Abstract
Humanity is opening up to cosmos in all its dimensions and areas of knowledge. In this context, Paraguay, due to its multicultural uniqueness and two official languages (Spanish and Guaraní), represents an emblematic example of how legends, traditions and its rich mythology are important in their sociocultural translation to space. They coexist as a link between the past and the future. Guarani traditions, mythology, their relationship with nature and their translation into cosmos are amazing and complex aspects of indigenous cultural heritage, which are still present in many Paraguayan initiatives. This article compiles and integrates the cultural information about this topic, which is dispersed in different sources, and frames it in its corresponding context. Likewise, it unequivocally confirms how this intangible heritage is crucial as a living roadmap and a contemporary challenge that should be preserved as it guides individuals, communities and initiatives to implement earth and space science and education. Guaraní cultural heritage offers valuable insights into how indigenous worldviews continue to shape contemporary ecological and cultural practices in our modern intersection pathway to the cosmos.
1. Introduction
There is a link between ancient cultural traditions and space. The names of deities and mythological figures associated with the inner worlds permeat the names of planets, moons and other celestial objects and their planetary features, transferring human sensibilities to the cosmos. For different reasons, there is an overrepresentation of certain cultures, while other minority cultures have been relegated to the background, although they are no less important. As Cebolla Badie indicates [1], the patterns of the Western mentality sometimes repress other conceptions of the universe of social interrelations, which, for certain indigenous peoples, usually encompasse contexts that transcend human society [2].
The Guarani, or “Ava,” is a group of South American native peoples who are geographically located in Paraguay, Uruguay, Argentina, Bolivia and Brazil. The Guarani constitute one of the most prominent Indigenous groups in South America, belonging to the Tupi-Guaraní linguistic family. Today, they exhibit remarkable sociocultural continuity despite centuries of Hispanic influence and modernization pressures. Population estimates vary due to self-identification challenges, intermarriage and differing census methodologies. Paraguay accounts for the majority: the UNFPA Census of 2024 reported there are approximately 140,000 people who identify themselves as indigenous, of whom Guaraní speakers predominate (over 80% of the Indigenous total). In Paraguay, Guaraní is co-official with Spanish under Article 140 of the 1992 Constitution, used in education, media and government. Guaraní resilience manifests in adaptive strategies blending tradition with modernity, integrating some key elements (e.g., land and economy, social organization, cultural revitalization and adaptation, among others).
In the Guarani’s ethnography and its relationships between nature, cosmos and culture, practically everything has a soul and can positively or negatively affect the actions of humanity (holistic conception). They have a humanized vision of the cosmos (cosmovision), where different species, spirits and human beings interact through myths, rituals and practices of their daily life. This constitutes an intangible cultural heritage where everything is interconnected.
However, this perception does not only constitute something ancestral. It is something that has survived today in the essence of the sociocultural background of modern Paraguayan society. These indigenous worldviews offer a meaningful alternative to the dominant techno-economic and geopolitical paradigms that currently shape humanity’s engagement with outer space. The core idea is powerful: space science and exploration can—and should—be influenced by holistic, relational and ecologically rooted cosmologies such as the Guaraní cosmovision. As indicated by Rojas Aranda, “the cosmovision of the Guarani people defines common notions, which apply to all fields of life, from politics, economics, or science to religion, morality or philosophy” https://granlogiafemenina.cl/la-cosmovision-guarani/ (accessed on 1 October 2025). In fact, it also takes part in many relevant educational and scientific actions. In order to try to arrange a clear, logical progression as a potential roadmap, integrating the present contribution, the following aspects would be treated: (1) contextualization of the link between Ancient Cultures and Space; (2) understanding the guarani cosmovision; (3) the geographical, historical and current context of the guarani; (4) integration into space and educational initiatives; and (5) strategical objectives and heritage preservation. These aspects define a conceptual evolutive line, which comprises cultural foundation, cosmological principles, existing manifestations in space science, national implementation and global ethical implications.
A central concept in Guaraní culture is the idea of “yvypóra”, or the Earth’s surface [3], which is not merely a terrestrial plane but a place where cosmic forces interact. These features of the landscape are seen as living entities. The way in which this indigenous cultural vision is transferred into space should also be preserved in the same way that other mythological aspects of Western culture are. Selected examples of how these perspectives are being or could be integrated into space exploration efforts are described below.
In this context, this article (a) aims to provide an overview of how Paraguay is opening up to space and how the heritage associated with Guarani traditions, legends and culture (particularly in Paraguay) has been incorporated into recent educational, societal and scientific initiatives and endeavors linked to space exploration. This also includes historical figures, who have played a crucial role in promoting initiatives related to the cosmos, from different perspectives. This article also aims (b) to bring to light this type of ethnic and cultural minority data, which has been frequently undervalued, beyond its purely historiographical interest, helping their preservation, and (c) synthetically compile and transfer this heritage information, which was dispersed in different sources, to the scientific–cultural global field.
2. Some Selected Traditional Concepts and Their Potential Modern Integration
The Guarani cosmovision, particularly its holistic perspective regarding interconnectedness, provides original approaches to current and future space exploration initiatives. The cosmovision is not only a religious system but also a philosophical framework, which differs from Western scientific epistemologies. Concepts such as “yvypóra” (Earth’s surface) and its symbolic relationship with celestial bodies offer a cultural heritage framework that aligns with sustainable and ethical practices in planetary science. Tupã—often mistranslated as “God” in Jesuit chronicles—is not a transcendent creator but the atmospheric principle of thunder, lightning and fecund rain. Tupã manifests through meteorological events that renew yvypóra. And so, without wishing to be exhaustive, many others live in a social–cultural context in which Guarani metaphysics posits a single ñandé (“ours”) continuum linking the microcosm and macrocosm. The human body (téte) mirrors yvypóra: blood is river, bones are stone and breath is wind. Some examples connecting indigenous traditions with the modern scientific areas are the following:
“Yvypóra” and Planetary Geology: The term “yvypóra,” representing the Earth’s surface as a living, interconnected system, could fit with modern considerations of planetary habitability and geological activity. In addition, “yvypóra” could also inspire the use of Earth analogues, such as studying different ecosystems in Paraguay, to model extraterrestrial environments, helping to understand the habitability of Martian paleoenvironments and to design future life-support systems and sustainable habitats. In some cases, it could relate to planetary exploration.
Likewise, during missions to Mars, the study of sedimentary layers and surface features (e.g., riverbeds or volcanic plains) could draw parallels with the Guarani’s recognition of land as a dynamic, evolving entity. For instance, the Paraná Valles region on Mars, named after the Paraná River https://www.icog.es/TyT/index.php/2024/01/del-parana-de-la-tierra-al-parana-de-marte-propuesta-del-primer-analogo-planetario-de-paraguay/ (accessed on 2 October 2025), could reflect, among other geological and astrobiological aspects [4], the Guarani’s appreciation of water as a life-sustaining force.
Astrobiology and Guarani Myths: Guaraní myths often describe celestial bodies as living entities with their own “souls” or essences. This perspective inspires a broader search for life beyond Earth by taking into account various definitions of “life” and its expressions. For example, the search for microbial life on icy moons like Europa or Enceladus could benefit from viewing their potential subsurface oceans as whole ecosystems rather than isolated environments.
Also, the myth of “Mbóra,” the tapir spirit guiding paths, could metaphorically lead the search for possible biomarkers in intricate cave systems on Mars or lava tubes on the Moon. Much more related to the ISRU (In Situ Resource Utilization) concept and methodologies [5], like techniques such as crop rotation and intercropping, rooted in Guaraní traditions, could motivate polyculture approaches in extraterrestrial greenhouses. For instance, growing complementary plants like beans and corn in controlled Martian environments could optimize nutrient cycles and soil health. Also, water recycling systems in space habitats could benefit from the Guaraní’s importance on preserving “karai”, within water ecosystems, ensuring minimal waste and maximum reuse. The concept karai—often glossed as “balance” or “propriety”—functions as an aesthetic–ethical imperative: every action must porã (be beautiful, fitting). Even some vanguardistic planetary protection, geoethical and astrobioethical approaches on the Moon or Mars [6,7] could be inspired by this Guarani environmental concept, which is implicit in how to face the issues of exploration and research. This type of indigenous epistemology could contribute to decolonizing space governance (e.g., the Artemis Accords), providing a wider holistic scope and marking the main goals.
In synthesis, Guarani thought articulates an immanent, processual ethics where ontological continuity, distributed agency and aesthetic reciprocity replace classical hierarchical dualisms.
3. Paraguay Opens up to Space
Humanity is opening up to space in all its sociocultural dimensions and areas of knowledge. Astrophysics, astronomy and aerospace engineering paved the way for the exploration of the cosmos. Nowadays, many other disciplines, such as planetary geology, astrobiology and astrochemistry as well as space medicine, space law, space architecture, space agriculture, etc., are demonstrating that humankind is immersed in an emerging paradigm, through which we are acquiring a new perception about the connection between humanity and the universe. This global achievement is also embedded in other societal aspects such as indigenous traditions (cultural heritage), apparently far from all these initiatives but much more rooted in science and technology that it is believed, although from a different approach.
This non-Western view of space exploration and astrobiology, which is based on mythical narratives, is not equivalent to scientific hypotheses. Its holistic focus on the interconnection between the cosmos, nature and life stimulates interdisciplinary and spiritual reflections. For instance, with regard to astrobiology and the search for extraterrestrial life (e.g., on Mars), Guarani traditions promote respect for the planet as the guardian of life, with an emphasis on reciprocity and cosmic balance. This integral vision of the cosmos, where sky and earth intertwine, reflects sophisticated ethno-astronomical knowledge, where life emerges from the union between the earthly and the celestial. This particular conception expands the motivation of the search for life as something, perhaps less scientific but much more profound and transcendent, giving an added value to the astrobiological goals. Paraguay is a perfect example of this.
It is not the objective of this work to provide a thorough description of everything carried out to date in Paraguay but rather to provide a general overview that allows us to understand the state of the art and the disciplinary foundations on which numerous current initiatives on space are being based in the country.
Some important contributions that delve deep into the topic can be found in [3,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30], among others. Astronomy as a discipline has marked the beginning of the sociocultural interest of modern Paraguayan society in space and, more recently in the last decade, also planetary geology and astrobiology [4,31], involving various initiatives related to terrestrial analogues, the Moon and Mars, which will be detailed later.
From the point of view of “modern astronomy”, the first steps in Paraguay were taken especially during the first half of the 18th century by the polymath and Jesuit priest Buenaventura Suarez, considered a pioneer and the first native astronomer of the southern region of South America [11,25] (Figure 1). Among other surprising things, he observed the first lunar eclipse with the naked eye in 1700, near the Argentina–Paraguay border. Suárez traveled to Jesuit missions among the Guarani people of the region (including areas of Paraguay and Argentina). Most of his work (mainly related to lunar and solar events, as well as the observation of 147 eclipses of Jupiter’s satellites) [8] was carried out in the Jesuit community of the Guarani Indigenous people of San Cosme and San Damián (Paraguay) (Figure 1). It included, in addition to its educational and scientific work, the construction of several astronomical instruments. Their activities laid the foundations and paved the way for many current studies on astronomy and also gave the population the necessary varnish for space to become part of the sociocultural heritage.

Figure 1.
Some images of the exterior of the facilities of the Buenaventura Suárez Astronomical Interpretation Center in Paraguay, San Cosme and San Damián reduction, south of the department of Itapúa (Paraguay). (a) entrance sign to the main facility; (b) small planetarium and other educational and public outreach devices.
In the 20th century, the main promoter and disseminator of astronomy in Paraguay and in the whole Guarani context was Prof. Blas Servín. His work was truly extraordinary, and he is considered a national and international key person, with awards and recognitions at the highest level. After his death, on April 16, 2020, in his obituary, he was defined as “the spirit of the Guaraní sky-Guarani arapy pytu-” [32,33]. Today, the “Blas Servín Mobile Astronomical Observatory” travels around the country offering an immersive experience, allowing children, young people and adults to explore the cosmos in an innovative way. Blas Rodrigo Servín, son of Blas Servín, is in charge of continuing his father’s legacy [34]. Also noteworthy are initiatives such as the inclusive conferences and workshops promoted by the astronomy communicator, Sebastian Musso, focused on the teaching and dissemination of astronomy for blind people [35], in which Blas Rodrigo Servín, representative of Astro TEs-Paraguay, has actively participated. In November 2024, the Science Museum of Paraguay presented the architectural design of its future premises that will be on the Costanera Norte of Asunción. It will house a planetarium, the most advanced in South America according to the organization, which will posthumously honor Blas Servín [36], who founded the first planetarium of the capital in 2001. This impressive new and forthcoming planetarium will undoubtedly be a worthy successor to the emblematic Buenaventura Suarez Planetarium (Astronomical Interpretation Center) in San Cosme and San Damián reduction and the Digital Planetarium.
Although today there are currently courses on astronomy and astronautics, in which some Paraguayan universities occasionally participate (e.g., Universidad Comunera, UCOM), unfortunately, there is still no specific degree on these topics, nor are there research centers or institutes that address them. However, during the last 40 years, important steps have been taken with notable initiatives on the subject, trying to connect space and society: The Astrophysics Club of Paraguay (CAP) was founded in 1985. Also, at the end of that year, there was great interest in preparing the Halley Pass in 1986 [15]. At the beginning of the nineties, the Association of Astronomy Fans was created, which today has become the Bicentennial Astronomical Center. In that same decade, the Society for Astronomical Studies (SEA) was established. The Paraguayan Center for Astronomical Information (CPIA) was created on February 20, 1995, under the name of the Paraguayan Society of Amateur Astronomy. It has maintained its objectives of the dissemination of astronomy, the development of this science in the framework of the country and the region and the promotion of activities carried out by astronomical groups and other scientific organizations [37,38,39]. The UNA (Universidad Nacional de Asunción) Polytechnic Faculty has its own Astronomical Observatory, inaugurated in 2000. The Astronomical Research Dissemination Center (CEDIA) was created in 2009. Moreover, in 2009, the International Astronomy Year (IYA) was constituted [40]. The event, held in the city of Concepción, was organized by the National Node and Advisors of the IYA2009 Paraguay Chapter, as well as the National University of Concepción. It was sponsored by the United Nations, UNESCO, International Astronomical Union, Directorate of Cultural Relations of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Regional Supervisors of Concepción. Other space-related events also have been taken place, such as the Paraguayan Astronomy, Astrophysics and Astronautics Olympics [15,38], which is being organized annually. Other organizations and groups, such as Astronomy Paraguay, develop intense public outreach activities about space-related science and instrumentation. In all activities of these groups and associations, the role of the amateur astronomers has been key as main promoters.
In a more official and institutional way, the Aerospace Research Center of Paraguay (CIAP) was established in 2011. The CIAP is a civil and non-profit institution of a scientific–academic nature, and it serves the society. Integrated by civil and military specialists in the field, the Center carried out its activities by “the promotion of research, knowledge, spread and improvement of legislation, aeronautics and aerospace policies and specific aspects of national and international interest, including environmental impact and climate change” [19]. In 2013, the first woman to be appointed as Minister of Defense in Paraguay (María Liz Garcia de Arnold) took the initiative to propose the creation of the Space Agency of Paraguay, AEP [19]. The founding of the AEP on March 26, 2014 has been a fundamental initiative at the country level. This has been a turning point for many scientific, engineering, educational and international relations activities. In short, its main goals are (a) to organize and promote space related actions such as training, seminars, conference and congresses; (b) to support activities in the public and private sector, as well as in academia by providing technical assistance, scholarships and networking, and (c) to regulate all policies and monitor all projects related to space technology applications in Paraguay [41]. The AEP has been a member, since 2018, of the International Astronautical Federation and the Latin American Astrobiology Network. In addition, the AEP has established agreements with different agencies and organizations related to space in Japan, Mexico, Taiwan, Spain, etc., and organized the First Space Conference of Paraguay in 2017 [19]. Another important success of the AEP was promoting the successful launch of its first satellite into space on March 14, 2021. Named Guaranisat-1, it is one of the three nanosatellites of the Birds-4 Project, which departed heading to the International Space Station (ISS). GuaraniSat-2 is in progress and its launch is scheduled for late 2025. Both Guaranisats belong to the AEP program “Paraguay to Space”.
As previously indicated, space science studies also recently opened their spectrum to planetary geology and astrobiology [4]. Initially through the AEP and the Universidad Nacional de Asunción (UNA), and later on at the Universidad Nacional de Itapúa (UNI), this involves the promotion of different scientific, educational and dissemination initiatives and a specific program on terrestrial analogues and astrobiology [4,42]. It is important to stress, and there is an initiative, which is currently in progress, launched by the Paraguayan Public Universities Association (AUPP), the AEP and other institutions, which aims at the incorporation of Paraguay as a member of the Artemis Accords [43].
Some of these descriptions about Guaranisats, the Agencia Espacial del Paraguay (AEP), educational programs and the legacy of figures like Buenaventura Suárez and Blas Servín exemplify how a nation is successfully integrating Indigenous heritage into its modern space ambitions. The incorporation of Guarani heritage into educational programs for students, and even astronauts and mission designers, could broaden perspectives on humanity’s place in the universe. It appears clear that Paraguay’s multicultural identity makes it uniquely positioned for this synthesis.
4. Guarani and Historical Names Move Beyond the Earth
The correspondence and interpretation of many Guarani names in relation to space and events in the cosmos were analyzed in detail by Prof. Blas Servín [22,23,24,26]. The Guarani were great observers of the sky. Many of their perceptions and much of their cultural heritage, which today form part of pre-Hispanic legends and traditions, denote a surprising and defining worldview of their own way of understanding nature, which is worth recognizing and preserving. In fact, they conceived the Earth as an island or continent that floats in an infinite flat ocean, and there are as many myths as there are tribes [22,23,24,26]. Table 1 shows some of these Guarani terms (Sun, The Moon, galaxy, eclipses, stars, etc.) and their astronomical meanings according to their traditional conceptions [23,26,44]. It is important to note that, to our knowledge, with the exception of the specific work of Pereira [44], which only partially addresses some of these terms, the present contribution is the first that globally transfers these analyses related to the Guarani worldview outside the Spanish-speaking context to the scientific field of international journals. In a certain way, it is a tribute to the extraordinary work of Prof. Blas Servín (Table 1).

Table 1.
Some selected terms from the Guaraní cultural tradition in relation to the cosmos and its interpretation. Compiled mainly from Servin [22,23,24,26] and other specific sources [13,21,44,45].
The Space Age is considered a period encompassing the activities related to the space race, space exploration, space technology and also the cultural developments influenced by these events [46], beginning with the launch of Sputnik 1 on 4 October 1957 and continuing to the present. In the context of the naming process, Jordan [47] describes the term “exonyms” as indicating the network of relations of a community extending beyond the boundaries of its own territory. Among other characteristics, this involves emotional ties between humans and space, fosters the formation of space-related identity and contributes, in this way, to space-related identity building, both of individuals and communities.
In this context, considering everything previously indicated, Table 2 describes a set of Guarani and historical figures related to space sciences which have been incorporated into the nomenclature of asteroids, stars, craters, volcanoes and other geomorphological lunar and planetary structures.

Table 2.
Set of terms from the Guaraní culture and also from renowned places and people, who have worked in relation to space and have given official names to asteroids, craters, volcanoes, mountains, stars and exoplanets.
4.1. Asteroids
1779 Paraná: It is an asteroid that is part of the inner region of the asteroid belt and was discovered by the astronomer Miguel Itzigsohn from the Astronomical Observatory of La Plata, Argentina, on 15 June 1950. The official naming citation was published by the Minor Planet Center (MPC) on 8 April 1982 [48]. It measures 4.09 km in diameter [49] and was named for the Paraná River that runs through northern Argentina, Brazil and Paraguay.
6438 Suárez: It is a mid-sized asteroid (diameter of 3014 km), orbiting between Mars and Jupiter in the main portion of the asteroid belt (Figure 2). It was discovered on 18 January 1988 at the La Silla Observatory by the Belgian astronomer Henri Debehogne [50]. In 2007, the Paraguayan astronomer, Waldemar Villamayor–Venialbo, proposed to the International Astronomical Union that it name asteroid 6438 (1988 BS3) Buenaventura Suárez, as compiled by the Astronomical Almanac, Bicentennial Edition of the Republic of Paraguay, as a tribute to the work carried out by the Jesuit, previously described [30].
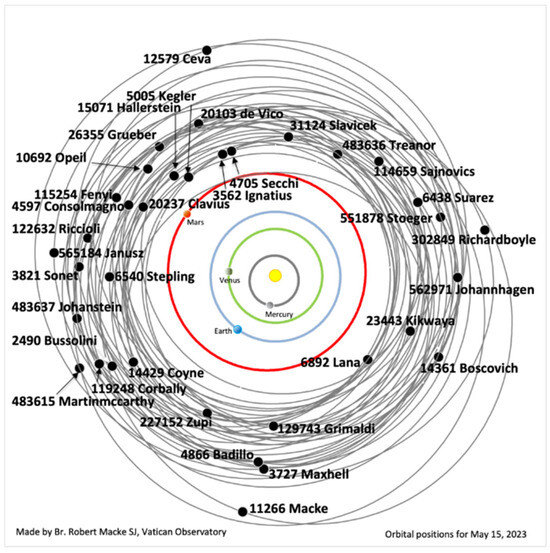
Figure 2.
Asteroids named for Jesuits. Artwork by Br. Bob Macke (Vatican Observatory) [51]. Note the position of 6438 Suarez.
4269 Bogado: Manuel D. Bogado was a Paraguayan amateur astronomer, known for his contributions to astronomy in his country and for his work involving astrophotography and variable stars. The name was suggested by W. A. Fröger [52]. 4269 Bogado: It is an asteroid (diameter of 5134 km) belonging to the asteroid belt, discovered on March 22, 1974 by Carmen Torres from the Cerro El Roble Astronomical Station, Chile. The Paraguayan Center for Astronomical Information and other related circles have highlighted as an anecdote that Manuel Bogado was born on 30 June, 26 years after the Tunguska event, which marks the “International Asteroid Day” [30].
15908 Bertoni: It is a main belt asteroid (diameter: 7937 km), discovered in 1997 by Spacewatch https://spacewatch.global/ (accessed on 28 September 2025) at Kitt Peak Observatory. It was named “Bertoni”, in honor of the Paraguayan-nationalized Swiss scientist Moisés Bertoni [14]. He was a Swiss–Paraguayan botanist, anthropologist and writer. He discovered, described and classified thousands of plants, most of them in Paraguay, during his lifetime, including Yerba Mate and Stevia Rebaudiana Bertoni (Ka’a He’e) [53]. Moisés Bertoni was buried in Puerto Bertoni.
15414 Pettirossi: Like the previous one, it was discovered on 26 January 1998 at the Kitt Peak Observatory of the Spacewatch program. It is an asteroid of 4171 km of diameter, which is part of the asteroid belt [54]. Silvio Pettirossi was a pioneer of aviation in Paraguay and the first president of the Aeroclub del Paraguay, which he founded in 1914. The name was suggested and reviewed by the Dutch astronomer W. Fröger, for his contributions to natural sciences and aeronautics [14].
16701 Volpe: It is an asteroid (diameter: 2791 km) discovered on 21 February 1995, like the previous three, at the Kitt Peak observatory by the Spacewatch program. The nomination was also proposed by Willem Albertus Froguer. Miguel A. Volpe Borgonon is a Paraguayan amateur astronomer, Professor of engineering at the Universidad Nacional de Asunción and one of the founders of the Club de Astrofísica del Paraguay [55]. Also, he was founding partner of the Astronomical Society of Paraguay, Member of the Scientific Society of Paraguay since 1996 and founder of the Paraguayan Center for Astronomical Information 1995, among other positions related to space issues [30].
15988 Parini: Like the previous ones, it is an asteroid in the asteroid belt discovered on December 11, 1998 from the Kitt Peak National Observatory, as part of the Spacewatch project [56]. Parini is about 3.4 km in diameter. Eduardo Parini (b. 1926) is a Paraguayan amateur astronomer who founded the Bueanaventura Suarez Observatory. His work is centered on deep-sky, solar observation and CCD astrophotography. The name was also suggested by W. A. Fröger [30].
5205 Servian: It is an asteroid (diameter of 4999 km), discovered on February 11, 1988 by Seiji Ueda and astronomer Hiroshi Kaneda, from the Kushiro Marsh Observatory, Hokkaido, Japan. It was named Servian in honor of the Paraguayan Berta E. Servián de Flores, who was the first Paraguayan aviator [57]. The airport in the city of Caazapá also bears her name, as well as the Cessna C172, training aircraft of the National Institute of Civil Aeronautics.
4.2. Craters
Yuty: Yuty is a crater on Mars located in Chrysias Planetia. It is a complex crater as opposed to a simple (bowl-shaped) crater. Complex craters are distinguished by having a raised central peak complex and terracing along the inner wall. The crater has a diameter of approximately 20 km and is surrounded by complex ejecta lobules [58,59], which is a distinctive feature of Martian impact craters. It is named after the town of Yuty in Paraguay [60] (Figure 3). Yuty is one of the oldest Paraguayan cities, located in the department of Caazapá, founded by Fray Luis de Bolaños in the year 1611. In accordance with Gobernaciones y Municipios [61], the origin of its name has two versions: one of them is that it means “place of thorns” in Guaraní (Ju = needle ty = place); in this case the J was replaced by Y. The second version says that the place was a meeting area and that when the original people were asked where they came from, they answered “Aju aty hágui” (I come from the meeting place), and by contraction it remained in Yuty. Yuty is known as “The Land of Itakaru.” It bears that name due to its Itakaru deposits and, from Guaraní, refers to magnetite [61,62].
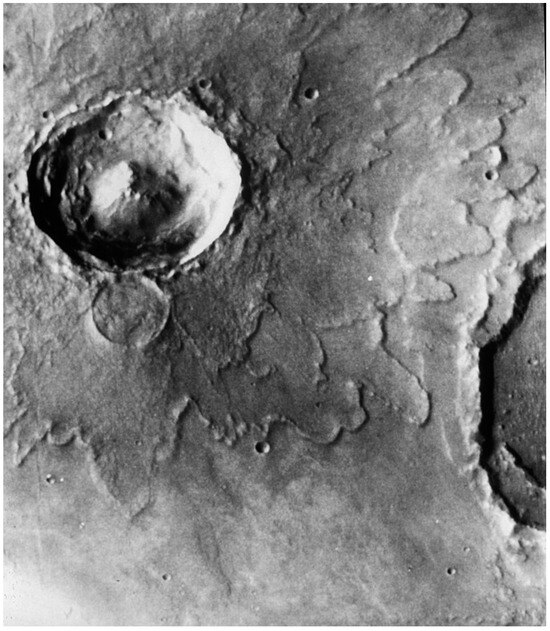
Figure 3.
Yuty impact crater (Mars). Note the well-defined ejecta deposits which consist of many overlapping lobes. This image was taken in 1977 by the Viking 1 orbiter. Credit: NASA.
Yegros: It is a Martian crater 14.5 km in diameter. It was approved in 1976 and named as a tribute to the Paraguayan hero and the city and district of the department of Caazapá [63,64]. Bernardo Nery Fariña describes it well in his book “Chronicle of the First Republic” by Fulgencio Yegros, first president of the Republic of Paraguay and a defender of national sovereignty and promoter of culture. “His life should constitute a paradigm for Paraguayans today, for his courage, selflessness, his complete dedication to the national cause, his concern for the education of the people, and above all, his selflessness and vocation for service without any ambition for personal gain.” [65]. The Yegros crater is located on Mars at the coordinates 22°18′00″ S 336°20′24″ E.
Mbir: It is a 46 km crater located on Saturn’s moon Rhea [66] at the coordinates Latitude: 46.6° Longitude: 311.9°. It was named in 2010. Rhea is the second largest moon orbiting Saturn; it is about half the size of our moon and is made entirely of ice. Within Guarani mythology, Mbir was the creative worm that emerged in the primeval waters and later became human and populated the world. Some have wanted to see an evolutionary connotation in it.
Yara: It is an 11 km diameter crater on Neptune’s moon Triton. Its approval is recent (17 December 2024) [67]. The origin of the term is Tupi/Guarani: beautiful mermaid in Amazon River. According to the Paraguayan Center for Astronomical Information (CPIA), Yara, also written Uiara, Yjara or Hiara in other spellings, is known as the “lady of the water” or “mother of the waters.” Its name comes from Ñeꞌengatú (modern Tupí) “y jara” = y (“water”) + jara (“lady; owner”). Depending on the legends, she is described as a water nymph or a beautiful mermaid who lives in large rivers. One of the best known Legends of Yjara says that “Yjara was a brave warrior, envied by her brothers. After a series of tragic events, she was thrown into the river and, during a full moon night and saved by fish, she was transformed into a mermaid. Another version tells that the god of the moon, Jasy, took pity on her after her death and transformed her into a mermaid. Since then, Yjara enchants men with her song, taking them to the depths of the river” [37].
4.3. Volcanoes
Tupan: Tupan Patera is an active volcano on Jupiter’s moon Io. The volcano was first seen in low-resolution observations by the two Voyager spacecraft in 1979, but volcanic activity was not seen at this volcano until June 1996, during the Galileo spacecraft’s first orbit [68]. This volcano was formally named Tupan Patera, after the god of the Tupi–Guarani people, by the International Astronomical Union in 1997. Tupã is the supreme god of the Guaranis, the primordial deity creator of light and the universe. His abode is Kuarahy (the sun), source of light, origin of humanity [69]. It is located on Io’s anti-Jupiter hemisphere at 18.73° S 141.13° W. Tupan consists of a volcanic crater, known as a patera, 79 km across and 900 m deep [70,71] (Figure 4). A large eruption at Tupan was observed by astronomers at the Keck Observatory on March 8, 2003. These data revealed warm, dark silicate lava on the eastern and western sides of the patera floor with an “island” of bright, cool material in the middle [70,71,72,73].
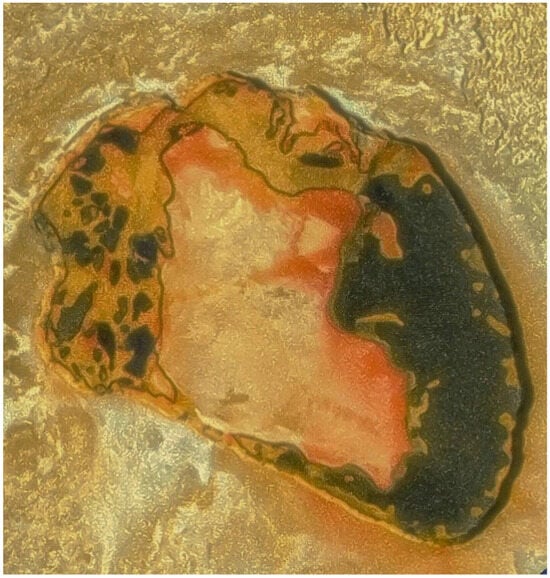
Figure 4.
Detail of the volcanic crater Tupan Patera on Jupiter’s moon Io, viewed from NASA’s Galileo spacecraft. It displays the complex result of lava interacting with sulfur-rich materials. Credit: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona.
Monan: It is a patera, or a complex structure with scalloped edges, like the previous one, on Jupiter’s moon Io. It is about 137 km in diameter and is located at 19.82° N 104.81° W [74]. It is named after Monan. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1997. Monan was the creator god in the mythology of the Tupi–Guarani people (mainly in Brazil).
According to legend, he created the world and humans but tried to exterminate them twice because he did not agree with the way they lived, on one occasion through fire and on another through a flood. It was also said that he only tried it once through fire and that a magician caused a rain to put out the fire, this rain causing the subsequent flood [69,72,73]. Monan Patera forms an unusual worm-shaped depression at the north end of the elongate mountain Monan Mons, south of which is Ah Peku Patera [74].
4.4. Mountains/Valleys
Dorsum Azara: It is a wrinkle ridge at 26.7° N 19.2° E in Mare Serenitatis on the Moon [75]. It has been proposed that these lunar tectonic structures occur as a consequence of cooling and contraction processes of basaltic lava masses (Figure 5). Dorsum Azara is 103 km long and was named after Spanish naturalist Félix de Azara in 1976. Azara was a geographer and naturalist who made studies of geographical descriptions in Paraguay. Even Darwin also owned a translation of Azara’s Notes for the Natural History of the Quadrupeds of Paraguay and Rio de la Plata [76].

Figure 5.
Oblique view of Dorsum Azara in Mare Serenitatis, on the Moon. It is a wrinkle ridge at 26.7° N 19.2° E in Mare Serenitatis that was named after Spanish naturalist Félix de Azara in 1976. Credit: NASA.
Monan Mons: Mountains on Jupiter’s moon Io (generally, structures rising above the surrounding plains) have a great variety of morphologies. More than 135 mountains have been identified on the surface; Monan is one of them [71]. The etymological meaning of Monan has already been described previously. Monan Mons is directly about two paterae: to its north lies the oddly shaped Monan Patera and to the south lies another patera, Ah Peku [71,72].
Parana Valles: A set of channels about 350 km long in a valley in the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle region (MC-19) of Mars, located at approximately 23.1° South and 10.2° West (Figure 6). This area has been studied from the perspectives of its river activity and geomorphology, the evolution and timing of drainage and its climatic implications. They received their name from an ancient and modern name of the Paraná River that runs through Brazil, Paraguay and Argentina [77]. Recently, within the framework of a scientific and educational program promoted by the National University of Itapúa (UNI), it has been proposed that the Parana River, together with some volcanic and riverbed alteration areas, could serve as a terrestrial analogue https://www.icog.es/TyT/index.php/2024/01/del-parana-de-la-tierra-al-parana-de-marte-propuesta-del-primer-analogo-planetario-de-paraguay/ (accessed on 2 October 2025) [31] in relation to this system, as well as other similar ones on Mars.
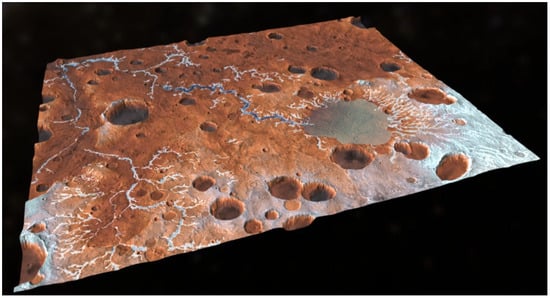
Figure 6.
3D representation of the Paraná Valleys and the basin system. It is located on Mars: 23.1° S 10.2° W. Credit: Gaia https://sketchfab.com/3d-models/parana-basin-mapped-mars-ec2bdff84e5c44339a457633366408d6 (accessed on 29 September 2025).
4.5. Stars/Exoplanets
Tupã: HD 108147, also known as Tupã, is a 7th magnitude star in the constellation of Crux in direct line with and very near to the bright star Acrux or Alpha Crucis. It is either a yellow–white or yellow dwarf. It is slightly brighter and more massive than the Sun. In December 2019, the International Astronomical Union announced the star will bear the name Tupã, after the God of the Guarani people of Paraguay. The name was the result of a contest ran in Paraguay by the “Centro Paraguayo de Informaciones Astronómicas”, along with the IAU100 NameExoWorlds 2019 global contest [78]. Tupã, or Tupan, is the word for God in the Tupí and Guaraní languages. Tupã is considered to be the creator of the universe, of humanity and of the spirits of good and evil. Tupã was not actually a god but rather a manifestation of God, in the form of thunder [79]. Since 2002, the existence of an extrasolar planet in orbit around this star has been known [80]. This star is accompanied by an exoplanet, Tume Arandu (Tume: refers to a paternal or central figure who guides and leads; Arandu: translates as knowledge, intelligence or wisdom). Tume Arandu is the first son created by Tupã and is considered the father of wisdom.
Tapecue: HD 63765, also known as Tapecue, is a subgiant star located in the constellation of Carina, at a distance of 106 light years. It is not part of the Carina constellation outline but is within the borders of the constellation [81]. Tapecue is a yellow star like the Sun, though slightly smaller and less massive (it has 0.85 of the Sun’s mass), and is also considerably further into its lifecycle. This star possesses a single known planet, a gas giant named Yvaga that is rather less massive than Jupiter and follows an orbit around its star comparable with that of Earth around the Sun. The name was selected during the 100th anniversary of the IAU as part of the IAU’s NameExoWorlds project. Tapecue (modern Tapekue), literally “eternal path” in Guarani, is the Milky Way, through which the first inhabitants of the Earth arrived and could return [22,23,24,26].
Tupi: HD 23079, also known as Tupi, is a star in the constellation of Reticulum. Measurements give a distance estimate of 109 light years from the Sun. The star is similar to the Sun but is slightly hotter and more massive. The metallicity of this star is below solar, meaning the abundance of elements other than hydrogen and helium is lower than in the Sun [82,83]. The name was selected in the NameExoWorlds campaigns by Brazil during the 100th anniversary of the IAU. The star is named after the Tupi people. Many Tupi people today are merged with the Guarani people, forming the Tupí–Guaraní languages [84]. In 2001, the existence of a giant planet, called HD 23079 b or Guarani, in orbit around Tupi was announced.
5. Final Remarks
Guarani traditions, mythology, their relationship with nature and their translation into cosmos, are amazing and complex aspects of cultural heritage, which are still present (mainly in many Paraguayan initiatives). They are not only fundamental to understanding the Guarani worldview but also illuminate the profound cultural and scientific connections and intersections between past, present and future. As previously described, the significance of this interplay lies in the way that space—both natural and human-made—has been conceptualized and structured within Guarani culture. This has often been achieved through myths and stories that transcend mere physical and geological locations, even beyond our planet. The spatial translations of these myths transform the environment into a canvas for the stories that have been passed down for generations. The land is not just a backdrop for human activity; it is an active participant in the cultural narrative, where everything must be understood as a whole cultural framework heritage (cosmovision).
This review compiles and integrates the cultural records about this topic, which are dispersed in different sources, and frames it in its corresponding context. Likewise, it unequivocally confirms how knowledge of Guarani legends and traditions is crucial to uniting the way in which they project themselves from the past to the future, in a contemporary challenge through an invisible threat. Guarani myths could enrich Western views (more focused on science- and technology-based approaches) by introducing a more spiritual lens. Such holistic integration might inspire ethical frameworks for space travel, blending science with spiritual awareness to address existential questions about humanity’s place in the stars. In a certain way, this set of elements represents a living roadmap that guides individuals, communities and initiatives about earth and space science and education. Finally, understanding this relationship helps preserve Guarani culture and offers valuable insights into how indigenous worldviews continue to shape and influence contemporary ecological and cultural practices in our modern pathway to the cosmos.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This article forms part of the Memorandum of Understanding between the “Universidad Nacional de Itapúa”, Encarnación (Paraguay) and the “Red Española de Planetología y Astrobiología” (REDESPA), Spain. The authors would like to thank both institutions for their support. They would also like to thank Beatriz Mantínez Martín for her expert revision of the English language. Finally, we are grateful to the two anonymous referees for their valuable comments and suggestions that greatly improved the original manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cebolla Badie, M.V. Cosmología y Naturaleza Mbya-Guaraní. Doctoral Thesis, Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 2013; 328p. Available online: https://diposit.ub.edu/dspace/handle/2445/35245 (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Aranda, R. Latin America and Caribbean Climate Week 2021/LACCWW2021. 2021. Available online: https://laccw21.site.calypso-event.net/ (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- De Mello, F.C. Astronomy and Cosmology of the Guarani of Southern Brazil. In Handbook of Archaeoastronomy and Ethnoastronomy; Ruggles, C., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Portillo, E.; Martínez-Frías, J.; Vera Gamarra, V.D.; Mendoza Jiménez, G.T.; Villalba Alderete, C.I.; Wieczorko Baran, T. Topografía de la Región del Valle del Paraná de Marte. II Congreso Multidisciplinario de Investigación e Innovación. Encarnación, Paraguay. 2024. Available online: https://www.facebook.com/photo?fbid=899380312217047&set=a.552554416899640&locale=es_ES (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Bowman, A. Missions. In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) 2024. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/mission/in-situ-resource-utilization-isru/ (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Martínez-Frías, J.; Horneck, G.; De la Torre, R.; Rull, F. A geoethical approach to the geological and astrobiological research and exploration of the Moon and Mars. In Proceedings of the 38th COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Bremen, Germany, 18–25 July 2010. PEX1-0007-10. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Frías, J. Ethics and Space Exploration. From Geoethics to Astrobioethics Search for Life: From Early Earth to Exoplanets—XIIth Rencontres du Vietnam. 2016. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S3OI0C-AuGU (accessed on 29 October 2025).
- Albergaria, D. The Sky as Seen from the Missions. Revista Pesquisa FAPESP. Retrospect. 2023. Available online: https://revistapesquisa.fapesp.br/en/the-sky-as-seen-from-the-missions/ (accessed on 28 September 2025).
- De Asúa, M. The publication of the astronomical observations of Buenaventura Suárez SJ (1679–1750) in European Scientific Journals. J. Astron. Hist. Herit. 2004, 7, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlong, G. Glorias Santafesinas: Estudios Biobibliográficos Precedidos de una Introducción; Surgo: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1929; 300p. [Google Scholar]
- Galindo, S.; Rodriguez Mezza, M.A. Buenaventura Suarez, S.J. (1679–1750) Part 1: Telescope maker, Jovian satellites observer. Rev. Mex. Fís. E 2011, 57, 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Laura, P.A.A. Suárez a Father of South American Astronomy. Phys. Today 2004, 57, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann-Nitsche, R. La Astronomía de los Chiriguanos; Mitología Sudamericana VIII, Revista del Museo de la Plata t. XXVIII, serie 3, N 4; Universidad Nacional de La Plata: La Plata, Argentina, 1924; pp. 80–102. [Google Scholar]
- Minniti Morgan, E.R. Astronomía en Latinoamérica. Astronomía de Paraguay. 2005. Available online: https://historiadelaastronomia.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/08/paraguay.pdf (accessed on 29 October 2025).
- Quintana, E. Fundamentos de la Olimpiada Paraguaya de Astronomía y Astronáutica. Rev. Científica Estud. Investig. 2016, 5, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Portillo, E. Aporte de la Tecnología Espacial a las Ciencias de la Tierra. Agencia Espacial del Paraguay. Cápsula Espacial. 2021. Available online: https://www.facebook.com/agenciaespacialpy/posts/aep-este-viernes-imperdible-nuestra-c%C3%A1psula-espacial-tenemos-la-participaci%C3%B3n-de/6858855720806533/ (accessed on 28 September 2025).[Green Version]
- Román, A.J. Semana de la Ciencia y la Tecnología. VI Conferencia Internacional, Educación, Ciencia y Tecnología. Colegio Politécnico Co-operativa Copiatá. Desarrollo Espacial y la Realidad Mundial. 2023. Available online: https://www.facebook.com/watch/live/?ref=watch_permalink&v=1594408837714148 (accessed on 28 September 2025).[Green Version]
- Román, A.J. Presentación del Proyecto Paraguay al Espacio—Primer Satélite Paraguayo GuaraniSat-1. In III Conferencia Espacial del Par-aguay, 2019 Asunción 2019. Available online: https://www.facebook.com/agenciaespacialpy/posts/la-iii-conferencia-espacial-del-paraguay-entre-otros-tendr%C3%A1-la-participaci%C3%B3n-com/3501903116501827/ (accessed on 30 September 2025).[Green Version]
- Romero, H. Paraguay. Space for Women Expert Meeting, 4-6 2017, NY. 2017. Available online: https://www.unoosa.org/documents/pdf/SpaceforWomen/Presentations/Day2/EXPERT_MEETING_PARAGUAY_HEBE_ROMERO_SAP.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2025).[Green Version]
- Romero, H. Alianzas Estratégicas de la Cooperación Internacional del Paraguay en Materia Espacial. I Jornada Iberoamericana Sobre el Espacio Ultraterrestre. Instituto de Derecho Aeronáutico y Espacial, del Colegio de Abogados de Loma de Zamora, CALZ, Buenos Aires, Argentina. 2021. Available online: https://www.facebook.com/agenciaespacialpy/posts/la-aep-presente-en-la-i-jornada-iberoamericana-sobre-el-espacio-ultraterestre-or/7037456609613109/?locale=ms_MY (accessed on 2 October 2025).[Green Version]
- Sersic, J.L. La astronomıa de los guaranıes. Tribuna de Astronomıa, September 1991. In Minniti Morgan, E.R. 2005. Astronomía en Lati-noamérica. Astronomía de Paraguay. 1991. Available online: https://historiadelaastronomia.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/08/paraguay.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2025).[Green Version]
- Servín, B.; Father Buenaventura Suárez, S.J. Pioneer Astronomer from South America: His work. In Proceedings of the VIII Reunión Regional Latino Americana de Astronomía Union Astronómica Internacional, Montevideo, Uruguay, 27 November–1 December 1995; Rev. Mex. A. A. (SC). Volume 4, p. 152. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Servin, B. El Cielo de los Guaraníes. Astronomía Cultural. SIMUOVE, 4: 16–18. 2012. Available online: https://planetario.buenosaires.gob.ar/sites/default/files/2018-02/simuove04baja.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2025).[Green Version]
- Servin, B. Taller de Astronomía. Primera Conferencia de Astronomía en el Guairá. Asociación Astronómica del Guairá. 2018. Available online: https://www.republicadelguaira.com/2018/09/primera-conferencia-sobre-astronomia.html (accessed on 27 September 2025).[Green Version]
- Troche-Boggino, A.E. The Relevance of the Teaching of Astronomy in the Developing Countries; a Case: Paraguay. International Astronomical Union Colloquium. Astron. Educ. Needs Dev. Ctries. 2016, 105, 424–426. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Servin, B. Astronomía guaraní. Sociedad Científica del Paraguay. Portal Guaraní. 2000. Available online: https://portalguarani.com/1187_blas_antonio_servin_bernal__/11528_astronomia_guarani.html (accessed on 27 September 2025).[Green Version]
- Troche Boggino, A.E. Centre for Astronomy for Paraguay; Selected Papers on Space Science Education, Remote Sensing, and Small Satellites. Seminars of the United Nations Programme on Space Applications; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 9, p. 167. Available online: https://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu//full/1998UNPSA...9..167T/0000168.000.html (accessed on 27 September 2025).[Green Version]
- Troche Boggino, A.E. Buenaventura Suárez SJ: The pioneer astronomer of Paraguay. J. Astron. Hist. Herit. 2000, 3, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vielman, L. La Política Espacial del Paraguay. IV Encuentro internacional de la red latinoamericana y del Caribe del Espacio. Centro de Investigación Aeroespacial del Paraguay (CIAP). Universidad San Carlos. Diario del Derecho. 2019. Available online: https://www.iustel.com/diario_del_derecho/noticia.asp?ref_iustel=1188794 (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Villamayor-Venialbo, W. (Ed.) Almanaque Astronómico; Edición Bicentenario de la República del Paraguay; Club de Astrofísica del Paraguay y Centro Paraguayo de Informaciones Astronómicas: Asunción, Paraguay, 2012; 254p. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza-Jiménez, G.; Rodríguez Portillo, E.; Martínez Frías, J.; Villalba Alderete, C.; Vera Gamarra, V.; Wieczorko Barán, T. Herramientas Didácticas en un Programa de Iniciación Científica: Astrobiología, Geología Planetaria y Análogos Terrestres. In Proceedings of the VI Congreso Internacional de Astrobiología, Neiva, Colombia, 20–22 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Galeano Olivera, D. Blas Servín: Espíritu del Cielo Guaraní. Cienciadelsur.com. 2020. Available online: https://cienciasdelsur.com/2020/04/19/blas-servin-guarani-arapy-pytu/?fbclid=IwAR3etDT_cL6jvucahpR2YaCs5n8UGMC3rRmtT2Jq-LUcDU1xc4fLMt4S4-g (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Quintana, E. Blas Servín, un Humano Extraordinario Que Amó y Enseñó la Ciencia. Ciencia del Sur. 2020. Available online: https://cienciasdelsur.com/2020/04/16/blas-servin-un-humano-extraordinario-que-amo-y-enseno-la-ciencia/ (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- CanalPRO. Legado del Profesor Blas Servín se Muestra a Través del Planetario Móvil. Blas Rodrigo Servín, Hijo de Blas Servín. 2024. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KWPZU_VKOaQ&t=64s (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- AstroTes. Astronomía para Personas Ciegas o con Baja Vision. Astronomía para Tocar, Escuchar y Sentir. Libros. 2025. Available online: https://astrotes.org/es/libros.html (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- MUCI. Planetario Blas Servín. Museo de Ciencias. Prof. Blas Servín. 2024. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QTrWWqPbTWE (accessed on 29 October 2025).
- CPIA. Noticia Astronómica-Mitológica. El Cráter “Yara” en Tritón, Luna de Neptuno. Centro Paraguayo de Informaciones As-tronómicas. 2024. Available online: https://www.facebook.com/story.php?story_fbid=1013491560822937&id=100064863063943 (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- CPIA. Olimpiada Paraguaya de Astronomía y Astronáutica—Material de Apoyo. 2011. Available online: https://es.scribd.com/document/382453136/Manual-Olimpiada-de-Astrofisica (accessed on 28 September 2025).
- CPIA. Centro Paraguayo de Informaciones Astronómicas. 2025. Available online: http://www.cpia.org/?i=2 (accessed on 28 September 2025).
- Volpe, M.A.; Schaerer, C.E. Breve reflexión sobre el Año Internacional de la Astronomía: Motivación para las matemáticas y las ciencias. UNIÓN—Rev. Iberoam. De Educ. Matemática 2009, 5, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Vielman, L. Génesis de la AEP, Agencia Espacial del Paraguay: Una Herramienta Más Para el Desarrollo y Defensa Nacional; Marben Editora & Gráfica S.A. Editorial: Asunción, Paraguay, 2014; BENMAR 9789996735769; 211p. [Google Scholar]
- OAP. Observatorio del Agua. Universidad Nacional de Itapúa, Paraguay. Programa UNI-REDESPA: Iniciación Científica en Análogos Terrestres, Geología Planetaria y Astrobiología. 2024. Available online: https://www.facebook.com/photo?fbid=889402999641599&set=a.573704157878153&locale=pt_BR (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Daines, G. The Artemis Accords. Principles for a Safe, Peaceful, and Prosperous Future in Space. 2025. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/artemis-accords/ (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Pereira, G. “Chiriguano” Astronomy—Venus and a Guarani New Year. In Handbook of Archaeoastronomy and Ethnoastronomy; Ruggles, C., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobierno de Santa Cruz. Secretaría de Educación, Cultura y Juventud (2012) Ceremonia Lucero del Alba, Yasitata Guazu—Koembiya 20 y 21 de Junio; Bajo Isoso—Santa Cruz—Samaipata, Leaflet. 2012. Available online: http://www.santacruz.gob.bo/imagenes/informacion2012/TripticoLuceroGuarani.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- García, M. 60 Years Ago, the Space Age Began. nasa.gov. On 4 October 1957, the Soviet Union opened the Space Age… 2017. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/history/60-years-ago-the-space-age-began/ (accessed on 28 September 2025).
- Jordan, P. Role of Place Names in Relating People and Space. In Handbook of the Changing World Language Map; Brunn, S., Kehrein, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MPC. MPC/MPO/MPS Archive. IAU. Minor Planet Center. 2025. Available online: https://www.minorplanetcenter.net/iau/ECS/MPCArchive/MPCArchive_TBL.html (accessed on 30 October 2025).
- Masiero, J.R.; Mainzer, A.K.; Grav, T.; Bauer, J.M.; Cutri, R.M.; Dailey, J.; Eisenhardt, P.R.; McMillan, R.S.; Spahr, T.B.; Skrutskie, M.F.; et al. Main Belt Asteroids with WISE/NEOWISE. I. Preliminary Albedos and Diameters. Astrophys. J. 2021, 741, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JPL. Small-Body Database Lookup. 6438 Suarez (1988 BS3). 2025a. Available online: https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/tools/sbdb_lookup.html#/?sstr=6438 (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Macke, R. Latest Batch of Named Asteroids Includes Three Jesuit Astronomers and a Pope. Vatican Observatory. 2023. Available online: https://www.vaticanobservatory.org/sacred-space-astronomy/latest-batch-of-named-asteroids-includes-three-jesuit-astronomers-and-a-pope/ (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- JPL. Small-Body Database Lookup. 4269 Bogado (1974 FN). 2025b. Available online: https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/tools/sbdb_lookup.html#/?sstr=4269&view=OPD (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- JPL. Small-Body Database Lookup. 15,908 Bertoni. 2025c. Available online: https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/tools/sbdb_lookup.html#/?sstr=15908 (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- JPL. Small-Body Database Lookup. 15,414 Pettirossi (1998 BC35). 2025d. Available online: https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/tools/sbdb_lookup.html#/?sstr=Pettirossi&view=VOPDCA (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- JPL. Small-Body Database Lookup. 16,701 Volpe (1995 DH4). 2025e. Available online: https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/tools/sbdb_lookup.html#/?sstr=16701 (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- JPL. Small-Body Database Lookup. 15,988 Parini (1998 XD24). 2025f. Available online: https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/tools/sbdb_lookup.html#/?sstr=15988 (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- JPL. Small-Body Database Lookup. 5205 Servian (1988 CU7). 2025g. Available online: https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/tools/sbdb_lookup.html#/?sstr=5205 (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Carr, M.H.; Saunders, R.S.; Strom, R.G. Geology of the Terrestrial Planets; NASA Scientific and Technical Information Branch: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; p. 220. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Chauham, M.; Sur, K.; Jain, N. Geological study of Martian Rampart cráter Yuti using high resolution remote sensing. In Proceedings of the 46th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 16–20 March 2015; p. 1726. [Google Scholar]
- USGS. Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. Mars—Yuty. 2025a. Available online: https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/6685 (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- Gobernaciones y Municipios. Yuty, Tierra del Itakaru. Portal de Gobernaciones y Municipios República del Paraguay. Portal Construido y Mantenido por el MITIC. 2025. Available online: https://www.municipios.gov.py/yuty/ (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Zevaco, S. Minería en el territorio paraguayo. a Fundación Rosa Luxemburgo con fondos del Ministerio Federal de Cooperación Económica y Desarrollo de Alemania (BMZ). baseis.org.py Asunción, Paraguay. 2019. ISBN: 978-99967-952-2-0, 163p. Available online: https://www.geologiadelparaguay.com.py/Mineria-en-el-territorio-paraguayo.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- HIRISE. Fan-Shaped Form at Intersection of Valley with Yegros Crater. Anaglyph. 2025. Available online: https://www.uahirise.org/anaglyph/ESP_045431_1575_PSP_010434_1575_RED (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- USGS. Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. Mars—Yegros. 2025b. Available online: https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/6650 (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- Fariña, B.N. Crónica de la Primera República; Paraguay, 12 de Octubre de 1813; Fausto Ediciones: Asunción, Paraguay, 2013; 188p. [Google Scholar]
- USGS. Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. Mbir. 2025c. Available online: https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/14723 (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- USGS. Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. Yara. 2025d. Available online: https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/16355 (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- USGS. Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. IO—Tupan Patera. 2025e. Available online: https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/6135 (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- Gonzalez Torres, D.M. Folklore del Paraguay Asunción, Paraguay. Portalguaraní. 1995. 602p. Available online: https://portalguarani.com/590_dionisio_gonzalez_torres__/37304_folklore_del_paraguay__autor_dionisio_m_gonzalez_torres__ano_1995.html (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Turtle, E.P.; Keszthelyi, L.P.; McEwen, A.S.; Radebaugh, J.; Milazzo, M.; Simonelli, D.P.; Geissler, P.; Williams, D.; Perry, J.; Jaeger, W.L.; et al. The final Galileo SSI observations of Io: Orbits G28-I33. Icarus 2004, 169, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turtle, E.P.; Jaeger, W.L.; Schenk, P.M. Appendix 2: Ionian mountains identified to date. In Io After Galileo; Lopes, R.M.C., Spencer, J.R., Eds.; Springer-Praxis: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes-Gautier, R.; McEwen, A.S.; Smythe, W.B.; Geissler, P.E.; Kamp, L.; Davies, A.G.; Spencer, J.R.; Keszthelyi, L.; Carlson, R.; Leader, F.E.; et al. Active volcanism on Io: Global distribution and variations in activity. Icarus 1999, 140, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, R.M.C.; Kamp, L.M.; Smythe, W.D.; Mouginis-Mark, P.; Kargel, J.; Radebaugh, J.; Turtle, E.P.; Perry, J.; Williams, D.A.; Carlson, R.W.; et al. Lava lakes on Io: Observations of Io’s volcanic activity from Galileo NIMS during the 2001 fly-bys. Icarus 2004, 169, 140–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. IO—Monan Patera. 2025f. Available online: https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/3963 (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- USGS. Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. Moon—Dorsum Azara. 2025g. Available online: https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/1606 (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- Parodiz, J.J. Darwin in the New World; Brill Archive: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1981; 152p, ISBN 978-90-04-06546-8. [Google Scholar]
- USGS. Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. Mars—Paraná Valles. 2025h. Available online: https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/4585 (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- Maidana-Montiel, J.L. Paraguay. Approved Names. Tupa, Tumearandu. NameExoWorlds National Committee. 2025. Available online: https://nameexoworlds.iau.org/paraguay (accessed on 28 October 2025).
- Lapenda, G.C. Etimologia da Palavra Tupã; Boletim Universitário. Biblioteca Digital Curt Nimuendaju (Diretório Acadêmico da Faculdade de Filosofia da Universidade Católica de Pernambuco); 1953; pp. 3–7. Available online: https://biblio.wdfiles.com/local--files/lapenda-1953-etimologia/lapenda_1953_etimologia.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Pepe, F.; Mayor, M.; Galland, F.; Naef, D.; Queloz, D.; Santos, N.C.; Udry, S.; Burnet, M. The CORALIE survey for southern extra-solar planets VII. Two short-period Saturnian companions to HD 108,147 and HD 168746. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 388, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M. Tapecue. HD 63765, HIP 38041. eSky: The Electronic Sky. 2025. Available online: https://www.glyphweb.com/esky/stars/tapecue.html (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Bonfanti, A.; Ortolani, S.; Piotto, G.; Nascimbeni, V. Revising the ages of planet-hosting stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 575, A18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, M.G.; Jenkins, J.S. Spectroscopic Parameters and atmosphEric ChemIstriEs of Stars (SPECIES). I. Code description and dwarf stars catalogue. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 615, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRosa, M.; Mejia, G.R. An Atlas and Survey of Latin American History, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2019; 198p, ISBN 9781138089068. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).