Using Negative Muons as a Probe for Depth Profiling Silver Roman Coinage
Abstract
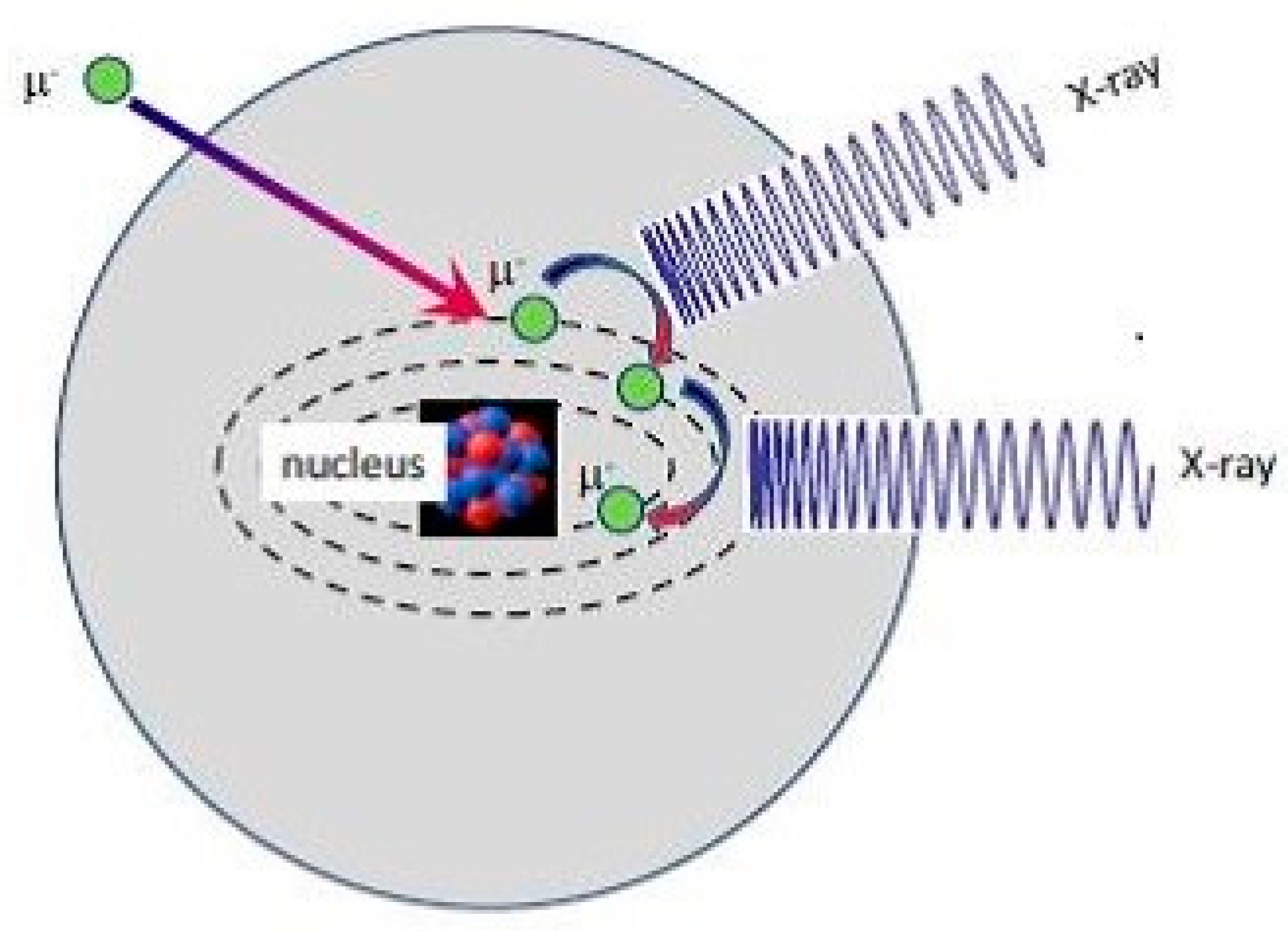
1. Introduction
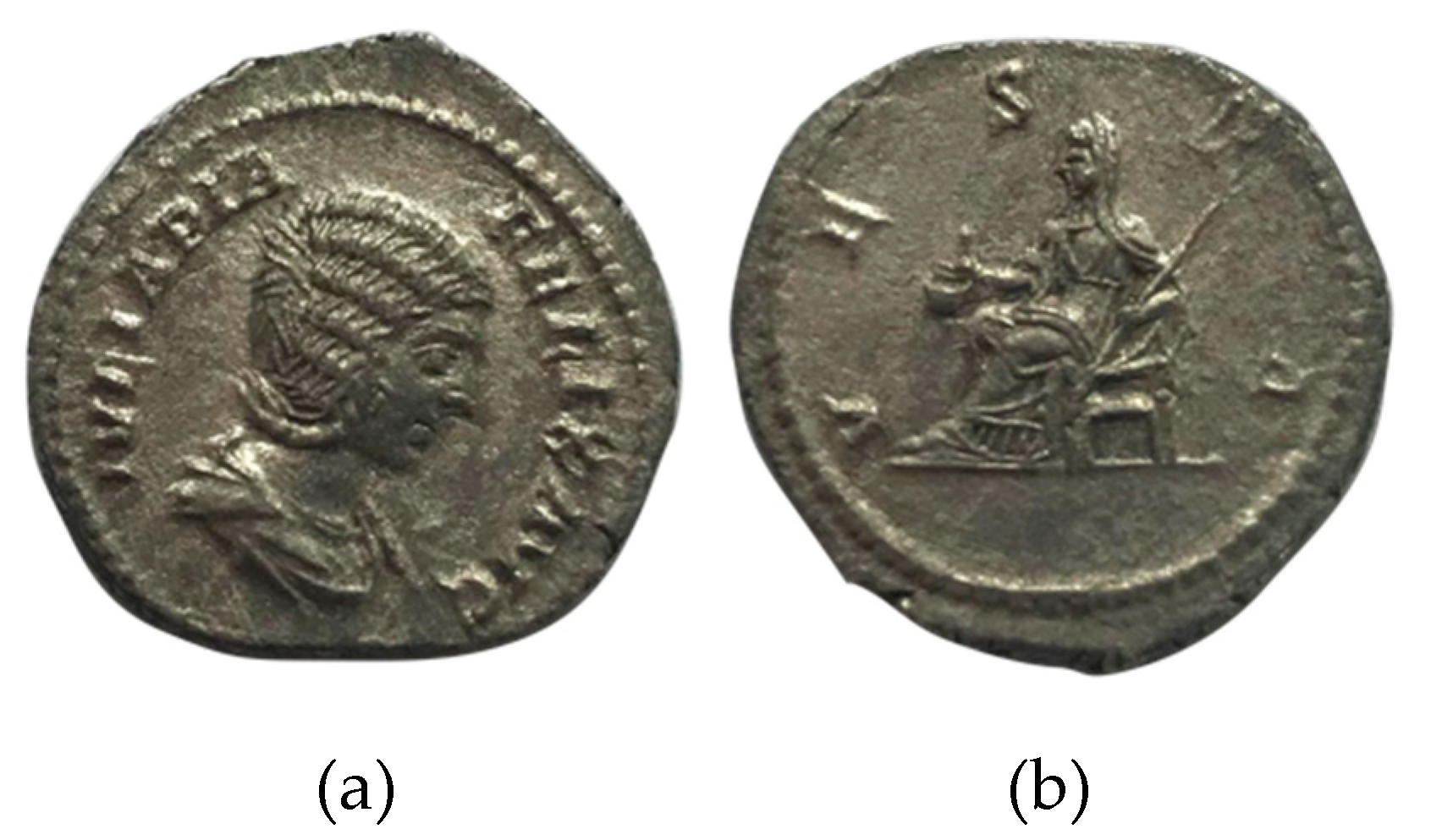
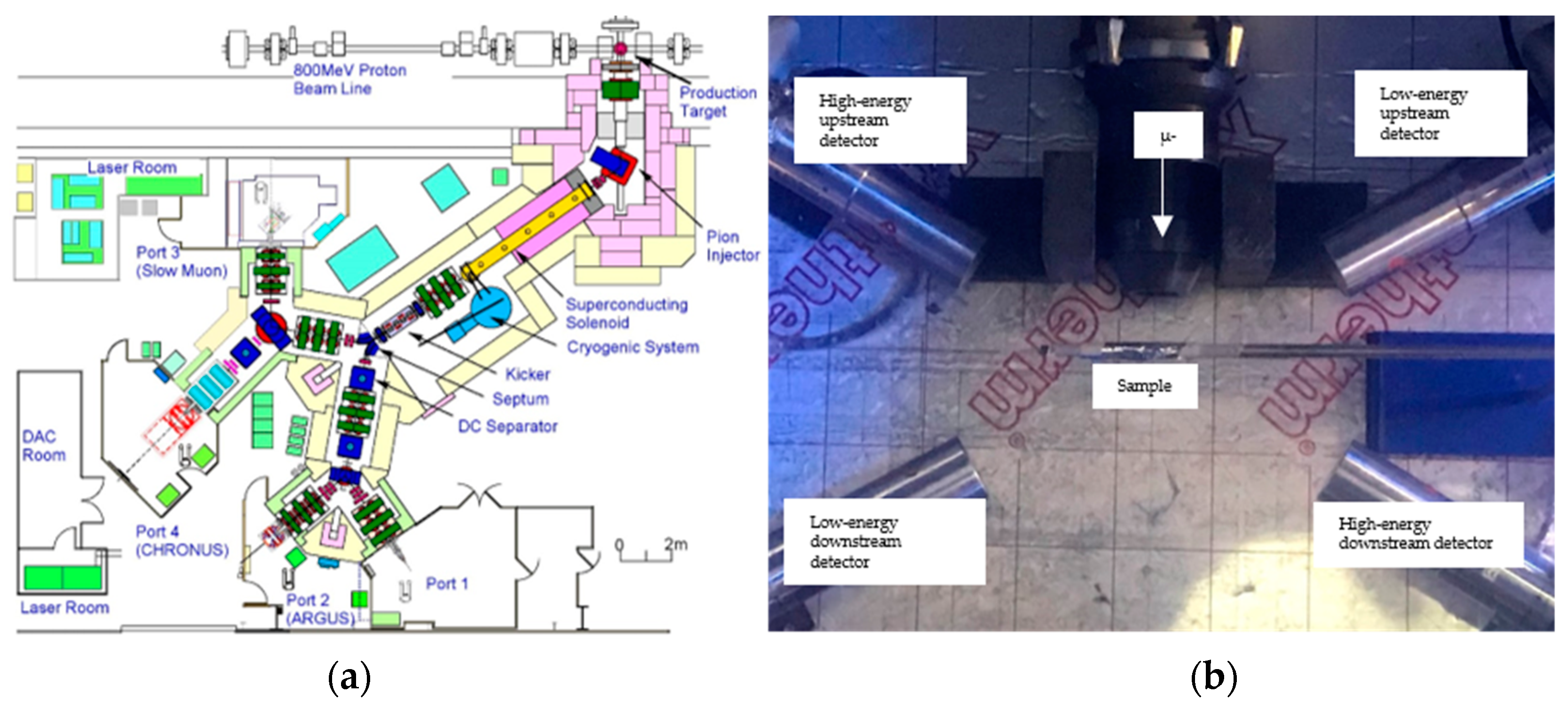
2. Materials and Methods
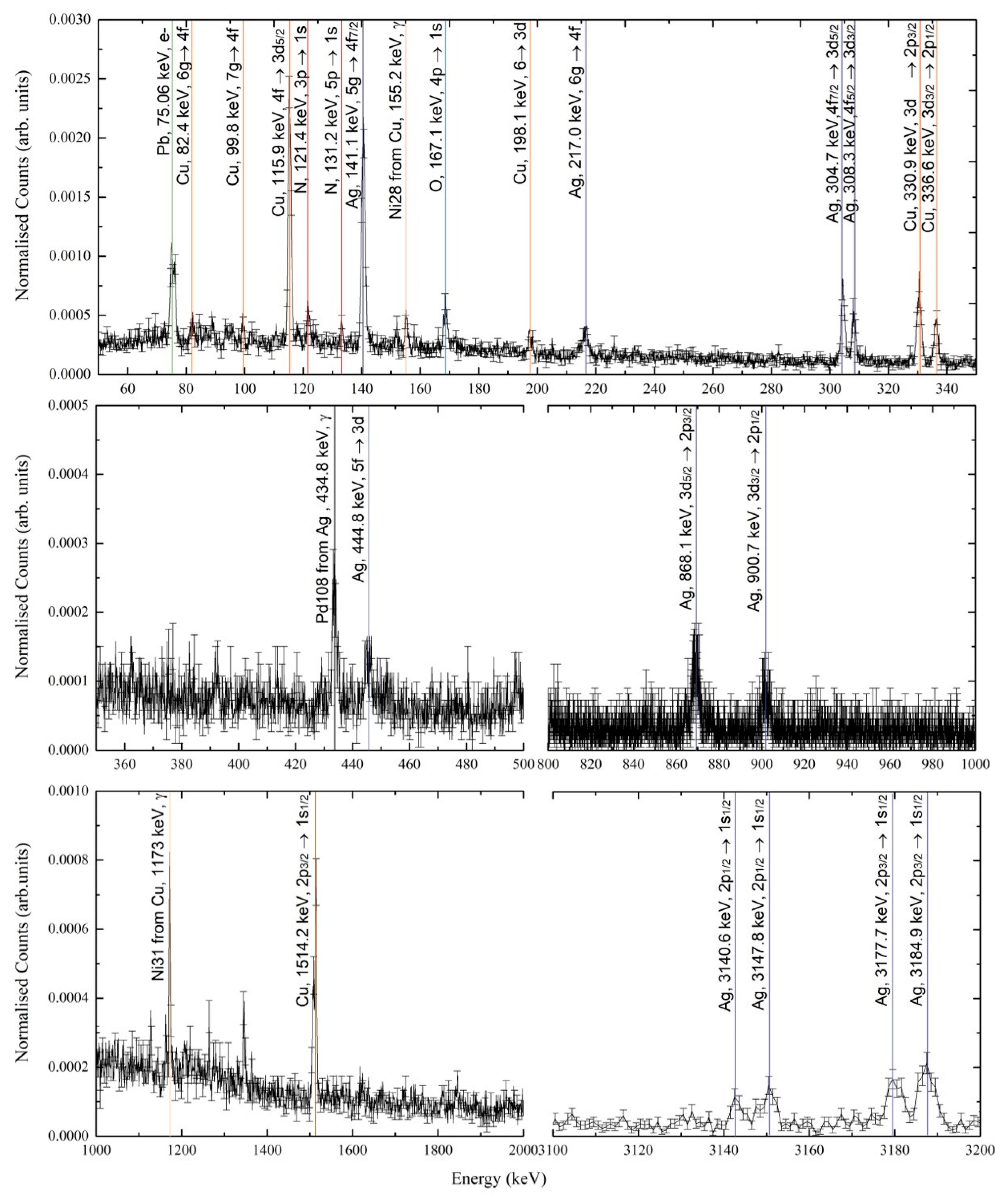
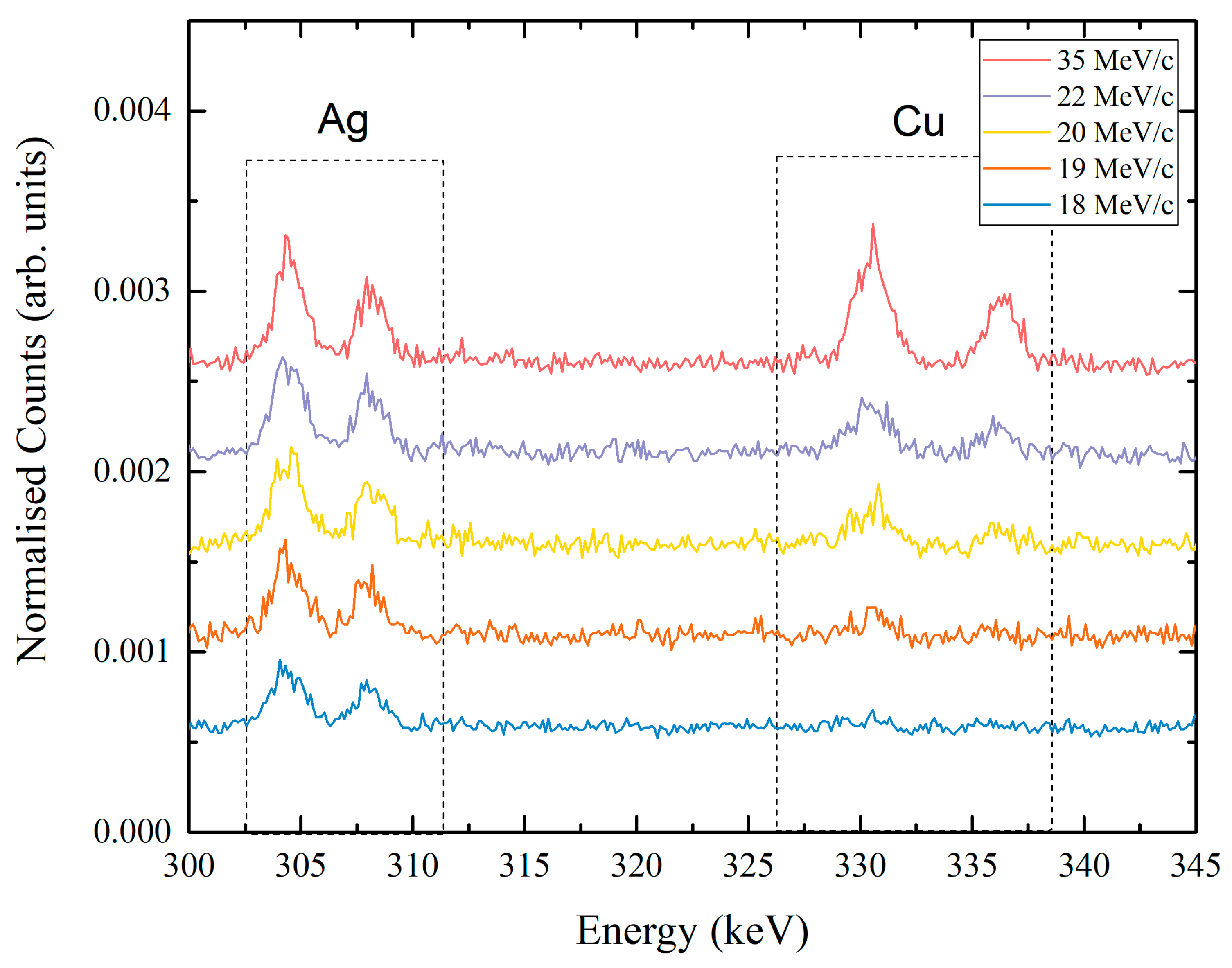
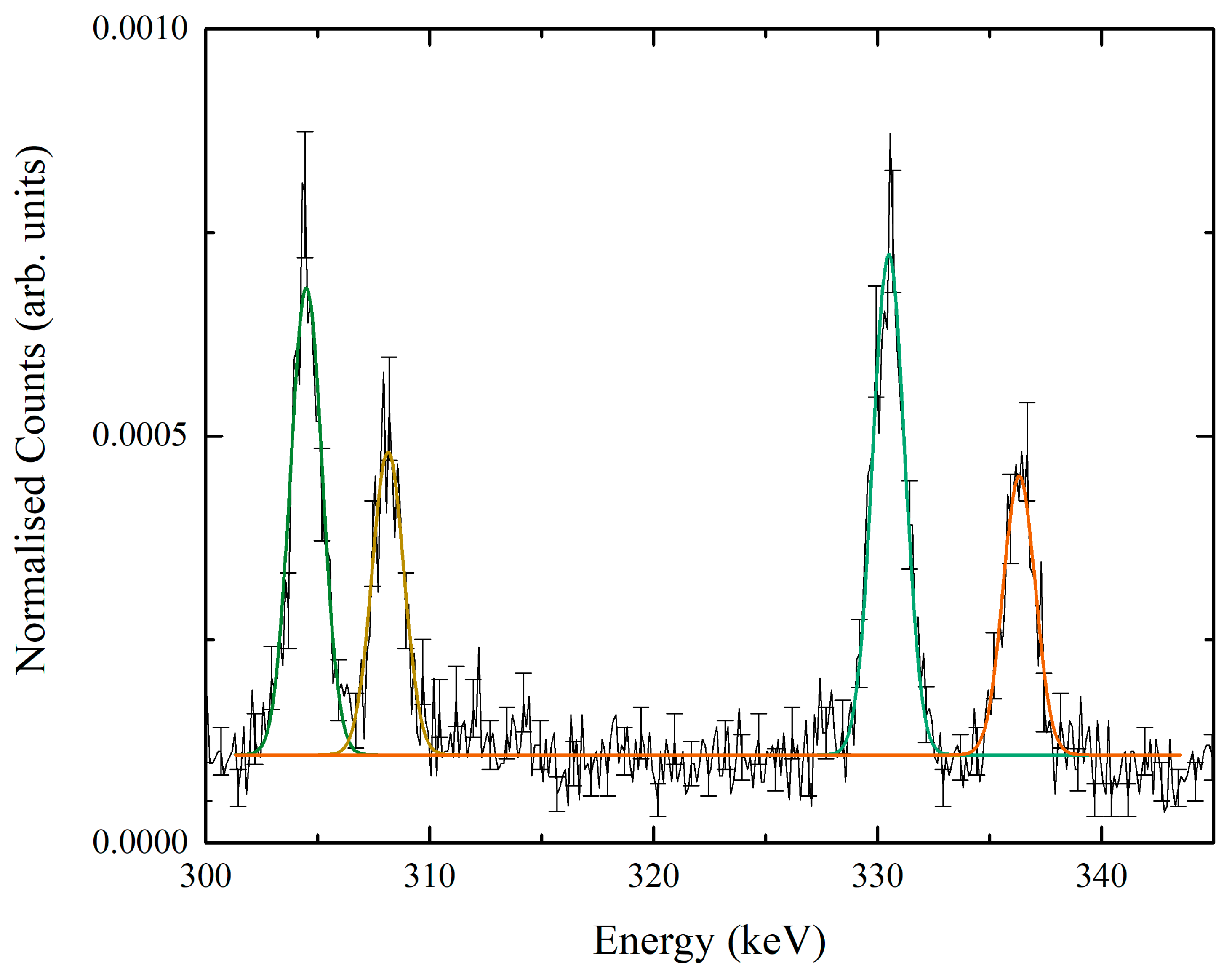
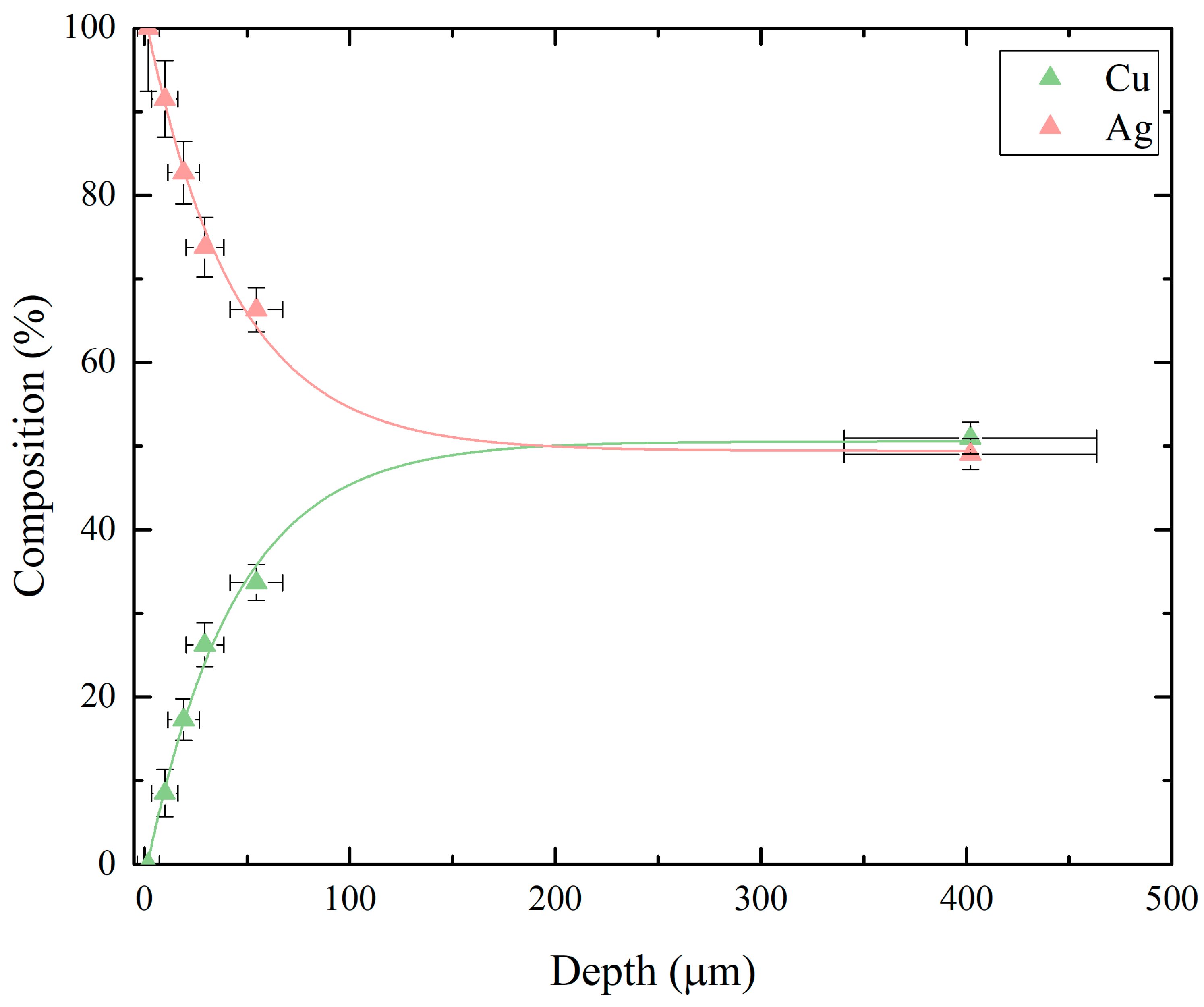
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Butcher, K.; Ponting, M. The Metallurgy of Roman Silver Coinage: From the Reform of Nero to the Reform of Trajan; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 100–129. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Suárez, A.I.; Ager, F.J.; Scrivano, S.; Ortega-Feliu, I.; Gómez-Tubío, B.; Respaldiza, M.A. First attempt to obtain the bulk composition of ancient silver–copper coins by using XRF and GRT. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2015, 358, 93–97. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168583X15005339?via%3Dihub (accessed on 14 December 2018). [CrossRef]
- Hillier, A.D.; Paul, D.M.; Ishida, K. Probing beneath the surface without a scratch—Bulk non-destructive elemental analysis using negative muons. Microchem. J. 2016, 125, 203–207. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0026265X1500301X?via%3Dihub (accessed on 14 December 2018). [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, K.; Kubo, M.K.; Nagatomo, T.; Higemoto, W.; Ito, T.U.; Kawamura, N.; Strasser, P.; Shimomura, K.; Miyake, Y.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Nondestructive Elemental Depth-Profiling Analysis by Muonic X-ray Measurement. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4597–4600. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b01169 (accessed on 14 December 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninomiya, K.; Nagatomo, T.; Kubo, K.M.; Strasser, P.; Kawamura, N.; Shimomura, K.; Miyake, Y.; Saito, T.; Higemoto, W. Development of elemental analysis by muonic X-ray measurement in J-PARC. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2010, 225, 012040. Available online: iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/225/1/012040/meta (accessed on 14 December 2018). [CrossRef]
- Daniel, H.; Hartmann, F.J.; Köhler, E.; Beitat, U.; Riederer, J. Application of Muonic X-Rays in Archaeology. Archaeometry 1987, 29, 110–119. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1475-4754.1987.tb00402.x (accessed on 14 December 2018). [CrossRef]
- Terada, K.; Ninomiya, K.; Osawa, T.; Tachibana, S.; Miyake, Y.; Kubo, M.K.; Kawamura, N.; Higemoto, W.; Tsuchiyama, A.; Ebihara, M.; et al. A new X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy for extraterrestrial materials using a muon beam. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 5072. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/srep05072 (accessed on 14 December 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagamine, K.; Matsuzaki, T.; Ishida, K.; Watanabe, I.; Kadono, R.; Eaton, G.H.; Jones, H.J.; Thomas, G.; Williams, W.G. Construction of Riken-ral muon facility at ISIS and advanced μSR. Hyperfine Interact. 1994, 87, 1091–1098. Available online: https://rd.springer.com/article/10.1007%2FBF02068509 (accessed on 14 December 2018). [CrossRef]
- King, P.J.C.; Cottrell, S.P.; Cox, S.F.J.; Eaton, G.H.; Hillier, A.D.; Lord, J.S.; Pratt, F.L.; Lancaster, T.; Blundell, S.J. New science with pulsed muons—Development ideas at ISIS. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 2003, 326, 260–264. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921452602016228?via%3Dihub (accessed on 14 December 2018). [CrossRef]
- Hillier, A.; Howgego, C.; Pollard, M.; Paul, D.; Wilson, A.; Ishida, K.; Hampshire, B.; Green, G. Using Negative Muons as a Non-Destructive Probe of Material Composition; STFC ISIS Facility: Didcot, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, T.; Ishida, K.; Nagamine, K.; Watanabe, I.; Eaton, G.H.; Williams, W.G. The RIKEN-RAL pulsed Muon Facility. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2001, 465, 365–383. Available online: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0168900201006945 (accessed on 14 January 2018). [CrossRef]
- Hillier, A.D.; Lord, J.S.; Ishida, K.; Rogers, C. Muons at ISIS. Philos. Trans. R. Soc A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2019, 377, 1–7. Available online: http://www.royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rsta.2018.0064 (accessed on 14 January 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncada, F.; Cruz, D.; Reyes, A. Muonic alchemy: Transmuting elements with the inclusion of negative muons. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2012, 539–540, 209–213. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009261412005829?via%3Dihub (accessed on 14 January 2018). [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, J.F.; Ziegler, M.D.; Biersack, J.P. SRIM—The stopping and range of ions in matter. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2010, 268, 1818–1823. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168583X10001862?via%3Dihub (accessed on 14 December 2018). [CrossRef]
- Engfer, R.; Schneuwly, H.; Vuilleumier, J.L.; Walter, H.K.; Zehnder, A. Charge-distribution parameters, isotope shifts, isomer shifts, and magnetic hyperfine constants from muonic atoms. Atom. Data Nuclear Data Tables 1974, 14, 509–597. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092640X74800033?via%3Dihub (accessed on 14 January 2018). [CrossRef]
- Zinatulina, D.; Briançon, C.; Brudanin, V.; Egorov, V.; Perevoshchikov, L.; Shirchenko, M.; Yutlandov, I.; Petitjean, C. Electronic catalogue of muonic X-rays. EPJ Web Conf. 2018, 177. Available online: https://www.epj-conferences.org/articles/epjconf/abs/2018/12/epjconf_ayss2018_03006/epjconf_ayss2018_03006.html (accessed on 14 January 2018). [CrossRef]
- Livechart—Table of Nuclides—Nuclear Structure and Decay Data. Available online: https://www-nds.iaea.org/relnsd/vcharthtml/VChartHTML.html (accessed on 14 January 2018).
- Ortega-Feliu, I.; Moreno-Suárez, A.I.; Gómez-Tubío, B.; Ager, F.J.; Respaldiza, M.A.; García-Dils, S.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, O. A comparative study of PIXE and XRF corrected by Gamma-Ray Transmission for the non-destructive characterization of a gilded roman railing. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2010, 268, 1920–1923. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168583X10001977?via%3Dihub (accessed on 14 December 2018). [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hampshire, B.V.; Butcher, K.; Ishida, K.; Green, G.; Paul, D.M.; Hillier, A.D. Using Negative Muons as a Probe for Depth Profiling Silver Roman Coinage. Heritage 2019, 2, 400-407. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage2010028
Hampshire BV, Butcher K, Ishida K, Green G, Paul DM, Hillier AD. Using Negative Muons as a Probe for Depth Profiling Silver Roman Coinage. Heritage. 2019; 2(1):400-407. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage2010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleHampshire, Bethany V., Kevin Butcher, Katsu Ishida, George Green, Don M. Paul, and Adrian D. Hillier. 2019. "Using Negative Muons as a Probe for Depth Profiling Silver Roman Coinage" Heritage 2, no. 1: 400-407. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage2010028
APA StyleHampshire, B. V., Butcher, K., Ishida, K., Green, G., Paul, D. M., & Hillier, A. D. (2019). Using Negative Muons as a Probe for Depth Profiling Silver Roman Coinage. Heritage, 2(1), 400-407. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage2010028



