Mixed-Reality Demonstration and Training of Glassblowing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Craft Representation and Craft Presentation
2.2. Interactive Technologies for CH
2.3. Mixed Reality Installations for Education and Training
2.4. Importance of Intangible Cultural Heritage for Sustainable Tourism
2.5. Cultural Context
2.5.1. About CNAM
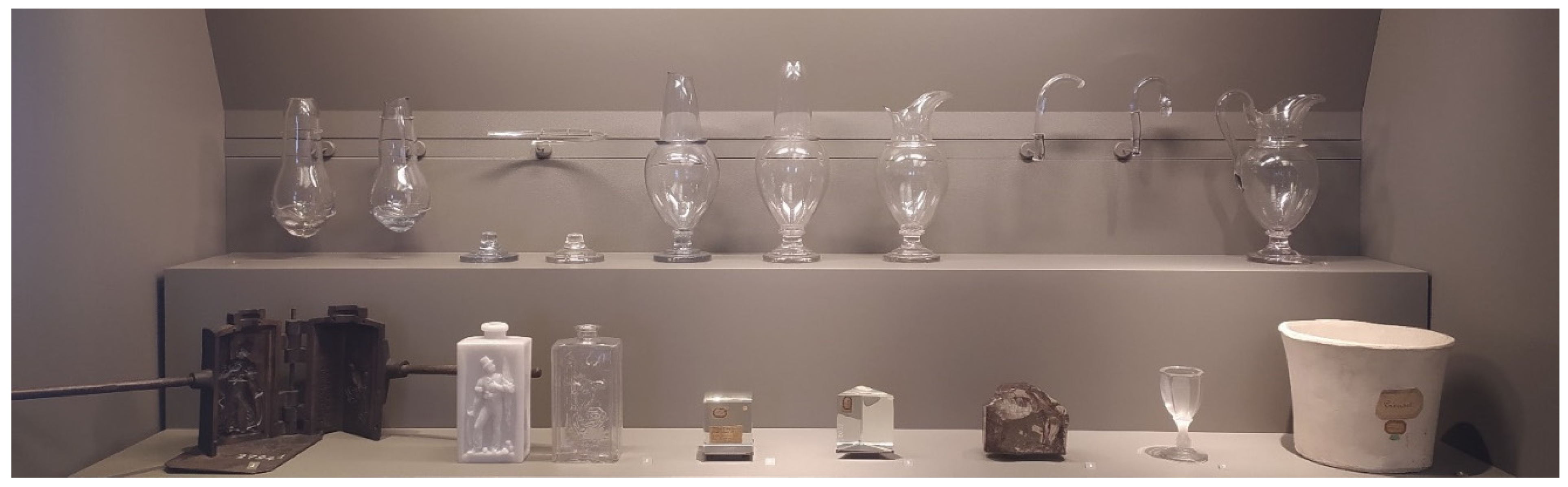
2.5.2. Rationale for the Selection of the Carafe as a Study Material
2.6. Direct versus Indirect Experiences for Presenting Cultural Context
2.7. Contribution of This Work
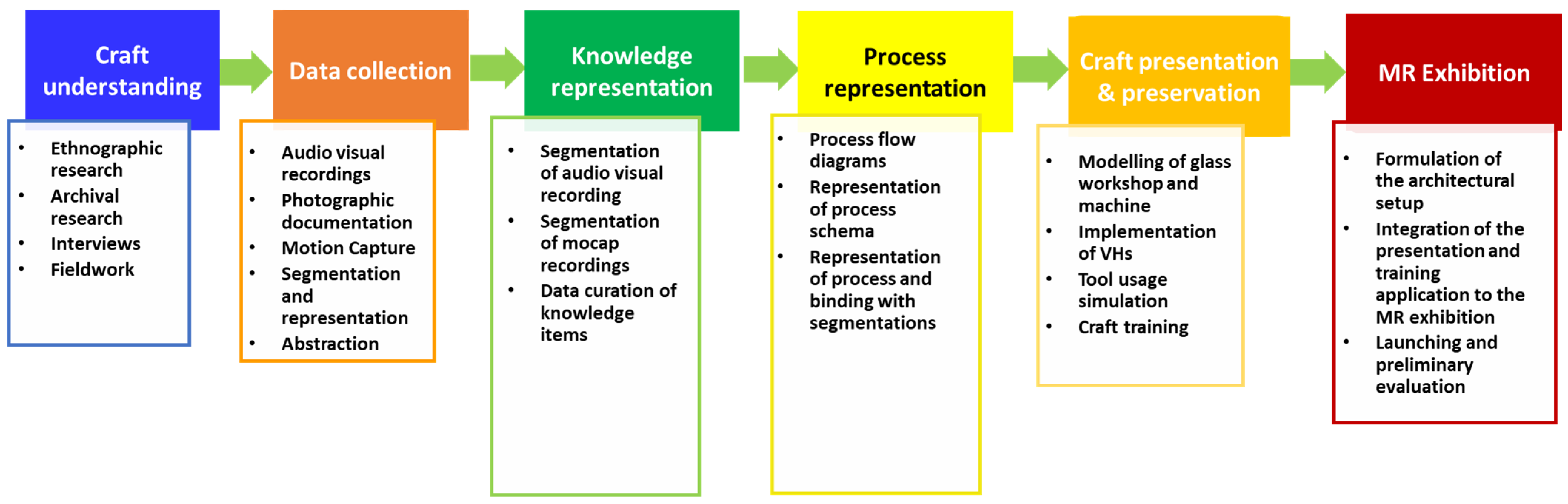
3. Crafting Process Modeling and Representation
3.1. Craft Understanding
3.2. Data Collection
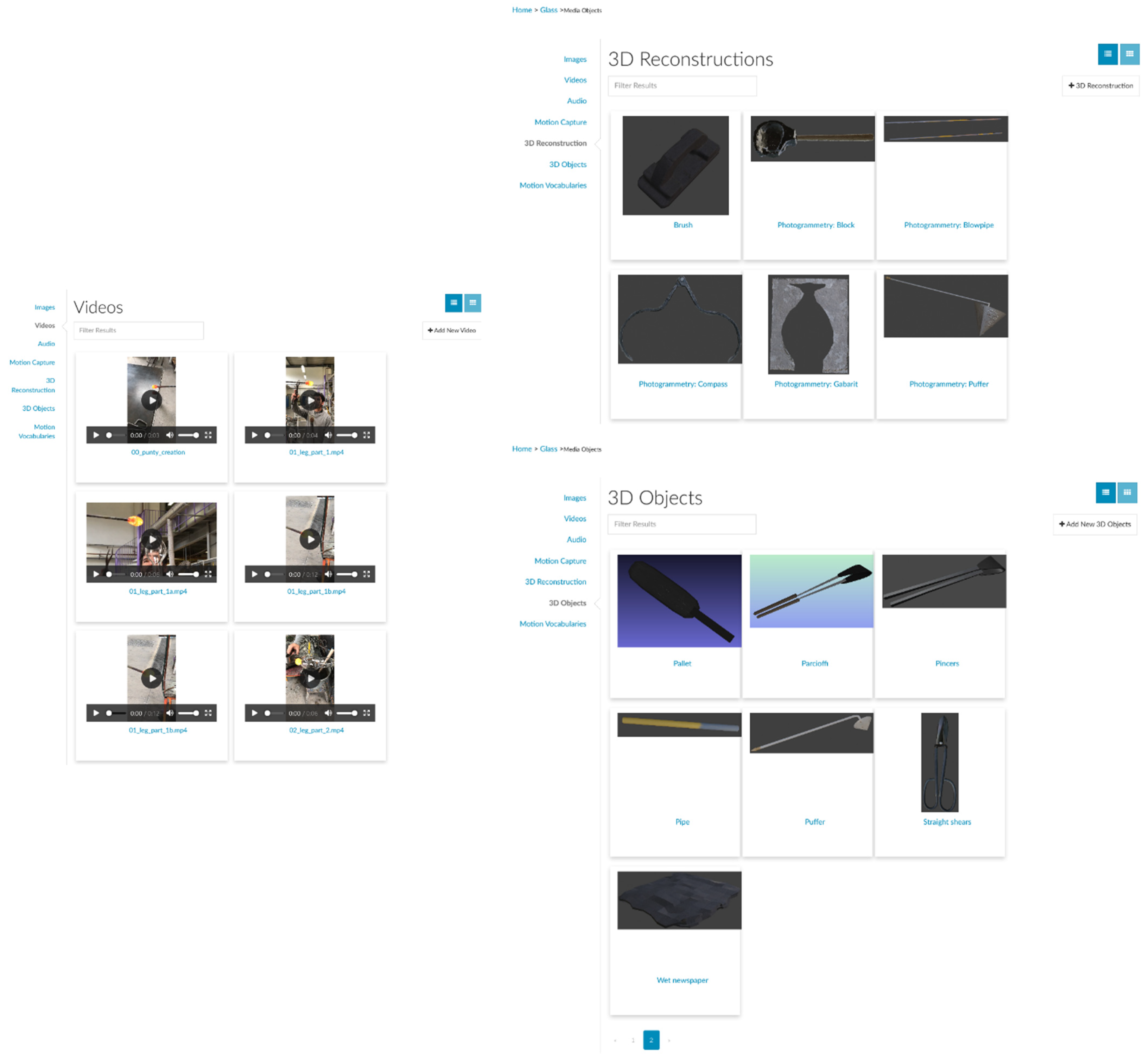
3.2.1. Audiovisual Recordings
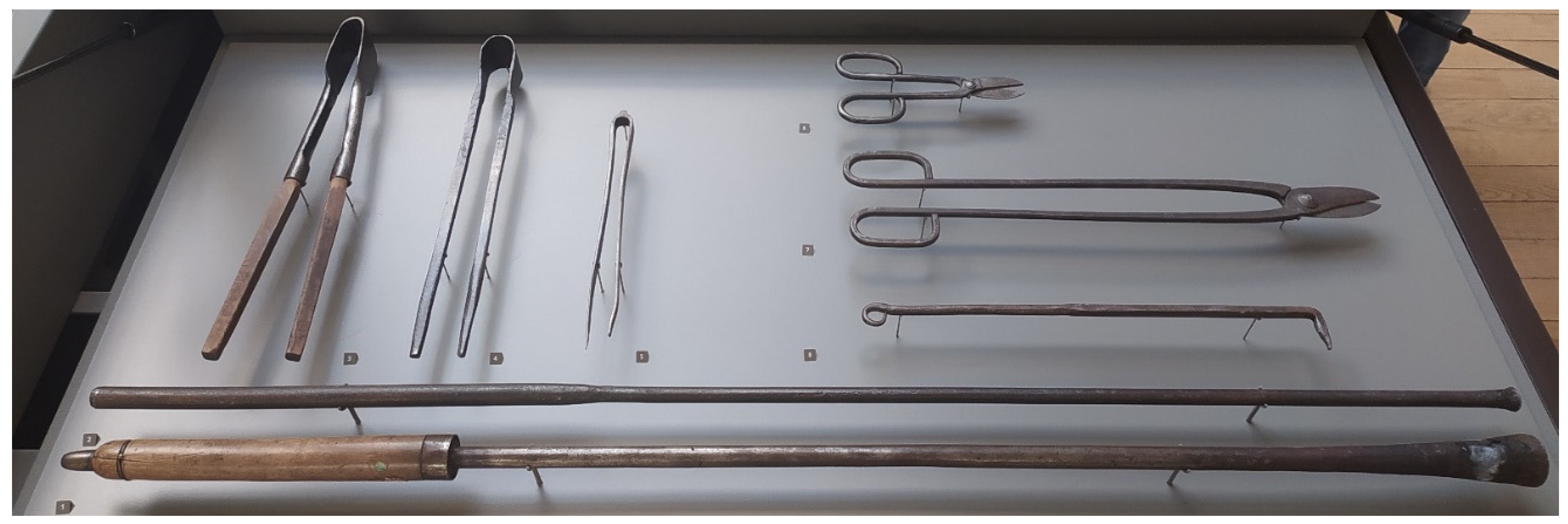
3.2.2. Documentation of Tools, Machinery, and Workspaces
3.2.3. Motion Capture
3.2.4. Data Curation
3.3. Knowledge Representation
3.4. Workflow Representation
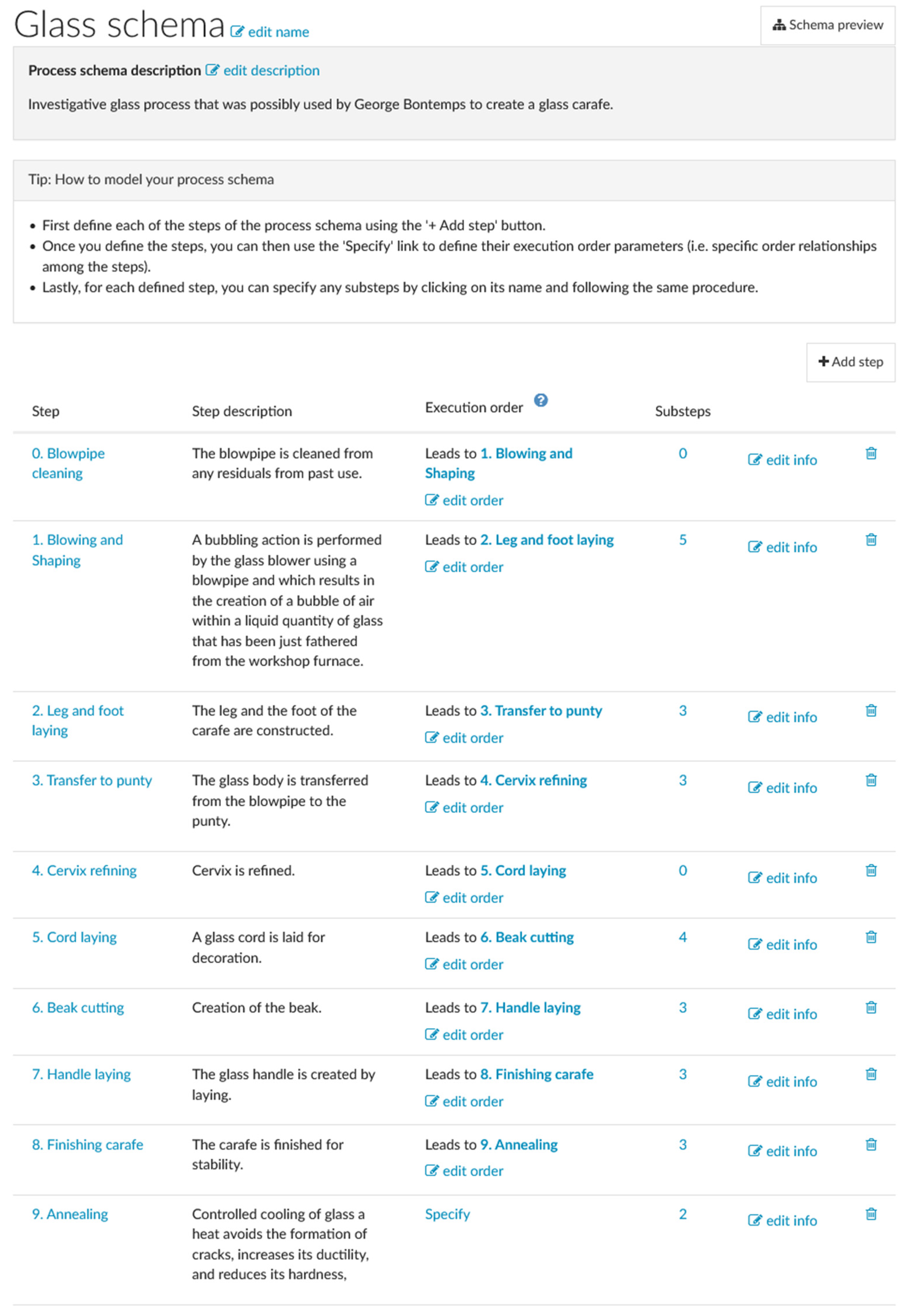
3.5. Process Schema Representation
3.6. Process Representation
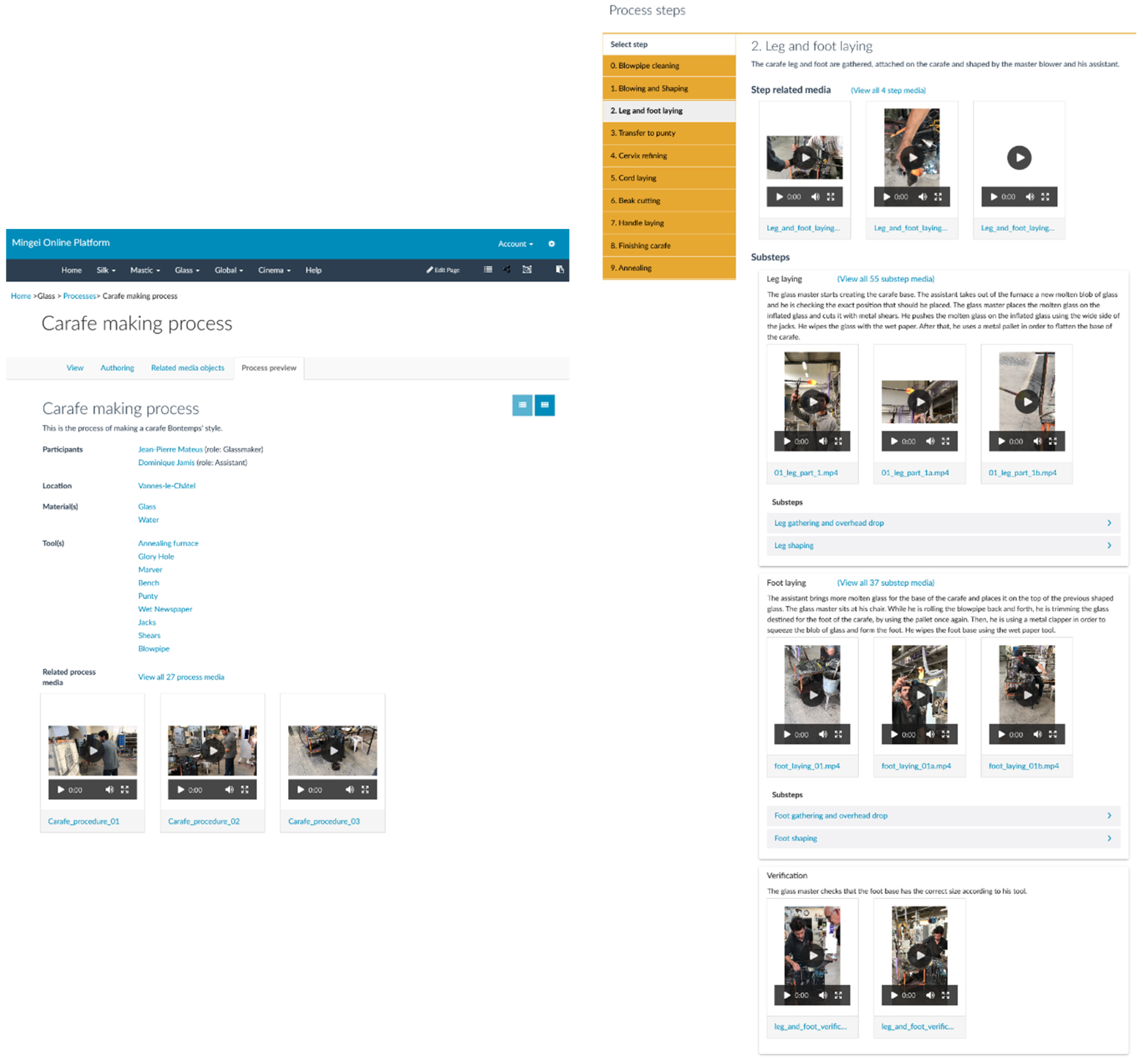
4. Craft Presentation and Preservation
4.1. Digital Preservation
4.2. Craft Documentation
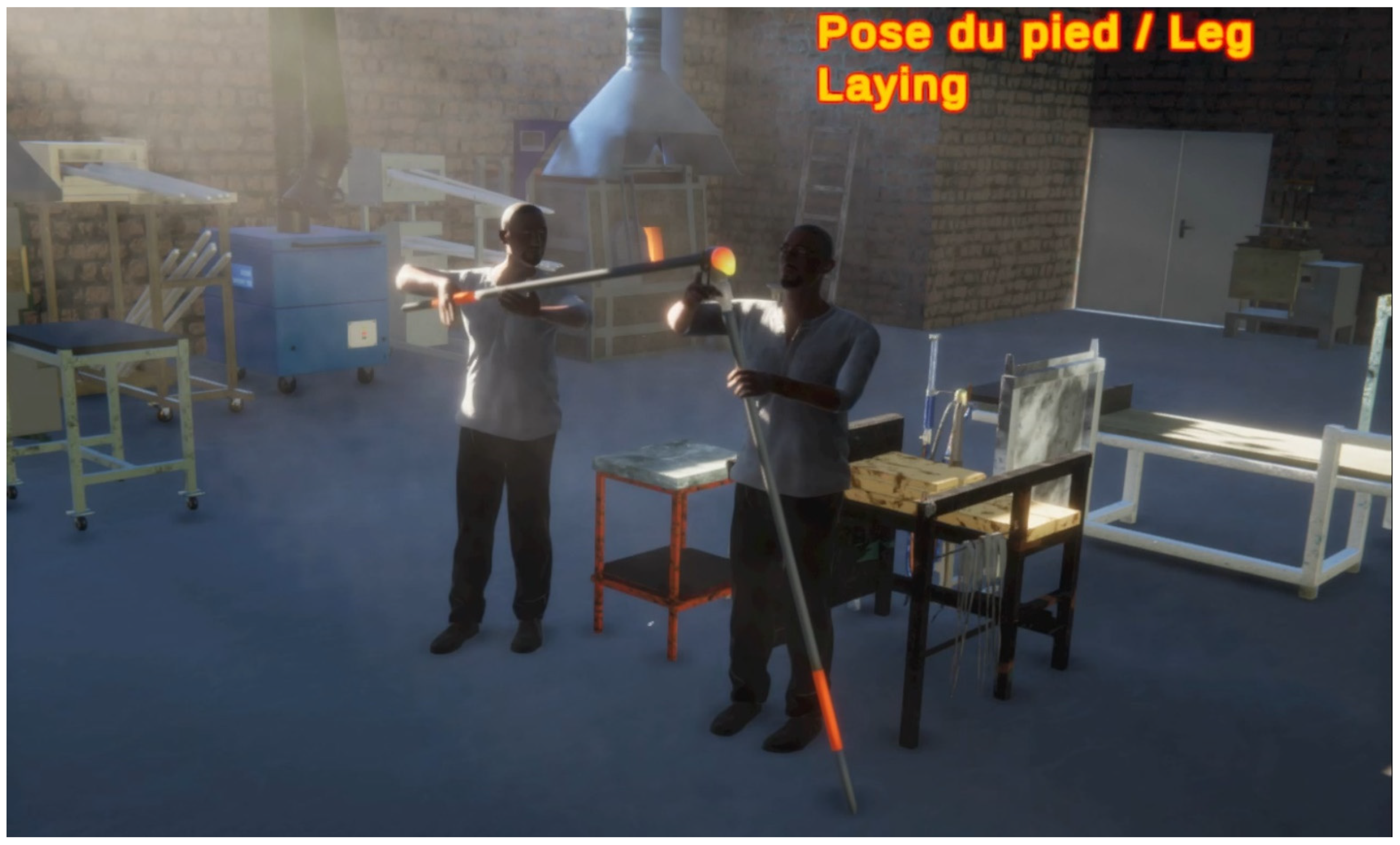
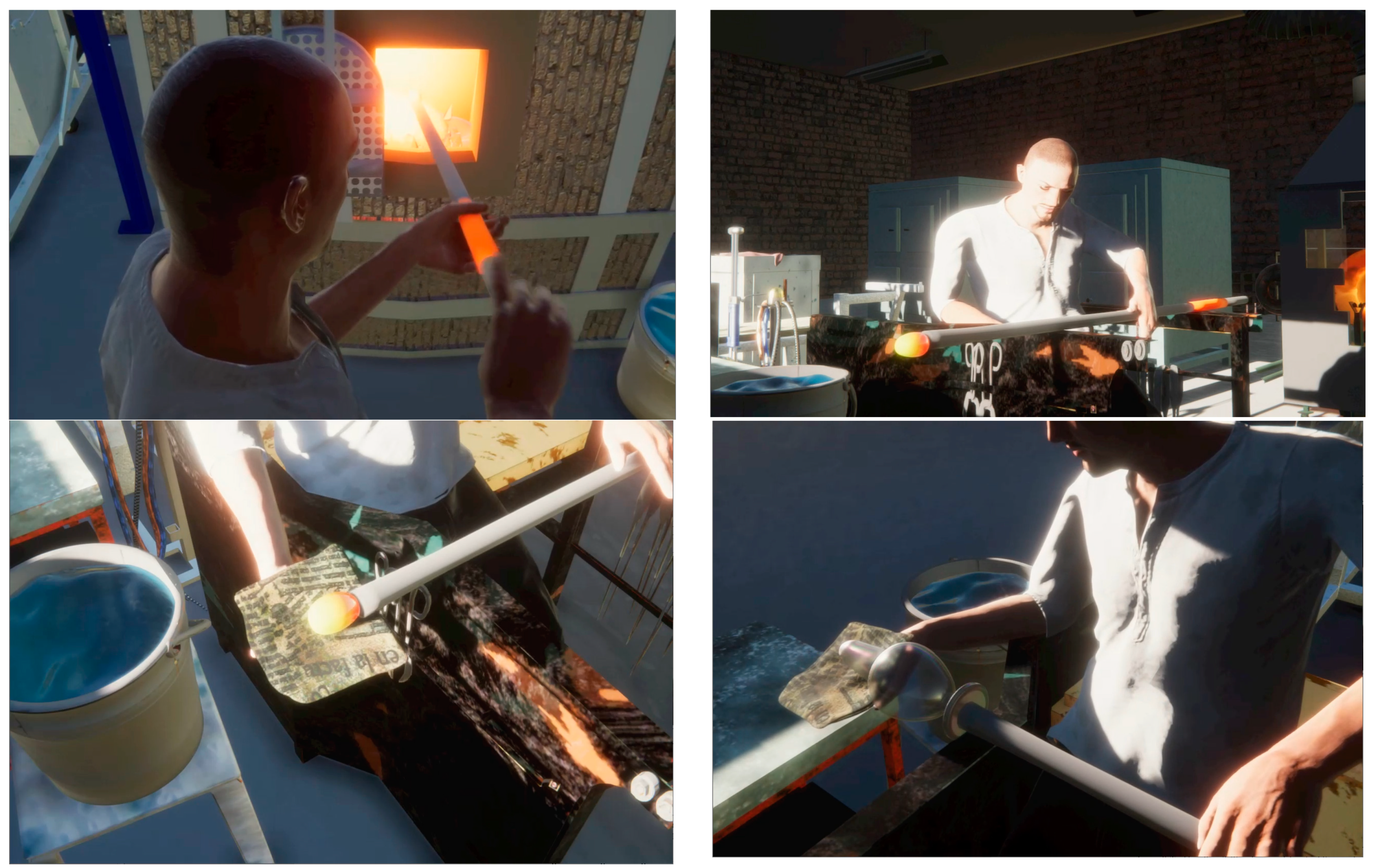
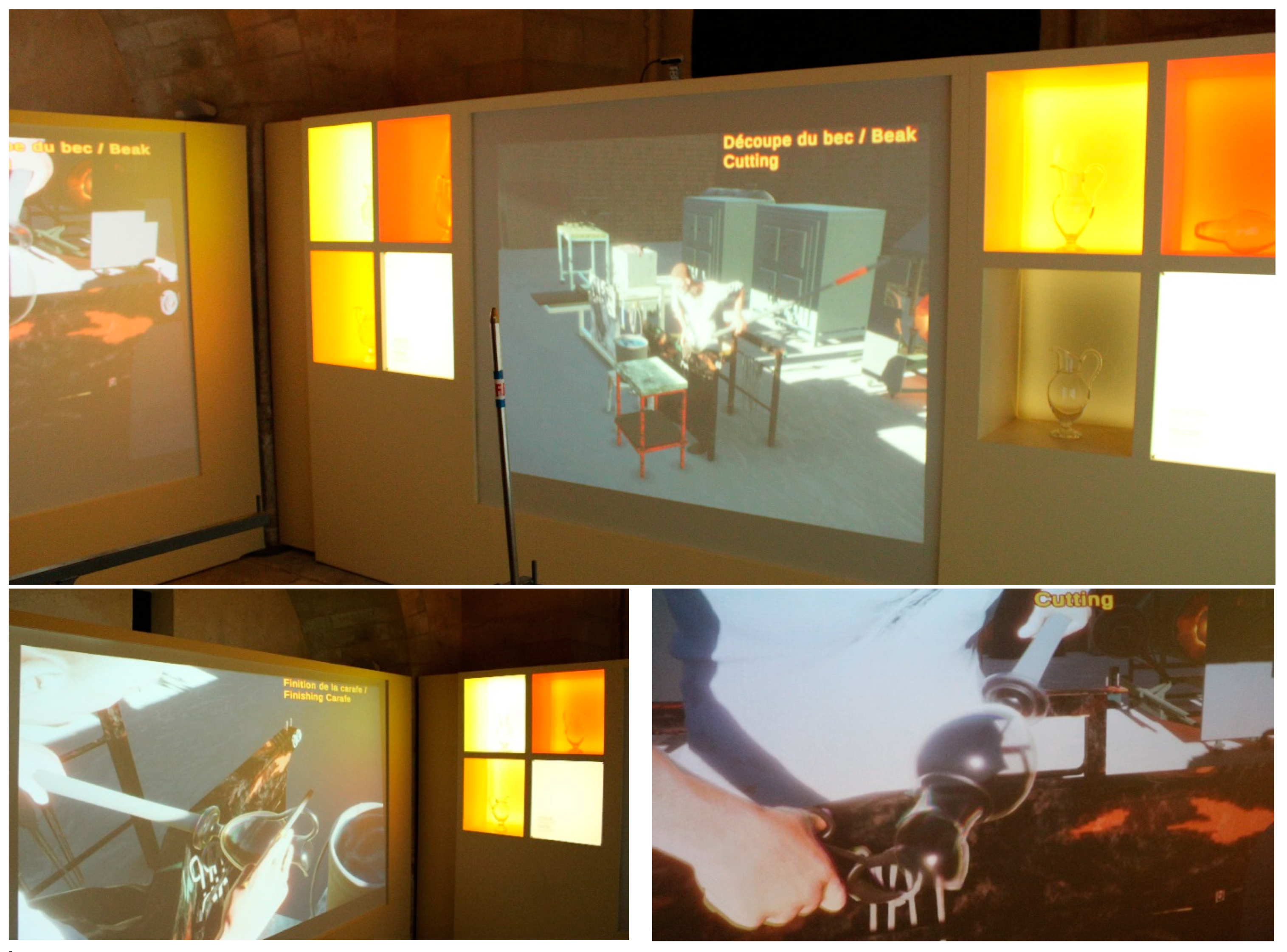
4.3. Craft Demonstration
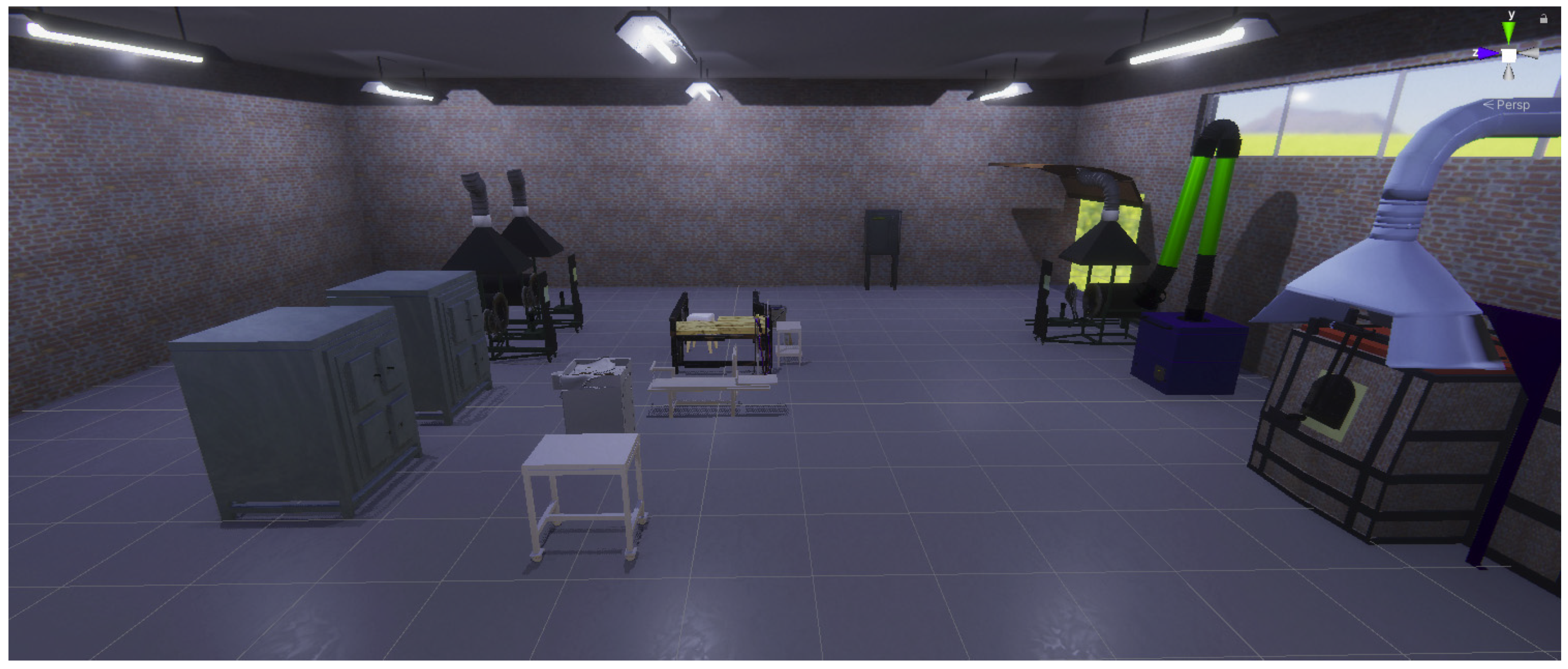
4.3.1. Workshop Implementation in 3D
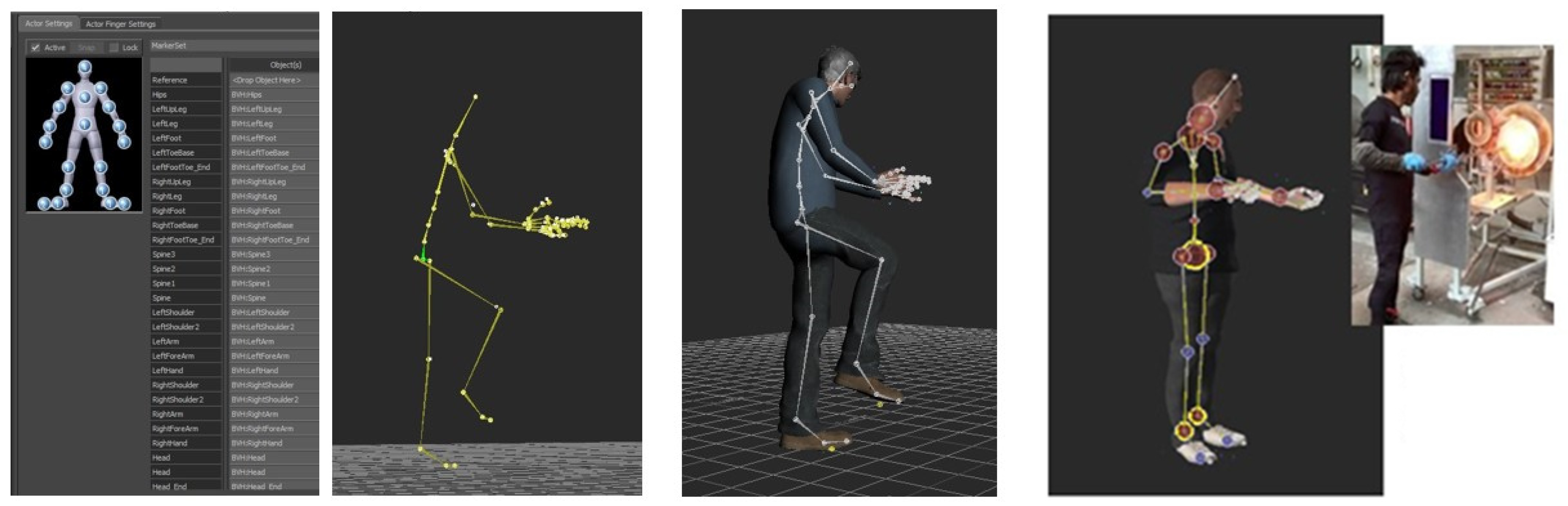
4.3.2. Implementation of Virtual Humans and Animation
- Creation of an “actor” in MotionBuilder with skeleton definition corresponding to the Biovision Hierarchy (BVH).
- Transposition of the received animations (.bvh files) on the actor
- Synchronization of the avatar with the actor by adjusting the the models so that the measurements match and the animations are correctly reproduced (retargeting).
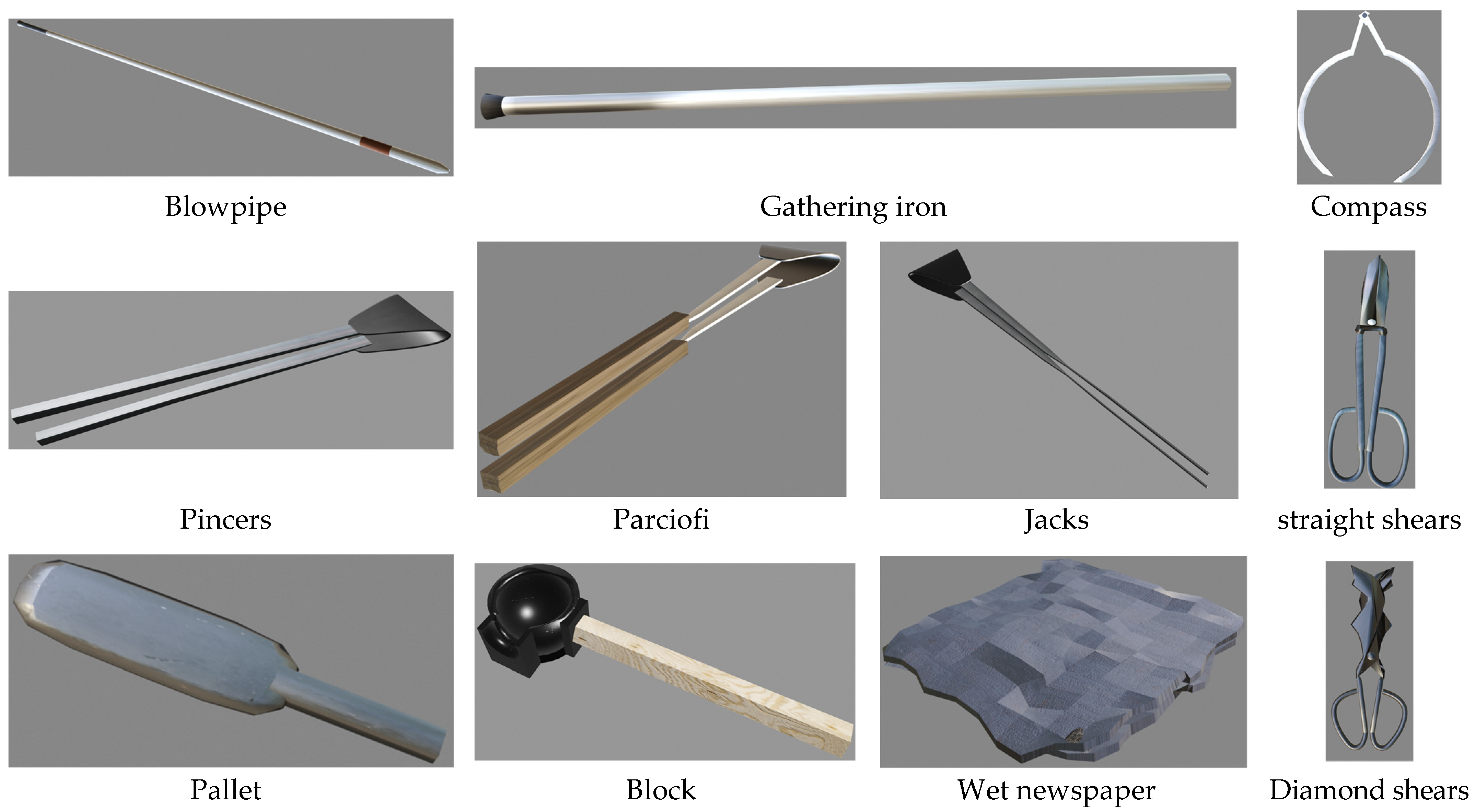
4.3.3. Tool Usage
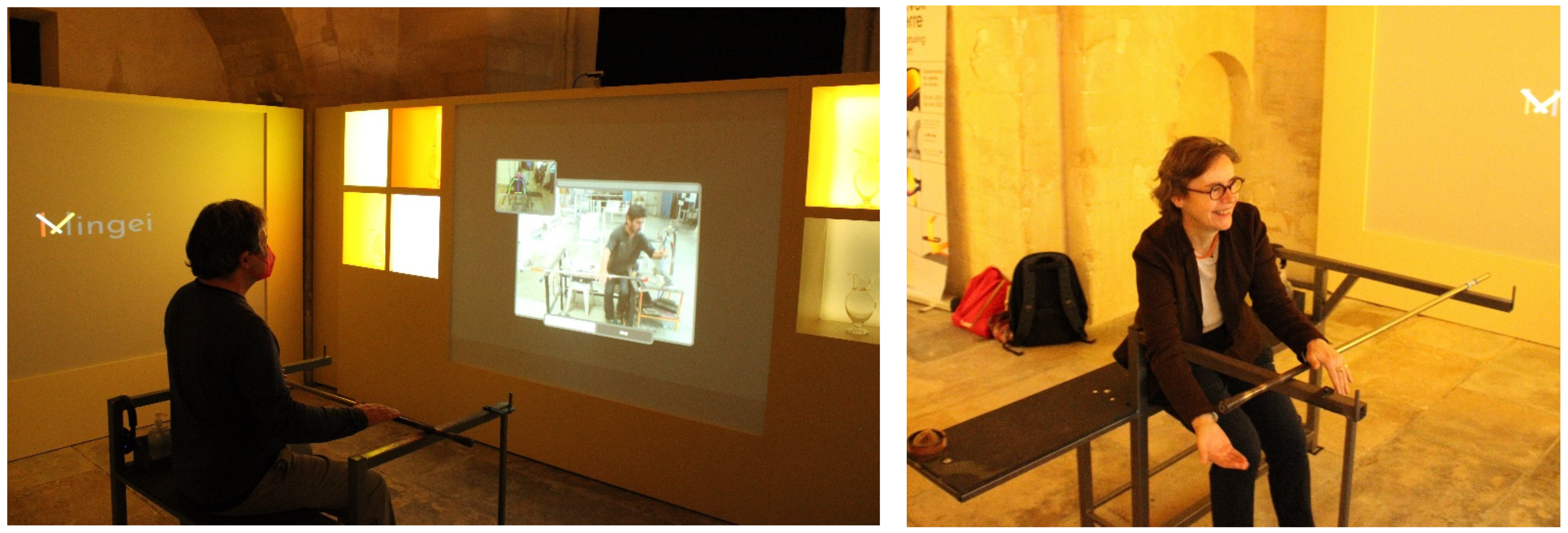
4.4. Workshop Demonstration
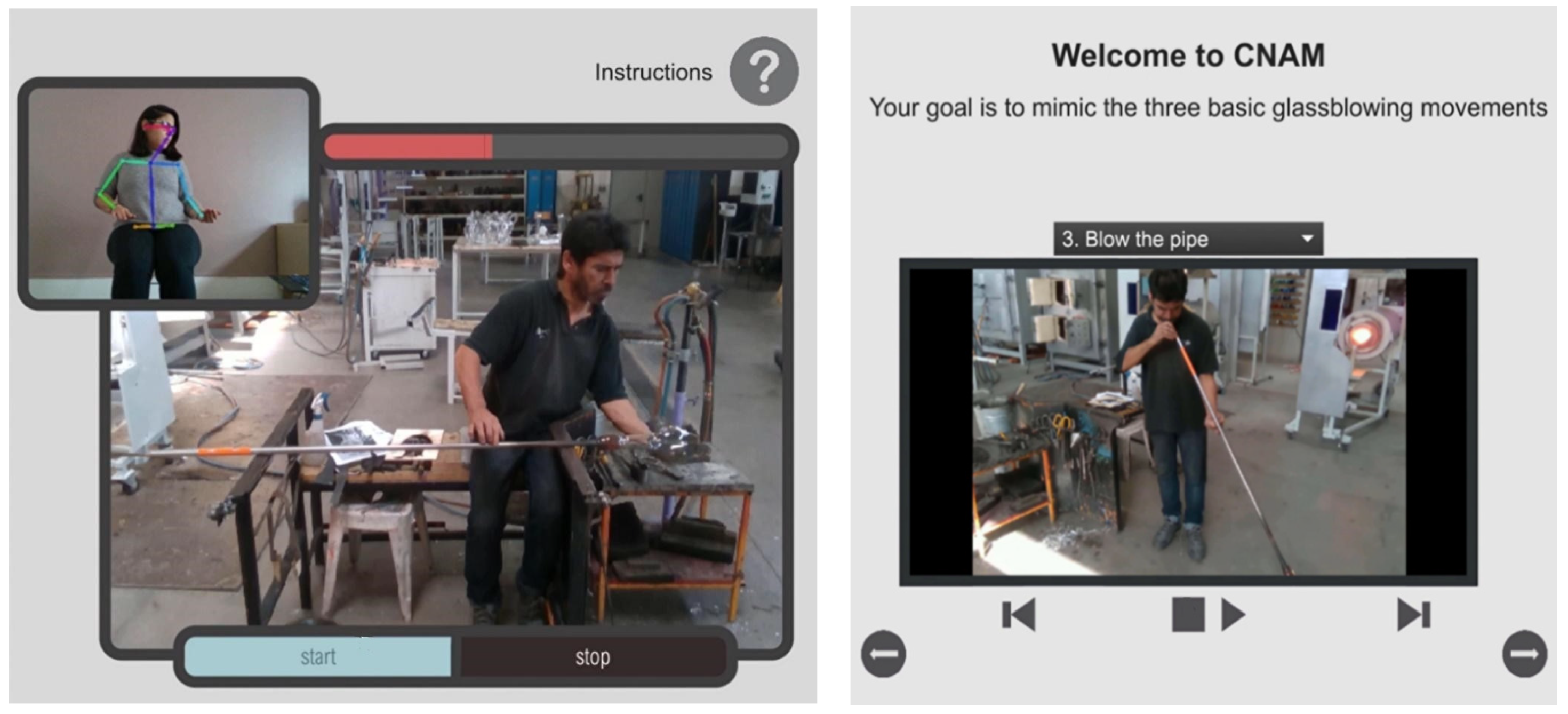
4.5. Craft Training
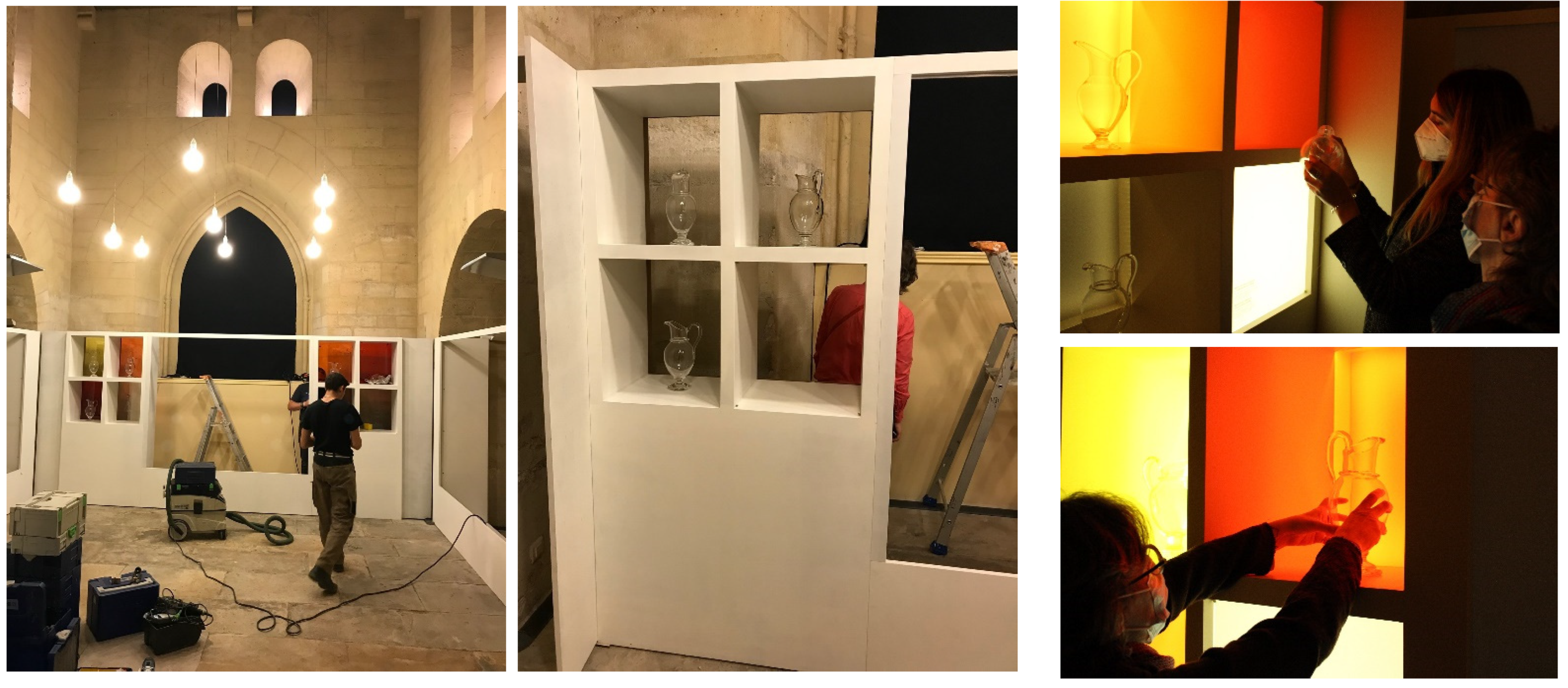
4.6. Exhibition
4.7. Preliminary Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNESCO. Traditional Craftsmanship. Available online: https://ich.unesco.org/en/traditional-craftsmanship-00057 (accessed on 16 January 2020).
- Zabulis, X.; Meghini, C.; Partarakis, N.; Beisswenger, C.; Dubois, A.; Fasoula, M.; Galanakis, G. Representation and preservation of Heritage Crafts. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zabulis, X.; Meghini, C.; Partarakis, N.; Kaplanidi, D.; Doulgeraki, P.; Karuzaki, E.; Stefanidi, E.; Evdemon, T.; Metilli, D.; Bartalesi, V. What Is Needed to Digitise Knowledge on Heritage Crafts. Mem. Rev. 2019. Available online: https://review.memoriamedia.net/ (accessed on 12 February 2020).
- Geijer, A. A History of Textile Art; Pasold Research Fund: London, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Hecht, A. The Art of the Loom; British Museum Press: London, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Donkin, L. Crafts, and Conservation: Synthesis Report for ICCROM. Available online: https://www.iccrom.org/publication/crafts-and-conservation-synthesis-report-iccrom (accessed on 17 January 2020).
- Costin, C.L. Introduction: Craft and social identity. Archeol. Pap. Am. Anthropol. Assoc. 1998, 8, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Guidelines for the Preservation of Digital Heritage. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000130071 (accessed on 17 January 2020).
- Fotopoulou, S.V.; Drinis, Y.N.; Bazini, E.; Fakiola, M. Rural Space as Cultural Heritage. Available online: http://ayla.culture.gr/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/1st_S_S_2018_Rural_Space_as_Cultural_Heritage_WebENG.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2020).
- Partarakis, N.; Zabulis, X.; Antona, M.; Stephanidis, C. Transforming Heritage Crafts to engaging digital experiences. In Visual Computing for Cultural Heritage; Liarokapis, F., Voulodimos, A., Doulamis, N., Doulamis, A., Eds.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanidi, E.; Partarakis, N.; Zabulis, X.; Zikas, P.; Papagiannakis, G.; Thalmann, N.M. TooltY: An approach for the combination of motion capture and 3D reconstruction to present tool usage in 3D environments. In Intelligent Scene Modelling and Human Computer Interaction; Thalmann, N.M., Zheng, J., Eds.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shen, C.; Lu, J.; Wu, Q. Heritage image annotation via collective knowledge. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 93, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Sperlì, G.; Moscato, V.; Picariello, A.; Esposito, C.; Choi, C. An edge intelligence empowered recommender system enabling cultural heritage applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 4266–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscheu, F.; Buhalis, D. Augmented reality at cultural heritage sites. In Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 607–619. [Google Scholar]
- Roussou, M. Learning by doing and learning through play: An exploration of interactivity in virtual environments for children. Comput. Entertain. CIE 2004, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Neira, C.; Sandin, D.J.; DeFanti, T.A. Surround-screen projection-based virtual reality: The design and implementation of the CAVE. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Anaheim, CA, USA, 1–6 August 1993; pp. 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Liarokapis, F.; White, M. Augmented reality techniques for museum environments. Mediterr. J. Comput. Netw. 2005, 1, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- ARCO (Augmented Representation of Cultural Objects) Consortium. Available online: http://www.arco-web.org (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- White, M.; Mourkoussis, N.; Darcy, J.; Petridis, P.; Liarokapis, F.; Lister, P.; Gaspard, F. ARCO-an architecture for digitization, management and presentation of virtual exhibitions. In Proceedings of the Computer Graphics International, Crete, Greece, 16–19 June 2004; pp. 622–625. [Google Scholar]
- Karuzaki, E.; Partarakis, N.; Patsiouras, N.; Zidianakis, E.; Katzourakis, A.; Pattakos, A.; Zabulis, X. Realistic Virtual Humans for Cultural Heritage Applications. Heritage 2021, 4, 4148–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milgram, P.; Kishino, F. A taxonomy of mixed reality visual displays. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 1994, 77, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, C.E.; Stapleton, C.B.; Hughes, D.E.; Smith, E.M. Mixed reality in education, entertainment, and training. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2005, 25, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.; Ciolfi, L.; Bannon, L.; Fraser, M.; Benford, S.; Bowers, J.; Flintham, M. The visitor as virtual archaeologist: Explorations in mixed reality technology to enhance educational and social interaction in the museum. In Proceedings of the 2001 Conference on Virtual Reality, Archeology, and Cultural Heritage, Glyfada, Greece, 28–30 November 2001; pp. 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Fast-Berglund, Å.; Gong, L.; Li, D. Testing and validating Extended Reality (xR) technologies in manufacturing. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 25, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margetis, G.; Papagiannakis, G.; Stephanidis, C. Realistic natural interaction with virtual statues in x-reality environments. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLll-2/W11, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papagiannakis, G.; Partarakis, N.; Stephanidis, C.; Vassiliadi, M.; Huebner, N.; Grammalidis, N.; Margetis, G. Mixed Reality Gamified Presence and Storytelling for Virtual Museums; No. IKEEBOOKCH-2019-233; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zabulis, X.; Grammenos, D.; Sarmis, T.; Tzevanidis, K.; Padeleris, P.; Koutlemanis, P.; Argyros, A. Multicamera human detection and tracking supporting natural interaction with large-scale displays. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2012, 24, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammenos, D.; Zabulis, X.; Michel, D.; Padeleris, P.; Sarmis, T.; Georgalis, G.; Koutlemanis, P.; Tzevanidis, K.; Argyros, A.; Sifakis, M.; et al. Macedonia from Fragments to Pixels: A Permanent Exhibition of Interactive Systems at the Archaeological Museum of Thessaloniki. In Proceedings of the Progress in Cultural Heritage Preservation—4th International Conference, EuroMed 2012, Limassol, Cyprus, 29 October–3 November 2012; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Volume 7616, pp. 602–609. [Google Scholar]
- Partarakis, N.; Kontaki, E.; Zidianakis, E.; Drossis, G.; Birliraki, C.; Metaxakis, G.; Barka, A.; Poutouris, V.; Mathioudakis, G.; Zidianaki, I.; et al. Digital Heritage Technology at the Archaeological Museum of Heraklion. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human Computer Interaction, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 15–20 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Partarakis, N.; Antona, M.; Stephanidis, C. Adaptable, personalizable and multi user museum exhibits. In Curating the Digital; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 167–179. [Google Scholar]
- Partarakis, N.; Antona, M.; Zidianakis, E.; Stephanidis, C. Adaptation and Content Personalization in the Context of Multi User Museum Exhibits. In Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Advanced Visual Interfaces for Cultural Heritage co-located with the International Working Conference on Advanced Visual Interfaces, Bari, Italy, 7–10 June 2016; pp. 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zidianakis, E.; Partarakis, N.; Ntoa, S.; Dimopoulos, A.; Kopidaki, S.; Ntagianta, A.; Stephanidis, C. The Invisible Museum: A User-Centric Platform for Creating Virtual 3D Exhibitions with VR Support. Electronics 2021, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather, P. Culture Vultures or the Boorish Masses—Who are Cultural Visitors in Australia? In Proceedings of the Tourism Research Australia, Cultural Tourism Conference, Canberra, Australia, February 2008. [Google Scholar]
- UNWTO. Study on Tourism and Intangible Cultural Heritage; UNWTO: Madrid, Spain, 2012; ISBN 978-92-844-1479-6. [Google Scholar]
- Acker, O.; Gröne, F.; Kropiunigg, L.; Lefort, T. The Digital Future of Creative Europe: The Impact of Digitization and the Internet on the Creative Industries in Europe Stategy; Booz & Company/PWC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- European Council. Framework Convention on the Value of Cultural Heritage for Society; CETS No.199; Faro: 27 October 2005. Available online: https://rm.coe.int/1680083746 (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Peligot, E. Douze Leçons Sur l’art de la Verrerie. In Le Verre, Son Histoire, Sa Fabrication; 1877; Available online: https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k918964.texteImage (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Ginzarly, M.; Srour, F.J. Cultural heritage through the lens of COVID-19. Poetics 2021, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, R.W.; Thompson, D.V. Is there a substitute for direct experience? Comparing consumers’ preferences after direct and indirect product experiences. J. Consum. Res. 2007, 34, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millar, M.G.; Millar, K.U. The effects of direct and indirect experience on affective and cognitive responses and the attitude–behavior relation. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 1996, 32, 561–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gino, F.; Argote, L.; Miron-Spektor, E.; Todorova, G. First, get your feet wet: The effects of learning from direct and indirect experience on team creativity. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Processes 2010, 111, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerden, M.D.; Witt, P.A. The impact of direct and indirect experiences on the development of environmental knowledge, attitudes, and behavior. J. Environ. Psychol. 2010, 30, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, T.; Li, H.; Biocca, F. Consumer learning and the effects of virtual experience relative to indirect and direct product experience. Psychol. Mark. 2008, 25, 568–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keng, C.J.; Liao, T.H.; Yang, Y.I. The effects of sequential combinations of virtual experience, direct experience, and indirect experience: The moderating roles of need for touch and product involvement. Electron. Commer. Res. 2012, 12, 177–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partarakis, N.; Zabulis, X.; Chatziantoniou, A.; Patsiouras, N.; Adami, I. An approach to the creation and presentation of reference gesture datasets, for the preservation of traditional crafts. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partarakis, N.; Doulgeraki, P.; Karuzaki, E.; Adami, I.; Ntoa, S.; Metilli, D.; Bartalesi, V.; Meghini, C.; Marketakis, Y.; Theodoridou, M.; et al. Representation of socio-historical context to support the authoring and presentation of multimodal narratives: The Mingei Online Platform. J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2021, 15, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabulis, X.; Meghini, C.; Dubois, A.; Doulgeraki, P.; Partarakis, N.; Adami, I.; Karuzaki, E.; Carre, A.; Patsiouras, N.; Kaplanidi, D.; et al. Digitisation of traditional craft processes. J. Comput. Cult. Herit. [CrossRef]
- MINERVA—Ministerial Network for Valorising Activities in Digitization. D6.2. Good Practice Handbook. MINERVA: November 2003. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/IST-2001-35461/it (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- 3D-ICONS. Guidelines & Case Studies. 3D-ICONS Is a Project Funded under the European Commission’s ICT Policy Support Programme; Project no. 297194. 2014. Available online: http://3dicons-project.eu/guidelines-and-case-studies (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Kokolantonakis, N. Requirements and Protocol of the 3D Documentation of the Heritage Crafts Tools. Dataset. 2020. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/3813287#.Yc5uyVkRWUk (accessed on 20 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. Human Motion Capture System and its Sensor Analysis. Sens. Transducers 2014, 172, 206–212. [Google Scholar]
- Field, M.; Stirling, D.; Naghdy, F.; Pan, Z. Motion capture in robotics review. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation, Christchurch, New Zealand, 9–11 December 2009; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. 2009; pp. 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceseracciu, E.; Sawacha, Z.; Cobelli, C. Comparison of Markerless and Marker-Based Motion Capture Technologies through Simultaneous Data Collection during Gait: Proof of Concept. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarafianos, N.; Boteanu, B.; Ionescu, B.; Kakadiaris, I. 3D Human pose estimation: A review of the literature and analysis of covariates. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2016, 152, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingei Online Platform. Available online: http://mop.mingei-project.eu (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Object Management Group. OMG Unified Modelling Language (OMG UML); Superstructure Version 2.1.1. 2007. Available online: https://www.omg.org/spec/UML/2.4.1/Superstructure/PDF (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Specification Formal/2007-02-05. W3C. Available online: https://www.omg.org/spec/UML/ (accessed on 21 September 2021).
- High Definition Render Pipeline. Available online: https://docs.unity3d.com/Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.high-definition@13.1/manual/index.html (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Mixamo. Available online: https://www.mixamo.com/ (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- 3ds-Max. Available online: https://www.autodesk.fr/products/3ds-max (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Motionbuilder. Available online: https://www.autodesk.com/products/motionbuilder (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Open Pose. Available online: https://github.com/CMU-Perceptual-Computing-Lab/openpose (accessed on 10 November 2021).




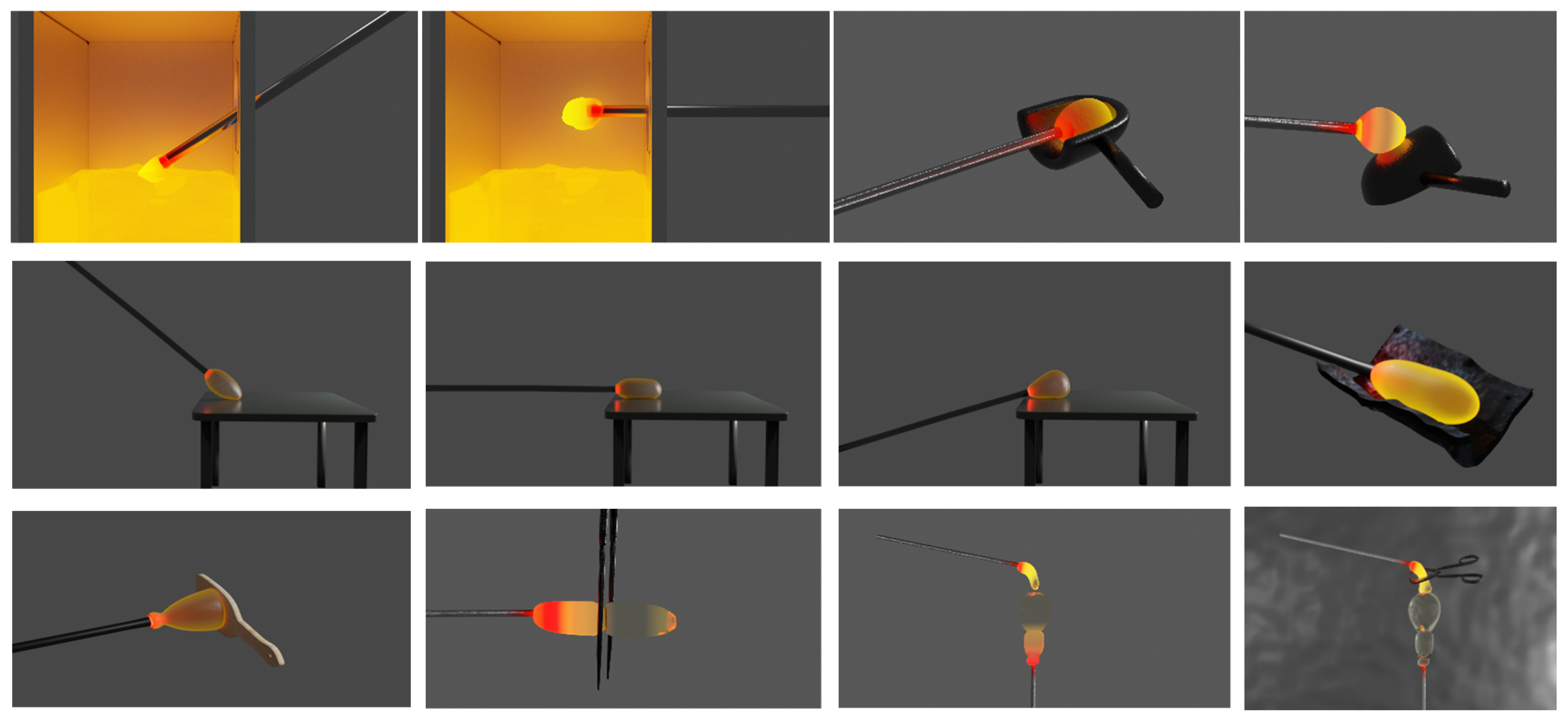
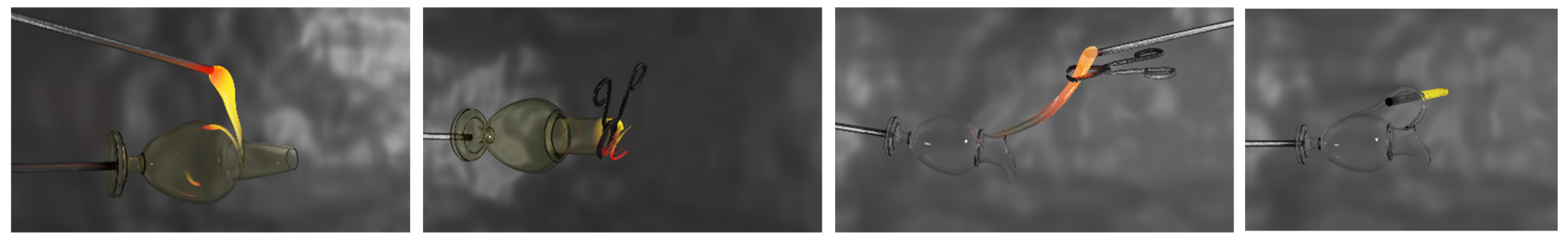







 |  |  |  |  |  |
| Insert the glass into the furnace | Moving the blowpipe | Shaping glass with the hand | Rotating the blowpipe | Blowing through the blowpipe | Shaping the glass with the tweezers |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
| Burn the base with the torch | Blowing through the blowpipe | Shaping the glass with the block | Pressing the glass on a metal base | Cutting the glass with the shears | Shaping the glass with the block |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
| Shaping the base of the carafe | Shaping the glass with the paddle | Shaping the glass with the jacks | Shaping the base of the carafe | Adding the handle to the jug | Shaping the glass with the tube |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carre, A.L.; Dubois, A.; Partarakis, N.; Zabulis, X.; Patsiouras, N.; Mantinaki, E.; Zidianakis, E.; Cadi, N.; Baka, E.; Thalmann, N.M.; et al. Mixed-Reality Demonstration and Training of Glassblowing. Heritage 2022, 5, 103-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5010006
Carre AL, Dubois A, Partarakis N, Zabulis X, Patsiouras N, Mantinaki E, Zidianakis E, Cadi N, Baka E, Thalmann NM, et al. Mixed-Reality Demonstration and Training of Glassblowing. Heritage. 2022; 5(1):103-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarre, Anne Laure, Arnaud Dubois, Nikolaos Partarakis, Xenophon Zabulis, Nikolaos Patsiouras, Elina Mantinaki, Emmanouil Zidianakis, Nedjma Cadi, Evangelia Baka, Nadia Magnenat Thalmann, and et al. 2022. "Mixed-Reality Demonstration and Training of Glassblowing" Heritage 5, no. 1: 103-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5010006
APA StyleCarre, A. L., Dubois, A., Partarakis, N., Zabulis, X., Patsiouras, N., Mantinaki, E., Zidianakis, E., Cadi, N., Baka, E., Thalmann, N. M., Makrygiannis, D., Glushkova, A., & Manitsaris, S. (2022). Mixed-Reality Demonstration and Training of Glassblowing. Heritage, 5(1), 103-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5010006











