Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis: Effect of CO Conversion over Ru/NaY Catalyst
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Catalyst Preparation
2.2. Catalyst Characterization
2.2.1. Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution
2.2.2. Hydrogen Chemisorption
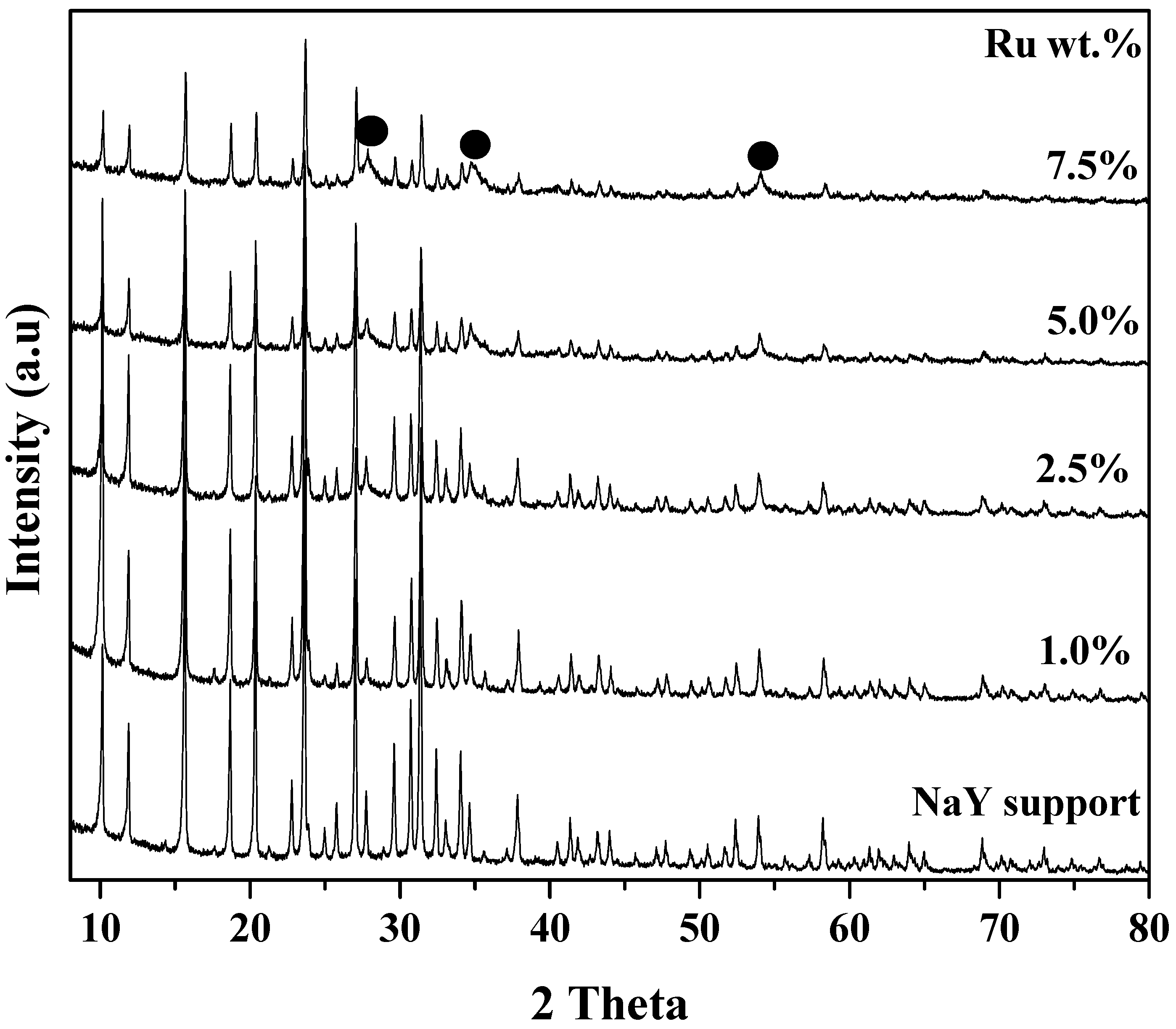
2.2.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
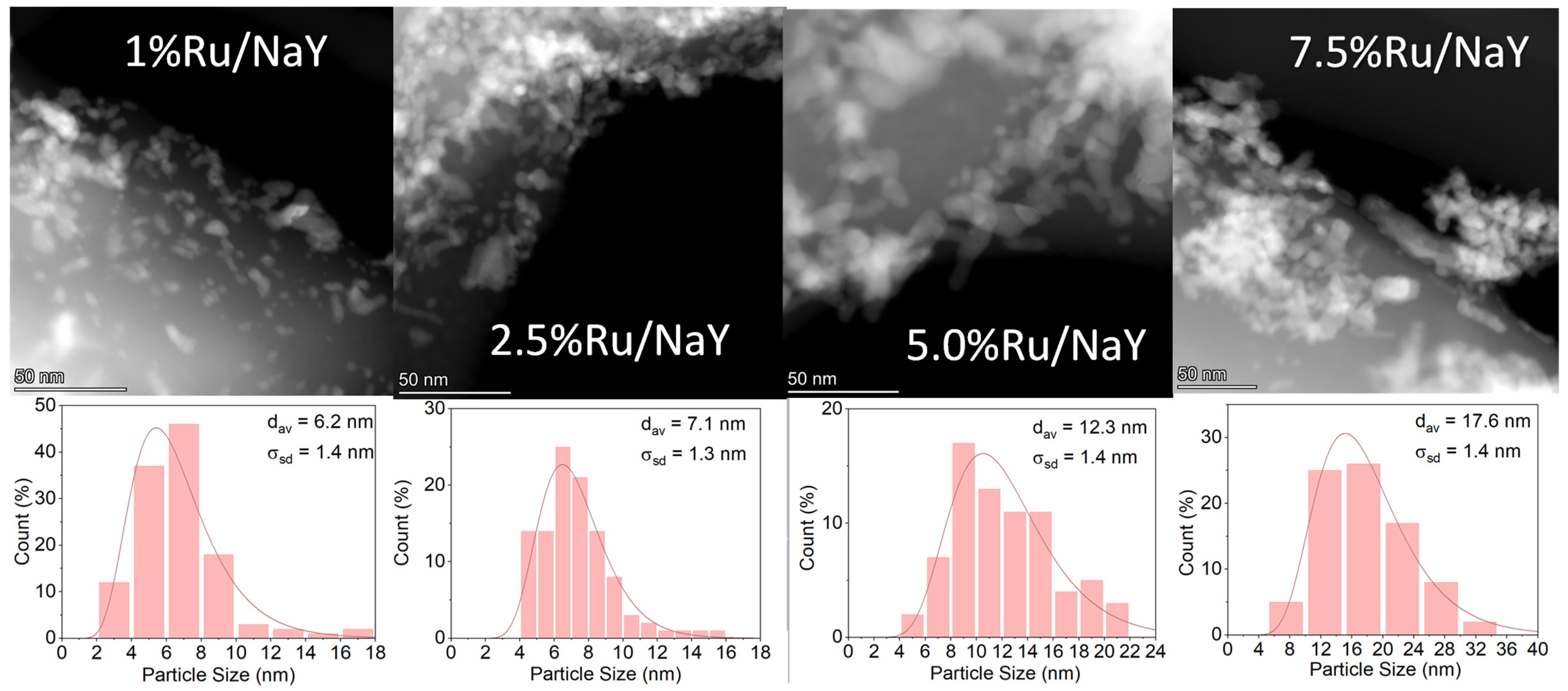
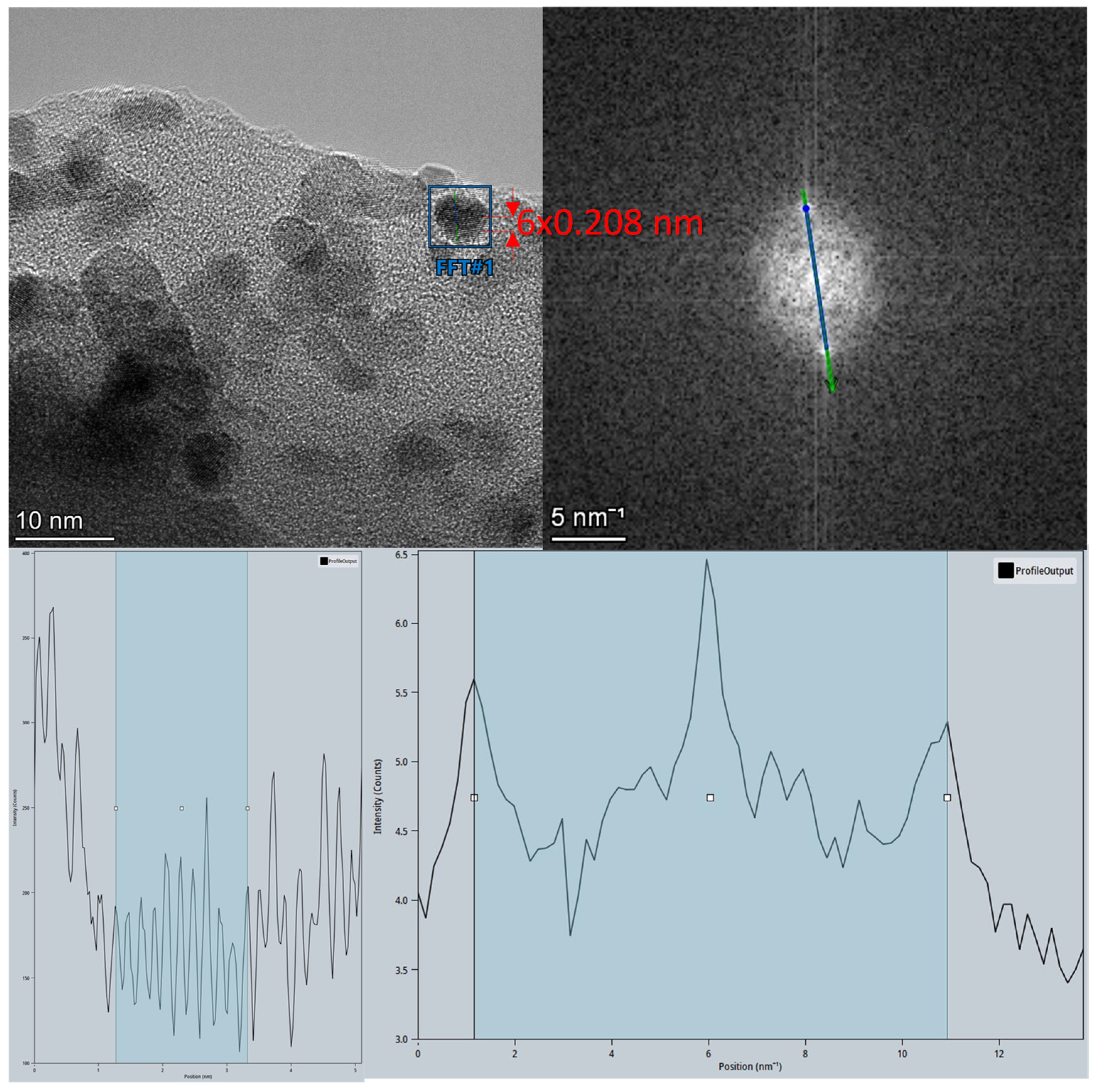
2.2.4. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HR-TEM)/HAADF-STEM
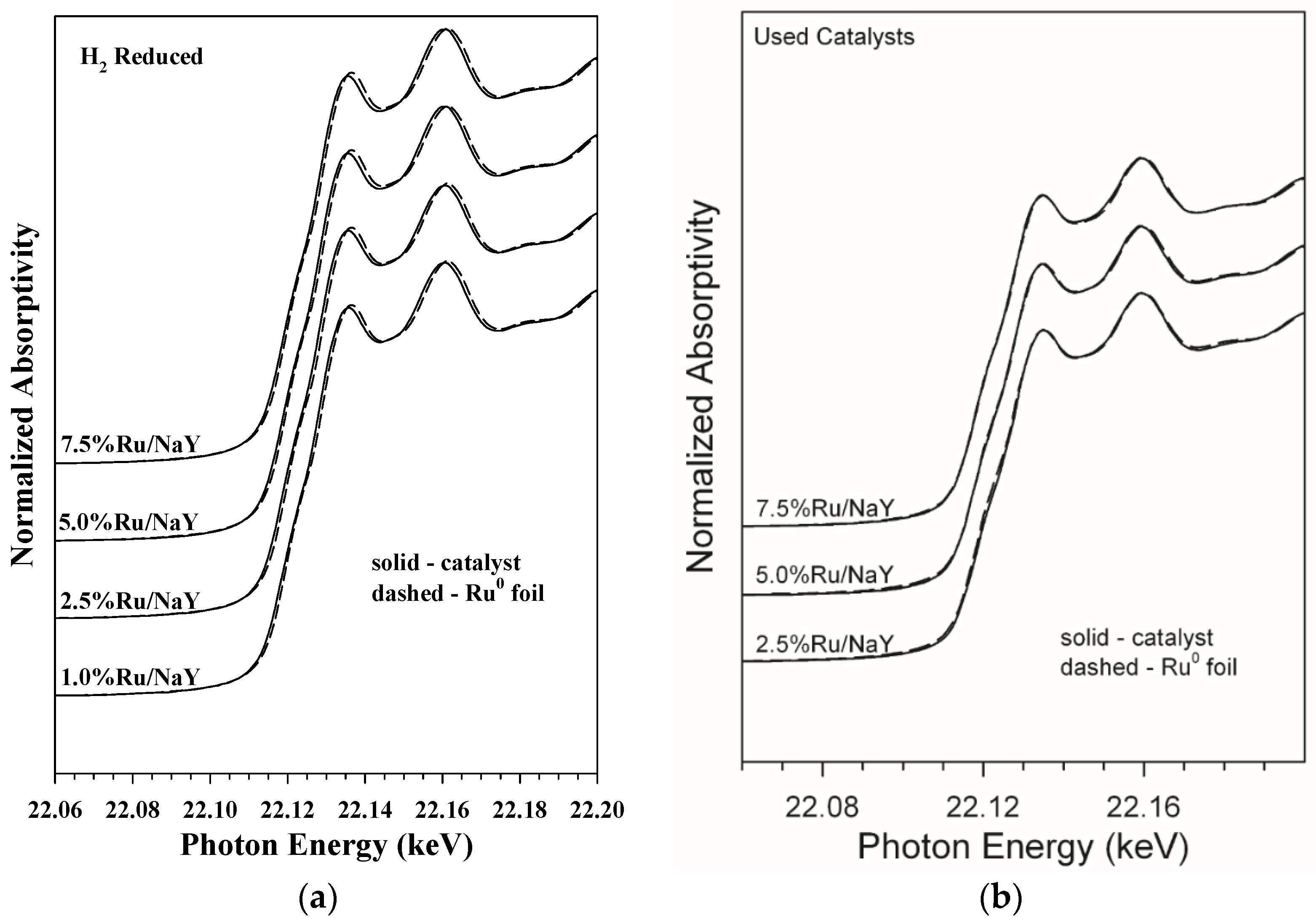
2.2.5. EXAFS/XANES
2.3. Catalytic Activity Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Catalyst Characterization
3.1.1. BET and Hydrogen Chemisorption/Pulse Reoxidation
3.1.2. XRD Study of NaY and Ru/NaY Catalysts
3.1.3. TEM/STEM Study of Ru/NaY Catalysts
3.1.4. XANES/EXAFS Results
3.2. Conversion Effect on Ru/NaY
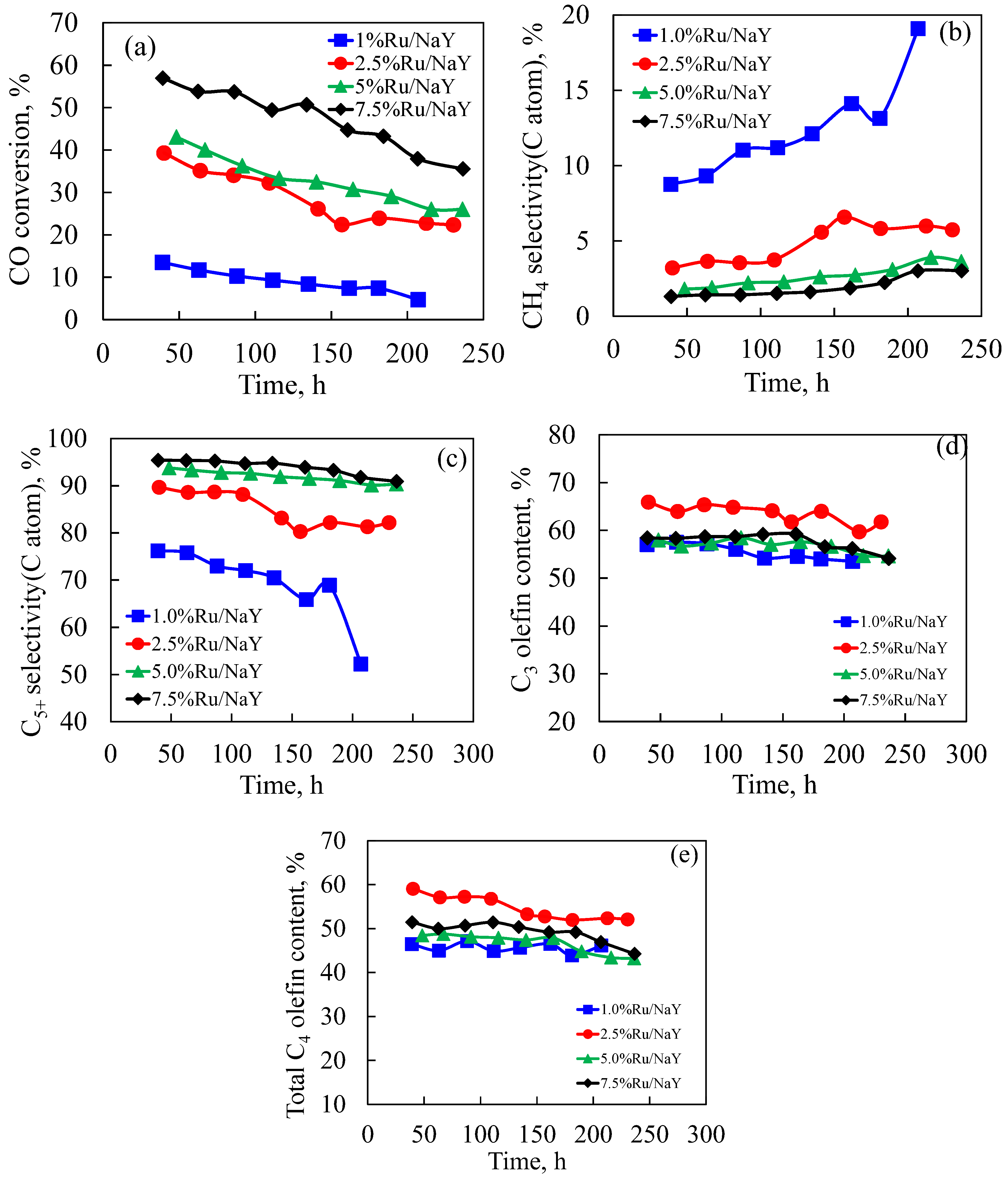
3.2.1. Performance of Ru/NaY Catalysts
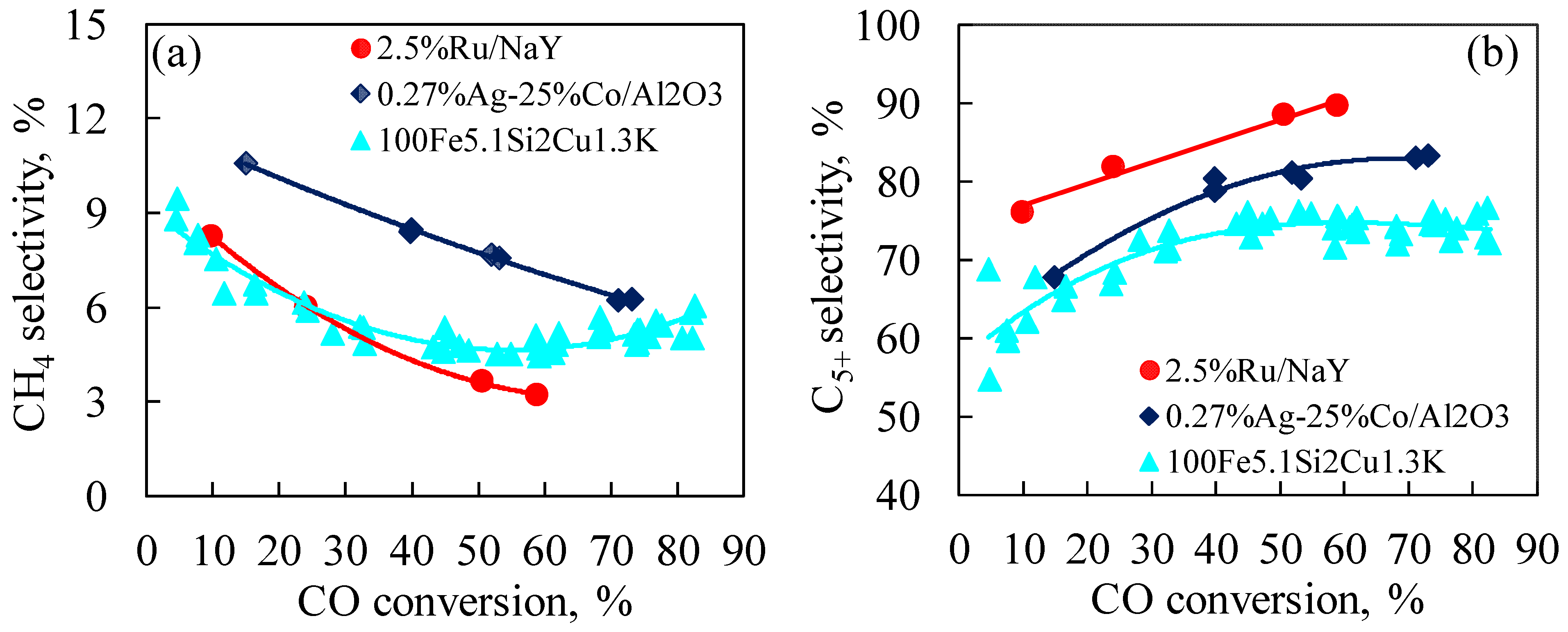
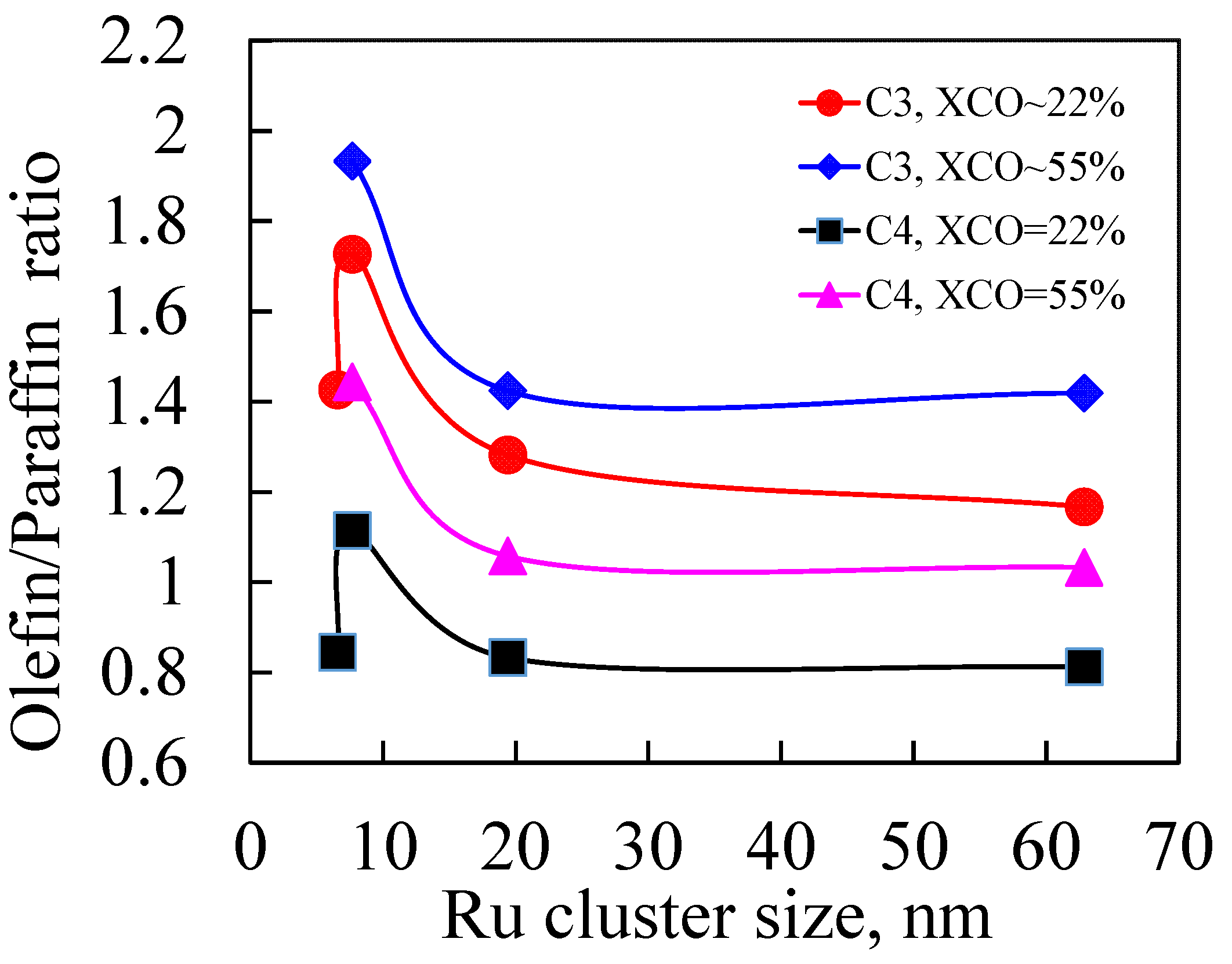
3.2.2. Effect of CO Conversion on Selectivity on Ru/NaY
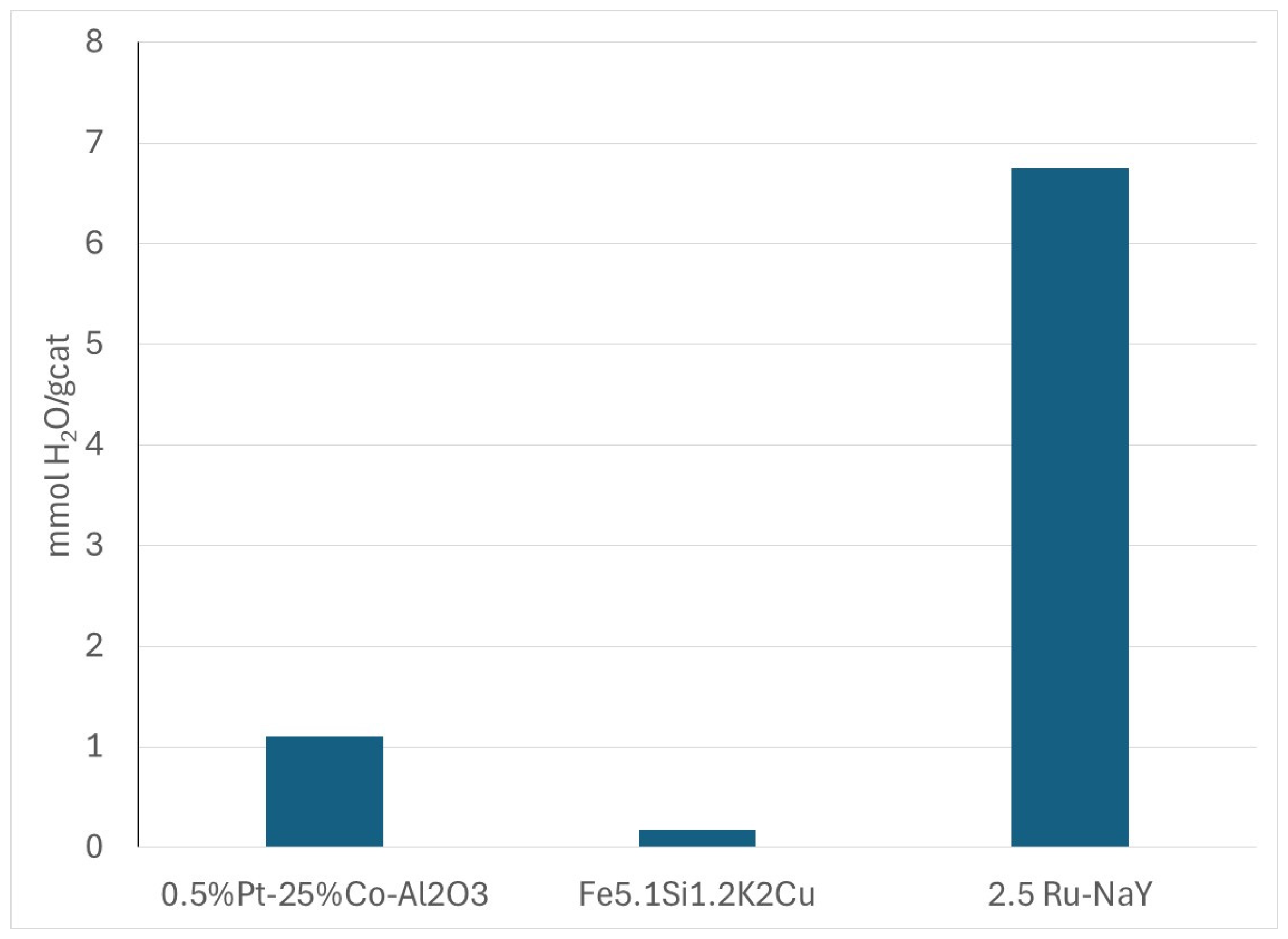
3.2.3. H2O Adsorption on Fe, Co, and Ru Catalysts by H2O-TPD
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/ieo/pdf/ieo2020.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Ma, W.P. COx hydrogenation on Fe and Co catalysts: An efficient approach to carbon neutrality. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Energy and Environment, Lexington, KY, USA, 16–19 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dry, M. The Fischer–Tropsch process: 1950–2000. Catal. Today 2002, 71, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.W.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.W. Indirect coal-to-liquids technology from fundamental research to commercialization. Sci. Sin. Chim. 2014, 14, 1876–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodakov, A.Y.; Chu, W.; Fongarland, P. Advances in the Development of Novel Cobalt Fischer-Tropsch Catalysts for Synthesis of Long-Chain Hydrocarbons and Clean Fuels. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 1692–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesia, E. Design, synthesis, and use of cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1997, 161, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, F.; Tropsch, H. The preparation of synthetic oil mixtures (synthol) from carbon monoxide and hydrogen. Brennst. Chem. 1923, 4, 276–285. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, G.H.M.; de Jong, K.P. Catalysts for Production of Lower Olefins from Synthesis Gas: A Review. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 2130–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.H. Fischer−Tropsch Synthesis: Comparison of Performances of Iron and Cobalt Catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 8938–8945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Smit, E.; Weckhuysen, B.M. The renaissance of iron-based Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: On the multifaceted catalyst deactivation behaviour. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 2758–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Kang, J.; Wang, Y. Development of Novel Catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis: Tuning the Product Selectivity-Review. ChemCatChem 2010, 2, 1030–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.B. The Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.; Bao, S.; Keogh, R.A.; Sarkar, A.; Jacobs, G.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: A Comparison of Iron and Cobalt Catalysts. In Proceedings of the AIChE 2006 National Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–17 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shafer, W.D.; Gnanamani, M.K.; Graham, U.M.; Yang, J.; Masuku, C.M.; Jacobs, G.; Davis, B.H. Fischer–Tropsch: Product Selectivity—The Fingerprint of Synthetic Fuels. Catalysts 2019, 9, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Jacobs, G.; Sparks, D.E.; Todic, B.; Bukur, D.B.; Davis, B.H. Quantitative comparison of iron and cobalt based catalysts for the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis under clean and poisoning conditions. Catal. Today 2020, 343, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.H. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: Overview of reactor development and future potentialities. Top Catal. 2005, 32, 143–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.H. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: Current mechanism and futuristic needs. Fuel Proc. Technol. 2001, 71, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukur, D.B.; Lang, X. Highly active and stable iron Fischer-Tropsch catalyst for synthesis gas conversion to liquid fuels. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 3270–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.-W. Recent development in converting coal to clean fuels in China. Fuel 2015, 152, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellner, C.S.; Bell, A.T. Effects of dispersion on the activity and selectivity of alumina-supported ruthenium catalysts for carbon monoxide hydrogenation. J. Catal. 1982, 75, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesia, E.; Soled, R.S.L.; Fiato, A. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis on cobalt and ruthenium. Metal dispersion and support effects on reaction rate and selectivity. J. Catal. 1992, 137, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo, J.M.G.; Yang, J.; Holmen, A.; Garcia-Rodriguez, S.; Rojas, S.; Ojeda, M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Catalytic effects of ruthenium particle size on the Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. J. Catal. 2011, 284, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslava, J.L.; Sun, X.H.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijnb, F.; Ramos, I. Ruthenium particle size and cesium promotion effects in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis over high surface-area graphite supported catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo, J.M.G.; Alonso, F.J.P.; Ojeda, M.; GarcIa-Garcia, F.J.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Rojas, S. Evidences of Two-Regimes in the Measurement of Ru Particle Size Effect for CO Dissociation during Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 2084–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Ruthenium nanoparticles supported on carbon nanotubes as efficient catalysts for selective conversion of synthesis gas to diesel fuel. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 2565–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.X.; Cai, Z.P.; Wang, T.; Kou, Y.; Yan, N. Aqueous-Phase Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis with a Ruthenium Nanocluster Catalyst. Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Dalai, A.K. Effects of Structure and Particle Size of Iron, Cobalt and Ruthenium Catalysts on Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. Reactions 2021, 2, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesia, E.; Reyes, S.C.; Madon, R.J.; Soled, S.L. Selectivity Control and Catalyst Design in the Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: Sites, Pellets, and Reactors. Adv. Catal. 1993, 39, 221–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, Ø.; Eri, S.; Blekkan, E.A.; Storsæter, S.; Wigum, H.; Rytter, E.; Holmen, A. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis overγ-alumina-supported cobalt catalysts: Effect of support variable. J. Catal. 2007, 248, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Jacobs, G.; Ji, Y.; Bhatelia, T.; Bukur, D.B.; Khalid, S.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Influence of CO conversion on selectivities, H2/CO usage ratios, and catalyst stability for a 0.27% Ru 25%Co/Al2O3 using a slurry-phase reactor. Top. Catal. 2011, 54, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukur, D.B.; Pan, Z.; Ma, W.; Jacobs, G.; Davis, B.H. Effect of CO conversion on the product distribution of a Co/Al2O3 Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst using a fixed bed reactor. Catal. Lett. 2012, 142, 1382–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.L.; van Steen, E. Activity and selectivity of a cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst operating at high conversion for once-through biomass-to-liquid operation. Catal. Today 2020, 342, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raje, A.P.; O’Brien, R.J.; Davis, B.H. Effect of Potassium Promotion on Iron-Based Catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. J. Catal. 1998, 180, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ma, W.P.; Chen, D.; Holmen, A.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: A review of the Effect of CO Conversion on Methane Selectivity. Appl. Catal. 2014, 470, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Shafer, W.D.; Jacobs, G.; Yang, J.; Sparks, D.E.; Hamdeh, H.H.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Effect of CO conversion on CH4 and oxygenate selectivities over precipitated Fe-K catalysts. Appl. Catal. 2018, 560, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, M. X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Chem. Eng. News 2001, 79, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ressler, T. WinXAS: A program for X-ray absorption spectroscopy data analysis under MS-Windows. J. Synch. Rad. 1998, 5, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravel, B. ATOMS: Crystallography for the X-ray absorption spectroscopist. J. Synch. Rad. 2001, 8, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehr, J.J.; Zabinsky, S.I.; Albers, R.C. High-order multiple-scattering calculations of X-ray-absorption fine structure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 69, 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newville, M.; Ravel, B.; Haskel, D.; Stern, E.A.; Yacoby, Y. Analysis of multiple-scattering XAFS data using theoretical standards. Phys. B Condens. Matter 1995, 208/209, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storsæter, S.; Borg, Ø.; Blekkan, E.A.; Holmen, A. Study of the effect of water on Fischer-Tropsch synthesis over supported cobalt catalysts. J. Catal. 2005, 231, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todic, B.; Ma, W.; Jacobs, G.; Nikacevic, N.; Davis, B.H.; Bukur, D.B. Kinetic modeling of secondary methane formation and 1-olefin hydrogenation in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis over a cobalt catalyst. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2017, 49, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, W. Water Adsorption on a Co(0001) Surface. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 17023–17029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
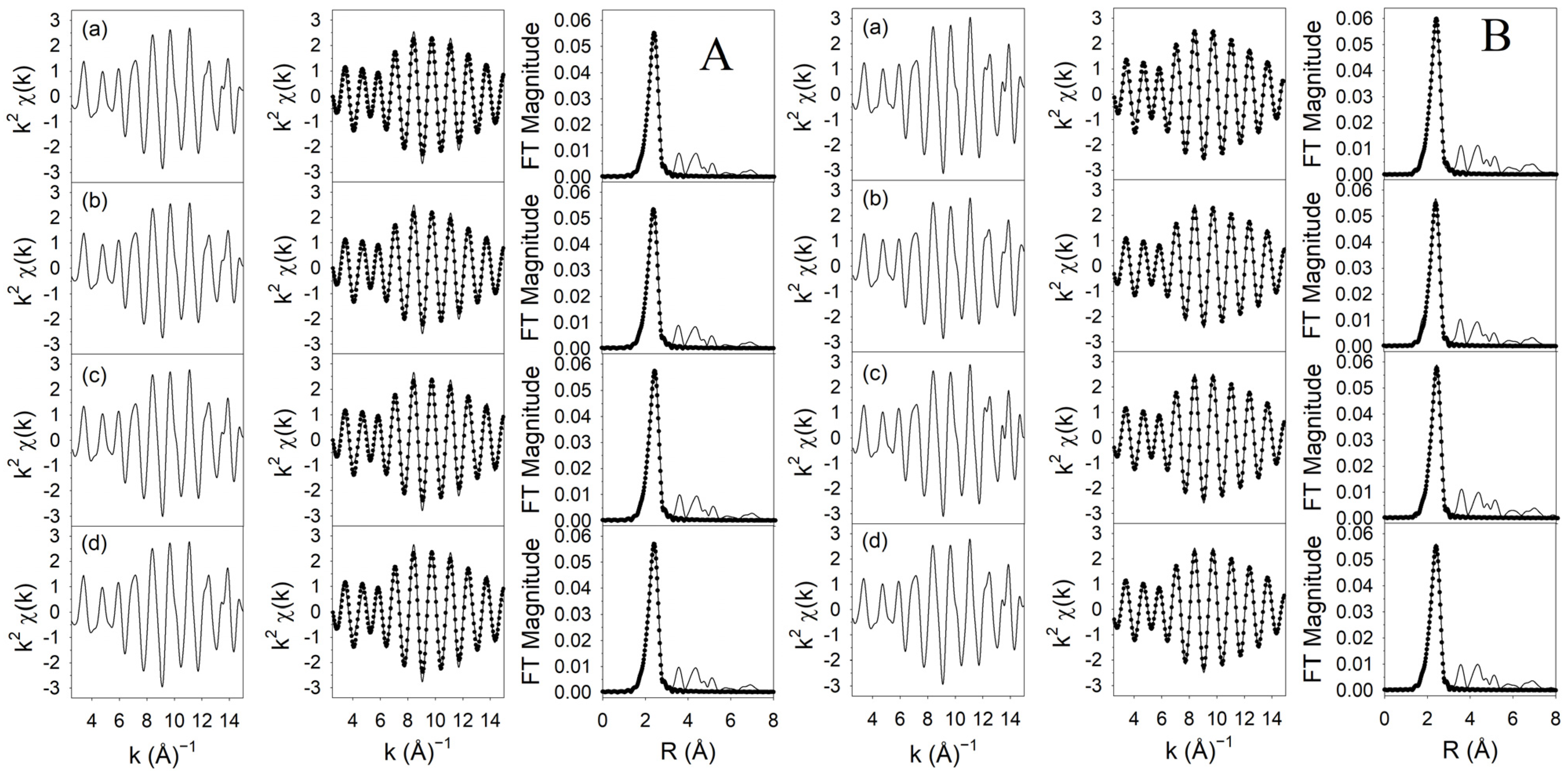


| Catalyst | BET SA (m²/g) | PV (cm³/g) | PD (nm) | H₂ desorbed (µmoles/g_cat) | Ru Disp. (%) | Ru Dia. (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaY support | 730.0 | 0.359 | 1.97 | 9.9 | ||
| 1.0%Ru/NaY | 661.2 | 0.330 | 2.00 | 2.0 | 20.1 | 6.6 |
| 2.5%Ru/NaY | 632.3 | 0.320 | 2.02 | 21.3 | 17.2 | 7.7 |
| 5.0%Ru/NaY | 560.2 | 0.288 | 2.06 | 16.8 | 6.8 | 19.4 |
| 7.5%Ru/NaY | 461.0 | 0.248 | 2.16 | 7.9 | 2.1 | 62.9 |
| Catalyst | N Ru-Ru | R Ru-Ru (Å) | e0 (eV) | σ2 (Å2) | R-Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ru0 foil (Argonne) | 12 (set) | 2.673 (0.0026) | 6.2 (0.6) | 0.0040 (0.0016) | 0.011 |
| Ru0 foil (Brookhaven) | 12 (set) | 2.675 (0.0031) | 5.1 (0.7) | 0.0042 (0.0018) | 0.014 |
| 1.0%Ru/NaY (fresh) | 10.2 (0.7) | 2.669 (0.0023) | 5.2 (0.60) | 0.0038 (0.00030) | 0.0087 |
| 2.5%Ru/NaY (fresh) | 10.0 (0.6) | 2.668 (0.0024) | 5.2 (0.56) | 0.0039 (0.00031) | 0.0080 |
| 2.5%Ru/NaY (used) | 9.6 (0.7) | 2.667 (0.0027) | 5.3 (0.65) | 0.0034 (0.00033) | 0.0096 |
| 5.0%Ru/NaY (fresh) | 10.4 (0.7) | 2.670 (0.0024) | 5.2 (0.56) | 0.0037 (0.00030) | 0.0076 |
| 5.0%Ru/NaY (used) | 10.3 (0.8) | 2.674 (0.0029) | 4.7 (0.70) | 0.0036 (0.00037) | 0.0114 |
| 7.5%Ru/NaY (fresh) | 10.4 (0.7) | 2.670 (0.0024) | 5.2 (0.57) | 0.0037 (0.00030) | 0.0078 |
| 7.5%Ru/NaY (used) | 10.1 (0.7) | 2.673 (0.0025) | 4.5 (0.60) | 0.0037 (0.00032) | 0.0086 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, W.; Yang, J.; Jacobs, G.; Qian, D. Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis: Effect of CO Conversion over Ru/NaY Catalyst. Reactions 2025, 6, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions6020031
Ma W, Yang J, Jacobs G, Qian D. Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis: Effect of CO Conversion over Ru/NaY Catalyst. Reactions. 2025; 6(2):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions6020031
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Wenping, Jia Yang, Gary Jacobs, and Dali Qian. 2025. "Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis: Effect of CO Conversion over Ru/NaY Catalyst" Reactions 6, no. 2: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions6020031
APA StyleMa, W., Yang, J., Jacobs, G., & Qian, D. (2025). Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis: Effect of CO Conversion over Ru/NaY Catalyst. Reactions, 6(2), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions6020031








