Investigation of Archaeological European White Elm (Ulmus laevis) for Identifying and Characterizing the Kind of Biological Degradation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Preparation of Samples
2.2. Analysis and Evaluation Methods
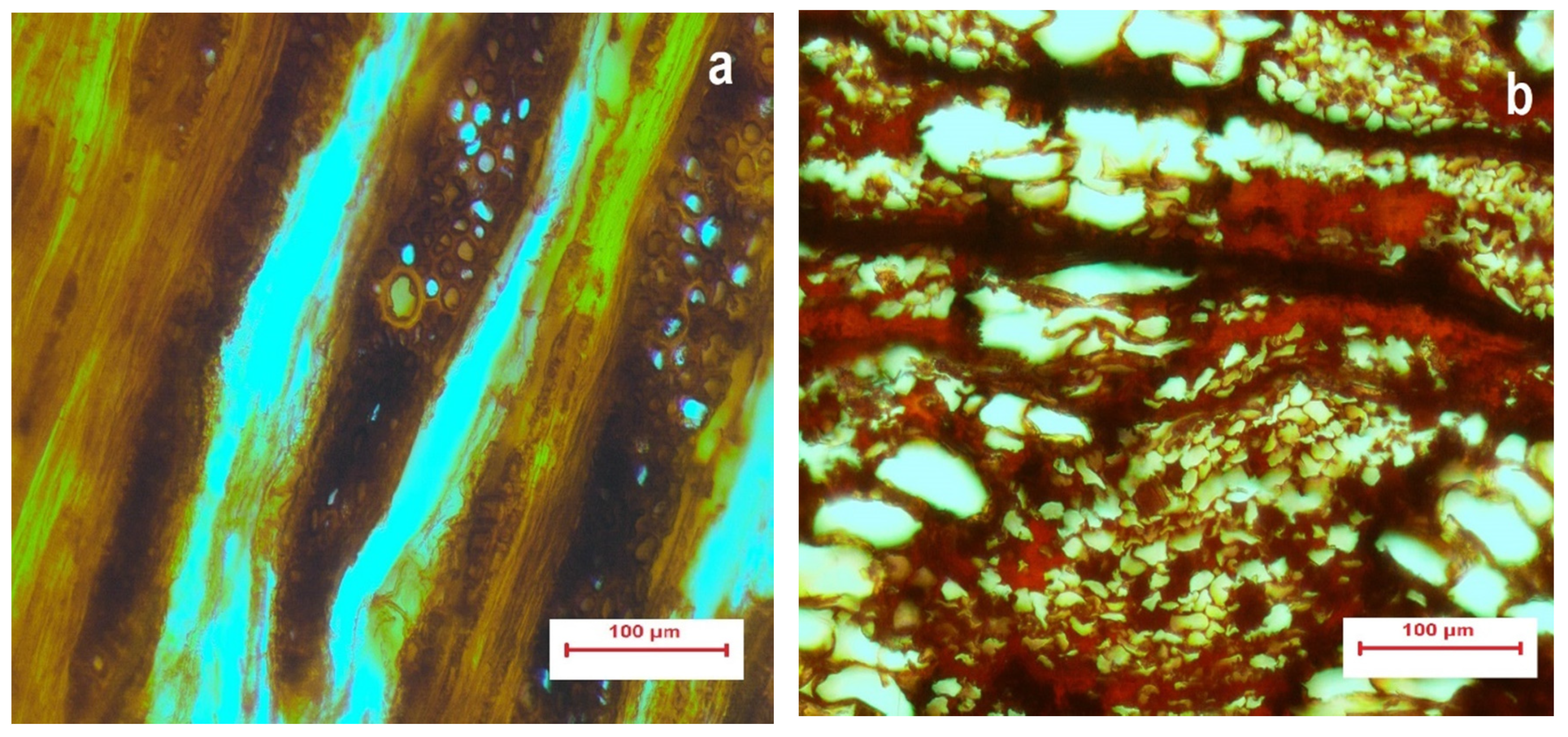
2.2.1. Microscopic Imaging
2.2.2. Moisture Content
2.2.3. Cyclohexane-Ethanol Extract
2.2.4. Chlorite Holocellulose Content
2.2.5. α—Cellulose Content
2.2.6. Kürschner–Hoffer Cellulose Content
2.2.7. Lignin Content
2.2.8. Ash Content
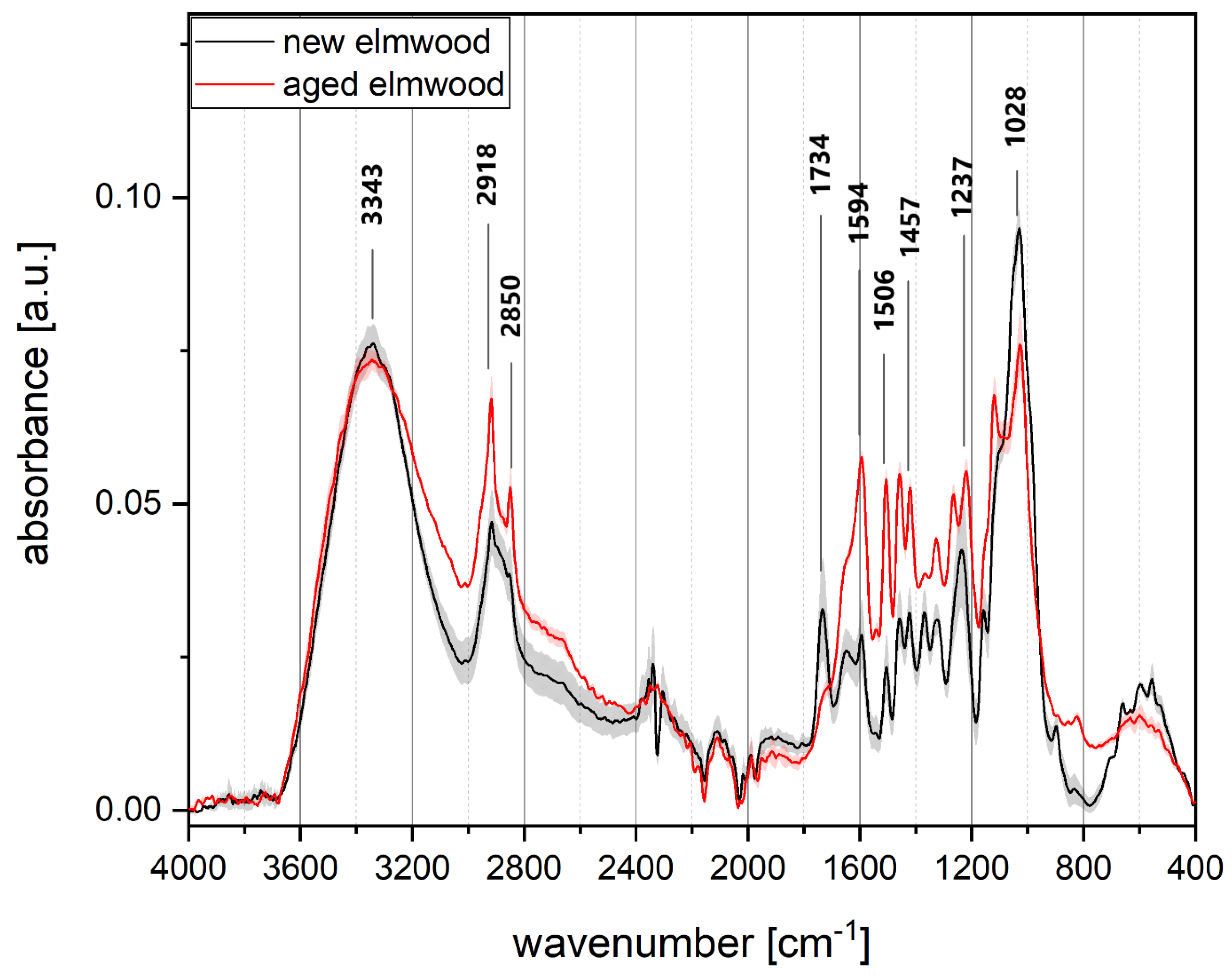
2.2.9. FTIR Analysis
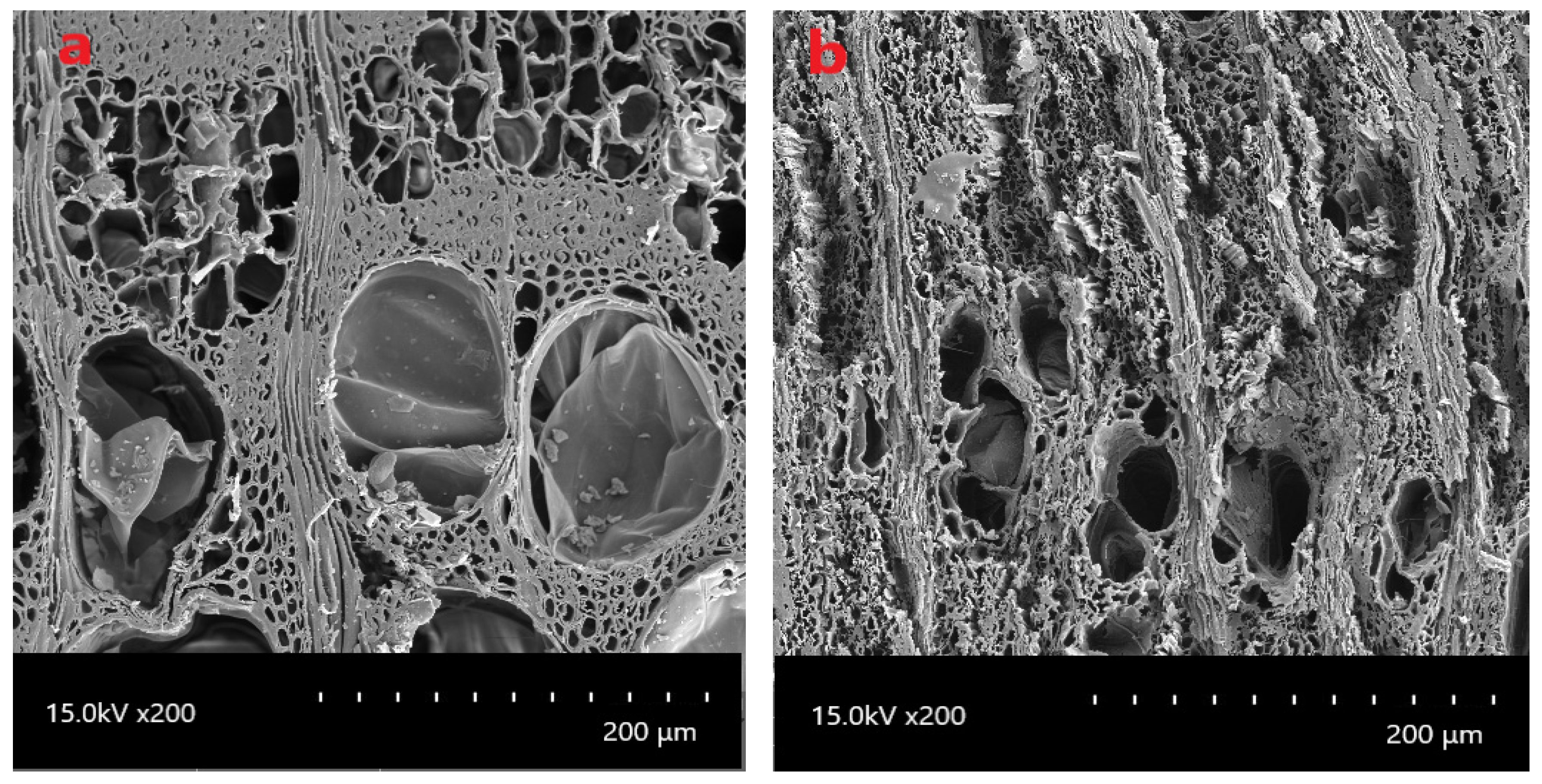
2.2.10. Characterization by Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.2.11. Statistical Analysis of the Results
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of Bacterial Attack by Light Microscopy
3.2. Chemical Analysis
3.3. FTIR Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feist, W.C. Structural Use of Wood in Adverse Environments; Meyer, R.W., Kellogg, R.M., Eds.; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 156–178. [Google Scholar]
- Feist, W.C.; Hon, D.N.-S. The Chemistry of Solid Wood; Rowell, R.M., Ed.; Advances in Chemistry, American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; Volume 207, pp. 401–451. [Google Scholar]
- Bjodal, C.G. Waterlogged Archaeological Wood, Biodegradation and Its Implications for Conservation. Ph.D. Thesis, Swedish University of Agricultural Science, Uppsala, Sweden, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette, R.A.; Hoffmann, P. Degradation processes in waterlogged wood. In Proceedings of the Fifth ICOM Group on Wet Organic Archaeological Materials Conference, Portland, ME, USA, 16–20 August 1993; pp. 111–137. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, K.E.; Johnsrud, S.C. Mineralization of carbon. In Experimental Microbial Ecology; Burns, R.G., Slater, J.H., Eds.; Blackwell: London, UK, 1982; pp. 134–153. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, T.; Daniel, G. Tunnelling Bacteria, International Research Group on Wood Preservation; International Research Group on Wood Preservation: Surfers Paradise, QLD, Australia, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, G.F.; Nilsson, T. Ultrastructural Observations on Wood Degrading Erosions Bacteria; International Research Group on Wood Preservation: Avignon, France, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Buttcher, J.A. Bacterial Degradation of Wood Cell Wall: A Review of Degradation Patterns; The International Research Group on Wood Preservation: Rotorua, New Zealand, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Björdal, C.G.; Nilsson, T.; Daniel, G.F. Microbial decay of waterlogged archaeological wood found in Sweden—Applicable to archaeology and conservation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1999, 43, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Singh, A.P. Ultrastructural aspects of bacterial attacks in a submerged ancient wood. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 1994, 40, 554–562. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.P.; Nilsson, T.; Daniel, G.F. Bacterial attack of Pinus sylvestris wood under near-anaerobic conditions. J. Inst. Wood Sci. 1990, 11, 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.P.; Wakeling, R.N.; Drysdale, J.A. Microbial attack of CCA-treated Pinus radiata timbers from a retaining wall. Holzforschung 1994, 48, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbrich, J. Bacterial Wood Degradation—A Study of Chemical Changes and Growth Conditions of Bacteria. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Göttingen, Sierke Verlag Göttingen, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, T.; Björdal, C.G. Culturing wood degrading erosion-bacteria. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2008, 61, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Kim, Y.S. Biodegradation of Wood in Wet Environments: A Review; International Research Group on Wood Preservation: Stockholm, Sweden, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Rowell, R.M. Handbook of Wood Chemistry and Wood Composites; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kürschner, K.; Hoffer, A. Ein neues Verfahren zur Bestimmung der Cellulose in Hölzern und Zellstoffen A new method for the determination of cellulose in wood and pulps. Technol. Chem. Papier. Zellstoff. Fabr. 1929, 26, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- EN 15403. Solid Recovered Fuels—Determination of Ash Content, Supersedes CEN/TS 15403:2006, 2011. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/0c9908dd-e915-4470-b9b9-b7c2011b71fa/en-15403-2011 (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Jusoh, I.B.; Nzokou, P.; Kamdem, P. The effect of silicone on some properties of flakeboard. Holz. Roh. Werkst. 2005, 63, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutelje, J.B.; Bravery, A.F. Observations on the bacterial attack of piles supporting a Stockholm building. J. Inst. Wood Sci. 1968, 4, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Boutelje, J.B.; Goransson, B. Decay in wood constructions below the ground water table. Swed. J. Agric. Res. 1975, 5, 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- Eslyn, W.E.; Clarke, J.W. Appraising deterioration in submerged piling. Mater. Org. Beih. 1976, 3, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kohlmeyer, J. Bacterial attack on wood and cellophane in the deep sea. In Biodeterioration, Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium, Berlin, Germany, August-September 1978; Oxley, T.A., Becker, G., Allsopp, D., Eds.; Pitman Publishing Ltd.: London, UK, 1978; pp. 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmar, E.I.; Gelbrich, J.; Militz, H.; Lamersdorf, N. Studying bacterial wood decay under low oxygen conditions—results of microcosm experiments. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2008, 61, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, D.J.; Manders, M.R.; Kretschmar, E.I.; Klaassen, R.K.W.M.; Lamersdorf, N. Burial conditions and wood degradation at archaeological sites in the Netherlands. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2008, 61, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbrich, J.; Kretschmar, E.I.; Lamersdorf, N.; Militz, H. Simulation and Investigation of Wood Degradation by Erosion Bacteria in Laboratory Experiments. In Proceedings of the International Research Group on Wood Preservation, Biarritz, France, 9–13 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Singh, A.P. Micromorphological characteristics of wood biodegradation in wet environments: A review. IAWA J. 2000, 21, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbrich, J.; Mai, C.; Militz, H. Chemical changes in wood degraded by bacteria. Int. Biodet. Biodeg. 2008, 61, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Nilsson, T.; Daniel, G. Variable resistance of Pinus sylvestris wood components to attack by wood degrading bacteria. In Proceedings of the 3rd Pacific Regional Wood Anatomy Conference, Rotorua, New Zeeland, 20–24 November 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, O. Holz- und Baumplilze-Biologie, Schaden, Schutz, Nutzen; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; Volume 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Initial pit borders in Pinus radiate are resistant to degradation by soft rot fungi and erosion bacteria but not tunnelling bacteria. Holzforschung 1997, 51, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Wakeling, R. Microscopic Characteristics of Microbial Attacks of CCA-Treated Radiate Pine Wood; International Research Group on Wood Preservation: Orlando, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Butcher, J.A. Bacterial degradation of wood cell walls: A review of degradation patterns. J. Int. Wood Sci. 1991, 12, 43–157. [Google Scholar]
- Pettersen, R.C. The Chemistry of Solid Wood, Advances in Chemistry Series 20; Chapter 2; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Krutul, D.; Radomski, A.; Zawadzki, J.; Zielenkiewicz, T.; Antczak, A. Comparison of the chemical composition of the fossil and recent oak wood. Wood Res. 2010, 55, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Bettazzi, F.; Giachi, G.; Staccioli, G.; Chimichi, S. Chemical Characterisation of Wood of Roman Ships Brought to Light in the Recently Discovered Ancient Harbour of Pisa (Tuscany, Italy). Holzforschung 2003, 57, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baar, J.; Paschová, Z.; Hofmann, T.; Kolář, T.; Koch, G.; Saake, B.; Rademacher, P. Natural durability of subfossil oak: Wood chemical composition changes through the ages. Holzforschung 2019, 74, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavidel, A.; Hofmann, T.; Bak, M.; Sandu, I.; Vasilache, V. Comparative archaeometric characterization of recent and historical oak (Quercus spp.) Wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2020, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiridon, P.; Sandu, I.C.A.; Nica, L.; Iurcovschi, C.T.; Colbu, D.E.; Negru, I.C.; Vasilache, V.; Cristache, R.A.; Sandu, I. Archaeometric and chemometric studies involved in the authentication of old heritage artefacts II. Old linden and poplar wood put into work. Rev. Chim. 2017, 68, 2422–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbrich, J.; Mai, C.; Militz, H. Evaluation of bacterial wood degradation by Fourier-Transform-Infrared (FTIR) measurements. J. Cult. Herit. 2012, 13, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | Kürschner-Hoffer Cellulose (wt%) | Chlorite Holo-Cellulose (wt%) | α-Cellulose (wt%) | Hemi-Cellulose (wt%) | Lignin (wt%) | Cyclohexane-Ethanol Extract (wt%) | Ash (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh-cut | 60.84(±0.98) a | 82.17(±1.30) a | 56.90(±0.60) a | 25.94(±0.24) a | 14.60(±0.36) a | 1.38(±0.01) a | 0.66(±0.01) a |
| Archaeological | 36.13(±0.77) b | 47.91(±1.08) b | 32.85(±0.34) b | 16.60(±0.13) b | 44.22(±0.53) b | 2.16(±0.02) b | 5.37(±0.04) b |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghavidel, A.; Gelbrich, J.; Kuqo, A.; Vasilache, V.; Sandu, I. Investigation of Archaeological European White Elm (Ulmus laevis) for Identifying and Characterizing the Kind of Biological Degradation. Heritage 2020, 3, 1083-1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage3040060
Ghavidel A, Gelbrich J, Kuqo A, Vasilache V, Sandu I. Investigation of Archaeological European White Elm (Ulmus laevis) for Identifying and Characterizing the Kind of Biological Degradation. Heritage. 2020; 3(4):1083-1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage3040060
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhavidel, Amir, Jana Gelbrich, Aldi Kuqo, Viorica Vasilache, and Ion Sandu. 2020. "Investigation of Archaeological European White Elm (Ulmus laevis) for Identifying and Characterizing the Kind of Biological Degradation" Heritage 3, no. 4: 1083-1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage3040060
APA StyleGhavidel, A., Gelbrich, J., Kuqo, A., Vasilache, V., & Sandu, I. (2020). Investigation of Archaeological European White Elm (Ulmus laevis) for Identifying and Characterizing the Kind of Biological Degradation. Heritage, 3(4), 1083-1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage3040060






