Abstract
Chemical UV filters are increasingly used in cosmetics to protect skin from UV radiation. As a consequence, they are released into the aquatic environment via recreational activities and wastewaters. In aquatic ecosystems, fish eggs in contact with sediment can be affected by organic and lipophilic pollutants such as UV filters. The present study aims to evaluate the toxicity of six individual UV filters, diethylhexyl butamido triazone (DBT), diethylamino hydroxybenzoyl hexyl benzoate (DHHB), ethylhexyl triazone (ET), 2-ethylhexyl salicylate (ES), homosalate (HS), and octocrylene (OC), in the embryo-larval stages of zebrafish Danio rerio. Contamination of fish eggs and larvae with UV filters occurred through contact with spiked sediment for 96 h at a concentration of 10 μg g−1. Among the six UV filters tested, OC delayed hatching success, whereas ES significantly increased the heartbeat rate of embryo–larvae after sediment exposure, probably as a stress response.
1. Introduction
Organic UV filters are used in a wide range of products and plastics to protect human skin and materials from the deleterious effects of UV radiation [1,2]. These compounds are found in many cosmetics, especially sunscreens, and environmental contamination by UV filters may occur via direct input from recreational activities and wastewaters [1,3,4,5]. As a consequence, UV filters are found in all aquatic compartments of freshwater and seawater and in the biota (rivers, lakes, coastal oceans, surface waters, and sediments). Their environmental concentrations have been summarized in recent reviews [1,3,5,6,7,8,9,10].
This study selected six compounds of interest (Table 1): diethylhexyl butamido triazone (DBT), diethylamino hydroxybenzoyl hexyl benzoate (DHHB), ethylhexyl triazone (ET), 2-ethylhexyl salicylate (ES), homosalate (HS), and octocrylene (OC).
UV filters have low solubility and tend to accumulate in organisms and sediment. Sediment contact is therefore an important method of contamination that was chosen in this study [11,12]. Among the six UV filters studied, OC is one of the most widely and increasingly used UV filters in cosmetics. Due to the high lipophilicity of OC and its low biodegradability [12], OC has a considerable tendency for bioaccumulation. This is especially true as we have demonstrated that OC can bioaccumulate in the form of analogues [12,13]. Previous studies reported OC concentrations ranging from 0.4 ng g−1 in Japanese river sediment to a concentration of 652 ng g−1 in lake sediment [14,15,16,17,18,19]. ES, which is also widely used, was detected at concentrations from 1.35 ng g−1 to maximal concentrations of 13.3 ng g−1 and 13.7 ng g−1 in Spanish and Chinese river sediments, respectively [20]. Kameda et al., (2011) measured an HS concentration of 26 ng g−1 in Japanese stream sediment. Lower concentrations of 0.6 ng g−1 [15], 0.89 ng g−1 and 1.2 ng g−1 dw were also found. Few studies have measured DBT and ET concentrations in the environment due to their more recent use in cosmetics. The maximum DBT concentration of 629 ng g−1 was measured in lake sediment [16]. DBT was recently detected at concentrations ranging from 22 to 210 ng g−1 in Banyuls Bay and Villeneuve-de-la-Raho Lake sediments [10]. Apel et al., (2018) measured 0.31 ng g−1 and 2 ng g−1 ET in the surface sediment of German lakes. Unfortunately, no measurement of the DHHB concentration in sediment is available. Table 1 provides a summary of the concentrations of the six selected UV filters measured in environmental sediment. In the present study, the tested concentration of 10 μg g−1 was 15 times higher than the OC and DBT environmental concentrations, and higher than the highest concentrations of DBT, DHHB, HS, and ES measured in aquatic sediment. Previous studies reported the bioaccumulation and toxicity of these UV filters in several aquatic organisms (see for a review), mainly on algae and coral [13,21], but also on crustaceans [22,23,24] and fishes [25,26]. Among the 60 UV filters found in the global market, only 15 appear in literature with a described toxicity on the biota. Most studies have investigated mortality, oxidative stress, or growth [8]. As UV filters are emerging pollutants, more toxicological data are needed to develop biomarker-based assays to evaluate UV filter toxicity.

Table 1.
UV filters tested and their environmental occurrence. a USA: United States of America; EU: European Union; Aus.: Australia; n.a.: not approved.
Table 1.
UV filters tested and their environmental occurrence. a USA: United States of America; EU: European Union; Aus.: Australia; n.a.: not approved.
| Abbr. | COSING Name | Alternative Names | CAS | Formula | Maximum Concentration in Final Product a | Higher Environmental Concentration Measured in Sediment (in ng·g−1) | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | EU | Aus. | |||||||
| DBT | Diethylhexyl butamido triazone | Iscotrizinol Uvasorb HEB | 154702-15-5 | C44H59N7O5 | n.a. | 10% | n.a. | 629 | [10,16] |
| DHHB | Diethylamino hydroxybenzoyl hexyl benzoate | Uvinul A+ | 302776-68-7 | C24H31NO4 | n.a. | 10% | 10% | - | - |
| ET | Ethylhexyl triazone | Uvinul T150 | 88122-99-0 | C48H66N6O6 | n.a. | 5% | n.a. | 2 | [20] |
| ES | 2-Ethylhexyl salicylate | 118-60-5 | C15H22O3 | n.a. | 5% | n.a. | 13.7 | [18,19,20] | |
| HS | Homosalate | Homomenthyl salicylate Sunobel®HMS | 118-56-9 | C16H22O3 | 15% | 10% | 15% | 26 | [14,18,19,20] |
| OC | Octocrylene | 6197-30-4 | C24H27NO2 | 10% | 10% | 10% | 652 | [14,15,16,17,18,19,20] | |
Fishes are suitable organisms that can be used to monitor the toxicity of persistent lipophilic contaminants. In this study, the fish Danio rerio was selected as a model species recommended for ecotoxicity testing [27,28,29,30,31], due to its many biological advantages. In fish, several studies have found that UV filters are reprotoxic as endocrine disruptors [1,32], genotoxic, and can impair the development of fish [31]. As UV filters are emerging pollutants, a major effort must be made to develop UV filter risk assessment and to understand their toxicity in the aquatic environment. In this context, this study investigated the effect of six UV filter-spiked sediment on the early life stages of zebrafish. Toxic responses of exposed embryos and larvae were examined through physiological parameters such as survival, hatching success, cardiac frequency, and aerobic metabolism.
2. Materials and Methods
The protocols used in the present study were described in detail in [33]. The preparation of UV filter-spiked sediments and the exposure processes were performed using a procedure adapted from Le Bihanic et al. [34,35].
2.1. Chemicals Used and the Preparation of Spiked Artificial Sediment
The UV filters used in this study are listed in Table 1, and were kindly provided by Pierre Fabre Laboratories (Toulouse, France). Analytical-grade dichloromethane (DCM), methanol (MeOH) and CaCO3 were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich.
The reconstituted sediment was composed of sand measuring 0.2–0.5 mm (sable de Loire SCALARE, Aquastore, Danieux, France), 5% kaolin clay (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), and Sphagnum blond peat (Florentaise, SaintMars-du-Désert, France). Briefly, the peat was dried for 48 h and sieved (0.5 mm). Milli-Q water (Elga Purelab Flex System (Veolia LabWater STI, Antony, France) was added to the peat (12:1, v/v) in glass bottles and shaken for 48 h at 180 rpm at room temperature. Sand and 5% kaolin clay were then mixed with humid peat and shaken for 24 h. The pH was adjusted to 6.5 with a 10% CaCO3 solution. After 7 days of stabilization at room temperature, 1:4 v/v of Milli-Q water was added to the sediment. After a 24-h equilibration period, the supernatant water was removed and the sediment was dried at 105 °C for 14 h. After cooling, 4 g artificial sediment added in glass Petri dishes was spiked with one of the UV filters at 10 μg g−1 dry weight sediment each, as follows: a solution of the UV filter in dichloromethane (10 μL, 4 mg mL−1) was mixed into the sediment, and then the solvent was left to evaporate overnight in the dark at room temperature under a fume hood. This ensures complete residual solvent removal. A control with solvent (dichloromethane without UV filters) and sediment was prepared in the same manner. A negative control was tested too (no solvent, only artificial water E3 and sediment).
2.2. Zebrafish Embryo-Larval Assay
The Institute of Functional Genomics of Lyon (IGFL) provided adult wild-type AB-TU strain (Tübingen, Germany) zebrafish (Danio rerio). The fish were maintained in groups of 10 individuals in 10 l aquaria were filled with a mix of 1/3 reverse osmosis-treated water and 2/3 tap water without chlorine, both filtered beforehand with dust and charcoal filters. The average pH measured was 7.8 ± 0.5 with a conductivity of 450 ± 50 μS cm−1. The oxygen level was maintained at ≥80% thanks to a rack aeration. The fish were maintained in groups of 10 individuals per tank at a water temperature of 28 ± 1 °C and under a photoperiod of 14-h light/10-h dark. Ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate were monitored weekly and remained within the recommended ranges [36]. The fish were fed twice a day with commercial pellets (Ocean Nutrition Europe, Essen, Belgique) and Artemia sp. nauplii (Artemia EG > 225,000 nauplii/g). Occasionally, food was supplied by red sludge worms (Boschetto-frozen fish food). The eggs were obtained from this culture by random pairwise mating of zebrafish. One adult male and one female were placed together in spawning boxes (AquaSchwarz, Göttingen, Germany) the evening before the eggs were required. Spawning and fertilization took place within 30 min after the onset of light in the morning. Fertilized and normally developed eggs were selected (this time was T0) to test the effect of the six selected UV filters. In order to do so, groups of 30 selected eggs were placed in contact with 4 g of spiked artificial sediment and 8 mL of artificial water (E3) in glass Petri dishes (35 mm diameter). Exposure to the UV filters spiked sediment lasted 96 h at 28 ± 0.5 °C, with the same photoperiod as the rearing room. At 96 h, the larvae were transferred into a freshly prepared E3 medium for an additional 6 days period (total of 10 days testing) for the analysis. The larvae were not fed during the experiment.
2.3. Survival and Hatching Success
Embryonic and larval survival were recorded daily until 10 dpf (days post fertilization). For each condition tested, four replicates of 30 individuals were observed. Dead individuals were removed. The survival rate (SR, %) was estimated as follows:
where SNtx and SNt0 are the number of live individuals at time tx (time of the measure, x hours post fertilization—hpf) and t0 (beginning of the experiment, 0 hpf).
SR = 100 × (SNtx/SNt0)
Similarly, hatched individuals were counted between 48 and 72 hpf. At the end of exposure (96 hpf), hatching success (HS, %) was calculated as follows:
where HIt96h is the number of hatched and living larvae.
HS = 100 × (HIt96h/SNt96h)
2.4. Cardiac Frequency
To assess cardiac frequency (fH), a total of 301 larvae were tested individually (nsolvent control = 33, nnegative control = 35, nOC = 41, nES = 39, nHS = 40, nUV = 38, nUA+ = 41, nUT150 = 35). The larvae were placed in a lateral position into 3% methylcellulose on Petri dishes (i.e., 6–7 mL) in order to see the heart by transparency and to measure fH. In addition, 2 h acclimation was needed to recover from the transfer [33]. Videos of 20 s were recorded three times (Olympus DP71) to observe the in vivo beating heart of each larva.
2.5. Static Respirometry
This study used intermittent flow respirometry to record the oxygen consumption of the fish [33,37]. The setup was composed of eight independent glass microrespirometer chambers (diameter d = 9 mm, volume V = 0.6 mL; Loligo Systems, Viborg, Denmark) submerged into buffer tanks (depth × length × height 14 × 35 × 13 cm) and filled with oxygenated E3 solution at a constant temperature of 28 °C. Dissolved oxygen levels were measured by an optic fiber system (PreSens, Witrox 4) during the phase of 30 min oxygen consumption alternating with phases of 15 min oxygen renewal. Ten groups of five larvae were tested for each trial, and each group of larvae was tested once. As described in Lucas et al. [33], two metabolic rates were measured: active metabolic rate (AMR), which represents the maximum oxygen transport capacity of an individual, estimated as the maximum energy expenditure reached after having chased the larvae, and standard metabolic rate (SMR), which corresponds to the minimal maintenance metabolic rate estimated at rest for 48 h. Aerobic metabolic scope (AMS) was calculated as the difference between AMR and SMR.
After 48 h of measurements, the larvae were removed from the respirometers and slightly anesthetized with benzocaine at a concentration of 50 mg L−1. The body mass of each individual was determined using a microbalance (Sartorius Secura 26-1S). A bacterial measurement was performed before and after each trial without fish to quantify the background respiration. Linear changes were assumed in background oxygen consumption over the 48-h experimental trial, and the calculated background was subtracted from the corresponding total oxygen consumption measured.
Oxygen consumption (MO2) is expressed in mgO2 g−1 h−1 and calculated using the following formula:
where Δ[O2] (in mgO2 · L−1) is the change in oxygen concentration during the measurement period Δt (in h), V (in L) is the volume of the respirometer minus the volume of the fish, and Mmeas (in g) is the mass of the corresponding group of five larvae.
MO2meas = Δ[O2] · Δt−1 · V · Mmeas−1
An allometric relationship exists between oxygen consumption and body mass, which encourages the correction of MO2meas using the following formula:
where MO2cor (in mg O2 g−1 h−1) is the oxygen consumption related to a standard fish of 1 g (Mcor), MO2meas (in mg O2 g−1 h−1) is the oxygen consumption estimated with Equation (3) for experimental fish whose mass is Mmeas (in g), and b is the allometric scaling exponent describing the relationship between oxygen consumption and fish mass. In the case of this study, we used bAMR = 0.926 for the correction of active metabolic rate and bSMR = 0.965 for the correction of the standard metabolic rate [38].
MO2cor = MO2meas · (Mmeas · Mcor−1)1 − b
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism software. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error. The results were statically evaluated with the Shapiro and Bartlett tests to check normality and homoscedasticity. An unpaired t-test was then used to determine which chemical treatment differed significantly from the solvent control. A significance level of 5% was used for all of the analyses.
3. Results and Discussion
The embryo larval stages of fish are particularly sensitive and vulnerable to pollutants in the aquatic environment. Thus, ecotoxicity tests on the early life stages of fish has been widely developed in the last decades. In the current study, sediment contact was used as a relevant test to evaluate the toxicity of six organic UV filters on the embryo–larval stages of the zebrafish [33,35]. This type of test allowed for reproducing the multiple sources of exposure of benthic organisms via sediment, particle, and dissolved phases. Four different physiological endpoints were assessed, namely: survival, hatching success, cardiac frequency, and aerobic metabolism. For all of the parameters, a negative control (sediment) and solvent control (solvent and sediment) were tested to estimate the impact of the solvent. No difference was observed between these two controls, regardless of the parameters measured (p > 0.05).
3.1. Impact on Survival and Hatching
For each UV filter tested at a concentration of 10 µg g−1, no significant mortality was observed compared to the solvent control (Table 2, t-test, p > 0.05). Hatching success decreased after exposure to OC (p < 0.05). This means that OC induced late hatching, which could impact fish development under environmental conditions. On the contrary, no effect on hatching success was observed for ES, HS, DBT, ET, and DHHB under our exposure conditions.

Table 2.
Survival and hatching success of zebrafish assessing UV filter toxicity. Mean values ± standard deviation. * indicates a significant difference from the solvent control experiment (t-test, p < 0.05).
3.2. Cardiotoxicity
No significant change in heart beat was observed for the OC (p = 0.2472), HS (p = 0.8892), DBT (p = 0.2345), ET (p = 0.3792), or DHHB (p = 0.0.0363) treatments compared to the solvent control (Figure 1).
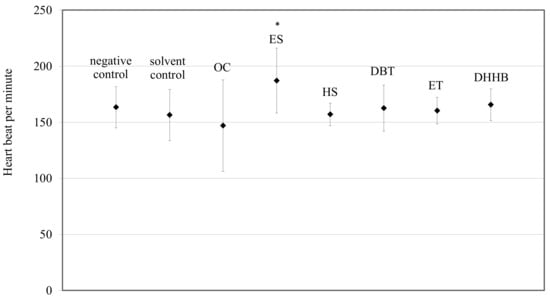
Figure 1.
Cardiac frequency of 5 dpf larvae zebrafish (Danio rerio) exposed to one of the following treatments: controls, and exposure to OC, ES, HS, DBT, ET, or DHHB. Mean values ± standard deviation are plotted; * indicates a significant difference from the solvent control experiment (t-test, p < 0.05).
These results are in the range of cardiac frequency measured in previous studies [39,40,41,42,43,44]. On the contrary, ES significantly increased the cardiac frequency by 19.7% compared to the solvent control (Figure 1, p < 0.0001). These results are in the range of the studies of Lucas et al. [33,41], who observed a 10.2% heart beat increase after exposure to the UV filter BEMT and 12.5% heart beat increase after parental exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. The increase was not lethal, and may be due to only a stress response; this requires further investigation. In fact, pollutants are known to increase stress hormone level such as cortisol, which could impair cardiac frequency [43,44]. In addition, antioxidant defenses or detoxification processes could be triggered by exposure to UV filters to prevent oxidative damage [45]. These additional energy-consuming activities could induce an increase in heart rate to meet the increased oxygen demand in order to produce more energy. This could in turn increase SMR and impair aerobic metabolic scope. To complete these results, it will be interesting to look at cardiac morphological deformities and any other ventricular cardiac dysfunctions such as measurement of the stroke volume, in order to observe all of the cardiac function.
3.3. Aerobic Metabolic Scope
All of the results regarding aerobic metabolism are synthesized in Figure 2. SMR, AMR, and AMS measured in 5 dpf embryo–larvae were not significantly different from the solvent control for OC (pSMR = 0.2034, pAMR = 0.2858, and pAMS = 0.4514), ES (pSMR = 0.8161, pAMR = 0.1335, and pAMS = 0.1787), HS (pSMR = 0.3923, pAMR = 0.7012, and pAMS = 0.8401), DBT (pSMR = 0.4365, pAMR = 0.9130, and pAMS = 0.8555), DHHB (pSMR = 0.4081, pAMR = 0.8107, and pAMS = 0.9271), and ET (pSMR = 0.6172, pAMR = 0.8899, and pAMS = 0.9971). Therefore, comparison with other studies is rather limited, as the UV filters tested were not the same in both studies. These results are similar to those reported by Lucas et al., for other UV filters, namely: benzophenone-3 (BP3), butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane (BM), bis-ethylhexyloxyphenol methoxyphenyl triazine (BEMT), and methylene bis-benzotriazolyl tetramethylbutylphenol (MBBT). At the concentration tested, the UV filters do not seem to impact the metabolic regulation. The lack of effect suggested that zebrafish larvae had an overall capacity to sustain oxygen supply for oxygen-consuming functions in these conditions of exposure.
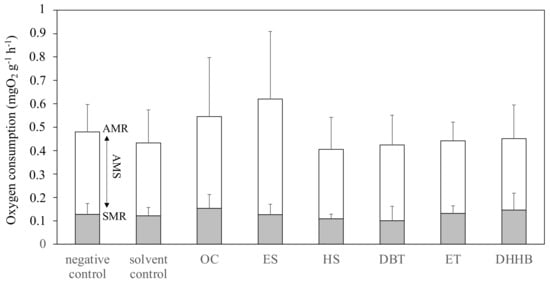
Figure 2.
Active metabolic rate (AMR), standard metabolic rate (SMR), and aerobic metabolic scope (AMS) of 5 dpf Danio rerio larvae in the controls or after exposure to one of the six UV filters tested: OC, ES, HS, DBT, ET, and DHHB. The results are expressed as the mean values ± standard deviation. No significant difference was observed between the solvent control and UV filters, regardless of the metabolic rate considered (t-test, p < 0.05).
This is only the second work on the impact of UV filters on fish metabolism [33]. Even if the metabolic rates of ES were not significantly different from those of the control, the high AMR may be related to the tachycardia observed in larvae. In fact, higher AMR resulted from an increase in energy demand. To produce more energy, organism increased oxygen consumption, which extends cardiac frequency, increases so as to regulate oxygen transport.
4. Conclusions
The current study showed that OC significantly delayed hatching and that ES significantly increased the heartbeat rate of embryo–larvae after sediment exposure. Our findings are consistent with numerous studies that report negative effects, especially for OC, on aquatic organisms (review by Lozano et al. [8]). As very high sediment concentrations of OC have been reported, it can be inferred that OC could significantly impact the local reproductive success of fish laying eggs on sediment. HS, DBT, DEBT, and ET did not induce any significant effect under our exposure conditions, regardless of the physiological endpoint studied. The test concentrations were higher than those encountered in a natural environment. In our experimental conditions and using standardized artificial sediment, the UV filter toxicity towards zebrafish embryo–larvae was low. However, xenobiotics bioavailability and toxicity may be affected by the nature and relative concentration of organic matter, as well as many other parameters such as ionic strength and salinity. It could be interesting to test different sediment compositions in future experiments.
This work is the first report on the effect of DHHB, DBT, and ET on fish development and larval metabolism. Some countries are beginning to address the environmental impact of sunscreen products, but more ecotoxicity data are urgently needed. In particular, a clearer definition of the products being marketed as “reef-safe” is necessary and should follow-up the advances of science in this matter. Considering the regular release and persistence of UV filters in the aquatic environment, long-term exposure studies should also be conducted. As UV filters are usually applied in mixtures, additional work should assess their combined effect on the environment.
Author Contributions
All of the authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by J.L., V.L. was responsible for fish rearing. A.M.S.R. and D.S. helped with the chemical protocols and analysis. P.L. supervised the project. The first draft of the manuscript was written by J.L. All of the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted under the agreement of the Animal Care Committee N° A66-01-601 on 28 January 2021.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
All experiments were carried out at USR 3579 SU-CNRS Laboratoire de Biodiversité et Biotechnologies Microbiennes (LBBM), Observatoire Océanologique, Banyuls-sur-Mer, France. We thank the BIO2MAR and BIOPIC platforms for providing technical support and access to instrumentation. We also thank LIENSs laboratories and especially Christel Lefrancois for providing part of the respirometry material. This study was conducted under the agreement of the Animal Care Committee N° A66-01-601 on 28 January 2021.
Conflicts of Interest
The work reported in this article was financed in the context of the Pierre Fabre Laboratories’ Conscious Care Approach and the Skin Protect Ocean Respect commitment of the brand Eau Thermale Avène. It was neither supervised nor audited by Pierre Fabre Laboratories. The interpretation and views expressed in this manuscript are not those of the company. The authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interest to disclose.
References
- Fent, K.; Zenker, A.; Rapp, M. Widespread occurrence of estrogenic UV-filters in aquatic ecosystems in Switzerland. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldman, R.A.; Grant-Kels, J.M. The role of sunscreen in the prevention of cutaneous melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giokas, D.L.; Sakkas, V.; Albanis, T.A.; Lampropoulou, D.A. Determination of UV-filter residues in bathing waters by liquid chromatography UV-diode array and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry after micelle mediated extraction-solvent back extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1077, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, S.; Homem, V.; Alves, A.; Santos, L. A review of organic UV-filters in wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, M.M.; Leung, H.; Kwan, B.K.; Ng, K.-Y.; Yamashita, N.; Taniyasu, S.; Lam, K.S.P.; Murphy, M.B. Occurrence, distribution and ecological risk assessment of multiple classes of UV filters in marine sediments in Hong Kong and Japan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 292, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molins-Delgado, D.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Ecological risk assessment associated to the removal of endocrine-disrupting parabens and benzophenone-4 in wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 310, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Grajales, D.; Fennix-Agudelo, M.A.; Miranda-Castro, W. Occurrence of personal care products as emerging chemicals of concern in water resources: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, C.; Givens, J.; Stien, D.; Matallana-Surget, S.; Lebaron, P. Bioaccumulation and Toxicological Effects of UV-Filters on Marine Species. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchelmore, C.L.; Burns, E.E.; Conway, A.; Heyes, A.; Davies, I.A. A Critical Review of Organic Ultraviolet Filter Exposure, Hazard, and Risk to Corals. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 967–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagervold, S.K.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Rohée, C.; Roe, R.; Bourrain, M.; Stien, D.; LeBaron, P. Occurrence and environmental distribution of 5 UV filters during the summer season in different water bodies. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodil, R.; Schrader, S.; Moeder, M. Non-porous membrane-assisted liquid–liquid extraction of UV filter compounds from water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 4887–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clergeaud, F.; Fagervold, S.K.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Thorel, E.; Stien, D.; Lebaron, P. Transfer of 7 organic UV filters from sediment to the ragworm Hediste diversicolor: Bioaccumulation of benzophenone-3 and further proof of octocrylene metabolism. Pollutants 2022, 2, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stien, D.; Clergeaud, F.; Rodrigues, A.M.S.; Lebaron, K.; Pillot, R.; Romans, P.; Fagervold, S.; Lebaron, P. Metabolomics reveal that octocrylene accumulates in Pocillopora damicornis tissues as fatty acid conjugates and triggers coral cell mitochondrial dysfunction. Anal. Chem. 2018, 91, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameda, Y.; Kimura, K.; Miyazaki, M. Occurrence and profiles of organic sun-blocking agents in surface waters and sediments in Japanese rivers and lakes. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1570–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amine, H.; Gomez, E.; Halwani, J.; Casellas, C.; Fenet, H. UV filters, ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate, octocrylene and ethylhexyl dimethyl PABA from untreated wastewater in sediment from eastern Mediterranean river transition and coastal zones. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2435–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, D.; Sieratowicz, A.; Zielke, H.; Oetken, M.; Hollert, H.; Oehlmann, J. Ecotoxicological effect characterisation of widely used organic UV filters. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combi, T.; Miserocchi, S.; Langone, L.; Guerra, R. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediments from the western Adriatic Sea: Sources, historical trends and inventories. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintado-Herrera, M.G.; Wang, C.; Lu, J.; Chang, Y.-P.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Lara-Martin, P.A. Distribution, mass inventories, and ecological risk assessment of legacy and emerging contaminants in sediments from the Pearl River Estuary in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, C.; Joerss, H.; Ebinghaus, R. Environmental occurrence and hazard of organic UV stabilizers and UV filters in the sediment of European North and Baltic Seas. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Brunete, C.; Miguel, E.; Albero, B.; Tadeo, J.L. Analysis of salicylate and benzophenone-type UV filters in soils and sediments by simultaneous extraction cleanup and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 4291–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorel, E.; Clergeaud, F.; Jaugeon, L.; Rodrigues, A.M.S.; Lucas, J.; Stien, D.; Lebaron, P. Effect of 10 UV Filters on the Brine Shrimp Artemia salina and the Marine Microalga Tetraselmis sp. Toxics 2020, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stien, D.; Suzuki, M.; Rodrigues, A.M.S.; Yvin, M.; Clergeaud, F.; Thorel, E.; LeBaron, P. A unique approach to monitor stress in coral exposed to emerging pollutants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langford, K.H.; Reid, M.J.; Fjeld, E.; Øxnevad, S.; Thomas, K.V. Environmental occurrence and risk of organic UV filters and stabilizers in multiple matrices in Norway. Environ. Int. 2015, 80, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gago-Ferrero, P.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. An overview of UV-absorbing compounds (organic UV filters) in aquatic biota. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 2597–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molins-Delgado, D.; Muñoz, R.; Nogueira, S.; Alonso, M.B.; Torres, J.P.; Malm, O.; Ziolli, R.L.; Hauser-Davis, R.; Eljarrat, E.; Barceló, D.; et al. Occurrence of organic UV filters and metabolites in lebranche mullet (Mugil liza) from Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.J.; Teraoka, H.; Heideman, W.; Peterson, R.E. Zebrafish as a model vertebrate for investigating chemical toxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 86, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lammer, E.; Carr, G.; Wendler, K.; Rawlings, J.; Belanger, S.; Braunbeck, T. Is the fish embryo toxicity test (FET) with the zebrafish (Danio rerio) a potential alternative for the fish acute toxicity test? Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 149, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrionuevo, W.R.; Burggren, W.W. O2 consumption and heart rate in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio): Influence of temperature and ambient O2. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1999, 276, R505–R513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- OECD. Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OCDE: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitsbergen, J.M.; Kent, M.L. The State of the Art of the Zebrafish Model for Toxicology and Toxicologic Pathology Research: Advantages and Current Limitations. Toxicol. Pathol. 2003, 31, 62–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazar, S.; Gökçek, Y. Assessment of in vitro genotoxicity effect of homosalate in cosmetics. Marmara Pharm. J. 2018, 22, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coronado, M.; De Haro, H.; Deng, X.; Rempel, M.A.; Lavado, R.; Schlenk, D. Estrogenic activity and reproductive effects of the UV-filter oxybenzone (2-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl-methanone) in fish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 90, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, J.; Logeux, V.; Rodrigues, A.M.S.; Stien, D.; Lebaron, P. Exposure to four chemical UV filters through contaminated sediment: Impact on survival, hatching success, cardiac frequency, and aerobic metabolic scope in embryo-larval stage of zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 29412–29420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bihanic, F.; Morin, B.; Cousin, X.; Le Menach, K.; Budzinski, H.; Cachot, J. Developmental toxicity of PAH mixtures in fish early life stages. Part I: Adverse effects in rainbow trout. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 13720–13731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Bihanic, F.; Perrichon, P.; Landi, L.; Clérandeau, C.; Le Menach, K.; Budzinski, H.; Cousin, X.; Cachot, J. Development of a reference artificial sediment for chemical testing adapted to the MELA sediment contact assay. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 13689–13702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, C. The husbandry of zebrafish (Danio rerio): A review. Aquaculture 2007, 269, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffensen, J.F.; Bushnell, P.G.; Schurmann, H. Oxygen consumption in four species of teleosts from Greenland: No evidence of metabolic cold adaptation. Polar Biol. 1994, 14, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, J.; Schouman, A.; Lyphout, L.; Cousin, X.; Lefrancois, C. Allometric relationship between body mass and aerobic metabolism in zebrafish Danio rerio. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 84, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burggren, W.W. Developing animals flout prominent assumptions of ecological physiology. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2005, 141, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Hui, M.N.; Cheng, S.H. Toxicity and cardiac effects of carbaryl in early developing zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 222, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, J.; Perrichon, P.; Nouhaud, M.; Audras, A.; Leguen, I.; Lefrançois, C. Aerobic metabolism and cardiac activity in the descendants of zebrafish exposed to pyrolytic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 13888–13897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucas, J.; Lefrancois, C.; Gesset, C.; Budzinski, H.; Labadie, P.; Baudrimont, M.; Coynel, A.; Le Menach, K.; Pardon, P.; Peluhet, L.; et al. Health status of juveniles of European sturgeon intended for reintroduction in Gironde-Garonne-Dordogne catchments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 225, 112720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccormick, M.I.; Nechaev, I.V. Influence of cortisol on developmental rhythms during embryogenesis in a tropical damselfish. J. Exp. Zoöl. 2002, 293, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesan, D.; Vijayan, M.M. Embryo exposure to elevated cortisol level leads to cardiac performance dysfunction in zebrafish. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 363, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ye, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Ou, H. UV-driven hydroxyl radical oxidation of tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate: Intermediate products and residual toxicity. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).