Radiological and Periodontal Evaluation of Stock and Custom CAD/CAM Implant Abutments—A One-Year Follow-Up Study
Abstract
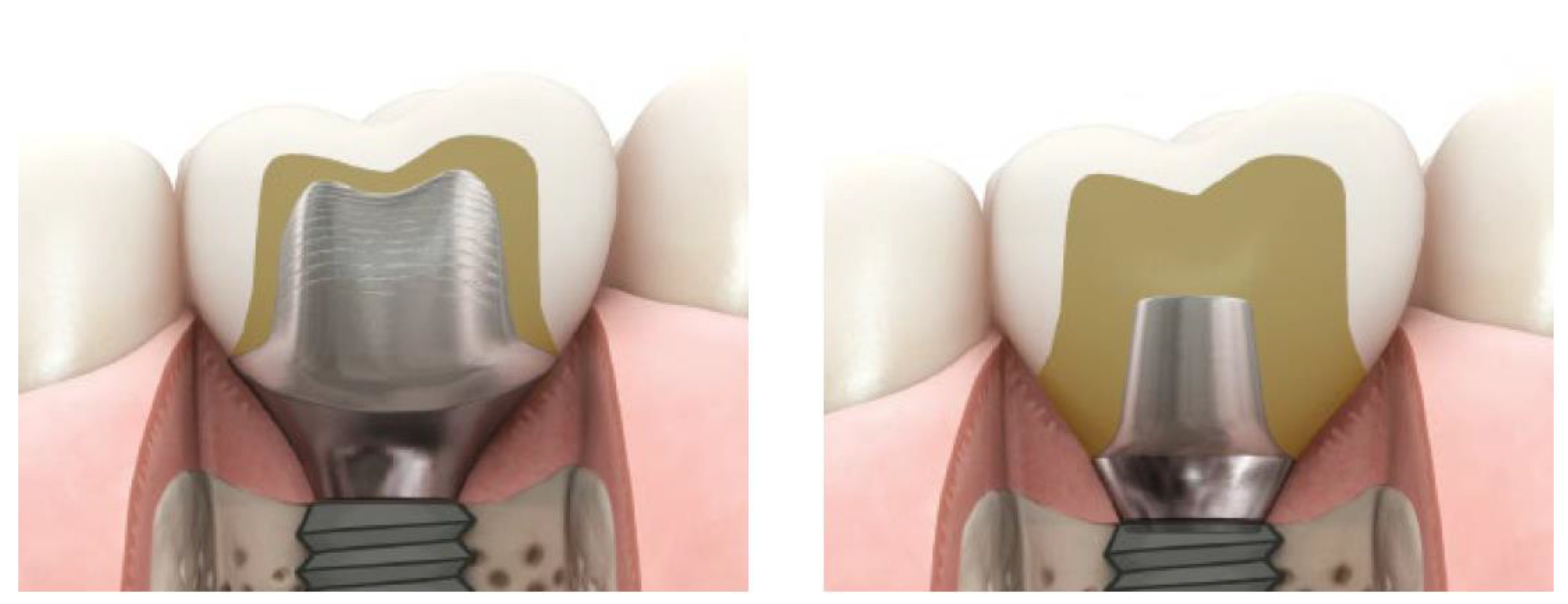
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamilton, A.; Judge, R.B.; Palamara, J.E.; Evans, C. Evaluation of the fit of CAD/CAM abutments. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2013, 26, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, S.; Pascadopoli, M.; Pellegrini, M.; Pulicari, F.; Manfredini, M.; Zampetti, P.; Spadari, F.; Maiorana, C.; Scribante, A. CAD/CAM Abutments versus Stock Abutments: An Update Review. Prosthesis 2022, 4, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.I.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.L.; Bae, J.M.; Cho, H.W. Comparison of fracture resistance and fit accuracy of customized zirconia abutments with prefabricated zirconia abutments in internal hexagonal implants. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2013, 15, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priest, G. Virtual-designed and computer-milled implant abutments. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 63, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkevicius, T.; Vindasiute, E.; Puisys, A.; Peciuliene, V. The influence of margin location on the amount of undetected cement excess after delivery of cement-retained implant restorations. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2011, 22, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Maltzahn, N.F.; Holstermann, J.; Kohorst, P. Retention Forces between Titanium and Zirconia Components of Two-Part Implant Abutments with Different Techniques of Surface Modification. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumbrigue, H.B.; Abanomi, A.A.; Cheng, L.L. Techniques to minimize excess luting agent in cement-retained implant restorations. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2002, 87, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentsply Implants. ATLANTIS™ beyond CAD/CAM: ATLANTIS™ Patient-Specific Abutments. Image p. 6. 2015. Available online: https://www.dentsplysirona.com/content/dam/dentsply/web/Implants/FranchiseContent/1224580-ATLANTIS-Abutments-beyond-CAD-CAM-1501-oonkuxc-en-1504.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Borges, T.; Lima, T.; Carvalho, A.; Carvalho, V. Clinical Outcome of Inter-Proximal Papilla between a Tooth and a Single Implant Treated with CAD/CAM Abutments: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2012, 3, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudrias, P.; Shoghikian, E.; Morin, E.; Hutnik, P. Esthetic option for the implant-supported single-tooth restoration-treatment sequence with a ceramic abutment. J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2001, 67, 508–514. [Google Scholar]
- Kapos, T.; Ashy, L.M.; Galluci, G.O.; Weber, H.P.; Wismeijer, D. Computer-aided design and computer-assisted manufacturing in prosthetic implant dentistry. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2009, 24, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Binon, P.P. Implants and components: Entering the new millennium. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2000, 15, 76–94. [Google Scholar]
- Parpaiola, A.; Norton, M.; Cecchinato, D.; Bressan, E.; Toia, M. Virtual Abutment Design: A Concept for Delivery of CAD/CAM Customized Abutments-Report of a Retrospective Cohort. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2013, 33, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkevicius, T.; Vaitelis, J. The effect of zirconia or titanium as abutment material on soft peri-implant tissues: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sailer, I.; Philipp, A.; Zembic, A.; Pjetursson, B.E.; Hammerle, C.H.; Zwahlen, M. A systematic review of the performance of ceramic and metal implant abutments supporting fixed implant reconstructions. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2009, 20, 4–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.E.; Da Silva, J.D.; Weber, H.P.; Ishikawa-Nagai, S. Optical phenomenon of periimplant soft tissue. Part I. Spectrophotometric assessment of natural tooth gingiva and periimplant mucosa. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2007, 18, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, R.E.; Holderegger, C.; Sailer, I.; Khraisat, A.; Suter, A.; Hammerle, C.H. The effect of all-ceramic and porcelain-fused-to-metal restorations on marginal peri-implant soft tissue color: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2008, 28, 357–365. [Google Scholar]
- Gutmacher, Z.; Levi, G.; Blumenfeld, I.; Machtei, E.E. Soft and Hard Tissue Changes around Tissue-Oriented Tulip-Design Implant Abutments: A 1-Year Randomized Prospective Clinical Trial. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 1, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rompen, E.; Raepsaet, N.; Domken, O.; Touati, B.; Van Dooren, E. Soft tissue stability at the facial aspect of gingivally converging abutments in the esthetic zone: A pilot clinical study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2007, 97, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, W.; Goldstein, M.; Becker, B.E.; Sennerby, L. Minimally invasive flapless implant surgery: A prospective multicenter study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2005, 7, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Oh, T.J.; Misch, C.E.; Wang, H.L. Occlusal considerations in implant therapy: Clinical guidelines with biomechanical rationale. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2005, 16, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, D.; Nagata, M.J.; Bell, M.; Bosco, A.F.; de Melo, L.G.; Richter, E.J. Influence of microgap location and configuration on the periimplant bone morphology in submerged implants. An experimental study in dogs. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008, 19, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, D.; Nagata, M.J.; Bosco, A.F.; de Melo, L.G. Influence of microgap location and configuration on radiographic bone loss around submerged implants: An experimental study in dogs. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2011, 26, 941–946. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamsson, I.; Berglundh, T.; Lindhe, J. The mucosal barrier following abutment dis/reconnection. An experimental study in dogs. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1997, 24, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rouck, T.; Eghbali, R.; De Bruyn, H.; Cosyn, J. The gingival biotype revisited: Transparency of the periodontal probe through the gingival margin as a method to discriminate thin from thick gingiva. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentsply Implants. Surgical Manual. Available online: http://www.dentsplyimplants.com/~/media/M3%20Media/DENTSPLY%20IMPLANTS/1212105%20ANKYLOS%20Surgical%20Manual.ashx?filetype=.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Mombelli, A.; van Oosten, M.A.; Schurch, E., Jr.; Land, N.P. The microbiota associated with successful or failing osseointegrated titanium implants. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 1987, 2, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brägger, U.; Hafeli, H.; Huber, B.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Lang, N.P. Evaluation of postsurgical crestal bone levels adjacent to non-submerged dental implants. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1998, 9, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutouzis, T.; Neiva, R.; Nonhoff, J.; Lundgren, T. Placement of implants with platform-switched Morse taper connections with the implant-abutment interface at different levels in relation to the alveolar crest: A short-term (1-year) randomized prospective controlled clinical trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2013, 28, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apicella, D.; Veltri, M.; Chieffi, N.; Polimeni, A.; Giovannetti, A.; Ferrari, M. Implant adaptation of stock abutments versus CAD/CAM abutments: A radiographic and Scanning Electron Microscopy study. Ann. Stomatol. 2010, 1, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, D.; Houston, F.; Cleary, R.; Claffey, N. The fit of cast and premachined implant abutments. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1998, 80, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemt, T.; Pettersson, P. A three-year follow-up study on single implant treatment. J. Dent. 1993, 21, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, G.E. Osseointegrated Dental Technology. Quintessence 1993, 1, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broggini, N.; McManus, L.M.; Hermann, J.S.; Medina, R.; Schenk, R.K.; Buser, D.; Cochran, D.L. Peri-implant inflammation defined by the implant-abutment interface. J. Dent. Res. 2006, 85, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirynen, M.; Bollen, C.M.; Eyssen, H.; van Steenberghe, D. Microbial penetration along the implant components of the Brånemark system. An in vitro study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1994, 5, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lops, D.; Bressan, E.; Parpaiola, A.; Sbricoli, L.; Cecchinato, D.; Romeo, E. Soft tissues stability of CAD/CAM and stock abutments in anterior regions: 2-year prospective multicentric cohort study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosyn, J.; Sabzevar, M.M.; De Bruyn, H. Predictors of inter-proximal and midfacial recession following single implant treatment in the anterior maxilla: A multivariate analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2012, 39, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairo, F.; Pagliaro, U.; Nieri, M. Soft tissue management at implant sites. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luterbacher, S.; Mayfield, L.; Brägger, U.; Lang, N.P. Diagnostic characteristics of clinical and microbiological tests for monitoring periodontal and periimplant mucosal tissue conditions during supportive periodontal therapy (SPT). Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2000, 11, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schou, S.; Holmstrup, P.; Stoltze, K.; Hjørting-Hansen, E.; Fiehn, N.E.; Skovgaard, L.T. Probing around implants and teeth with healthy or inflamed peri-implant mucosa/gingiva. A histologic comparison in cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2002, 13, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, G.R.; Mills, M.; Rapley, J.W.; Hallmon, W.H. Clinical parameters of evaluation during implant maintenance. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1992, 7, 220–227. [Google Scholar]
- Salvi, G.E.; Lang, N.P. Diagnostic parameters for monitoring peri-implant conditions. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2004, 19, 116–127. [Google Scholar]
- Karoussis, I.K.; Muller, S.; Salvi, G.E.; Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.; Bägger, U.; Lang, N.P. Association between periodontal and peri-implant conditions: A 10-year prospective study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2004, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.E.; Zarb, G.A. Criteria for success of osseointegrated endosseous implants. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1989, 62, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feloutzis, A.; Lang, N.P.; Tonetti, M.S.; Bürgin, W.; Brägger, U.; Buser, D.; Duff, G.W.; Kornman, K.S. IL-1 gene polymorphism and smoking as ris IL-1 gene polymorphism and smoking as risk factors for periimplant bone loss in a well-maintained population. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2003, 14, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brägger, U.; Pasquali, L.; Rylander, H.; Carnes, D.; Kornman, K.S. Computer-assisted densitometric image analysis in periodontal radiography. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1988, 15, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, N.P.; Hill, R.W. Radiographs in periodontics. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1977, 4, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewerin, I.P.; Gotfredsen, K.; Stoltze, K. Accuracy of radiographic diagnosis of periimplant radiolucencies—An in vitro experiment. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1997, 8, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zembic, A.; Sailer, I.; Jung, R.E.; Hämmerle, C.H. Randomized-controlled clinical trial of customized zirconia and titanium implant abutments for single-tooth implants in canine and posterior regions: 3-year results. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2009, 20, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Wennström, J.L. Peri-implant soft tissue and bone crest alterations at fixed dental prostheses: A 3-year prospective study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2010, 21, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-T.; Lin, J.C.-Y.; Salamanca, E.; Dorj, O.; Pan, Y.-H.; Wu, Y.-F.; Hsu, Y.-S.; Fang, C.-Y.; Chang, W.-J. Marginal Bone Level Evaluation of Fixed Partial Dental Prostheses Using Preformed Stock versus CAD/CAM Customized Abutments. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.-C.; Liang, C.-H.; Shen, Y.-F.; Hsu, K.-W. Retrospective comparison of posterior fixed dental prostheses supported by two different titanium abutments on tissue level implants. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 125, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpaiola, A.; Toia, M.; Norton, M.; Cecchinato, D.; Bressan, E.; Lops, D. CAD/CAM Implant Abutments: Peri-implant Hard and Soft Tissue Response with Up to 4 Years of Follow-up- A Retrospective Cohort Study Evaluation. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2020, 40, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitzan, D.; Mamlider, A.; Levin, L.; Schwartz-Arad, D. Impact of smoking on marginal bone loss. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2005, 20, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- French, D.; Grandin, H.M.; Ofec, R. Retrospective cohort study of 4591 dental implants: Analysis of risk indicators for bone loss and prevalence of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis. J. Periodontol. 2019, 90, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, R.T.; Pasquinelli, K. Thick vs. thin gingival tissue: A key determinant in tissue response to disease and restorative treatment. J. Calif. Dent. Assoc. 2002, 30, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, M.; Cagidiaco, M.C.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Goracci, C.; Cairo, F. Effect of different prosthetic abutments on peri-implant soft tissue. A randomized controlled clinical trial. Am. J. Dent. 2015, 28, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.W.; Lim, Y.J.; Kim, B.; Lee, S.P. A new method of measuring the volumetric change of alveolar bone around dental implants using computed tomography. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Abbreviation | Definition |
|---|---|
| CAD/CAM | computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (milling) |
| PI | plaque index |
| mPI | modified plaque index |
| API | average plaque index |
| mAPI | modified average plaque index |
| i-API | initial average plaque index |
| 4m-API | four-month average plaque index |
| 8m-API | eight-month average plaque index |
| 12m-API | twelve-month average plaque index |
| mBI | modified bleeding index |
| ABI | average bleeding indeks |
| mABI | modified average bleeding index |
| i-ABI | inital average bleeding index |
| 4m-ABI | four-month average bleeding index |
| 8m-ABI | eight-month average bleeding index |
| 12m-ABI | twelve-month average bleeding index |
| 8m-ABI-D | eight-month average bleeding index dichotomized |
| 12m-ABI-D | twelve-month average bleeding index dichotomized |
| PPD | pocket probing depth |
| APPD | average probing pocket depth |
| i-APPD | initial pocket probing depth |
| 4m-APPD | four-month pocket probing depth |
| 8m-APPD | eight-month pocket probing depth |
| 12m-APPD | twelve-month pocket probing depth |
| CBLE | crestal bone loss evaluation |
| CBLEm | crestal bone loss evaluation mesialy |
| CBLEd | crestal bone loss evaluation distaly |
| ACBLE | average crestal bone loss evaluation |
| TCBLE | total crestal bone loss evaluation |
| i-ACBLE | inital average crestal bone loss evaluation |
| 12m-ACBLE | twelve-month average crestal bone loss evaluation |
| SH | smoking habit |
| GB | gingival biotype |
| OH | oral hygiene |
| AM | arithmetic mean |
| SD | standard deviation |
| CI | confidence interval |
| Type of Abutment | Number of Subjects | Gingival Biotype (GB) | Smoking Habits (SH) | Oral Hygiene Level (OH) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thin | Thick | Yes | No | Poor | Good | Excellent | ||
| STOCK | 34 | 5 | 29 | 9 | 25 | 0 | 13 | 21 |
| CUSTOM | 30 | 6 | 24 | 11 | 19 | 0 | 12 | 18 |
| TOTAL | 64 | 11 | 53 | 20 | 44 | 0 | 25 | 39 |
| i-mAPI | 4m-mAPI | 8m-mAPI | 12m-mAPI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STOCK | Median | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| Range | 0–1.75 | 0–1.5 | 0–1.5 | 0–1.5 | |
| CUSTOM | Median | 0 | 0.125 | 0 | 0.125 |
| Range | 0–1.5 | 0–1.5 | 0–1.25 | 0–1.5 | |
| Mann–Whitney’s U test | p | 0.333 | 0.744 | 0.150 | 0.108 |
| Total for all subjects (STOCK + CUSTOM) | Median | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0 | 0.25 |
| Range | 0–1.75 | 0–1.5 | 0–1.5 | 0–1.5 | |
| Friedman’s two-way analysis of variance for repeated measures | χ2 (number of degrees of freedom) p | χ2 = 16.76 (3); p = 0.001 | |||
| i-mABI | 4m-mABI | 8m-mABI | 12m-mABI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STOCK | Median | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Range | 0–2 | 0–2.5 | 0–1.25 | 0–1.75 | |
| CUSTOM | Median | 0.25 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Range | 0–1.25 | 0–0.75 | 0–0.5 | 0–0.5 | |
| Mann–Whitney’s U test | p | 0.427 | 0.132 | 0.002 | <0.001 |
| Total for all subjects (STOCK + CUSTOM) | Median | 0.25 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Range | 0–2 | 0–2.5 | 0–1.25 | 0–1.75 | |
| Friedman’s two-way analysis of variance for repeated measurements | χ2 (number of degrees of freedom) p | χ2 = 3.15 (3); p = 0.369 | |||
| i-APPD | 4m-APPD | 8m-APPD | 12m-APPD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STOCK | AM | 2.53 | 2.67 | 2.62 | 2.6 |
| SD | 0.83 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.76 | |
| CUSTOM | AM | 2.55 | 2.58 | 2.64 | 2.66 |
| SD | 0.58 | 0.64 | 0.59 | 0.56 | |
| Student’s t-test for independent samples | T | −0.09 | 0.44 | −0.16 | −0.38 |
| P | 0.928 | 0.657 | 0.870 | 0.709 | |
| Total for all subjects | AM | 2.53 | 2.62 | 2.63 | 2.62 |
| SD | 0.72 | 0.73 | 0.68 | 0.66 | |
| ANOVA for repeated measurements with Greenhouse–Geisser correction | F (number of degrees of freedom) p | F = 2.17 (1.45; 91.24) p = 0.135 | |||
| i-ACBLE | 12m-ACBLE | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| STOCK | AM | −0.32 | −0.24 |
| SD | 0.88 | 0.94 | |
| CUSTOM | AM | −0.27 | −0.15 |
| SD | 0.47 | 0.54 | |
| Student’s t-test for independent samples | T | −0.29 | −0.45 |
| p | 0.775 | 0.652 | |
| Total for all subjects | AM | −0.29 | −0.2 |
| SD | 0.71 | 0.78 | |
| Student’s t-test for dependent samples | t | −3.7 | |
| p | <0.001 | ||
| TCBLE | ||
|---|---|---|
| STOCK | AM | 0.05 |
| SD | 0.17 | |
| CUSTOM | AM | 0.11 |
| SD | 0.15 | |
| Student’s t-test for independent samples | T | 1.66 |
| p | 0.105 | |
| Total for all subjects (N = 63) * | Average | 0.76 |
| SD | 0.16 |
| Variable | Value | N | TCBLE AM | TCBLE SD | Student’s t-Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH | YES | 20 | 0.01 | 0.14 | t = 1.94 |
| NO | 43 | 0.11 | 0.13 | p = 0.028 | |
| GB | Thin | 11 | 0.13 | 0.24 | t = 1.25 |
| Thick | 52 | 0.06 | 0.14 | p = 0.218 | |
| OH | Good | 24 | 0.09 | 0.13 | t = 0.58 |
| Excellent | 39 | 0.07 | 0.17 | p = 0.564 |
| 8m-mABI-D | 12m-mABI-D | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Type of abutment | STOCK | 11 | 23 | 6 | 28 |
| CUSTOM | 18 | 12 | 17 | 13 | |
| Total | 29 | 35 | 23 | 41 | |
| Pearson χ2 | 4.92 | 10.54 | |||
| p | 0.027 | 0.001 | |||
| Oral hygiene | Good | 7 | 18 | 5 | 20 |
| Excellent | 22 | 17 | 18 | 39 | |
| Total | 29 | 35 | 23 | 41 | |
| Pearson χ2 | 4.96 | 4.53 | |||
| p | 0.026 | 0.033 | |||
| Gingival biotype | Thin | 6 | 5 | 3 | 8 |
| Thick | 23 | 30 | 20 | 33 | |
| Total | 29 | 35 | 23 | 41 | |
| Fischer’s exact test p | 0.526 | 0.732 | |||
| Coefficient | Statistical Error | Wald (df) | p | Chance Ratio | 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8m-mABI-D | Type of abutment | 1.29 | 0.56 | 5.29 (1) | 0.022 | 3.62 | 1.2–10.82 |
| Oral hygiene | 1.35 | 0.59 | 5.28 (1) | 0.022 | 3.85 | 1.22–12.15 | |
| Constant | −0.98 | 0.47 | 4.3 (1) | 0.038 | 0.38 | ||
| 12m-mABI-D | Type of abutment | 2.04 | 0.63 | 10.36 (1) | 0.001 | 7.65 | 2.22–26.41 |
| Oral hygiene | 1.55 | 0.67 | 5.31 (1) | 0.021 | 4.7 | 1.26–17.51 | |
| Constant | −0.91 | 0.49 | 3.5 (1) | 0.061 | 0.4 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pelivan, I.; Šeparović, I.; Vuletić, M.; Dulčić, N.; Gabrić, D. Radiological and Periodontal Evaluation of Stock and Custom CAD/CAM Implant Abutments—A One-Year Follow-Up Study. Prosthesis 2023, 5, 437-452. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis5020030
Pelivan I, Šeparović I, Vuletić M, Dulčić N, Gabrić D. Radiological and Periodontal Evaluation of Stock and Custom CAD/CAM Implant Abutments—A One-Year Follow-Up Study. Prosthesis. 2023; 5(2):437-452. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis5020030
Chicago/Turabian StylePelivan, Ivica, Ivan Šeparović, Marko Vuletić, Nikša Dulčić, and Dragana Gabrić. 2023. "Radiological and Periodontal Evaluation of Stock and Custom CAD/CAM Implant Abutments—A One-Year Follow-Up Study" Prosthesis 5, no. 2: 437-452. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis5020030
APA StylePelivan, I., Šeparović, I., Vuletić, M., Dulčić, N., & Gabrić, D. (2023). Radiological and Periodontal Evaluation of Stock and Custom CAD/CAM Implant Abutments—A One-Year Follow-Up Study. Prosthesis, 5(2), 437-452. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis5020030








