Electrochemical Detection of Adrenaline Using Nafion–Trimethylsilyl and Nafion–Trimethylsilyl–Ru2+-Complex Modified Electrodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals
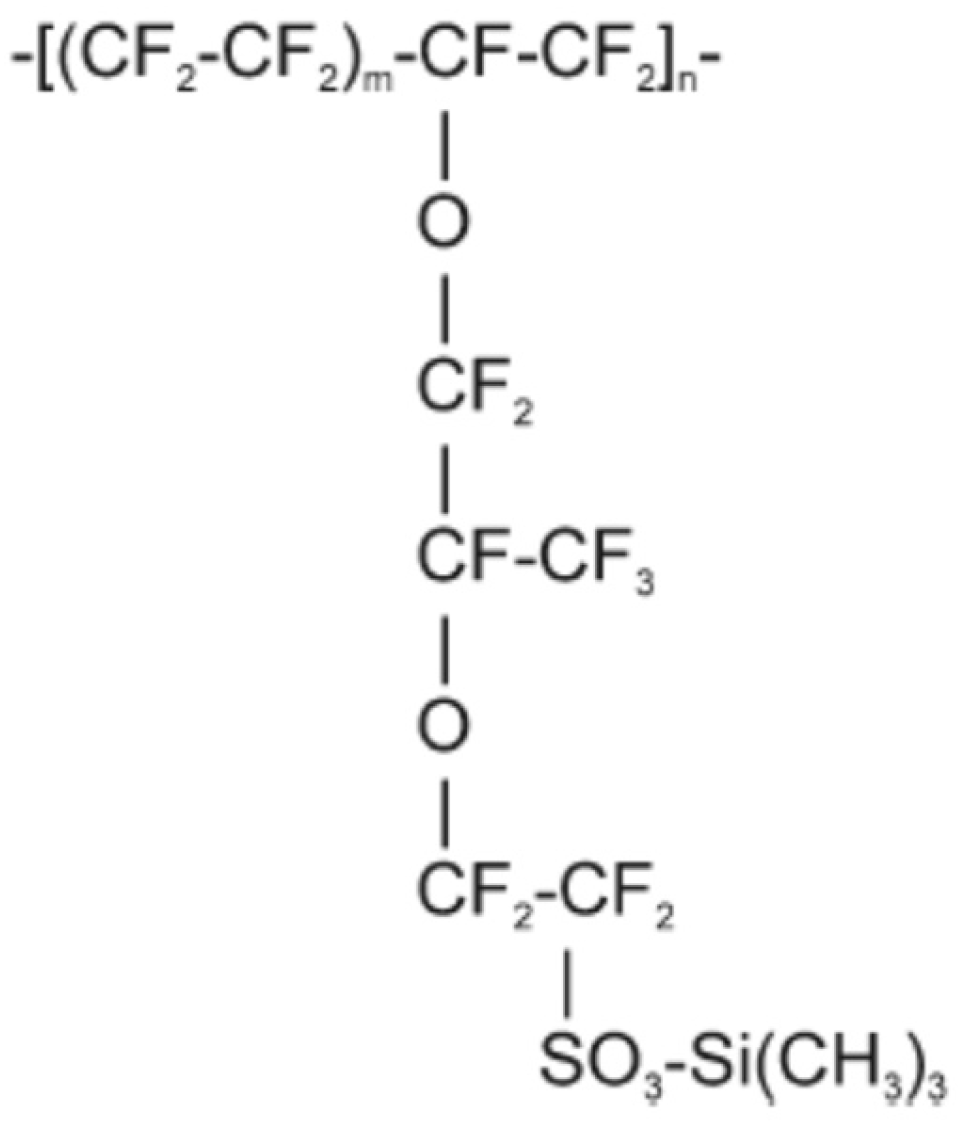
2.2. Nafion–TMS Dissolution Process and Preparation of Nafion–TMS–Ru2+ Complex Films
2.3. Surface Characterization
2.4. Spectroscopic Measurements
2.5. Electrode Preparation and Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
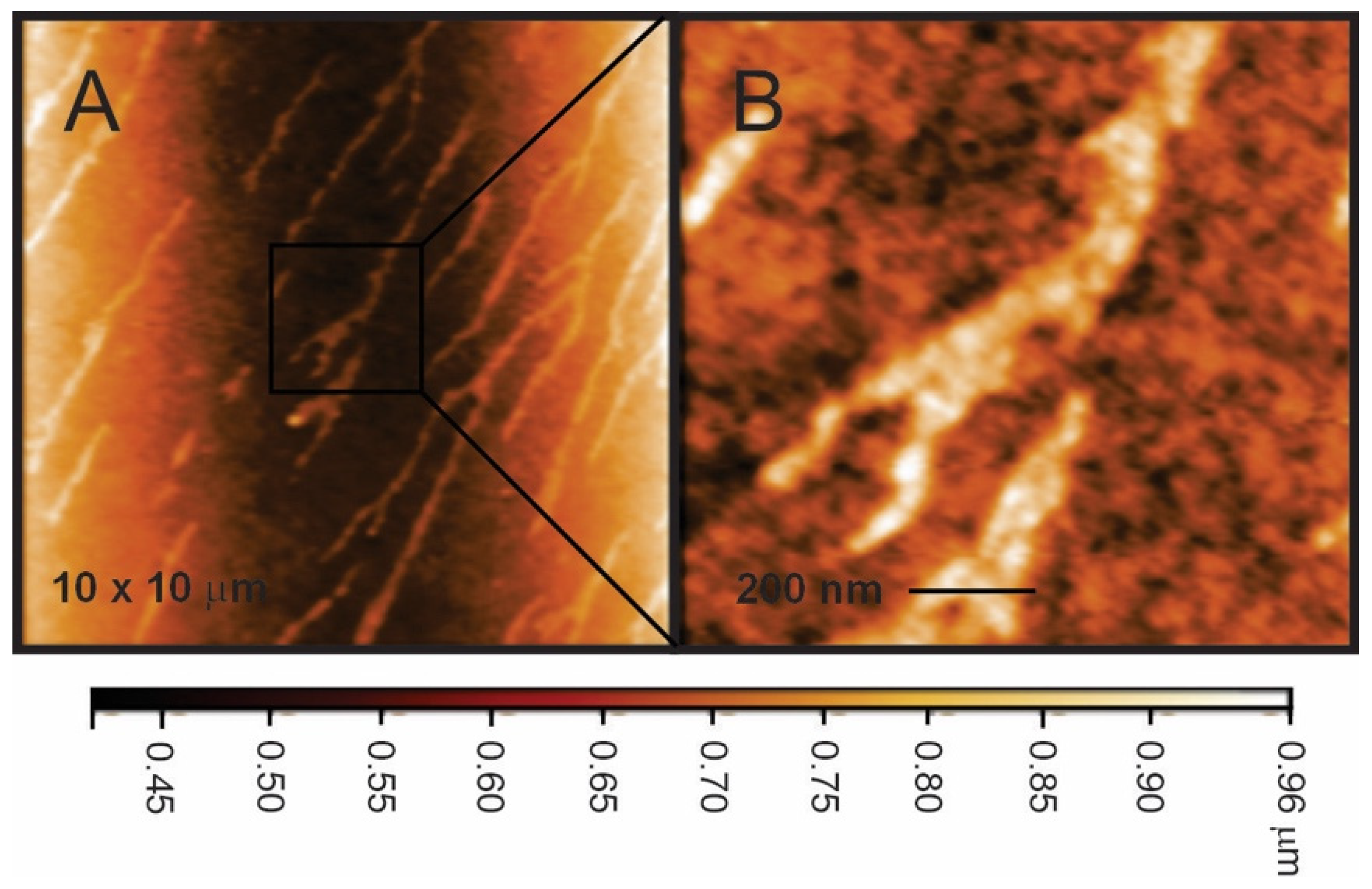
3.1. Surface Structure of Nafion–TMS
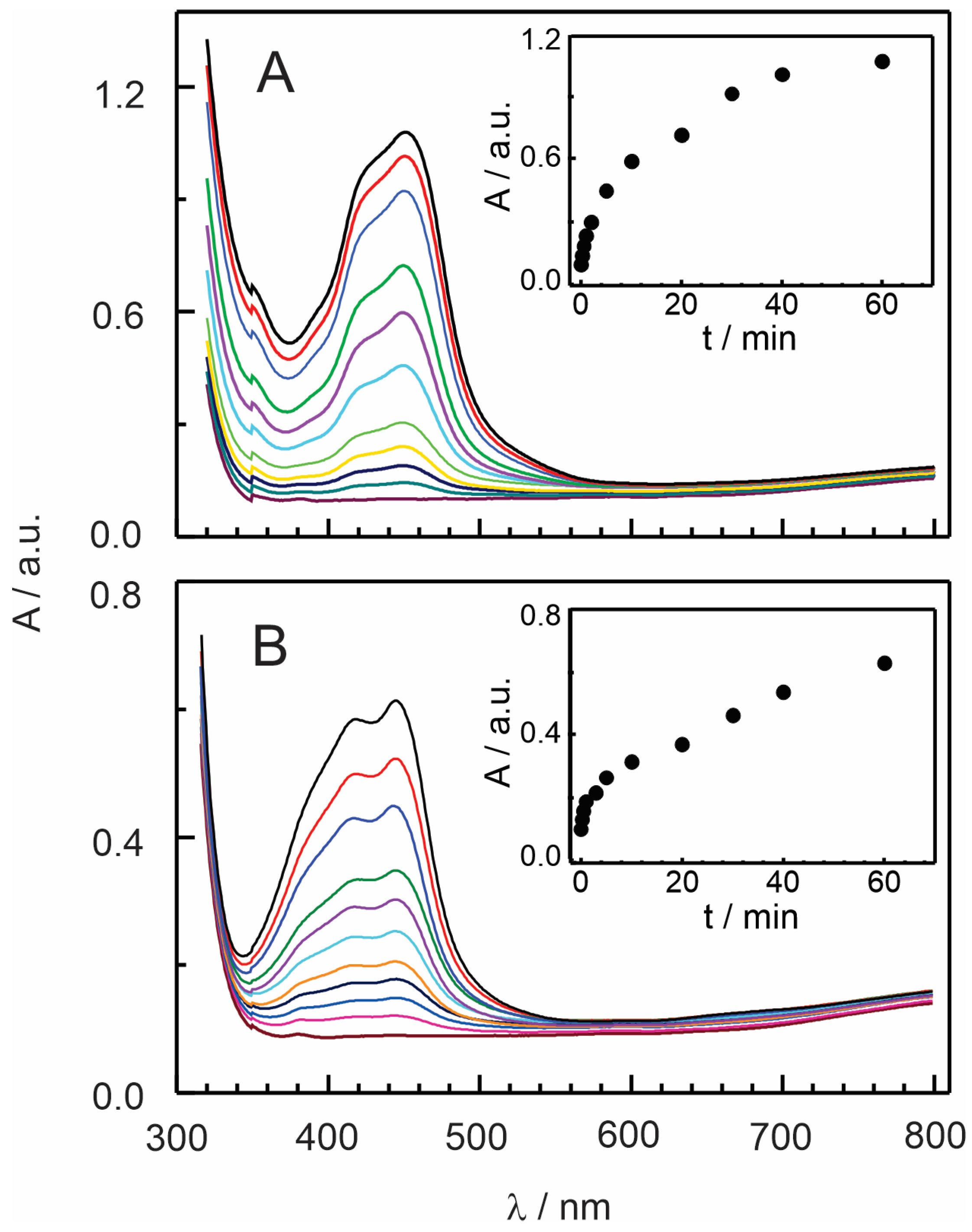
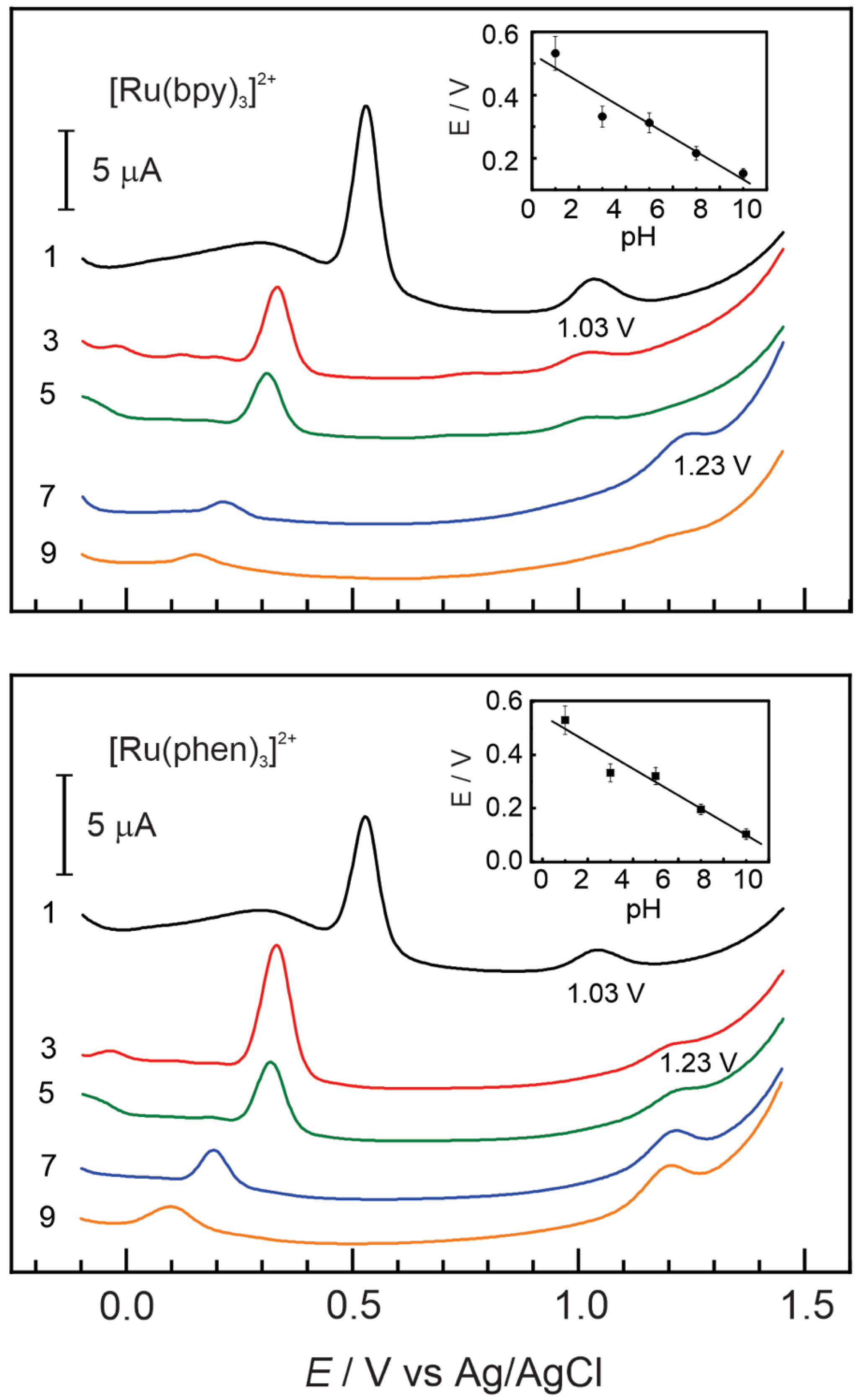
3.2. Insertion of [Ru(bpy)3]2+ and [Ru(phen)3]2+ Complexes in Nafion–TMS
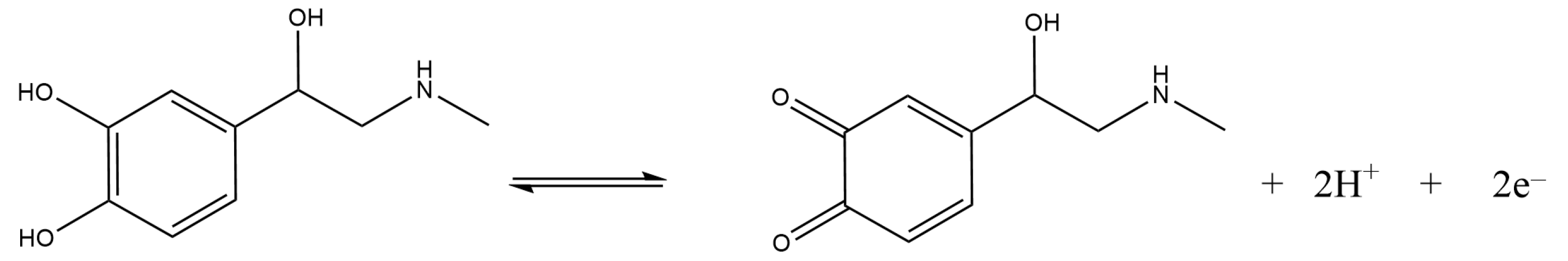
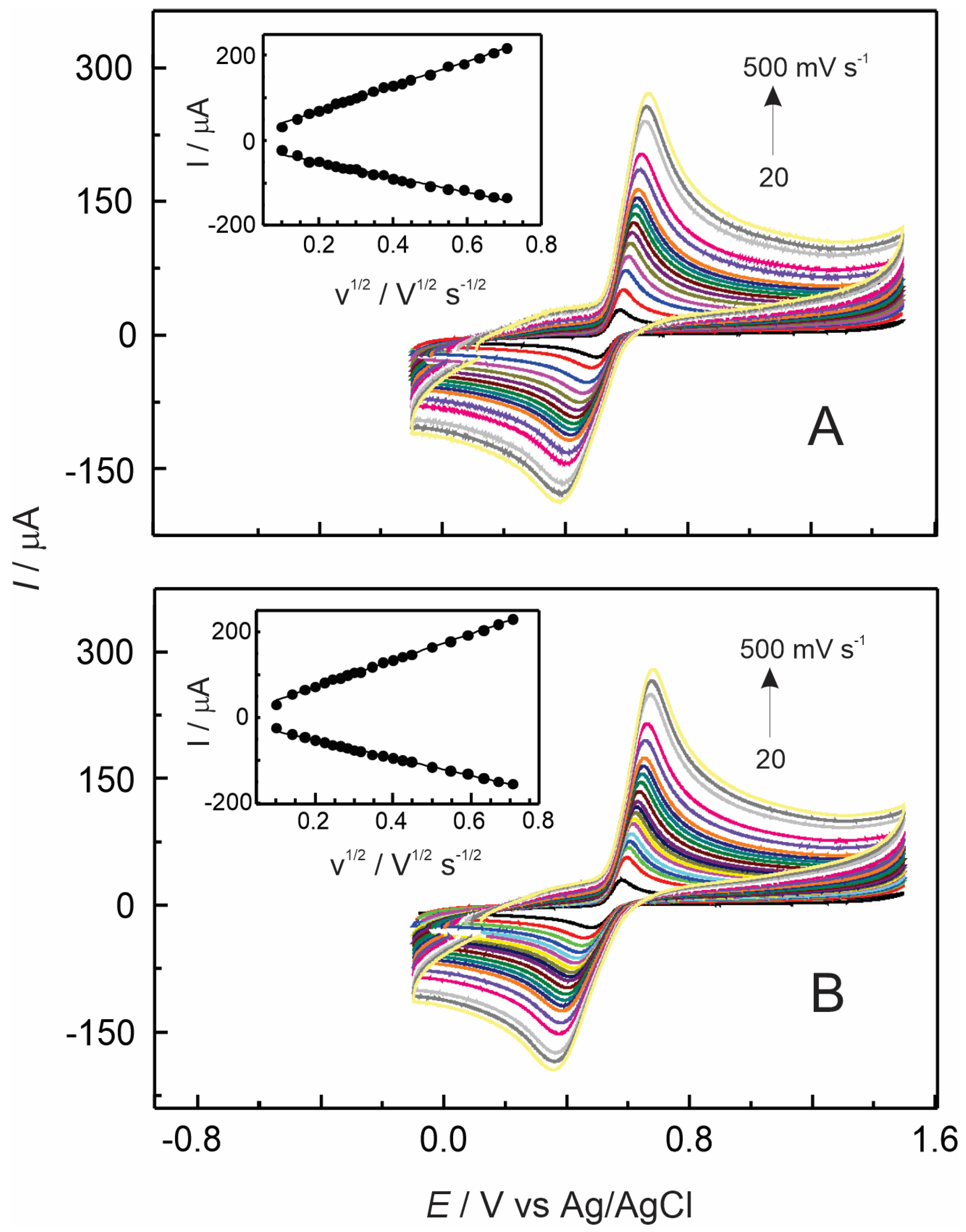
3.3. Electrochemical Detection of Adrenaline at GC/Nafion–TMS Modified Electrodes
Effect of pH
3.4. Electrochemical Detection of Adrenaline Using Nafion–TMS–Ru2+-Complex Modified GC Electrodes
Effect of pH on Nafion–TMS–Ru2+ Complex
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schweigert, N.; Zehnder, A.J.B.; Eggen, R.I.L. Chemical properties of catechols and their molecular modes of toxic action in cells, from microorganisms to mammals. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 3, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, G.N. Determination of epinephrine based on its enhancement for electrochemiluminescence of lucigenin. Talanta 2005, 65, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Michalowski, J.; Halabura, P. Flow-injection chemiluminescence determination of epinephrine in pharmaceutical preparations using raw apple juice as enzyme source. Talanta 2001, 55, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, T.; Sahu, R.; Mukherjee, V. Molecular modeling and spectroscopic investigation of a neurotransmitter: Epinephrine. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1176, 94–109. [Google Scholar]
- Solich, P.; Polydorou, C.K.; Koupparis, M.A.; Efstathiou, C.E. Automated flow injection spectrophotometric determination of catecholamines (epinephrine and isoproterenol) in pharmaceutical formulations based on ferrous complex formation. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2000, 22, 781–789. [Google Scholar]
- Adeniyi, W.K.; Wright, A.R. Novel fluorometric assay of trace analysis of epinephrine in human serum. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2009, 74, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, W.; Fan, Y.Z.; Dong, J.X.; Zhang, H.; Luo, H.Q.; Li, N.B. Label-free fluorescent discrimination and detection of epinephrine and dopamine based on bioinspired in situ copolymers and excitation wavelength switch. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1054, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Fotopoulou, M.A.; Ioannou, P.C. Post-column terbium complexation and sensitized fluorescence detection for the determination of norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine using high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2002, 462, 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Özel, R.E.; Hayat, A.; Andreescu, S. Recent developments in electrochemical sensors for the detection of neurotransmitters for applications in biomedicine. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 1044–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Madhurantakama, S.; Babua, K.J.; Rayappana, J.B.B.; Krishnan, U.M. Nanotechnology-based electrochemical detection strategies for hypertension markers. Biosen. Bioelectron. 2018, 116, 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Tadi, K.K.; Motghare, R.V.; Ganesh, V. Electrochemical detection of epinephrine using a biomimic made up of hemin modified molecularly imprinted microspheres. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 99115–99124. [Google Scholar]
- Zare, H.R.; Ghanbari, Z.; Nasirizadeh, N.; Benvidi, A. Simultaneous determination of adrenaline, uric acid, and cysteine using bifunctional electrocatalyst of ruthenium oxide nanoparticles. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2013, 16, 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Charithra, M.M.; Manjunatha, J.G. Electrochemical sensing of adrenaline using surface modified carbon nanotube paste electrode. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 262, 124293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canevaria, T.C.; Nakamura, M.; Cincotto, F.H.; de Melo, F.M.; Toma, H.E. High performance electrochemical sensors for dopamine and epinephrine using nanocrystalline carbon quantum dots obtained under controlled chronoamperometric conditions. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 209, 464–470. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Ji, H.; Tang, J.; Tao, F.; Zhang, X.; Yao, Z.; Song, H.; Li, C.; Wang, F. Electrochemical activation and renewal of pyrrole nitrogen sites in porphyrin-based conjugated polymer for simultaneous determination of uric acid and adrenaline. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 884, 115055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Zhou, J.; Xi, Y.; Lan, B.; Guo, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, Z. Solid-state hybrid photovoltaic cells with a novel redox polymer and nanostructured inorganic semiconductors. J. Power Sources 2009, 194, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirunavukkarasu, V.S.; Kozhushkov, S.I.; Ackermann, L. C–H nitrogenation and oxygenation by ruthenium catalysis. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Loague, Q.R.; Zhu, J.; Lin, S.; Usov, P.M.; Morris, A.J. Ruthenium (II)-polypyridyl doped zirconium (IV) metal–organic frameworks for solid-state electrochemiluminescence. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 16807–16812. [Google Scholar]
- Sheth, S.; Li, M.; Song, Q. New luminescent probe for the selective detection of dopamine based on in situ prepared Ru(II) complex-sodium dodecyl benzyl sulfonate assembly. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 371, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, K.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J. Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor for dopamine based on ZnSe, graphene oxide@multi walled carbon nanotube and Ru(bpy)32+. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 286, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Song, B.; Ye, Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, R.; Yuan, J. A highly selective phosphorescence probe for histidine in living bodies. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 18671–18676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkušić, E.; Redžić, S.; Kahrović, E.; Zahirović, A. Electrochemical Determination of Adrenaline at Ru(III) Schiff Base Complex Modified Carbon Electrodes. Croat. Chem. Acta 2017, 90, 345–352. [Google Scholar]
- Ruifang, W.S.; Jiao, G.K. Electrochemistry and Electrocatalysis of Hemoglobin in Nafion/nano-CaCO3 Film on a New Ionic Liquid BPPF6 Modified Carbon Paste Electrode. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4560–4567. [Google Scholar]
- Toh, R.J.; Peng, W.K.; Han, J.; Pumera, M. Direct In Vivo Electrochemical Detection of Haemoglobin in Red Blood Cells. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauritz, K.A.; Payne, J.T. [Perfluorosulfonate ionomer]/silicate hybrid membranes via base-catalyzed in situ sol–gel processes for tetraethylorthosilicate. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 168, 39–51. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, S.; Noyori, R. Silylation with a perfluorinated resinsulfonic acid trimethylsilyl ester. Tetrahedron Lett. 1980, 21, 767–768. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, R.; Gautun, H.; Westelund, A. A convenient procedure for the synthesis of acetals from α-halo ketones. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2002, 344, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Sánchez, R.; Díaz-Caballeros, R.J.; Méndez-Bermúdez, J.A.; Gárate-Morales, J.L.; Domínguez-Meneses, G. Electrochemical studies of nafion–trimethylsilyl and nafion–trimethylsilyl/Ru complex-modified electrodes. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2012, 16, 2867–2876. [Google Scholar]
- Yeager, H.L.; Steck, A. Cation and water diffusion in Nafion ion-exchange membranes: Influence of polymer structure. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1981, 128, 1880–1884. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, W.Y.; Gierke, T.D. Ion transport and clustering in nafion perfluorinated membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1983, 13, 307–326. [Google Scholar]
- Juris, A.; Balzani, V.; Barigelletti, F.; Campagna, S.; Belser, P.; von Zelewsky, A. Ru(II) polypyridine complexes: Photophysics, photochemistry, eletrochemistry, and chemiluminescence. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1988, 84, 85–277. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, J.K.; Goldberg, J.M.; Kumar, C.V.; Turro, N.J. Binding modes and base specificity of tris (phenanroline) ruthenium (II) enantiomers with nucleic acids: Tuning the stereoselectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 2081–2088. [Google Scholar]
- Yonemoto, E.H.; Saupe, G.B.; Schmeh, R.H.; Hubig, S.M.; Riley, R.L.; Iverson, B.L.; Mallouk, T.E. Electron-Transfer Reactions of Ruthenium Trisbipyridyl-Viologen Donor-Acceptor Molecules: Comparison of the Distance Dependence of Electron Transfer-Rates in the Normal and Marcus Inverted Regions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 4786–4795. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, Y.; Friedman, A.E.; Turro, N.J.; Barton, J.K. Characterization of dipyridophenazine complexes of ruthenium(II): The light switch effect as a function of nucleic acid sequence and conformation. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 10809–10816. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aguilar Sánchez, R.; Durán Tlachino, D.A.; Cabrera Hilerio, S.L.; Gárate Morales, J.L.; Cerna Cortez, J.R. Electrochemical detection of adrenaline employing nafion-tms modified electrodes. Tend. Doc. Inv. Quim. 2018, 4, 421–425. [Google Scholar]
- De Pelichy, L.G.; Smith, E.T. A study of the oxidation pathway of adrenaline by cyclic voltammetry: An undergraduate analytical chemistry laboratory exercise. Chem. Educ. 1997, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bretti, C.; Cigala, R.M.; Crea, F.; de Stefano, C.; Vianelli, G. Solubility and modeling acid–base properties of adrenaline in NaCl aqueous solutions at different ionic strengths and temperatures. Eur. J. Pharmac. Sci. 2015, 78, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Fundamentals, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980; p. 218. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, F.; Zhang, X. Electrochemical sensor for epinephrine based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with graphene/gold nanocomposites. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2012, 669, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chen, M.; Ma, X. Selective determination of epinephrine in the presence of ascorbic acid using a glassy carbon electrode modified with graphene. Anal. Sci. 2012, 28, 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; Liu, M.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, B. Hydroxylamine electrochemical sensor based on electrodeposition of porous ZnO nanofilms onto carbon nanotubes films modified electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 2835–2840. [Google Scholar]
- Raoof, J.B.; Ojani, R.; Baghayeri, M. A selective sensor based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with carbon nanotubes and ruthenium oxide/hexacyanoferrate film for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, epinephrine and uric acid. Anal. Meth. 2011, 3, 2367–2373. [Google Scholar]
- Tsele, T.P.; Adekunle, A.S.; Fayemi, O.E.; Ebenso, E.E. Electrochemical detection of Epinephrine using Polyaniline nanocomposite films doped with TiO2 and RuO2 Nanoparticles on Multi-walled Carbon Nanotube. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 243, 331–348. [Google Scholar]
- Volkov, V.; Lobanov, A.; Voronkov, M.; Baygildiev, T.; Misin, V.; Tsivileva, O. Kinetics and Mechanism of Epinephrine Autoxidation in the Presence of Plant Superoxide Inhibitors: A New Look at the Methodology of Using a Model System in Biological and Chemical Research. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzov, E.A.; Kazin, V.N.; Moshareva, V.A.; Zhukova, A.A. Application of electronic spectroscopy and quantum-chemical modelling for analysis of products of autoxidation of adrenaline. J. Appl. Spectros. 2019, 85, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar]
- Umek, N. Cyclization step of noradrenaline and adrenaline autoxidation: A quantum chemical study. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 16650. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Cui, H.; Lin, X.-Q. Determination of adrenaline by using inhibited Ru(bpy)32+ electrochemiluminescence. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 471, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Bretti, C.; Crea, F.; De Stefano, C.; Sammartano, S. Solubility and activity coefficients of 2,2-bipyridyl, 1,10-phenanthroline and 2,2′,6′,2″-terpyridine in NaCl(aq) at different ionic strengths and T = 298.15 K. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2008, 272, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Holten-Andersen, N.; Harrington, M.J.; Birkedal, H.; Lee, B.P.; Messersmith, P.B.; Lee, K.Y.C.; Waite, J.H. pH-induced metal-ligand cross-links inspired by mussel yield self-healing polymer networks with near-covalent elastic moduli. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2651–2655. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Diduk, R.; Galano, A. Adrenaline and Noradrenaline: Protectors against Oxidative Stress or Molecular Targets? J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 3479–3491. [Google Scholar]
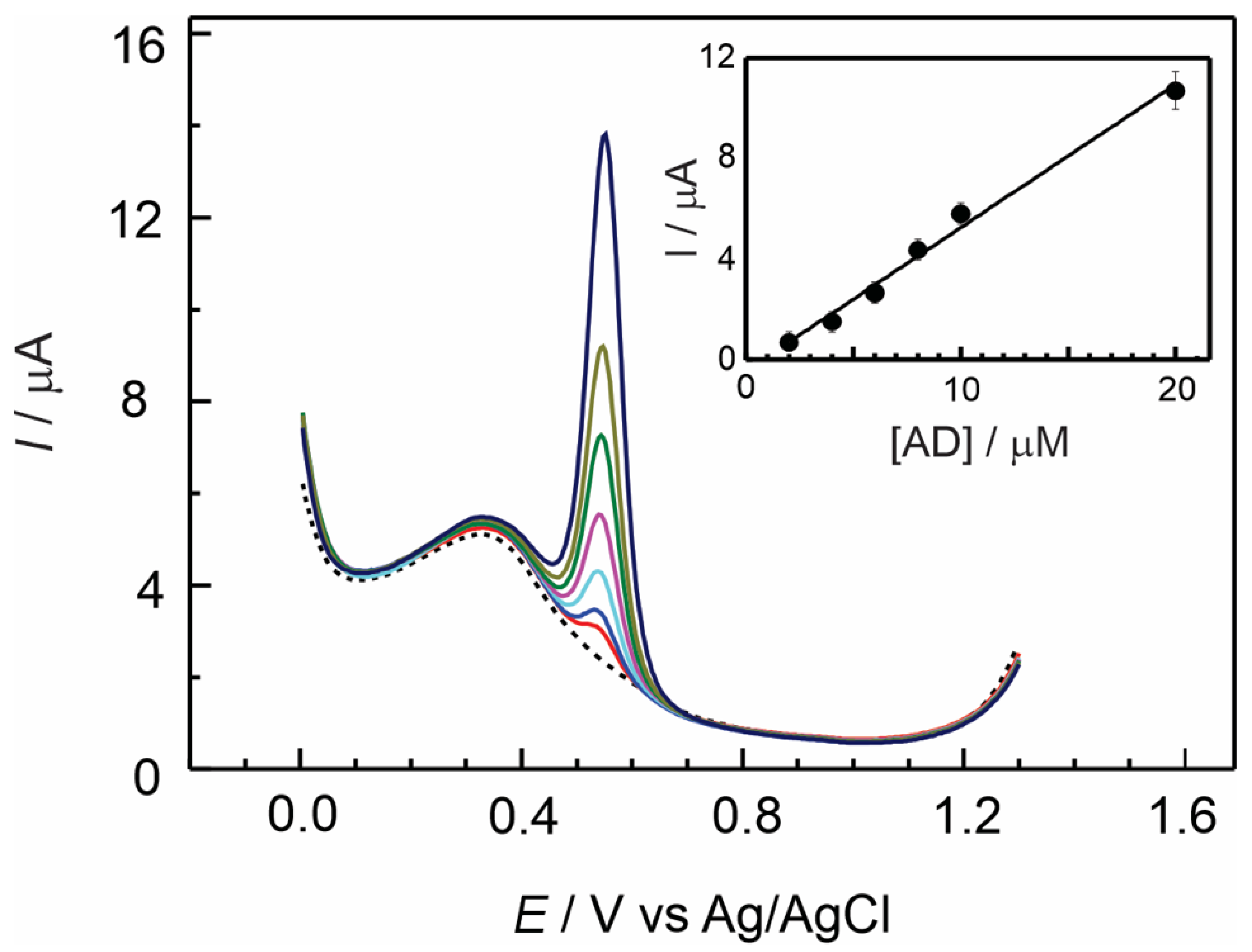
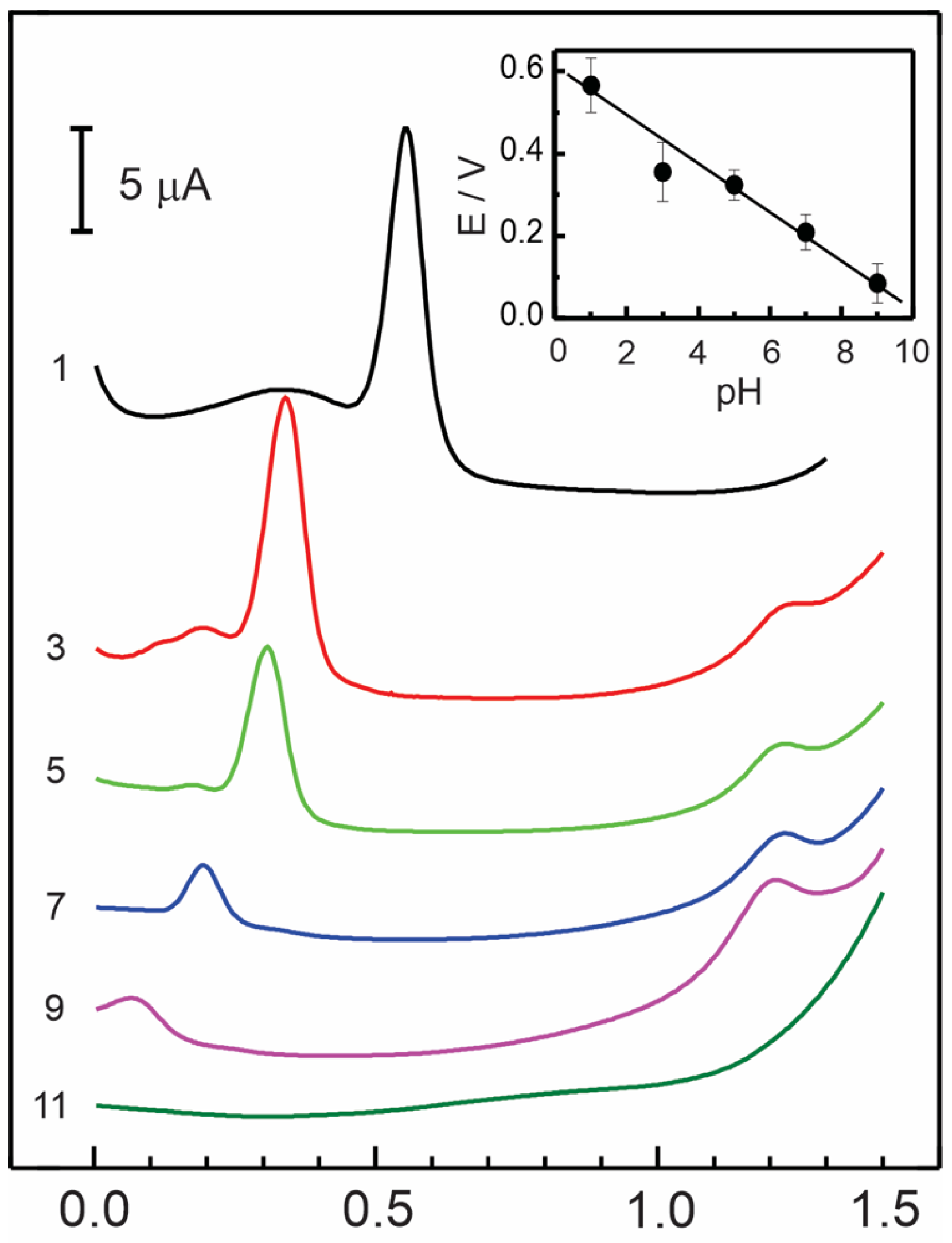
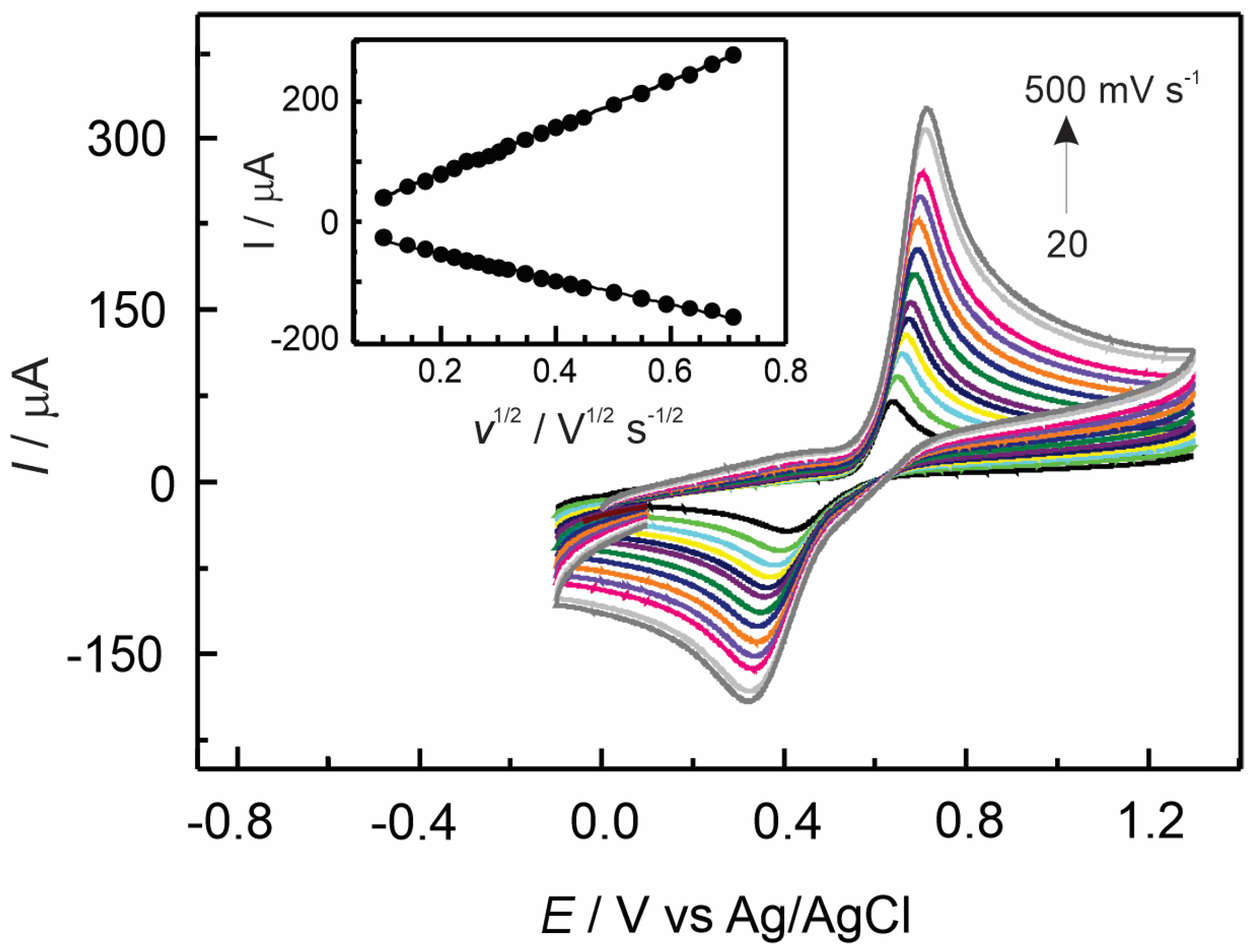
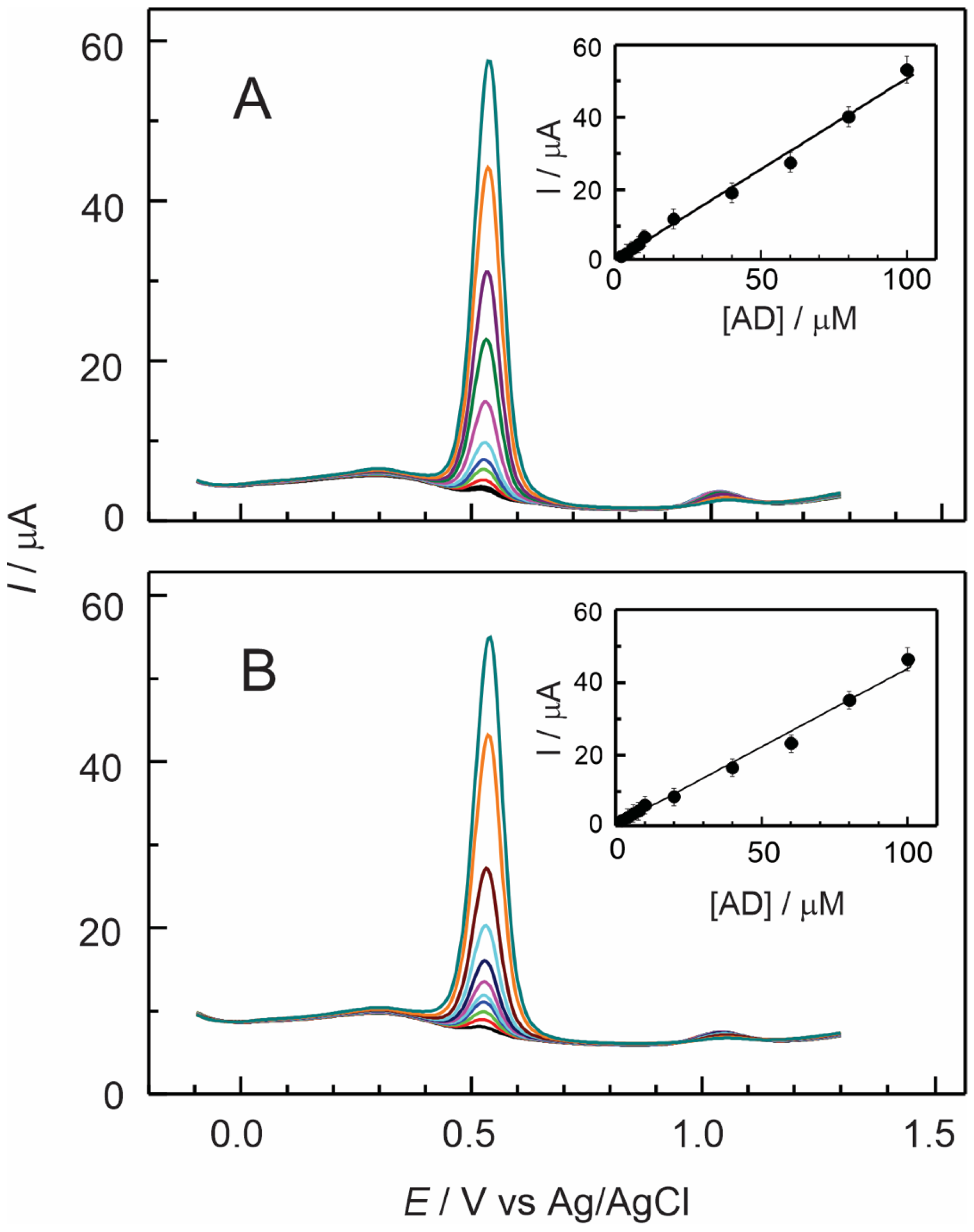
| Electrode Modifier | [AD] 10−6 M | Sensitivity μA/μM | Detection Limit μM | ΔE a mV | D cm2 s−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naf-TMS | 1–20 | 0.57 ± 0.02 | 0.52 ± 0.02 | 312 ± 8 | (7.9 ± 0.5) × 10−5 |
| Naf-TMS/[Ru(bpy)3]2+ | 1–100 | 0.51 ± 0.01 | 0.58 ± 0.04 | 178 ± 5 | (4.6 ± 0.4) × 10−5 |
| Naf-TMS/[Ru(phen)3]2+ | 1–100 | 0.45 ± 0.01 | 0.68 ± 0.05 | 225 ± 5 | (5.1 ± 0.4) × 10−5 |
| Electrode Modifier | Concentration Linear Range μM | Limit of Detection μM | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemin modified MIP, DPV | 0.05–40 | 0.012 | [11] |
| RuO NP on GCE | 3–56 | 0.47 | [12] |
| 56–750 | |||
| POXMCNTPE | 10–110 | 0.03 | [13] |
| GCE/C-dots | 0.05–2.0 | 0.0061 | [14] |
| P-TP/rGO/GCE | 0.05–100 | 0.0045 | [15] |
| RuOHCF/MWCNT on GCE | 0.1–10 | 0.052 | [42] |
| MWCNT-PANI-RuO2/AuE | 4.9–76.9 | 0.18 | [43] |
| Nafion–TMS on GC | 1–20 | 0.52 | This work |
| Nafion–TMS–[Ru(bpy)3]2+ | 1–100 | 0.58 | |
| Nafion–TMS– [Ru(phen)3]2+ | 1–100 | 0.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguilar-Sánchez, R.; Durán-Tlachino, D.A.; Cabrera-Hilerio, S.L.; Gárate-Morales, J.L. Electrochemical Detection of Adrenaline Using Nafion–Trimethylsilyl and Nafion–Trimethylsilyl–Ru2+-Complex Modified Electrodes. Electrochem 2025, 6, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem6020010
Aguilar-Sánchez R, Durán-Tlachino DA, Cabrera-Hilerio SL, Gárate-Morales JL. Electrochemical Detection of Adrenaline Using Nafion–Trimethylsilyl and Nafion–Trimethylsilyl–Ru2+-Complex Modified Electrodes. Electrochem. 2025; 6(2):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem6020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguilar-Sánchez, R., D. A. Durán-Tlachino, S. L. Cabrera-Hilerio, and J. L. Gárate-Morales. 2025. "Electrochemical Detection of Adrenaline Using Nafion–Trimethylsilyl and Nafion–Trimethylsilyl–Ru2+-Complex Modified Electrodes" Electrochem 6, no. 2: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem6020010
APA StyleAguilar-Sánchez, R., Durán-Tlachino, D. A., Cabrera-Hilerio, S. L., & Gárate-Morales, J. L. (2025). Electrochemical Detection of Adrenaline Using Nafion–Trimethylsilyl and Nafion–Trimethylsilyl–Ru2+-Complex Modified Electrodes. Electrochem, 6(2), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem6020010






