Influence of Mg2+ Ions on the Formation of Green Rust Compounds in Simulated Marine Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of (Fe,Mg)II-FeIII LDH
2.2. XRD Analysis
3. Results
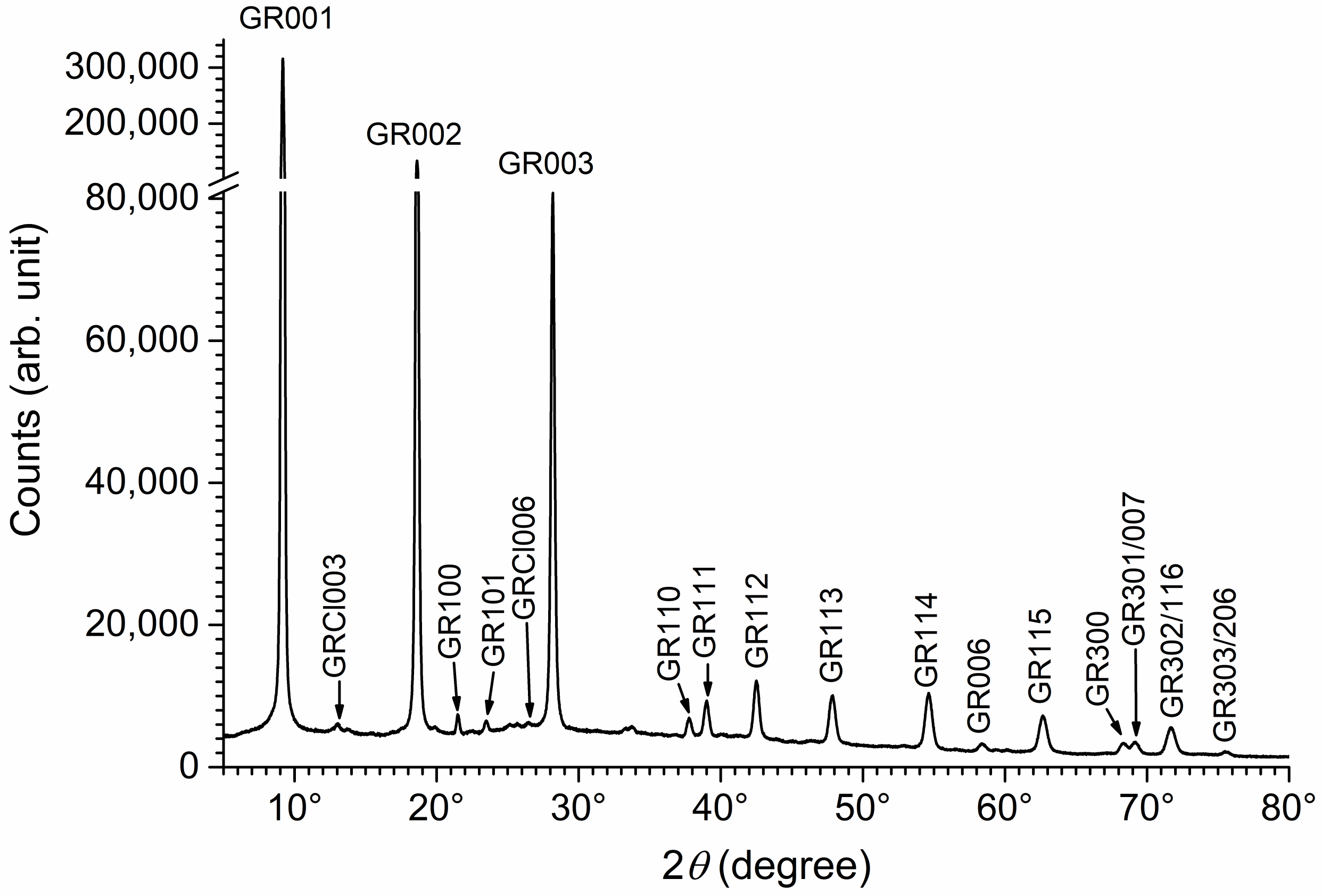
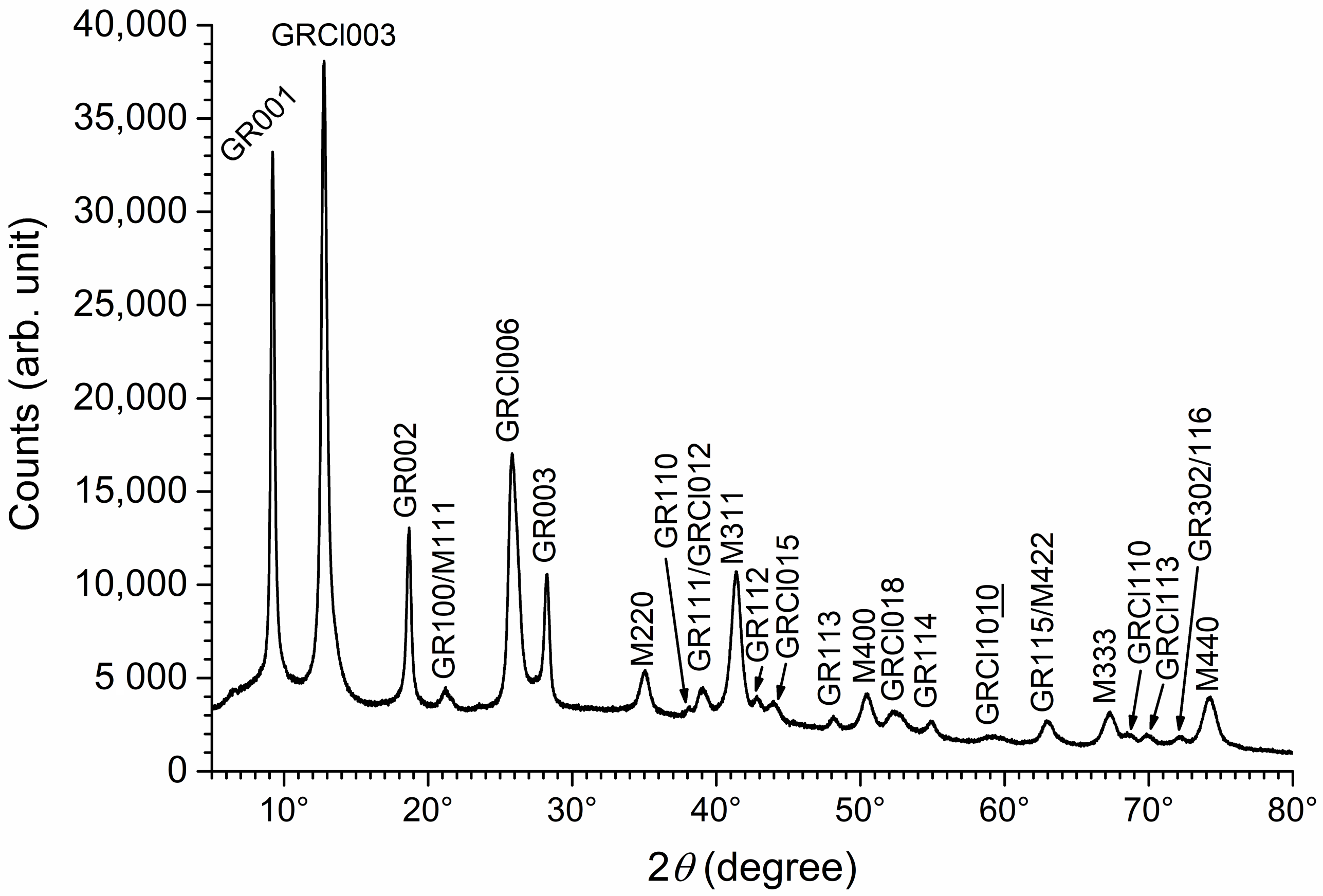
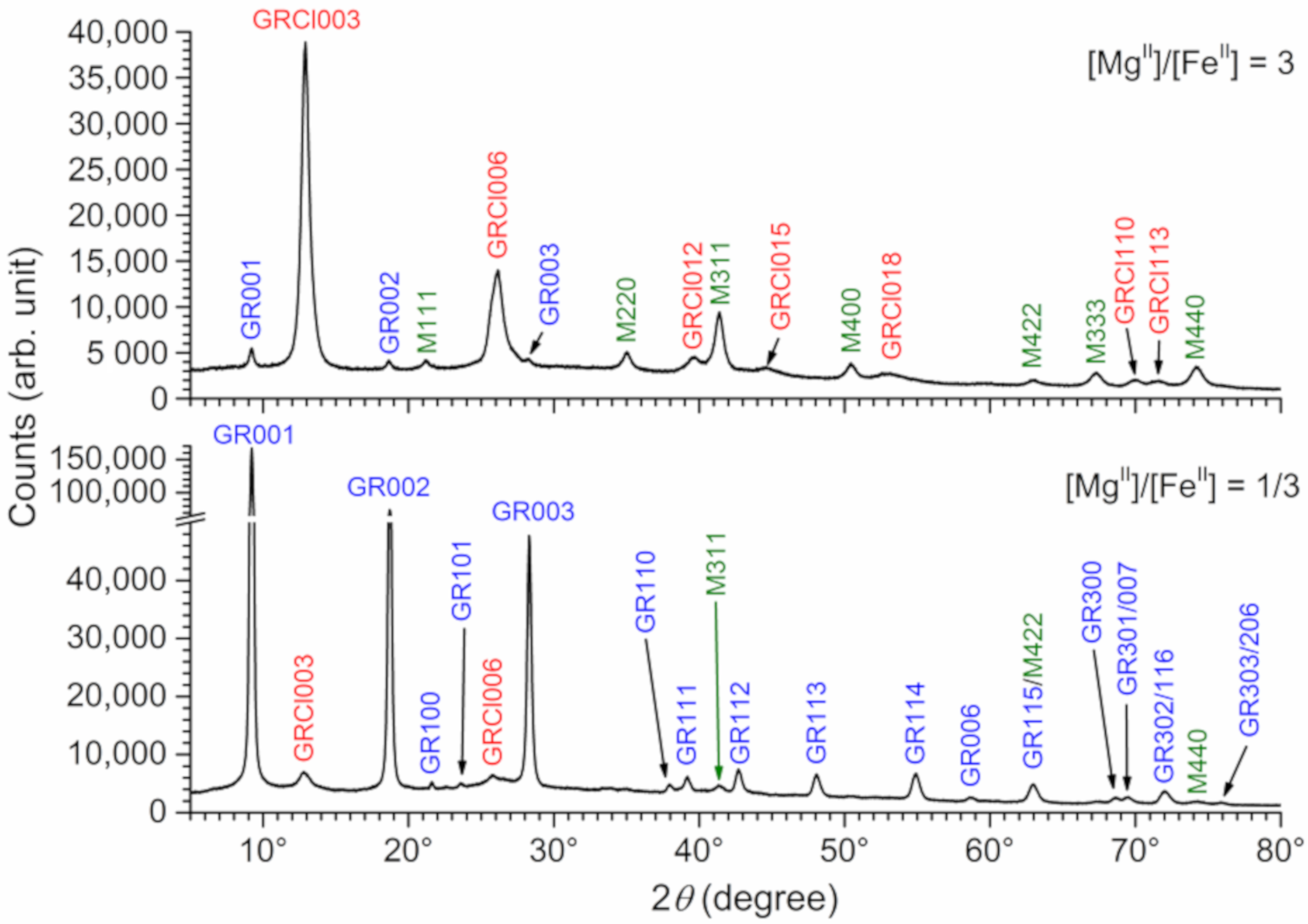
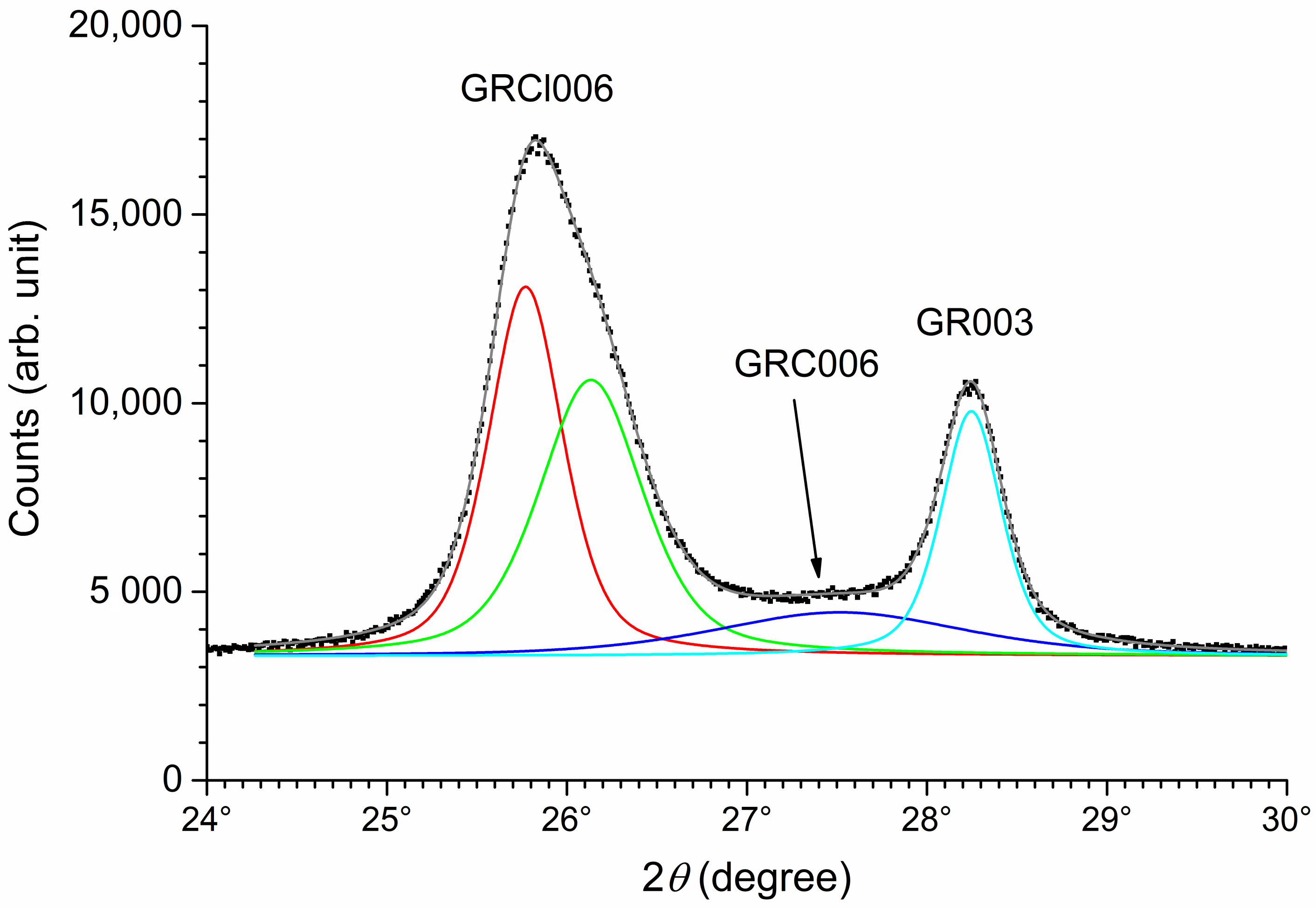
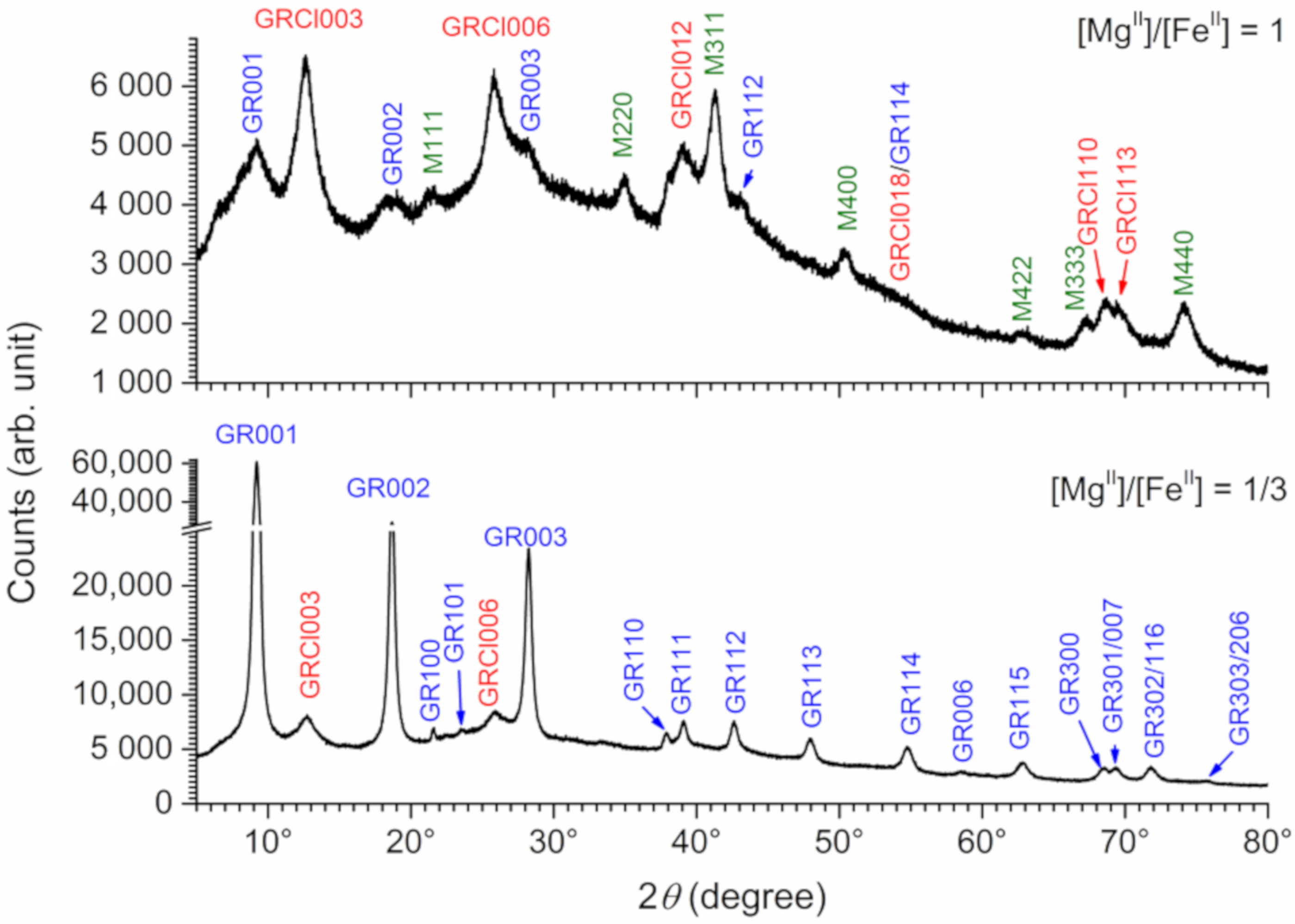
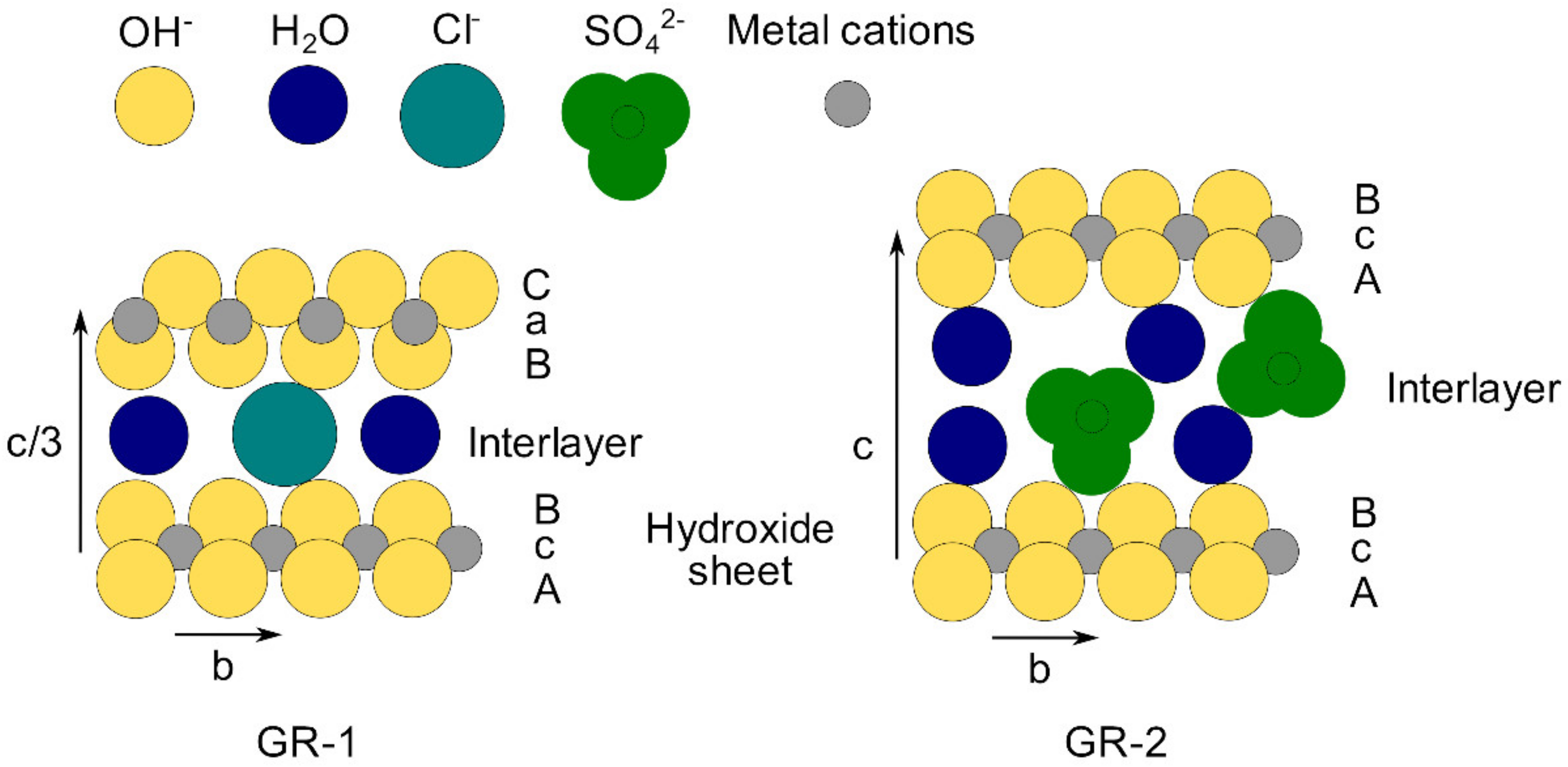
3.1. XRD Analysis of Aged Precipitates
3.2. XRD Analysis of Unaged Precipitates
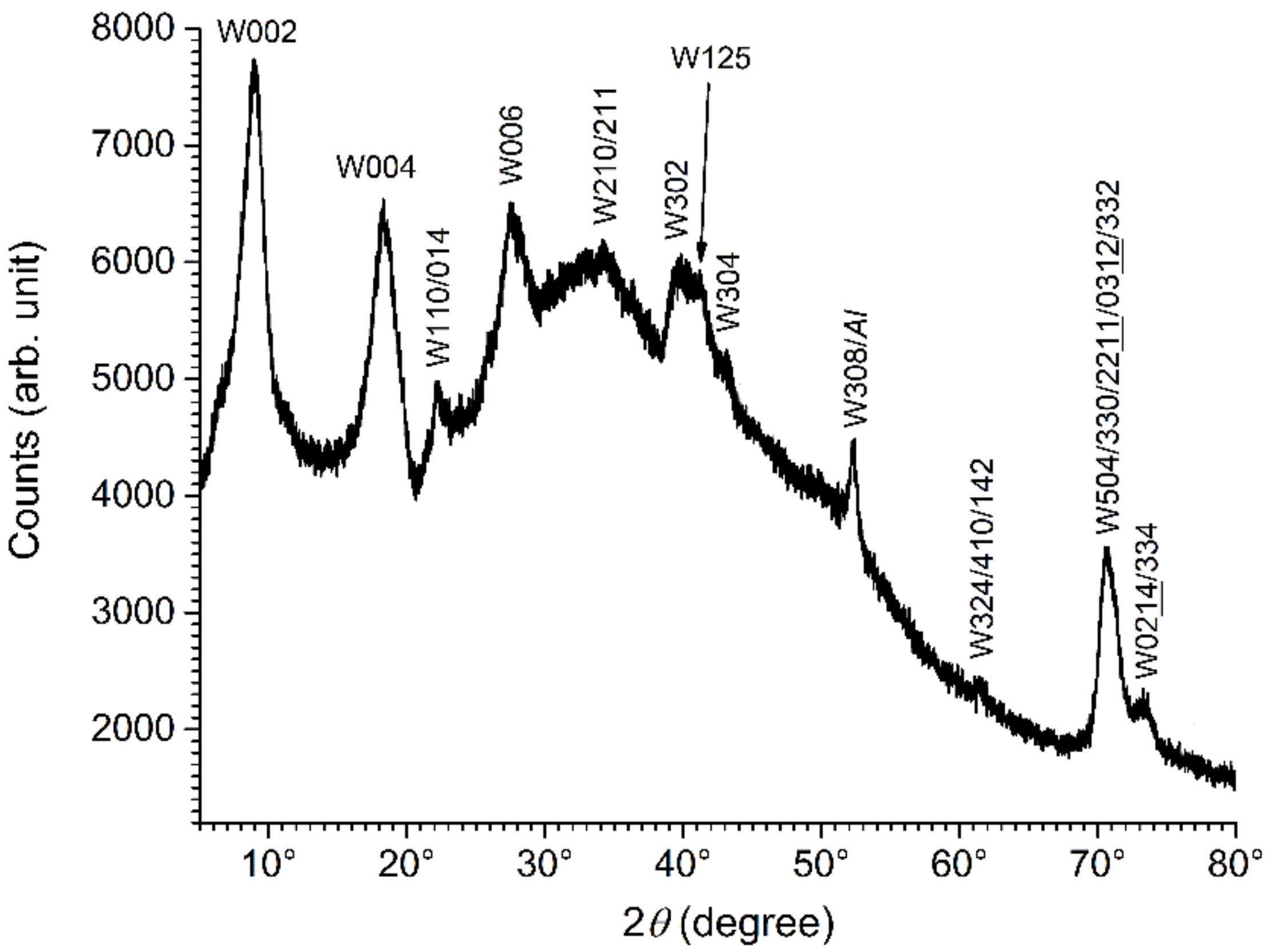
3.3. Analysis of the Mg(II)-Fe(III) Solid Phases Obtained in the Absence of Chloride
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- For [MgII]/[FeII] ratios higher than 1, the influence of Mg(II) is strong and induces the formation of GR(Cl−) and magnetite. In the absence of Fe(II), the Mg(II)-Fe(III) Cl-LDH, i.e., iowaite, is the only solid phase obtained.
- The influence of Mg2+ cations on the formation of the sulfated GR is not significant up to a [MgII]/[FeII] ratio of 1/3, where only a slight increase of the proportion of GR(Cl−) is observed. In the absence of Mg(II), only GR(SO42−) is obtained, with only traces of GR(Cl−), in agreement with the previous work [11].
- It is forwarded that the presence of Mg2+ cations in the hydroxide layers of the LDH structure of GR compounds favors the Cl- and CO3-GR-1 structure, thus hindering the formation of the SO4-GR-2 structure.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Refait, P.; Grolleau, A.-M.; Jeannin, M.; Rémazeilles, C.; Sabot, R. Corrosion of carbon steel in marine environments: Role of the corrosion product layer. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2020, 1, 198–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanneluc, I.; Langumier, M.; Sabot, R.; Jeannin, M.; Refait, P.; Sablé, S. On the bacterial communities associated with the corrosion product layer during the early stages of marine corrosion of carbon steel. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 99, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detournay, J.; De Miranda, L.; Dérie, R.; Ghodsi, M. The region of stability of green rust II in the electrochemical potential-pH equilibrium diagram of iron in sulphate medium. Corros. Sci. 1975, 15, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowe, A.; Génin, J. The mechanism of oxidation of ferrous hydroxide in sulphated aqueous media: Importance of the initial ratio of the reactants. Corros. Sci. 1991, 32, 965–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineau, S.; Sabot, R.; Quillet, L.; Jeannin, M.; Caplat, C.; Dupont-Morral, I.; Refait, P. Formation of the Fe(II-III) hydroxy-sulphate green rust during marine corrosion of steel associated to molecular detection of dissimilatory sulphite-reductase. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; Huang, G.; Du, M.; Hou, B. Corrosion of carbon steel influenced by anaerobic biofilm in natural seawater. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 54, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Grolleau, A.-M.; Jeannin, M.; François, E.; Sabot, R. Localized corrosion of carbon steel in marine media: Galvanic coupling and heterogeneity of the corrosion product layer. Corros. Sci. 2016, 111, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Jeannin, M.; Sabot, R.; Antony, H.; Pineau, S. Electrochemical formation and transformation of corrosion products on carbon steel under cathodic protection in seawater. Corros. Sci. 2013, 71, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Jeannin, M.; Sabot, R.; Antony, H.; Pineau, S. Corrosion and cathodic protection of carbon steel in the tidal zone: Products, mechanisms and kinetics. Corros. Sci. 2015, 90, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.P.; Chester, R. Introduction to Marine Chemistry; Academic Press: London, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Refait, P.; Sabot, R.; Jeannin, M. Role of Al(III) and Cr(III) on the formation and oxidation of the Fe(II-III) hydroxysulfate green rust. Colloids Surf. A Phys. Eng. Asp. 2017, 531, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucherit, M.N.; Goff, A.H.-L.; Joiret, S. Raman studies of corrosion films grown on Fe and Fe-6Mo in pitting conditions. Corros. Sci. 1991, 32, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.C.B. Composition, stabilisation, and light absorption of Fe(II)-Fe(III) hydroxycarbonate (green rust). Clay Miner. 1989, 24, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braithwaite, R.S.W.; Dunn, P.J.; Pritchard, R.G.; Paar, W.H. Iowiate, a re-investigation. Miner. Mag. 1994, 58, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohls, D.W.; Rodda, J.L. Iowaite, a new hydrous magnesium hydroxide-ferric oxychloride from the precambrian of iowa. Am. Miner. 1967, 52, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar]
- McGill, I.R.; McEnaney, B.; Smith, D.C. Crystal structure of green rust formed by corrosion of cast iron. Nat. Cell Biol. 1976, 259, 200–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Abdelmoula, M.; Génin, J.-M. Mechanisms of formation and structure of green rust one in aqueous corrosion of iron in the presence of chloride ions. Corros. Sci. 1998, 40, 1547–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rius, J.; Allmann, R. The superstructure of the double layer mineral wermlandite [Mg7(Al0.57, Fe3+0.43) (OH)18]2+ [(Ca0.6, Mg0.4) (SO4)2(H2O)12]2−. Z. Für Krist. Cryst. Mater. 2015, 168, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Bookin, A.S.; Cherkashin, V.I.; Drits, V.A. Polytype diversity of the hydrotalcite-like minerals II: Determination of the polytypes of experimentally studied varieties. Clays Clay Miner. 1993, 41, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grégoire, B.; Ruby, C.; Carteret, C. Structural cohesion of MII-MIII layered double hydroxides crystals: Electrostatic forces and cationic polarizing power. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 4324–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaldi, M.; De Roy, A.; Chaouch, M.; Besse, J. New varieties of zinc–chromium–sulfate lamellar double hydroxides. J. Solid State Chem. 1997, 130, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, L.; François, M.; Refait, P.; Renaudin, G.; Lelaurain, L.; Génin, J.M. Structure of the Fe(II-III) layered double hydroxysulphate green rust two from Rietveld analysis. Solid State Sci. 2003, 5, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, J.D.; Dasgupta, D.R.; Mackay, A.L. The oxides and hydroxides of iron and their structural inter-relationships. Clay Min. Bull. 1959, 4, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, T.L.P.; Neves, C.S.; Caetano, A.P.F.; Maia, F.; Mata, D.; Malheiro, E.; Ferreira, M.J.; Bastos, A.C.; Salak, A.N.; Gomes, J.R.B.; et al. Control of crystallite and particle size in the synthesis of layered double hydroxides: Macromolecular insights and a complementary modeling tool. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 468, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Reactants | Concentrations (mol L−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M4s 1 | |
| NaOH | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 |
| NaCl | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0 |
| Na2SO4·10H2O | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0 |
| FeCl2·4H2O | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 |
| MgCl2·4H2O | 0 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0 |
| FeCl3·6H2O | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0 |
| MgSO4·7H2O | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.12 |
| Fe2(SO4)3·5H2O | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.12 |
| Diffraction Peak | Parameter | M0 | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d | 11.18 Å | 11.14 Å | 11.13 Å | 11.16 Å | - | |
| GR001 | I | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | - |
| FWHM | 0.21° | 0.24° | 0.34° | 0.35° | - | |
| d | 5.53 Å | 5.51 Å | 5.52 Å | 5.52 Å | - | |
| GR002 | I | 51 | 51 | 40 | 52 | - |
| FWHM | 0.25° | 0.28° | 0.36° | 0.41° | - | |
| d | - | 8.01 Å | 8.04 Å | 7.96 Å | 8.14 Å | |
| GRCl003 | I | - | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| FWHM | - | 0.80° | 0.46° | 0.64° | 1.53° | |
| d1 | - | 4.01 Å | 4.01 Å | 4.02 Å | 4.04 Å | |
| I1 | - | 82 | 27 | 7 | 57 | |
| GRCl006 | FWHM1 | - | 0.80° | 0.49° | 0.53° | 1.79° |
| d2 | - | - | 3.96 Å | 3.95 Å | - | |
| I2 | - | - | 28 | 35 | - | |
| FWHM2 | - | - | 0.68° | 0.81° | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Refait, P.; Duboscq, J.; Aggoun, K.; Sabot, R.; Jeannin, M. Influence of Mg2+ Ions on the Formation of Green Rust Compounds in Simulated Marine Environments. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2021, 2, 46-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd2010003
Refait P, Duboscq J, Aggoun K, Sabot R, Jeannin M. Influence of Mg2+ Ions on the Formation of Green Rust Compounds in Simulated Marine Environments. Corrosion and Materials Degradation. 2021; 2(1):46-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd2010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleRefait, Philippe, Julien Duboscq, Kahina Aggoun, René Sabot, and Marc Jeannin. 2021. "Influence of Mg2+ Ions on the Formation of Green Rust Compounds in Simulated Marine Environments" Corrosion and Materials Degradation 2, no. 1: 46-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd2010003
APA StyleRefait, P., Duboscq, J., Aggoun, K., Sabot, R., & Jeannin, M. (2021). Influence of Mg2+ Ions on the Formation of Green Rust Compounds in Simulated Marine Environments. Corrosion and Materials Degradation, 2(1), 46-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd2010003






