Abstract
In this study, we present the effects of time and temperature on the formation of urea deposits and their composition under conditions realistic to mobile heavy-duty SCR applications. To this end, various synthesis times were evaluated (1 h, 4 h and 24 h), as well as temperatures (298–673 K). The formed urea deposits were qualitatively evaluated using ATR FTIR to elucidate their molecular composition. Furthermore, the effect of dry and moist synthesis conditions were evaluated to simulate water rich and deficient exhaust gas composition. This was achieved by conducting the synthesis in open or closed containers to simulate dry and humid conditions, respectively. The findings are presented in this paper in two maps covering dry and moisture conditions. The trend reveals that at low temperatures the deposits mainly consist of urea derived compounds, like biuret and cyanuric acid. Increasing the temperature leads to an increase in more aminated mono-triazine compounds. At the highest synthesis temperature of 673 K, the main constituents are cyamuleric compounds, consisting of fused triazine rings like melem. Humid synthesis conditions hampers the formation of highly aminated compounds up to a synthesis temperature of 573 K, even after a synthesis period of 24 h. Temperatures higher than 573 K, and a long synthesis period of 24 h, results only in minor differences and are observed between samples prepared under dry or humid conditions. The decomposition properties of the synthesized materials are optimal for the samples prepared at 523 K, whereas the lowest decomposition rates were observed for samples prepared at 623 K and 673 K. A humid air gas flow was shown to be beneficial for the decomposition rate under these conditions.
1. Introduction
Air pollutant emissions from exhaust gasses of diesel engines, especially NOx, are causing environmental and health problems [1]. Regulators are restricting the amount of NOx that is allowed to be emitted from such diesel engines to improve air quality. In order to reach air pollutant emission standards, typically a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalyst is installed, reducing NOx to N2 and O2, using urea as the reducing agent [2], which is usually injected into the installation as a 32.5 wt% aqueous solution. Typical SCR catalysts are zeolite-based materials with mono-atomic and di-atomic Cu1+/2+ centers introduced into the zeolite framework [3]. The copper species are considered to be the active species in the SCR reaction [4]. The introduction of mono-atomic Cu introduces Lewis acid Sites (LAS) into the catalyst, whereas the zeolite material itself provides Brønsted Acidic Sites (BAS) [5]. Next to the zeolite, formation of larger CuO particles upon agglomeration of monoatomic Cu1+/2+ species introduces Brønsted acidic properties [6]. During the SCR reaction, NOx components (NO and NO2) are converted towards N2 upon reaction with NH3 as the reducing agent, which originates from a water solution with urea acting as the NH3 precursor [2,7,8].
During operation, this urea solution is injected in the gas stream, where urea is decomposed during evaporation and exposure to heat [9]. Previously, many studies have extensively investigated the decomposition pathways of urea, and found they can be roughly divided into a pyrolysis (water deficient conditions) [10,11,12,13,14] and hydrolysis (water rich conditions) [12,15] route. Under the preferred hydrolysis conditions, urea is exposed to heat and water vapor leading to full and rapid decomposition into NH3 [12,15]. In this ideal situation, the urea decomposes to gaseous ammonia and CO2 (1) [12,15]. When an alternative pathway is followed (2), urea decomposes to ammonia and isocyanic acid. The isocyanic acid can decompose further when reacting with water to ammonia and CO2 (3) [12,15]. Isocyanic can however also react to biuret, which can subsequently react via condensation reactions to aromatic components like cyanuric acid, ammeline, melamine, and eventually to large polyaromatic structures like melon [12,15].
Alternatively, when the gas stream is deficient of water, a pyrolysis mechanism is followed. In this reaction regime, urea decomposes due to exposure to heat. Schaber et al. [10] have extensively investigated the decomposition of urea and reported the existence of four reaction regions which are largely determined by temperature. The first reaction region (room temperature–463 K) involves the incomplete decomposition of urea into cyanic acid [10]. The formed isocyanic acid can react further with urea to biuret, which can react further to aromatic compounds like cyanuric acid, and ammelide consisting of triazine rings [10]. The second region (463–523 K) involves besides the decomposition of urea, the decomposition of biuret into isocyanic acid, and the reaction of biuret towards more aminated aromatic compounds, like ammeline and melamine [10]. The formation of these compounds proceeds via cyclization of biuret towards ammelide, which then undergoes amination with ammonia [10]. Above 523 K up to 623 K the aromatic compounds cyanuric acid, ammeline, and melamine start to decompose into isocyanic acid [10]. At high temperatures (>623 K) melamine and melamin derived components can react via the formation of partial decomposition products to larger polytriazine products [16].
Closely related to the formation of the urea deposits, is the decomposition of such solids, which strongly depends on the molecular structure of the formed materials. Decomposition becomes more difficult when the molecular structure has proceeded from urea and biuret towards more (poly)aromatic compounds. To illustrate this, the decomposition temperatures of various compounds as reported in the literature [10,13,14], which are assumed to play a role in deposit formation are presented in Table 1. As can be seen the thermal decomposition temperature of most compounds is high and lay often outside the operation window of the SCR catalyst. Hydrolysis of these compounds often takes place at lower temperatures [10,13].

Table 1.
Formation, sublimation and decomposition temperatures of key compounds in the formation mechanism of urea deposits.
Important in commercial applications is to understand the formation and decomposition of urea deposits during operation. Although previously reaction networks have been studied using solid pure urea, the current state of knowledge lacks investigations on the formation and decomposition mechanisms of urea deposits prepared under realistic conditions. Such knowledge is essential in order to develop more efficient operation strategies. An example is that the regeneration strategy aimed to mitigate deposit formation could be tailored to specific scenarios of operation. In this study, urea deposits were prepared by heating a typical urea solution as used in heavy-duty SCR applications. Various parameters were adjusted during the preparation of the solids, i.e., temperature, time and dry or wet atmosphere. The latter was done by leaving the container open (dry) or closed (wet). In this way, the effect of water rich and deficient exhaust gas on the formation of urea deposits was simulated. The prepared materials were then analyzed by FTIR in order to identify the compounds present in these deposits and compared to reference materials which are involved in the formation of urea deposits. Furthermore, we investigated the decomposition of the prepared deposits in a Temperature Programmed Decompostion (TPD) setup under oxidative air conditions. During these decomposition experiments, besides thermal effects, the influence of water in the exhaust gas stream was studied. The materials retrieved after the TPD experiments were then subsequently analyzed in FTIR. This shows the effect of exposure of urea deposits to thermal treatment and the chemical composition of the solids recovered after TPD.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Deposit Synthesis
The aqueous urea solution was prepared by weighing 32.5 g of urea (Merck, extra pure) into a 100 mL volumetric flask, followed by addition of demineralized water until 100 mL. This in order to achieve a similar concentration as used by commercial products, i.e., diesel exhaust fluid (DEF). In total, 10 mL of this urea solution was added to a porcelain container. This container could optionally be closed using a porcelain cover in order to create different humidity conditions during synthesis. The materials where then heated in a static oven to the desired temperature (5 K/min) for a period of 1, 4 or 24 h. The materials were recovered from the porcelain container and stored in a closed plastic container. Samples were denoted Urea_xK_y_z, with x being the temperature of heat treatment, y indicating whether the container was open or closed during sample preparation, and z for the preparation time in hours.
2.2. FTIR Analysis
The prepared samples were measured on a Spectrum II FTIR machine equipped with an ATR crystal (Manufacturer Perkin-Elmer, www.perkinelmer.com). The obtained spectra were analyzed using the Spectrum II software (Manufacturer Perkin-Elmer, www.perkinelmer.com). Melamine, biuret, ammelide, and cyanuric acid where purchased from Acros Organics (https://nl.vwr.com as reference compounds.
2.3. TPD Experiments
Typically, 100 mg of synthesized urea deposit powder was loaded in a stainless-steel tube reactor and placed in a custom-made oven. An air gas flow of 30 mL/min was fed to the reactor. To increase humidity, this gas stream was led through a water filled saturator, kept in a heating bath to obtain the desired water concentration. The gas stream was analyzed using a Temperature Conductivity Detector (TCD). During the experiment, the temperature was increased (5 K/min) to 673 K and kept for 35 min. After the experiment, the reactor was left to cool to room temperature and the remaining powder was weighed for determining the mass loss.
3. Results
3.1. FTIR Analysis of Synthesized Compounds
3.1.1. Urea Deposits Prepared Below and at 423 K
The FTIR spectra for urea deposits prepared in the temperature range between room temperature and 423 K are shown in Figure 1. The spectra of the samples prepared below the decomposition temperature of urea (406 K) correspond closely to the spectrum recorded for pure urea. The spectrum of urea shows in the higher wavenumber region a medium band at 3425 cm−1, corresponding to the N-H out-of-phase stretching vibration [20]. The band at 3300 cm−1 and the small shoulder band visible at 3260 cm−1 correlates to N-H in-phase stretching vibrations [20]. In the fingerprint region, bands at 1148, 1458, 1589 and 1674 cm−1 indicate the presence of urea. The band at 1680 cm−1 has been assigned previously to C = O stretching mode, whereas the bands at 1589 cm−1 and 1458 cm−1 originate from C = O stretch vibrations and anti-symmetrical stretch C-N vibrations [21]. Weeks et al. [22] have identified the 3429 cm−1 and 1148 cm−1 bands to be indicative for the presence of urea in samples, consisting of urea derived mixtures formed upon thermal decomposition of urea.
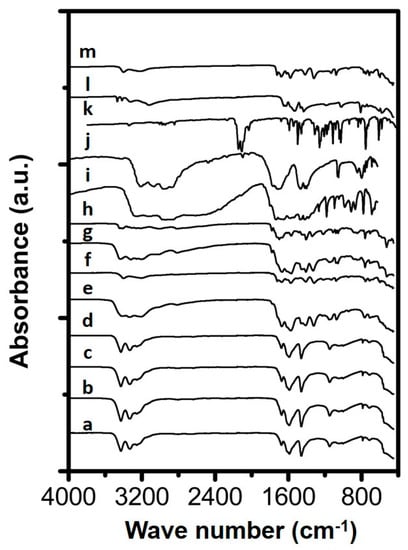
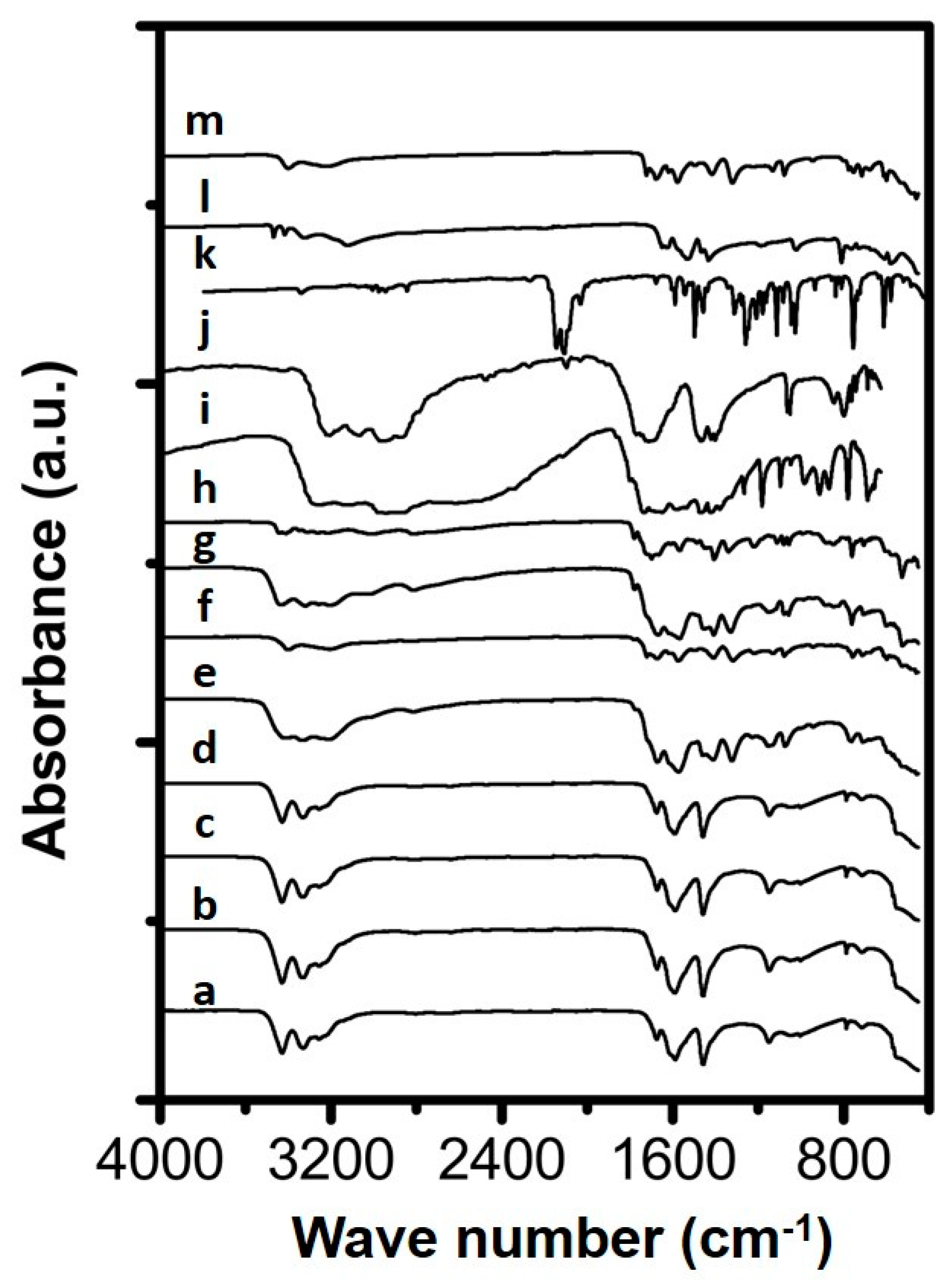
Figure 1.
Spectra of synthesized samples and reference materials being (a) Urea solution evaporated (b) Urea_RT_open_24h, (c) Urea_323K_open_24h, (d) Urea_373K_open_24h, (e) Urea_406K_closed_24h, (f) Urea_406K_open_24h, (g) Urea_423K_closed_24h, (h) Urea_423K_open_24h, (i) Ammelide reference, (j) Cyanuric acid reference, (k) Carmobodi-imide reference, (l) Melamine reference and (m) Biuret reference.
When inspecting the spectrum of the sample prepared overnight at 406 K in an open container (Urea_406K_open_24h), a clear correlation can be made with the reference spectrum recorded for biuret. This suggests the transformation of urea towards biuret. The absorbance bands in the fingerprint region at 1321, 1414 and 1579 cm−1 are indicative for the formation of biuret. The absorbance at higher wavenumbers in the spectrum at 3399 and 3217 cm−1 are indicative for the O-H and N-H vibrations, respectively. When comparing the spectral lines of Urea_406K_closed_24h and Urea_406K_open_24h some difference can be observed. The spectrum of the material prepared in a closed container contained besides features representative for biuret at 1321, 1414 and 1579 cm−1, also small features at 1148, 1458, 1589 and 1674 cm−1 indicative for the presence of urea in the sample. This implies that this sample consists of a mixture of both urea and biuret as the main constituents. The spectrum of Urea_406K_closed_24h also contains a broad absorbance band in the 3500–3000 cm−1 wavenumber region which can be attributed to N-H stretching bands originating from urea and urethane like components [23]. Furthermore, the presence of some physisorbed water could possibly contribute to the widening of the band in the 3500–3000 region. When looking at the spectrum of the urea sample treated overnight at 423 K in an open container, Urea_423K_open_24h, again a clear correspondence can be observed with the spectrum of biuret, indicating biuret is the main compound in the solid. The spectrum of the analogue material prepared in a closed container (Urea_423K_closed_24h), shows some small features suggesting the presence of urea, similar to that of the Urea_406K_closed_24h sample. The sample prepared at 423 K, however, contained a less broad band in the 3500–3000 cm−1 region, suggesting a lower content of physisorbed water possibly due to a faster rate of evaporation and decomposition. No features could be observed suggesting the presence of other model compounds involved in the formation of urea deposit formation such as ammelide, carbodiimide, melamine and cyanuric acid.
3.1.2. Urea Deposits Prepared Above 423 K
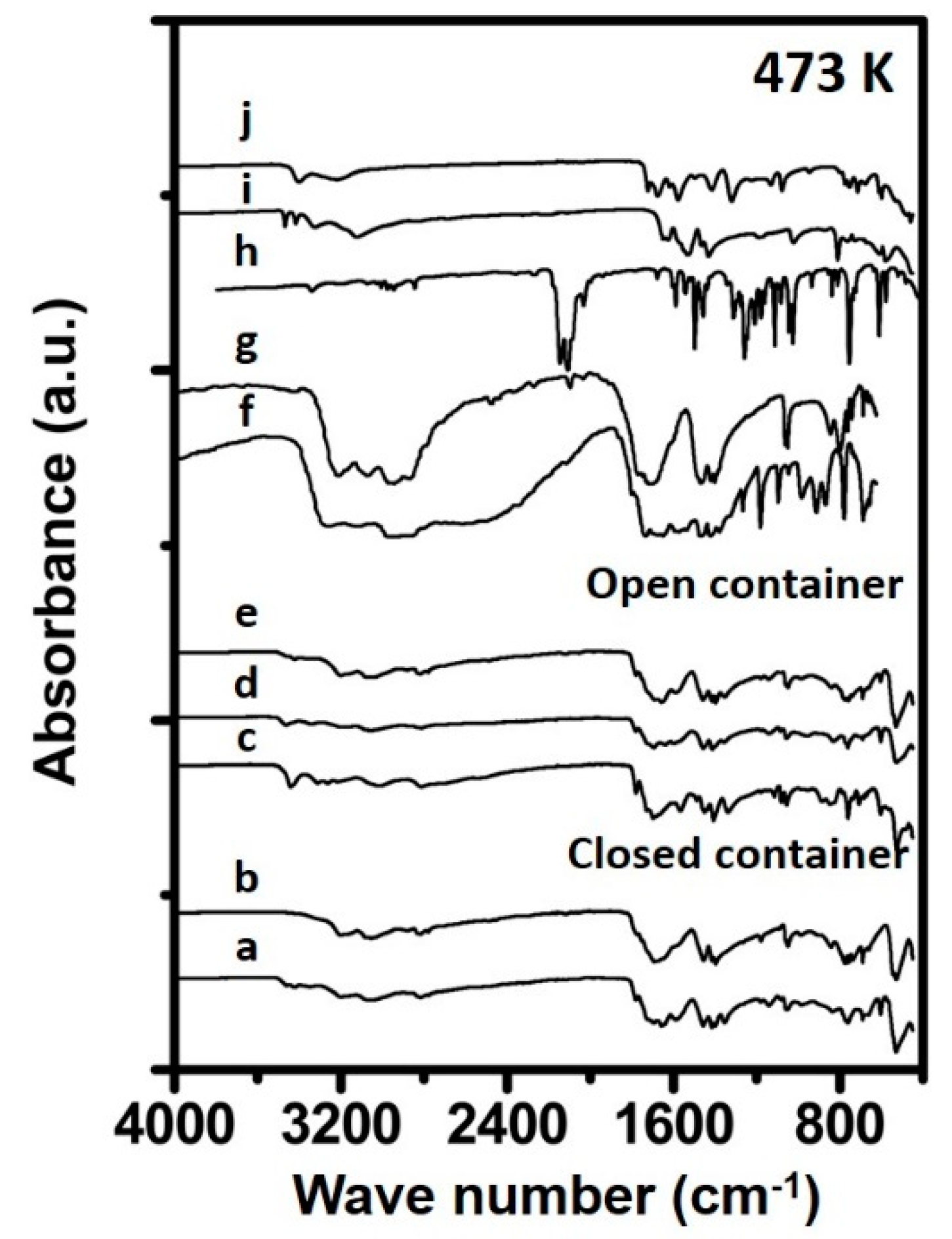
The FTIR spectra measured for the samples prepared at 473 K are shown in Figure 2. The spectrum recorded for Urea_473K_open_1h reveals some features in the fingerprint region indicative for biuret, being 1321, 1414 and 1579 cm−1 and suggests mainly biuret to be present in the sample. The sample prepared in a closed container for 1 h still consisted as an aqueous solution and could therefore not be measured in FTIR due to strong adsorption by water. The spectra recorded for the samples prepared for 4 h in an open (Urea_473K_open_4h) and closed container (Urea_473K_closed_4h) suggest that the compositions of these materials resemble a mixture consisting mainly of biuret and cyanuric acid. From the FTIR spectrum of Urea_473K_closed_24h, a strong resemblance can observed with the FTIR spectrum recorded of solid cyanuric acid. Bands in the fingerprint region which are especially indicative for cyanuric acid are located at 1048, 1459 and in the higher region at 3196 cm−1. Furthermore, bands were observed at 1560, 1470 and 1440 cm−1 which are assigned to triazine ring absorption [18,24] When comparing the spectrum line of the sample measured over the full region (4000–400 cm−1) with that of the reference cyanuric acid a strong resemblance is evident between both materials. This suggests that the major part of the prepared sample consists of cyanuric acid. Similar observations apply to the FTIR spectrum of Urea_473K_open_24h is, suggesting this sample also mainly consists of cyanuric acid.
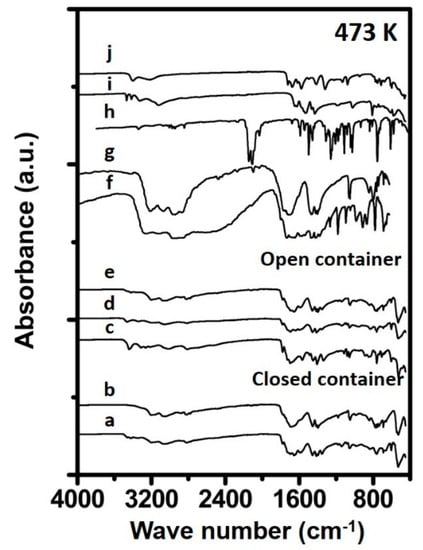
Figure 2.
Spectra of synthesized samples and reference materials prepared at 473 K. The spectra correspond to (a) 4 h in closed container, (b) 24 h in closed container (c) 1 h in open container, (d) 4 h in open container, (e) 24 h in open container, (f) Ammelide reference, (g) Cyanuric acid reference, (h) Carmobodi-imide reference, (i) Melamine reference and (j) Biuret reference.
The FTIR spectrum of the sample prepared for 1 h at 523 K in a closed container (Figure 3), only shows one small feature indicative for urea, at 3442 cm−1. Samples for 1 h treated in an open container, or for longer times, do not show such feature, suggesting the absence of a urea phase in the prepared samples. Both the samples, prepared in an open or closed container, retrieved from the oven after 1 h contain a small feature at 3417 cm−1 is indicative of the presence of biuret. This feature was not observable for the samples subjected to 4 h of heat treatment at 523 K. However, a feature at 1048 cm−1 is visible, suggesting the presence of a cyanuric acid phase in the solid materials. The spectral lines of samples prepared in an open container, and close container, correlate close to each other. This suggests that at 523 K and a preparation time of 4 h the final composition of the prepared urea deposit is highly similar between samples prepared in a closed and open container. Besides features corresponding to cyanuric acid vibrations, new absorbance bands can also be observed, which indicates the presence of an ammelide phase. The comparison of the spectra of Urea_523K_open_4h and Urea_523K_closed_4h, with that of reference ammelide reveals an indicative band at 1178 cm−1, suggesting the presence of such phase. The Urea_523K_closed_24h spectrum shows features indicative for both cyanuric acid and ammelide, although the intensity of the absorbance band at 1178 cm−1 increases with longer thermal treatment times. This suggests an increased concentration of ammelide to be present in the sample prepared for 24 h compared to that of the sample prepared for 4 h in a closed container. The spectrum Urea_523K_open_24h closely correlates to that of the reference ammelide. From this it can be assumed that the Urea_523K_open_24h consists mainly of an ammelide type phase.
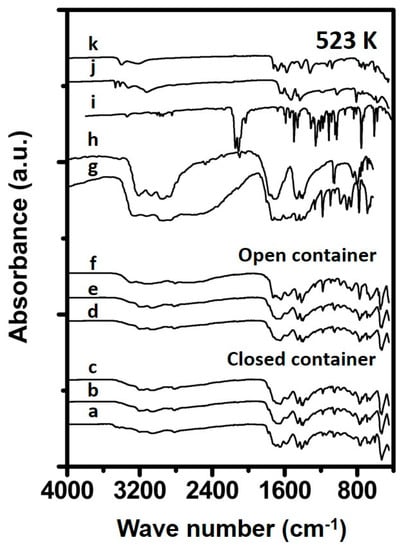
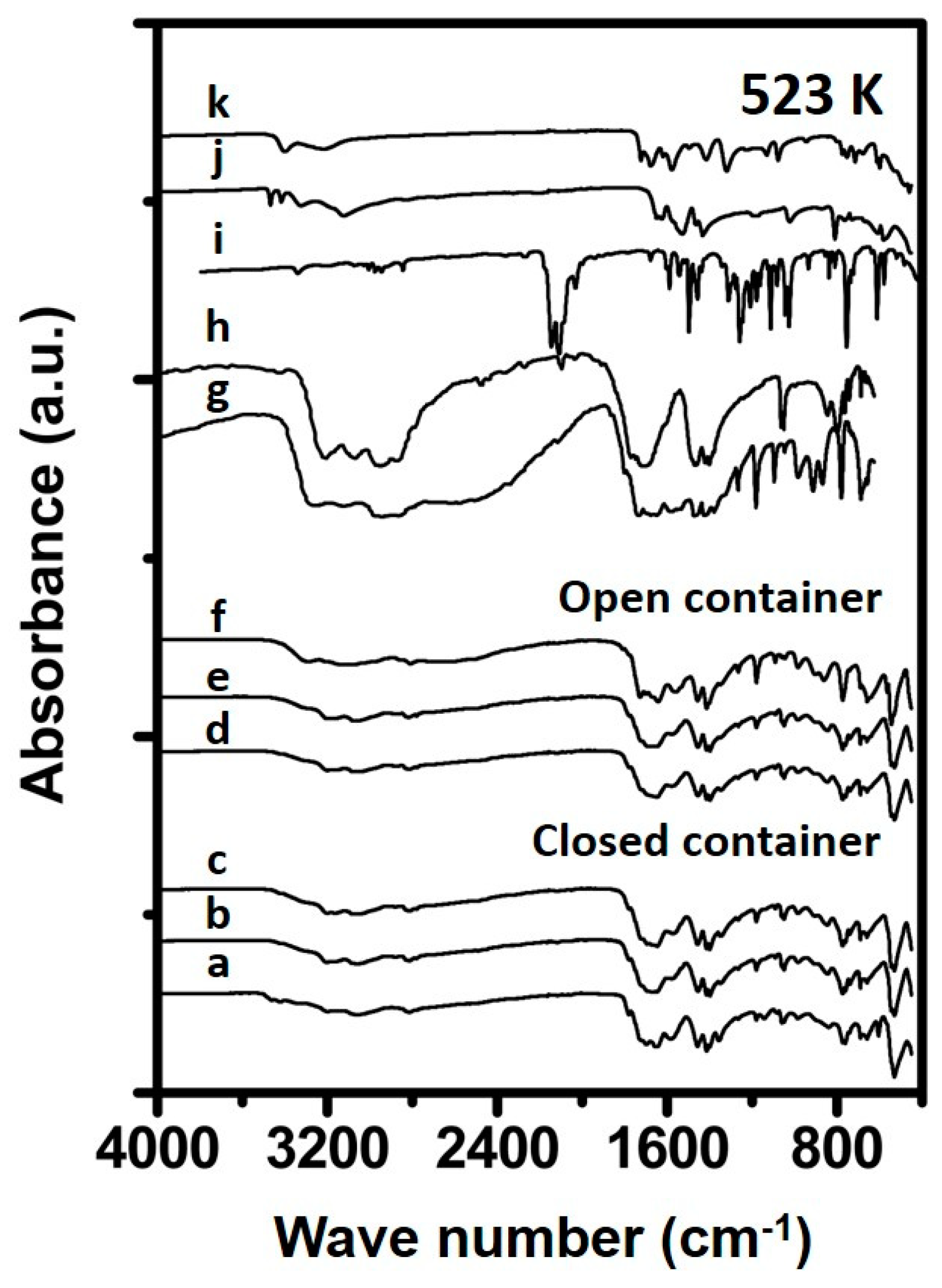
Figure 3.
Spectra of synthesized samples and reference materials prepared at 523 K. The spectra correspond to (a) 1 h in closed container, (b) 4 h in closed container, (c) 24 h in closed container (d) 1 h in open container, (e) 4 h in open container, (f) 24 h in open container (g) Ammelide reference, (h) Cyanuric acid reference, (i) Carmobodi-imide reference, (j) Melamine reference and (k) Biuret reference.
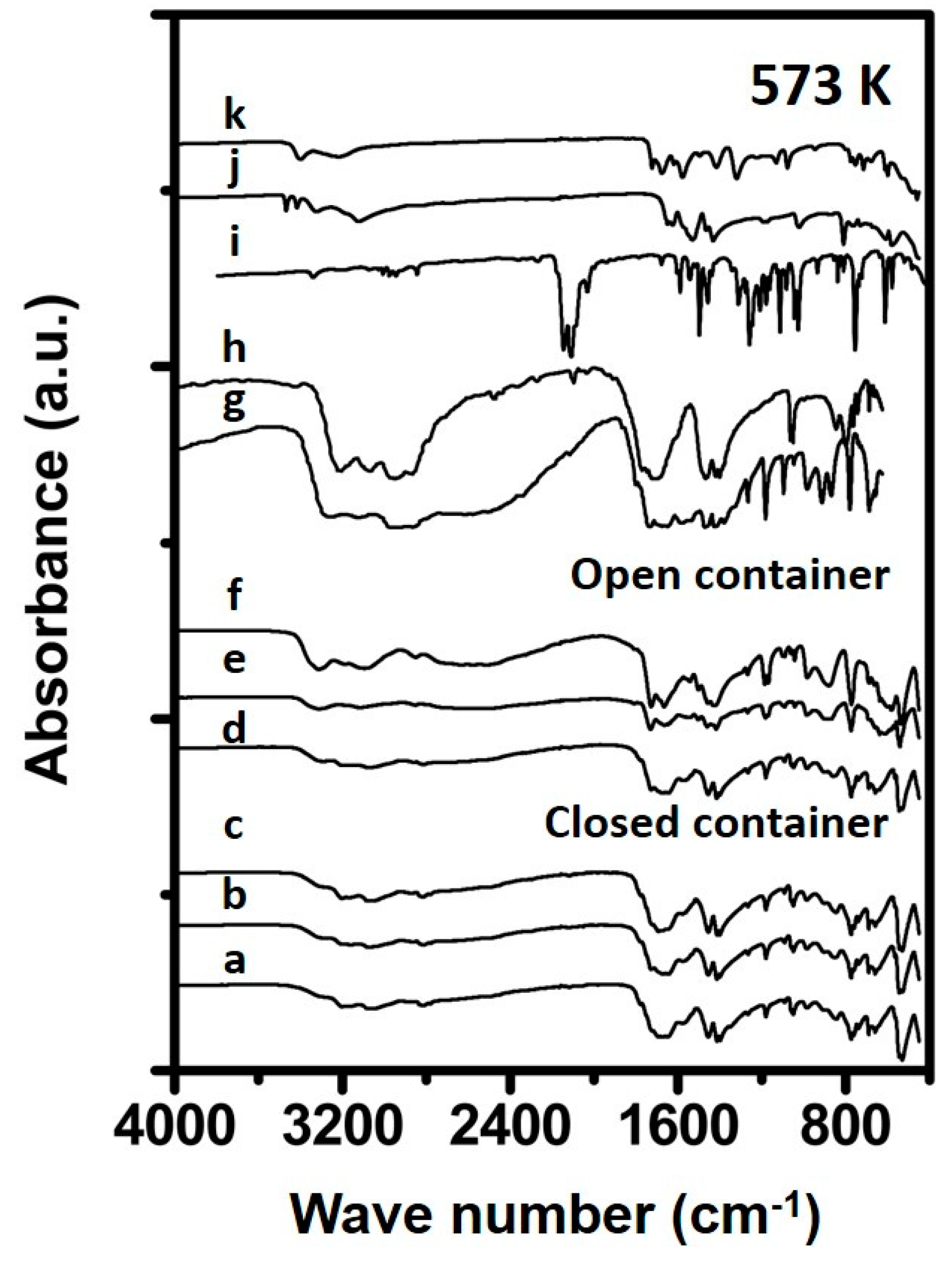
The spectra of the samples prepared at 573 K are shown in Figure 4. The FTIR spectra of the samples Urea_573K_open_1h and Urea_573K_closed_1h contain features in the fingerprint region at 1048 and 1459 cm−1 indicative for cyanuric acid. Furthermore, a feature at 1178 cm−1 and a small feature at 1735 cm−1 can be seen in the spectra, indicative for the presence of ammelide in the solid phase material. Increasing the exposure time to 4 h results in an increase of intensity of the 1178 cm−1 band in the FTIR spectrum. The bands at 1057 and 1459 cm−1 decrease in intensity upon increasing the exposure time to a temperature of 573 K from 1 to 4 h, suggesting a lower content of cyanuric acid. This agrees with the literature, which suggests the formation of ammelide and more aminated products from cyanuric acid upon heat exposure above 573 K [10]. Differences are observable between the materials prepared in an open and a closed container. The material prepared in an open container contains, besides the ammelide features at 1178, 1660 and 1735 cm−1, also features indicative for melamine-like features, namely absorbance bands at 3121 and 3332 cm−1. These bands have been attributed previously to symmetric and asymmetric stretching vibrations of N-H [24]. The material prepared in a closed container contained mainly features related to ammelide and some small features originating from cyanuric acid. When increasing the treatment time to 24 h, these differences between spectra of Urea_573K_open_24h and Urea_573K_closed_24h samples become more apparent, showing high concentrations of cyanuric acid for the material prepared in the closed container. Whilst the material prepared in the open container consists mainly of ammelide and melamine. These findings suggest that the presence of moisture at a treatment temperature of 573 K inhibits the formation of highly aminated triazine materials, while under dry conditions, triazine and tri-triazine type frameworks start to form.
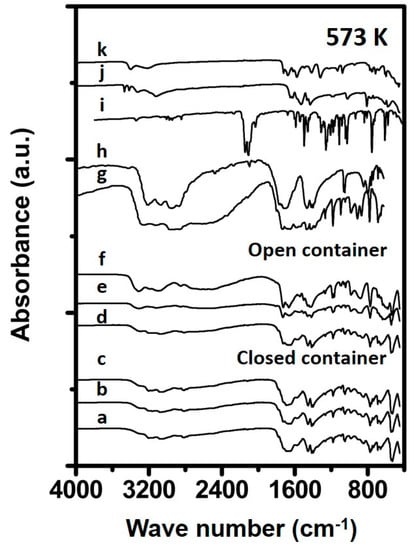
Figure 4.
Spectra of synthesized samples and reference materials prepared at 573 K. The spectra correspond to (a) 1 h in closed container, (b) 4 h in closed container, (c) 24 h in closed container (d) 1 h in open container, (e) 4 h in open container, (f) 24 h in open container, (g) Ammelide reference, (h) Cyanuric acid reference, (i) Carmobodi-imide reference, (j) Melamine reference and (k) Biuret reference.
When studying the FTIR spectra of the materials prepared at 623 K for 1 and 4 h in a closed container (Figure 5), one can observe spectral features resembling those of reference ammelide, while the material prepared for 24 h, results in a spectrum strongly suggesting a large melamine phase. The spectra of the deposits prepared in an open container for 1 and 4 h resemble to that of melamine. Interestingly, the spectrum of Urea_623K_open_24h shows new bands at 1610, 1440 and 803 cm−1 which have been attributed to cyameluric ring vibrations which consist of fused triazine rings [16,24]. Such rings are likely formed upon breakage, and formation of triazine rings, and have been reported to be formed at temperatures of 623 K [16,24].
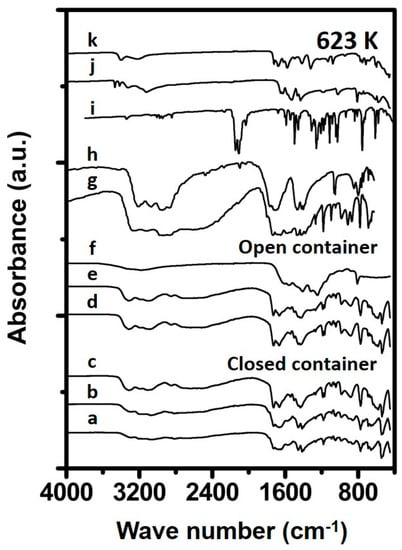
Figure 5.
Spectra of synthesized samples and reference materials prepared at 623 K. The spectra correspond to (a) 1 h in closed container, (b) 4 h in closed container, (c) 24 h in closed container (d) 1 h in open container, (e) 4 h in open container, (f) 24 h in open container, (g) Ammelide reference, (h) Cyanuric acid reference, (i) Carmobodi-imide reference, (j) Melamine reference and (k) Biuret reference.
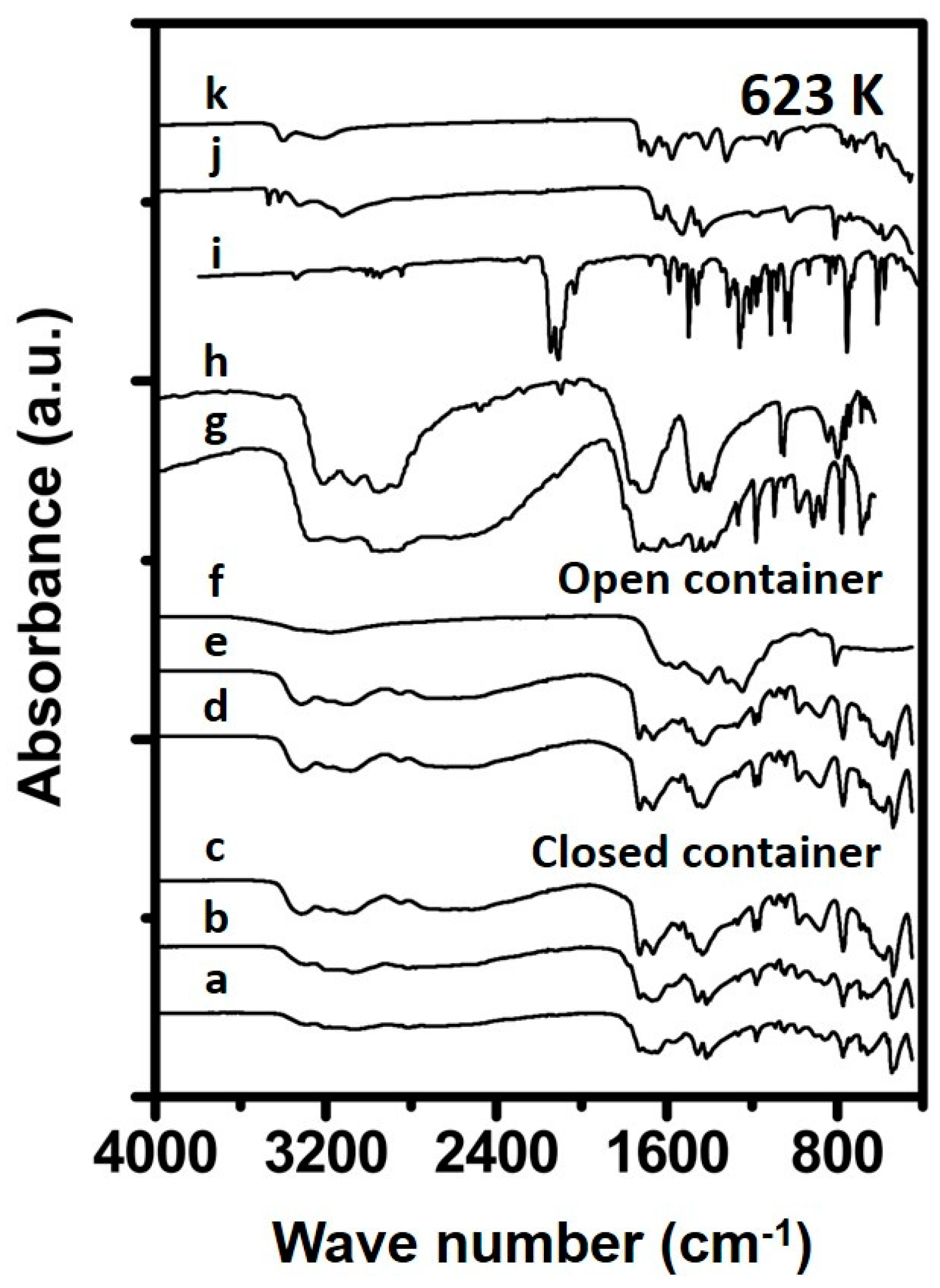
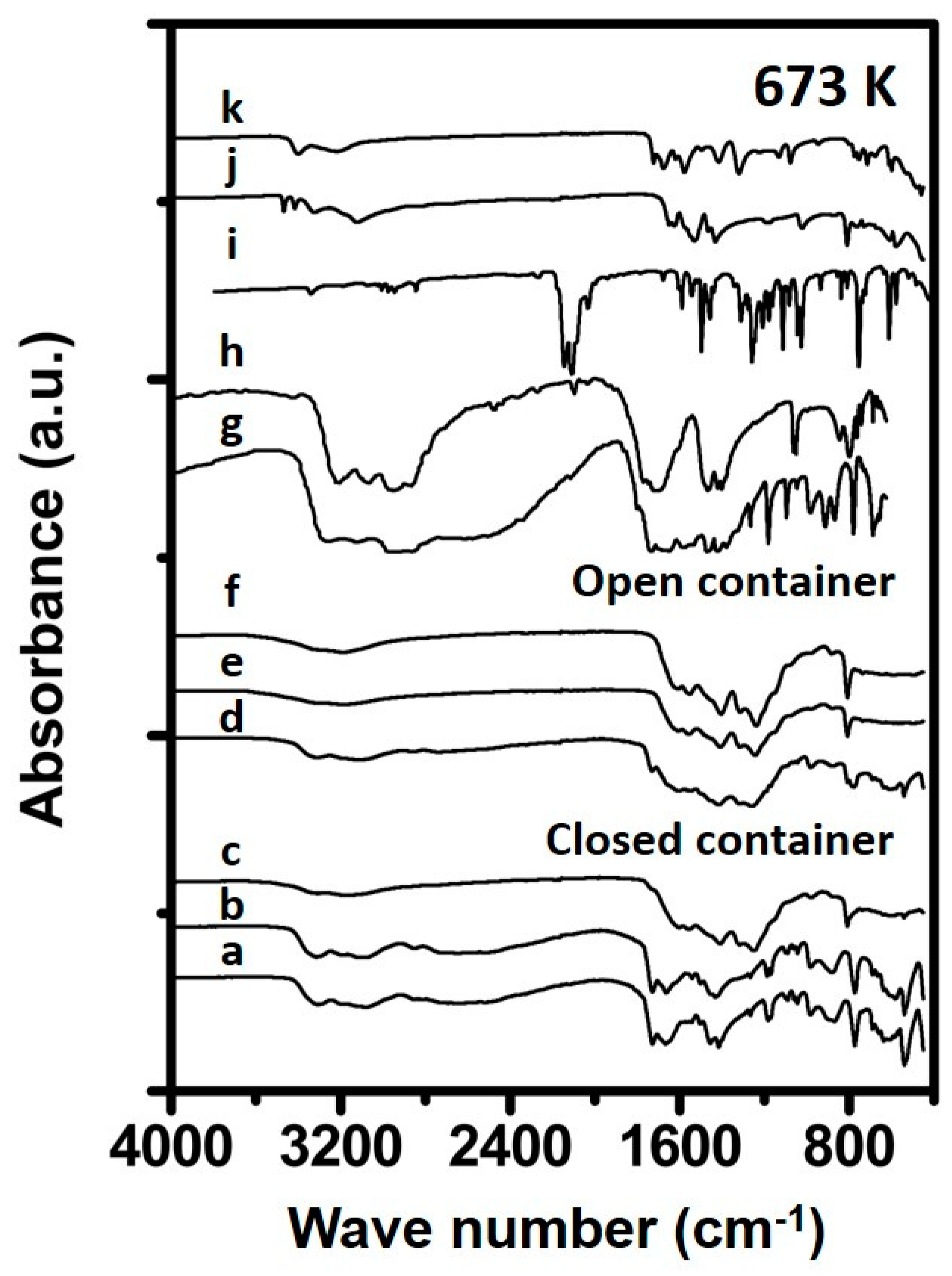
The spectra of Urea_673K_open_4h reveals a substantial different spectrum (Figure 6) compared to the spectra shown before, having bands at 1610, 1440 and 803 cm−1, indicating cyameluric rings, originating from fused triazine rings [16] which are likely formed upon breakage and formation of single triazine rings originating from components like melamine [16]. The samples prepared in a closed container for 1 (Urea_673K_closed_1h) and 4 h (Urea_673K_closed_4h) contain features indicating ammeline to be the main constituent in the sample. The sample prepared for 24 h shows features comparable to that of the samples prepared in an open container, suggesting the formation of substances containing fused triazine rings.
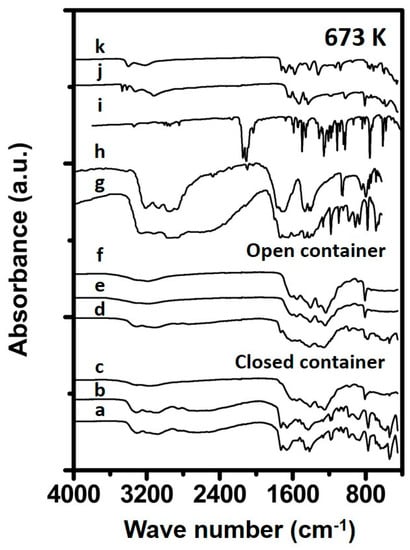
Figure 6.
Spectra of synthesized samples and reference materials prepared at 673 K. The spectra correspond to (a) 1 h in closed container, (b) 4 h in closed container, (c) 24 h in closed container (d) 1 h in open container, (e) 4 h in open container, (f) 24 h in open container, (g) Ammelide reference, (h) Cyanuric acid reference, (i) Carmobodi-imide reference, (j) Melamine reference and (k) Biuret reference.
3.2. Thermal Decomposition Experiments
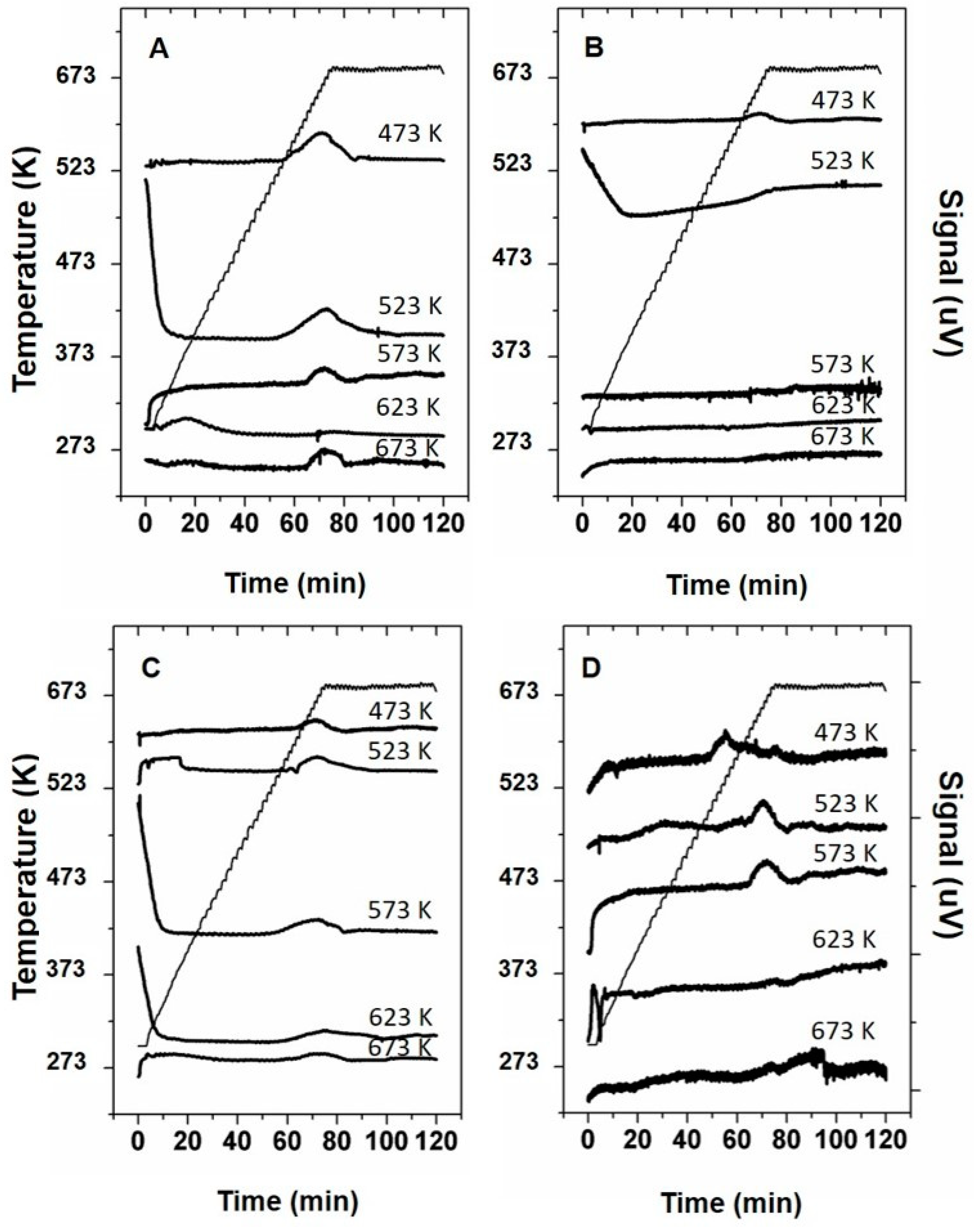
The qualitative analysis of the Temperature Programmed Decomposition (TPD) properties for samples prepared in the 473–673 K temperature region was done by conducting TPD experiments. The curves recorded during the TPD experiments are shown in Figure 7. The effect of humidity on the thermal decomposition of the samples prepared in an open container was evaluated by comparing the curves between experiments conducted under dry or humid conditions. Interestingly, materials prepared at 473 and 523 K in an open container and treated under dry conditions reveal a relatively large peak, starting at approximately 583 K. Such peak is indicative for the evolution of decomposition products originating from the deposit materials [11,15] or sublimation of volatile components present in the deposit materials [11]. The decomposition of the materials prepared at higher temperatures results in smaller peak at higher treatment temperatures starting at ~623 K. Conducting TPD experiments on the same samples prepared in an open container under wet conditions but treated in dry of humid conditions only results in an small peak for the sample prepared at 473 K at a temperature of 623 K. The other samples show an increase In TPD signal at ~623 K suggesting a broad decomposition peak.
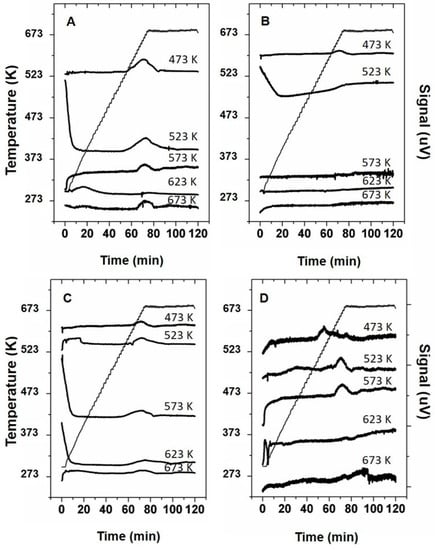
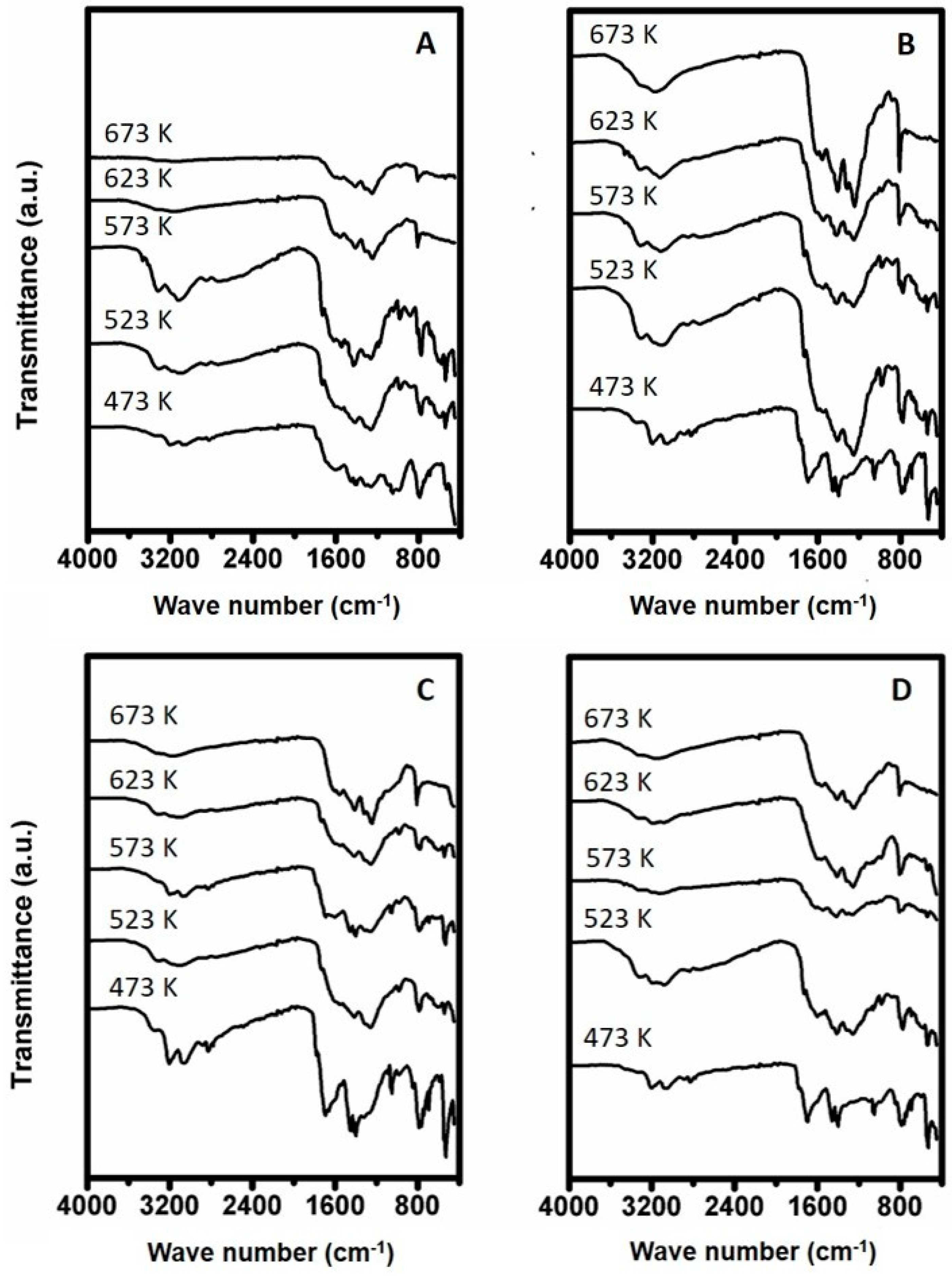
Figure 7.
Temperature Programmed Decomposition (TPD) curves of urea deposit samples prepared between 473 K and 673 K being prepared in (A) open container and treated in dry air, (B) open container and treated in 10% humid air, (C) closed container and treated in dry air and (D) closed container and treated in 10% humid air.
When comparing the TPD curves of the samples prepared in a closed container, the samples prepared at 473 K show a decomposition peak starting to evolve at ~533 K under moist conditions. From the literature as reported in Table 1, this suggests that this peak represent cyanuric acid sublimating from the samples. A second smaller peak starts to evolve at ~583 K suggesting the sublimation of ammelide. Furthermore, a third large peak is observable for this sample starting at 633 K, which can be correlated to the decomposition of cyanuric acid. Similar peaks, but lower in intensity are observable for the sample prepared at 523 K. The sample prepared at 573 K only shows a peak at 623 K. The samples prepared at higher temperatures only contain minor features. When conducting the same experiment under dry conditions the peaks at 533 and 583 K are not observable for the sample prepared at 473 and 523 K and only contain a feature starting at 623 K. The sample prepared at 623 K contains a broader feature starting from 583 K, suggesting sublimation of ammelide. The feature observable in the TPD curve of the sample prepared at 523 K extends well into the 673 K temperature region, indicating sublimation and/or degradation of larger triazine compounds, like melamine or the degradation of polymeric triazine species.
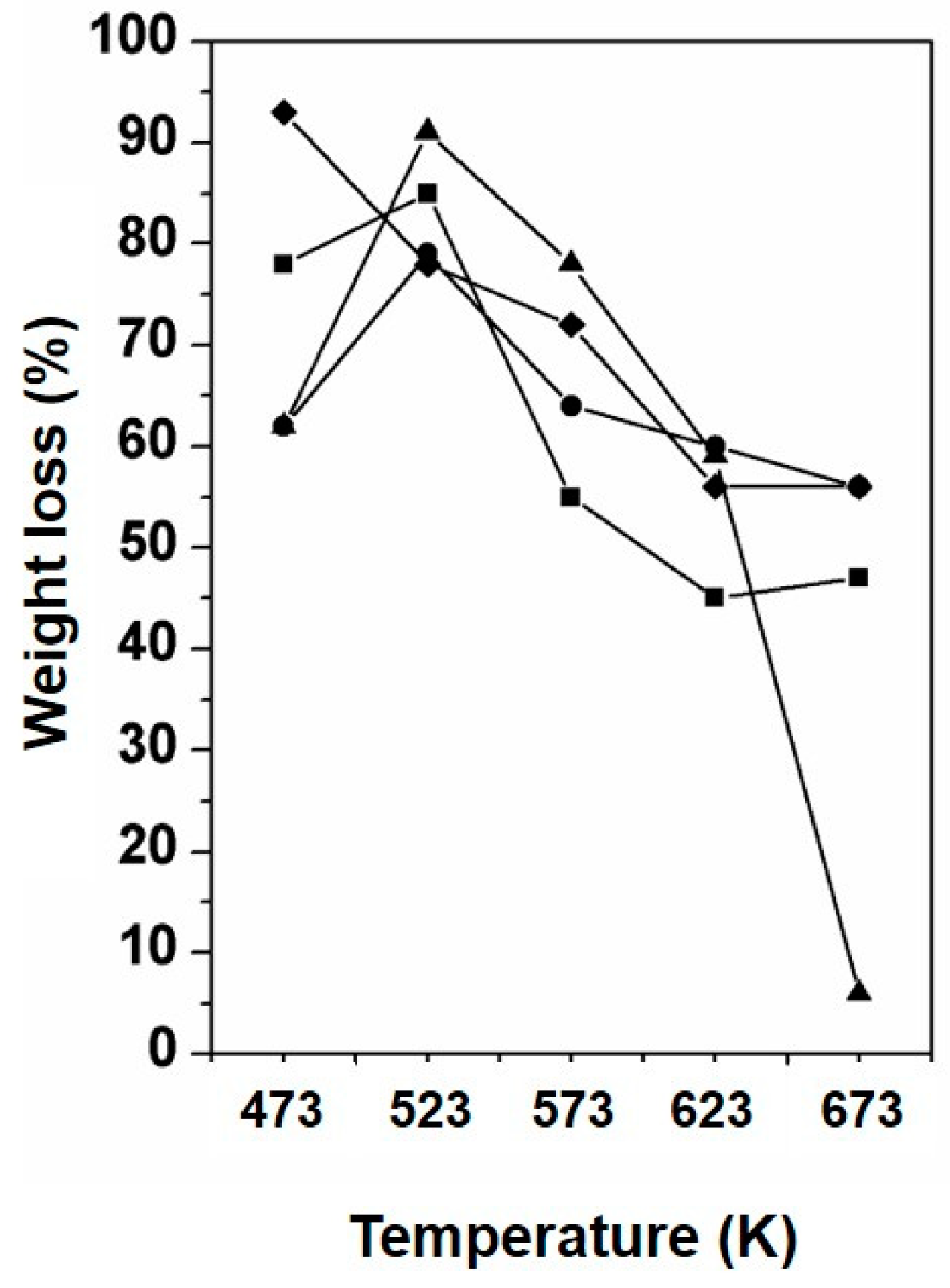
The weight loss of the sample upon the TPD experiments was measured and is presented in Figure 8. The weight loss curves for samples prepared in an open container show the highest weight loss when these samples were prepared at 523 K. At higher preparation temperatures the weight loss during TPD levels off at ~45% under dry conditions and ~55% under humid conditions. The weight loss curve for the samples prepared in a closed container also reveals an optimum in weight loss under dry conditions for the sample prepared at 523 K. Interestingly, the weight loss under these conditions drops for the samples prepared above 623 K to approximately 10%. Under humid conditions the weight loss decreases steadily from 94% for the sample prepared at 473 K to ~55% for the sample prepared at 673 K. Furthermore, the TPD experiment was repeated for the sample prepared at 673 K under N2 gas flow. The weight loss measured for these samples was ~1 wt% for samples prepared in open and closed containers and treated under dry and wet conditions.
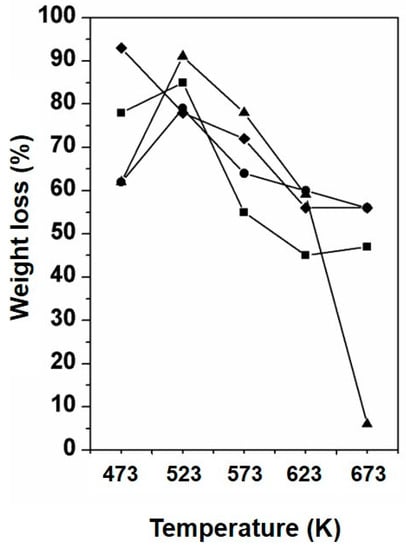
Figure 8.
Weight loss after TPD experiments of urea deposit samples prepared between 473 K and 673 K and treated in; (■) open container and treated in dry air, (●) open container and in 10% humid air, (▲) closed container and in dry air, and (♦) closed container and in 10% humid air.
The FTIR spectra of the samples recovered after the TPD experiments are shown in Figure 9. The spectra of the remaining solids originating from urea deposit prepared at 523 K, in an open container, and having been treated in dry air gas, contain absorbance bands which closely resemble that of cyanuric acid such as the vibrational band at 3196 cm−1. The sample prepared at 523 K resembles an FTIR spectrum more closely relating to ammelide, containing bands at 3121 cm−1. These bands become more distinctive for the sample prepared at 573 K after TPD. Furthermore, bands start to appear indicative for the presence of melamine at 3190 and 3332 cm−1. Furthermore, a small band start to appear at 803 cm−1 which has been attributed to cyameluric ring vibrations [16,24]. This band becomes more distinctive with higher preparation temperature, whereas the bands in the higher vibration region (4000–3000 cm−1) decrease in intensity suggesting loss in functional groups. This would indicate the formation of large molecules consisting of a polymeric triazine type.
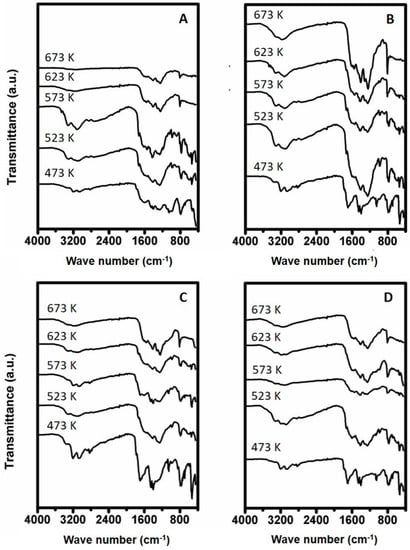
Figure 9.
FTIR spectra recorded of the samples recovered after TPD experiments of urea deposit samples prepared between 473 and 673 K being prepared in (A) open container and treated in dry air, (B) open container and treated in 10% humid air, (C) closed container and treated in dry air and (D) closed container and treated in 10% humid air.
The samples prepared in an open container but treated in humid air are shown in Figure 9B. The sample prepared at 473 K contains vibrations closely relating to that of cyanuric acid at 3196 cm−1, 3050, 2930 and 2860 cm−1. Furthermore, the fingerprint region contains bands representative for cyanuric acid with a sharp band at 1046 cm−1 being the most distinctive. The material prepared at 523 K reveals absorbance bands to be present in the FTIR spectrum correlating to a melamine type of compound to be the main constituent. Bands present at 3121 and 3332 cm−1 are indicative for the presence of such phase. Furthermore, some minor features indicative for ammelide are present at 1735 cm−1, suggesting the presence of a small concentration of such phase. When comparing the spectra of samples after TPD the spectra reveal a stronger resemblance to that of reference melamine with increasing preparation temperature. Interestingly, the FTIR spectrum recorded for the sample prepared at 673 K reveals the bands in the higher absorption region (4000–3000 cm−1) to be seemingly less distinctive, suggesting a lower concentration of functional groups. Furthermore, a strong absorbance band is observed at 803 cm−1, indicating the presence of a large amount of cyameluric type of compounds.
The FTIR spectra of the samples prepared in a closed container recovered after TPD under dry conditions are depicted in Figure 9C. The FTIR spectra of samples prepared at 473 and 523 K reveal strong correlation to that of cyanuric acid. The samples prepared at 573 and 623 K contain features indicative for more aminated species, being melamine and ammelide. The sample prepared at 673 K shows spectral features comparable to that of larger polymeric triazine species or cyameluric properties. The spectra recorded for the materials prepared in a closed container and treated under moist conditions (Figure 9D), reveals that the recovered sample prepared at 473 K has features strongly corresponding to that of cyanuric acid. The sample prepared at 523 K resembles strongly to that of ammelide. The samples prepared at higher temperatures (573–673 K) correlate to compounds with a low concentration of functional groups and a high concentration of cyameluric rings.
4. Discussion
4.1. Formation Temperature versus Urea Deposit Composition
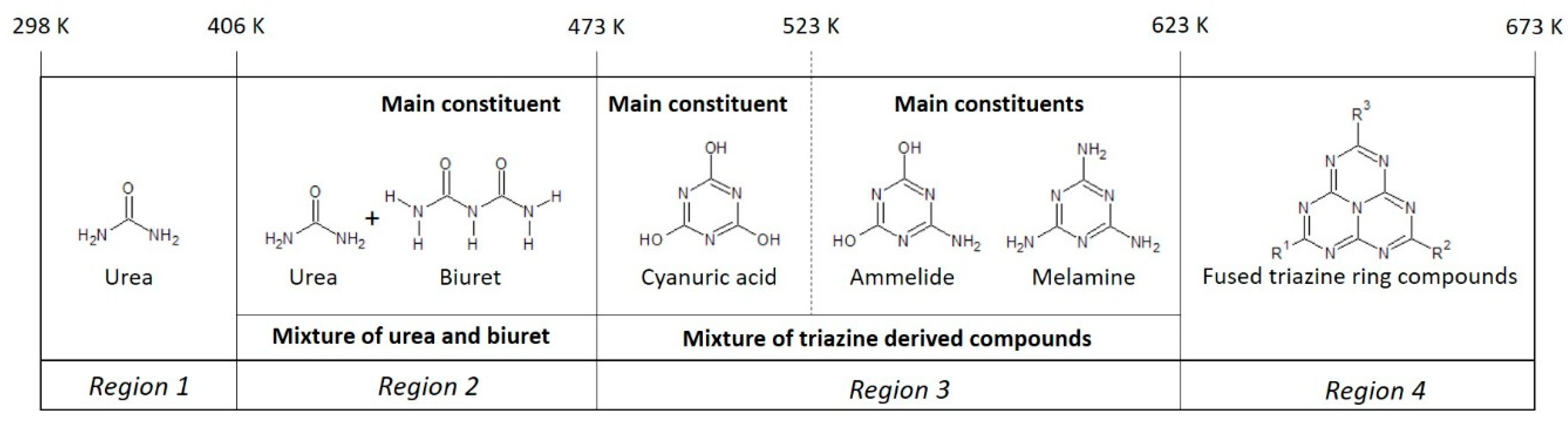
The effect of temperature and humidity of the formation on the molecular composition of the formed solids starting from a 32 wt% urea solution was investigated by conducting FTIR analysis on the prepared materials. Based on these results, two maps are proposed, relating the synthesis temperature to the final molecular composition of the formed urea deposit solids after 24 h of heat treatment in an open container (Figure 10) and a closed container (Figure 11). The temperature windows for the samples prepared in a closed container are shifted towards higher temperatures. Figure 10 shows the composition-temperature relation map of the urea deposits formed in an open container. From the map one can observe that in the first temperature window (298–406 K) urea remains the main constituent of the formed solid. In the second temperature (406–473 K) region solid biuret becomes the main constituent of the formed material. In the temperature window of 473–573 K triazine ring (C3N3) derivatives start being formed. At the low range of this region, at around 473 K, the main compound is cyanuric acid, while with increasing temperature, the molecules become increasingly more aminated. This eventually leads to the formation of high concentrations of ammelide, ammeline and melamine at 573 K. The decrease in concentration of cyanuric acid at increasing temperatures, can be attributed to its sublimation, starting at 523 K, and the decomposition into isocyanic acid starting in the temperature region of 593–603 K [15]. In the fourth and final temperature window (623–673 K), melamine is transformed into compounds consisting of connected triazine rings (melam, 633 K) or even fused triazine rings (melem, 673 K). The formation of such compounds has been suggested earlier to originate from the decomposition of melamine into cyanamide which can react with other melamine or melamine derivative molecules resulting in larger carbonitride networks [16]. This reaction is considered to start at a temperature 623 K. Increasing the temperature to 673 K, and above results in the faster formation of larger polytriazine ring compounds.
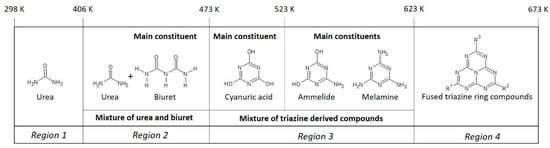
Figure 10.
Proposed map describing the compounds to be most prominent present in solids prepared upon 24 h of heat treatment of a 32 wt% urea solution in an open container.
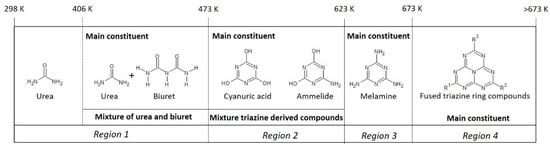
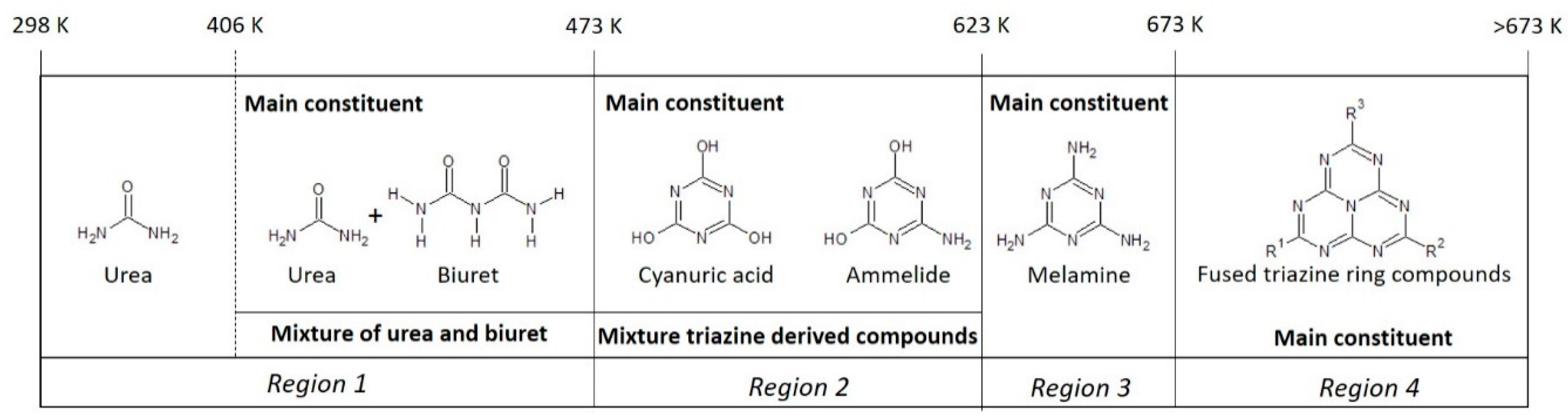
Figure 11.
Proposed map describing the compounds to be most prominent present in solids prepared upon 24 h of heat treatment of a 32 wt% urea solution in a closed container.
Similar to the solid samples prepared in an open container, a map has been constructed based on the FTIR results for the synthesized solids prepared in a closed container which is shown in Figure 11. The map shows the compounds mainly present in the solids, as obtained after 24 h of heat treatment of a 32 wt% urea solution, at various temperatures in a closed container. From this map, one can observe that the solids prepared in a closed container follow a similar pattern compared to the solids prepared in an open container, however the temperature regions seem to have shifted to higher temperatures. For instance, the map presents that the solids prepared in the first temperature region (298–473 K), consist mainly of urea and the presence of minor concentrations of biuret at the higher end of this temperature region. This indicates that the formation temperatures of the various compounds have shifted to higher temperatures, when being prepared in a closed container, as compared to thermal treatment in an open container. A possible explanation is that the closed container hampers the evaporation of water, causing a moist environment during the thermal treatment of urea. The water seems to inhibit the condensation reaction of urea to biuret and the formation of condensed triazine derived compounds, like cyanuric acid, ammeline and ammelide. This effect is likely due to the competing hydrolysis reactions caused by water, and thereby shifting the equilibrium back to urea. In the second temperature region (473–623 K) solids start to be formed consisting mainly of triazine derived compounds, with cyanuric acid being the main compound and some small concentrations of ammelide. At the higher end of the temperature region 2 (~573–623 K) ammelide becomes more prominently present in the solid. In temperature region 3 (623–673 K) melamine is the main constituent, whereas in temperature region 4 (>673 K) the molecular composition consists mostly of fused triazine rings.
4.2. Decomposition Behavior of Urea Deposits
The decomposition experiment reveals an optimum in decomposition rate for the samples prepared in an open container. These materials show an optimum in weight loss when deposits formed at 523 K are thermally treated under oxidative conditions. The measured TPD curves also show a strong peak at ~623 K for these samples, which suggests the sublimation of ammelide/ammeline/melamine molecules present in the material and the decomposition of cyanuric acid. Furthermore, such temperature has been identified by TGA as the oxidation temperature of melamine [25]. These findings correlate with the FTIR results, suggesting cyanuric acid, ammelide and melamine compounds to be mainly present in the materials prepared in the temperature region of 473–573 K. The relatively lower weight losses for the samples prepared at 623 K and 673 K can be explained by the presence of larger amounts of cyameluric compounds in the initially synthesized sample, like melem. Such compounds like melem first partially decomposes (~50 wt%) at 623 K, but not completely, and decompose further at ~773 K [26,27,28]. Furthermore, the formation of new melem molecules from melamine, present in relatively high concentrations in the samples synthesized at 623 K and 673 K [16]. The mechanism for the melem formation is the partial decomposition of melamine into cyanamide [16] and dicyanamide [16], which can react with other melamine molecules to form melem [16]. The samples treated under humid conditions follow a similar trend with an optimum in decomposition rate for the samples prepared at 523 K. The weight loss however is somewhat higher in the 623–673 K region. A possible explanation for the extended weight loss could be the competing hydrolysis reaction of melamine into cyanuric acid [15] preventing the alternative reaction pathway towards melem. The cyanuric acid formed upon hydrolysis can sublimate from the sample [11,15].
Alternatively, the samples prepared in a closed container show somewhat different trends compared to the samples prepared in an open container. The samples prepared in a closed container, but treated under dry conditions revealed the highest weight loss for the sample prepared at 523 K. The high degree in weight loss could be explained by the high concentration of cyanuric acid present in the initial deposit sample, as observed from the recorded FTIR spectrum after synthesis. The sublimation of cyanuric acid is indicated by the signal in the TPD curve at ~623 K. Interesting is the low decomposition rate for the sample prepared at 673 K. An explanation could be an exceptional high concentration of melamine which is transformed into cyameluric compounds via a partial decomposition pathway [16,28]. Treating the samples prepared in a closed container, in a humid atmosphere, show that the weight loss rates decrease with increasingly higher preparation temperature. The decomposition behavior in the 623–673 K region is similar to that of the samples prepared in a closed container. The discrepancy in decomposition behavior between dry and humid conditions could possibly be explained by the existence of hydrolysis reactions under wet conditions. The hydrolysis reaction competes in this way with formation of melem-type molecules via the partial decomposition reaction [16].
The use of oxidative conditions was shown to be beneficial in the decomposition of the samples prepared at 673 K regardless the synthesis conditions. Likely, the oxidative conditions contribute to the decomposition of melamine and cyamuleric type molecules. These findings coincide with findings reported in literature [15,27].
5. Conclusions
Herein, we report the effect of time (1 h, 4 h and 24 h) and temperature (298–673 K) on the molecular composition of urea deposits in the field of mobile heavy-duty SCR applications under conditions representative for real life. The synthesis under dry and moist conditions simulate both water deficient and water rich exhaust gas compositions, in order to investigate the effect of water on the formation of urea deposits and the final molecular composition. The findings are presented in two maps covering dry and moist conditions. The trend as observed in this study, reveals that at low temperatures the deposits mainly consist of urea derived compounds, like biuret and cyanuric acid. Increasing the temperature leads to an increase of more aminated mono-triazine compounds. At the highest synthesis temperature of 673 K, the main constituents are cyamuleric compounds consisting of fused triazine rings, like melem. Humid synthesis conditions hamper the formation of highly aminated compounds up to a synthesis temperature of 573 K, even after a synthesis period of 24 h. At higher temperatures (623 and 673 K) and a long synthesis period of 24 h, only minor differences are observed between samples prepared under dry or humid conditions.
The decomposition properties of the synthesized materials are optimal for the samples prepared at 523 K, whereas the lowest decomposition rates were observed for samples prepared at 623 and 673 K. A humid air gas flow was shown to be beneficial. The lowest decomposition rate was observed for the material prepared at 673 K under humid conditions and when the decomposition was performed under dry conditions. The decomposition behavior of samples prepared at 673 K was compared under oxidative and inert conditions and the rate of decomposition was shown to be substantially higher for these samples under oxidative conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.T., N.W., J.v.G., F.v.B., K.L., M.H., J.S., M.G., E.L.; methodology, C.T., N.W., J.v.G., F.v.B., K.L., M.H., J.S., M.G., E.L.; validation, C.T., N.W., J.v.G., F.v.B., K.L., M.H., J.S., M.G., E.L.; formal analysis, C.T., N.W., J.v.G., F.v.B., K.L., M.H., J.S., M.G., E.L.; investigation, C.T., N.W., J.v.G., F.v.B., K.L., M.H., J.S., M.G., E.L.; resources, C.T., N.W., J.v.G., F.v.B., K.L., M.H., J.S., M.G., E.L.; data curation, C.T., N.W., J.v.G., F.v.B., K.L., M.H., J.S., M.G., E.L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.T.; writing—review and editing, C.T.; visualization, C.T.; supervision, C.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Anenberg, S.C.; Miller, J.; Minjares, R.; Du, L.; Henze, D.K.; Lacey, F.; Malley, C.S.; Emberson, L.; Franco, V.; Klimont, Z.; et al. Impacts and mitigation of excess diesel-related NOx emissions in 11 major vehicle markets. Nature 2017, 545, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebel, M.; Elsener, M.; Kleemann, M. Urea-SCR: A promising technique to reduce NOx emissions from automotive diesel engines. Catal. Today 2000, 59, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Szanyi, J. On the hydrothermal stability of Cu/SSZ-13 SCR catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 560, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, U.; Lezcano-Gonzalez, I.; Weckhuysen, B.M.; Beale, A. Local environment and nature of Cu active sites in zeolite-based catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeets, M.; Resasco, D.E.; Wang, B. Enhanced chemical activity and wettability at adjacent Brønsted acid sites in HZSM-5. Catal. Today 2018, 312, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, R.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, R. Zeolite structure effects on Cu active center, SCR performance and stability of Cu-zeolite catalysts. Catal. Today 2018, 327, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, H.T.; Mayer, A.; Hartenstein, A. Off-Highway Exhaust Gas After-Treatment: Combining Urea-SCR, Oxidation Catalysis and Traps; SAE Paper No. 930363; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, W.R.; Klein, J.T.; Mueller, R.; Doelling, W.; Zuerbig, J. The Development of Urea SCR Technology for U.S. Heavy Duty Trucks; SAE Paper No. 2000-01-0190; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, S.D.; Kim, S.J.; Baik, J.H.; Nam, I.S.; Mok, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Cho, B.K.; Oh, S.H. Decomposition of Urea into NH3 for the SCR Process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 4856–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaber, P.M.; Colson, J.; Higgins, S.; Thielen, D.; Anspach, B.; Brauer, J. Thermal decomposition (pyrolysis) of urea in an open reaction vessel. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 424, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaber, P.M.; Colson, J.; Higgins, S.; Dietz, E.; Thielen, D.; Anspach, B.; Brauer, J. Study of the urea thermal decomposition (pyrolysis) reaction and importance to cyanuric acid production. Am. Lab. 1999, 31, 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Koebel, M.; Strutz, E.O. Thermal and hydrolytic decomposition of urea for automotive selective catalytic reduction systems: Thermochemical and practical aspects. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 2093–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koryakin, A.; Gal’perin, V.; Sarbaev, A.N.; Finkel’shtein, A.I. Thermographic analysis of urea and products of its pyrolysis. Zhurnal. Org. Khimii 1971, 7, 972–977. [Google Scholar]
- Asaoka, T.; Shimasaki, C.; Toriyama, H.; Yamada, H.; Sakano, M. Influence of Some Pretreatments on Thermal Decomposition of Urea. J. Soc. Chem. Ind. Jpn. 1969, 72, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard, A.M.; Peitz, D.; Elsener, M.; Wokaun, A.; Kröcher, O. Hydrolysis and thermolysis of urea and its decomposition byproducts biuret, cyanuric acid and melamine over anatase TiO2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 115, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jürgens, B.; Irran, E.; Senker, J.; Kroll, P.; Müller, H.; Schnick, W. Melem (2, 5, 8-triamino-tri-s-triazine), an important intermediate during condensation of melamine rings to graphitic carbon nitride: Synthesis, structure determination by X-ray powder diffractometry, solid-state NMR, and theoretical studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 10288–10300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, Z.; Müllner, M.; Lercher, J.A. Catalytic hydrolysis of s-triazine compounds over Al2O3. Catal. Today 1996, 27, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devallencourt, B.; Saiter, J.M.; Fafet, A.; Ubrich, E. Thermogravimetry/Fourier transform infrared coupling investigations to study the thermal stability of melamine formaldehyde resin. Thermochim. Acta 1995, 259, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Ahmad, F. Effects of zirconium silicate reinforcement on expandable graphite based intumescent fire retardant coating. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 103, 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Piasek, Z.; Urbanski, T. The Infra-red Absorption Spectrum and Structure of Urea. Bull. Acad. Pol. Sci. 1962, 10, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, Y.M.; Czarnik-Matusewicz, B.; Kim, S.B. Characterization of concentration-dependent infrared spectral variations of urea aqueous solutions by principal component analysis and two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 13008–13014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, C.L.; Ibeling, D.R.; Han, S.; Ludwig, L.; Ayyappan, P. Analytical investigation of urea deposits in SCR system. SAE Int. J. Engines 2015, 8, 1219–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querioz, D.P.; de Pinho, M.N. Structural characteristics and gas permeation properties of polydimethylsiloxane/poly(propylene oxide) urethane/urea bi-soft segment membranes. Polymer 2005, 46, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lv, P.; Hu, Y.; Hu, K. Thermal degradation study of intumescent flame retardants by TG and FTIR: Melamine phosphate and its mixture with pentaerythritol. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2009, 86, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzi-Nshuti, C.; Hossenlopp, J.M.; Wilkie, C.A. Fire retardancy of melamine and zinc aluminum layered double hydroxide in poly (methyl methacrylate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.L.; Walters, R.; Lyon, R.E.; Savitski, E.P. Thermal decomposition of cyanate ester resins. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 78, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gamel, N.E.A.; Seyfarth, L.; Wagler, J.; Ehrenberg, H.; Schwarz, M.; Senker, J.; Kroke, E. The tautomeric forms of cyameluric acid derivatives. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 1158–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzer, A.; Saplinova, T.; Kroke, E. Tri-s-triazines (s-heptazines)—From a “mystery molecule” to industrially relevant carbon nitride materials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 2032–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).