An Insight into Gandharan Art: Materials and Techniques of Polychrome Decoration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Instruments and Methods
2.2.1. Optical Microscopy
2.2.2. Raman Spectroscopy
2.2.3. Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
3. Results
3.1. Inorganic Composition
3.2. Organic Composition
4. Discussion in the Framework of Gandharan Art Technical Literature
4.1. Gandharan Polychromy: Support
4.1.1. Stone
4.1.2. Clay
4.1.3. Stucco
4.2. Ground/Preparation Layers
4.3. Pigments
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foucher, A. L’Art Greco-Bouddhique du Gandhara. Étude sur les Origines de Lìinfluence Classique Dans L’Art Bouddhique de l’Inde et de l’Extrême-Orien; Nabu Press: Charleston, SC, USA, 1918–1922; Volumes 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Ingholt, H. Gandharan Art in Pakistan; Pantheon Books: New York, NY, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, J. The Buddhist Art of Gandhara: The Story of the Early School, Its Birth, Growth and Decline; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Taddei, M. Iconographic Considerations on a Gandhāra Relief in the National Museum of Oriental Art in Rome. East West 1963, 14, 38–55. [Google Scholar]
- Faccenna, D. Le prime testimonianze di arte figurativa: Il centro artistico di Butkara I ed i gruppi stilistici. In Il Maestro di Saidu Sharif. Alle Origini dell’Arte del Gandhara; Museo Nazionale d’Arte Orientale, Istituto Italiano per l’Africa e l’Oriente (IsIAO): Rome, Italy, 2002; Volume 2002, pp. 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Bussagli, M. L’Arte del Gandhara; UTET: Turin, Italy, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Filigenzi, A. Non-Buddhist customs of buddhist people: Visual and archaeological evidence from north-west Pakistan. In Buddhism and the Dynamics of Transculturality; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 53–84. [Google Scholar]
- Faccenna, D. Butkara I (Swat, Pakistan) 1956–1962—Vol. III—Reports and Memoirs; ISMEO—Istituto Italiano per il Medio ed Estremo Oriente: Rome, Italy, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Taddei, M. Arte Narrativa tra India e Mondo Ellenistico; ISIAO: Rome, Italy, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Filigenzi, A. Orientalised Hellenism versus Hellenised Orient: Reversing the Perspective on Gandharan Art. Anc. Civiliz. Scythia Sib. 2012, 18, 111–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callieri, P. Gli Indo-Greci nel Pakistan settentrionale. In Il Maestro di Saidu Sharif. Alle Origini dell’Arte del Gandhara; Istituto Italiano per l’Africa e l’Oriente (IsIAO): Rome, Italy, 2002; Volume 2002, pp. 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K. The evidence of white-wash, plaster and pigment on North Indian sculpture with special reference to Sarnath. Artibus Asiae 1984, 45, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filigenzi, A.; Alram, M.; Paiman, Z. Afghanistan’s pre-Islamic archaeology: Vulnerability, resilience and perspectives. In Religions, Society, Trade and Kingship: Archaeology and Art in South Asia and along the Silk Road, 5500 BCE-5th Century CE, Proceeding of the Twenty-Third Conference of the European Association for South Asian Archaeology and Art, Cardiff, United Kingdom, 2016; Greaves, L.R., Hardy, A., Eds.; Dev Publishers & Distributors: New Delhi, India, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 223–233. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, C.; Theye, T.; Pannuzi, S. Geological overwiew of Gandharan sites and petrographical analysis on Gandharan stucco and clay artefacts. Restauro Archeol. 2019, 27, 12–39. [Google Scholar]
- Guida, G.; Piersanti, M.; Vidale, M.; Vignaroli, G. Osservazioni petrografiche preliminari sulle sculture gandhariche (Swat, Pakistan) del MNAO. In Gandhara: Tecnologia, Produzione e Conservazione: Indagini Preliminari su Sculture in Pietra e Stucco del Museo Nazionale d’Arte Orientale "Giuseppe Tucci"; Pannuzi, S., Ed.; Gangemi Editore: Rome, Italy, 2015; pp. 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Talarico, F.; Biocca, P.; Sidoti, G.; Torre, M. Caratterizzazione delle policromie delle sculture del Gandhara. In Gandhara: Tecnologia, Produzione e Conservazione: Indagini Preliminari su Sculture in Pietra e Stucco del Museo Nazionale d’Arte Orientale “Giuseppe Tucci”; Pannuzi, S., Ed.; Gangemi Editore: Rome, Italy, 2015; pp. 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Pannuzi, S.; Talarico, F.; Guida, G.; Rosa, C. Polychromy and gilding in the Gandharan sculptures from Pakistan and Afghanistan: Samplings from Museum Guimet in Paris, Civic Archaeological Museum of Milan and Museum of Oriental Art of Turin. Restauro Archeol. 2019, 27, 40–81. [Google Scholar]
- Bonaduce, I.; Tenorio, A.L.; Andreotti, A.; Orsini, S.; Colombini, M.P.; Dilillo, M.; McDonnell, L.A. The characterisation of paint binders in the polychromies and gildings of the Gandharan artworks. Restauro Archeol. 2019, 27, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Pannuzi, S.; Talarico, F. Pigments and gold in Gandharan stone and stucco sculptures. In Proceedings of 7th Round Table on Polychromy in Ancient Sculpture and Architecture, Florence, Italy, 4–6 November 2015; Bracci, S., Giachi, G., Liverani, P., Pallecchi, P., Paolucci, F., Eds.; Sillabe: Florence, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Patrizi, M.G. Metodi di pulitura a confronto per la rimozione delle concrezioni su sculture dell’arte del Gandhara. In Gandhara: Tecnologia, Produzione e Conservazione: Indagini Preliminari su Sculture in Pietra e Stucco del Museo Nazionale d’Arte Orientale “Giuseppe Tucci”; Pannuzi, S., Ed.; Gangemi Editore: Rome, Italy, 2015; pp. 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Patrizi, M.G. Le sculture in “scisto” dell’arte del Gandhara conservate presso il MNAO. Note conservative. In Gandhara: Tecnologia, Produzione e Conservazione: Indagini Preliminari su Sculture in Pietra e Stucco del Museo Nazionale d’Arte Orientale “Giuseppe Tucci”; Pannuzi, S., Ed.; Gangemi Editore: Rome, Italy, 2015; pp. 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Festa, L.; Pannuzi, S. Conservative data on polychrome stucco, stone and clay sculptures and architectonical decoration of Gandharan art. Restauro Archeol. 2019, 27, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- Olivieri, L.M. A short note on contexts and chronology of the materials from Saidu Sharif, Amluk-dara, Gumbat and Barikot (Swat). Restauro Archeol. 2019, 27, 112–129. [Google Scholar]
- Olivieri, L.M.; Cupitò, M.; Genchi, F. The Buddhist Sites of Gumbat and Amluk-Dara (Barikot): The Last Phases of the Urban Site at Bir-Kot-Ghwandai (Barikot); Sang-e-Meel Publications: Lahore, Pakistan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Olivieri, L.M. Amluk-dara (AKD 1) A Revised Excavation Report. J. Asian Civiliz. 2018, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Meister, M.W.; Olivieri, L.M. Conservation and Studies at Gumbat-Balo Kale Site (Tahsil Barikot, District Swat, Pakistan). J. Asian Civiliz. 2012, 35, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Lluveras, A.; Bonaduce, I.; Andreotti, A.; Colombini, M.P. GC/MS analytical procedure for the characterization of glycerolipids, natural waxes, terpenoid resins, proteinaceous and polysaccharide materials in the same paint microsample avoiding interferences from inorganic media. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluveras-Tenorio, A.; Mazurek, J.; Restivo, A.; Colombini, M.P.; Bonaduce, I. Analysis of plant gums and saccharide materials in paint samples: Comparison of GC-MS analytical procedures and databases. Chem. Cent. J. 2012, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaduce, I.; Cito, M.; Colombini, M.P. The development of a gas chromatographic—Mass spectrometric analytical procedure for the determination of lipids, proteins and resins in the same paint micro-sample avoiding interferences from inorganic media. J. Chrom. A 2009, 1216, 5931–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgio, L.; Clark, R.J.H. Library of FT-Raman spectra of pigments, minerals, pigment media and varnishes, and supplement to existing library of Raman spectra of pigments with visible excitation. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2001, 57, 1491–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadezky, A.; Muckenhuber, H.; Grothe, H.; Niessner, R.; Pöschl, U. Raman microspectroscopy of soot and related carbonaceous materials: Spectral analysis and structural information. Carbon 2005, 43, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyssac, O.; Goffé, B.; Petitet, J.-P.; Froigneux, E.; Moreau, M.; Rouzaud, J.-N. On the characterization of disordered and heterogeneous carbonaceous materials by Raman spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2003, 59, 2267–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluveras-Tenorio, A.; Spepi, A.; Pieraccioni, M.; Legnaioli, S.; Lorenzetti, G.; Palleschi, V.; Vendrell, M.; Colombini, M.P.; Tinè, M.R.; Duce, C. A multi-analytical characterization of artists’ carbon-based black pigments. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 3287–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, S.; Kröger, R.; Robson, H.K.; Rowley, C.C.A.; Taylor, B.; Jones, A.G.; Conneller, C.; Needham, A. The application of micro-Raman for the analysis of ochre artefacts from Mesolithic palaeo-lake Flixton. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2018, 17, 650–656. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, B.J.; Seyssel, K.; Chiu, S.; Pan, P.-H.; Lin, S.-Y.; Stanley, E.; Ament, Z.; West, J.A.; Summerhill, K.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Odd Chain Fatty Acids; New Insights of the Relationship Between the Gut Microbiota, Dietary Intake, Biosynthesis and Glucose Intolerance. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verri, G.; Luczanits, C.; Borges, V.; Barnard, N.; Clarke, J. Investigations of a Gandharan stucco head of the Buddha at the Victoria and Albert Museum (IM. 3-1931). In Technè. La Science au Service de L’Histoire de L’Art et de la Préservation des Biens Culturels; Centre de Recherche et de Restauration des Musées de France: Paris, France, 2019; pp. 136–149. [Google Scholar]
- Varma, K.M. Technique of Gandharan and Indo-Afghan Stucco Images (Including Images of Gypsum Compound); Motilal Banarsidass Publishers Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, P.; Gill, A. Technical examination and conservation of the stucco sculture. In A Catalogue of the Gandhara Sculpture in the British Museum; Zwalf, A., Ed.; BMP: London, UK, 1996; Volume 1, pp. 363–368. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, P.; Mora, L.; Philippot, P. The Conservation of Wall Paintings; Butterworths: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Fazio, G. Sulla tecnica della pittura murale. In II Restauro del Monastero di San Mose l’Abissino, Nebek, Siria; Ministero degli Affari Esteri di Roma: Rome, Italy, 1998; pp. 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ohlídalová, M. Technical analyses. In Afghanistan. Rescued Treasures of Buddhism; Tisucká, M., Stančo, L., Eds.; National Museum: Prague, Czech Republic, 2016; pp. 104–143. [Google Scholar]
- Fussman, G.R.; Le Berre, M. Monuments Bouddhiques de la Région de Caboul. 1: Le Monastère de Gul Dara; Diffusion De Boccard: Paris, France, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Verardi, G. Osservazioni sulla coroplastica di epoca Kusana nel Nord-Ovest e in Afghanistan in relazione al materiale di Tapa Sardar, seguite da una precisazione sulla natura e la data delle sculpture di Ushkur. Ann. Ist. Orient. Napoli 1983, 43, 479–502. [Google Scholar]
- Tarzi, Z. La technique du modelage en argile en Asie Centrale et au Nord-Ouest de l’Inde sous les Kouchans: La continuité malgré les ruptures. Ktema 1986, 11, 57–93. [Google Scholar]
- Khanmoradi, M.; Niknami, K.A. An Analytical Approach to Investigate the Parthians Painted Stuccoes from Qal ‘eh-i Yazdigird, Western Iran. Hist. Świat 2017, 6, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, S.; Ambers, J.; Verri, G.; Deviese, T.; Kirby, J. Painted Parthian stuccoes from southern Iraq. In Proceedings of the 7th International Congress on the Archaeology of the Ancient Near East, London; Harrassowitz: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2010; pp. 209–220. [Google Scholar]
- Bollati, A. Le sculture. In Nisa Partica: Ricerche nel Complesso Monumentale Arsacide, 1990–2006; Invernizzi, A., Lippolis, C., Eds.; Casa Ed. Le Lettere: Florence, Italy, 2008; pp. 167–194. [Google Scholar]
- Lapierre, N. La peinture monumentale de l’Asie centrale soviétique: Observations techniques. Arts Asiat. 1990, 45, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.A.; Ziemann, M.A.; Pentzien, S.; Gabsch, T.; Koch, W.; Krüger, J. Technical analysis of a Central Asian wall painting detached from a Buddhist cave temple on the northern Silk Road. Stud. Conserv. 2016, 61, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Giuliano, L. Investigando le materie del Gandhara. Alcune riflessioni preliminari sulle indagini diagnostiche condotte presso il MNAO. In Gandhara: Tecnologia, Produzione e Conservazione: Indagini Preliminari su Sculture in Pietra e Stucco del Museo Nazionale d’Arte Orientale “Giuseppe Tucci”; Pannuzi, S., Ed.; Gangemi Editore: Rome, Italy, 2015; pp. 16–27. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliano, L. Le tecniche pittoriche nell’India antica e l’arte della grotta 17. In Ajanta Dipinta: Studio Sulla Tecnica e Sulla Conservazione del Sito Rupestre Indiano; Bon Valsassina, C., Capanna, F., Ioele, M., Eds.; Gangemi: Rome, Italy, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 89–116. [Google Scholar]
- Scharff, M.; Hast, R.; Kalsbeek, N.; Stubbe Østergaard, J. Investigatin the polychromy of a Classical Attic Greek marble female head NCG IN 2830. In Tracking Colour: The Polychromy of Greek and Roman Sculpture in the Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek, Preliminary Report; Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2009; pp. 13–40. [Google Scholar]
- Rosing, M.T.; Østergaard, J.S. Preliminary results from geochemical analysis of pigments on ancient Greek and Roman marble sculptures. In Tracking Colour: The Polychromy of Greek and Roman Sculpture in the Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek, Preliminary Report; Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2009; pp. 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Siotto, E. La Policromia sui Sarcofagi Romani: Catalogo e Risultati Scientifici; L’Erma di Bretschneider: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann, V. I colori della scultura arcaica e protoclassica. In I Colori del Bianco. Policromia Nella Scultura Antica; Liverani, P., Ed.; De Luca Editori d’Arte: Rome, Italy, 2004; pp. 41–66. [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann, V. Colori e tecnica pittorica. In I Colori del bianco. Policromia Nella Scultura Antica; Liverani, P., Ed.; De Luca Editori d’Arte: Rome, Italy, 2004; pp. 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- Sargent, M.L. Recent Investigation of the polychromy of a Metropolitan Roman Garland Sarcophagus. In Tracking Colour: The Polychromy of Greek and Roman Sculpture in the Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek, Preliminary Report; Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012; pp. 14–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ioele, M.; Giovagnoli, A.; Artioli, D. La parete nord del portico: Caratterizzazione dei pigmenti attraverso analisi non invasive. In Ajanta Dipinta: Studio Sulla Tecnica e Sulla Conservazione del Sito Rupestre Indiano; Bon Valsassina, C., Capanna, F., Ioele, M., Eds.; Gangemi: Rome, Italy, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Ioele, M.; Giovagnoli, A.; Mariottini, M. Analisi micro-distruttive di prelievi dalle grotte 17, 1 e 15. In Ajanta Dipinta: Studio Sulla Tecnica e Sulla Conservazione del Sito Rupestre Indiano; Bon Valsassina, C., Capanna, F., Ioele, M., Eds.; Gangemi: Rome, Italy, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 65–104. [Google Scholar]
- Giovagnoli, A.; Artioli, D.; Ioele, M.; Mariottini, M. Riconoscimento dei pigmenti. I test non distruttivi (XRF). In Ajanta Dipinta: Studio Sulla Tecnica e Sulla Conservazione del Sito Rupestre Indiano; Bon Valsassina, C., Capanna, F., Ioele, M., Eds.; Gangemi: Rome, Italy, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 64–104. [Google Scholar]
- Appolonia, L.; Radicati, B.; Piccirillo, A.; Chatel, V. La materia e i colori. In Nisa Partica. Ricerche nel Complesso Monumentale Arsacide 1990–2006; Invernizzi, A., Lippolis, C., Eds.; Le Lettere: Florence, Italy, 2008; pp. 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Jia, C.; Chen, Z.; Gong, Y.; Cheng, H.; Wang, J. Analytical study of Buddha sculptures in Jingyin temple of Taiyuan, China. Herit. Sci. 2020, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariottini, M.; Della Ventura, G.; Sodo, A.; Vidale, M. The Lapis Lazuli industry. In Lapis Lazuli Bead Making at Shahr-i Sokhta; Vidale, M., Lazzari, A., Eds.; Antilia: Padova, Italy, 2016; pp. 159–199. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchetti, P.; Talarico, F.; Vigliano, M.G.; Ali, M.F. Production and characterization of Egyptian blue and Egyptian green frit. J. Cult. Herit. 2000, 1, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verri, G. The spatially resolved characterisation of Egyptian blue, Han blue and Han purple by photo-induced luminescence digital imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, M.L.; Therkildsen, R.H. Research on Ancient Sculptural polychromy with Focus on a 2nd Century C.E. Marble Amazon. In Tracking Colour: The Polychromy of Greek and Roman Sculpture in the Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek, Preliminary Report; Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2010; pp. 27–49. [Google Scholar]
- Skoumøller, A.; Sargent, M.L. Painted portrait sculpture from the Sanctuary of Diana at Nemi. In Tracking Colour: The Polychromy of Greek and Roman Sculpture in the Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek, Preliminary Report; Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013; pp. 9–35. [Google Scholar]
- Dyer, J.; Sotiropoulou, S. A technical step forward in the integration of visible-induced luminescence imaging methods for the study of ancient polychromy. Herit. Sci. 2017, 5, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verri, G.; Opper, T.; Deviese, T. The Treu Head: A case study in Roman sculptural polychromy. Br. Mus. Tech. Res. Bull. 2010, 4, 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Therkildsen, R.H. A 2nd century C.E. colossal marble head of a woman: A case study in Roman sculptural polychromy. In Tracking Colour: The Polychromy of Greek and Roman Sculpture in the Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek, Preliminary Report; Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012; pp. 45–63. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, J. Natural adhesives in East Asian paintings. Stud. Conserv. 1984, 29, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, O.P. A study on the techniques of Indian wall paintings. J. Indian Mus. 1969, 25, 99–118. [Google Scholar]
- van Valen, L.M. The Matter of Chinese Painting, Case Studies of 8th Century Murals; Leiden University: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi, K.; Taniguchi, Y. Mural Paintings of the Silk Road: Cultural Exchanges Between East and West: Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Symposium on the Conservation and Restoration of Cultural Property, National Research Institute for Cultural Properties, Tokyo, January 2006; Archetype Publications: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gunasinghe, S. La Technique de la Peinture Indienne D’Après les Textes du Silpa; Presses Universitaires de France (PUF): Paris, France, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Orsini, S.; Parlanti, F.; Bonaduce, I. Analytical pyrolysis of proteins in samples from artistic and archaeological objects. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 2017, 124, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoulders, M.D.; Raines, R.T. Collagen structure and stability. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 929–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B. Identification of organic binders in ancient Chinese paintings by immunological techniques. Microsc. Microanal. 2015, 21, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhen, G.; Hao, X.; Tong, T.; Ni, F.; Wang, Z.; Jia, J.; Li, L.; Tong, H. Spectroscopic investigation and comprehensive analysis of the polychrome clay sculpture of Hua Yan Temple of the Liao Dynasty. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 240, 118574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyao, L.; Wei, S.; Zhang, B.; Youcheng, H. Determination of Proteinaceous Binders For Polychrome Relics of Xumi Mountain Grottoes by Using Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Immunofluorescence Microscopy. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2016, 7, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Shen, W.; Zhang, B.; Ma, Q. Microchemical study of pigments and binders in polychrome relics from Maiji Mountain Grottoes in Northwestern China. Microsc. Microanal. 2016, 22, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ge, R.; Yang, L.; Shen, M.; Sun, W. Investigating the composition and application of an ancient multipurpose material discovered on the Qin Terracotta Army statues. Archaeometry 2021, 64, 422–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Schreiner, M.; Rosenberg, E.; Guo, H.; Ma, Q. The Identification of the Binding Media in the Tang Dynasty Chinese Wall Paintings By Using PY-GC/MS And GC/MS Techniques. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2011, 2, 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Ma, Q.; Schreiner, M. Scientific investigation of the paint and adhesive materials used in the Western Han dynasty polychromy terracotta army, Qingzhou, China. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 39, 1628–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Yan, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, L. Multi-analytical study of the suspected binding medium residues of wall paintings excavated in Tang tomb, China. J. Cult. Herit. 2017, 24, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluveras-Tenorio, A.; Bonaduce, I.; Sabatini, F.; Degano, I.; Blaensdorf, C.; Pouyet, E.; Cotte, M.; Ma, L.; Colombini, M.P. The organic materials in the Five Northern Provinces’ Assembly Hall: Disclosing the painting technique of the Qing dynasty painters in civil buildings. Appl. Phys. A Mater. 2015, 121, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayerová, T. Buddhist wall paintings at Nako monastery, North India: Changing of the technology throughout centuries. Stud. Conserv. 2018, 63, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecoulaki, H.; Sotiropoulou, S.; Perdikatsis, V.; Lluveras-Tenorio, A.; Bonaduce, I.; Colombini, M. A technological investigation of the painting materials. In The Wall Paintings of the West House at Mycenae; Tournavitou, I., Ed.; INSTAP Academic Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 147–158. [Google Scholar]
- Brøns, C.; Rasmussen, K.L.; Di Crescenzo, M.M.; Stacey, R.; Lluveras-Tenorio, A. Painting the Palace of Apries I: Ancient binding media and coatings of the reliefs from the Palace of Apries, Lower Egypt. Herit. Sci. 2018, 6, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elert, K.; García Sánchez, R.M.; Benavides-Reyes, C.; Linares Ordóñez, F. Influence of animal glue on mineralogy, strength and weathering resistance of lime plasters. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 226, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinciguerra, R.; Galano, E.; Vallone, F.; Greco, G.; Vergara, A.; Bonaduce, I.; Marino, G.; Pucci, P.; Amoresano, A.; Birolo, L. Deglycosylation Step to Improve the Identification of Egg Proteins in Art Samples. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 10178–10182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecoulaki, H.; Zaitoun, C.; Stocker, S.R.; Davis, J.L.; Karydas, A.G.; Colombini, M.P.; Bartolucci, U. An archer from the palace of Nestor: A new wall-painting fragment in the Chora Museum. Hesperia 2008, 77, 363–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecoulaki, H.; Andreotti, A.; Bonaduce, I.; Colombini, M.P.; Lluveras, A. Characterization of organic media in the wall-paintings of the “Palace of Nestor” at Pylos, Greece: Evidence for a secco painting techniques in the Bronze Age. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 39, 2866–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linn, R.; Bonaduce, I.; Ntasi, G.; Birolo, L.; Yasur-Landau, A.; Cline, E.H.; Nevin, A.; Lluveras-Tenorio, A. Evolved Gas Analysis-Mass Spectrometry to Identify the Earliest Organic Binder in Aegean Style Wall Paintings. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2018, 130, 13441–13444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakoulli, I. Late Classical and Hellenistic painting techniques and materials: A review of the technical literature. Stud. Conserv. 2002, 47, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaduce, I.; Blaensdorf, C.; Dietemann, P.; Colombini, M.P. The binding media of the polychromy of Qin Shihuang’s Terracotta Army. J. Cult. Herit. 2008, 9, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, L.M. The Last phases at Barikot: Urban cults and preliminary chronology: Data from the 2012 excavation campaign in Swat. J. Inner Asian Art Archaeol. 2011, 6, 7–40. [Google Scholar]


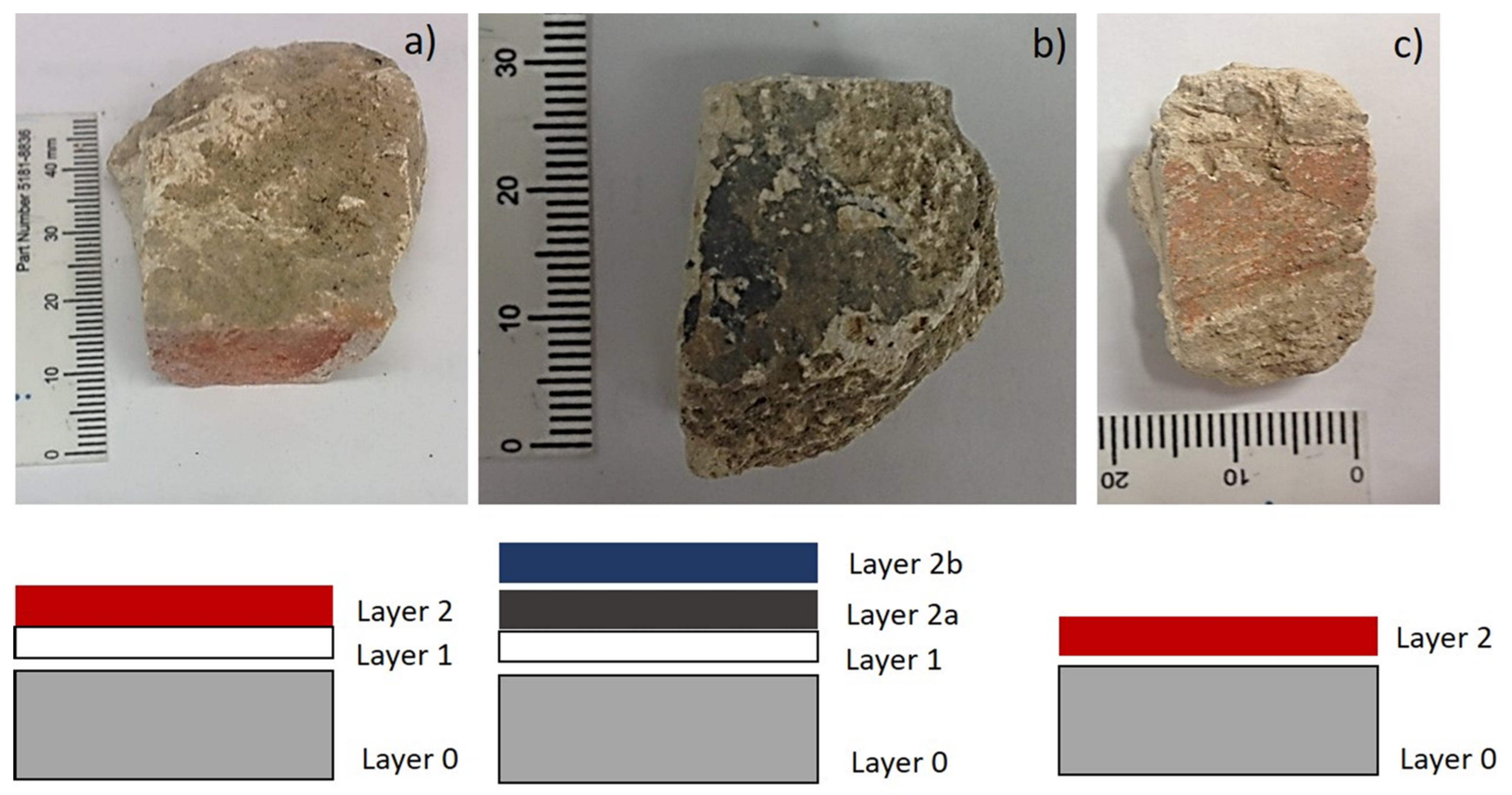
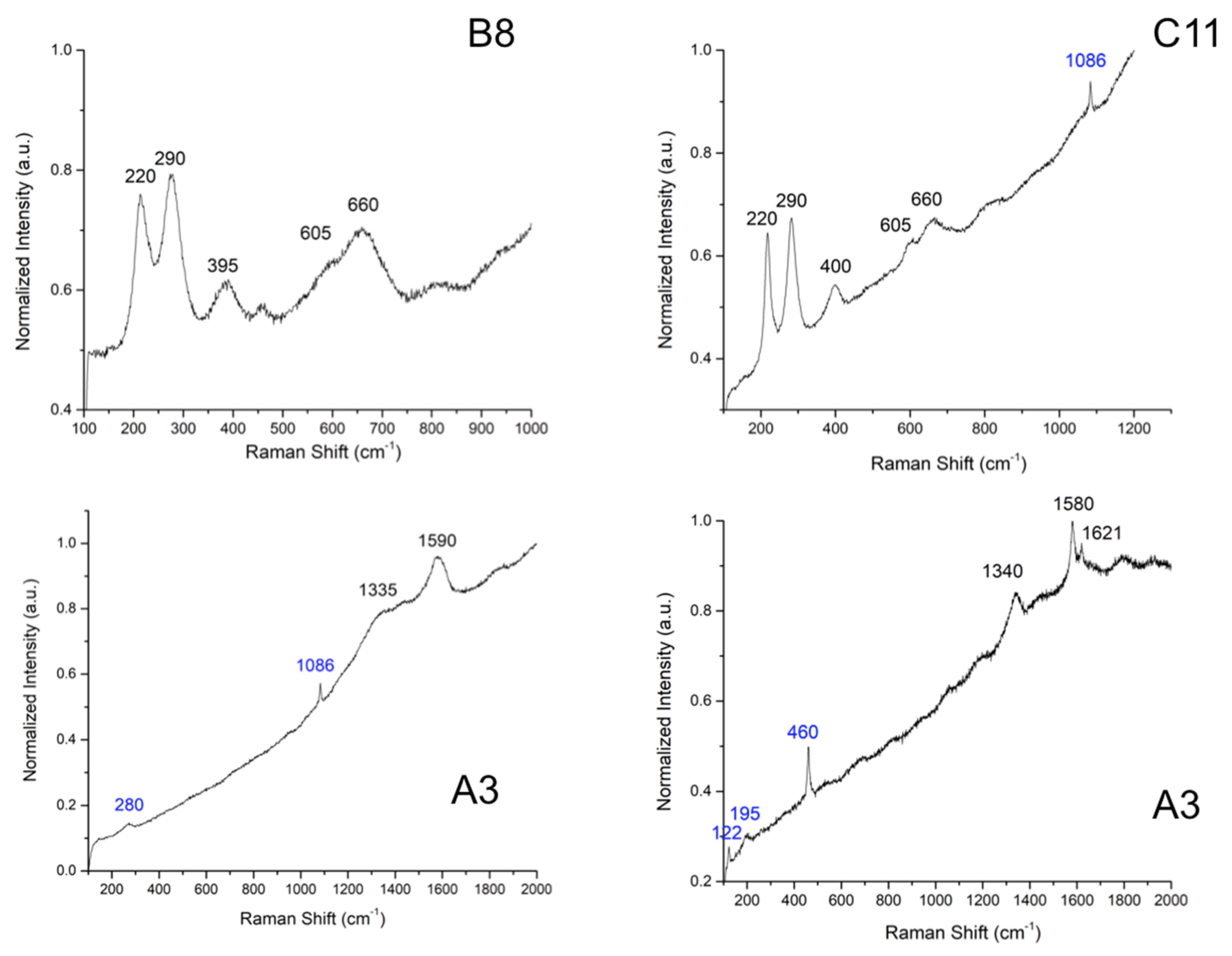
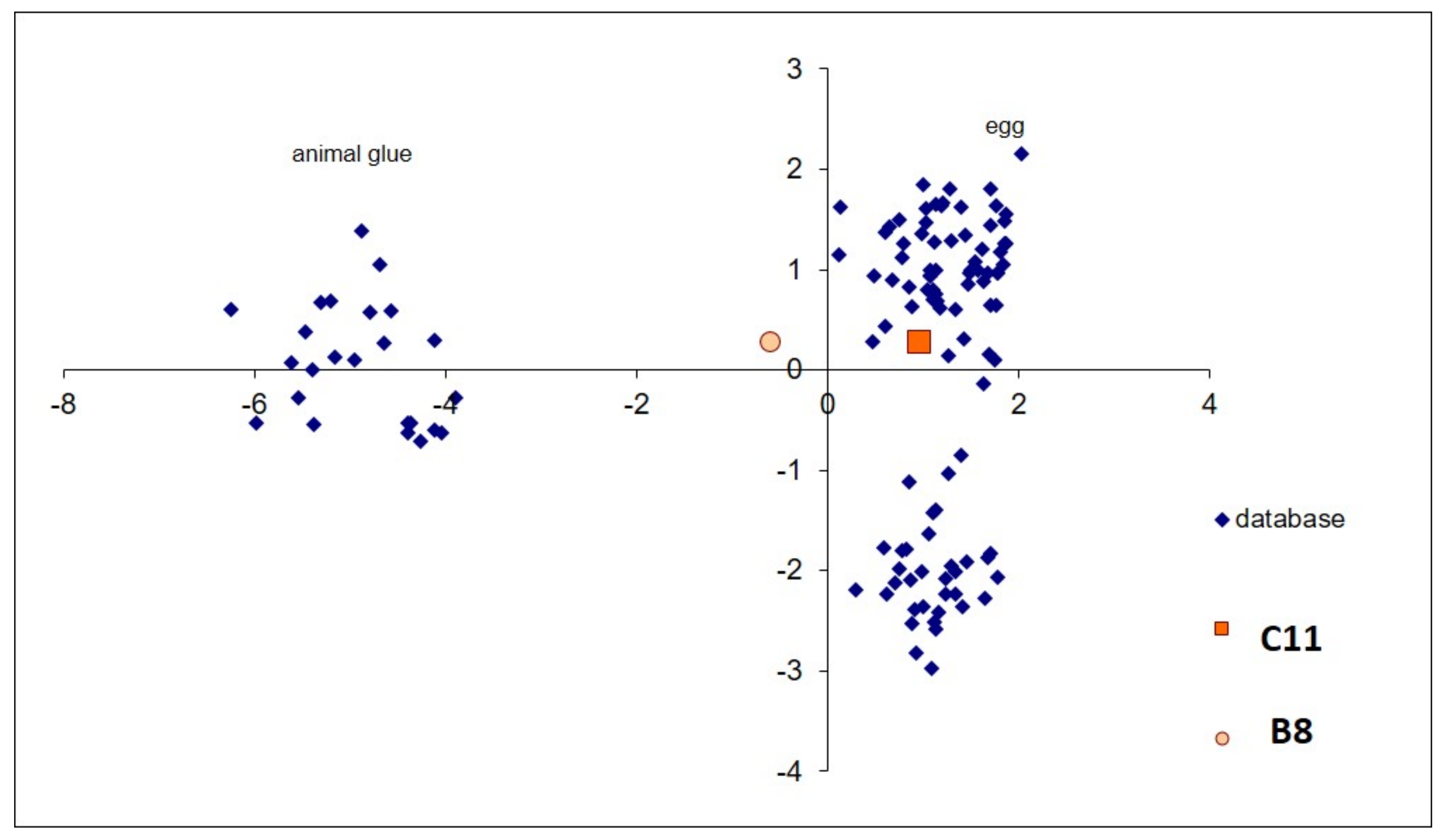
| Sample Description | Analyses Carried Out | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Name | Colour of the Polychrome Layer | Presence of a Preparation Layer | Archaeological Site | Period | Raman | GC-MS | Sample Type |
| GBK (18) | red | yes | Gumbat/Balo Kale (Pakistan) | end 2nd century–early 3rd century CE | x | powder | |
| GBK (17) | red | yes | x | powder | |||
| BKG 1123 (15) | red | yes | Barikot (Pakistan) | middle-end 2nd century CE | x | x | fragment two sub-samples analysed (pl and prep) |
| C11 | red | yes | Amlukdara (Pakistan) | late 3rd–early 4th century CE | x | x | paint layer |
| A3 | black and blue paint layer | yes | Gumbat/Balo Kale (Pakistan) | beginning of the 2nd century CE | x | x | paint layer |
| B8 | red | no | Barikot (Pakistan) | ca. 3rd century CE | x | x | paint layer |
| Sample | Inorganic Composition | Binder Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raman Shift (cm−1) | Pigments Identified | Subsample Analysed | Lipid-Resinous Fraction | Saccharide Fraction | Proteinaceous Fraction | |
| GBK (18) | n.p. | Paint and preparation layer powder (0.3 mg) | animal fat | n.d. | n.d. | |
| GBK (17) | n.p. | Paint and preparation layer powder (0.7 mg) | animal fat | n.d. | n.d. | |
| BKG 1123 (15)_pl | n.p. | Red paint layer | n.d. | n.d. | present, below LOQ | |
| BKG 1123 (15)_prep | n.p. | White preparation layer | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | |
| C11 | 220, 290, 400, 605, 660 1086 | Red ochre Calcite | Red paint layer | n.d. | n.d. | egg, animal glue (minor component) |
| A3 | 283, 1086 122, 195, 460 1335, 1590 | Calcite quartz Carbon black (graphite) | Black and blue paint layer | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| B8 | 220, 290, 395, 605, 660 | Red ochre | Red paint layer | n.d. | n.d. | egg, animal glue (minor component) |
| Sample | Ref | Century CE | Provenance | Statue | Architectural Decoration | Support | GC-MS | Proteomics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ex-MNAO 1 (Rome Museum) inv.1240 | [16] | ca. 2nd–3rd | Butkara (Pakistan) | X | stucco | traces of proteinaceous material (present, below LOQ) | ||
| ex-MNAO 1° (Rome Museum) inv.1240 | [16] | ca. 2nd–3rd | Butkara (Pakistan) | X | stucco | traces of proteinaceous material (present, below LOQ) | ||
| ex- MNAO 5A (Rome Museum) inv.4423 | [16] | ca. 1st–2nd | Panr (Pakistan) | X | stone | n.d. | ||
| ex-MNAO 7A (Rome Museum) inv.2519 | [16] | ca. 2nd–3rd | Butkara (Pakistan) | X | stone | n.d. | ||
| ex-MNAO 11A (Rome Museum) inv. 435 | [16] | ca. 3rd–4th | unknown | X | stucco | traces of proteinaceous material, (present, below LOQ) | ||
| AKD14C | [18] | late 3rd | Amlukdara (Pakistan) | X | stucco | traces of proteinaceous material, (present, below LOQ) | animal glue egg | |
| BKG1123A | [18] | 3rd | Barikot (Pakistan) | X | stucco | traces of proteinaceous material, (present, below LOQ) | ||
| BKG1123B | [18] | 3rd | Barikot (Pakistan) | X | stucco | n.d. | ||
| MG18957 (Museum Guimet of Paris) | [18] | 7th | Fundukistan (Afghanistan) | X | clay | - | animal glue milk egg | |
| MG18959 (Museum Guimet of Paris) | [18] | 7th | Fundukistan (Afghanistan) | X | clay | - | animal glue milk egg | |
| MCM4 (Civic Archaeological Museum of Milan) | [18] | 2nd–3rd | unknown | x | stone | - | animal glue | |
| MCM5 (Civic Archaeological Museum of Milan) | [18] | 4th–5th | unknown | x | clay | - | animal glue | |
| MCM25 (Civic Archaeological Museum of Milan) | [18] | unknown | unknown | x | clay | - | animal glue | |
| GBK (18) | present work | 2 nd–3rd | Gumbat/Balo kale (Pakistan) | X | stucco | animal fat | - | |
| GBK (17) | present work | 2nd–3rd | Gumbat/Balo kale (Pakistan) | X | stucco | animal fat | - | |
| BKG 1123 (15) | present work | 2nd | Barikot (Pakistan) | X | stucco | traces of proteinaceous material, (present, below LOQ) | - | |
| A3 | present work | 2nd | Gumbat/Balo kale (Pakistan) | X | stucco | n.d. | - | |
| C11 | present work | 3rd–4th | Amlukdara (Pakistan) | X | stucco | egg, animal glue | - | |
| B8 | present work | 3rd | Barikot (Pakistan) | X | stucco | egg, animal glue | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lluveras-Tenorio, A.; Andreotti, A.; Talarico, F.; Legnaioli, S.; Olivieri, L.M.; Colombini, M.P.; Bonaduce, I.; Pannuzi, S. An Insight into Gandharan Art: Materials and Techniques of Polychrome Decoration. Heritage 2022, 5, 488-508. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5010028
Lluveras-Tenorio A, Andreotti A, Talarico F, Legnaioli S, Olivieri LM, Colombini MP, Bonaduce I, Pannuzi S. An Insight into Gandharan Art: Materials and Techniques of Polychrome Decoration. Heritage. 2022; 5(1):488-508. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleLluveras-Tenorio, Anna, Alessia Andreotti, Fabio Talarico, Stefano Legnaioli, Luca M. Olivieri, Maria Perla Colombini, Ilaria Bonaduce, and Simona Pannuzi. 2022. "An Insight into Gandharan Art: Materials and Techniques of Polychrome Decoration" Heritage 5, no. 1: 488-508. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5010028
APA StyleLluveras-Tenorio, A., Andreotti, A., Talarico, F., Legnaioli, S., Olivieri, L. M., Colombini, M. P., Bonaduce, I., & Pannuzi, S. (2022). An Insight into Gandharan Art: Materials and Techniques of Polychrome Decoration. Heritage, 5(1), 488-508. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5010028








