: Current status and future developments. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2013, 20, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, J.T.; Garvey, K.C.; Laffel, L.M. Developmental Changes in the Roles of Patients and Families in Type 1 Diabetes Management. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2015, 11, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovc, K.; Battelino, T. Evolution of Diabetes Technology. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 2019, 49, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battelino, T.; Danne, T.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Amiel, S.A.; Beck, R.; Biester, T.; Bosi, E.; Buckingham, B.A.; Cefalu, W.T.; Close, K.L.; et al. Clinical Targets for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Interpretation: Recommendations from the International Consensus on Time in Range. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Toma, A.; Volta, U.; Auricchio, R.; Castillejo, G.; Sanders, D.S.; Cellier, C.; Mulder, C.J.; Lundin, K.E.A. European Society for the Study of Coeliac Disease (ESsCD) guideline for coeliac disease and other gluten-related disorders. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2019, 7, 583–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, E.; Antonucci, N.; Marinelli, M.; Bartolomei, B.; Franceschini, E.; Gatti, S.; Catassi, G.N.; Verma, A.K.; Monachesi, C.; Catassi, C. Nutritional Status, Dietary Intake, and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet of Children with Celiac Disease on a Gluten-Free Diet: A Case-Control Prospective Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, K.; Barclay, A.; Colagiuri, S.; Brand-Miller, J. Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load of Carbohydrates in the Diabetes Diet. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2011, 11, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham-Short, A.; Donaghue, K.C.; Ambler, G.; Garnett, S.; Craig, M.E. Quality of Life in Type 1 Diabetes and Celiac Disease: Role of the Gluten-Free Diet. J. Pediatr. 2016, 179, 131–138.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciari, E.; Milani, S.; Balsamo, A.; Spada, E.; Bona, G.; Cavallo, L.; Cerutti, F.; Gargantini, L.; Greggio, N.; Tonini, G.; et al. Italian cross-sectional growth charts for height, weight and BMI (2 to 20 yr). J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2006, 29, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciari, E.; Milani, S.; Balsamo, A.; Dammacco, F.; De Luca, F.; Chiarelli, F.; Pasquino, A.; Tonini, G.; Vanelli, M. Italian cross-sectional growth charts for height, weight and BMI (6–20 y). Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 56, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, L.; Colette, C.; Wojtusciszyn, A.; Dejager, S.; Renard, E.; Molinari, N.; Owens, D.R. Toward Defining the Threshold Between Low and High Glucose Variability in Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 40, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rewers, M.; Eisenbarth, G.S. Celiac disease in T1DM—The need to look long term. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jabri, B.; Sollid, L.M. Tissue-mediated control of immunopathology in coeliac disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, S.; McMahon, N.; Henderson, J. Guidelines for diagnosing coeliac disease: European Society Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. Arch. Dis. Child.-Educ. Pr. Ed. 2021, 106, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohn, A.; Sofia, A.M.; Kupfer, S.S. Type 1 Diabetes and Celiac Disease: Clinical Overlap and New Insights into Disease Pathogenesis. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2014, 14, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, A.; Lovati, E.; Biagi, F.; Corazza, G.R. Coeliac disease and type 1 diabetes mellitus: Epidemiology, clinical implications and effects of gluten-free diet. Endocrine 2012, 43, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascuñán, K.A.; Vespa, M.C.; Araya, M. Celiac disease: Understanding the gluten-free diet. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffel, L.M.; Kanapka, L.G.; Beck, R.W.; Bergamo, K.; Clements, M.A.; Criego, A.; DeSalvo, D.J.; Goland, R.; Hood, K.; Liljenquist, D.; et al. Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adolescents and Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 323, 2388–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control. Diabetes Metab. J. 2023, 47, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajjan, R.A.; Cummings, M.H.; Jennings, P.; Leelarathna, L.; Rayman, G.; Wilmot, E.G. Optimising use of rate-of-change trend arrows for insulin dosing decisions using the FreeStyle Libre flash glucose monitoring system. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2019, 16, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majithia, A.R.; Wiltschko, A.B.; Zheng, H.; Walford, G.A.; Nathan, D.M. Rate of Change of Premeal Glucose Measured by Continuous Glucose Monitoring Predicts Postmeal Glycemic Excursions in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: Implications for Therapy. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2018, 12, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, F.H.; Clarke, A.B.M.; Joachim, K.C.; Assor, E.; McDonald, C.; Saibil, F.; Lochnan, H.A.; Punthakee, Z.; Parikh, A.; Advani, A.; et al. Screening and Treatment Outcomes in Adults and Children with Type 1 Diabetes and Asymptomatic Celiac Disease: The CD-DIET Study. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1553–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Agarwala, A.; Makharia, G.; Bhatnagar, S.; Tandon, N. Effect of Gluten-FREE Diet on Metabolic Control and Anthropometric Parameters in Type 1 Diabetes with Subclinical Celiac Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Endocr. Pract. 2020, 26, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).