The Role of Phlorotannins to Treat Inflammatory Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Structure of Phlorotannin and General Information
1.2. Recent Eco-Friendly Extraction Methods Reported for Phlorotannin Isolation and Identification
2. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms Reported from Phlorotannin
2.1. NLRP3 Inhibitory Properties Reported from Phlorotannins
2.2. MAPK Inhibitory Properties Reported from Phlorotannins
| Seaweed/Phlorotannin | Signal Mechanism/Bioactivity | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| pyrogallol-phloroglucinol-6,6-bieckol | Inhibit pyroptosis in endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells induced by high-fat diets and palmitate. | [45] |
| Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol | Downregulation of JNK, ERK, and p38 phosphorylation. | [48,53] |
| Dieckol | Downregulation of JNK, ERK, and p38 phosphorylation in macrophages. | [52] |
| Eckmaxol | Downregulation of JNK, ERK, and p38 phosphorylation. | [54] |
| Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol | Inhibit MAPK activation in UVB-exposed human dermal fibroblasts and in zebrafish. | [56] |
| 6,6′-bieckol | Reduce UVB-induced oxidative stress damage in HaCaT cells. | [57] |
| Phloroglucinol (1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene | Protect against UVB-exposed cell damage via AKT and ERK-mediated Nrf2/Ogg1 signaling pathways. | [58] |
| Dieckol | Inhibit the activation of MAPK pathways in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW Macrophages and Ovalbumin-Induced Asthma Mouse Model. | [59] |
| Dieckol | Promote collagen synthesis and protect against UVB-induced damage by inhibiting MAPK activation. | [60] |
| Phlorofucofuroeckol A from E. cava | Ameliorates TGF-β1-induced fibrotic response of human tracheal fibroblasts via the downregulation of MAPKs and SMAD 2/3 pathways inactivated TGF-β receptor. | [61] |
| Triphlorethol-A | Promote apoptosis by modulating MAPK and ERK pathways. | [62] |
| I. okamurae extract | Attenuate amyloid beta peptide (Aβ25-35) induced neurotoxicity by suppressing MAPK activation. | [63] |
| Ishophloroglucin | Downregulation of JNK, ERK, and p38 phosphorylation. | [47,48] |
| Trifuhalol A | Inhibit the degranulation of immune cells and the biosynthesis of IL-33 and IgE in differentiated B cells and keratinocytes. | [64] |
| Sargahydroquinoic acid (a hydroquinone derivative) from Sargassum macrocarpum | Downregulation of JNK, ERK, and p38 phosphorylation. | [65] |
| Ecklonia cava extract | Suppressed both the expression of the fibrotic phenotypic marker and cell migration by inhibiting the activation of the MAPK and Smad2/3 signaling pathways in human vocal fold fibroblasts. | [66] |
| Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol | Suppress the inflammatory myopathy-related protein expression through p-JNK/p-p38 in C2C12 myoblasts. | [67] |
| Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol | p38 MAPK expression in H2O2-induced zebrafish mussels. | [68] |
| Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol | Downregulate methylglyoxal-induced JNK, ERK, and p38 phosphorylation and reduce renal damage in Mouse glomerular mesangial cells | [69] |
| Phlorofucofuroeckol A from E. cava | Downregulate MAPK protein expression in TNF-α/IFN-γ-stimulated HaCaT keratinocytes and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate-induced ear edema in BALB/c mice. | [70] |
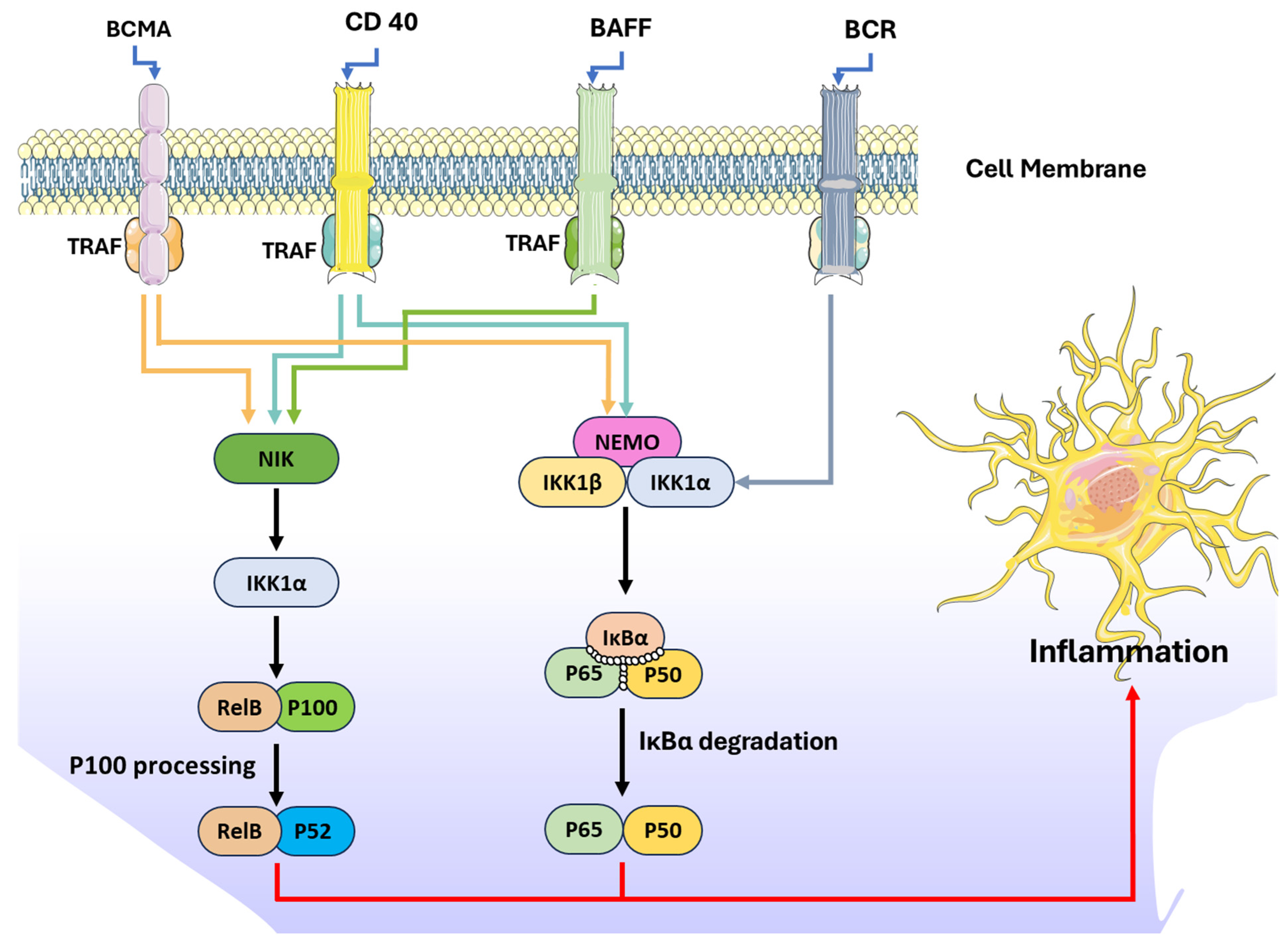
2.3. NF-kB Inhibitory Properties Reported from Phlorotannins
2.4. JAK/STAT3 Inhibitory Properties Reported from Phlorotannins
3. Synergistic Anti-Inflammatory Effects Reported Between Phlorotannins and Other Algal Components
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gusev, E.; Zhuravleva, Y. Inflammation: A New Look at an Old Problem. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Chenli, Z. Inflammation. In Textbook of Pathologic Anatomy; Chen, K., Liang, L., Li, M., Pan, Y., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 75–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; He, S.; Guo, N.; Tian, W.; Zhang, W.; Luo, L. Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and relevance to inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 72, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardelcikova, A.; Soltys, J.; Mojzis, J. Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Colorectal Cancer: An Overview. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loo, G.; Bertrand, M.J.M. Death by TNF: A road to inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massironi, S.; Vigano, C.; Palermo, A.; Pirola, L.; Mulinacci, G.; Allocca, M.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S. Inflammation and malnutrition in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.; Lopes, G.; Andrade, P.B.; Valentão, P. Bioprospecting of brown seaweeds for biotechnological applications: Phlorotannin actions in inflammation and allergy network. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.J.; Kwon, O.I.; Hwang, H.J.; Shin, H.C.; Yang, S. Therapeutic effects of phlorotannins in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1193590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheda, S.; Naby, M.A.; Mohamed, T.; Pereira, L.; Khamis, A. Antidiabetic and antioxidant activity of phlorotannins extracted from the brown seaweed Cystoseira compressa in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 22886–22901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.T.; Park, Y. Trifuhalol A, a phlorotannin from the brown algae Agarum cribrosum, reduces adipogenesis of human primary adipocytes through Wnt/beta-catenin and AMPK-dependent pathways. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 7, 100646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotas, J.; Leandro, A.; Monteiro, P.; Pacheco, D.; Figueirinha, A.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; da Silva, G.J.; Pereira, L. Seaweed Phenolics: From Extraction to Applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswari, V.; Babu, P.A.S. Phlorotannin and its Derivatives, a Potential Antiviral Molecule from Brown Seaweeds, an Overview. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2022, 48, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glombitza, K.W.; Rosener, H.U.; Vilter, H.; Rauwald, W. Antibiotics from Algae. 8. Phloroglucinol from Phaeophyceae (author’s transl). Planta Medica 1973, 24, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glombitza, K.W.; Pauli, K. Fucols and Phlorethols from the Brown Alga Scytothamnus australis Hook. et Harv. (Chnoosporaceae). Bot. Mar. 2003, 46, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glombitza, K.W. Highly Hydroxylated Phenols of the Phaeophyceae. In Marine Natural Products Chemistry; Faulkner, D.J., Fenical, W.H., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1977; pp. 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Lee, W.; Ahn, G. Marine algal flavonoids and phlorotannins; an intriguing frontier of biofunctional secondary metabolites. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpena, M.; Pereira, C.S.G.P.; Silva, A.; Barciela, P.; Jorge, A.O.S.; Perez-Vazquez, A.; Pereira, A.G.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Prieto, M.A. Metabolite Profiling of Macroalgae: Biosynthesis and Beneficial Biological Properties of Active Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.D.; Pires, S.M.G.; Silva, S.; Costa, F.; Braga, S.S.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Overview of Phlorotannins’ Constituents in Fucales. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, M.M.; El Zokm, G.M.; El Sikaily, A.M.; Selim, A.I.; Ismail, G.A. Chemodiversity and bioactivity assessment of phlorotannins from some Phaeophyta species from the Red Sea. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 35, 1769–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, R.; Howlader, S.; Mamun-Or-Rashid, A.N.M.; Rafiquzzaman, S.M.; Ashraf, G.M.; Albadrani, G.M.; Sayed, A.A.; Peluso, I.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Uddin, M.S. Antioxidant and Signal-Modulating Effects of Brown Seaweed-Derived Compounds against Oxidative Stress-Associated Pathology. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 9974890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, L. A Bioactive Substance Derived from Brown Seaweeds: Phlorotannins. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.D.; Marçal, C.; Bonifácio-Lopes, T.; Campos, D.; Mateus, N.; Silva, A.M.S.; Pintado, M.M.; Cardoso, S.M. Impact of Phlorotannin Extracts from Fucus vesiculosus on Human Gut Microbiota. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, L.; Curry, C.; Campbell, M.; Theodoridou, K.; Sheldrake, G.; Dick, J.; Stella, L.; Walsh, P.J. Effect of Phlorotannins from Brown Seaweeds on the In Vitro Digestibility of Pig Feed. Animals 2020, 10, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarino, M.D.; Garcia, C.J.; Garcia-Villalba, R.; Silva, A.M.S.; Campos, D.A.; Manuela Pintado, M.; Neves, B.; Cardoso, S.M.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A. Exploring the fate of phlorotannins from Laminaria digitata across the gastrointestinal tract: Insights into susceptibility and bioactivity prior and post gastrointestinal digestion. Food Res. Int. 2024, 191, 114641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarewicz, M.; Drożdż, I.; Tarko, T.; Duda-Chodak, A. The Interactions between Polyphenols and Microorganisms, Especially Gut Microbiota. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassani, L.; Gomez-Zavaglia, A.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Lourenco-Lopes, C.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Seaweed-based natural ingredients: Stability of phlorotannins during extraction, storage, passage through the gastrointestinal tract and potential incorporation into functional foods. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, G.; Ji, Y.; Anegboonlap, P.; Hotchkiss, S.; Gill, C.; Yaqoob, P.; Spencer, J.P.; Rowland, I. Gastrointestinal modifications and bioavailability of brown seaweed phlorotannins and effects on inflammatory markers. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shevyrin, V.A.; Kovaleva, E.G.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Shikov, A.N. Optimization of Extraction of Phlorotannins from the Arctic Fucus vesiculosus Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their HPLC Profiling with Tandem High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percevault, L.; Limanton, E.; Gauffre, F.; Lagrost, C.; Paquin, L. Extraction of Plant and Algal Polyphenols Using Eutectic Solvents. In Deep Eutectic Solvents for Medicine, Gas Solubilization and Extraction of Natural Substances; Fourmentin, S., Costa Gomes, M., Lichtfouse, E., Eds.; Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 241–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misan, A.; Nadpal, J.; Stupar, A.; Pojic, M.; Mandic, A.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. The perspectives of natural deep eutectic solvents in agri-food sector. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2564–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.M.; Jesus, B.C.; Ribeiro, H.; Martins, A.; Marto, J.; Fitas, M.; Pinto, P.; Alves, C.; Silva, J.; Pedrosa, R.; et al. Extraction of macroalgae phenolic compounds for cosmetic application using eutectic solvents. Algal Res. 2024, 79, 103438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavina, I.; Rodrigues, M.J.; Pereira, C.G.; Mansinhos, I.; Romano, A.; Ślusarczyk, S.; Matkowski, A.; Custódio, L. Greener Is Better: First Approach for the Use of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADES) to Extract Antioxidants from the Medicinal Halophyte Polygonum maritimum L. Molecules 2021, 26, 6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, L.; Gerhardt, A.S.; Johannesen, B.A.; Underhaug, J.; Jordheim, M. Ultrasonic-Assisted Water-Rich Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for Sustainable Polyphenol Extraction from Seaweed: A Case Study on Cultivated Saccharina latissima. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 14921–14929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Nunez, G. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Activation and regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2023, 48, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Tian, C.; Liu, Y.; Aung, L.H.H.; Li, P.F.; Yu, T.; Chu, X.M. NLRP3 inflammasome in endothelial dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; Genovese, T.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R. Focus on the Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Bi, L. Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in autoimmune diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, R.; Manan, A.; Kim, J.; Choi, S. NLRP3 inflammasome: A key player in the pathogenesis of life-style disorders. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbal, A.; Dernst, A.; Lovotti, M.; Mangan, M.S.J.; McManus, R.M.; Latz, E. How location and cellular signaling combine to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.H.; Shin, H.Y.; Park, J.H.; Koo, S.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Yang, S.H. Fucoxanthin from microalgae Phaeodactylum tricornutum inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines by regulating both NF-kappaB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, L.; Shi, X. NLRP3 inflammasome and its role in autoimmune diseases: A promising therapeutic target. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, K.-A.; Park, Y.; Oh, S.; Batsukh, S.; Son, K.H.; Byun, K. Co-Treatment with Phlorotannin and Extracellular Vesicles from Ecklonia cava Inhibits UV-Induced Melanogenesis. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-M.; Kim, H.-Y.; Jang, J.-T.; Hong, S. Preventive Effect of Ecklonia cava Extract on DSS-Induced Colitis by Elevating Intestinal Barrier Function and Improving Pathogenic Inflammation. Molecules 2023, 28, 8099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Yang, J.; Park, C.; Son, K.; Byun, K. Dieckol Attenuated Glucocorticoid-Induced Muscle Atrophy by Decreasing NLRP3 Inflammasome and Pyroptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Son, M.; Park, C.-H.; Jang, J.T.; Son, K.H.; Byun, K. The Reducing Effects of Pyrogallol-Phloroglucinol-6,6-Bieckol on High-Fat Diet-Induced Pyroptosis in Endothelial and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells of Mice Aortas. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Son, M.; Byun, K.-A.; Jang, J.T.; Choi, C.H.; Son, K.H.; Byun, K. Attenuating Effects of Dieckol on High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Decreasing the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Pyroptosis. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Cho, C.; Lee, C.; Ryu, B.; Kim, S.; Hur, J.; Lee, S.-H. Ishige okamurae Ameliorates Methylglyoxal-Induced Nephrotoxicity via Reducing Oxidative Stress, RAGE Protein Expression, and Modulating MAPK, Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway in Mouse Glomerular Mesangial Cells. Foods 2021, 10, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Ahn, J.; Ryu, B.; Jea, J.G.; Lee, K.; Kim, K.; Ahn, G.; Lee, W.; Choi, K.M.; et al. Effect of Ishige okamurae Extract on Osteoclastogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Kang, J.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, H.-J.; Heo, H.J. Ecklonia cava Attenuates PM2.5-Induced Cognitive Decline through Mitochondrial Activation and Anti-Inflammatory Effect. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behl, T.; Upadhyay, T.; Singh, S.; Chigurupati, S.; Alsubayiel, A.M.; Mani, V.; Vargas-De-La-Cruz, C.; Uivarosan, D.; Bustea, C.; Sava, C.; et al. Polyphenols Targeting MAPK Mediated Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Molecules 2021, 26, 6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, H.-S.; Asanka Sanjeewa, K.K.; Han, E.J.; Jee, Y.; Ahn, G.; Rho, J.-R.; Jeon, Y.-J. Loliolide, isolated from Sargassum horneri; abate LPS-induced inflammation via TLR mediated NF-κB, MAPK pathways in macrophages. Algal Res. 2021, 56, 102297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Kim, H.-S.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Ryu, B.; Yang, H.-W.; Ahn, G.; Lee, W.; Jeon, Y.-J. Dieckol: An algal polyphenol attenuates urban fine dust-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 cells via the activation of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant signaling pathways. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 32, 2387–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kim, H.S.; Je, J.-G.; Oh, J.Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Cha, S.-H.; Jeon, Y.-J. Protective Effect of Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol Isolated from Ishige okamurae Against Particulate Matter-Induced Skin Damage by Regulation of NF-κB, AP-1, and MAPKs Signaling Pathways In Vitro in Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Molecules 2020, 25, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahawatta, D.P.; Liyanage, N.M.; Jayawardhana, H.H.A.C.K.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Lee, H.-G.; Heo, M.-S.; Jeon, Y.-J. Eckmaxol Isolated from Ecklonia maxima Attenuates Particulate-Matter-Induced Inflammation in MH-S Lung Macrophage. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, M.J.; Hewage, S.R.; Han, X.; Kang, K.A.; Kang, H.K.; Lee, N.H.; Hyun, J.W. Protective Effect of Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol against Ultraviolet B Radiation-Induced DNA Damage by Inducing the Nucleotide Excision Repair System in HaCaT Human Keratinocytes. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5629–5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Kim, H.S.; Oh, J.Y.; Je, J.G.; Jeon, Y.J.; Ryu, B. Protective effect of diphlorethohydroxycarmalol isolated from Ishige okamurae against UVB-induced damage in vitro in human dermal fibroblasts and in vivo in zebrafish. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 110963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.L.; Xiao, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhou, C.; Sun, S.; Hong, P.; Qian, Z.J. A Phlorotanin, 6,6′-bieckol from Ecklonia cava, Against Photoaging by Inhibiting MMP-1, -3 and -9 Expression on UVB-induced HaCaT Keratinocytes. Photochem. Photobiol. 2022, 98, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, M.J.; Kim, K.C.; Kang, K.A.; Fernando, P.; Herath, H.; Hyun, J.W. Phloroglucinol Attenuates Ultraviolet B-Induced 8-Oxoguanine Formation in Human HaCaT Keratinocytes through Akt and Erk-Mediated Nrf2/Ogg1 Signaling Pathways. Biomol. Ther. 2021, 29, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Park, C.-H.; Kwon, S.-O.; Lee, S.-G. ED Formula, a Complex of Ecklonia cava and Chrysanthemum indicum, Ameliorates Airway Inflammation in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW Macrophages and Ovalbumin-Induced Asthma Mouse Model. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Je, J.-G.; Yang, H.-W.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Lee, S. Dieckol, an Algae-Derived Phenolic Compound, Suppresses UVB-Induced Skin Damage in Human Dermal Fibroblasts and Its Underlying Mechanisms. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.Y.; Jeong, M.S.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, S.H.; Jung, W.K. Phlorofucofuroeckol A from Ecklonia cava ameliorates TGF-beta1-induced fibrotic response of human tracheal fibroblasts via the downregulation of MAPKs and SMAD 2/3 pathways inactivated TGF-beta receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 522, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, W.; Wu, A.; Su, Z.; Jiang, B.; Ganesan, S. Triphlorethol-A attenuates U251 human glioma cancer cell proliferation and ameliorates apoptosis through JAK2/STAT3 and p38 MAPK/ERK signaling pathways. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e23138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.Y.; Lee, S.H. Ameliorating Activity of Ishige okamurae on the Amyloid Beta-Induced Cognitive Deficits and Neurotoxicity through Regulating ERK, p38 MAPK, and JNK Signaling in Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Mice Model. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, e1901220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bong, S.K.; Park, N.J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, A.T.; Liu, X.; Kim, S.M.; Yang, M.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, S.N. Trifuhalol A Suppresses Allergic Inflammation through Dual Inhibition of TAK1 and MK2 Mediated by IgE and IL-33. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Lee, B.; Lee, B.-H.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.-R. Sargahydroquinoic acid from Sargassum macrocarpum attenuates TNF-α and UV-induced skin aging in human dermal fibroblasts. Algal Res. 2024, 78, 103410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Lee, H.S.; Oh, S.J.; Hwang, C.W.; Jung, W.K. Phlorotannins ameliorate extracellular matrix production in human vocal fold fibroblasts and prevent vocal fold fibrosis via aerosol inhalation in a laser-induced fibrosis model. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2020, 14, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Ahn, G.; Kim, H.-S.; Je, J.-G.; Kim, K.-N.; Jeon, Y.-J. Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol (DPHC) Isolated from the Brown Alga Ishige okamurae Acts on Inflammatory Myopathy as an Inhibitory Agent of TNF-α. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-G.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, K.-N.; Jeon, Y.-J. DPHC from Ishige okamurae mitigates oxidative stress-induced myopathy by regulating MuRF-1/MAFbx signaling in C2C12 cells. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.H.; Yoo, G.; Kim, M.; Lee, C.J.; Choi, I.-W.; Ryu, B.; Kim, B.-M.; Lee, S.-H. Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol, a phlorotannin contained in brown edible seaweed Ishige okamurae, prevents AGE-related diabetic nephropathy by suppression of AGE-RAGE interaction. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirindage, K.G.I.S.; Jayasinghe, A.M.K.; Han, E.-J.; Han, H.-J.; Kim, K.-N.; Wang, L.; Heo, S.-J.; Jung, K.-S.; Ahn, G. Phlorofucofuroeckol-A refined by edible brown algae Ecklonia cava indicates anti-inflammatory effects on TNF-α/IFN-γ-stimulated HaCaT keratinocytes and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate-induced ear edema in BALB/c mice. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 109, 105786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. Targeting NF-kappaB pathway for the therapy of diseases: Mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinatizadeh, M.R.; Schock, B.; Chalbatani, G.M.; Zarandi, P.K.; Jalali, S.A.; Miri, S.R. The Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-kB) signaling in cancer development and immune diseases. Genes. Dis. 2021, 8, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, B.F.; Li, J.; Yao, Z.; Xing, L. Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Regulation of Osteoclastogenesis and Osteoblastogenesis. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 38, 504–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, A.; Street, L.; Ghosh, S.; Burns, B.F.; Elyamany, G.; Shabani-Rad, M.T.; Stewart, D.A.; Mansoor, A. Concomitant high expression of Toll-like receptor (TLR) and B-cell receptor (BCR) signalling molecules has clinical implications in mantle cell lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacobazzi, D.; Convertini, P.; Todisco, S.; Santarsiero, A.; Iacobazzi, V.; Infantino, V. New Insights into NF-κB Signaling in Innate Immunity: Focus on Immunometabolic Crosstalks. Biology 2023, 12, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarino, M.D.; Amarante, S.J.; Mateus, N.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Brown Algae Phlorotannins: A Marine Alternative to Break the Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Cancer Network. Foods 2021, 10, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yang, S.; Xiao, Z.; Hong, P.; Sun, S.; Zhou, C.; Qian, Z.-J. The Inhibition Effect of the Seaweed Polyphenol, 7-Phloro-Eckol from Ecklonia Cava on Alcohol-Induced Oxidative Stress in HepG2/CYP2E1 Cells. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarino, M.D.; Silva, A.; Cruz, M.T.; Mateus, N.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Phlorotannins from Fucus vesiculosus: Modulation of Inflammatory Response by Blocking NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.J.; Kim, H.-S.; Jung, K.; Asanka Sanjeewa, K.K.; Iresha Nadeeka Madushani Herath, K.H.; Lee, W.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Lee, J.; Kim, T.; et al. Sargassum horneri ethanol extract ameliorates TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced inflammation in human keratinocytes and TPA-induced ear edema in mice. Food Biosci. 2021, 39, 100831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Ahn, G.; Kim, H.-J.; Fu, X.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.-J. Ethanol extract separated from Sargassum horneri (Turner) abate LPS-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 22, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, E.J.; Cao, L.; Lee, B.; Gwon, W.G.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.R. Sargahydroquinoic Acid, a Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitor, Attenuates Inflammatory Responses by Regulating NF-kappaB Inactivation and Nrf2 Activation in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Cells. Inflammation 2021, 44, 2120–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, R.; Hemaiswarya, S.; Arunkumar, K.; Mathiyazhagan, N.; Kandasamy, S.; Arun, A.; Ramasamy, P. Efficacy of Eisenia bicyclis phlorotannins in the treatment of diabetes and reducing inflammation. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, Y.G.; Wang, Q.; Park, J.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, H. Phlorotannins Isolated from Eisenia bicyclis and Lactobacillus casei Ameliorate Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice through the AhR Pathway. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, W.; Han, E.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Ahn, G.; Kim, K.N. Eckol from Ecklonia cava ameliorates TNF-alpha/IFN-gamma-induced inflammatory responses via regulating MAPKs and NF-kappaB signaling pathway in HaCaT cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 82, 106146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Park, J.-H.; Park, S.-A.; Joo, N.-R.; Lee, B.H.; Lee, K.B.; Oh, S.-M. Dieckol or phlorofucofuroeckol extracted from Ecklonia cava suppresses lipopolysaccharide-mediated human breast cancer cell migration and invasion. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 32, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.D.; Silva, A.M.S.; Mateus, N.; Cardoso, S.M. Optimization of Phlorotannins Extraction from Fucus vesiculosus and Evaluation of Their Potential to Prevent Metabolic Disorders. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, H.G.; Je, J.G.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.J. Sargassum horneri (Turner) inhibit urban particulate matter-induced inflammation in MH-S lung macrophages via blocking TLRs mediated NF-kappaB and MAPK activation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 249, 112363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, M.; Oh, S.; Choi, J.; Jang, J.T.; Choi, C.H.; Park, K.Y.; Son, K.H.; Byun, K. The Phlorotannin-Rich Fraction of Ecklonia cava Extract Attenuated the Expressions of the Markers Related with Inflammation and Leptin Resistance in Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 2020, 9142134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, G.R.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. The JAK-STAT pathway at twenty. Immunity 2012, 36, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Yao, Q.; Gu, X.; Shi, Q.; Yuan, X.; Chu, Q.; Bao, Z.; Lu, J.; Li, L. Evolving cognition of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway: Autoimmune disorders and cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, J.; Etemadi, N.; Hollande, F.; Ernst, M.; Buchert, M. The JAK/STAT3 axis: A comprehensive drug target for solid malignancies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 45, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceyzeriat, K.; Abjean, L.; Carrillo-de Sauvage, M.A.; Ben Haim, L.; Escartin, C. The complex STATes of astrocyte reactivity: How are they controlled by the JAK-STAT3 pathway? Neuroscience 2016, 330, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imada, K.; Leonard, W.J. The Jak-STAT pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2000, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Ross, J.L.; Cowell, J.K. The involvement of JAK-STAT3 in cell motility, invasion, and metastasis. JAKSTAT 2014, 3, e28086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.J.; Kim, H.-S.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Herath, K.H.I.N.M.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Jee, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, T.; Shim, S.-Y.; Ahn, G. Eckol from Ecklonia cava Suppresses Immunoglobulin E-mediated Mast Cell Activation and Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis in Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Buettner, R.; Jove, R. Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected biological functions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Jia, J.; Sheng, J.; Zhang, S.; Huang, K.; Li, H.; He, F. Protective and anti-inflammatory role of REG1A in inflammatory bowel disease induced by JAK/STAT3 signaling axis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 92, 107304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Wei, S.; Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, J. Protective Effect and Mechanisms of Eckol on Chronic Ulcerative Colitis Induced by Dextran Sulfate Sodium in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Oh, S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Ahn, H.; Son, M.; Heo, S.-J.; Byun, K.; Jeon, Y.-J. Anti-obesity effects of Ishophloroglucin A from the brown seaweed Ishige okamurae (Yendo) via regulation of leptin signal in ob/ob mice. Algal Res. 2022, 61, 102533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.H.; Zhang, S.; Bong, S.-K.; Kim, A.T.; Lee, H.; Liu, X.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, S.-N. Anti-Allergic Inflammatory Effect of Agarum cribrosum and Its Phlorotannin Component, Trifuhalol A, against the Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Asthma Model. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 8882–8893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Won Choi, J.; Jeong Kim, H.; Kim, B.; Kim, Y.; Hwejin Lee, E.; Kim, R.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Jeong, Y.; et al. Phloroglucinol Derivatives Exert Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Attenuate Cognitive Impairment in LPS-Induced Mouse Model. ChemMedChem 2024, 19, e202400056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.; Valentao, P.; Ferreres, F.; Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Andrade, P.B. In vitro multifunctionality of phlorotannin extracts from edible Fucus species on targets underpinning neurodegeneration. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Fucoidans from Five Species of Brown Seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, B.; Baroutian, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Ying, T.; Lu, J. Combination of marine bioactive compounds and extracts for the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1047026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouh, A.; Nouadri, T.; Catarino, M.D.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Phlorotannins of the Brown Algae Sargassum vulgare from the Mediterranean Sea Coast. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.J.; Park, S.K.; Kang, J.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Yoo, S.K.; Kim, D.-O.; Kim, G.-H.; Heo, H.J. Mixture of Phlorotannin and Fucoidan from Ecklonia cava Prevents the Aβ-Induced Cognitive Decline with Mitochondrial and Cholinergic Activation. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Cui, J.; Kang, I.; Zhang, G.; Lee, Y. Potential Antidiabetic Effects of Seaweed Extracts by Upregulating Glucose Utilization and Alleviating Inflammation in C2C12 Myotubes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Seaweed/Phlorotannin | Signal Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Ecklonia cava extract | TXNIP/NLRP3/IL-18 pathway. | [42] |
| Dieckol | Attenuated dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy by reducing NLRP3 inflammasome formation and pyroptosis. | [44] |
| E. cava extract and pyrogallol-phloroglucinol-6,6-bieckol | Attenuate pyroptosis in endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells induced by high-fat diets and palmitate (reduced NLRP3 inflammasome formation, and normalized inflammatory markers such as IL-1β and IL-18) | [45] |
| Dieckol | Reduced NLRP3 expression, pyroptosis, triglyceride accumulation, and lipogenic gene expression effectively through attenuating NAFLD. | [46] |
| Ishophloroglucin | Downregulation of JNK, ERK, and p38 phosphorylation. | [47,48] |
| 2′-phloroeckol | Protect PM2.5-induced cognitive dysfunction via downregulating NLRP3 activation | [49] |
| Seaweed/Phlorotannin | Reported Phlorotannins | Signal Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ishige okamurae | Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol | suppressed the inflammatory myopathy-related protein expression through the NF-κB (p-IκB-α/p-p65NF-κB) signaling cascade. | [67] |
| Inhibit p-IκB-α and p65 NF-κB expression in H2O2 exposed zebrafish muscle. | [68] | ||
| Fucus vesiculosus | fucofurodiphlorethol, fucofurotriphlorethol and fucofuropentaphlorethol | Modulate NF-kB-related protein expressions. | [78,86] |
| Sargassum horneri | Up to ~15% phlorotannins. Compounds not specified | TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced inflammation in human keratinocytes and TPA-induced ear edema in mice. Protection against particulate matter-induced inflammation in MH-S lung macrophages via blocking TLRs mediated NF-κB and activation. | [79,80,87] |
| Sargassum macrocarpum | Sargahydroquinoic acid (a hydroquinone derivative) | Inhibit NF-κB activation by blocking the degradation of inhibitor κB-α (IκBα) in LPS-stimulated murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. | [81] |
| Eisenia bicyclis | dieckol,8,8′-bieckol, fucofuroeckol | downregulate the gene expression levels of NF-κB in LPS-stimulated THP-1 macrophages. | [82] |
| Phloroglucinol, 7-Phloroeckol, Phlorofucofuroeckol A, Dieckol | Ameliorate dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice through the Ahr pathway via downregulating NF-κB gene expression. | [83] | |
| Ecklonia cava | Phlorofucofuroeckol-A 7-Phloroeckol eckol, dieckol, phlorofucofuroeckol | Down-regulate NF-κB protein expression in TNF-α/IFN-γ-stimulated HaCaT keratinocytes and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate-induced ear edema in BALB/c mice. | [70,77] |
| Downregulate NF-κB expression in alcohol-induced oxidative stress in HepG2/CYP2E1 cells and other in vivo and in vitro models | [77,84,85] | ||
| Attenuated the NF-κB Expressions in Adipose Tissue | [88] |
| Seaweed/Phlorotannin | Signal Mechanism/Bioactivity | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Trifuhalol A | Reduces IL-33, IL-4, and IL-13 in house dust mite-treated dorsal mice skin inflammation | [64] |
| Phlorotannin-rich fraction (E. cava) | Downregulates the JAK/STAT3 activation via reducing expression levels of IL-6 and IL-10 mRNA in HFD-induced obese mice | [88] |
| Eckol (from E. cava) | Inhibits TLR4/STAT3/NF-κB in DSS-induced colitis | [99] |
| Eckol (from E. cava) | Suppresses IgE-mediated mast cell activation, downregulates the JAK/STAT3 activation via reducing IL-4, IL-5, and IL-6 expression | [96] |
| Ishophloroglucin A (I. okamurae) | Inhibits JAK/STAT3 protein expression in ob/ob mice model | [100] |
| Trifuhalol A | Inhibits IL-6 in OVA-induced allergic asthma | [101] |
| Synthetic phloroglucinol derivative | Inhibits IL-6 and TNF-α in LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells | [102] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herath, K.H.I.N.M.; Nagahawatta, D.P.; Wang, L.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A. The Role of Phlorotannins to Treat Inflammatory Diseases. Chemistry 2025, 7, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7030077
Herath KHINM, Nagahawatta DP, Wang L, Sanjeewa KKA. The Role of Phlorotannins to Treat Inflammatory Diseases. Chemistry. 2025; 7(3):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7030077
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerath, K. H. I. N. M., Dineth Pramuditha Nagahawatta, Lei Wang, and K. K. Asanka Sanjeewa. 2025. "The Role of Phlorotannins to Treat Inflammatory Diseases" Chemistry 7, no. 3: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7030077
APA StyleHerath, K. H. I. N. M., Nagahawatta, D. P., Wang, L., & Sanjeewa, K. K. A. (2025). The Role of Phlorotannins to Treat Inflammatory Diseases. Chemistry, 7(3), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7030077






