Raw Milk for Provolone Valpadana PDO Cheese: Impact of Modified Cold Storage Conditions on the Composition of the Bacterial Biota
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
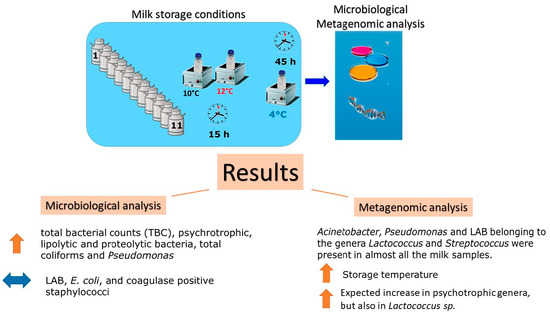
2.1. Milk Sampling and Storage Conditions
2.2. Microbiological Analysis
2.3. Total DNA Extraction
2.4. Metagenomic Analysis
2.5. Bioinformatic and Data Analysis
2.6. Statistic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Raw Milk Microbiota
3.1.1. Microbiological Analysis
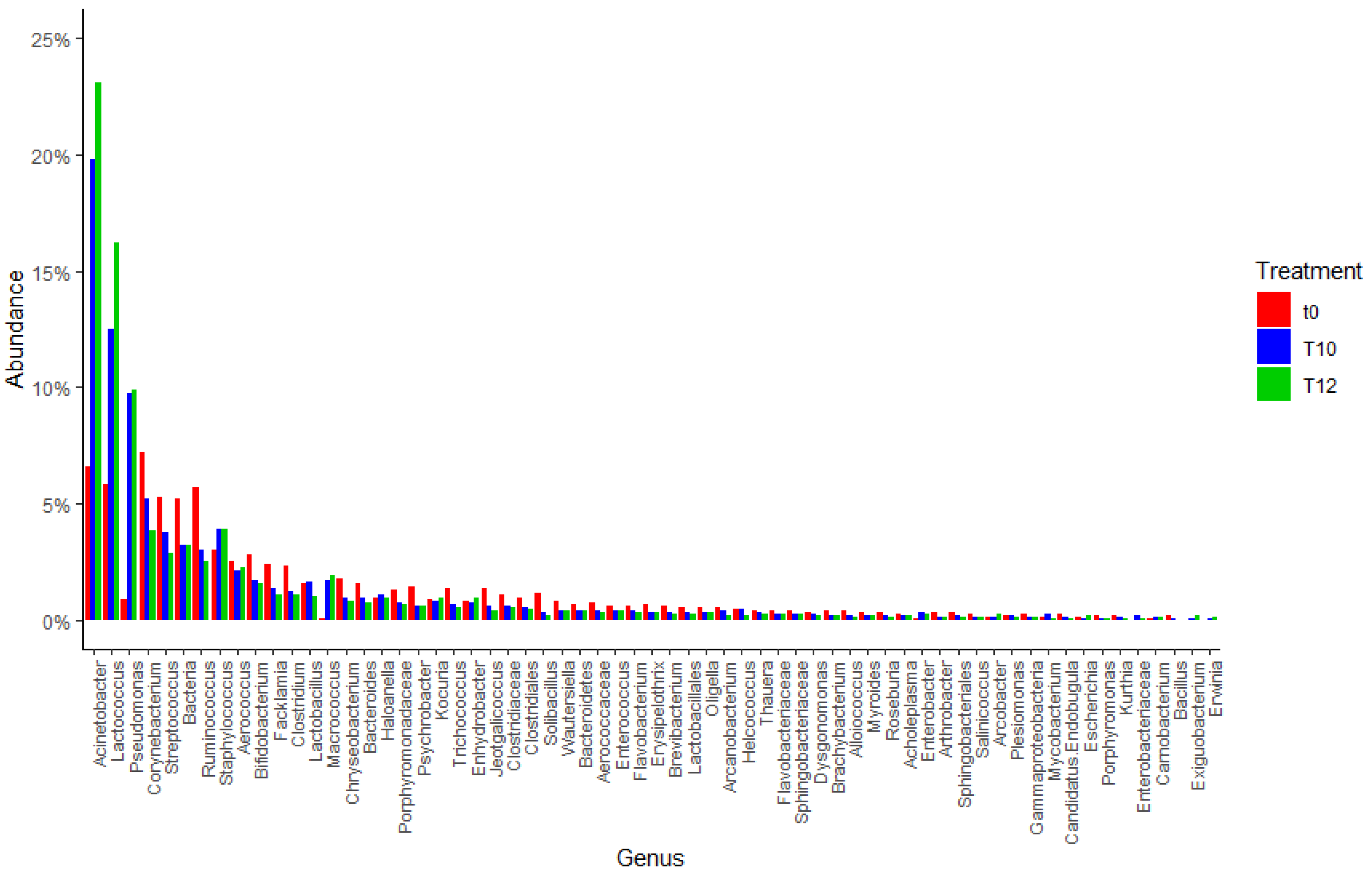
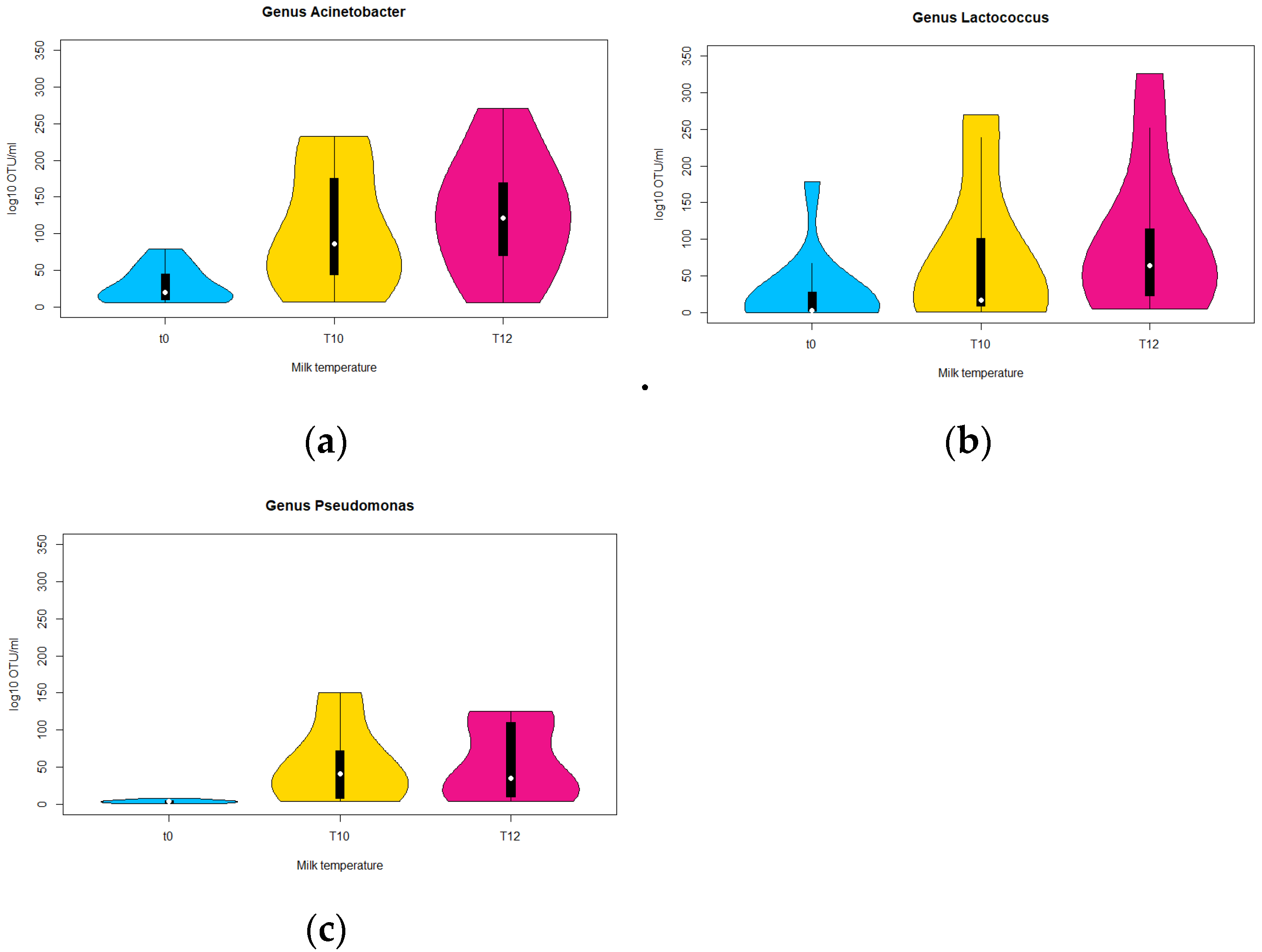
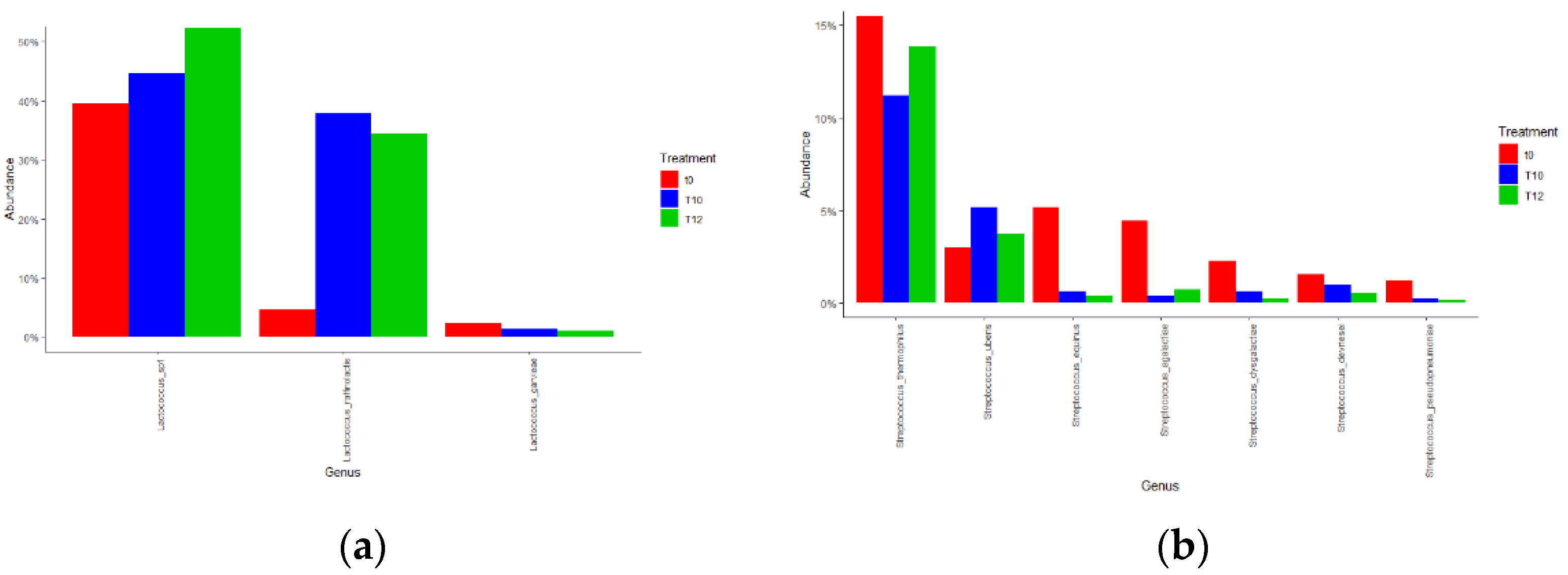
3.1.2. DNA Metabarcoding Data
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murphy, S.C.; Boor, K.J. Trouble-shooting sources and causes of high bacteria counts in raw milk. Dairy Food Environ. Sanit. 2000, 20, 606–611. [Google Scholar]
- Franciosi, E.; Settanni, L.; Cologna, N.; Cavazza, A.; Poznanski, E. Microbial analysis of raw cows’ milk used for cheese-making: Influence of storage treatments on microbial composition and other technological traits. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falardeau, J.; Keeney, K.; Trmčić, A.; Kitts, D.; Wang, S. Farm-to-fork profiling of bacterial communities associated with an artisan cheese production facility. Food Microbiol. 2019, 83, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malacarne, M.; Summer, A.; Franceschi, P.; Formaggioni, P.; Pecorari, M.; Panari, G.; Vecchia, P.; Sandri, S.; Fossa, E.; Scotti, C.; et al. Effects of storage conditions on physico-chemical characteristics, salt equilibria, processing properties and microbial development of raw milk. Int. Dairy J. 2013, 29, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankai, M.; Boulares, M.; Ben Moussa, O.; Karoui, R.; Hassouna, M. The effect of refrigerated storage of raw milk on the physicochemical and microbiological quality of Tunisian semihard Gouda-type cheese during ripening. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2012, 65, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, L.; O’Sullivan, O.; Stanton, C.; Beresford, T.P.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Cotter, P.D. The complex microbiota of raw milk. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 664–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Neubeck, M.; Baur, C.; Krewinkel, M.; Stoeckel, M.; Kranz, B.; Stressler, T.; Fischer, L.; Hinrichs, J.; Scherer, S.; Wenning, M. Biodiversity of re-frigerated raw milk microbiota and their enzymatic spoilage potential. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 211, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithanage, N.R.; Dissanayake, M.; Bolge, G.; Palombo, E.A.; Yeager, T.R.; Datta, N. Microbiological quality of raw milk attributable to prolonged refrigeration conditions. J. Dairy Res. 2017, 84, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministero delle Politiche Agricole Alimentari Forestali e del Turismo. Modifica minore del disciplinare di produzione della denominazione «Provolone Valpadana» registrata in qualità di denominazione di origine protetta in forza al regolamento (CE) n. 1107 del 12 giugno 1996. In Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana n. 91; Istituto Poligrafico e Zecca dello Stato: Roma, Italy, 2019; pp. 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of 29 April 2004 laying down specific hygiene rules for food of animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2004, 50, 55–205. [Google Scholar]
- Franciosi, E.; Gardini, F.; Monfredini, L.; Tabanelli, G.; Fabris, A.; Endrizzi, I.; Poznanski, E.; Gasperi, F.; Cavazza, A. Does milk treatment before cheesemaking affect microbial and chemical traits of ripened cheese? Grana Trentino as a case study. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 5485–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, M.; Bottari, B.; Lazzi, C.; Neviani, E.; Mucchetti, G. Microbial evolution in raw-milk, long-ripened cheeses produced using undefined natural whey starters. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morandi, S.; Battelli, G.; Silvetti, T.; Goss, A.; Cologna, N.; Brasca, M. How the biodiversity loss in natural whey culture is affecting ripened cheese quality? The case of Trentingrana cheese. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 115, 1084802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celestino, E.L.; Iyer, M.; Roginski, H. The effects of refrigerated storage on the quality of raw milk. Aust. J. Dairy Technol. 1996, 51, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Lafarge, V.; Ogier, J.-C.; Girard, V.; Maladen, V.; Leveau, J.-Y.; Gruss, A.; Delacroix-Buchet, A. Raw cow milk bacterial population shifts attributable to refrigeration. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5644–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raats, D.; Maya, O.; Dror, M.; Malka, H. Molecular analysis of bacterial communities in raw cow milk and the impact of refrigeration on its structure and dynamics. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithanage, N.R.; Dissanayake, M.; Bolge, G.; Palombo, E.A.; Yeager, T.R.; Datta, N. Biodiversity of culturable psychrotrophic microbiota in raw milk attributable to refrigeration conditions, seasonality and their spoilage potential. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 57, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbetti, M.; Neviani, E.; Fox, P. The Cheeses of Italy: Science and Technology, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Malacarne, M.; Summer, A.; Formaggioni, P.; Franceschi, P.; Sandri, S.; Pecorari, M.; Vecchia, P.; Mariani, P. Dairy maturation of milk used in the manufacture of Parmigiano-Reggiano cheese: Effects on physico-chemical characteristics, rennet-coagulation aptitude and rheological properties. J. Dairy Res. 2008, 75, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brändle, J.; Heinzle, L.; Fraberger, V.; Berta, J.; Zitz, U.; Schinkinger, M.; Stocker, W.; Kneifel, W.; Domig, K.J. Novel approach to enumerate clostridial endospores in milk. Food Control. 2018, 85, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, M.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Bardelli, T.; Egli, M.; Insam, H.; Ascher-Jenull, J. Bacterial communities of decaying Norway spruce follow distinct slope exposure and time-dependent trajectories. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 3657–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, G.F.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-5. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/ (accessed on 26 February 2021).
- De Mendiburu, F. Package ‘Agricolae’. R Package Version 1.2-8. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=agricolae (accessed on 4 July 2019).
- Caporaso, J.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Meth. 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Reshape2: Flexibly Reshape Data: A Reboot of the Reshape Package. R Package Version. 2012. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/ (accessed on 26 February 2021).
- Oliveira Dumont, A.C.; Nogueira Souza, F.; Machado de Sant’Anna, F.; Faula, L.L.; Gasparotto Chande, C.; Cortez, A.; Melville Paiva Della Libera, A.M.; Costa, M.; Resende Souza, M.; Heinemann, M.B.; et al. Temporal and geographical comparison of bulk tank milk and water microbiota composition in Brazilian dairy farms. Food Microbiol. 2021, 98, 103793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: http://www.sthda.com/english/wiki/correlation-matrix-an-r-function-to-do-all-you-need (accessed on 2 March 2020).
- Decimo, M.; Morandi, S.; Silvetti, T.; Brasca, M. Characterization of Gram-negative psychrotrophic bacteria isolated from Italian bulk tank milk. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, M2081–M2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jonghe, V.; Coorevits, A.; Van Hoorde, K.; Messens, W.; Van Landschoot, A.; De Vos, P.; Heyndrickx, M. Influence of storage conditions on the growth of Pseudomonas species in refrigerated raw milk. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hantsis-Zacharov, E.; Halpern, M. Culturable psychrotrophic bacterial communities in raw milk and their proteolytic and lipolytic traits. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7162–7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahne, J.; Isele, D.; Berning, J.; Lipski, A. The contribution of fast growing, psychrotrophic microorganisms on biodiversity of refrigerated raw cow’s milk with high bacterial counts and their food spoilage potential. Food Microbiol. 2019, 79, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narvhus, J.A.; Bækkelund, O.N.; Tidemann, E.M.; Østlie, H.M.; Abrahamsen, R.K. Isolates of Pseudomonas spp. from cold-stored raw milk show variation in proteolytic and lipolytic properties. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 123, 105049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinot-Thomas, P.; Al Ammoury, M.; Laurent, F. Effects of storage conditions on the composition of raw milk. Int. Dairy J. 1995, 5, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paludetti, L.F.; Jordan, K.; Kelly, A.L.; Gleeson, D. Evaluating the effect of storage conditions on milk microbiological quality and composition. Irish J. Agric. Food Res. 2018, 57, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraffa, G. The Microbiota of Grana Padano Cheese. A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimoto-Nira, H.; Aoki, R.; Mizumachi, K.; Sasaki, K.; Naito, H.; Sawada, T.; Suzuki, C. Interaction between Lactococcus lactis and Lactococcus raffinolactis during growth in milk: Development of a new starter culture. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 2175–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.J.; Lee, C.; Seo, M.; Roh, S.W.; Lee, S.H. Characterization of a potential probiotic bacterium Lactococcus raffinolactis WiKim0068 isolated from fermented vegetable using genomic and in vitro analyses. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, J.C., Jr.; de Oliveira, A.M.; Silva, F.D.G.; Tamanini, R.; de Oliveira, A.L.M.; Beloti, V. The main spoilage-related psychrotrophic bacteria in refrigerated raw milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 101, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doulgeraki, A.I.; Ercolini, D.; Villani, F.; Nychas, G.J.E. Spoilage microbiota associated to the storage of raw meat in different conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 157, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, C.N.; Sousa-Gallagher, M.J.; McSweeney, P.L.H. Effect of prematuration conditions on the proteolytic and rheological properties of cheesemilk. Lait 2001, 81, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coloretti, F.; Chiavari, C.; Nocetti, M.; Reverberi, P.; Bortolazzo, E.; Musi, V.; Grazia, L. Whey starter addition during maturation of evening milk: Effects on some characteristics of cheese milk and Parmigiano–Reggiano cheese. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2015, 96, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No Stored Milk | Stored Milk 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Populations 2 | t0 | T10 | T12 | Significance |
| Total mesophilic bacteria | 4.13 ± 0.56 a | 5.12 ± 0.70 b | 5.23 ± 0.87 b | ** |
| Total psychrotrophic bacteria | 2.77 ± 1.05 a | 4.82 ± 0.89 b | 4.94 ± 1.09 b | ** |
| Proteolytic bacteria | 2.63 ± 0.60 a | 3.72 ± 0.61 b | 3.99 ± 0.68 b | ** |
| Lipolytic bacteria | 3.56 ± 0.51 a | 4.64 ± 0.87 b | 4.94 ± 0.88 b | ** |
| Pseudomonas spp. | 2.92 ± 1.02 a | 4.85 ± 1.01 b | 5.08 ± 0.95 b | ** |
| Lactic acid bacteria | 2.99 ± 0.57 a | 3.14 ± 0.48 a | 3.15 ± 0.52 a | - |
| Total coliforms | 2.29 ± 0.64 a | 3.17 ± 1.09 a | 3.48 ± 0.95 b | * |
| E. coli | 1.70 ± 1.02 a | 1.93 ± 1.11 a | 2.15 ± 1.09 a | - |
| Coagulase positive staphylococci | 1.10 ± 0.59 a | 1.08 ± 0.58 a | 1.13 ± 0.62 a | - |
| Butyric clostridia spores | 1.92 ± 0.53 a | 1.89 ± 0.43 a | 1.90 ± 0.43 a | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zago, M.; Bonvini, B.; Rossetti, L.; Fergonzi, G.; Tidona, F.; Giraffa, G.; Carminati, D. Raw Milk for Provolone Valpadana PDO Cheese: Impact of Modified Cold Storage Conditions on the Composition of the Bacterial Biota. Dairy 2022, 3, 700-709. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy3040048
Zago M, Bonvini B, Rossetti L, Fergonzi G, Tidona F, Giraffa G, Carminati D. Raw Milk for Provolone Valpadana PDO Cheese: Impact of Modified Cold Storage Conditions on the Composition of the Bacterial Biota. Dairy. 2022; 3(4):700-709. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy3040048
Chicago/Turabian StyleZago, Miriam, Barbara Bonvini, Lia Rossetti, Giorgia Fergonzi, Flavio Tidona, Giorgio Giraffa, and Domenico Carminati. 2022. "Raw Milk for Provolone Valpadana PDO Cheese: Impact of Modified Cold Storage Conditions on the Composition of the Bacterial Biota" Dairy 3, no. 4: 700-709. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy3040048
APA StyleZago, M., Bonvini, B., Rossetti, L., Fergonzi, G., Tidona, F., Giraffa, G., & Carminati, D. (2022). Raw Milk for Provolone Valpadana PDO Cheese: Impact of Modified Cold Storage Conditions on the Composition of the Bacterial Biota. Dairy, 3(4), 700-709. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy3040048