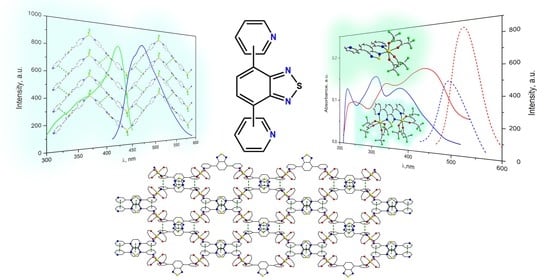
Dimensionality Control in Crystalline Zinc(II) and Silver(I) Complexes with Ditopic Benzothiadiazole-Dipyridine Ligands †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
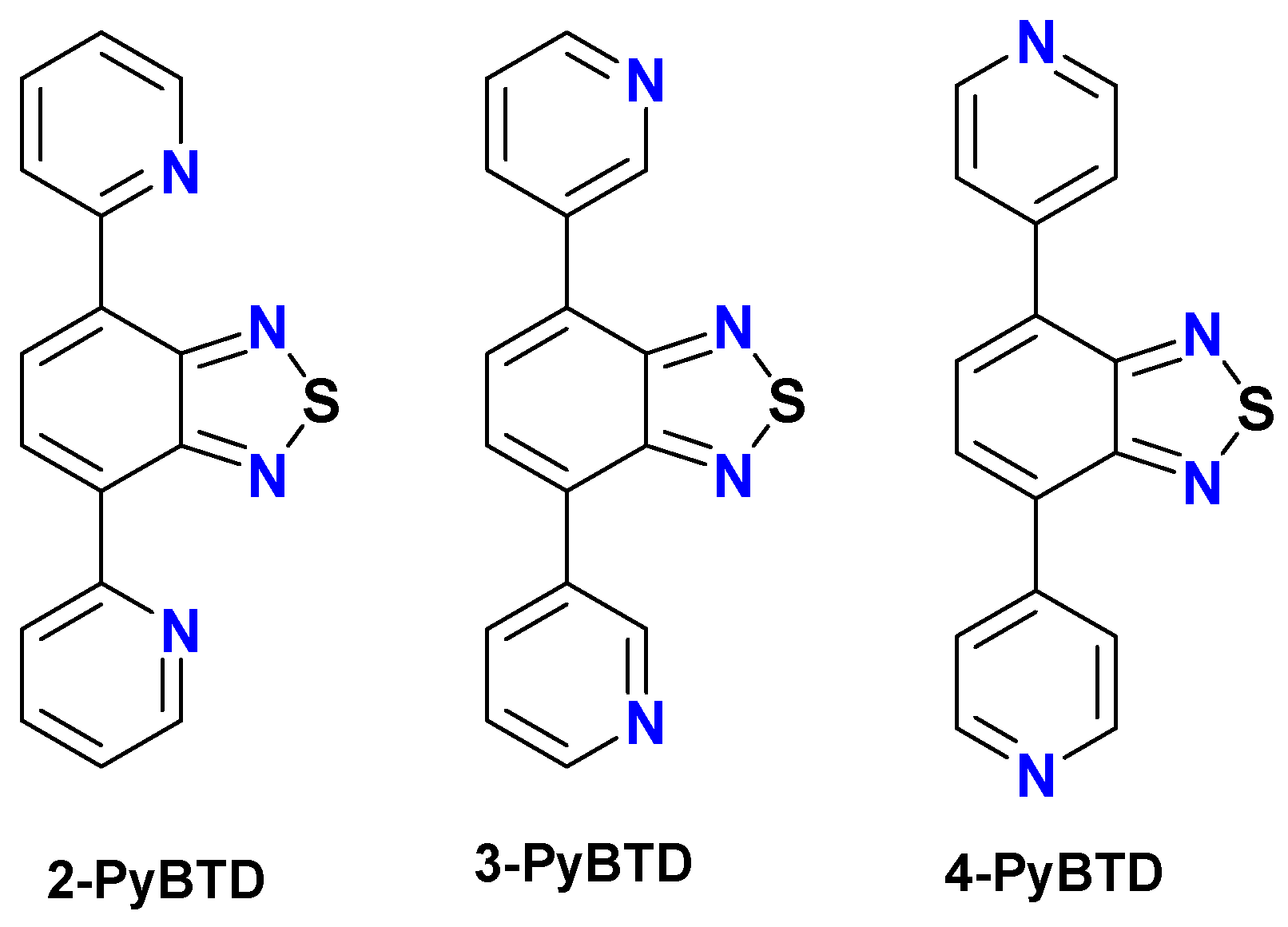
3.1. Discrete Complexes and Coordination Polymers with the 2-PyBTD Ligand
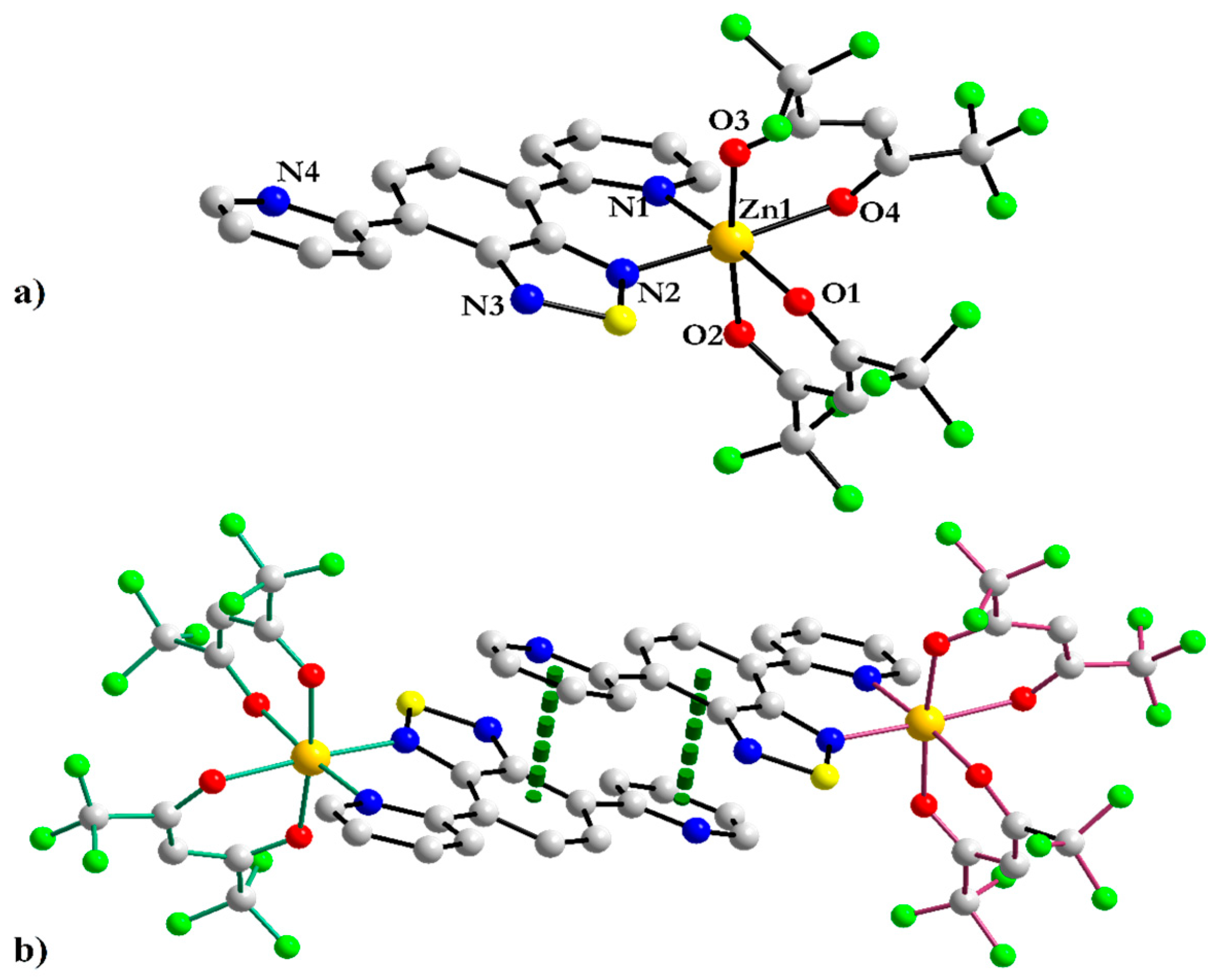
3.1.1. Mononuclear [Zn(hfac)2(2-PyBTD)] 1 and Binuclear [Zn2(hfac)4(2-PyBTD)] 2 Complexes
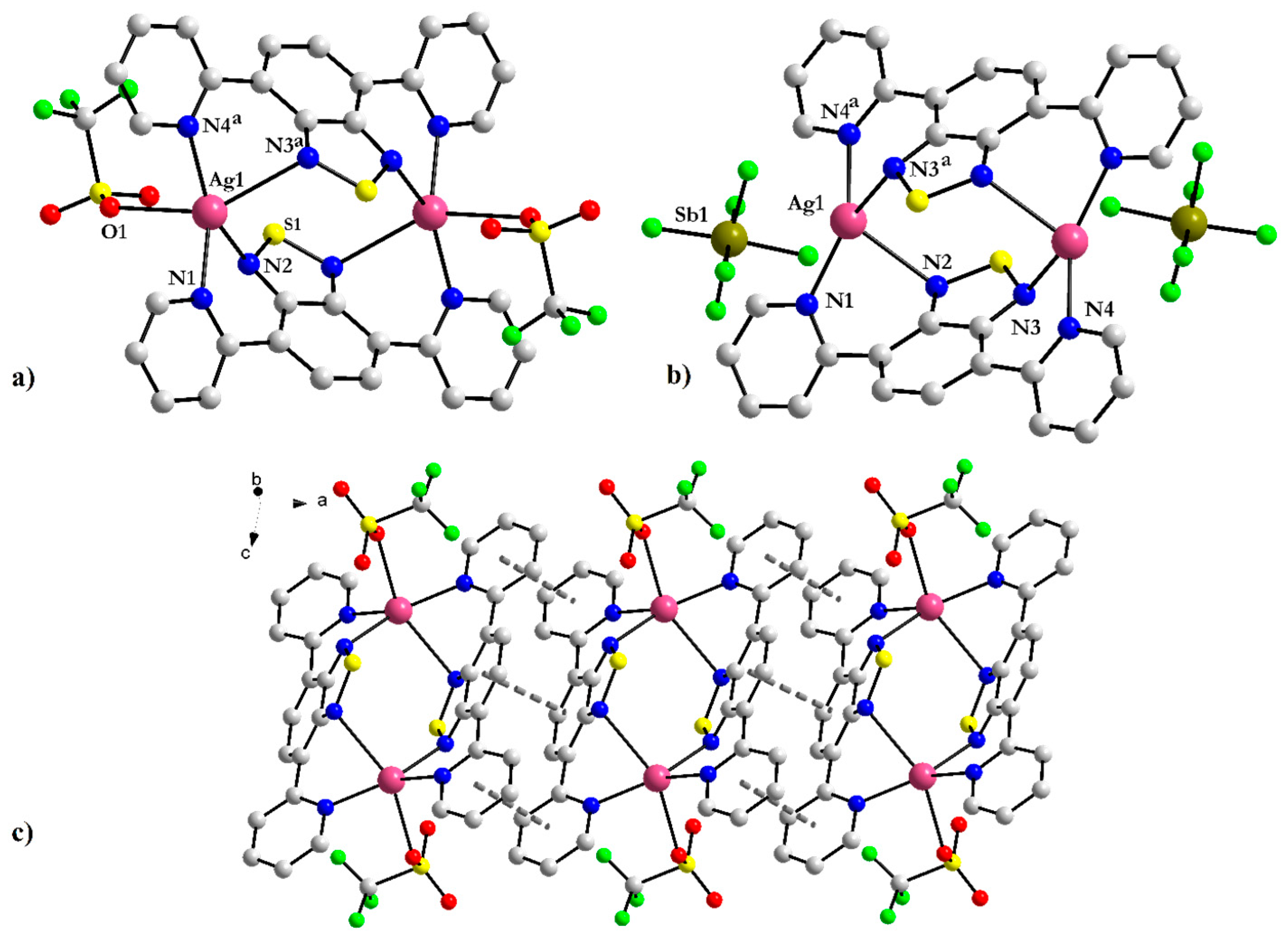
3.1.2. Binuclear [Ag(CF3SO3)(2-PyBTD)]2 3 and [Ag(2-PyBTD)]2(SbF6)2 4 Complexes
3.1.3. Coordination Polymer [Ag2(NO3)2(2-PyBTD)(CH3CN)] 5
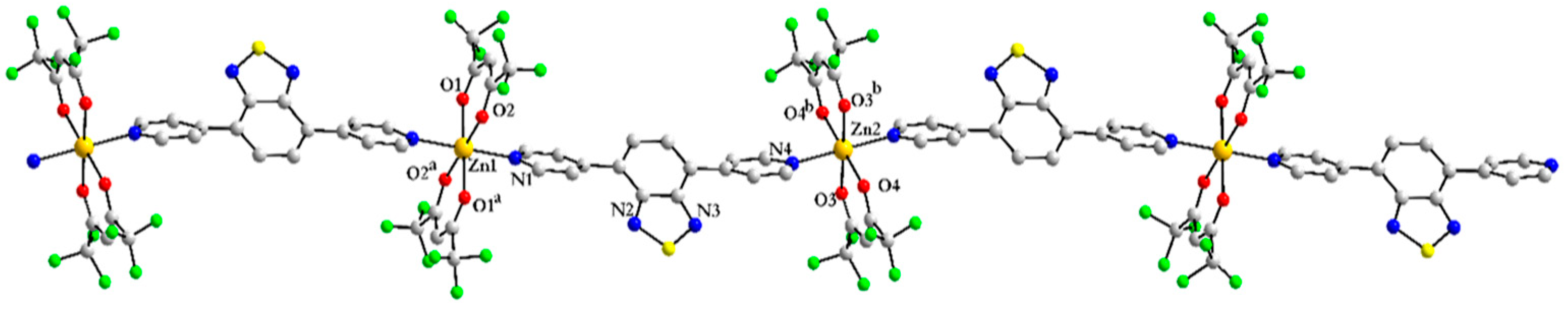
3.2. Coordination Polymer with the 3-PyBTD Ligand
3.3. Discrete Complexes and Coordination Polymers with the 4-PyBTD Ligand
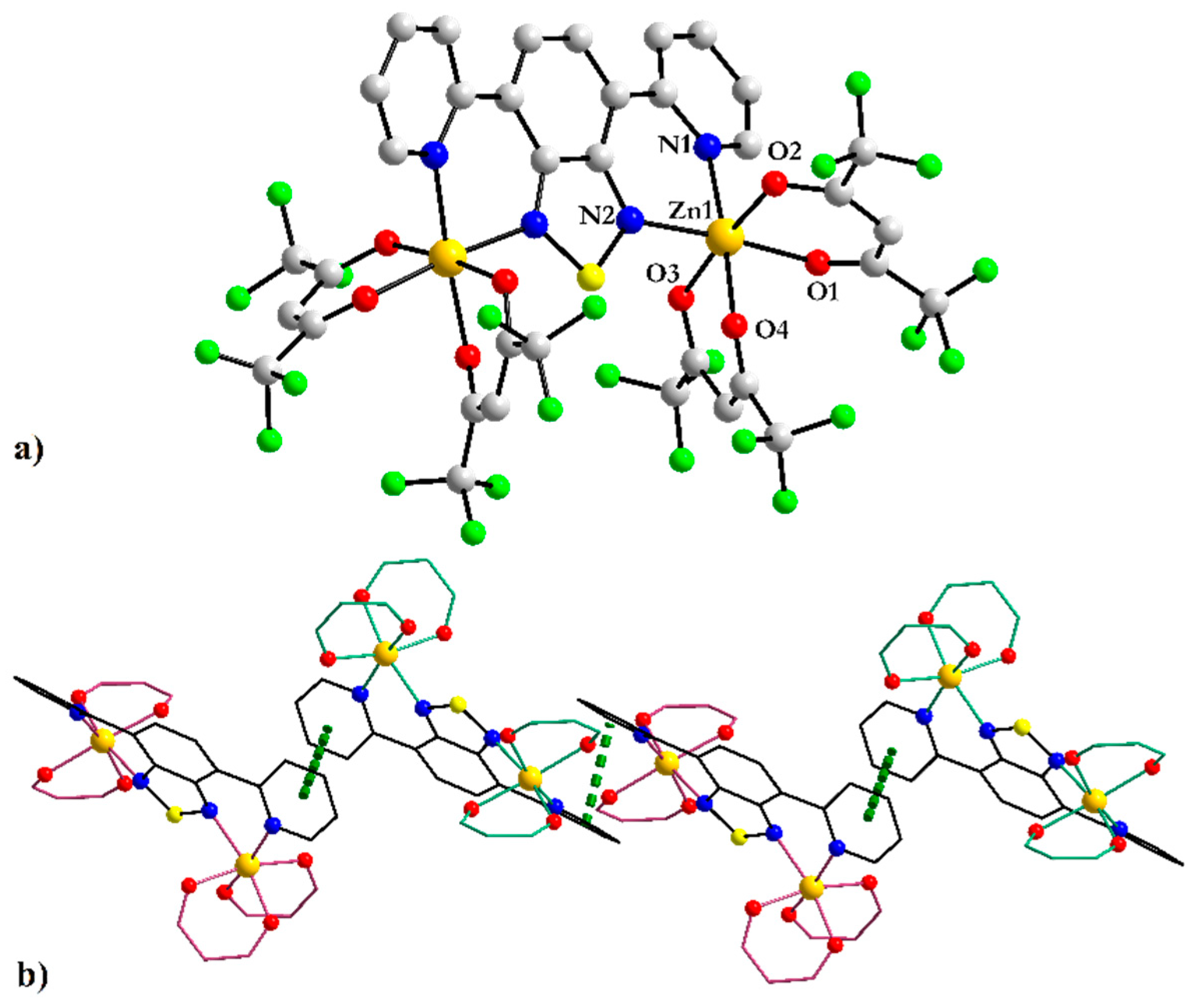
3.3.1. Coordination Polymer [Zn(hfac)2(4-PyBTD)] 7
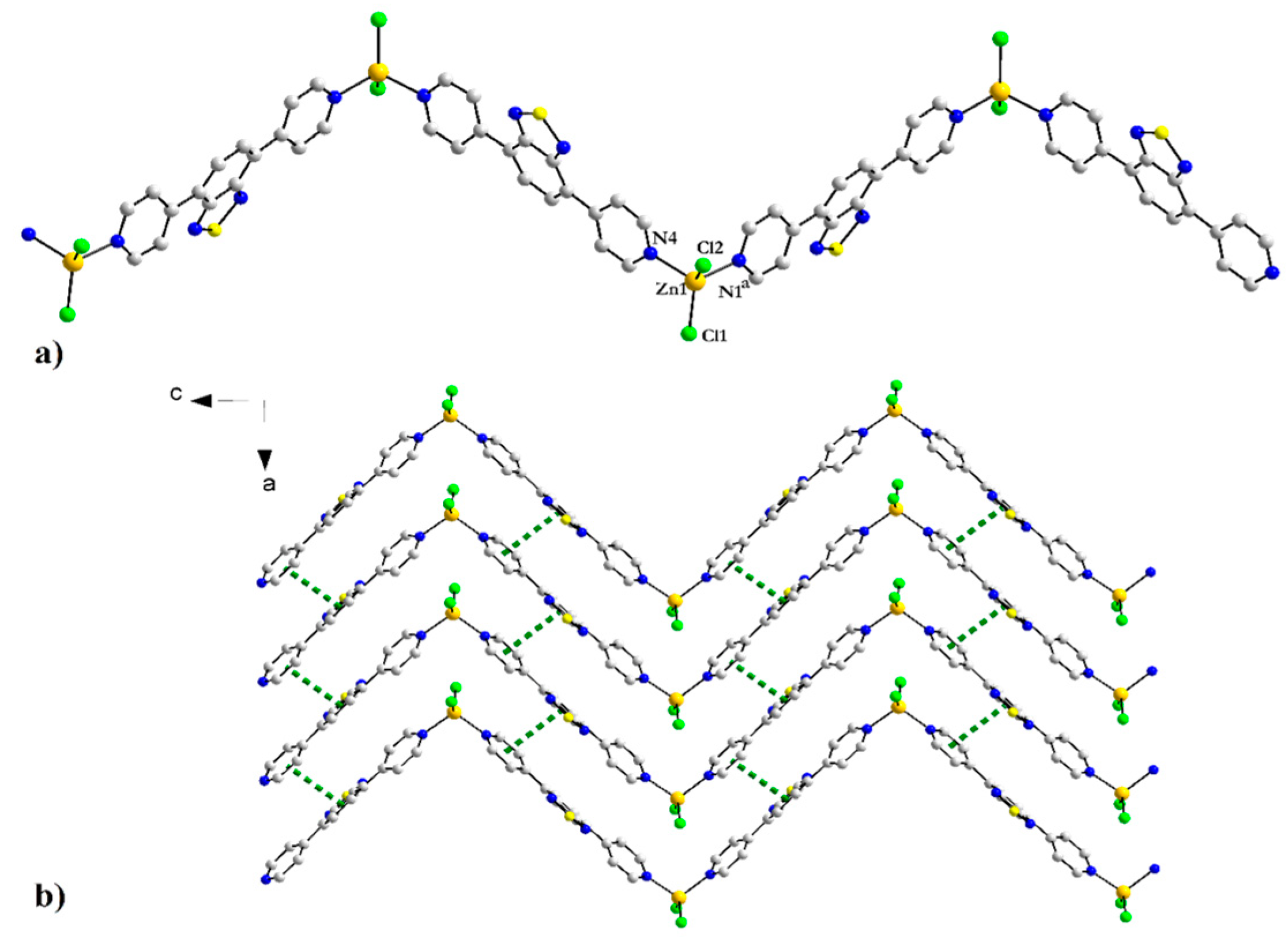
3.3.2. Coordination Complexes of 4-PyBTD with ZnCl2
3.4. Photophysical Properties
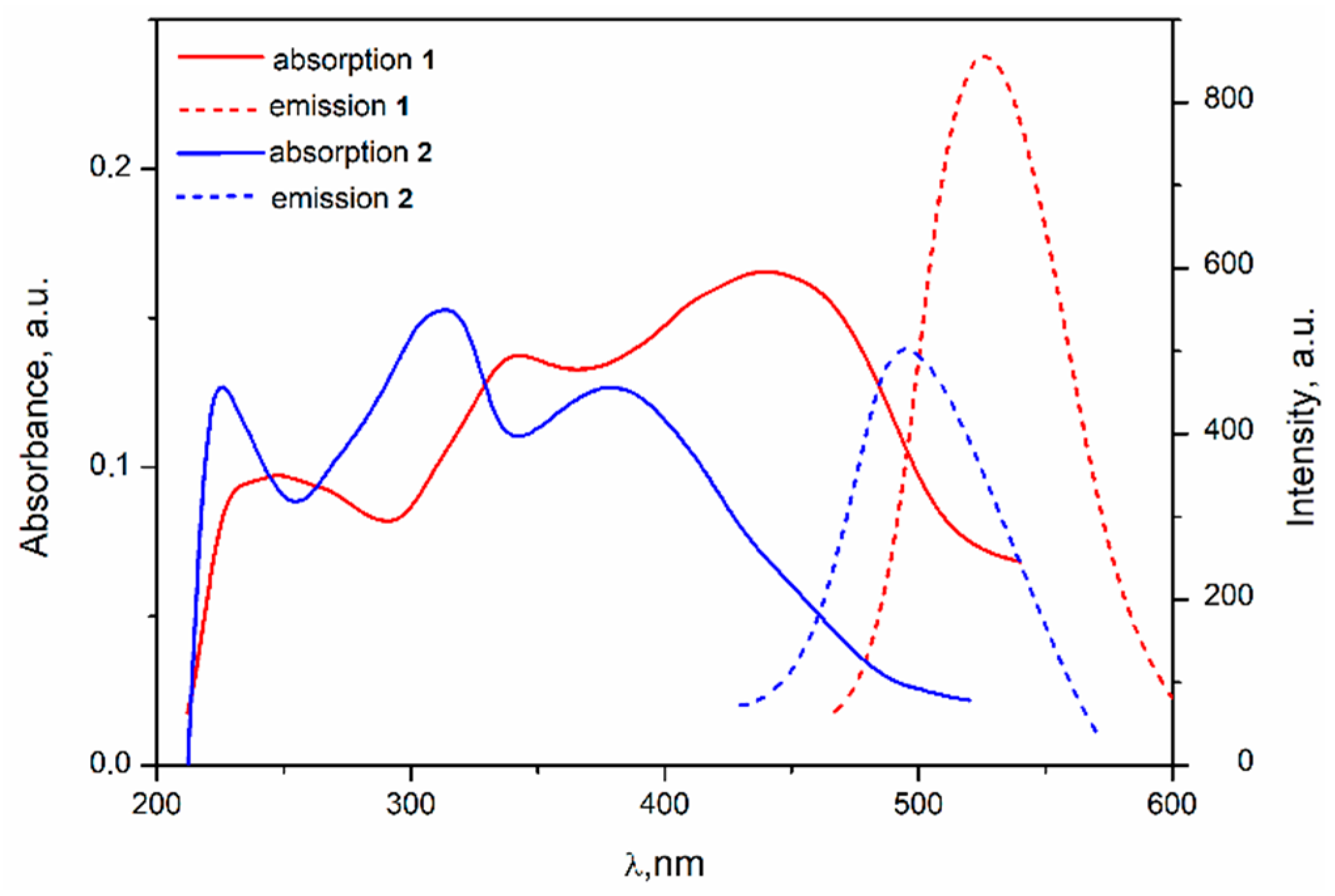
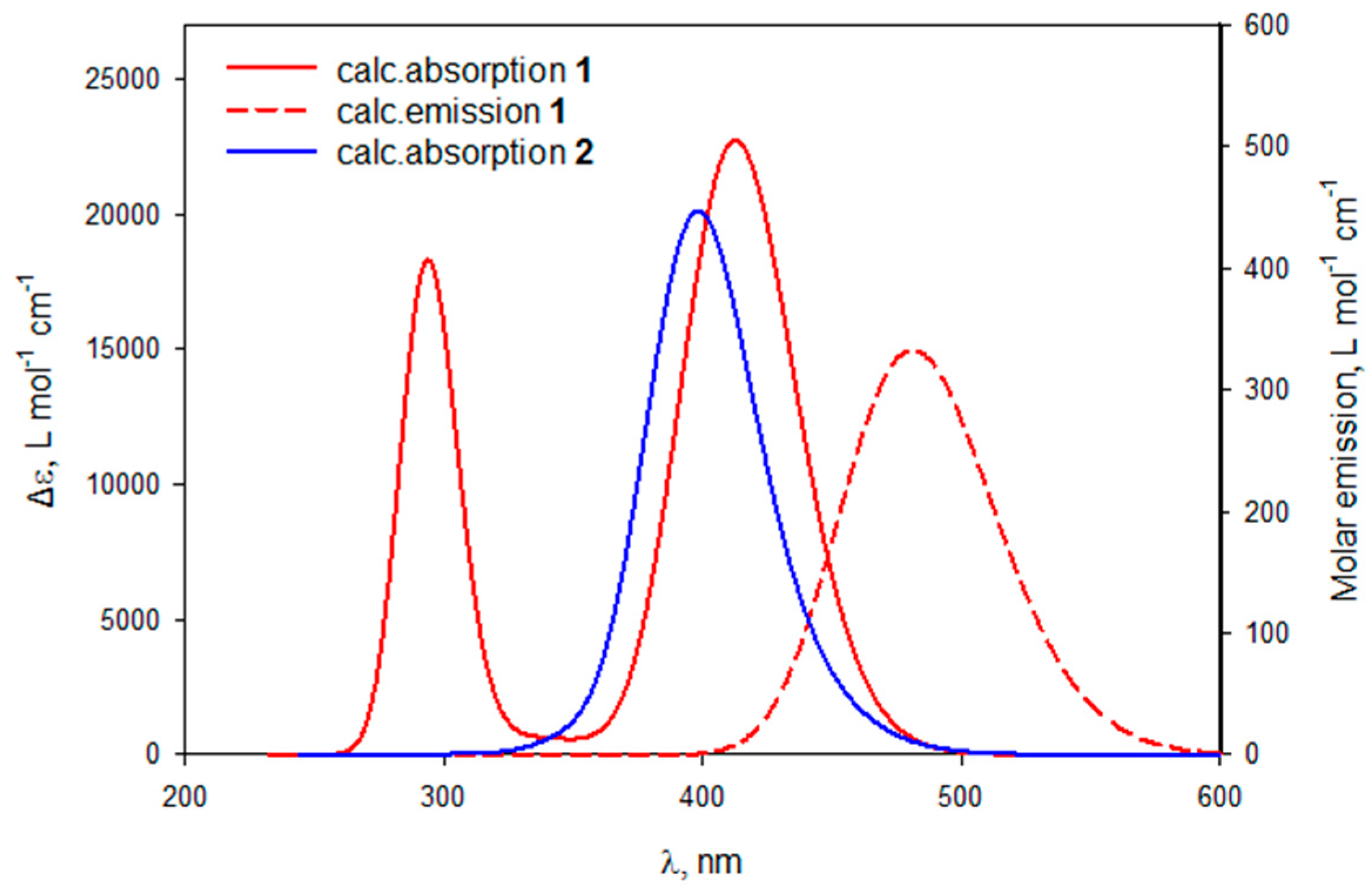
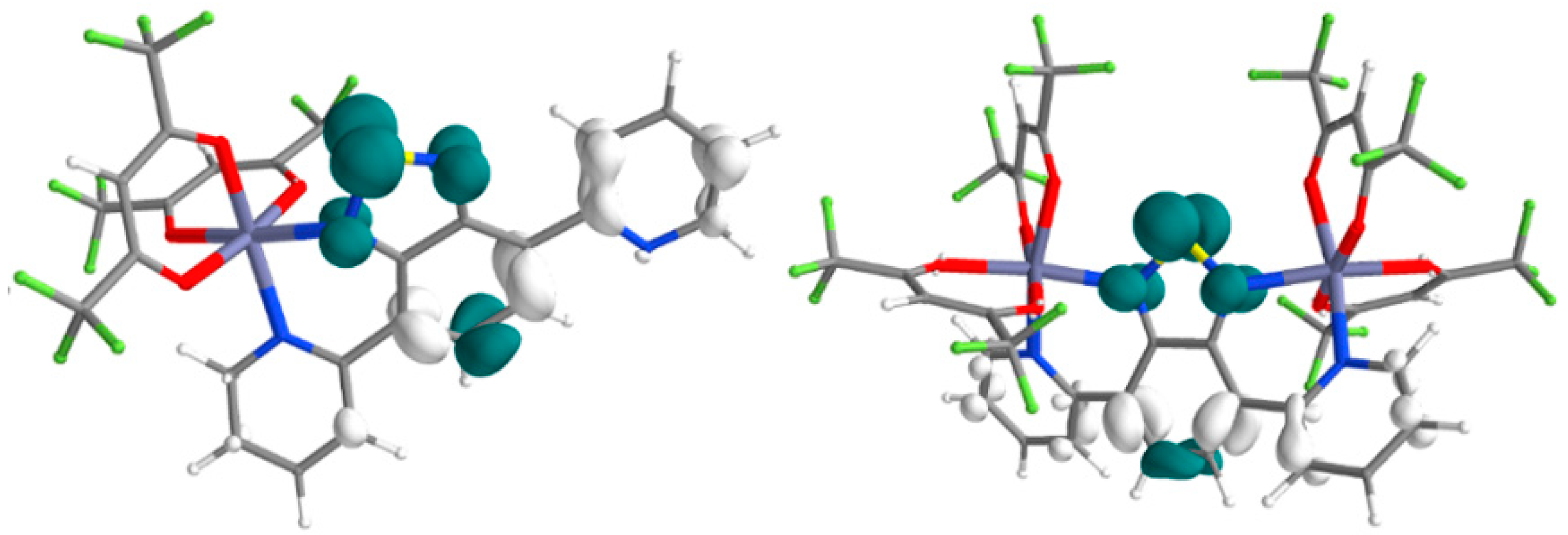
3.4.1. Complexes 1 and 2
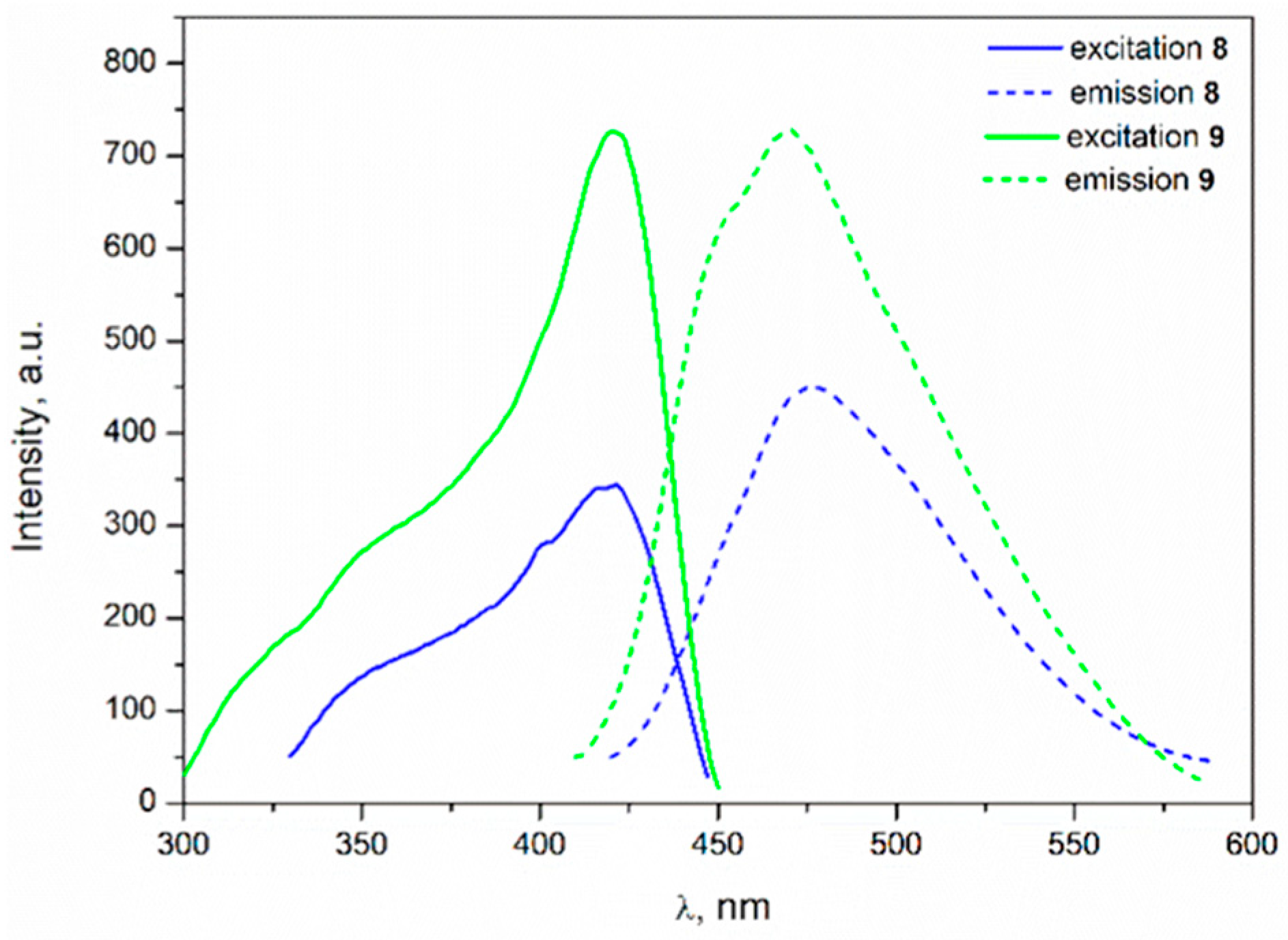
3.4.2. Complexes 7–9
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, K.R.J.; Lin, J.T.; Velusamy, M.; Tao, Y.-T.; Chuen, C.-H. Color Tuning in Benzo[1,2,5]thiadiazole-Based Small Molecules by Amino Conjugation/Deconjugation: Bright Red-Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, T.; Kumaki, D.; Nishida, J.; Sakanoue, T.; Kakita, M.; Tada, H.; Tokito, S.; Yamashita, Y. High-Performance and Light-Emitting n-Type Organic Field-Effect Transistors Based on Dithienylbenzothiadiazole and Related Heterocycles. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 1218–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tsao, H.N.; Pisula, W.; Yang, C.; Mishra, A.K.; Müllen, K. Field-Effect Transistors Based on a Benzothiadiazole−Cyclopentadithiophene Copolymer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 3472–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Pfattner, R.; Campos, A.; Hauser, J.; Laukhin, V.; Puigdollers, J.; Veciana, J.; Mas-Torrent, M.; Rovira, C.; Decurtins, S.; et al. A Compact Tetrathiafulvalene–Benzothiadiazole Dyad and Its Highly Symmetrical Charge-Transfer Salt: Ordered Donor π-Stacks Closely Bound to Their Acceptors. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 7136–7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.T. Evolution of Red Organic Light-Emitting Diodes: Materials and Devices. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 4389–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, B.A.D.; Lapis, A.A.M.; da Silva Júnior, E.N.; Dupont, J. 2,1,3-Benzothiadiazole and Derivatives: Synthesis, Properties, Reactions and Applications in Light Technology of Small Molecules. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 228–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, M.; Thomas, K.R.J.; Lin, J.T.; Hsu, Y.; Ho, K. Organic Dyes Incorporating Low-Band-Gap Chromophores for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 1899–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-Y.; Lu, C.-W.; Huang, W.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lin, H.-W.; Wong, K.-T. New A-A-D-A-A-Type Electron Donors for Small Molecule Organic Solar Cells. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 4962–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Lin, H.-W.; Chou, S.-H.; Lin, F.; Chen, C.-W.; Liu, Y.-H.; Wong, K.-T. A Low-Energy-Gap Organic Dye for High-Performance Small-Molecule Organic Solar Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15822–15825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haid, S.; Marszalek, M.; Mishra, A.; Wielopolski, M.; Teuscher, J.; Moser, J.-E.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Grätzel, M.; Bäuerle, P. Significant Improvement of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Performance by Small Structural Modification in π-Conjugated Donor–Acceptor Dyes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Pop, F.; Yi, C.; Avarvari, N.; Grätzel, M.; Decurtins, S.; Liu, S.-X. Electronic tuning effects via π-linkers in tetrathiafulvalene-based dyes. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 3269–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, F.; Amacher, A.; Avarvari, N.; Ding, J.; Lawson Daku, L.M.; Hauser, A.; Koch, M.; Hauser, J.; Liu, S.-X.; Decurtins, S. Tetrathiafulvalene-Benzothiadiazoles as Redox-Tunable Donor-Acceptor Systems: Synthesis and Photophysical Study. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 2504–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, F.; Seifert, S.; Hankache, J.; Ding, J.; Hauser, A.; Avarvari, N. Modulation of the charge transfer and photophysical properties in non-fused tetrathiafulvalene-benzothiadiazole derivatives. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, B.A.D.; Carvalho, P.H.P.R.; Correa, J.R. Benzothiadiazole Derivatives as Fluorescence Imaging Probes: Beyond Classical Scaffolds. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldakov, D.; Palacios, M.A.; Anzenbacher, P. Benzothiadiazoles and Dipyrrolyl Quinoxalines with Extended Conjugated Chromophores−Fluorophores and Anion Sensors. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 5238–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, A.F.; Vargas-Baca, I.; Mansour, S.; Mahmoudkhani, A.H. The Nature of the Supramolecular Association of 1,2,5-Chalcogenadiazoles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3184–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ams, M.R.; Trapp, N.; Schwab, A.; Milić, J.V.; Diederich, F. Chalcogen Bonding “2S–2N Squares” versus Competing Interactions: Exploring the Recognition Properties of Sulfur. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcock, N.W.; Hill, A.F.; Roe, M.S. Hydrido(benzochalcogenadiazole) complexes of ruthenium: Crystal structure of [RuCl(H)(CO)(PPh3)(SN2C6H4)]. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1990, 5, 1737–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munakata, M.; Kuroda-Sowa, T.; Maekawa, M.; Nakamura, M.; Akiyama, S.; Kitagawa, S. Architecture of 2D Sheets with Six-Membered Rings of Coppers Interconnected by 2,1,3-Benzothiadiazoles and a Layered Structure Composed of the 2D Sheets. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, M.W.; Barkigia, K.M.; Melamed, D.; Smith, K.M.; Fajer, J. Ligand-Bridged Heterobimetallic Polymers: Silver(I)-Benzothiadiazole-Nickel Porphyrin Cation-Benzothiadiazole Arrays. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 5120–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaefstathiou, G.S.; Perlepes, S.P.; Escuer, A.; Vicente, R.; Gantis, A.; Raptopoulou, C.P.; Tsohos, A.; Psycharis, V.; Terzis, A.; Bakalbassis, E.G. Topological Control in Two-Dimensional Cobalt(II) Coordination Polymers by π–π Stacking Interactions: Synthesis, Spectroscopic Characterization, Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties. J. Solid State Chem. 2001, 159, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Papaefstathiou, G.S.; Tsohos, A.; Raptopoulou, C.P.; Terzis, A.; Psycharis, V.; Gatteschi, D.; Perlepes, S.P. Crystal Engineering: Stacking Interactions Control the Crystal Structures of Benzothiadiazole (btd) and Its Complexes with Copper(II) and Copper(I) Chlorides. Cryst. Growth Des. 2001, 1, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashirov, D.A.; Sukhikh, T.S.; Kuratieva, N.V.; Naumov, D.Y.; Konchenko, S.N.; Semenov, N.A.; Zibarev, A.V. Iridium complexes with 2,1,3-benzothiadiazole and related ligands. Polyhedron 2012, 42, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhikh, T.S.; Ogienko, D.S.; Bashirov, D.A.; Konchenkoa, S.N. Luminescent complexes of 2,1,3-benzothiadiazole derivatives. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2019, 68, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, R.J.; Kalinovskyy, Y.; Griffin, S.L.; Wilson, C.; Blight, B.A.; Forgan, R.S. Functional Versatility of a Series of Zr Metal–Organic Frameworks Probed by Solid-State Photoluminescence Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6253–6260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-Q.; Li, Q.-Y.; Cheng, J.-Y.; Cheng, K.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.-J. Ratiometric Luminescent Detection of Organic Amines Due to the Induced Lactam–Lactim Tautomerization of Organic Linker in a Metal–Organic Framework. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 31352–31356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Yue, D.; Jiang, K.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Qian, G. Ratiometric dual-emitting MOF⊃dye thermometers with a tunable operating range and sensitivity. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Han, X.; Tong, Y.; Huang, C.; Ding, J.; Hou, H. Two 3D Cd(II) Metal–Organic Frameworks Linked by Benzothiadiazole Dicarboxylates: Fantastic S@Cd6 Cage, Benzothiadiazole Antidimmer and Dual Emission. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.-C.; Liang, L.; Cui, X.-Z.; Wang, X.-G.; Yang, E.-C.; Zhao, X.-J. Assembly of ZnII-coordination polymers constructed from benzothiadiazole functionalized bipyridines and V-shaped dicarboxylic acids: Topology variety, photochemical and visible-light-driven photocatalytic properties. CrystEngComm 2018, 20, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Tomura, M.; Nishida, J.; Yamashita, Y. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Dipyridylbenzothiadiazole and Bisbenzothiadiazole Derivatives. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 2953–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Z.; Yan, W.; Gao, X.; Shi, Z.; Wang, T.; Zheng, H. Syntheses, Characterization and Luminescence Properties of Four Metal–Organic Frameworks Based on a Linear-Shaped Rigid Pyridine Ligand. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 2496–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Ju, Z.; Qin, L.; Wang, T.; Zheng, H. Two sTable 3D porous metal-organic frameworks with high selectivity for detection of PA and metal ions. Dyes Pigm. 2017, 136, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELX. Acta Cryst. 2015, C71, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT–Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Cryst. 2015, A71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; et al. Gaussian∼09 Revision D.01.
- Schäfer, A.; Huber, C.; Ahlrichs, R. Fully optimized contracted Gaussian basis sets of triple zeta valence quality for atoms Li to Kr. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 100, 5829–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauchy, T.; Da Mota, B. Quchemreport. A Python Program for Control Quality and Automatic Generation of Quantum Chemistry Results. University of Angers, Angers, France, 2020.
- O’boyle, N.M.; Tenderholt, A.L.; Langner, K.M. Cclib: A Library for Package-Independent Computational Chemistry Algorithms. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-J.; Wei, H.-H. Synthesis, crystal structure and magnetic properties of zinc(II)-hexafluoro-acetylacetonate complexes with pyridyl-substituted nitronyl and imino nitroxide radicals. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2000, 310, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.B.; Udachin, K.A.; Ripmeester, J.A. One-dimensional coordination polymers generated from 1,2-bis(x-pyridyl)butadiyne (x = 3 and 4) and bis(hexafluoroacetylacetonato)M(II) (M = Cu, Mn, Zn). CrystEngComm 2002, 4, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W.L.; Palenik, G.J. Infrared and Crystal Structure Study of σ vs. π Bonding in Tetrahedral Zinc(II) Complexes. Crystal and Molecular Structures of Dichlorobis(4-substituted pyridine)zinc(II) Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1977, 16, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudron, S.A. Ag(I)-π interactions with pyrrolic derivatives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 380, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addition, A.W.; Nageswara, R.T.; Reedjik, J.; van Rijn, J.; Verschoor, G.C. Synthesis, structure and spectroscopic properties of copper(II) compounds containing nitrogen–sulphur donor ligands; the crystal and molecular structure of aqua[1,7-bis(N-methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)-2,6-dithiaheptane]copper(II) perchlorate. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1984, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Powell, D.R.; Houser, R.P. Structural variation in copper(I) complexes with pyridylmethylamide ligands: Structural analysis with a new four-coordinate geometry index, τ4. Dalton Trans. 2007, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova, D.; Llunell, M.; Alemany, P.; Alvarez, S. The Rich Stereochemistry of Eight-Vertex Polyhedra: A Continuous Shape Measures Study. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 1479–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llunell, M.; Casanova, D.; Cirera, J.; Bofill, J.M.; Alemany, P.; Alvarez, S.; Pinsky, M.; Avnir, D. SHAPE; Version 2.3; University of Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain; Hebrew University of Jerusalem: Jerusalem, Israel, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Lu, H.-Y.; Liu, R.-L.; Chen, J.-D.; Chen, C.-F. Turn-On Fluorescent Sensor for Selective Detection of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ in Water. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 3670–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducloiset, C.; Jouin, P.; Paredes, E.; Guillot, R.; Sircoglou, M.; Orio, M.; Leibl, W.; Aukauloo, A. Monoanionic Dipyrrin–Pyridine Ligands: Synthesis, Structure and Photophysical Properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 5405–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.S.; Kumar, S.K.A.; Vijayakrishna, K.; Sivaramakrishna, A.; Paira, P.; Rao, C.V.S.B.; Sivaraman, N.; Sahoo, S.K. Bipyridine bisphosphonate-based fluorescent optical sensor and optode for selective detection of Zn2+ ions and its applications. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 8494–8502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, R.; Panunzi, B. The Role of Zinc(II) Ion in Fluorescence Tuning of Tridentate Pincers: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stetsiuk, O.; Abhervé, A.; Avarvari, N. 1,2,4,5-Tetrazine based ligands and complexes. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 5759–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn1–N1 Zn1–N2 Zn1–O1 Zn1–O2 Zn1–O3 Zn1–O4 | 2.105(6) 2.101(7) 2.092(5) 2.092(6) 2.135(6) 2.087(6) | Zn1–N1 Zn1–N2 Zn1–O1 Zn1–O2 Zn1–O3 Zn1–O4 | 2.104(2) 2.171(2) 2.115(2) 2.111(2) 2.088(2) 2.064(2) |
| 3 | 4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ag1–N1 Ag1–N2 Ag1–N3a Ag1–N4a Ag1–O1 | 2.274(3) 2.361(3) 2.770(3) 2.216(3) 2.657(3) | Ag1–N1 Ag1–N2 Ag1–N3a Ag1–N4a | 2.192(5) 2.587(5) 2.415(5) 2.221(5) |
| a = 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z | a = 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z | ||
| 5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ag1–N1 Ag1–O1 Ag1–O3 Ag1–O4 Ag1–O5a Ag1–O6a | 2.302(6) 2.474(5) 2.793(6) 2.571(6) 2.767(5) 2.436(5) | Ag2–N2 Ag2–N4b Ag2–N7 Ag2–O6 Ag2–O5c | 2.294(4) 2.374(6) 2.275(6) 2.736(6) 2.654(5) |
| a = 1 − x, 0.5 + y, 0.5 − z; b = 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z; c = 1 − x, −0.5 + y, 0.5 − z | |||
| 6 | |
|---|---|
| Zn1–O1 Zn1–O2 Zn1–O3 Zn1–O4 Zn1–N1 Zn1–N4a | 2.120(3) 2.124(3) 2.112(3) 2.119(3) 2.124(4) 2.120(4) |
| a = −0.5 + x, 1.5 − y, −0.5 + z | |
| 7 | |
|---|---|
| Zn1–O1 Zn1–O2 Zn1–N1 Zn2–O3 Zn2–O4 Zn2–N4 | 2.076(3) 2.075(2) 2.161(2) 2.073(2) 2.096(2) 2.136(2) |
| 8 | 9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn1–N1 Zn1–N5 Zn1–Cl1 Zn1–Cl2 | 2.049(2) 2.060(2) 2.217(2) 2.214(1) | Zn1–N1a Zn1–N4 Zn1–Cl1 Zn1–Cl2 | 2.064(5) 2.068(5) 2.202(2) 2.232(2) |
| a = 1.5 − x, 1 − y, 0.5 + z | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mocanu, T.; Plyuta, N.; Cauchy, T.; Andruh, M.; Avarvari, N. Dimensionality Control in Crystalline Zinc(II) and Silver(I) Complexes with Ditopic Benzothiadiazole-Dipyridine Ligands. Chemistry 2021, 3, 269-287. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3010020
Mocanu T, Plyuta N, Cauchy T, Andruh M, Avarvari N. Dimensionality Control in Crystalline Zinc(II) and Silver(I) Complexes with Ditopic Benzothiadiazole-Dipyridine Ligands. Chemistry. 2021; 3(1):269-287. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleMocanu, Teodora, Nataliya Plyuta, Thomas Cauchy, Marius Andruh, and Narcis Avarvari. 2021. "Dimensionality Control in Crystalline Zinc(II) and Silver(I) Complexes with Ditopic Benzothiadiazole-Dipyridine Ligands" Chemistry 3, no. 1: 269-287. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3010020
APA StyleMocanu, T., Plyuta, N., Cauchy, T., Andruh, M., & Avarvari, N. (2021). Dimensionality Control in Crystalline Zinc(II) and Silver(I) Complexes with Ditopic Benzothiadiazole-Dipyridine Ligands. Chemistry, 3(1), 269-287. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3010020