Evaluating Preventive Measures for Flooding from Groundwater: A Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3. FEFLOW Model Setup
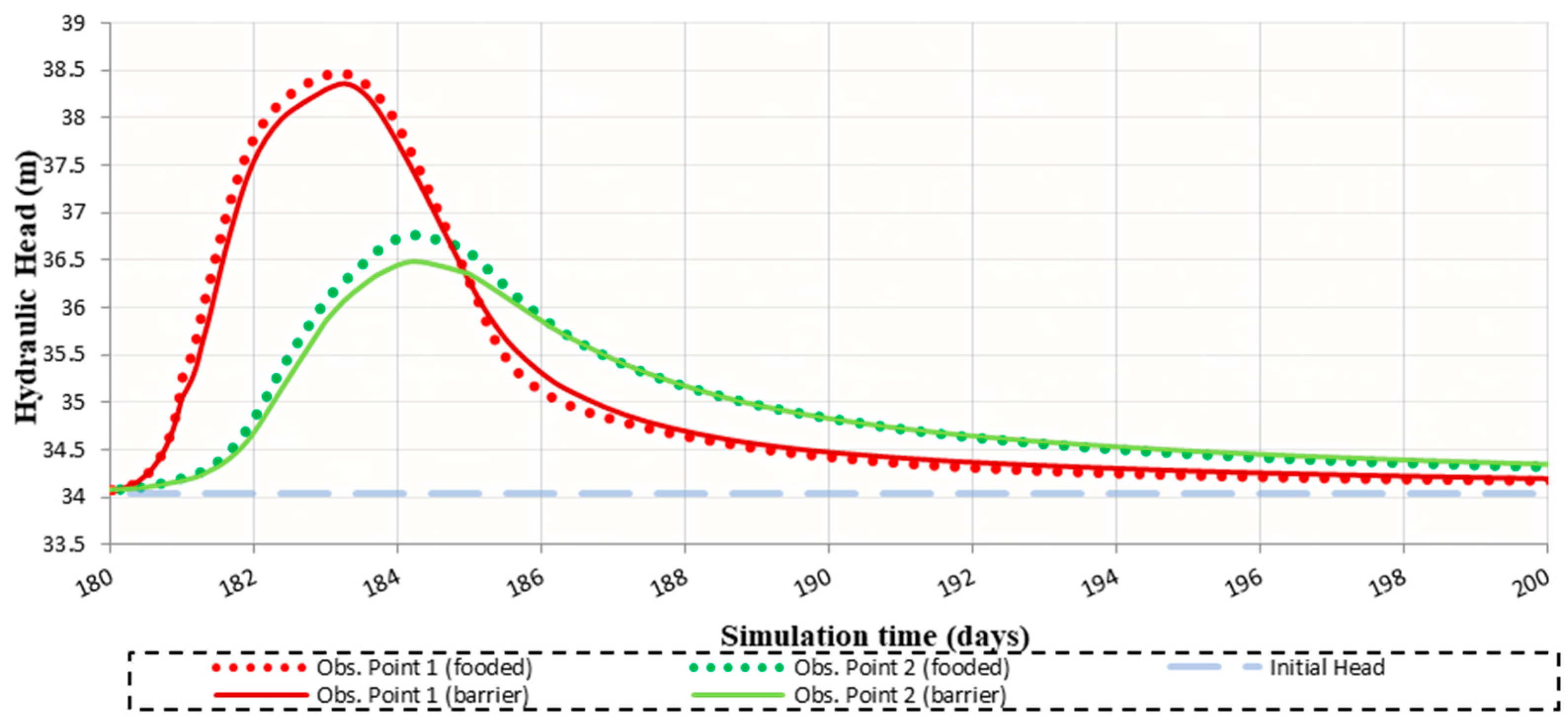
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sensitivity Analysis
3.2. Flood Control Strategies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macdonald, D.; Dixon, A.; Newell, A.; Hallaways, A. Groundwater Flooding within an Urbanised Flood Plain. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2011, 5, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Ji, K.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ealotswe, T.K.; Qin, W.; Lu, J.; Liu, B.; Shu, L. Estimation of the Interaction between Groundwater and Surface Water Based on Flow Routing Using an Improved Nonlinear Muskingum-Cunge Method. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 2649–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C. Climate Change and Its Impact on Groundwater Resources. Res. Inventy Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2012, 1, 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdan, M.M.S.; Kumar, R.; Leung, S.W. The Environmental and Health Impacts of Steroids and Hormones in Wastewater Effluent, as Well as Existing Removal Technologies: A Review. Ecologies 2022, 3, 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemčić-Jurec, J.; Ruk, D.; Oreščanin, V.; Kovač, I.; Ujević Bošnjak, M.; Kinsela, A.S. Groundwater Contamination in Public Water Supply Wells: Risk Assessment, Evaluation of Trends and Impact of Rainfall on Groundwater Quality. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elaty, I.; Negm, A.; Hamdan, A.M.; Nour-Eldeen, A.S.; Zeleňáková, M.; Hossen, H. Assessing the Hazards of Groundwater Logging in Tourism Aswan City, Egypt. Water 2022, 14, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehedi, M.A.A.; Yazdan, M.M.S. Automated Particle Tracing & Sensitivity Analysis for Residence Time in a Saturated Subsurface Media. Liquids 2022, 2, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurqani, H.A.; Al-Bukhari, A.; Aldaikh, A.O.; Elfadli, K.I.; Bataw, A.A. Geospatial Mapping and Analysis of the 2019 Flood Disaster Extent and Impact in the City of Ghat in Southwestern Libya Using Google Earth Engine and Deep Learning Technique. Environ. Appl. Remote Sens. GIS Libya 2022, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehedi, M.A.A.; Reichert, N.; Molkenthin, F. Sensitivity Analysis of Hyporheic Exchange to Small Scale Changes in Gravel-Sand Flumebed Using a Coupled Groundwater-Surface Water Model. Available online: https://meetingorganizer.copernicus.org/EGU2020/EGU2020-20319.html (accessed on 30 July 2022).
- Moran, B.J.; Boutt, D.F.; McKnight, S.V.; Jenckes, J.; Munk, L.A.; Corkran, D.; Kirshen, A. Relic Groundwater and Prolonged Drought Confound Interpretations of Water Sustainability and Lithium Extraction in Arid Lands. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Dahlke, H.; Duncan, R.; Doll, D.; Martinez, P.; Lampinen, B.; Volder, A. Winter Flooding Recharges Groundwater in Almond Orchards with Limited Effects on Root Dynamics and Yield. Calif. Agric. 2022, 76, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehedi, M.A.A.; Yazdan, M.M.S.; Ahad, M.T.; Akatu, W.; Kumar, R.; Rahman, A. Quantifying Small-Scale Hyporheic Streamlines and Resident Time under Gravel-Sand Streambed Using a Coupled HEC-RAS and MIN3P Model. Eng 2022, 3, 276–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, B.; Morrissey, P.; Gill, L.W. Application of Nonlinear Time Series and Machine Learning Algorithms for Forecasting Groundwater Flooding in a Lowland Karst Area. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR029576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C. An Overview of Commonly Used Groundwater Modelling Software. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2019, 6, 7854–7865. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Al Mehedi, M.A.; Yazdan, M.M.S.; Kumar, R. Development of Machine Learning Flood Model Using Artificial Neural Network (ANN) at Var River. Liquids 2022, 2, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdan, M.M.S.; Ahad, M.T.; Kumar, R.; Mehedi, M.A.A. Estimating Flooding at River Spree Floodplain Using HEC-RAS Simulation. Preprints 2022, 5, 410–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehedi, M.A.A.; Khosravi, M.; Yazdan, M.M.S.; Shabanian, H. Exploring Temporal Dynamics of River Discharge using Univariate Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Recurrent Neural Network at East Branch of Delaware River. Preprints 2022, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdan, M.M.S.; Khosravia, M.; Saki, S.; Mehedi, M.A.A. Forecasting Energy Consumption Time Series Using Recurrent Neural Network in Tensorflow. Preprints 2022, 2022090404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, D.M.J.; Bloomfield, J.P.; Hughes, A.G.; MacDonald, A.M.; Adams, B.; McKenzie, A.A. Improving the understanding of the risk from groundwater flooding in the UK. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Flood Risk Management, Oxford, UK, 30 September–2 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cobby, D.; Morris, S.; Parkes, A.; Robinson, V. Groundwater flood risk management: Advances towards meeting the requirements of the EU floods directive. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2009, 2, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinault, J.-L.; Amraoui, N.; Golaz, C. Groundwater-induced flooding in macropore-dominated hydrological system in the context of climate changes. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, J.W.; Bradford, R.B.; Hudson, J.A. The spatial distribution of groundwater flooding in a chalk catchment in southern England. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allocca, V.; Coda, S.; Calcaterra, D.; De Vita, P. Groundwater rebound and flooding in the Naples’ periurban area (Italy). J. Flood Risk Manag. 2022, 15, e12775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Belvedere, P.; Tosco, T.; Prigiobbe, V. Studying the effect of sea level rise on nuisance flooding due to groundwater in a coastal urban area with aging infrastructure. Urban Clim. 2022, 43, 101164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, A.C.; Brown, C.M.; Thompson, S.P.; Piehler, M.F. Inundation of stormwater infrastructure is common and increases risk of flooding in coastal urban areas along the US Atlantic coast. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, L.; Tawfiq, M.; Jabber, A. Solve the Groundwater Model Equation Using Fourier Transforms Method Research Article. Int. J. Adv. Appl. Math. Mech. 2017, 5, 2347–2529. [Google Scholar]
- Pinder, G.F. An Overview of Groundwater Modelling. Groundw. Flow Qual. Model. 1988, 224, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdan, M.M.S.; Ahad, M.T.; Mallick, Z.; Mallick, S.P.; Jahan, I.; Mazumder, M. An Overview of the Glucocorticoids’ Pathways in the Environment and Their Removal Using Conventional Wastewater Treatment Systems. Pollutants 2021, 1, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepe, N.; Romero, M.; Bau, M. High-Technology Metals as Emerging Contaminants: Strong Increase of Anthropogenic Gadolinium Levels in Tap Water of Berlin, Germany, from 2009 to 2012. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 45, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlemann, L.; Tetzlaff, D.; Soulsby, C. Urban Water Systems under Climate Stress: An Isotopic Perspective from Berlin, Germany. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 3758–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, D.L. Bioremediation of Contaminated Soils; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; ISBN 9780429078040. [Google Scholar]
- García Revilla, M.R.; Martínez Moure, O. Wine as a Tourist Resource: New Manifestations and Consequences of a Quality Product from the Perspective of Sustainability. Case Analysis of the Province of Málaga. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.; Massmann, G.; Taute, T.; Duennbier, U. Investigation of the Fate of Sulfonamides Downgradient of a Decommissioned Sewage Farm near Berlin, Germany. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2009, 106, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinzelbach, W. Groundwater Modelling: An Introduction with Sample Programs in BASIC; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, C.P. “IJMSET Promotes Research Nature, Research Nature Enriches the World’s Future” Modelling of Groundwater Flow and Data Requirements. Int. J. Mod. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2015, 2, 18–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ohara, N.; Steven Holbrook, W.; Yamatani, K.; Flinchum, B.A.; St. Clair, J.T. Spatial Delineation of Riparian Groundwater within Alluvium Deposit of Mountainous Region Using Laplace Equation. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 32, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Jian, C.; Haobo, N.; Li, L.; Leyi, Y.; Yaqiang, W. Numerical simulation of three-dimensional soil-groundwater coupled chromium contamination based on FEFLOW. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2022, 49, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Ahmad, Z. Regional Groundwater Flow Modelling of Upper Chaj Doab of Indus Basin, Pakistan Using Finite Element Model (FEFLOW) and Geoinformatics. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 173, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdan, M.M.S.; Ahad, M.T.; Jahan, I.; Mazumder, M. Review on the Evaluation of the Impacts of Wastewater Disposal in Hydraulic Fracturing Industry in the United States. Technologies 2020, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, B. Simulation of the Effects of Groundwater Level on Vegetation Change by Combining FEFLOW Software. Ecol. Model. 2005, 187, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diersch, H.-J.G. FEFLOW: Finite Element Modeling of Flow, Mass and Heat Transport in Porous and Fractured Media; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman, A.Z.; Yazdan, M.M.S.; Noor, F.; Duti, B.M. Establishment of Co-Relation Between Remote Sensing Based Trmm Data and Ground Based Precipitation Data in North-East Region of Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD-2014), KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh, 14–16 February 2014. Deep Convection for Thunderstorm: CAPE and Shear Analysis in Present and Future Climate View Project Seven River Dredging Project: Case of Old Brahmaputra River View Project. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, B.; Binns, A.; Sandink, D.; Gharabaghi, B.; McBean, E. Reducing the Risk of Basement Flooding through Building- and Lot-Scale Flood Mitigation Approaches: Performance of Foundation Drainage Systems. Lect. Notes Civ. Eng. 2022, 250, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, B.M.T.A.; Ahmed, T.; Aktar, N.; Khan, F.; Islam, A.; Yazdan, M.M.S.; Noor, F.; Rahaman, A. Climate Change Impacts on Water Availability in the Meghna Basin. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Water and Flood Management (ICWFM-2015), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 6–8 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Humnicki, W.; Krogulec, E.; Małecki, J.; Szostakiewicz-Hołownia, M.; Wojdalska, A.; Zaszewski, D. Groundwater impact assessment of Lake Czorsztyn after 25 years of its operation. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2022, 48, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Components | Layer 1 | Layer 2 | Layer 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| In/outflow on top/bottom | 19.5 cm/s | N/A | N/A |
| K_xx | N/A | 2 × 10−2 cm/s | 1 × 10−4 cm/s |
| K_yy | N/A | 2 × 10−2 cm/s | 1 × 10−4 cm/s |
| K_zz | N/A | 2 × 10−3 cm/s | 1 × 10−5 cm/s |
| Drain/fillable porosity | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
| Head from Base Case (m) | Changed Head (m) | Change in Hydraulic Head (%) | Global Change in Material Property (%) (TRI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 35.55 | 35.55 | −0.001 | −100 |
| 35.55 | 35.55 | −0.001 | −50 |
| 35.55 | 35.55 | −0.0003 | 50 |
| 35.55 | 35.55 | −0.0006 | 100 |
| 35.55 | 35.55 | −0.0008 | 150 |
| Head from Base Case (m) | Changed Head (m) | Change in Hydraulic Head (%) | Global Change in Material Property (%) (TRO) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 35.55 | 35.55 | 0.001 | −100 |
| 35.55 | 35.59 | 0.109 | −50 |
| 35.55 | 35.55 | 0.0000 | 50 |
| 35.55 | 35.55 | 0.0014 | 100 |
| 35.55 | 35.55 | 0.0006 | 150 |
| Scenario Name (ID) | Transfer Rate in (L/d) | Percent Change (%) | Transfer Rate Out (L/d) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SnScBase | 200 | n/a | 800 | Base scenario |
| SnSc1_TRI_Ex1 | 1200 | 500 | 4800 | Change in transfer rate out |
| SnSc1_TRI_Ex2 | 2200 | 1000 | 8800 | |
| SnSc1_TRI_Ex3 | 4200 | 2000 | 16,800 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, R.; Yazdan, M.M.S. Evaluating Preventive Measures for Flooding from Groundwater: A Case Study. J 2023, 6, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/j6010001
Kumar R, Yazdan MMS. Evaluating Preventive Measures for Flooding from Groundwater: A Case Study. J. 2023; 6(1):1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/j6010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Raaghul, and Munshi Md. Shafwat Yazdan. 2023. "Evaluating Preventive Measures for Flooding from Groundwater: A Case Study" J 6, no. 1: 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/j6010001
APA StyleKumar, R., & Yazdan, M. M. S. (2023). Evaluating Preventive Measures for Flooding from Groundwater: A Case Study. J, 6(1), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/j6010001









