1. Introduction
Several cyclic laboratory tests may be employed to evaluate the liquefaction potential of soils by simulating earthquake-induced loading conditions. The cyclic triaxial test is one of the most widely used methods due to its relatively simple setup and ability to control drainage and confining pressure. However, it induces non-uniform stress conditions that differ from actual field conditions [
1]. The cyclic simple shear test better replicates in situ shear stress conditions by allowing constant volume shearing, though its apparatus is more complex [
2]. The hollow torsional shear test provides control over principal stress rotation and shear strain, making it useful for advanced studies involving anisotropy and stress path dependency [
3]. Additionally, laboratory shear wave velocity (Vs) tests, such as bender element or resonant column tests, are increasingly used as non-destructive alternatives to monitor stiffness degradation and infer liquefaction susceptibility indirectly. These methods help determine cyclic resistance, excess pore pressure generation, and stiffness changes, all of which are critical for evaluating liquefaction behavior under cyclic loading.
Cyclic triaxial testing has long been regarded as a reliable and widely accepted method for evaluating the liquefaction susceptibility of cohesionless soils, with its origins traceable to the mid-1960s. Cyclic triaxial-based liquefaction analyses typically involve subjecting soil specimens to controlled cyclic loading at a range of cyclic stress ratios (CSRs), while carefully monitoring the number of cycles required to trigger liquefaction. These test results are then interpreted in the context of anticipated seismic loading by comparing them to the expected CSR and the number of cycles that would be induced by an earthquake, thereby enabling a prediction of whether liquefaction is likely to occur under field conditions. Additionally, energy-based liquefaction evaluations can predict liquefaction by comparing the amount of energy that must be dissipated in the soil to cause liquefaction to the amount on energy dissipation that is expected to occur in the field.
Cyclic triaxial tests may be either stress-controlled (a stress is applied to the specimen and the resulting strain measured) or they can be strain-controlled (a strain is applied and the stress required to cause the strain is measured). While possibly self-evident, it is worth noting that while stress-based liquefaction criteria (e.g., initial liquefaction) can be used with either stress-controlled or strain-controlled tests, strain-based liquefaction criteria are only meaningful for stress-controlled tests.
Although there is broad consensus on the general procedures for conducting cyclic triaxial tests [
4], the definition of liquefaction within the context of these tests continues to be a subject of ongoing discussion and variability. The most frequently used liquefaction criteria is initial liquefaction, which is defined as the point at which the effective stress acting on the soil specimen first reaches zero. However, several alternative definitions have also been proposed in the literature, incorporating both stress-based and strain-based failure criteria. The selection of a particular liquefaction criterion can substantially influence how test results are interpreted and, in turn, affect subsequent geotechnical design and seismic risk assessments. Among the definitions cited in published studies are initial liquefaction [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9], as well as various threshold values of single-amplitude and double-amplitude axial strain [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16].
In the present study, a dataset comprising results from 42 cyclic triaxial tests performed on specimens prepared to the same relative density but different levels of plasticity were analyzed to evaluate the influence of different liquefaction criteria. These included both stress-based and strain-based definitions.
This section provides a foundational review of the background necessary to contextualize the present work. First, a brief overview of previous studies examining the effects of plastic fines on the liquefaction behavior of sands is presented. This is followed by a discussion of the two primary modes of liquefaction failure, namely: liquefaction and cyclic mobility. Subsequently, the concept of energy dissipation during cyclic loading and its relevance to the onset of liquefaction are reviewed. Finally, the rules adopted in this study to classify fines content into categories of non-plastic, low plasticity, and high plasticity are clearly defined.
1.1. Modes of Liquefaction Failure
Soil liquefaction typically manifests in two distinct and well-recognized failure modes: liquefaction and cyclic mobility [
17]. These modes are primarily governed by the soil’s plasticity and relative density. In non-plastic soils and soils with low levels of plasticity, liquefaction is the more commonly observed behavior, unless the material is in a dense to very dense state. Liquefaction is characterized by contractive volumetric behavior during shearing, which leads to a rapid buildup of excess pore water pressure. This results in the sudden loss of effective stress and the initiation of large, permanent, monotonic strains. The deformation typically occurs abruptly and continues even after the applied cyclic loading has ceased. It should be noted that large deformations may also initiate after cyclic loading ceases due to the redistribution of pore-water pressures.
In contrast, soils with high levels of plasticity (e.g., liquid limits greater than 20 and plasticity indexes greater than 5), such as those containing significant amounts of plastic fines, tend to exhibit dilative behavior. This leads to cyclic mobility, a failure mode marked by transient strain excursions and fluctuating pore pressure generation during cyclic loading. Although such specimens can reach zero or near-zero effective stress conditions and may experience significant axial strains during loading, the post-loading deformations are typically negligible or limited. Permanent strains remain relatively small once the cyclic loading ends, distinguishing cyclic mobility from the more catastrophic response observed in liquefaction.
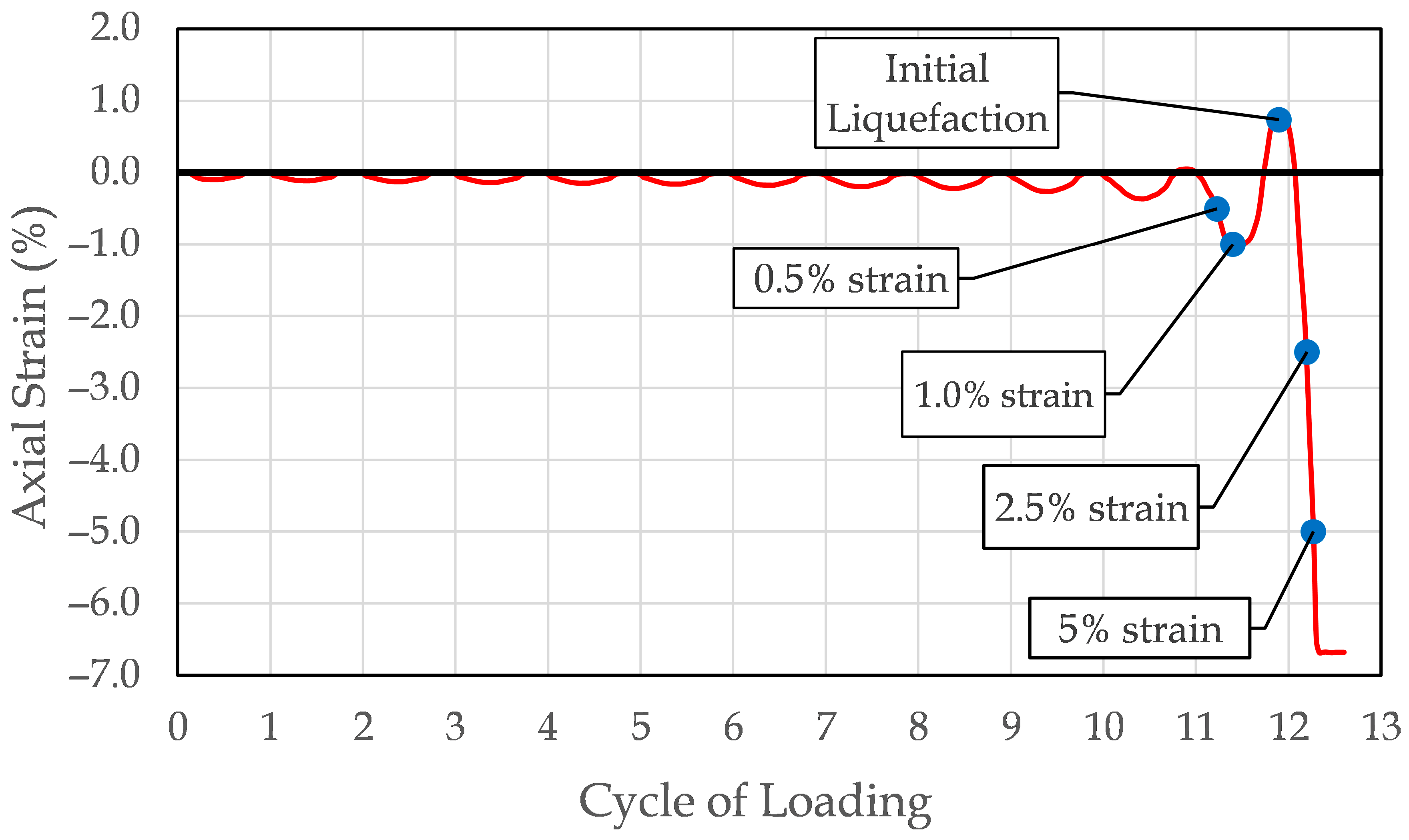
Figure 1 illustrates a representative axial strain versus number of loading cycles curve obtained from a cyclic triaxial test performed on a specimen of Yatesville sand blended with 12% non-plastic silt prepared to a relative density of 37.0%. The behavior of this specimen is indicative of liquefaction. The plot is annotated to show the specific points during the test at which each of the liquefaction criteria adopted in this study, both stress-based and strain-based, were met. Initially, the specimen exhibits very small axial strain amplitudes, which persist through the early stages of cyclic loading. As the test progresses, a notable increase in axial strain occurs just prior to the onset of initial liquefaction. Once initial liquefaction is reached, a rapid and pronounced axial strain develops, signaling the transition into a liquefaction state. This abrupt increase in strain occurring nearly simultaneously with initial liquefaction is a hallmark of liquefaction and is consistent with the contractive response typical of loose, non-plastic soils.
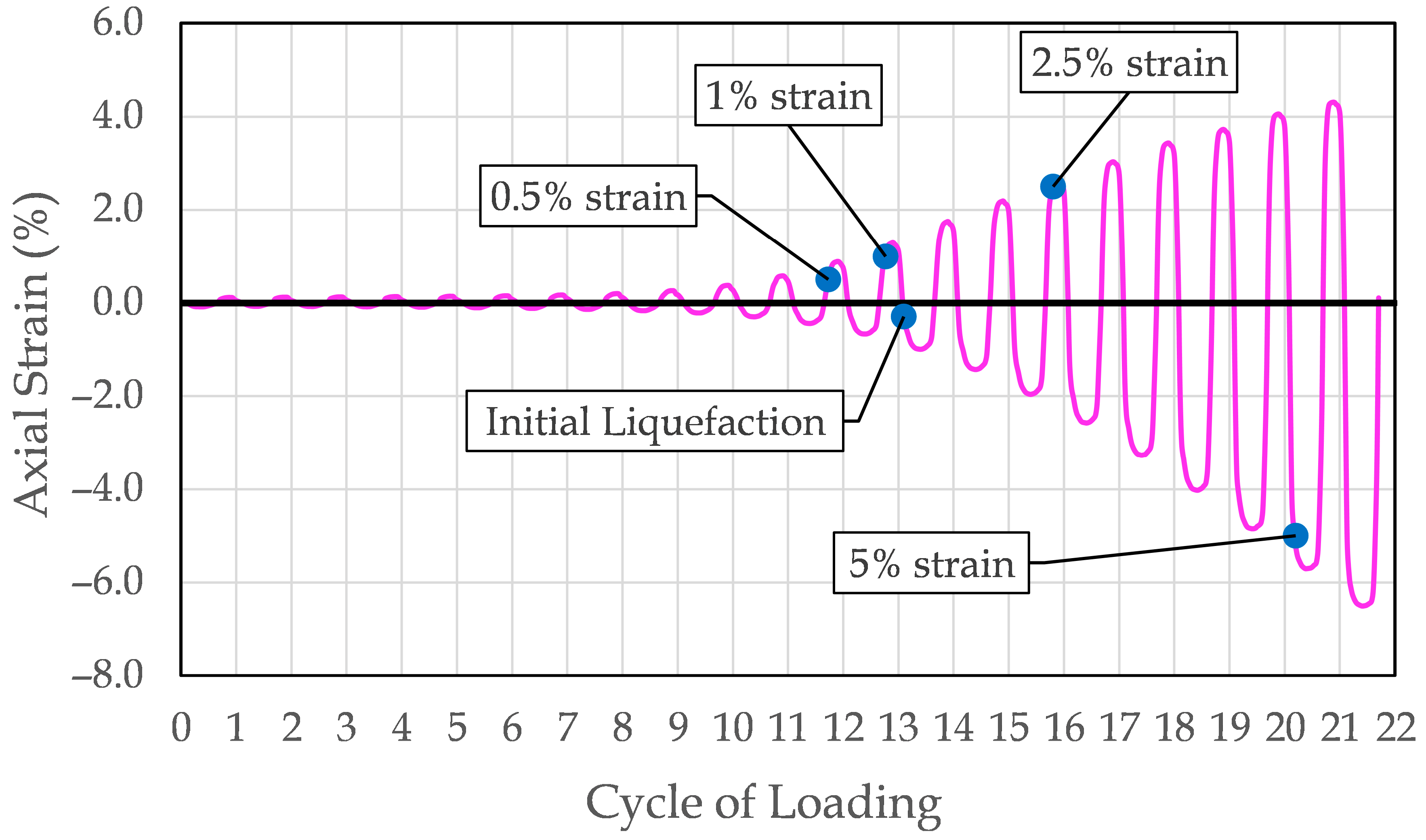
Figure 2 displays a representative axial strain–versus–number of loading cycles curve obtained from a cyclic triaxial test conducted on a specimen of Yatesville sand with a relative density of 67%. The observed behavior of this specimen is characteristic of cyclic mobility, a form of liquefaction response typically associated with dense sandy soils and sandy soils with high plasticity. The plotted data are annotated to indicate the points at which the various liquefaction criteria, both stress-based and strain-based, were satisfied during the course of the test.
Throughout the cyclic loading process, the specimen demonstrates a nearly symmetric and repeatable pattern of axial strain development, with strains gradually increasing and decreasing within each loading cycle. Importantly, the axial strain returns to approximately zero at the conclusion of each cycle, indicating that the deformations are largely recoverable and not permanent. This repetitive strain behavior, coupled with the absence of a sharp, monotonic strain excursion, distinguishes cyclic mobility from liquefaction. The response seen in this test is consistent with dilative soil behavior under cyclic loading conditions, wherein the buildup of excess pore pressure is mitigated by the soil’s tendency to dilate, preventing a sudden collapse of structure [
18,
19].
This behavior, as evidenced in the test data, aligns with previously reported trends for soils with higher plasticity and supports the identification of cyclic mobility as the prevailing mode of deformation in this specimen [
20]. Such patterns are of particular importance in seismic design, as they suggest resilience against catastrophic failure despite the potential for large transient strains during strong ground motions.
As shown in
Figure 1 and
Figure 2, the development of strain is not perfectly symmetrical. This asymmetry arises due to slightly greater strain magnitudes occurring during the extension phase of loading (defined here as negative strain), which is associated with a reduction in deviator stress. During extension, the specimen tends to deform more easily than during compression (positive strain), where greater particle rearrangement is required for deformation to occur. Consequently, smaller strains are observed during compression for an equivalent change in deviator stress. This minor asymmetry is an inherent feature of the cyclic triaxial test mechanics and is typically considered negligible. In contrast, under field conditions where a uniform pure shear stress is applied, one would expect the resulting shear strains to be symmetric.
1.2. Normalized Dissipated Energy per Unit Volume
The normalized dissipated energy per unit volume represents the energy lost within a soil specimen due to cyclic loading and is a function of both the stress conditions and the resulting strains experienced by the soil. This parameter has gained significant relevance in geotechnical engineering, particularly as a key input in energy-based pore pressure generation models [
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29]. These models are rooted in the understanding that excess pore pressure generation during cyclic loading is not merely a function of stress amplitude, but also of the cumulative energy imparted to the soil mass.
Historically, before the development and adoption of energy-based approaches, liquefaction assessments relied primarily on stress-based methods. These traditional approaches typically evaluate the cyclic stress ratio (CSR) required to trigger liquefaction over a given number of loading cycles. However, energy-based methods have proven advantageous due to their closer alignment with the underlying physical mechanisms that govern pore pressure evolution and deformation in soils subjected to repeated loading.
The effectiveness of energy-based models lies in their ability to capture the irreversible rearrangement of soil particles that results from cyclic shearing. This rearrangement gives rise to both energy dissipation and excess pore pressure, creating a direct relationship between the two phenomena. The energy dissipated per unit volume is usually normalized by the initial mean effective confining pressure, yielding a dimensionless quantity known as the normalized dissipated energy per unit volume, denoted as Ws.
During a cyclic triaxial test, W
s can be calculated using Equation (1) [
23]:
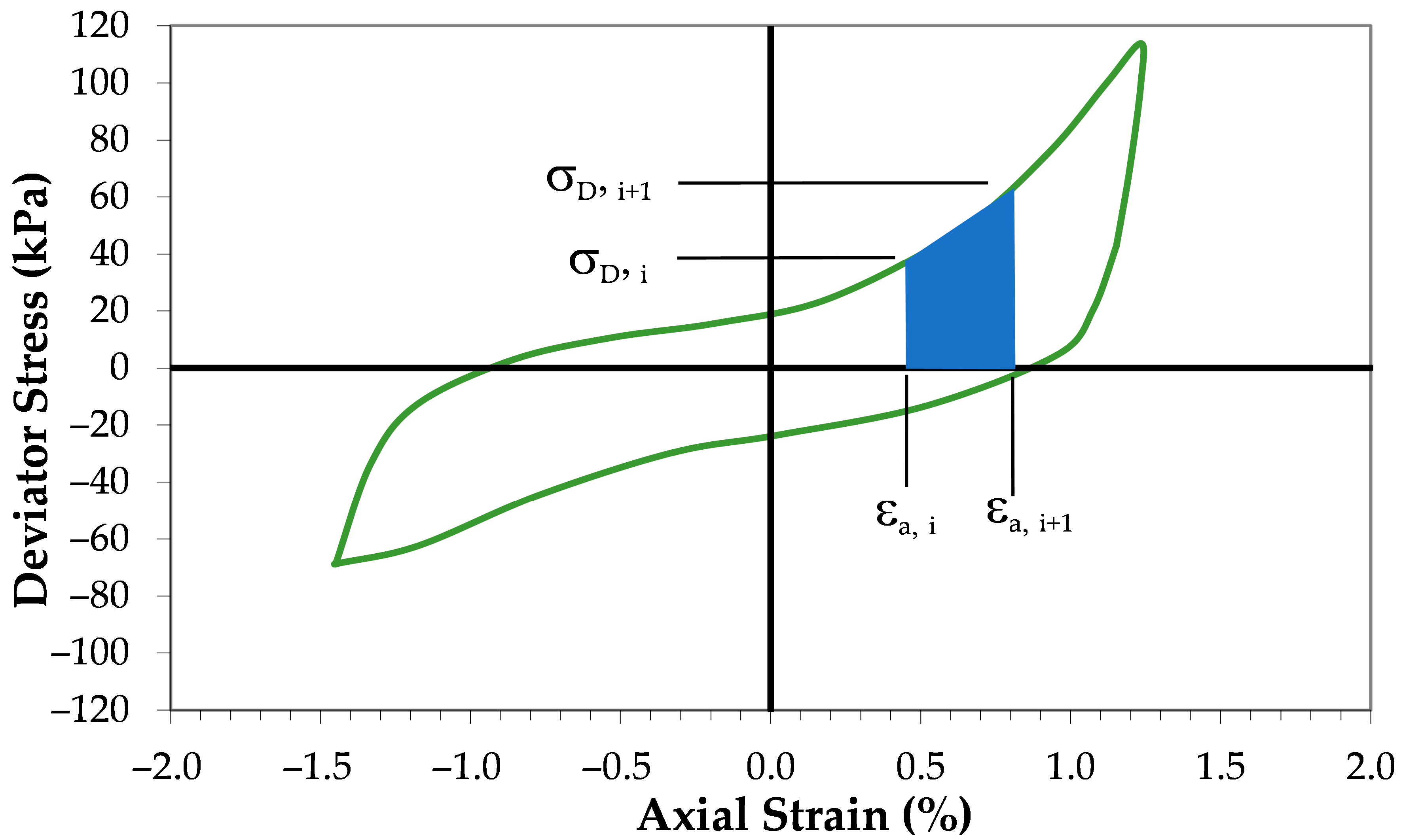
Here, σD,i and σD,i+1 represent the axial stresses at two successive loading increments, εa,i and εa,i+1 are the corresponding axial strains, n is the total number of increments considered, and σo′ is the initial effective confining pressure applied to the specimen.
Figure 3 demonstrates the graphical interpretation of Equation (1). In the figure, the dissipated energy per unit volume corresponds to the area enclosed by the stress–strain hysteresis loops, with the area for each cycle computed using the average deviator stress and incremental strain. This energy is then normalized by the initial effective confining pressure σ
o′ to yield the normalized dissipated energy per unit volume for that increment of loading, dWs. The summation of these increments up to the point of liquefaction, which is determined based upon the liquefaction criterion chosen, produces the cumulative value, Ws.
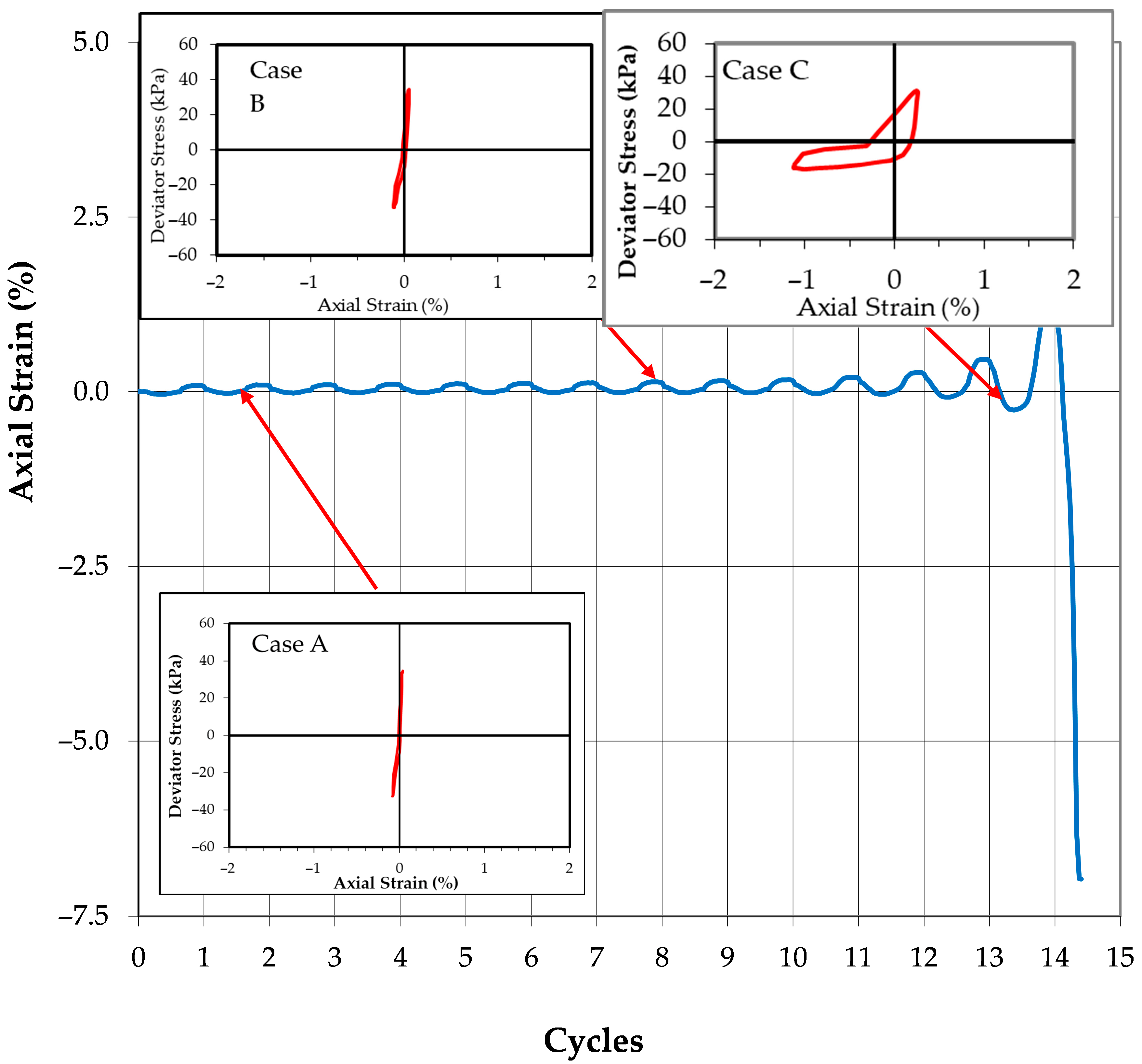
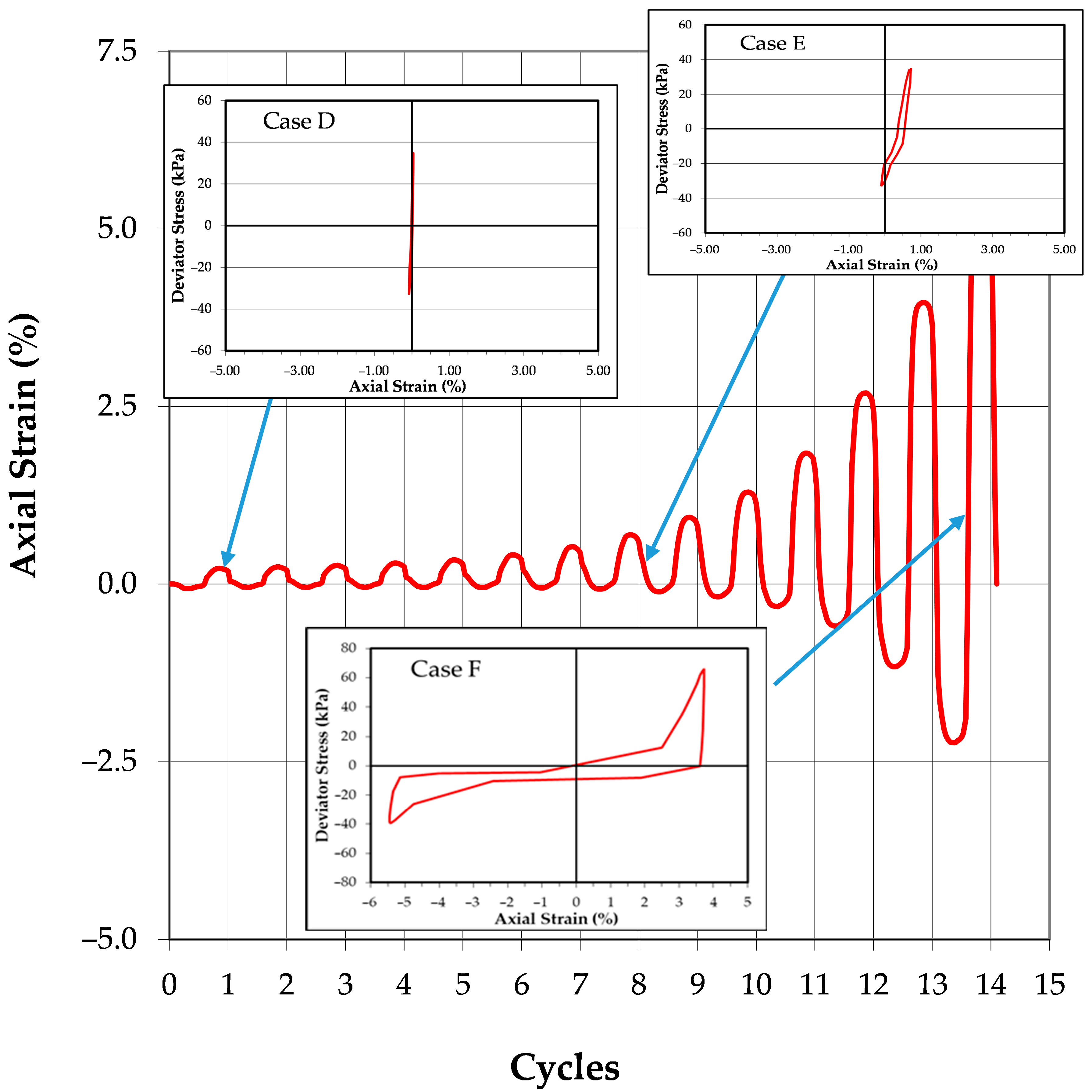
During the earliest stages of cyclic loading, the soil exhibits high stiffness with minimal inelastic deformation, resulting in very low or negligible energy dissipation. The hysteresis loop for this condition essentially collapses into a single straight line, indicating a nearly elastic response with almost complete recovery of input energy. This phenomenon is observed in both liquefaction and cyclic mobility scenarios during the first cycle of loading and is illustrated in Case A of
Figure 4 and Case D of
Figure 5.
As cyclic loading progresses, the energy dissipation behaviors of the two failure modes begin to diverge. In the case of liquefaction (
Figure 4), the soil remains largely unstrained after several cycles, with minimal energy loss. This is shown in Case B, where the hysteresis loop remains nearly identical to that seen in Case A, indicating that little plastic deformation has occurred.
In contrast, the specimen progressing toward cyclic mobility (
Figure 5) begins to exhibit noticeable axial straining and increased energy dissipation after a similar number of loading cycles. This condition is represented by Case E, where the hysteresis loop expands from the initial straight-line behavior of Case D, reflecting the accumulation of inelastic deformation and corresponding energy loss within the soil. The area within the hysteresis loop in Case E quantifies the energy dissipated during that loading increment.
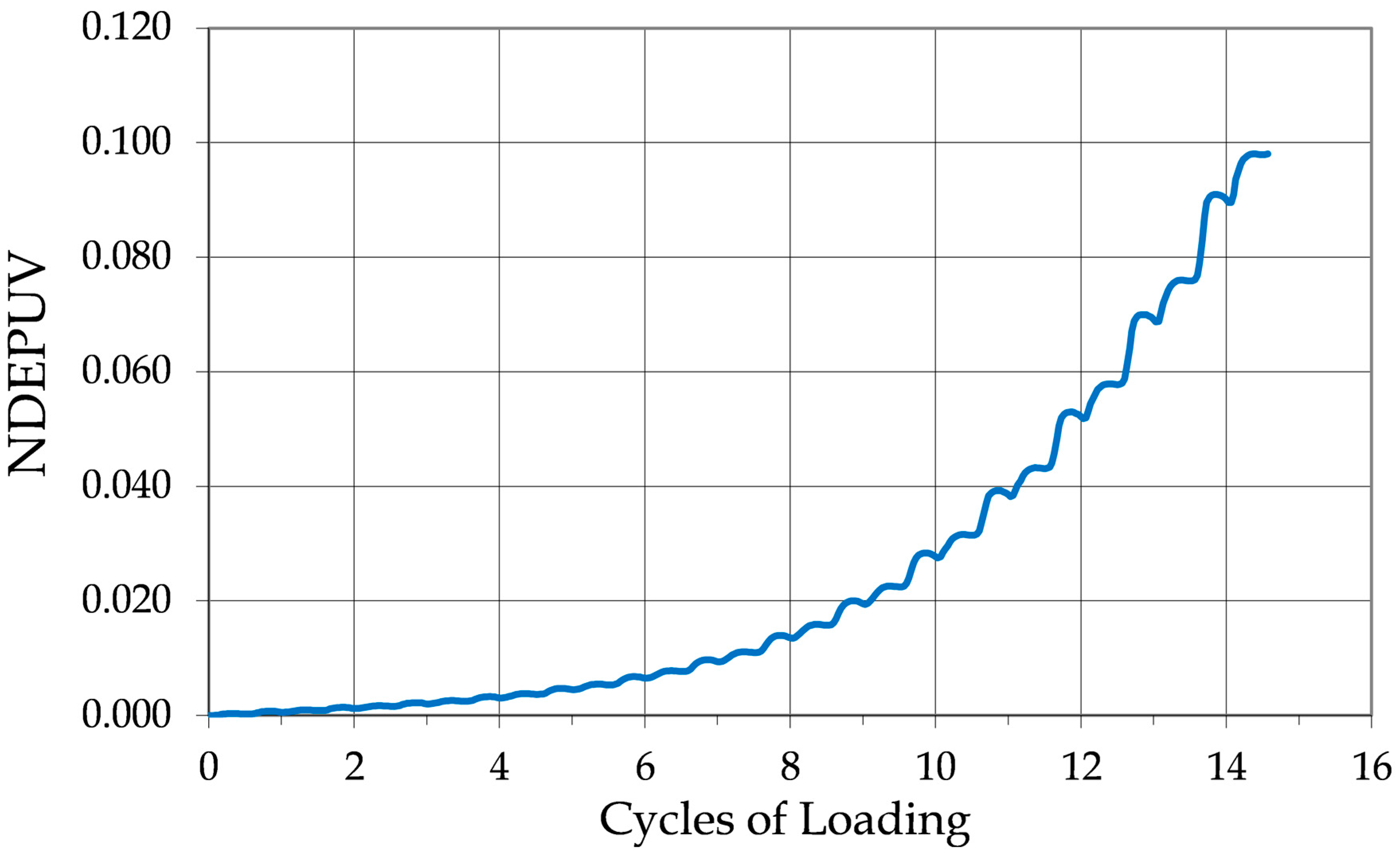
As the specimen undergoing liquefaction approaches the onset of initial liquefaction, it begins to exhibit a sharp increase in axial strain. The hysteresis loop in Case C grows significantly, signifying a rapid rise in energy dissipation. This sudden and dramatic increase in dissipated energy is a common feature of liquefaction and is illustrated in
Figure 6, which plots the cumulative normalized dissipated energy per unit volume versus the number of loading cycles for the test shown in
Figure 4.
In
Figure 6, it is apparent that more than half of the energy lost in the specimen is dissipated in the last half a cycle of loading. This is due to the collapse of the specimen, the rapid straining, and the permanent deformation of the soil skeleton that occurs during liquefaction.
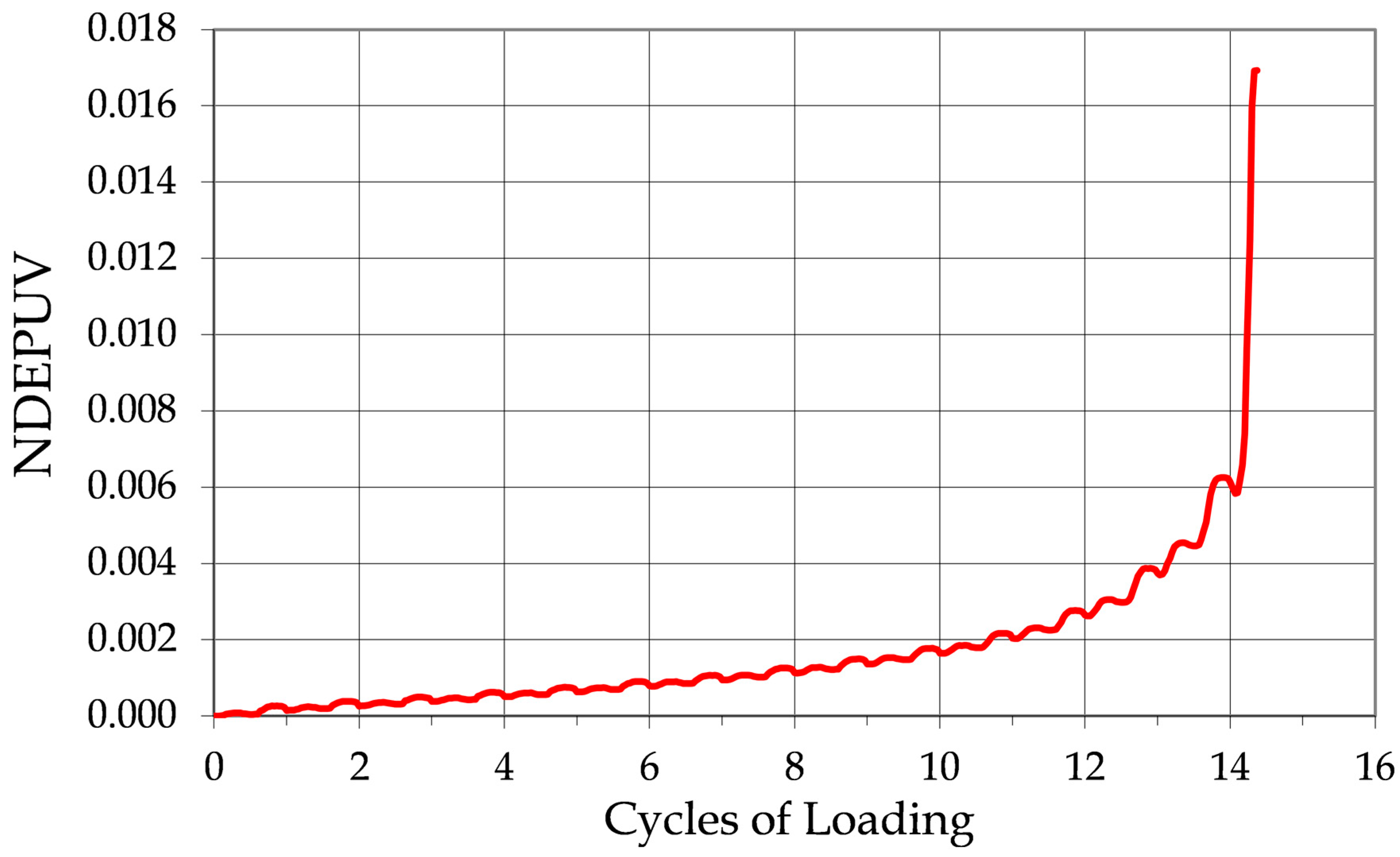
In contrast, the specimen undergoing cyclic mobility (
Figure 5) continues to accumulate strain at a gradual and consistent rate. The hysteresis loop shown in Case F exhibits a steady and proportional increase in size, indicating that energy dissipation is occurring incrementally rather than abruptly. This behavior reflects the gradual buildup of excess pore pressure and deformation typical of cyclic mobility. The pattern is shown in
Figure 7, which presents the cumulative normalized dissipated energy versus loading cycles for the case in
Figure 5.
As seen in
Figure 7, nearly half of the total dissipated energy is distributed relatively evenly across the final 20% of loading cycles. Unlike liquefaction, there is no sharp spike in energy loss; instead, energy dissipation progresses at a nearly constant rate. The absence of runaway straining and abrupt collapse reinforces the classification of this specimen’s behavior as cyclic mobility.
1.3. Plasticity-Based Liquefaction Criteria
The Liquid Limit (LL) and Plasticity Index (PI) are fundamental Atterberg limits used to assess the consistency and plastic behavior of fine-grained soils. In the context of liquefaction analysis, these parameters serve as indirect indicators of soil susceptibility, particularly for silts and clays that fall outside the traditional sands-focused frameworks [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36]. While coarse-grained soils are typically evaluated using Standard Penetration Tests (SPT) and Cone Penetration Tests (CPT), the liquefaction potential of fine-grained soils necessitates additional parameters, among which LL and PI are crucial.
Research has demonstrated that soils with LL < 35% and PI < 10% are more susceptible to liquefaction under cyclic loading [
30]. The Chinese criteria, widely referenced in practice, use LL and PI thresholds to categorize potentially liquefiable fine-grained soils. Moreover, the Modified Chinese Criteria also emphasize the importance of low PI values (typically PI < 12) in indicating a lack of cohesion and higher pore pressure buildup during seismic events [
31].
PI is especially useful as it reflects the plasticity and cohesion of soils, with higher PI values typically suggesting more stable, clay-rich soils less prone to liquefaction. On the other hand, LL correlates with water content behavior and is often associated with soil compressibility and shear strength characteristics. These Atterberg limits are now regularly incorporated into empirical and semi-empirical liquefaction screening procedures for fine-grained soils [
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39].
1.4. Definitions of Classifications
Two sets of terminology critical to the interpretation of results in this study are clarified in this section to ensure consistency and transparency in how they are applied throughout the analysis. These terminologies pertain specifically to the classification of liquefaction modes and the categorization of soil plasticity levels.
The liquefaction behavior observed in the tested specimens was categorized into two distinct modes. These modes are defined based on the correlation between the stress-based and strain-based liquefaction criteria:
Liquefaction Failure: This mode was assigned to specimens in which initial liquefaction occurred within ±5% of the number of loading cycles required to reach 0.5% axial strain. For example, if a specimen developed 0.5% axial strain at 20.0 cycles of loading, it was classified as experiencing liquefaction if the effective stress reached zero, i.e., initial liquefaction occurred, between 19 and 21 loading cycles. This classification indicates a near-simultaneous onset of significant deformation and loss of effective stress, typically associated with more abrupt and catastrophic failure behavior.
Cyclic Mobility Failure: Specimens falling into this category reached initial liquefaction more than ±5% beyond the cycle count at which 0.5% axial strain was recorded. In these cases, the specimen exhibited 0.5% axial strain before pore pressure buildup was sufficient to trigger initial liquefaction. This behavior reflects a more gradual and progressive accumulation of deformation and pore pressure, characteristic of cyclic mobility phenomena.
This classification framework enables a clearer interpretation of soil response under cyclic loading, separating the two main liquefaction behaviors and helping to distinguish between sudden, flow-like failure and more incremental, mobility-dominated behavior.
The plasticity characteristics of the tested soils were classified into three distinct categories based on their liquid limit (LL) and plasticity index (PI). This classification scheme follows the criteria proposed by Polito and Martin [
40], whose study highlighted behavioral distinctions among soils of varying plasticity under cyclic loading. These distinctions align with findings from several other studies [
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50], which have reported correlations between plasticity level and observed liquefaction mode.
The soil plasticity classifications employed in this study are as follows:
Non-Plastic Soils: These soils exhibit a plasticity index (PI) of zero, indicating no measurable plastic behavior during Atterberg limit testing.
Low-plasticity soils: Defined by a liquid limit ranging from 1% to 20% and a plasticity index of less than 7%. These soils exhibit some plastic behavior but fall below the threshold for high plasticity classification.
High-plasticity soils: Characterized by a liquid limit of 20% or greater and a plasticity index equal to or exceeding 7%. These soils display more pronounced plastic deformation behavior, which can significantly influence pore pressure generation and strain accumulation during cyclic loading.
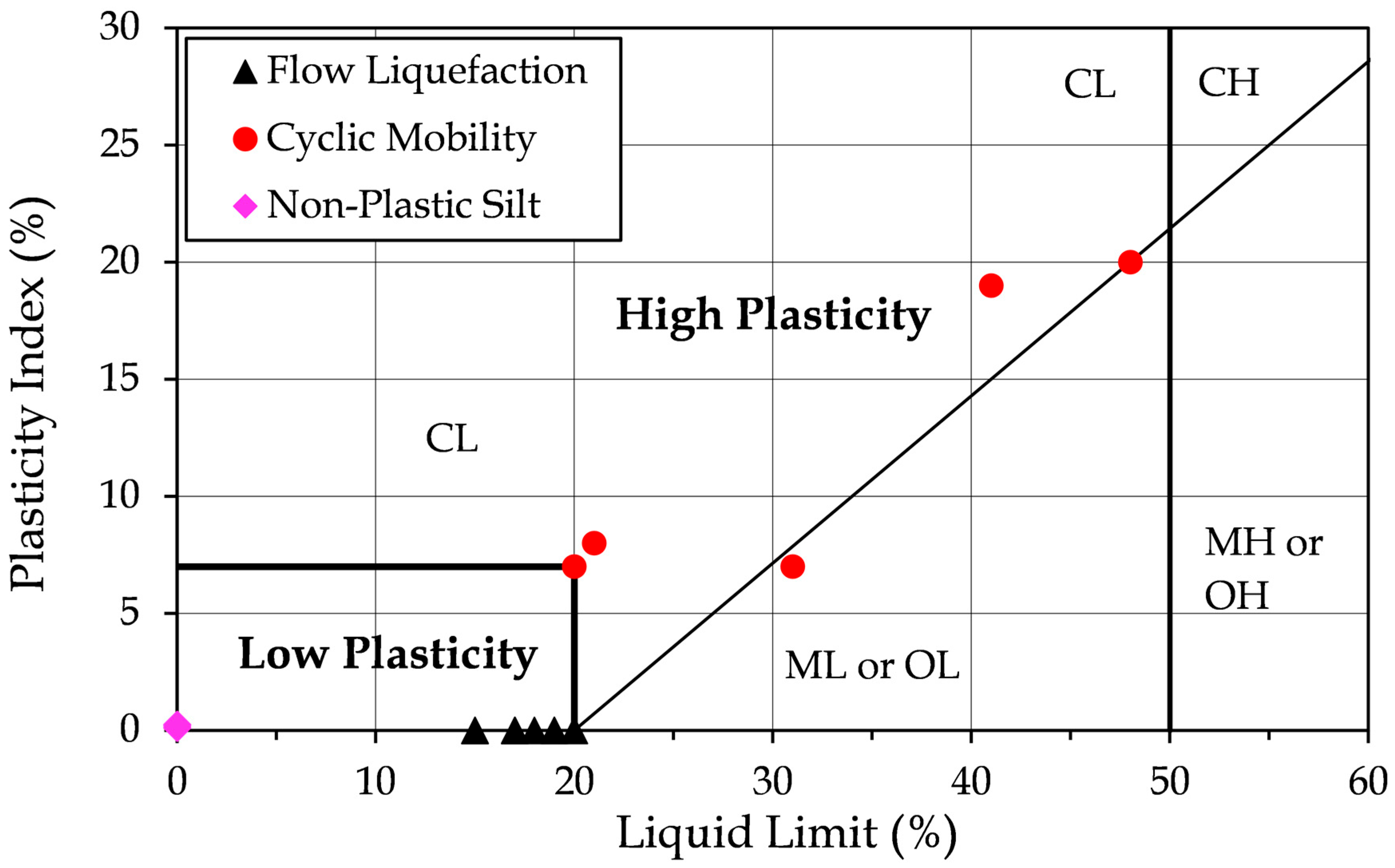
The boundaries for these definitions of low plasticity and high plasticity are depicted on the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) plasticity chart [
51], as shown in
Figure 8. Non-plastic soils are plotted along the horizontal axis of the chart (PI = 0), clearly demarcating their classification. Additionally, the soils that underwent liquefaction and cyclic mobility are plotted by liquefaction mode and plasticity characteristics.
The USCS (Unified Soil Classification System) plasticity chart classifies fine-grained soils based on their liquid limit (LL) and plasticity index (PI). It is a graph with LL on the x-axis and PI on the y-axis. The A-line separates clays (above the line) from silts (below the line). Soils are further classified as low or high plasticity based on whether LL is below or above 50. For example, CL indicates low-plasticity clay, while CH indicates high-plasticity clay. This chart helps identify soil behavior and engineering properties relevant for construction and geotechnical analysis.
This two-fold classification system, based on liquefaction mode and soil plasticity, provides a robust framework for evaluating the influence of liquefaction criteria on cyclic behavior, offering insight into the complex interactions governing liquefaction susceptibility.
2. Laboratory Testing Program
The dataset analyzed was comprised 42 stress-controlled cyclic triaxial tests previously conducted by the author [
8]. The soils tested consisted of sands with fines content ranging from 0% to 37%. The fines consisted of non-plastic silt, kaolinite clay and bentonite clay, and mixtures thereof.
In this study, the number of cycles to liquefaction and the normalized dissipated energy per unit volume were determined for each cyclic triaxial test using multiple liquefaction criteria. The following section provides detailed information on the tested soils and the experimental procedures employed.
2.1. Soils Tested
The soils used in this study included one sand, one non-plastic silt, and two high-plasticity clays; kaolinite and bentonite. The coarse-grained component of the specimens consisted of Yatesville sand, a poorly graded medium-to-fine sand sourced from a dam site in Lawrence County, Kentucky. This sand, derived from the coarse fraction of Yatesville silty sand, is light brown in color and characterized by sub-angular to sub-rounded grains.
The non-plastic fine-grained component comprised Yatesville silt, which was also obtained from Yatesville silty sand. This silt is light brown and exhibits no measurable liquid or plastic limits.
The plastic fine-grained components were commercially available kaolinite and bentonite, both classified as high-plasticity clays. The kaolinite was sourced from a supplier in Georgia, while the bentonite was obtained from a supplier in Wyoming. Specimens were prepared using various proportions and combinations of Yatesville silt, kaolinite, and bentonite to evaluate a range of fine-grained soil behaviors. The index properties for the soils are provided in
Table 1.
2.2. Soil Mixtures
Cyclic triaxial tests were conducted on 42 specimens of Yatesville sand with fines contents ranging from 0% to 37%. The fine-grained portion of these specimens comprised 14 different combinations of kaolinite, bentonite and Yatesville non-plastic silt. These soil mixtures were selected to provide a representative range of fines contents and plasticity, including soils that met and did not meet the requirements of several common plasticity-based liquefaction criteria [
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50].
The plasticity of each soil mixture was determined based on the portion passing the No. 40 sieve, following ASTM D4318: Standard Test Method for Liquid Limit, Plastic Limit, and Plasticity Index of Soils [
52]. Liquid and plastic limit tests were conducted for all mixtures containing plastic fines. A summary of all soil mixtures and their corresponding plasticity data is presented in
Table 2.
2.3. Cyclic Triaxial Testing
The cyclic resistance of the tested soils was evaluated using stress-controlled cyclic triaxial tests conducted in accordance with ASTM D5311—Standard Test Method for Load-Controlled Cyclic Triaxial Strength of Soil [
4]. Testing was performed using an electropneumatic cyclic triaxial apparatus, following the procedures established by Silver [
53].
All triaxial specimens were cylindrical, with a diameter of 71 mm and a height of 154 mm, and they were prepared using the moist tamping method. Specimens were compacted at a water content corresponding to approximately 50% saturation. To ensure uniform density throughout the specimen, the undercompaction technique was employed [
54].
After determining the target void ratio and density for the test, the soil was prepared by dividing the required dry mass of soil into seven portions, each corresponding to a single lift, and placing them in separate containers. The dry mixtures were then thoroughly mixed with a spoon to ensure uniformity. The appropriate amount of water was then added to each portion based on the desired moisture content. The soil and water were thoroughly mixed, and the containers were sealed to minimize moisture loss. For mixtures with a high non-plastic fines content and for mixtures containing clay, the mixtures were allowed to rest overnight to promote uniform moisture distribution.
The amount of water added to each lift was calculated to achieve approximately 50% saturation in the compacted state. This saturation level was selected in lieu of the 70% recommended by Silver [
39], as it enabled specimen preparation across a wider range of densities.
After placement in the triaxial cell, specimens were saturated by flushing with CO2 and then further flushing with de-aired water to remove the CO2. Full saturation was achieved by applying sufficient back pressure, after which the specimens were isotropically consolidated under a confining stress of 100 kPa.
Following consolidation, specimens were subjected to a sinusoidal deviator stress at a prescribed cyclic stress ratio until liquefaction was observed.
For each combination of fines type and fines content, the cyclic resistance ratio (CRR) was determined based on a minimum of three cyclic triaxial tests conducted on identically prepared specimens. For the purposes of this summary, the cyclic resistance ratio is defined as the cyclic stress ratio (CSR) that must be applied to the soil in order to trigger initial liquefaction within 10 cycles of loading. This definition is consistent with commonly adopted practice in liquefaction research, where a fixed number of cycles (often 10 or 15) is used as a benchmark for evaluating cyclic resistance. By standardizing to a fixed number of cycles, the cyclic resistance ratio provides a direct measure of a soil’s inherent resistance to liquefaction under controlled loading conditions.
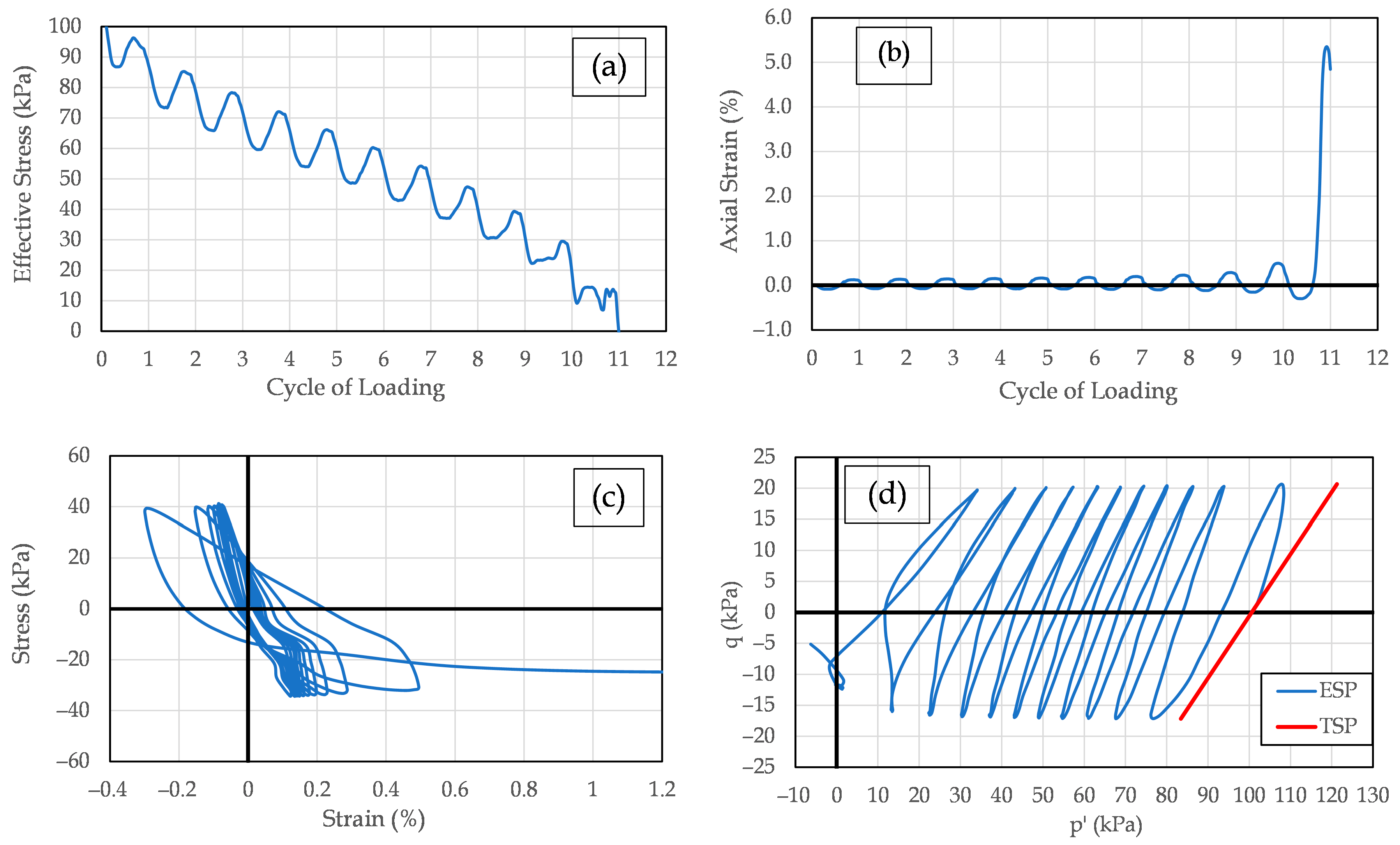
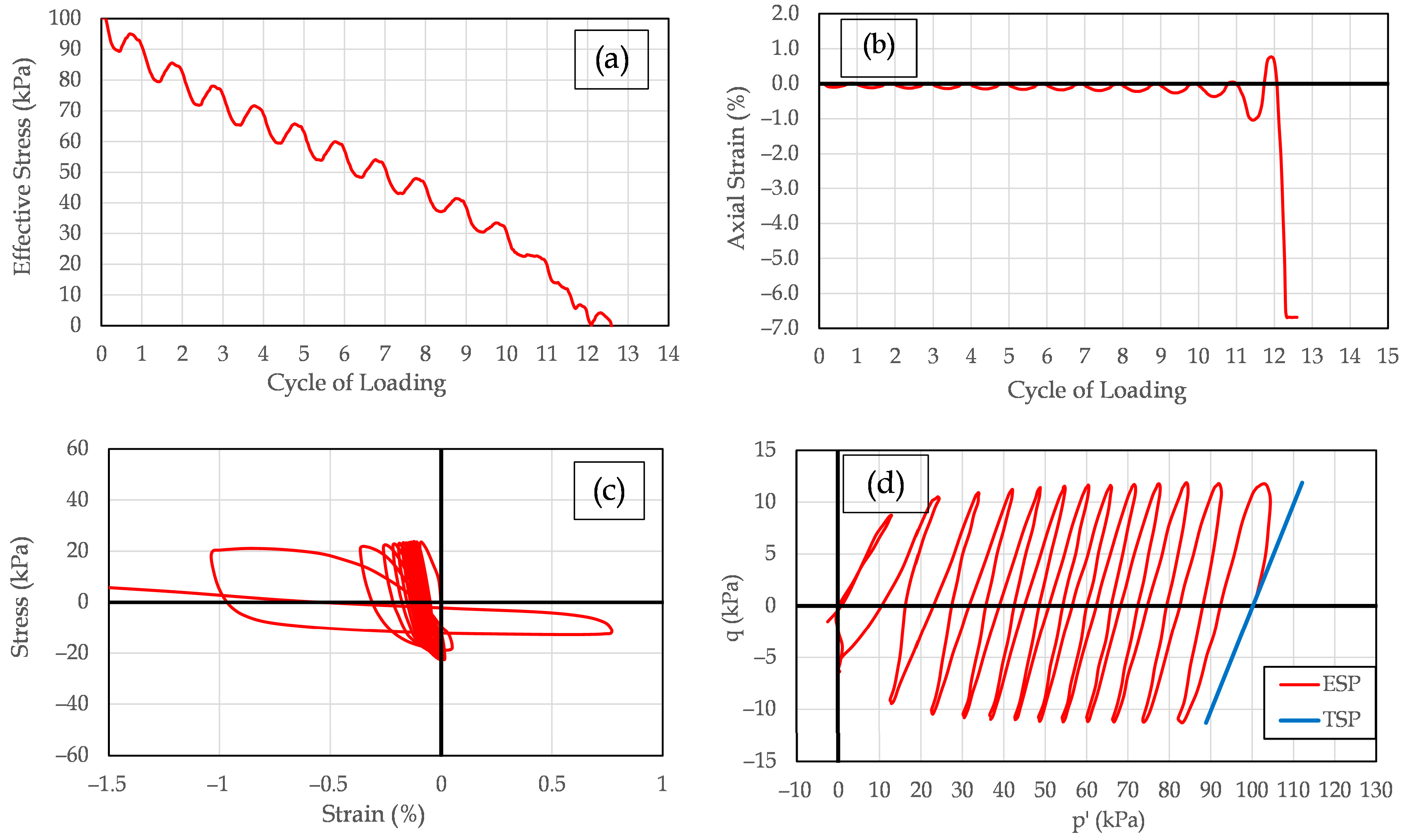
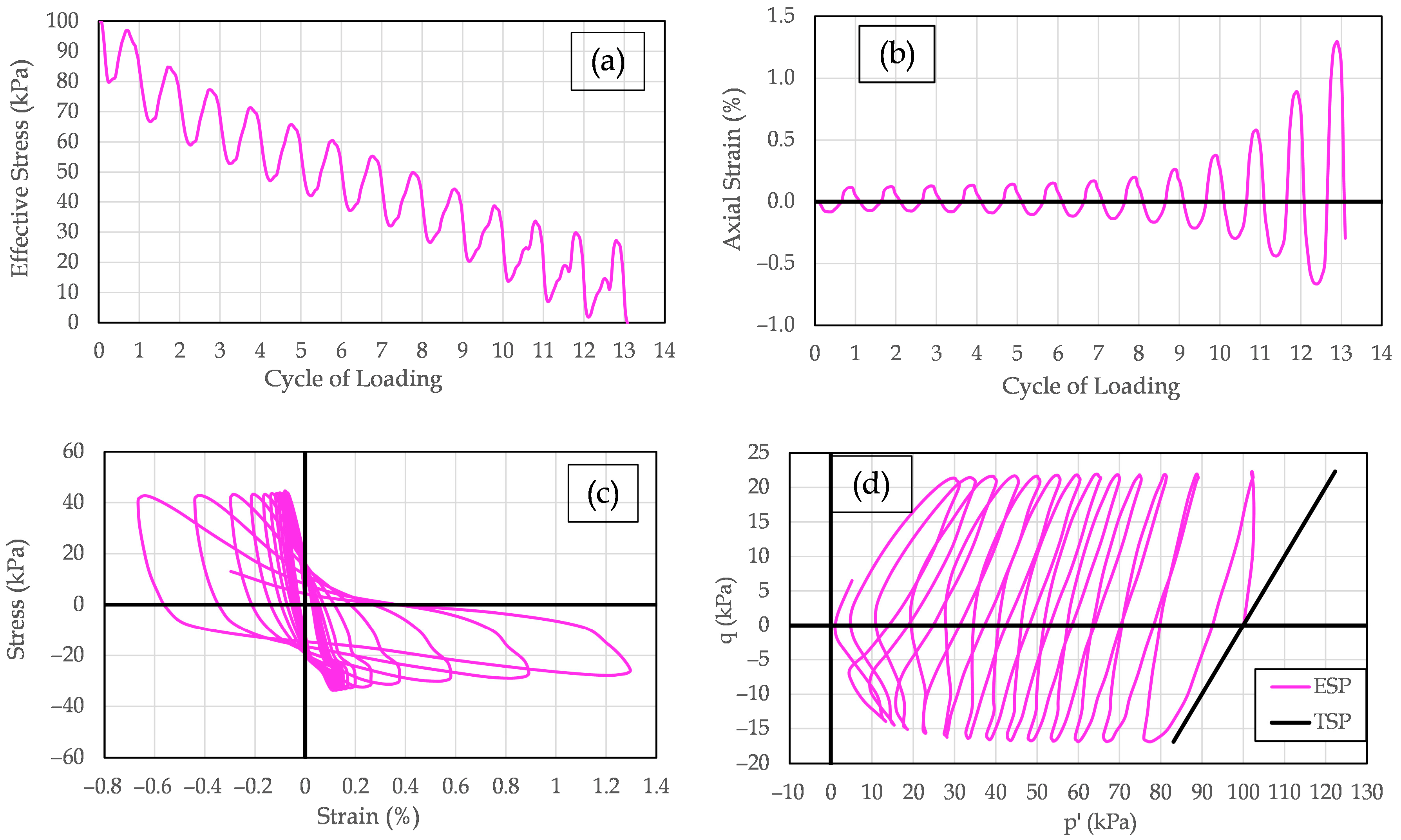
Representative results from cyclic triaxial tests performed on mixtures of Yatesville sand and 12% fines are presented in
Figure 9,
Figure 10 and
Figure 11. These figures illustrate test outcomes for specimens with Yatesville silt, kaolinite, and bentonite corresponding to non-plastic (LL = 0, PI = 0), low plasticity (LL = 17, PI = 0), and high plasticity (LL = 48, PI = 20), respectively. This data first appeared in Polito [
36].
Figure 9 presents typical test results for a specimen of Yatesville sand and 12% Yatesville silt loaded to a cyclic stress ratio of 0.22 and failing in 11.0 cycles.
Figure 10 presents typical test results for a specimen of Yatesville sand and 12% kaolinite loaded to a cyclic stress ratio of 0.11 and failing in 12.6 cycles.
Figure 11 presents typical test results for a specimen of Yatesville sand and 12% bentonite loaded to a cyclic stress ratio of 0.19 and failing in 13.1 cycles.
The number of loading cycles required to induce liquefaction was determined based on both stress-based and strain-based criteria, as outlined below:
Stress-Based Criterion: The stress-based approach for identifying the onset of liquefaction was centered on the concept of initial liquefaction. This condition was defined as the point at which the effective stress within the soil specimen dropped to zero kilopascals (0 kPa), indicating a complete or near complete loss of shear strength. In terms of pore pressure, this corresponds to a pore pressure ratio, ru, equal to 1.0. The pore pressure ratio is defined as the ratio of the excess pore water pressure generated during cyclic loading to the initial effective confining stress applied to the specimen.
Strain-Based Criteria: In addition to the stress-based definition, liquefaction was also evaluated using a set of strain-based thresholds. Specifically, four levels of single-amplitude axial strain, 0.5%, 1%, 2%, and 5%, were used as strain-based indicators of liquefaction. A given strain threshold was considered to be reached when the measured single-amplitude axial strain in either the extension or compression direction attained the specified value.
Initial liquefaction [
8,
55,
56,
57] and the four values of single-amplitude axial strain, 0.5% [
8,
58,
59], 1.0% [
8,
55,
60,
61], 2.5% [
8,
62,
63,
64], and 5.0% [
8,
65], selected for use as the liquefaction criteria, were chosen because each has been used in multiple studies reported in the literature.
The influence of plastic fines content and overall soil plasticity on the susceptibility to different liquefaction failure modes was subsequently investigated. This was followed by a detailed analysis of how the selected liquefaction failure criterion affected both the number of loading cycles necessary to trigger liquefaction and the amount of normalized dissipated energy per unit volume required to initiate the liquefaction response.
2.4. Limitations of Cyclic Triaxial Testing
Cyclic triaxial testing is a widely used laboratory method for evaluating the liquefaction potential of soils under controlled conditions. However, despite its popularity and standardization, it has several limitations that can affect the reliability and applicability of its results in real-world scenarios.
One of the primary limitations is that cyclic triaxial tests do not replicate the true stress conditions experienced by soils during an actual earthquake. In the field, soils are subjected to multidirectional loading and complex stress paths, while the triaxial test applies only axial loading in a unidirectional manner. This simplification can lead to underestimation or overestimation of liquefaction potential, particularly in soils that are sensitive to stress path variations [
66].
Another significant limitation is related to sample disturbance and scale effects. Soil samples used in triaxial tests are often reconstituted in the lab or undergo some degree of disturbance during extraction, transportation, and preparation, which can alter their structure and stress history. These changes may reduce the accuracy of the test results, especially for sensitive or loose sands. Moreover, the small scale of laboratory specimens cannot capture the inherent spatial variability present in natural soil deposits [
67].
Additionally, cyclic triaxial tests typically impose uniform cyclic loading patterns, which may not reflect the irregular and non-uniform nature of earthquake motions. The frequency and amplitude of applied loads are often idealized, leading to a mismatch between laboratory and field conditions. Furthermore, the test does not simulate the effects of drainage conditions, aging, and cementation, which are known to influence liquefaction resistance [
68].
Despite these limitations, cyclic triaxial testing remains a valuable tool for controlled comparative studies and parameter estimation. However, its results should be interpreted with caution and, when possible, supplemented with field tests or more advanced laboratory techniques like cyclic simple shear or centrifuge modeling.
4. Discussion
The results of the laboratory testing were first examined to evaluate the interaction of the different failure criteria and the soil plasticity. This interaction was evaluated in two ways. First, the number of cycles required to trigger liquefaction for the different liquefaction criteria were evaluated. Next, the differences in the amount of normalized dissipated energy per unit volume required to initiate liquefaction for the different liquefaction criteria were also examined.
4.1. Effect of Failure Criteria on the Number of Cycles Required to Trigger Liquefaction
In the assessment of soil liquefaction potential through laboratory-based methods, particularly stress-controlled cyclic triaxial tests, the selection of an appropriate failure criterion is a critical step in ensuring accurate interpretation of test outcomes. The geotechnical literature offers a range of strain-based liquefaction criteria, spanning from initial liquefaction, which is marked by the onset of excess pore pressure generation and effective stress reduction, to specific axial strain thresholds such as 0.5%, 1%, 2.5%, or 5% single-amplitude or double-amplitude axial strain. Each of these criteria are grounded in different theoretical frameworks and carries distinct implications for engineering applications.
The choice of a specific liquefaction criterion can significantly affect the parameters used to characterize soil behavior under seismic loading, particularly when assessing the number of cycles to liquefaction and the cyclic resistance ratio (CRR). The most commonly adopted criterion, initial liquefaction, is often favored for its direct link to pore pressure buildup, which is a critical factor in evaluating seismic vulnerability. However, in contexts where deformation and serviceability are of greater concern, strain-based criteria may be more appropriate, as they can reflect the mechanical response of the soil in terms of irreversible strain accumulation.
This section investigates the influence of failure criterion selection on the interpreted liquefaction resistance, using results from a comprehensive suite of cyclic triaxial tests performed on soils mixtures with various level of plasticity. Specifically, the impact of different liquefaction definitions is examined in terms of the cyclic resistance ratio. The analysis highlights the variability introduced by different criteria, especially in soils with varying degrees of plasticity.
While hypothesis testing at the 5% level failed to reject the null hypothesis that the means of the cyclic resistance ratios were the same for soils that underwent liquefaction and the soils that underwent cyclic mobility, there is still evidence that the means are different. The probability of the means being the same was between 10% and 18% for each of the failure criteria, indicating that there is still a very good chance that the means are different.
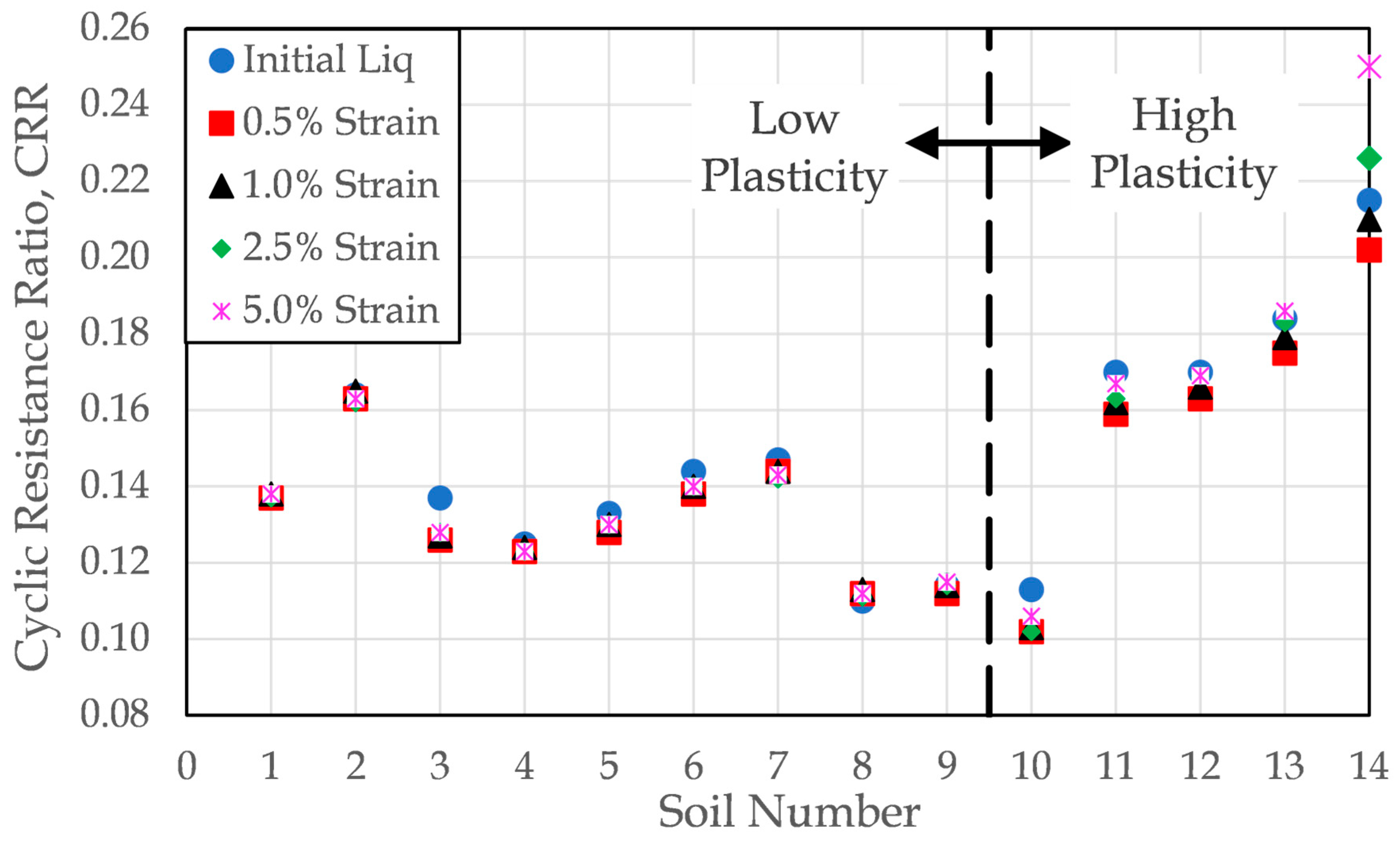
The comparison of liquefaction criteria is illustrated through both
Table 6 and
Figure 12.
Table 6 presents the cyclic resistance ratio values associated with five different liquefaction criteria, initial liquefaction, and the four specified axial strain thresholds over a range of soil mixtures. Each row in the table corresponds to a unique soil mixture, and cyclic resistance ratio values are provided for each failure definition.
Figure 12 complements this summary by plotting the cyclic resistance ratio values for each soil group, as identified in
Table 6, across the different criteria. This graphical representation enables a clear visualization of how the interpreted liquefaction resistance shifts depending on both the selected failure criterion and the plasticity of the soil. The trends shown in
Figure 12 underscore the significance of criterion selection, particularly in cases involving high-plasticity soils, where the strain-based criteria may diverge substantially from the initial liquefaction interpretation.
For soils with low plasticity, the choice of liquefaction criterion exerts a minimal influence on the interpreted cyclic resistance. This is made visible in
Figure 12 for soil numbers 1 through 9 by the fact that the data points representing each failure criteria tend to be tightly clustered. This is because strain accumulation occurs rapidly following the onset of initial liquefaction; as a result, regardless of the failure criterion employed, the point of liquefaction is reached within a similar number of cycles leading to nearly identical cyclic resistance ratios across the different liquefaction criteria.
For soils with high plasticity, the choice of liquefaction criterion exerts a large influence on the interpreted cyclic resistance. This is again made visible in
Figure 12 for soil numbers 10 through 14 by the fact that the data points representing each failure criteria are quite spread out, indicating that it takes different number of cycles to meet each of the different liquefaction criteria. This is because the cyclic increase and decrease in strain occurs both before and following the onset of initial liquefaction; as a result, depending upon the liquefaction criteria chosen, the point of liquefaction will be reached at different cycles of loading for the different liquefaction criteria.
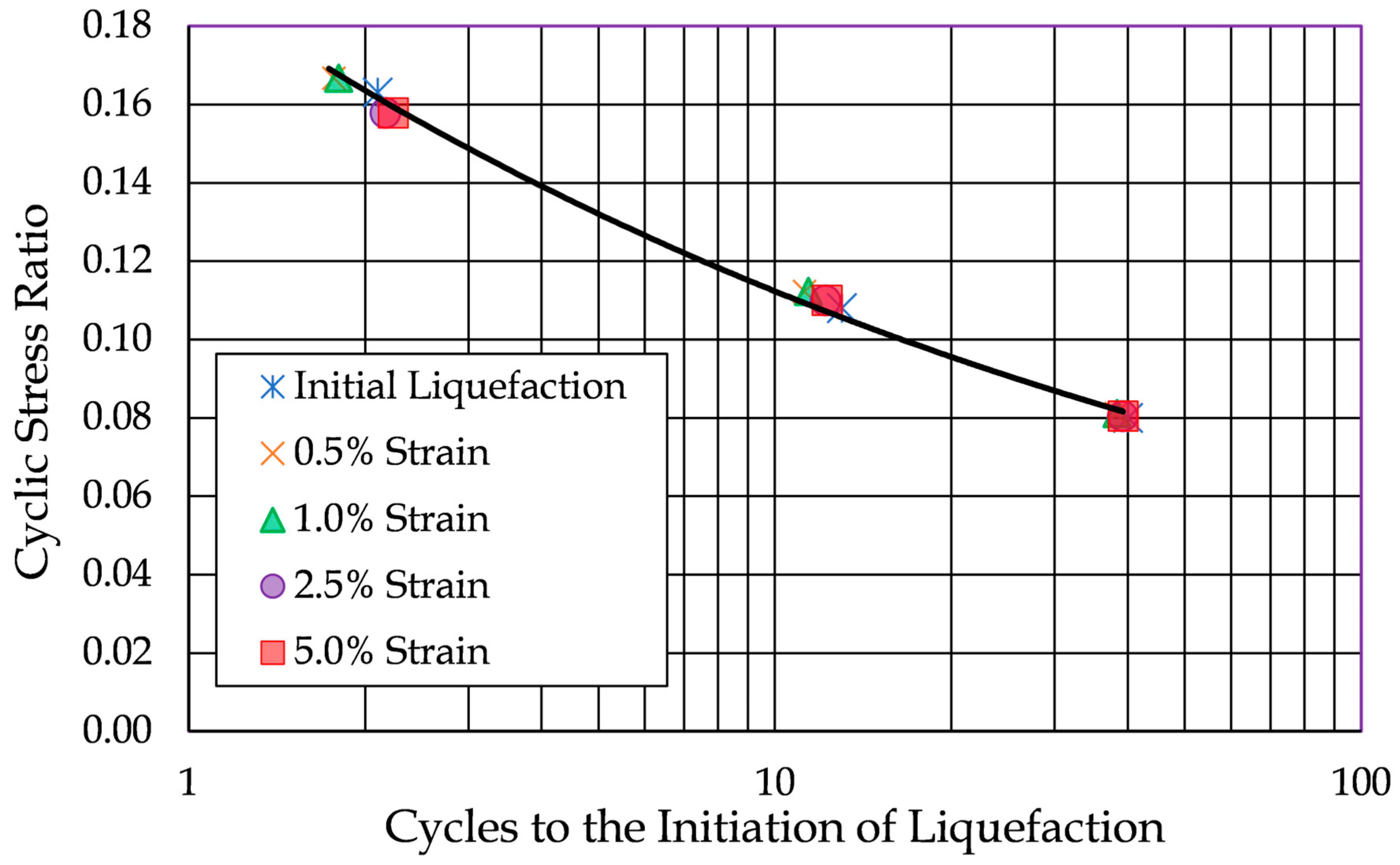
Figure 13 further illustrates the minimal impact of the chosen liquefaction on low-plasticity soils by presenting cyclic resistance curves derived from the five different liquefaction criteria on a single plot. The results presented in the figure are from tests on Soil Number 8, which consisted of Yatesville sand with 12% kaolinite at a relative density of 31%. The soil’s liquid limit was 17%, and its plasticity index was not discernable.
As shown, the curves are nearly indistinguishable from one another, highlighting that in low-plasticity soils, failure is sudden, and the strain criteria are met nearly simultaneously with the development of initial liquefaction. Each of the five criteria produce the same cyclic resistance ratio (based on 10 cycle of loading to produce initial liquefaction) of 0.112.
For soils with high plasticity, the choice of liquefaction criterion exerts a large influence on the interpreted cyclic resistance. This is made visible in for soil numbers 10 through 14 in
Figure 12 by the fact that the data points representing each failure criteria are quite spread out, indicating that it takes different number of cycles to meet each of the different liquefaction criteria. This is because of the cyclic increase and decrease in strain occurs both before and following the onset of initial liquefaction. As a result, dependent upon the liquefaction criteria chosen, the point of liquefaction is reached at different cycles of loading for the different liquefaction criteria.
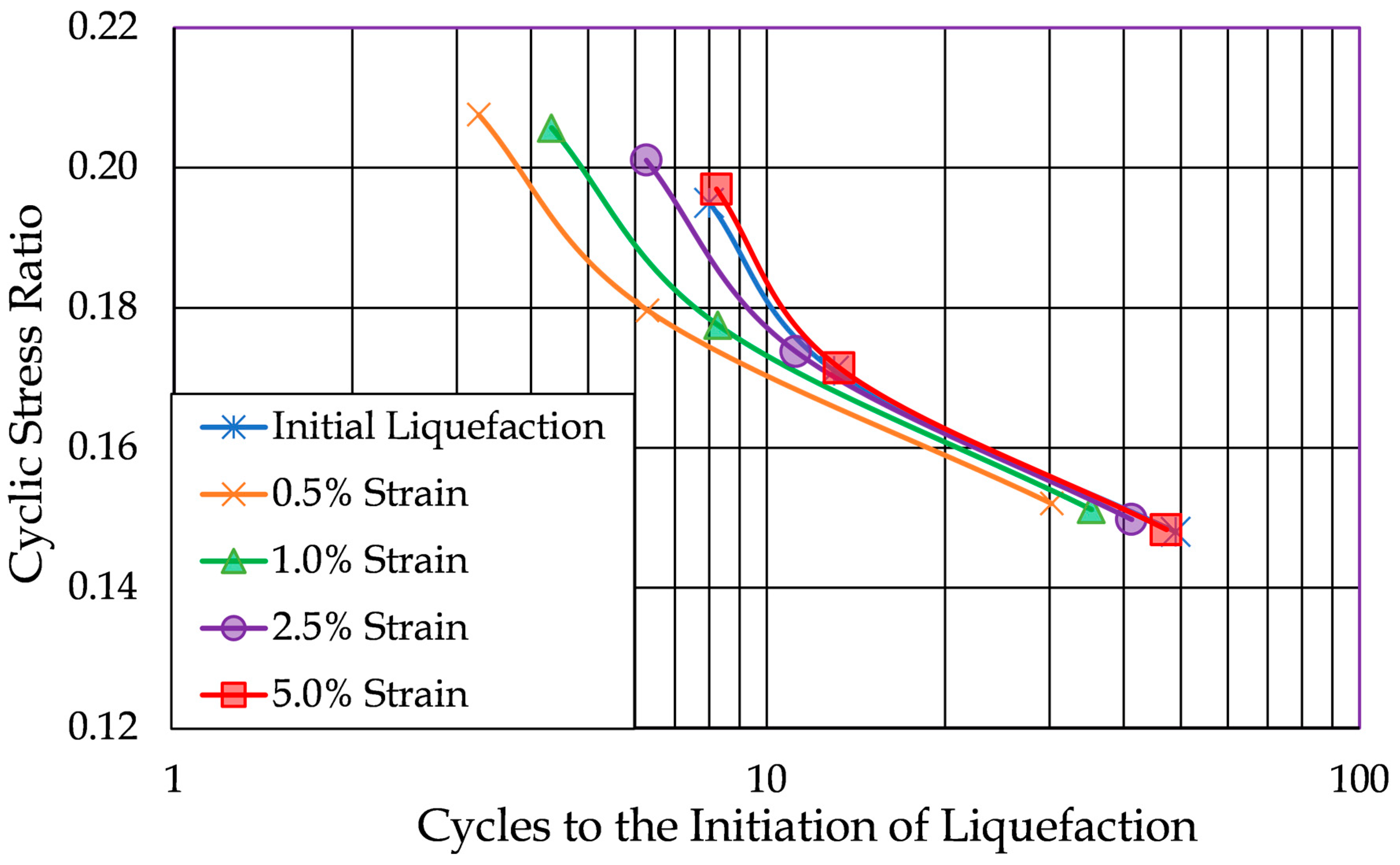
Figure 14 further illustrates this behavior by comparing cyclic resistance curves derived from the five different liquefaction criteria on a single plot. The results presented in the figure are from tests on Soil Number 14, which consisted of Yatesville sand with 12% clay (which was a mixture of half kaolinite and half bentonite) and a relative density of 29%. The soil’s liquid limit was 41%, and its plasticity index was 19%.
As shown, the curves are clearly distinguishable from one another, highlighting that in high-plasticity soils, straining is more gradual and the different strain criteria are met at different points in the loading than each other as well as different than initial liquefaction. The five criteria produce cyclic resistance ratios (based on 10 cycle of loading to produce initial liquefaction) ranging between 0.170 and 0.184.
This finding has important implications for design and analysis: for high-plasticity soils, reliance on a single strain-based threshold without consideration of the broader strain development behavior may lead to misleading assessments of soil stability under seismic loading.
4.2. Dissipated Energy in Specimens Based on Different Liquefaction Criteria
The normalized dissipated energy per unit volume required to initiate liquefaction varies significantly between low- and high-plasticity soils, even under similar loading conditions.
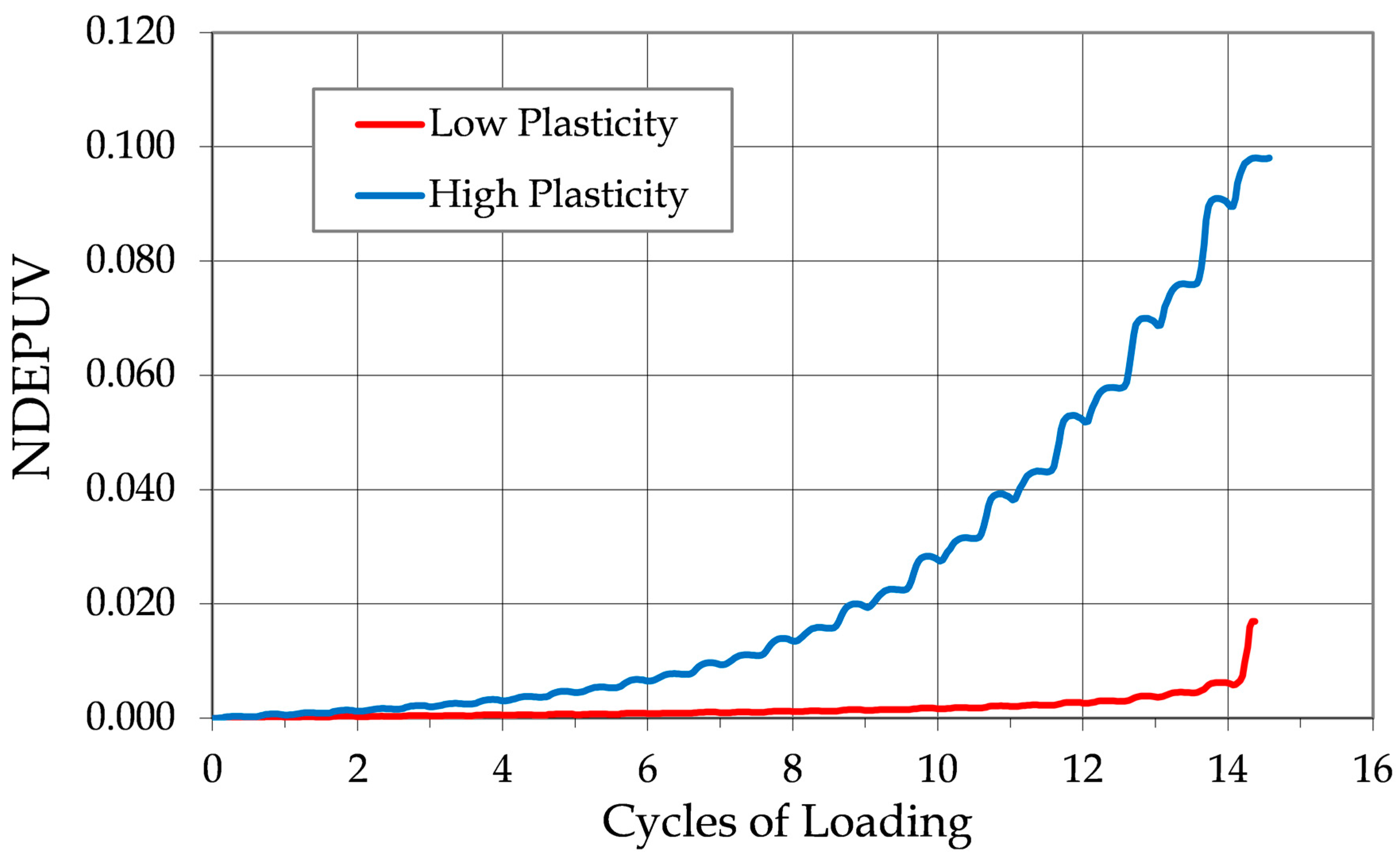
Figure 15 compares normalized dissipated energy per unit volume as a function of load cycles for two specimens, one with low plasticity and one with high plasticity. The high-plasticity specimen required nearly six times more dissipated energy to reach liquefaction than the low-plasticity specimen, despite undergoing a similar number of loading cycles.
This discrepancy in normalized dissipated energy per unit volume required for liquefaction between the two specimens reflects the differences in the strain development. In low-plasticity soils, the majority of energy dissipation occurs rapidly during the final loading cycles that lead to large, irreversible displacement. In contrast, high-plasticity soils accumulate and dissipate energy more gradually over many cycles, reflecting incremental increases in both axial strain and pore pressure.
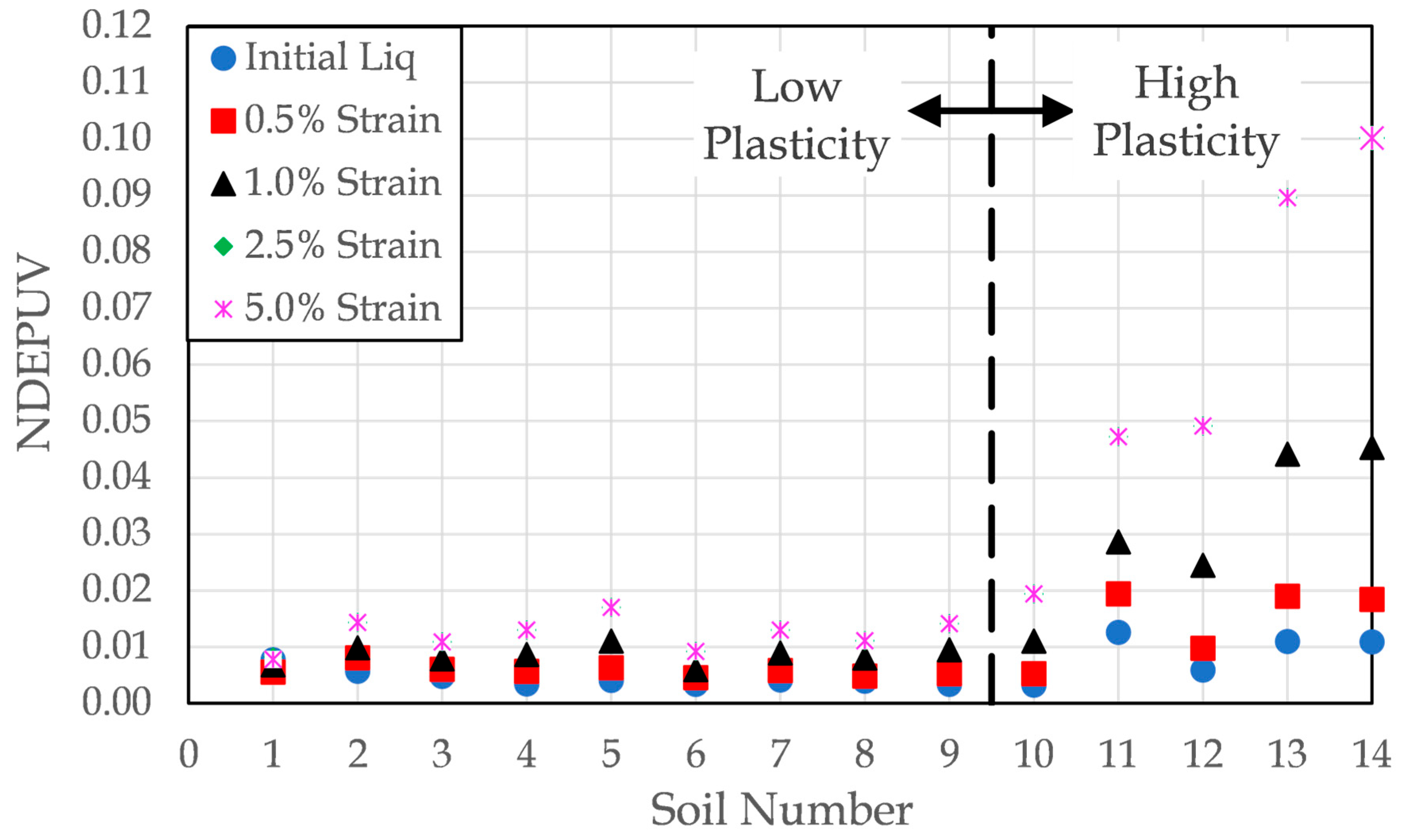
For soils with low plasticity, the choice of liquefaction criterion exerts a minimal influence on the interpreted normalized dissipated energy per unit volume required to cause liquefaction. This is made visible in for soil numbers 1 through 9 in
Figure 16 by the fact that the data points representing each failure criteria tend to cluster tightly together. This is because strain accumulation occurs rapidly following the onset of initial liquefaction; as a result, regardless of the failure criterion employed, the point of liquefaction is reached within a similar number of cycles leading to nearly identical quantities of energy dissipation to cause liquefaction across the different liquefaction criteria.
For soils with high plasticity, the choice of liquefaction criterion exerts a large influence on the normalized dissipated energy per unit volume. This is made visible in for soil numbers 10 through 14 in
Figure 16 by the fact that the data points representing each failure criteria are quite spread out, indicating that it takes different number of cycles and, thus, a different amount of energy dissipation to meet each of the different liquefaction criteria. This is because of the cyclic increase and decrease in strain occurs both before and following the onset of initial liquefaction. As a result of the failure criterion employed, the point of liquefaction is reached at different cycles of loading for the different liquefaction criteria; therefore, the amount of energy dissipated in the soil can differ greatly between the different criteria.
5. Impact of Study Results on Engineering Practice
The findings of this study provide practical guidance for selecting appropriate liquefaction criteria when conducting laboratory-based liquefaction analyses. These analyses typically proceed in two primary stages. The first stage involves evaluating the liquefaction resistance of the soil through laboratory testing, most commonly via cyclic triaxial or cyclic simple shear tests. The resulting measure of soil capacity is usually expressed either as a cyclic resistance ratio (CRR) or as the normalized dissipated energy per unit volume required to initiate liquefaction.
The second stage involves estimating the seismic demand imposed by the design earthquake. This demand is quantified either through the cyclic stress ratio (CSR), calculated based on anticipated peak ground acceleration and adjusted for earthquake magnitude, confining stress, and other relevant factors, or by determining the normalized dissipated energy per unit volume generated by the target seismic event, typically via numerical simulation.
Once both the soil capacity and the seismic demand have been established, their ratio is used to compute a factor of safety against liquefaction.
The results of this study inform the selection of liquefaction criteria based on the expected mode of liquefaction failure. Specifically,
Liquefaction Failures: When soils are susceptible to flow-type liquefaction, the choice of liquefaction criterion is less critical. This is because both stress-based criteria (e.g., initial liquefaction) and commonly used strain-based criteria tend to occur within a narrow range of conditions and can be considered approximately equivalent for practical purposes.
Cyclic Mobility Failures: In contrast, for cyclic mobility-type failures, it is essential to consider the acceptable level of strain for the specific geotechnical system under analysis. While cyclic mobility typically does not result in large permanent deformations, it may still produce significant transient strains that must be accounted for in design.
In practice, the expected mode of liquefaction failure may not be known in advance. Accordingly, the most robust approach is to adopt a dual-criteria framework, where feasible, requiring both the occurrence of initial liquefaction and the attainment of a substantial axial strain threshold. This approach enables the engineer to capture a broader range of potential failure mechanisms. When dual criteria cannot be implemented due to testing system limitations, it is recommended that a single, relatively large axial strain criterion be used (e.g., a minimum of 5% single-amplitude axial strain). At such strain levels, initial liquefaction is almost certainly exceeded, regardless of whether the failure mode is liquefaction or cyclic mobility.
7. Conclusions
This study has demonstrated that the selection of a liquefaction failure criterion significantly influences the interpreted cyclic resistance and normalized dissipated energy required to trigger liquefaction, particularly in soils with high plasticity. Through a systematic series of stress-controlled cyclic triaxial tests, it was shown that while low-plasticity soils exhibit relatively consistent behavior across different liquefaction definitions, high-plasticity soils respond in a more complex and criterion-sensitive manner.
For low-plasticity soils, the results indicate that the onset of initial liquefaction is closely followed by the attainment of strain-based criteria, leading to minimal variation in both cyclic resistance ratio (CRR) and normalized dissipated energy across the different failure definitions. This consistency suggests that, for such soils, the choice of failure criterion has limited impact on design outcomes. Consequently, a range of strain thresholds, including initial liquefaction and commonly used axial strain criteria, can be used interchangeably with negligible influence on the assessment of liquefaction potential.
In contrast, high-plasticity soils displayed pronounced variability in both CRR and normalized dissipated energy depending on the selected criterion. This is attributable to the more gradual accumulation of strain and energy dissipation, both before and after the onset of initial liquefaction. The divergence among criteria leads to significant differences in the number of cycles required to reach each failure definition, emphasizing that a single criterion may not capture the full deformation behavior of such soils. As a result, engineering assessments that rely solely on one criterion risk either underestimating or overestimating the severity of cyclic loading effects in high-plasticity soils.
Overall, the findings underscore the need for careful selection of liquefaction criteria in laboratory testing protocols, especially when evaluating fine-grained or plastic soils. Where feasible, a dual-criteria approach is recommended to capture both pore pressure development and strain accumulation, thereby ensuring a more comprehensive evaluation of soil performance under cyclic loading. These insights contribute to improving the accuracy and reliability of seismic soil assessments and support more resilient geotechnical design practices.