Surface-Tuned Quartz Particles for Oil–Water Separation: SEM Characterization, Coating Effects, and Predictive Modelling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Characterization by SEM–EDS
2.3. Oil–Water Separation Testing
2.4. Predictive Modeling of Separation Efficiency
3. Results
3.1. Surface Morphology and Elemental Composition of Quartz Particles Before and After Surface Modification
3.2. Oil and Grease Removal Performance of Quartz Samples
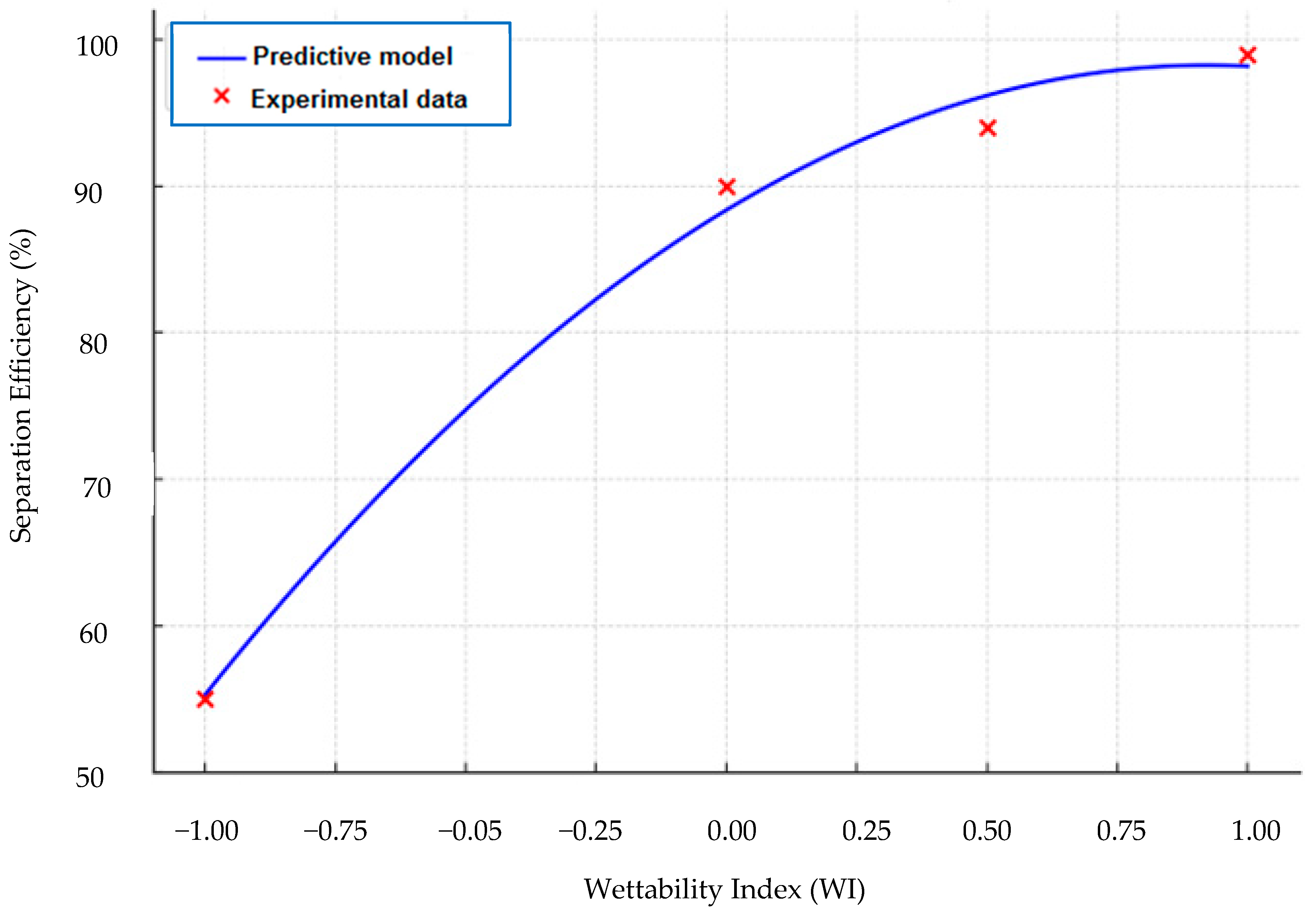
3.3. Predictive Modelling of Surface Wettability and Separation Efficiency
3.4. Industrial Applicability, Up Scalability, and ComSparative Evaluation with Conventional Techniques
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, C.; Feng, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, R. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering Research progress of phosphorus adsorption by attapulgite and its prospect as a filler of constructed wetlands to enhance phosphorus removal from mariculture wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Cui, W.; Yu, Z.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.Z. Multifunctional nanofibrous membranes for highly efficient harsh environmental air filtration and oil–water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 670, 160600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, Z.; Ren, T.; Zhang, Y. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering A combined mechanism (the open pores-cake dissolution) model for describing the trans-membrane pressure (P b (t)) reduction in the backwash process at a constant flow rate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.X.; Hao, B.; Xi, X.Y.; Wang, R.; Ma, P.C. Aggregation-induced demulsification technology for the separation of highly emulsified oily wastewater produced in the petrochemical industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 134017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomar, T.; Hameed, B.H.; Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Almomani, F.A.; Han, D.S. A review on recent developments and future prospects in the treatment of oily petroleum refinery wastewater by adsorption. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 64, 105616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-Z.; Zhao, M.-W.; Wu, Y.-N.; Liu, J.-W.; Sun, N.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Li, L.; Dai, C.-L. Quantitatively probing interactions between membrane with adaptable wettability and oil phase in oil/water separation. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 2564–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Ding, W.; Li, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wei, X.; Hakkarainen, M.; Wu, M. Nano graphene oxide creates a fully biobased 3D-printed membrane with high-flux and anti-fouling oil/water separation performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, I.; Bilal, M. Recent advances in the development of MXene-based membranes for oil/water separation: A critical review. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 29, 101674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrasa, S.; Hoseinzadeh, M.; Mohammadpour, S.; Saboor, F.H. Decontamination of Oily and Micro-pollutant Loaded Wastewater Using Metal Organic Framework. In Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Abuhantash, F.; Abuhasheesh, Y.H.; Hegab, H.M.; Aljundi, I.H.; Al Marzooqi, F.; Hasan, S.W. Hydrophilic, oleophilic and switchable Janus mixed matrix membranes for oily wastewater treatment: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 56, 104310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Chauhan, P.; Kumar, A. Superwetting Materials for Modification of Meshes for Oil/Water Separation. ACS Symp. Ser. 2022, 1408, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, Z.; Weng, S.; Yue, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Z.; You, X.; Li, R.; Fu, Q. Submicron-ultrathin PE/PDVB composite membrane for efficient oil/water separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2024, 701, 122701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, E.J.; Alves, M.E.; Arias, S.; Camara, A.G.; Cavalvanti, J.V.; Silva, G.L.; Barbosa, C.M.; Pacheco, J.G.A. Cellulose-MIL-88A photocatalytic membrane to treat effluents containing dyes and oil emulsions. Catal. Today 2024, 441, 114846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, S.A.; Al-Jubouri, S.M.; Sadek, S.M.A.-J.S.A.; Sadek, S.A.; Al-Jubouri, S.M. Highly efficient oil-in-water emulsion separation based on innovative stannic oxide/polyvinylchloride (SnO2/PVC) microfiltration membranes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 140, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Qiu, M.; Chen, X.; Verweij, H.; Fan, Y. One-step sintering for anti-fouling piezoelectric α-quartz and thin layer of alumina membrane. J. Memb. Sci. 2023, 667, 121188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Tanudjaja, H.J.; Ouda, M.; Hasan, S.W. Journal of Water Process Engineering Membrane fouling mitigation techniques for oily wastewater: A short review. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 43, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutrisna, P.D.; Kurnia, K.A.; Siagian, U.W.R.; Ismadji, S.; Wenten, I.G. Membrane fouling and fouling mitigation in oil–water separation: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Cao, X.; Chan, W.; Jing, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhu, Z.; Liang, W.; Li, J.; Li, A. Removal of PM and oil mist from automobile exhaust by a ‘hamburger’ structured conjugated microporous polymers membrane. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 195, 112167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guo, Z. Natural polymers-based separation membrane for high-efficient separation of oil water mixture. Nano Today 2024, 57, 102367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, K. An asymmetric super-wetting Janus PVDF oil-water separation membrane fabricated by a simple method on a non-woven substrate. React. Funct. Polym. 2024, 202, 105982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lin, L.; Wang, Q.; Ma, W.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Xu, M.; Cheng, Q.; Zhao, K.; et al. Engineering a superwetting membrane with spider-web structured carboxymethyl cellulose gel layer for efficient oil-water separation based on biomimetic concept. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 2603–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Du, J.; Wang, L.; Yao, A.; Song, Z.; Liu, L.; Cao, D.; Ma, J.; Lim, W.; He, W.; et al. Smart superwetting COF membrane for controllable oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 317, 123825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, S.; Wu, X.; You, H.; Yang, G.; Zhang, K.; Sun, C.; Liu, S. A Degradable Photo-Thermal Aerogel with Biomimetic Structure and Selective Wettability for High-Throughput Recovery of Viscous Crude Oil. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 495, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Z.; He, Z. Non-fluorinated and photothermal lignin microspheres/candle soots-based superhydrophobic sponge for crude oil recovery and separation of oil/water mixtures and emulsions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 495, 138909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, W.; Li, C.; Liu, P.; Shen, X. Fabrication of a superhydrophilic/underwater superoleophobic PVDF membrane via thiol–ene photochemistry for the oil/water separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 664, 131138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bai, T.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Feng, L. Sugarcane-based superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic membrane for efficient oil-in-water emulsions separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Pan, G.; Xu, S.; Liu, Q.; Shan, H.; Fu, Q.; Ge, J. Carbonaceous nanofibrous membranes with enhanced superhydrophilicity and underwater superoleophobicity for effective purification of emulsified oily wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; He, D.; Luo, Z.; Wang, R.; Shi, F.; Pang, Y.; Sun, W.; Peng, L.; He, J. Facile preparation of a multifunctional superhydrophilic PVDF membrane for highly efficient organic dyes and heavy metal ions adsorption and oil/water emulsions separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 637, 128231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Barma, S.; Majumdar, S.; Ghosh, S. Silane-modified bentonite clay-coated membrane development on ceramic support for oil/water emulsion separation using tuning of hydrophobicity. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 681, 132812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesak, G.V.G.; Xavier, L.A.; de Oliveira, T.V.; Fontana, E.; Santos, A.F.; Cardoso, V.L.; Vieira, R.B. Enhancement of pozzolanic clay ceramic membrane properties by niobium pentoxide and titanium dioxide addition: Characterization and application in oil-in-water emulsion microfiltration. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 217, 110892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Barma, S.; Majumdar, S.; Ghosh, S. Role of silane grafting in the development of a superhydrophobic clay-alumina composite membrane for separation of water in oil emulsion. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 26638–26650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khader, E.H.; Mohammed, T.J.; Albayati, T.M.; Rashid, K.T.; Cata, N.M.; Zendehboudi, S. Green nanoparticles blending with polyacrylonitrile ultrafiltration membrane for antifouling oily wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 353, 128256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggraeni, V.S.; Sutrisna, P.D.; Goh, P.S.; Chan, E.W.C.; Wong, C.W. Development of antifouling membrane film for treatment of oil-rich industrial waste. Mater. Today Proc. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, D.; Huang, H.; Zhou, W.; Chu, Z. Cysteine-based antifouling superhydrophilic membranes prepared via facile thiol-ene click chemistry for efficient oil-water separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjlef, A.; Farsad, S.; Chaoui, A.; Ben Hamou, A.; Ezzahery, M.; Et-Taleb, S.; El Alem, N. Effective adsorption of Orange G dye using chitosan cross-linked by glutaraldehyde and reinforced with quartz sand. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Qi, Y.; Zhao, M.; Li, B.; Jing, W.; Wei, X. A composite structure pressure sensor based on quartz DETF resonator. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 346, 113883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, G.; Hermansson, A.; Jönsson, A.S.; Lipnizki, F. In situ real-time investigations on adsorptive membrane fouling by thermomechanical pulping process water with quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Cao, H.; Fan, W.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Qiu, M.; Verweij, H.; Fan, Y. Application of piezoelectric quartz for self-cleaning membrane preparation. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 16599–16610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Fan, W.; Cao, H.; Chen, X.; Qiu, M.; Verweij, H.; Fan, Y. Self-cleaning performance of in-situ ultrasound generated by quartz-based piezoelectric membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 120031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, L.F.; Pataroque, K.E.; Pan, W.; Cao, T.; Kaneda, M.; Violet, C.; Ritt, C.L.; Hoek, E.M.; Elimelech, M. Orientation matters: Measuring the correct surface of polyamide membranes with quartz crystal microbalance. J. Membr. Sci. Lett. 2023, 3, 100048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, C.; Lin, J.; Yin, H.; Shi, J.; Tang, J.; Ma, B.; Li, T.; Ren, K. Fabrication of recyclable, superhydrophobic-superoleophilic quartz sand by facile two-step modification for oil-water separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grad, P.; Hernández, V.A.; Edwards, K. Improved accuracy and reproducibility of spontaneous liposome leakage measurements by the use of supported lipid bilayer-modified quartz cuvettes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 221, 113022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Luo, Z.; Su, C.; Tong, L.; Liu, H. Mechanism of reactive co-transport of Fe2+ and antibiotics in hyporheic zone simulated by quartz sand column. J. Hydrol. 2023, 621, 129641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, D.; Yi, R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L. Selective transport properties of graphene oxide membranes for various cations observed in situ using quartz crystal microbalance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 541, 148502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Deng, Y.; Dai, M.; Wu, Y.; Ali, I.; Peng, C. Preparation of super-hydrophobic/super-oleophilic quartz sand filter for the application in oil-water separation. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Cao, H.; Hu, X.; Mao, H.; Chen, X.; Qiu, M.; Verweij, H.; Fan, Y. Piezoelectric porous α-quartz membrane by aqueous gel-casting with enhanced antifouling and mechanical properties. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 43, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordoyiannis, G.; Bar, L.; Losada-Pérez, P. Recent advances in quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring: Phase transitions as descriptors for specific lipid membrane studies. Adv. Biomembr. Lipid Self-Assem. 2021, 34, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph-Schöpping, G.; Schagerlöf, H.; Jönsson, A.S.; Lipnizki, F. Comparison of membrane fouling during ultrafiltration with adsorption studied by quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D). J. Memb. Sci. 2023, 672, 121313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, J.; Kong, D.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Wei, B. Solvent-responsive switching wettability of superoleophobic/superhydrophilic quartz sand filter medium facilitates rapidly oil/water separation and demulsification. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 697, 134418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xue, C.; Ding, G.; Cheng, G.; Cui, J.; Pan, J. Robust antifouling NH2-MIL-88B coated quartz fibrous membrane for efficient gravity-driven oil-water emulsion separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2022, 644, 120093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombom, M.; Zaman, B.T.; Bozyiğit, G.D.; Şaylan, M.; Bayraktar, A.; Arvas, B.; Yolaçan, Ç.; Bakırdere, S. T-cut slotted quartz tube-atom trap strategy for the on-line preconcentration of thallium in well water samples. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2023, 220, 113363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadhban, M.Y.; Rashid, K.T.; Abdulrazak, A.A.; Alsalhy, Q.F. A novel poly (lactic-acid) and poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blend membrane modified with hesperidin for oily water emulsions separation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2024, 206, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Bai, R.; Cao, X.; Song, C.; Xu, D. Modification of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) membrane with anchored long and short anionic chains for highly effective anti-fouling performance in oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 316, 123769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.B.; Zhang, Z. Ceramic membrane technology for water and wastewater treatment: A critical review of performance, full-scale applications, membrane fouling and prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouadja, F.; Bouzerara, F.; Guvenc, C.M.; Demir, M.M. Fabrication and properties of novel porous ceramic membrane supports from the (Sig) diatomite and alumina mixtures. Bol. La. Soc. Esp. Ceram. Y Vidr. 2022, 61, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Qi, R.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H. Porous ceramic membranes from coal fly ash with addition of various pore-forming agents for oil-in-water emulsion separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Sun, C.; Yang, F.; Dong, Y. Superhydrophilic spinel ceramic membranes for oily emulsion wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.U.; Purkayastha, D.D. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering Superhydrophilic ZnO nano-needle decorated over nanofibrous PAN membrane and its application towards oil / water separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloulou, W.; Aloulou, H.; Romdhani, M.; Dammak, L.; Amar, R.B. Effectiveness evaluation of a flat smectite membrane for wastewaters purification: Characterization, cost and energy estimation. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 318, 100390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Feng, B.; Hao, L.; Pan, C.; Song, H.; Gai, H.; Zhu, Q.; Xiao, M.; Huang, T. Preparation and application of low-cost fibers for efficient adsorption of oil from coal pyrolysis wastewater and establishment of quantitative equation for calculating oil contact angle under water. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 51, 103461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Xu, J.; Qiu, F.; Zhang, T. Enhanced separation of dual pollutants from wastewater containing Cr (Ⅵ) and oil via Fe-doped sludge derived membrane. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 292, 120020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.M.; Chen, X.H.; Lü, Q.F.; Lin, Q. 2D Ti3C2Tx modified with nano-AgPNPs antioxidant constructed hierarchical interface for high-throughput oily wastewater separation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 185, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Gong, J.; Sun, Y.; Yan, W.; Jin, R.; Li, J. High permeability PEG/MXene@MOF membrane with stable interlayer spacing and efficient fouling resistance for continuous oily wastewater purification. J. Memb. Sci. 2024, 691, 122247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Sun, F.; Ma, H.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Xia, C. A comprehensive review of lignocellulosic biomass derived materials for water/oil separation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Critic, C.A.C.; Framework, C. Evaluating Material Alternatives for low cost Robotic Wheelchair. Jordan Journal of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering. 2023, 17, 653–669. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, K.; Kong, N.; Ma, J.; Lin, H.; Gao, C.; Lei, J.; Zeng, Z.; Hu, J.; Qi, J.; Shen, L. Enhanced management and antifouling performance of a novel NiFe-LDH@MnO2/PVDF hybrid membrane for efficient oily wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Dai, P.; Liu, Y.; Lu, H.; Yang, Q. Superhydrophilic and superhydrophobic quartz sand hybrid filters for efficient on-demand oil/water separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wu, H.; Dong, Y. Biomimetic hydrophilic modification of poly (vinylidene fluoride) membrane for efficient oil-in-water emulsions separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 329, 125227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Xiao, X.; Chen, Z.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y. A novel hydroxyapatite super-hydrophilic membrane for efficient separation of oil-water emulsions, desalting and removal of metal ions. Desalination 2023, 565, 116864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
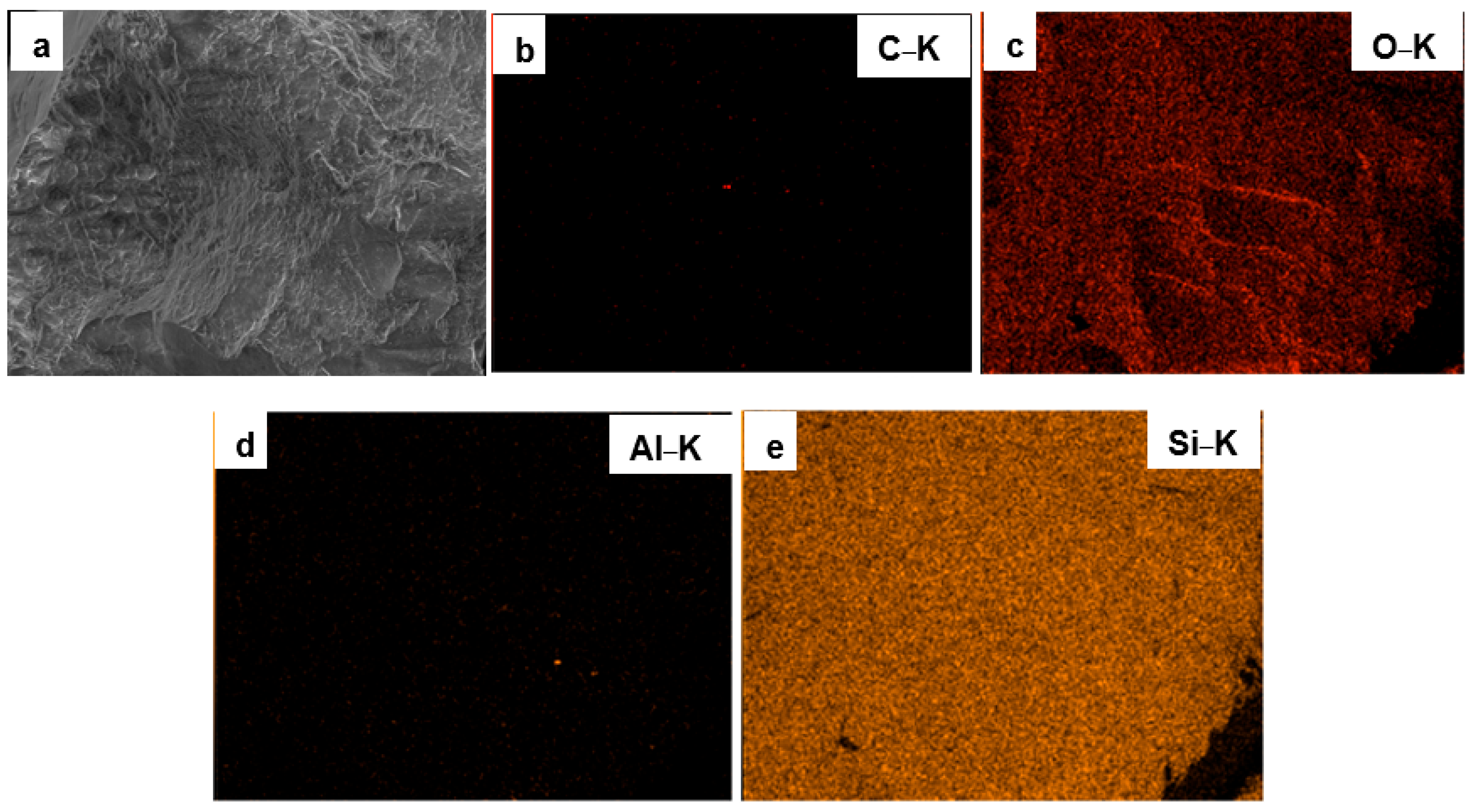
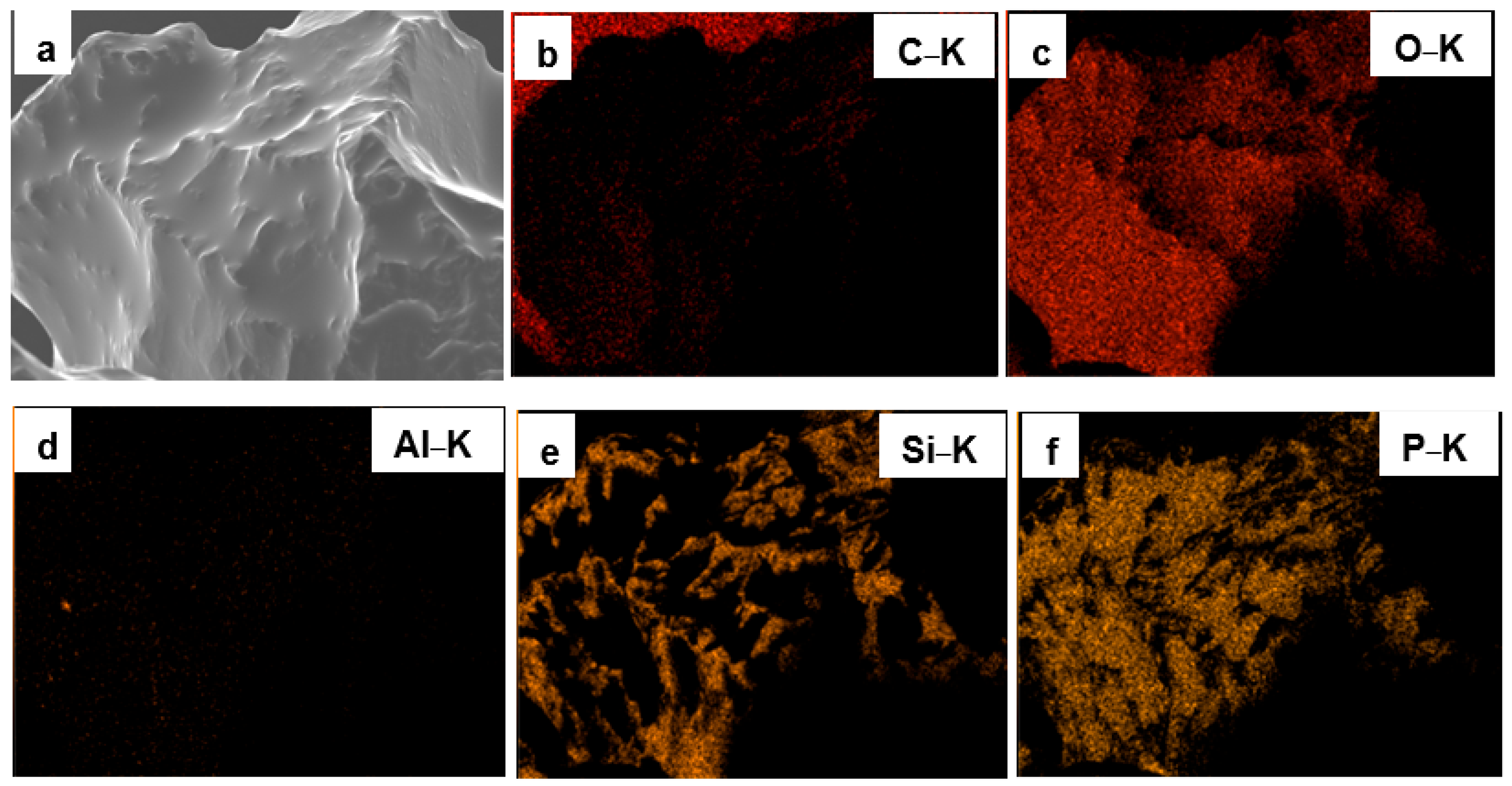
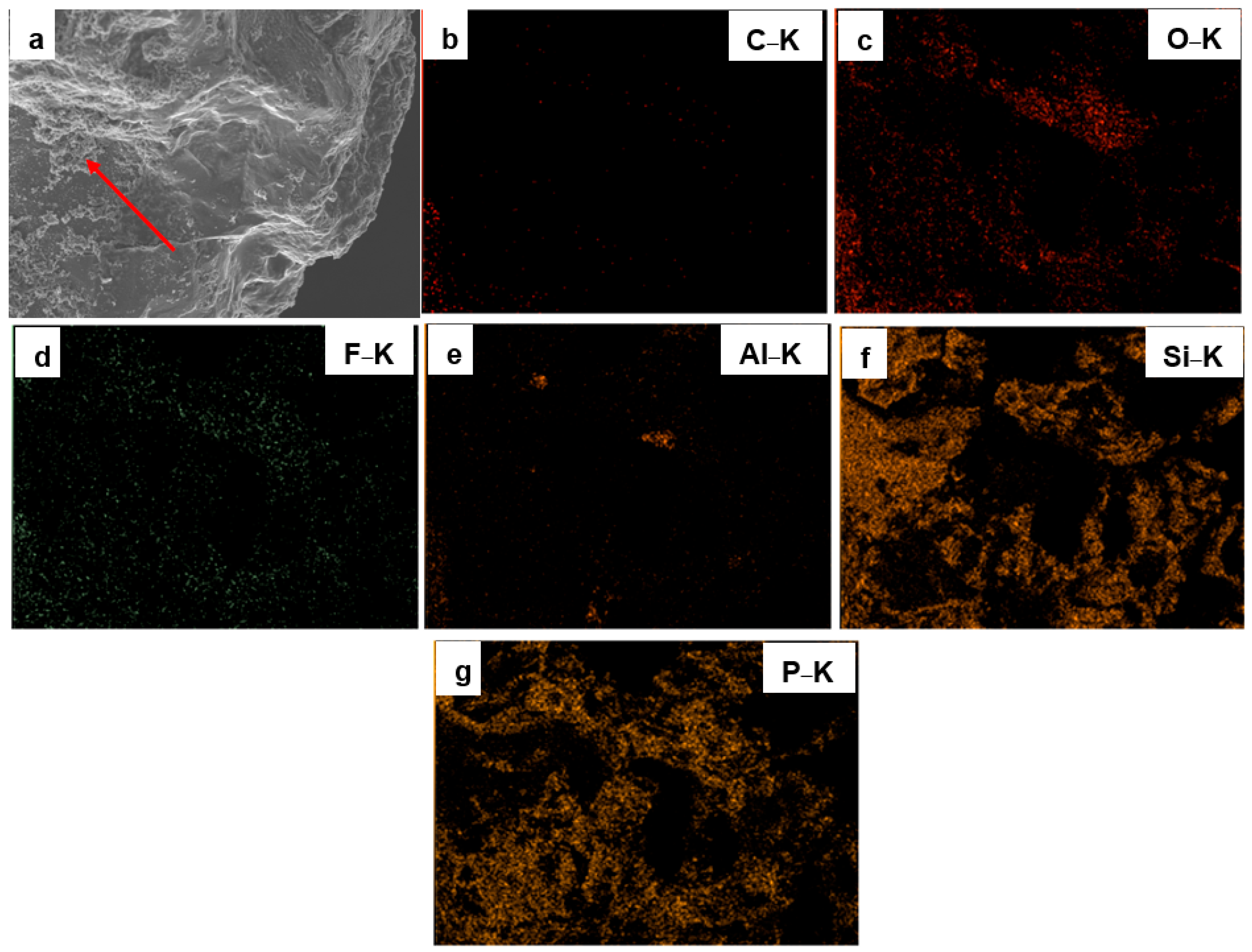
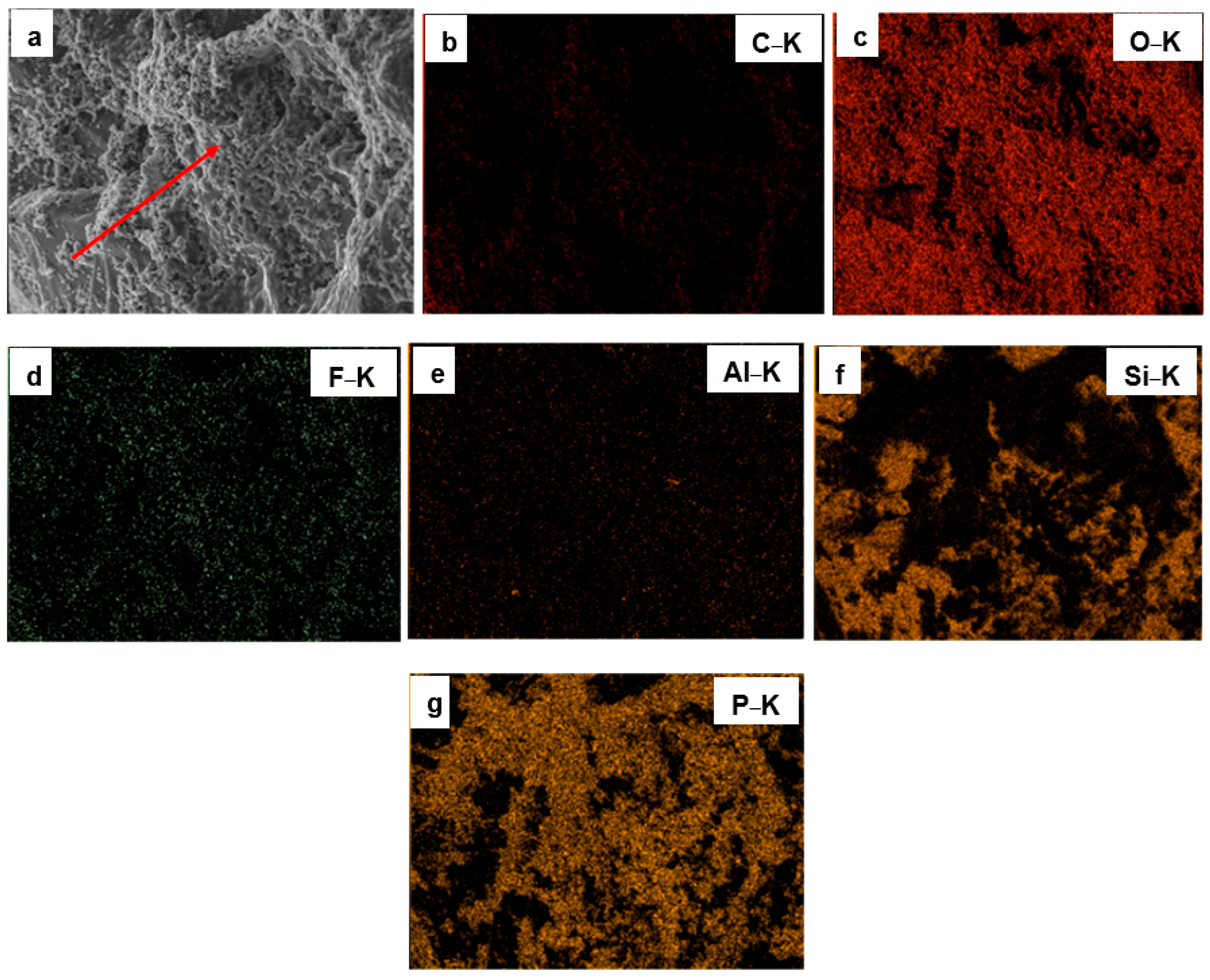
| Sample Type | O&G (mg/L) | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Oil–water mixture (untreated) | 142,955.9 | Extremely high oil content, representing the baseline untreated effluent. This confirms the severe level of oil contamination requiring treatment. |
| Raw quartz | 13.4 | Very low residual oil concentration, indicating highly effective oil removal due to strong adsorption and surface affinity properties of raw quartz particles. |
| Washed quartz | 837.1 | Higher residual oil compared to raw quartz, suggesting partial loss of natural surface features and adsorption capacity after washing. |
| Hydrophilic-coated quartz | 751.3 | Improved oil removal compared to washed quartz, but less effective than raw quartz, possibly due to water affinity promoting oil repulsion rather than adsorption. |
| Hydrophobic-coated quartz | 64,198.9 | Significantly reduced oil compared to untreated mixture, but much higher residual oil than raw and hydrophilic quartz, likely due to oil affinity causing re-deposition or poor phase separation. |
| Parameter | Quartz-Based Membrane (This Study) | Conventional Membrane Techniques (Polymeric/Ceramic) |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Application | Suitable for oily wastewater treatment in mining, petrochemical, and food-processing industries; withstands harsh chemical and thermal environments. | Widely used in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment, but limited resistance to extreme pH, temperature, and abrasive feed streams. |
| Up scalability | Readily up scalable using low-cost raw quartz and simple coating techniques; potential integration into existing filtration units with minimal design changes. | Commercially established scaling pathways, but high capital and operating costs for ceramic membranes and complex fabrication for polymeric membranes. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to chemical and mechanical robustness; easy surface cleaning; longer operational lifespan with minimal flux decline. | Polymeric membranes require frequent cleaning and replacement due to fouling; ceramic membranes have better durability but higher replacement costs. |
| Manufacturing Techniques | Utilizes abundant quartz, processed via washing, particle size control, and surface modification through hydrophilic/hydrophobic coatings; low energy and material costs. | Polymeric membranes use phase inversion or electrospinning; ceramics require high-temperature sintering (>1200 °C), increasing costs and environmental footprint. |
| Surface Modification | Flexible modification with hydrophilic or hydrophobic coatings to tailor wettability and separation efficiency; coatings improve selectivity and anti-fouling performance. | Surface functionalization possible but may involve expensive reagents or complex plasma/chemical treatments; durability of modifications can be limited under industrial conditions. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramanamane, N.; Pita, M. Surface-Tuned Quartz Particles for Oil–Water Separation: SEM Characterization, Coating Effects, and Predictive Modelling. Surfaces 2025, 8, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8030067
Ramanamane N, Pita M. Surface-Tuned Quartz Particles for Oil–Water Separation: SEM Characterization, Coating Effects, and Predictive Modelling. Surfaces. 2025; 8(3):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8030067
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamanamane, Nthabiseng, and Mothibeli Pita. 2025. "Surface-Tuned Quartz Particles for Oil–Water Separation: SEM Characterization, Coating Effects, and Predictive Modelling" Surfaces 8, no. 3: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8030067
APA StyleRamanamane, N., & Pita, M. (2025). Surface-Tuned Quartz Particles for Oil–Water Separation: SEM Characterization, Coating Effects, and Predictive Modelling. Surfaces, 8(3), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8030067





