1. Introduction
The east coast of Africa from Somalia to Mozambique and parts of Madagascar saw the emergence of a vibrant, culturally coherent society at the beginning of the second millennium CE. The Swahili peoples as they became known shared a range of linguistic, religious, material, and architectural expressions [
1,
2]. This important pre-colonial culture on the African seaboard enjoyed extensive connections around the Indian Ocean as well as its hinterland. Early historiographies of the Swahili characterized them as Arab, urban, and mercantile based on their religion and supposed origins, the remains of their notable stone towns, and the extent of their trading links e.g., [
3,
4]. Over the past 40 years, the indigenous African origins and contributions to Swahili culture have entirely eclipsed the previous colonial interpretative frameworks [
5,
6]. This has been accompanied by an interest in the less ‘elite’ expressions of urban settlements, to include firstly, the houses of earth and wattle that existed alongside the more prestigious stone towns; and secondly, an attempt to move beyond the settlements located within town walls to recognize broader landscapes of settlement and activity on a variety of scales fulfilling a variety of purposes [
7,
8,
9]. This welcome development has produced a much more subtle understanding of the differing strata within Swahili society. The characterization of the Swahili as a maritime culture, relying primarily on long-distance trade for their wealth and existence is one that has been reiterated and developed over the years e.g., [
10]. Equally, a concern to acknowledge the contribution and resources of the continental hinterland has counterpoised such views e.g., [
11,
12,
13]. To some degree, this debate is further evidence of a growing understanding of the Swahili as a society which is more diverse in material and social terms than previously thought. The emergence of Swahili culture in the second millennium having developed local and long-distance trade, while exploiting a full range of marine and agricultural resources found on the coast and inland, would tend to obviate an overly essentialized definition of this society.
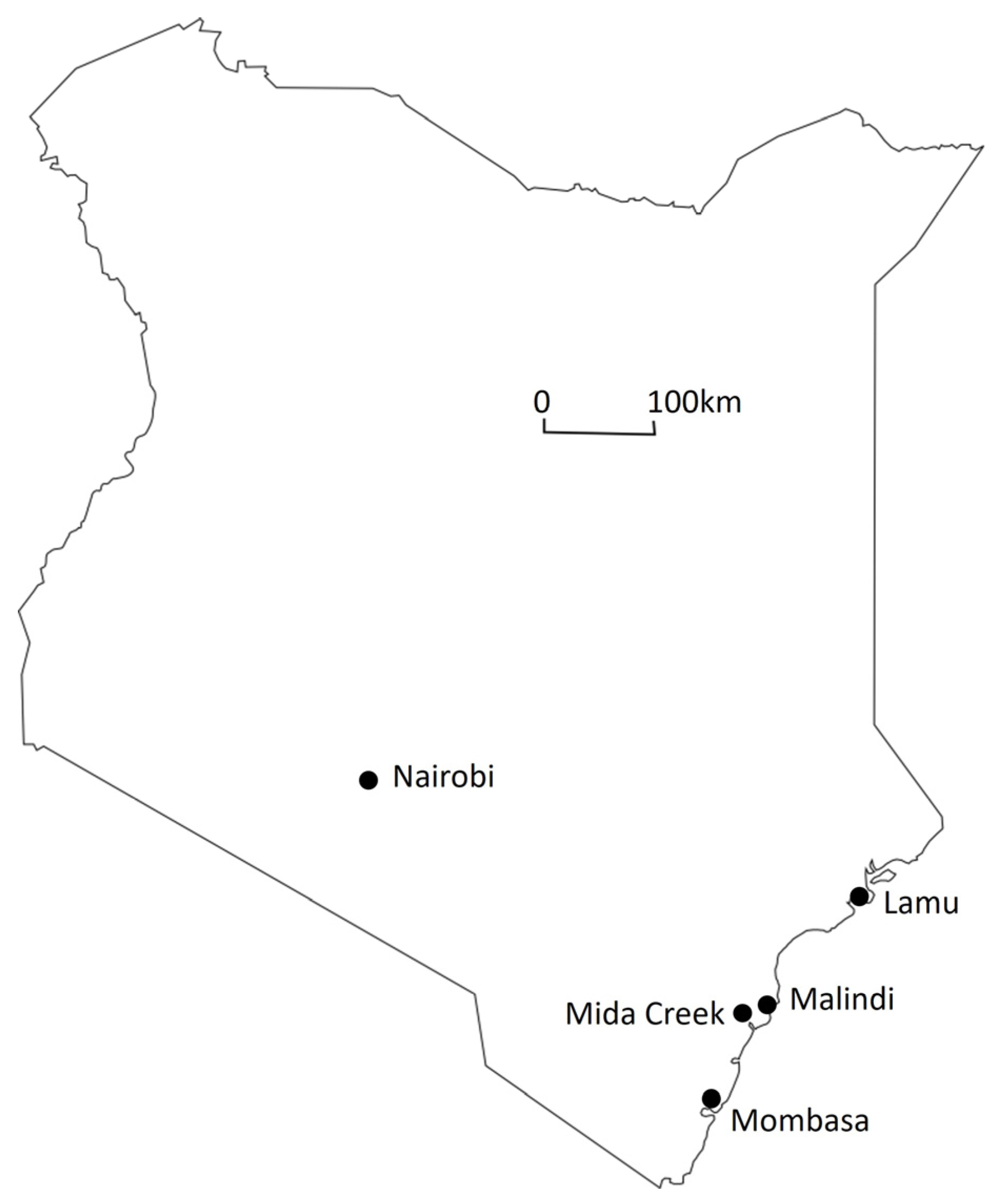
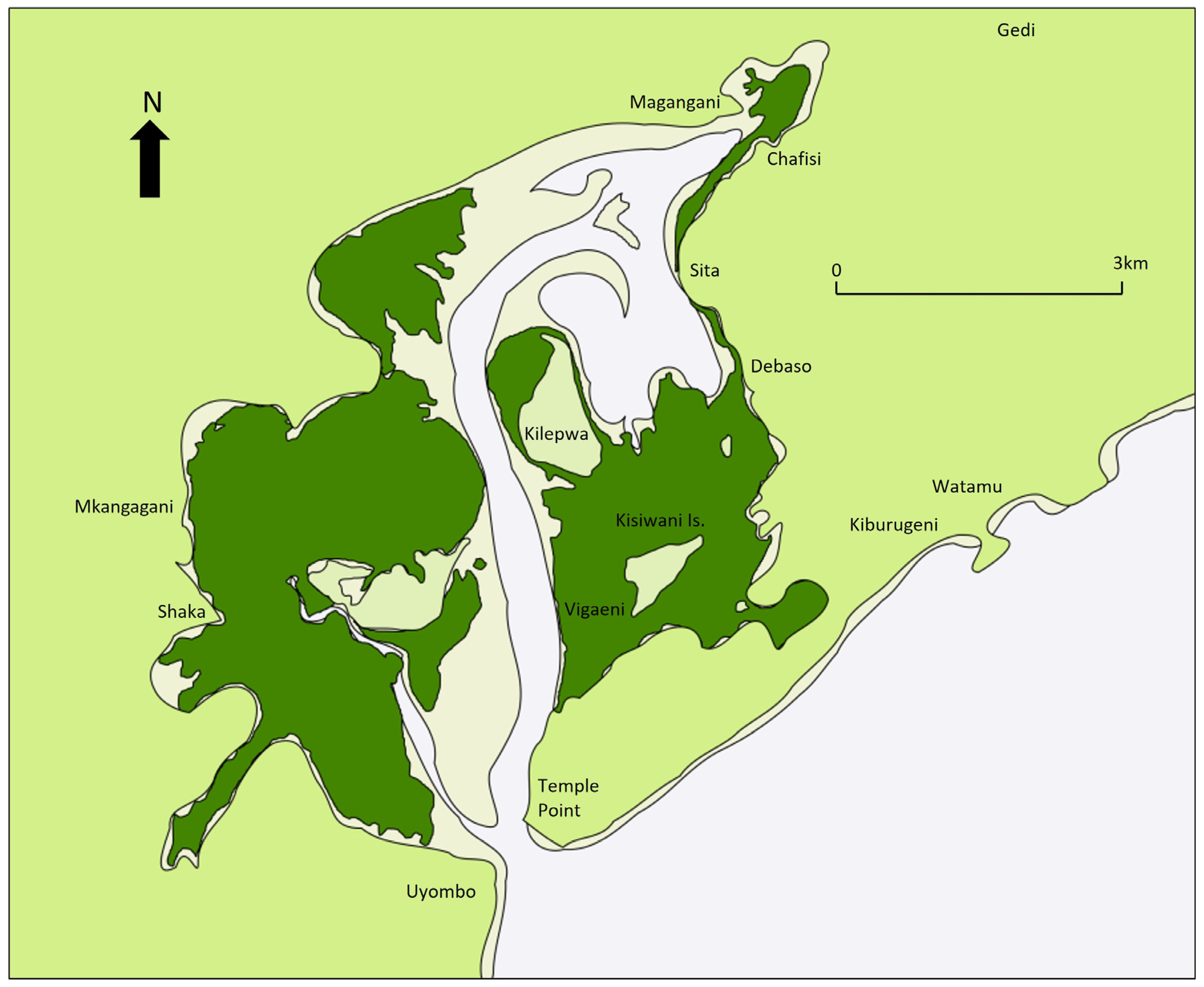
One of the first Swahili settlements to be examined by archaeologists was the well-preserved town of Gedi situated in the immediate hinterland of Mida Creek (
Figure 1). Unlike the coastal and island settlements elsewhere, Gedi is located a distance inland and seems to have been of less importance than nearby Malindi and Mambrui, which were mentioned in medieval texts [
14]. Work on the site is to some degree a microcosm of the development in the study of Swahili culture outlined above [
15]. The initial interest was the architectural remains of the stone town, described by James Kirkman e.g., [
16,
17] within a solely Arab context. Nevertheless, Kirkman’s excavation of Gedi provided an important chronology for the site which was occupied between the 12th and 16th centuries and reached the peak of its prosperity in the 15th to early 16th centuries [
16]. The site was later the focus of renewed work to re-examine and refine an understanding of its earlier chronology and spatial development throughout its occupation [
18,
19]. Stéphane Pradines’ work recognized the earlier forms of occupation and the enduring African contribution to the origins and development of the town. This study also made contributions to understanding architecture and ritual and moved beyond the town walls to identify areas occupied by the lower social status of society [
15,
19]. A broader consideration of the landscape around Gedi was the focus of Lynn Koplin’s study, which contributed to the identification of non-elite spaces via settlement evidence around the stone town. Furthermore, artefactual and faunal analysis of Koplin’s data allowed a more refined insight into social variability within these spaces [
9]. Work at Gedi has advanced from architectural analysis and excavation to careful chronological and spatial re-assessment and a re-positioning of Arab/African and elite/non-elite dichotomies to provide a fuller and more nuanced view of the site and its environs. While Gedi forms a key point of interest for Swahili historiography, it is important to acknowledge that early scholars did examine points of interest in the broader landscape, albeit their focus remained within relatively established frameworks. One such site in Mida Creek is the stone town comprising houses, a well, a mosque, and pillar tombs on Kilepwa Island, which James Kirkman [
20] excavated to find it broadly contemporary with Gedi. He was aware of other stone monuments around the Creek, although many received scant attention being ruined and robbed out see also [
21]. Further archaeological investigations at Kilepwa clarified its occupation to the 13th–17th centuries [
21,
22]. Much subsequent work in Mida continued to focus on buildings above the shore as points of architectural interest, e.g., mosques as indicators of settlement [
21,
23,
24]. Some sites within the intertidal zone did attract note, e.g., Vigaeni with its concentration of ceramics [
16]; however, it was not until the beginning of this century that archaeologists began to take a more explicitly maritime focus to site prospection at landscape scale see e.g., [
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31]. This approach sought to explore maritime material expression on its own terms though the infrastructure (e.g., landing places), industrial sites (e.g., salt and lime processing), economy (e.g., fish procurement sites), and water craft, as well as the place of the sea in social and religious practice. In addition, it allowed a more critical understanding of the place of the ‘maritime’ in Swahili society and the differing levels of access to its resources [
30]. In Mida Creek, the assessment of marine resources and complimentary surveys and trial excavation work at sites such as Shaka and the ship graffiti at Kilepwa Island best exemplify this approach [
22,
32].
This paper presents the results from a coastal survey of Mida Creek and seeks to re-evaluate the relationship between the Creek and the town of Gedi. As the closest navigable point on the shore to Gedi, the question of the utilization of the Creek and its resources naturally arises and a range of evidence is considered. The results of the survey in site and artefactual evidence, the geography and environment of the Creek, its resources and documented trade, and the vessels that plied its waters, both in ethnographic accounts and contemporary depictions (graffiti) are assessed.
The work described in this paper took place as part of the ‘MUCH to Discover in Mida Creek’ Project. A joint initiative of the National Museums of Kenya, Ulster University, and the British Institute in East Africa; the project was one of twenty-nine across the coast of East Africa under the stewardship of the UK-based Rising from the Depths Network (
https://risingfromthedepths.com/, accessed on 25 September 2023). This network sought to promote marine cultural heritage in the service of broader social and environmental aims and align work in this field more fully with ethical and sustainable development goals [
33]. Accordingly, the MUCH project worked with Mida Creek community partners to improve their visibility and sense of custodianship within Watamu Marine Park and nearby Arabuko Sokoke Forest Park. The project attempted to recognise and revive traditional ways of sustainably managing the marine environment in a manner that produced improved economic outcomes for contemporary households [
34]. Part of realising such a vision was to improve knowledge of coastal cultural heritage via a survey of archaeological sites and traditional boats around the Creek. The MUCH Project ran from 2018 to 2021, with much of the work discussed in this paper undertaken in August and September 2019.
3. Results: Chafisi and Eastern Mida
Chafisi is located at the northeastern-most inlet of Mida, on the east side of the Creek. This branch of Mida is archaeologically sensitive from a prospection viewpoint as it is the closest part of the Creek to Gedi. As such, it represents the most convenient area of the Creek to facilitate Gedi should the Creek, rather than a route to the open ocean shore, be chosen. To the northwest (opposing shore of the inlet) is Magangani, another candidate site for a landing place useful to Gedi. Magangani features a mosque, a well, and possible house mounds [
3,
21]. However, Garlake [
23] noted the mosque had Somalian architectural parallels typical of the 18th century; therefore, the settlement seems later than Gedi see also [
3].
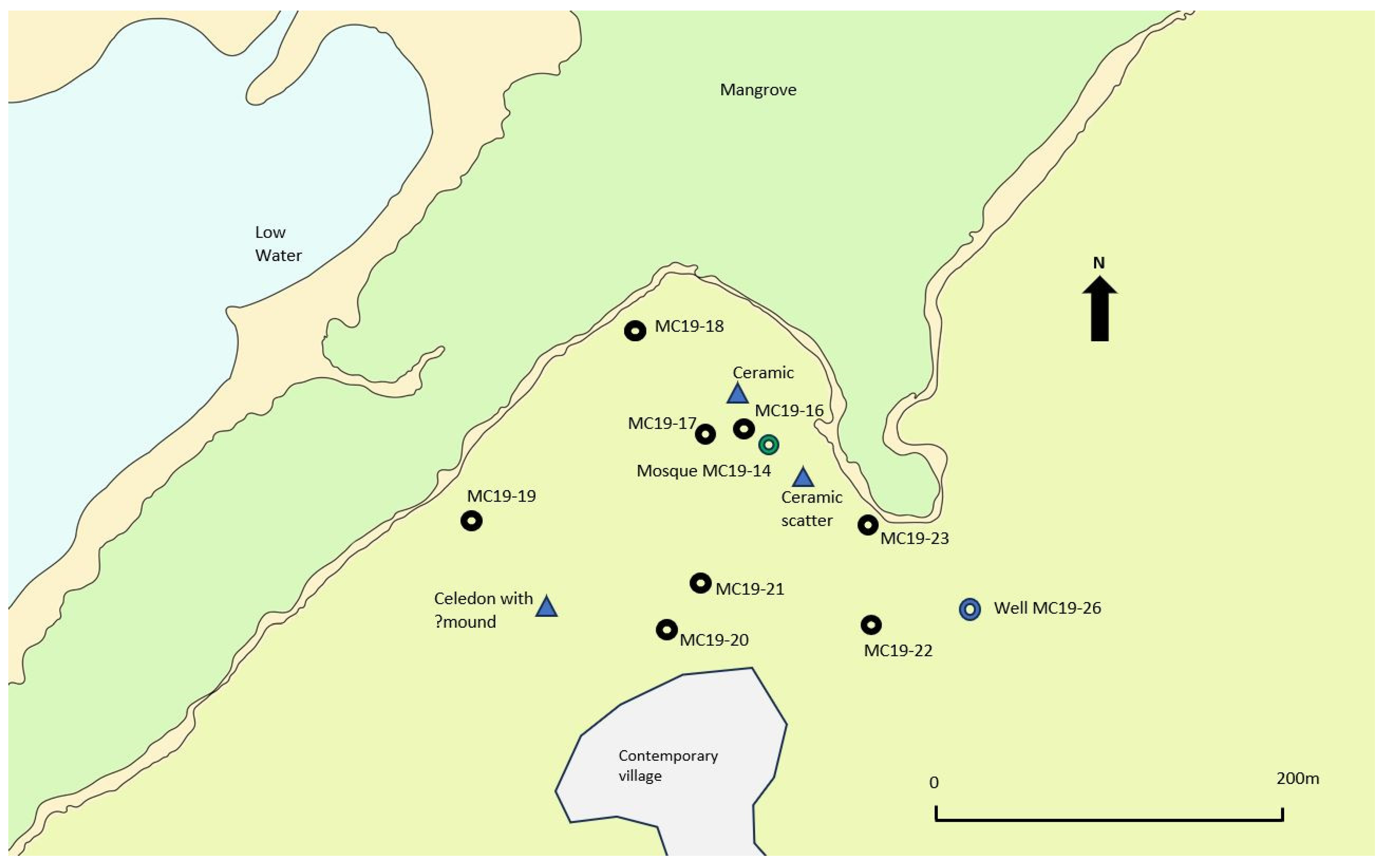
Like Magangani, Chafisi has the ruined remains of a documented mosque (MC19-14), although it does not survive to offer architectural analysis. A well is also present around 150 m to the southeast. Inspection of the area revealed no less than eight undocumented house mounds (MC19-16 to MC19-23,
Figure 3), four of which displayed partially exposed walling, while the rest were scatters of undressed coral blocks. The sites were variously located on open or cultivated ground within 110 m of the shore. They presented as sub-rectangular or sub-circular slightly raised mounds, although in two cases the edges of the features were hard to define (
Figure 4). Internally, differential ground levels in house MC19-16 and MC19-19 hinted at internal subdivision within the buildings. Some of the sites had clearly been disturbed with pit damage probably to rob out coral blocks. The dimensions of the original structures were difficult to ascertain as clearly the sites had been ruinous for some time and measurements included collapse. An average length of 19.6 m (range: 9.4–26.8 m) and width of 15.6 m (range: 9.3–17.6 m) is a reflection of building deterioration. In some cases, the surviving elements could act as a guide. The possible footings of house MC19-23 implied building dimensions of 6 × 5 m within an overall site measuring 18 × 15 m; at house MC19-22, the remaining internal walling implied dimensions of 14 × 9 m within an overall site measuring 23 × 17.3 m. Evidently, a range of house sizes are present with hints of internal features, but excavation would be required to define these more clearly.
The house mounds also featured surface scatters of pottery. A sample of 95 sherds was recovered from houses MC19-16 to MC19-22 and the mosque site (MC19-14) that included local and imported wares. Local wares included a range of decorated and undecorated fragments, while the imported wares included celadon and Islamic and far eastern monochrome wares indicative of contemporary occupation with Gedi (
Table 1).
Chronologies for Swahili sites have tended to rely predominantly on the presence of imported wares, given the broad period of usage for local Swahili types. The emergence of Tana ware (TIW) and Swahili Tradition Ware (SW) distributed across a wide area in the second millennium CE suggest a social coherence for the Swahili coast and culture but have a broad date range, spanning the 11th to 18th century [
14]. Nevertheless, the assemblage is dominated by SW wares (n = 82). The decorated items in this assemblage are mainly in the form of incised lines (
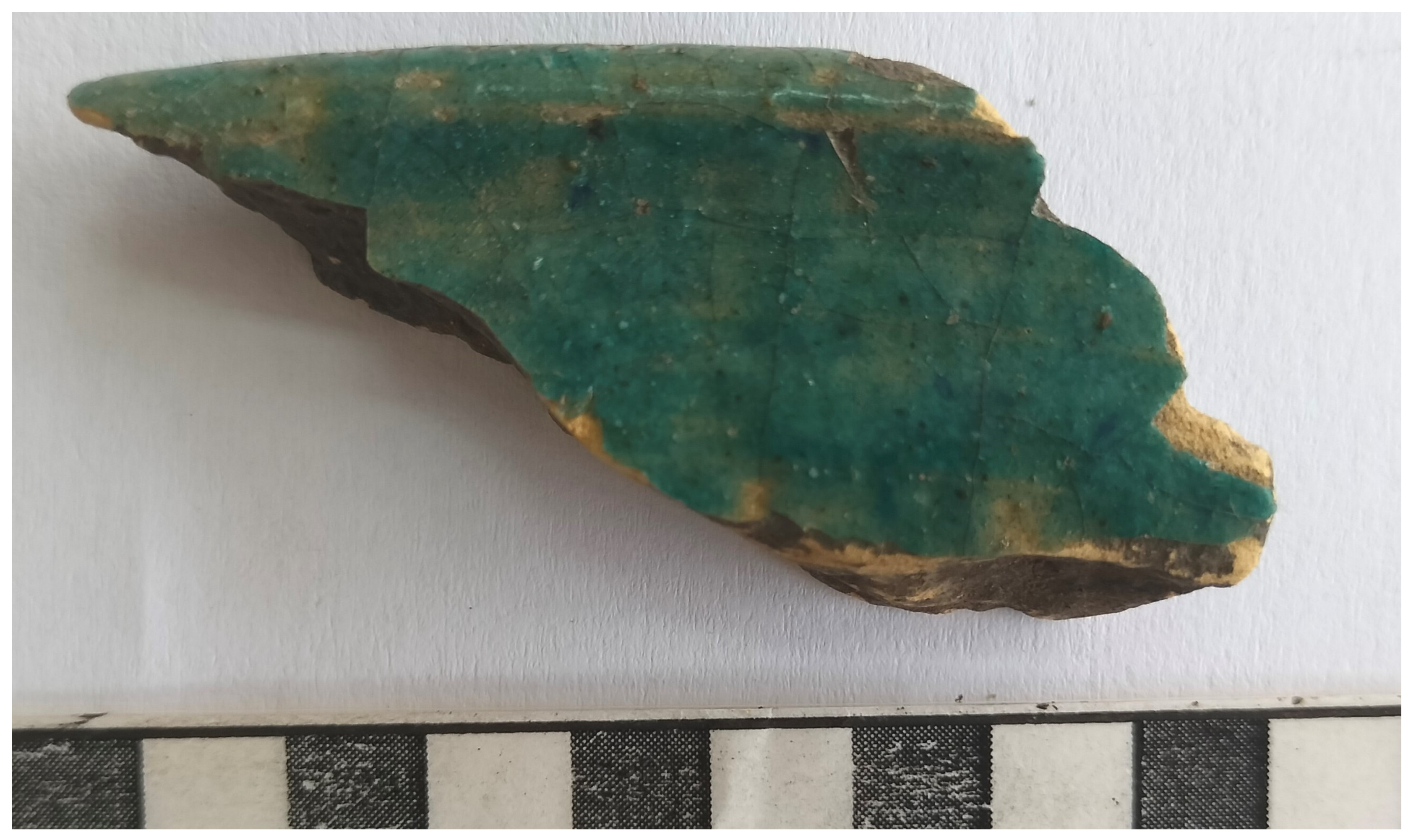
Figure 5). Of the imported wares, the Yemini black-on-yellow ware is common in Swahili sites from the mid-13th century until the end of the 15th century when it was eclipsed by Islamic monochromes [
6,
35,
36]. These monochromes appear from the mid-14th century and continue in use until the 18th century [
6]
Figure 6. The pottery from the far east includes celadon from the Longquan kilns dated to the Yuan Dynasty around the 14th century. Chinese monochrome stoneware was imported into eastern Africa from the 10th to the 13th century [
37]. In summary, the ceramics collected from the house sites at Chafisi appear to indicate activity contemporaneous with Gedi and indeed Kilepwa. The size of the recovered collection from Chafisi is modest and from an unsecured context; however, a valuable assemblage for preliminary comparison is that presented by Matthew Pawlowicz [
9] which was based on work in the environs of Gedi by Lynn Koplin. Importantly, Koplin’s study attempted to extend examination of the settlement beyond the stone town and in doing so, incorporate those living in earth-and-thatch dwellings. The results of this wider landscape study shed a more nuanced light on the social strata within the Swahili town, both between those living within and without the town walls, as well as within the earth houses of the ‘commoners’. Using shovel-test pits across the site and targeted excavation within earth-and-thatch neighbourhoods, Koplin recovered a substantial artefactual assemblage of which the ceramics are most relevant to this survey. Local ceramics dominated the assemblage, with decorated and undecorated examples present (undecorated body sherds being the most prevalent). Islamic monochromes were the most numerous of the imported ceramics (with green and blue glaze being the most common,
Figure 6), followed by celadons [
9]. Black-on-yellow ceramics were also a significant component of the assemblage. While the much smaller surface sample from Chafisi finds a degree of agreement with the nature and relative ratios of local-to-imported wares recovered by Koplin, there are some notable contrasts, in particular the absence of blue-and-white porcelain at Chafisi which became popular from the 15th century [
36]. Nevertheless, it can be concluded that even the limited sample from the Chafisi houses appears to find broad parallels with material recovered in the landscape around Gedi.
The shore to the south of Chafisi along the eastern edge of the Creek has a fringe of mangrove (30–100 m wide) but is relatively close to a deeper water channel. At Sita, c.1.5 km to the southwest of Chafisi, a landing place (MC19-11) marked by a break in the mangrove was investigated. The hinterland revealed two more house mounds (MC19-12/13) in proximity to a well. One of these (MC19-12) was recalled by a local informant as being constructed of coral rag and having two apartments in living memory. It may have been relatively recent and the earth-fast remains contained no diagnostic artefacts to aid dating. The area between Sita and Debaso constitutes the last open shore before the intertidal zone succumbs to thick stands of mangrove. Landing places in this area (notably MC19-07) featured a number of scatters of local wares in the immediate hinterland. This section of the shore provides an access point to reach Kilepwa Island, which must be crossed to reach the stone town.
4. Results: Central and Western Mida
Located on the southwestern edge of Kilepwa Island, the stone town stood close to the main channel entering the Creek and is clearly sited to be served by it. Rather than re-examine the town, the survey chose to investigate the hinterland and shore and once again a previously undocumented house mound (MC19-39) was discovered. Situated in a maize field
c.200 m to the southeast of the main archaeological complex, it formed a prominent rise and featured a good deal of local ware pottery fragments. Kilepwa’s neighbouring island of Kisiwani is engulfed by mangrove; however, more local wares were found at the north end of the island (MC19-44), where a drainage channel passes a raised area featuring baobab trees and current clay extraction. The channel empties northward into the basin to the east of Kilepwa and would have been navigable by canoe. Off the southwest end of Kisiwani is one of the Creek’s most enigmatic sites. Located in an area where the mangrove forest thins is a raised mound called Vigaeni ‘place of the sherds’. This natural rise is covered in many thousands of fragments of local pottery (MC19-72) over its entire surface, with evidence of later shell exploitation (
Figure 7). It has been interpreted by Pollard (2018) as a late medieval dumping site. However, inspection of the sherds suggest they were relatively new and the effort to take them to this location to dispose of seems untenable. An alternative might be that under earlier conditions, the island was more advantageously located to trade the pottery or their contents to passing vessels. Further local ceramics (MC19-81/82) on an island 500 m southwest on the edge of the current channel demonstrate these wares were moving on to more central locations which would have been served more readily by passing vessels.
Like the southeast of Mida Creek, the west coast is blocked from navigable channels by thick mangrove forest. At the face of the back shore at Mkangagani, an eroding bank produced significant deposits of ceramics (MC19-62), which included monochrome wares indicating a possibly more significant area of activity than the current landscape has yielded thus far. Further south near Shaka Point, ceramics and shells were found eroding from the back shore (MC19-31). Previously identified house sites (MC19-63) were located on a bluff overlooking one of the channels through the mangrove. Like Kisiwani, these narrow waterways connect to the main channel, but would be accessible by only the smallest of craft. Shaka is a settlement site comprising a mosque and tombs that Kirkman (1952) speculated might have been 16th century in date; however, recent work by Edward Pollard and Caesar Bita testing an eroding section face on the bluff recovered 15th century occupation evidence bringing the site within the zenith of occupation and trade experienced by Kilepwa and Gedi.
5. Discussion
The archaeological survey of the Mida Creek’s coast revealed a range of evidence for activity on islands, the foreshore, and beach fringes. While most of this evidence comprised artefactual scatters in the form of ceramics and shell middens, more substantial indicators of occupation included house mounds and infrastructure. While the work has gone some way to refining the distribution and chronology of activity around the Creek, it is clear that the results justify a more concentrated campaign in future.
Mida Creek’s relationship with Gedi as a small but important and wealthy Swahili site is of particular interest, given its unusual location in relation to the coast. Gedi is 6 km from the open ocean at Watamu and 3 km from the shore of Mida. The sites of Watamu and nearby Kiburugeni feature mosques and tombs, with the tombs having produced blue-and-white porcelain dated to the 14–15th century [
21,
23]. The sites overlook a small bay which features rocky islets and submerged rocks; furthermore, there is a fringing reef to negotiate on approach to the shore. Nevertheless, the sites are contemporary with the period of Gedi’s expansion and a fringing reef did not prove an impediment to other Swahili sites, indeed it extends toward the entrance to Mida Creek. Of the sites around Mida, Kilepwa and Shaka appear to be contemporary with Gedi. Kirkman [
20] dismissed any relationship between these sites and Gedi, presumably on the grounds of local conditions, in particular for maritime transport. Assessment of the suitability of the Creek to serve Gedi or indeed its settlements to function as entities in their own right is limited by the relative paucity of the work on its environmental history. The origins and development of the bay are not well understood. Lacking any discharging rivers, Oostrom [
38] speculated that it might have been formed as a result of eroding wave action. The absence of a channel across the reef at the entrance to the bay suggests there was never any riverine influence and that tidal scouring is not of sufficient strength to effect the reef [
38]. The dominant current is the flood tide evidenced by the direction and form of fans of sediment that can be seen in the upper reaches of the Creek. This current introduced calcareous sediments from the open ocean, some of which have been dated as Holocene deposits
c.2.3ky BP [
38,
39]. Despite an environment of ongoing sediment accretion, the main channel maintains a depth of 4-11 m as far as the north of Kilepwa Island [
40]. After this point, it shallows until 0.5 m opposite Chafisi at HW Spring tide. The rate at which sediment built up in the past is not known, nor any previous configuration of sands within the bay; nevertheless, the limited dating evidence would tend to indicate a stable, slow accumulation of sand over the past millennium. This would inevitably have affected the efficiency of settlements in the Creek as trading or trans-shipment points over the centuries. The meaning of Kilepwa as ‘the place that dried up’ has been interpreted as referring to the wells on the island, but as the site today is over 200 m from the edge of the navigable channel, another interpretation could be that it was bestowed as a result of the gradual inundation of the island waterfront see [
20,
22].
A key motivation for settlement around the Creek is the resources it offers to its inhabitants. Shallow-water fish species and shellfish are evidenced not just in the coastal middens, but the faunal remains from the environs of Gedi demonstrate that the inhabitants had a diet rich in fish [
9]. Over 75% of Koplin’s faunal assemblage were fish, with the majority being reef and nearshore species [
9]. The relative rarity of deep-water species only emphasizes the importance of areas like Mida and hints at an intensive regime of exploitation, perhaps by using fish traps that have not yet been detected archaeologically. Furthermore, the Creek offered resources for trade; this is particularly true of the mangrove forest, which by the second millennium was a significant African export to the timber-impoverished Persian Gulf for roofing materials [
41,
42]. Mangrove was noted in the Red Sea and Somalia as early as the classical period, with Greek and Roman writers referring to it as laurel or olive groves growing in salty water [
43]. Used for building, a potential food source, musical instruments, and medicine, in modern times it continued to be exploited for fuel, boat-building, tanning, furniture, and charcoal [
43,
44]. Mida contains seven of the nine Kenyan species of mangrove, each with characteristics of use to humans [
32,
45]. Notably, mangroves in the vicinity of Kilepwa Island are dominated by
Rhizophora mucronata, which were the desired species for export to the Middle East [
32,
46].
A consideration of Swahili boat-building traditions is also of relevance for understanding how the Creek might have functioned. These can be gleaned from historical sources and traditions, although these are clearly limited by how far they might be relevant to Swahili sites when under occupation. A second line of evidence are the depictions of boats present in the graffiti from Kilepwa, assuming that those responsible witnessed the vessels depicted in the environs of the island. Kirkman [
20] noted that jahazis or ocean-going dhows entered the Creek for mangrove timber within living memory. While this example demonstrates the functionality of the Creek and the scale of vessels that could operate in its waters, these motor dhows with nailed planks are a late manifestation of an east African ship [
41]. One of the most striking aspects of earlier Swahili boat-building is the technique of sewn planking. Sewn vessels were known along the East African coast as early as the 1st century, and references to them re-appear from the 13th century to the modern period [
47]. The most notable Swahili craft of this type was the mtepe (pl. mitepe). One of the advantages of sewn craft operating in shallow-water creeks was their tolerance to being beached in comparison to nailed ships. Such vessels could be floated as far inshore as possible at high tide, where they could dry in the shallows as their crew transferred the cargo. As a vessel dries, its weight puts strain on the planks of the hull; however, a sewn boat flexes and the cordage stretches with little damage to the planks. Maintenance comprises the periodic replacement of cordage and re-caulking the hull. By contrast, nailed hulls flex less causing stress around the nails which slowly damages planks, eventually requiring expensive replacement [
48]. For a tidal environment like Mida Creek with no formal port structures in the form of quays or wharves, the benefits of this shallow-draft traditional craft are obvious. Furthermore, their particular suitability for transporting mangroves, including draft, cargo, and crew space has been noted [
41]. Indirect evidence of the presence of such craft is offered by their depictions in the form of graffiti within buildings. These are found on plaster at Kilepwa, with examples also occurring at Gedi. In Gedi, the House of the Cowries features a simple sailing vessel with a lateen sail regarded as 16th century, while the 15–16th century House of the Dhow features a depiction of the launching of a vessel with a rising prow, likely a mtepe [
49,
50]. At Kilepwa, all or partial depictions of four vessels are incised in a manner that suggests they were added to over time. At least two of the depictions in a 15th century house feature a detail or form that suggest a sewn mtepe [
22]. Dating graffiti, notably where depictions have been overwritten, is inevitably difficult. Garlake and Garlake [
49] suggested that graffiti were incised on plaster after its initial hardening but not completely set, judging by the lack of flaking; therefore, it may be dated close to the initial occupation. Plaster was re-applied in buildings and this was in evidence at Kilepwa, so it is not entirely the case that it may be early, although it is unlikely it was added post-abandonment. The graffiti at Kilepwa and Gedi supports the presence of vessels suitable to local tidal conditions. Such vessels would have entered the Creek perhaps using the mosque at Temple Point as an aid to navigation see [
10,
28]. Entering the Creek, they would have had a clear, deep channel to arrive at Kilepwa and beach to unload their cargo. Shallower parts of the Creek could be approached via channels and inlets as the tide allowed, or goods could have been moved to smaller vessels such as mashua or dugout canoes. Mitepe could have manoeuvred close to mangrove cutting areas and waited to load and move off on the tide.
To effectively function within the vibrant Indian Ocean maritime trade networks of the 10th to 16th centuries CE, Gedi needed access to the sea. Pradines [
19,
51] claimed that Gedi began as a village connected to the ocean at Mida Creek in the 11th century. Arguably, small settlements like Chafisi had a role to play in the movement of resources around the Creek and given its position between Kilepwa and Gedi, it must have been a site of interaction for goods, fishermen, and visitors. The presence of a mosque and stone houses would tend to support it as a settlement of some importance and the comparative nature of the surface finds also demonstrate that contemporary goods were passing through this entrepôt. Nevertheless, the scale, distribution, and nature of the house sites would imply a secondary status to Gedi and indeed Kilepwa. It is suggested, therefore, that this site operated as a shoreline facility to accommodate beached or moored vessels carrying goods destined for Gedi and the return journey out to Kilepwa and the Indian Ocean. Taking advantage of its geographical position, Chafisi may have been established as an outport to serve Gedi and to secure a strategic foothold on an important section of the shore. Clearly more investigation of this site and nearby Sita would be desirable to fully assess its role in any such activity. Furthermore, the area between these shoreline sites and Gedi (currently a patchwork of houses, garden plots, and fields) should be subject to future scrutiny where possible. Other nodes of activity, Shaka, Mkangagani, Temple Point, Kiburungeni, and Uyombo, have been impacted by farming and development and few standing remains are evident. While some of these sites have been dismissed as late, and others are not suitable for port facilities due to their situation, sites such as Shaka and Mkangagani do hint at contemporary activity in superficially less auspicious parts of the Creek and caution against reading this landscape with a too restrictive maritime or navigational lens.
The archaeological survey in Mida Creek successfully broadened the known number of sites in the region, reflected the multi-period nature of the settlement in the area, and presented new avenues for future research. One challenge is establishing the environmental history of Mida and the sedimentation regime that has so clearly had an effect on settlement preferences around the Creek. Future, cross-disciplinary work to investigate the physical and cultural aspects of the marine zone would be desirable to understand and assess more fully the place of Mida Creek in Swahili society.