Study of a Late Bronze Age Casting Mould and Its Black Residue by 3D Imaging, pXRF, SEM-EDS, Micro-FTIR and Micro-Raman
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Mould
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. 3D Reconstruction and Optical Imaging
2.2.2. Portable X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry (pXRF)
2.2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy Coupled with Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (SEM-EDS)
2.2.4. Micro-Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (Micro-FTIR)
2.2.5. Micro-Raman Spectroscopy
3. Results and Discussion
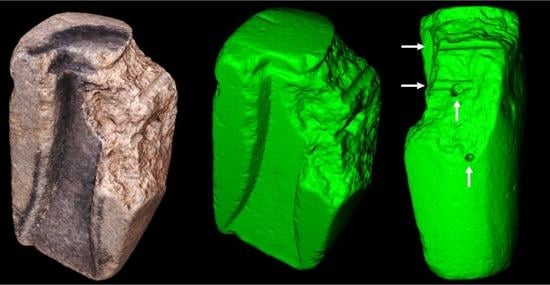
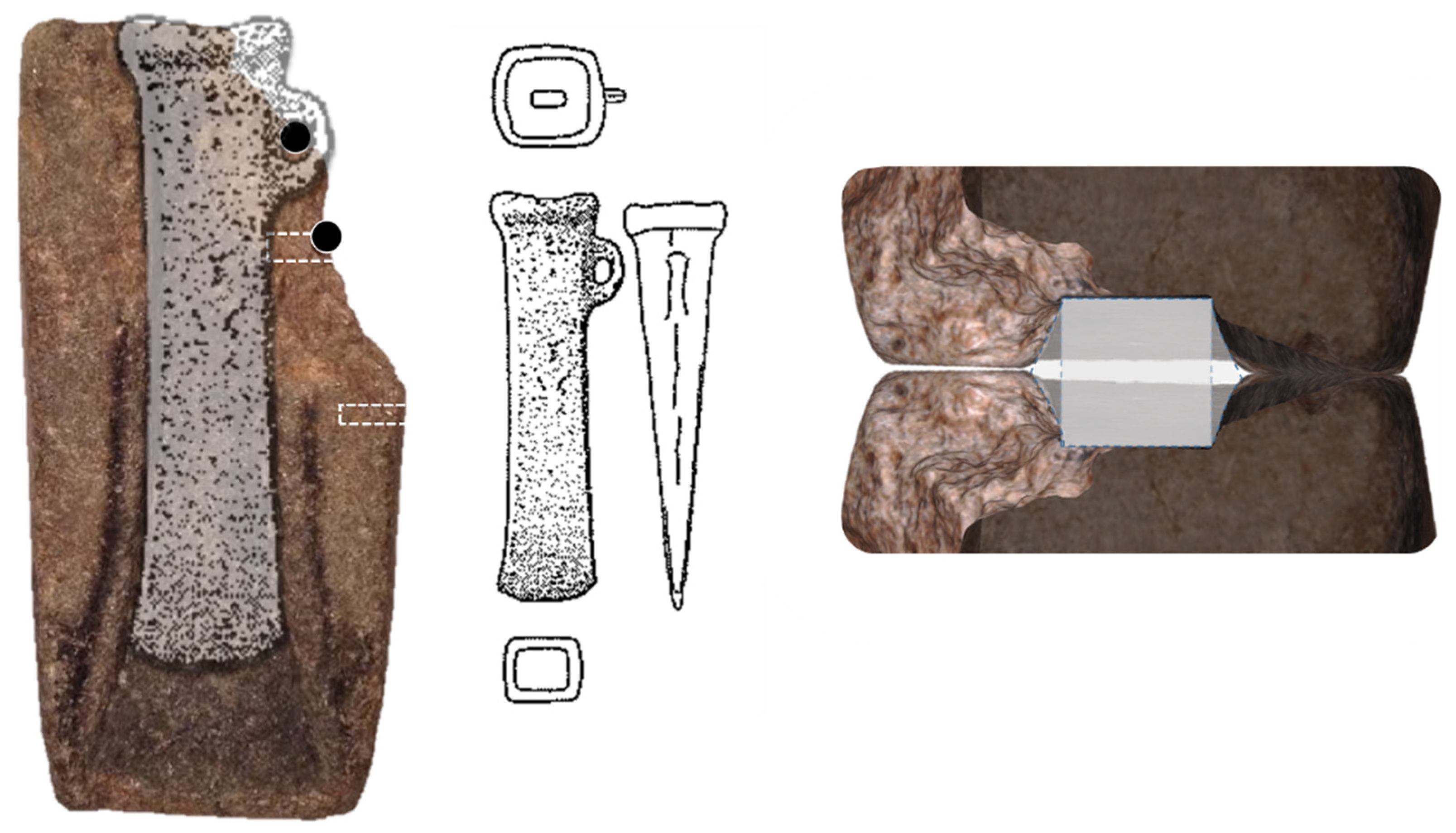
3.1. Shape of the Mould and Black Residue Distribution
3.2. Analysis of the Mould by pXRF
3.3. Analysis of the Black Residue by SEM-EDS
3.4. Analysis of the Black Residue by Micro-FTIR and Micro-Raman
3.5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | three dimensions |
| BCE | before common era |
| BSE | backscattered electron (imaging mode in SEM-EDS) |
| EDXRF | energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry |
| GC/MS | gas chromatography mass spectrometry |
| Micro-FTIR | micro-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| pXRF | portable X-ray spectrometry |
| SDD | silicon drift detector |
| SE | secondary electron (imaging mode in SEM-EDS) |
| SEM-EDS | variable pressure scanning electron microscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| ZAF | atomic-number effect, absorption effect, and fluorescence excitation effect (quantitative correction method) |
References
- Cardoso, J.L.; Boutille, L.; Brandherm, D. Instrumentos líticos para a deformação plástica de metais do povoado calcolítico de Outeiro Redondo (Sesimbra). Estud. Arqueol. Oeiras 2018, 24, 291–306. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado-Raack, S.; Risch, R. Lithic perspectives on metallurgy: An example from Copper and Bronze Age south-east Iberia. In “Prehistoric Technology” 40 Years Later. Functional Studies and the Russian Legacy; BAR International Series 1783; Longo, L., Skakun, N., Eds.; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 235–252. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, M.; Cavazzuti, C. Stone Moulds from Terramare (Northern Italy): Analytical Approach and Experimental Reproduction. EXARC Online J. 2014. Available online: https://exarc.net/ark:/88735/10145 (accessed on 4 November 2018).
- Boutoille, L. Les dépôts de moules lithiques de fondeur de l’Âge du Bronze découverts en France. In Du matériel au spirituel: Réalités archéologiques et historiques des «dépôts» de la Préhistoire à nos jours; Bonnardin, S., Hamon, C., Lauwers, M., Quilliec, B., Eds.; Éditions APDCA: Antibes, France, 2009; pp. 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Fraile Vicente, A. Moldes de fundición de la Edad del Bronce en la Península Ibérica: Ensayo Tipológico y Cartográfico. Master’s Thesis, Universidad de Valladolid, Valladolid, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ó Faoláin, S. Bronze Artefacts Production in Late Bronze Age Ireland. A Survey; British Series 382; BAR: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Armbruster, B.; Jockenhövel, A.; Kapuran, A.; Ramadanski, R. The moulds from Velebit and European Bronze Age metal anvils. Starinar 2019, 69, 139–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Webley, L.; Adams, S. Material genealogies: Bronze moulds and their castings in Later Bronze Age Britain. Proc. Prehist. Soc. 2016, 82, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vilaça, R.; Almeida, S.; Bottaini, C.; Marques, J.N.; Montero-Ruiz, I. Metalurgia do Castro do Cabeço da Argemela (Fundão): Formas, conteúdos, produções e contextos. In Povoamento e exploração dos recursos minérios na Europa Atlântica Ocidental; Martins, C.M.B., Bettencourt, A.M.S., Martins, J.I.F.P., Carvalho, J., Eds.; CITCEM: Braga, Portugal, 2011; pp. 427–452. [Google Scholar]
- Iaia, C. Smith and smithing in Bronze Age “Terramare”. In Archaeology and Craft, Proceedings of the VI OpenArch-Conference in Albersdorf, Germany, 23–27 September 2013; Kelm, R., Ed.; Husum Druck: Husum, Germany, 2015; pp. 78–93. [Google Scholar]
- Monteagudo, L. Die Beile auf der Iberischen Halbinsel; Prähistorische Bronzefunde Abteilung IX, 6. Band; C.H. Beck: München, Germany, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, C. Molde de fundição para machados de bronze de duplo anel. Trab. Soc. Port. Antropol. E Etnol. 1939, 9, 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- García-Vuelta, O.; Cuesta-Gómez, F.; Galán Domingo, E.; Montero Ruiz, I. Los moldes de fundición de bronce para hachas de talón de La Macolla (Linares de Riofrío, Salamanca). Nuevos datos sobre viejos hallazgos. Zephyrus 2014, 74, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senna-Martinez, J.C.; Valério, P.; Casimiro, M.H.; Ferreira, L.M.; Araújo, M.F.; Peixoto, H. Foundry in the Late Bronze Age Baiões/Santa Luzia Cultural Group: Some reflections starting from a new metallic mould for unifacial palstaves. Ophiussa 2018, 4, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R. A Late Bronze Age mould from Los Oscos (prov. Oviedo). Madr. Mitt. 1980, 21, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, J.M.; Vilaseco, X.I. Guidoiro Areoso. Megalithic cemetery and Prehistoric settlement in the Ría de Arousa (Galicia, NW Spain). In Environmental Changes and Human Interaction Along the Western Atlantic Edge; Campar Almeida, A., Bettencourt, A.M.S., Moura, D., Monteiro-Rodrigues, S., Caetano Alves, M.I., Eds.; Associação Portuguesa para o Estudo do Quaternário: Coimbra, Porgugal, 2012; pp. 243–258. [Google Scholar]
- Comendador Rey, B.; Reborelda-Morillo, S.; Kockelmann, W.; Macdonald, M.; Bell, T.; Pantos, M. Early Bronze Technology at the Land’s End, North Western Iberia. In Science and Technology in Homeric Epics; Paipetis, S.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 113–131. [Google Scholar]
- Comendador, B.; Bettencourt, A.M.S. Nuevos datos sobre la primera metalurgia del Bronce en el Noroeste de la Península Ibérica: La contribución de Bouça da Cova da Moura (Ardegães, Maia, Portugal). Estud. Quaternário 2011, 7, 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- López-Romero, E.; Güimil-Fariña, A.; Mañana Borrazás, P.; Otero Vilariño, C.; Prieto Martínez, M.P.; Rey García, J.M.; Vilaseco Vázquez, X.I. Later prehistoric settlements and monuments on the islet of Guidoiro Areoso (Ría de Arousa, Pontevedra): Research on present-day littoral dynamics on the Atlantic coast. Trab. Prehist. 2015, 72, 353–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kearns, T.; Martinón-Torres, M.; Rehren, T. Metal do mould: Alloy identification in experimental casting moulds using XRF. Hist Metall. 2010, 44, 48–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, M.S. Petrography and provenance interpretation of the stone moulds from bronze daggers from the Galdon Prehistoric site, Republic of Korea. Archaeometry 2010, 52, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, K.; Cai, Q.; Chen, J. Microscopic study of Chinese bronze casting moulds from the Eastern Zhou period. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 2402–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.M.M.; Valério, P.; Frade, J.C.; Oliveira, M.J.; Patoilo, D.; Ribeiro, I.; Arez, L.; Santos, F.J.C.; Araújo, M.F. A Late Bronze Age stone mould for flat axes from Casarão da Mesquita 3 (São Manços, Évora, Portugal). In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Archaeometallurgy in Europe, Aquileia, Italy, 17–21 June 2007; Craddock, P.T., Giumlia-Mair, A., Hauptman, A., Eds.; Associazione Italiana di Metallurgia: Milan, Italy, 2007; pp. 145–157. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, J.; Miazga, B.; Ntaflos, T.; Puziewicz, J.; Szummy, A. Beeswax remnants, phase and major element chemical composition of the bronze age mould from Gaj Olawsky (SW Poland). Archaeol. Anthrop. Sci. 2016, 8, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomasini, E.; Siracusano, G.; Maier, M.S. Spectroscopic, morphological and chemical characterization of historic pigments based on carbon. Paths for the identification of an artistic pigment. Microchem J. 2012, 102, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasini, E.P.; Gómez, B.; Halac, E.B.; Reinoso, M.; Di Liscia, E.J.; Sirusano, G.; Maier, M.S. Identification of carbon-based black pigments in four South American polychrome wooden sculptures by Raman microscopy. Heritage Sci. 2015, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardaker, R. Las hachas de cubo en la Península Ibérica. Cad. De Prehist. Y Arqueol. Castellon. 1976, 3, 151–171. [Google Scholar]
- Bottaini, C.; Giardino, C.; Paternoster, G. Estudo de um conjunto de machados metálicos no Norte de Portugal. Estud. Arqueol. Oeiras 2012, 19, 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Bottaini, C. Depósitos Metálicos no Bronze Final (Sécs. XIII-VII a.C.) Do Centro e Norte de Portugal. Aspectos Sociais e Arqueometalúrgicos. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shipman, P.; Foster, G.; Schoeninger, M. Burnt bones and teeth: And experimental study of color, morphology, crystal structure and shrinkage. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1984, 11, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, R.A. A morphological investigation of burnt animal bone and an evaluation of its utility in archaeology. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1993, 20, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, C.; Clarke, M.; Melo, M.J.; Lopes, J.A. Combining infrared spectroscopy with chemometric analysis for the characterization of proteinaceous binders in medieval paints. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2012, 119, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.P.M.; Mamede, A.P.; Vassalo, A.R.; Makhoul, C.; Cunha, E.; Gonçalves, D.; Parker, S.F.; Batista de Carvalho, L.A.E. Heat-induced bone diagenesis probed by vibrational spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coccato, A.; Jehlicka, J.; Moens, L.; Vandenabeele, P. Raman spectroscopy for the investigation of carbon-based black pigments. J. Raman. Spectrosc. 2015, 46, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Figueiredo, E.; Bottaini, C.; Miguel, C.; Lackinger, A.; Mirão, J.; Comendador Rey, B. Study of a Late Bronze Age Casting Mould and Its Black Residue by 3D Imaging, pXRF, SEM-EDS, Micro-FTIR and Micro-Raman. Heritage 2021, 4, 2960-2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4040165
Figueiredo E, Bottaini C, Miguel C, Lackinger A, Mirão J, Comendador Rey B. Study of a Late Bronze Age Casting Mould and Its Black Residue by 3D Imaging, pXRF, SEM-EDS, Micro-FTIR and Micro-Raman. Heritage. 2021; 4(4):2960-2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4040165
Chicago/Turabian StyleFigueiredo, Elin, Carlo Bottaini, Catarina Miguel, Aaron Lackinger, José Mirão, and Beatriz Comendador Rey. 2021. "Study of a Late Bronze Age Casting Mould and Its Black Residue by 3D Imaging, pXRF, SEM-EDS, Micro-FTIR and Micro-Raman" Heritage 4, no. 4: 2960-2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4040165
APA StyleFigueiredo, E., Bottaini, C., Miguel, C., Lackinger, A., Mirão, J., & Comendador Rey, B. (2021). Study of a Late Bronze Age Casting Mould and Its Black Residue by 3D Imaging, pXRF, SEM-EDS, Micro-FTIR and Micro-Raman. Heritage, 4(4), 2960-2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4040165