Adsorptive and Coagulative Removal of Trace Metals from Water Using Surface Modified Sawdust-Based Cellulose Nanocrystals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
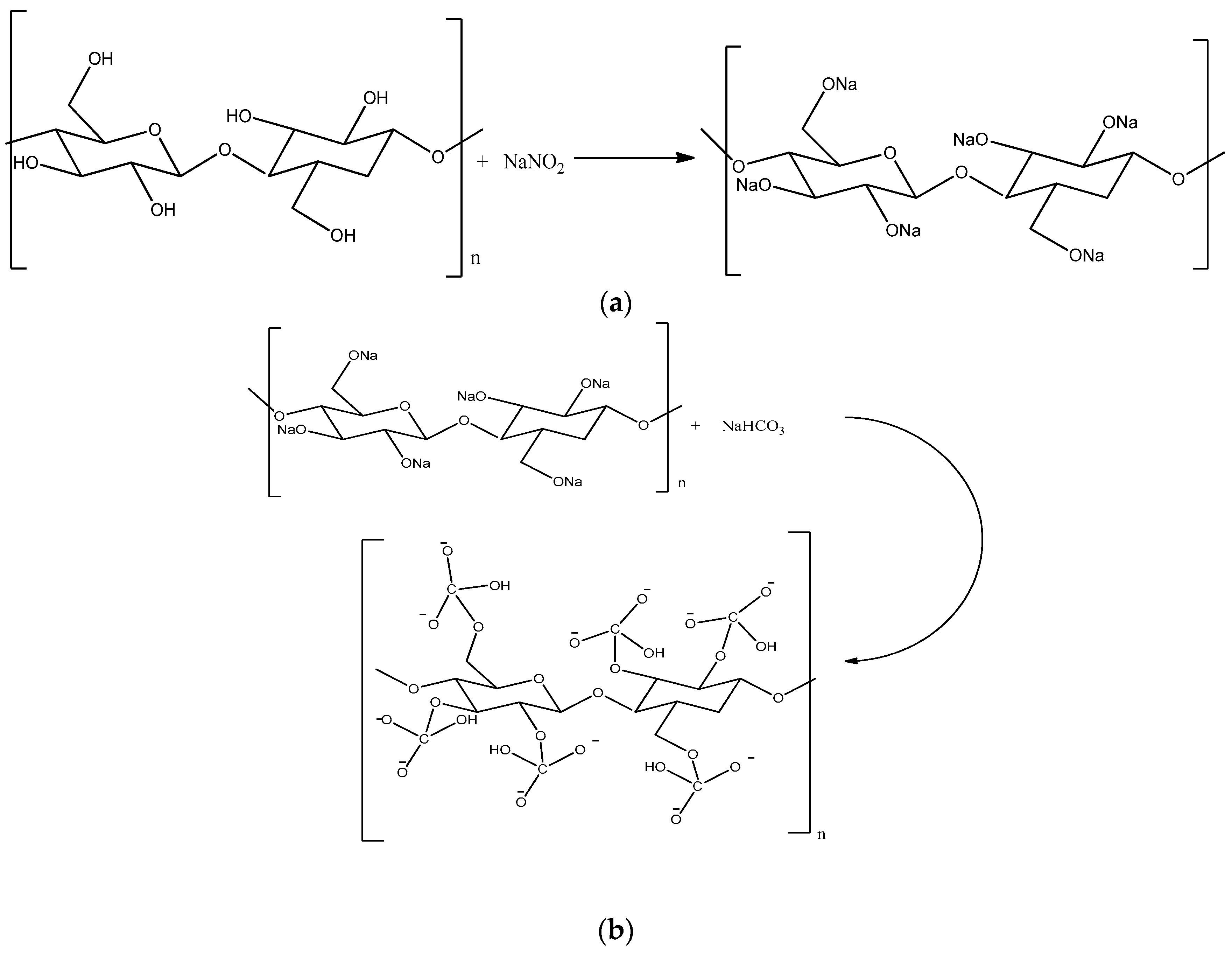
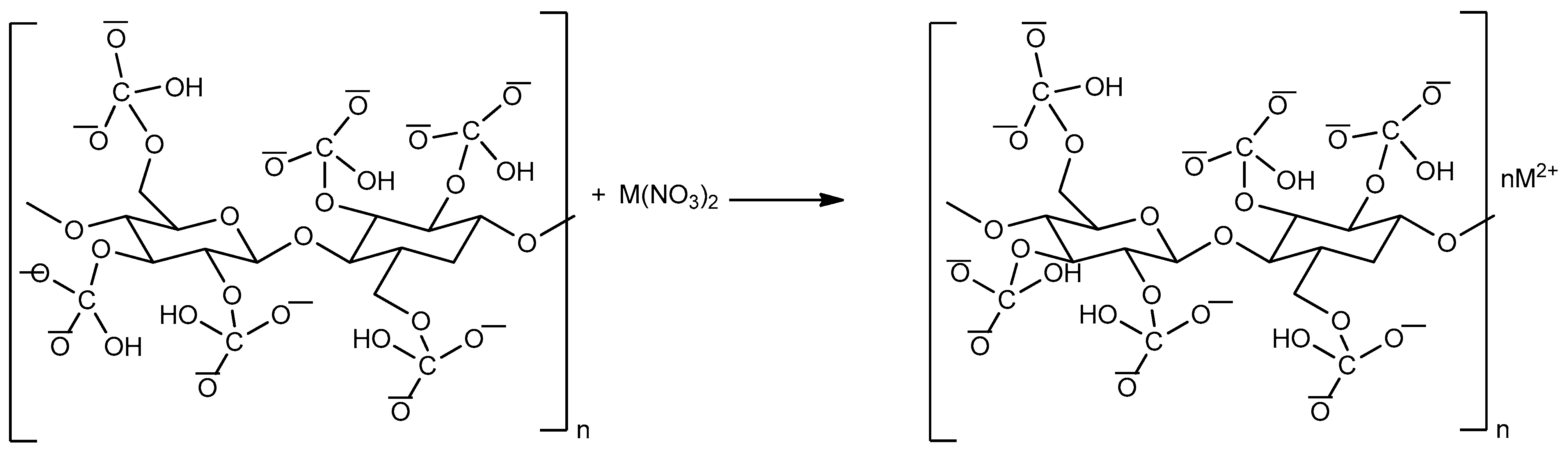
2.2.1. Surface Modification of Cellulose Nanocrystals (CNC)
2.2.2. Characterization of Synthesized and Spent Cellulose Nanocrystals Coagulants
2.2.3. Coagulation-Flocculation Studies
2.2.4. Adsorption Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization Results
3.1.1. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
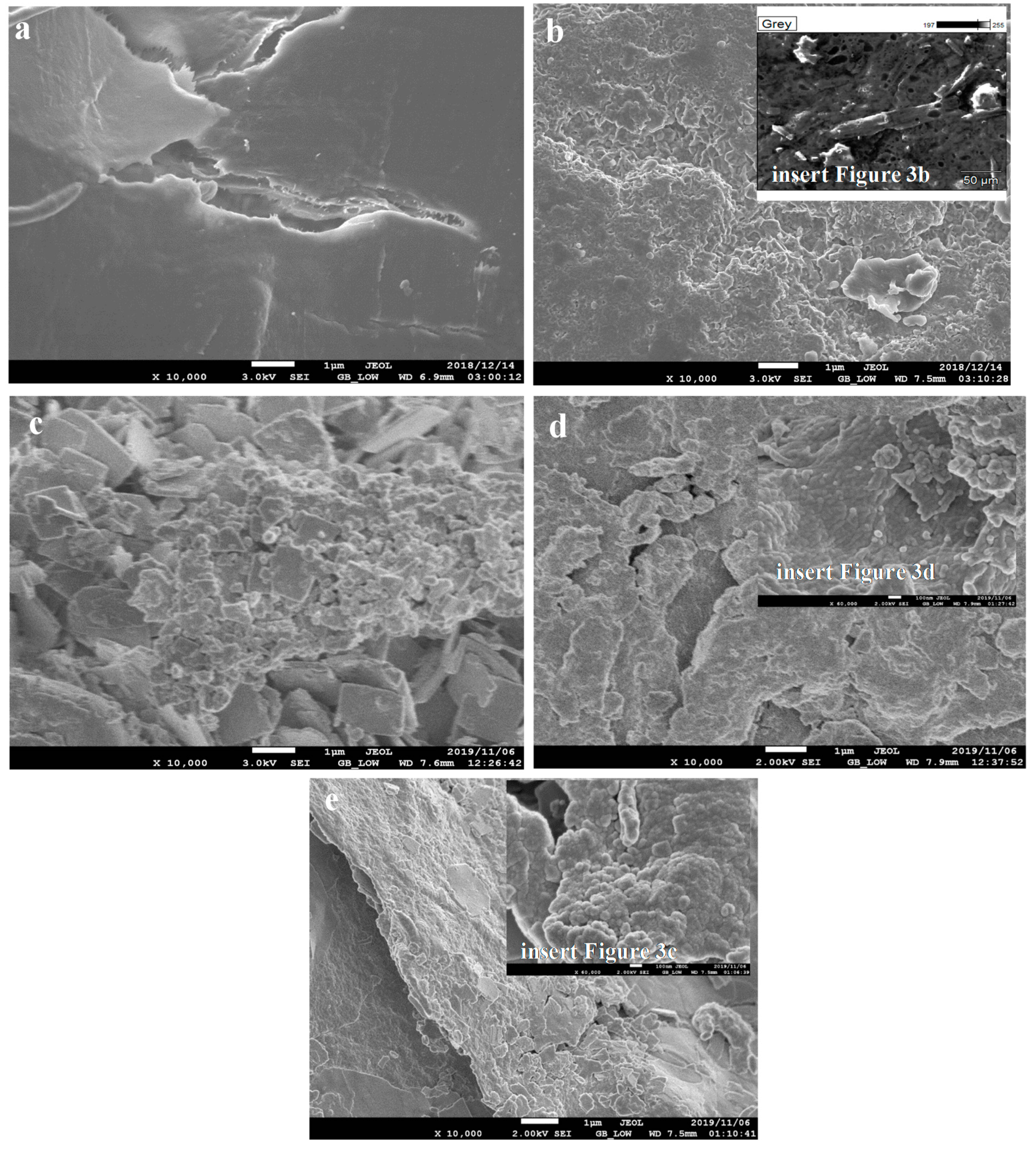
3.1.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
3.1.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
3.2. Coagulation Results
3.2.1. Effect of Metals Solution pH
3.2.2. Effect of Coagulant Dosage
3.3. Adsorption Isotherm Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shanbehzadeh, S.; Vahid Dastjerdi, M.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Kiyanizadeh, T. Heavy Metals in Water and Sediment: A Case Study of Tembi River. J. Environ. Public Health 2014, 2014, 858720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Exp. Suppl. 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Gautam, N.; Mishra, A.; Gupta, R. Heavy metals and living systems: An overview. Indian J. Pharm. 2011, 43, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Alattar, M.; Jiang, S.; Han, J.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, C. The preferential accumulation of heavy metals in different tissues following frequent respiratory exposure to PM2.5 in rats. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbier, O.; Jacquillet, G.; Tauc, M.; Cougnon, M.; Poujeol, P. Effect of Heavy Metals on, and Handling by, the Kidney. Nephron. Physiol. 2005, 99, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnlund, J.R.; Jacob, R.A.; Keen, C.L.; Strain, J.; Kelley, D.S.; Domek, J.M.; Keyes, W.R.; Ensunsa, J.L.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Coulter, J. Long-term high copper intake: Effects on indexes of copper status, antioxidant status, and immune function in young men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.A.; Tsuji, J.S.; Garry, M.R.; McArdle, M.E.; Goodfellow, W.L.; Adams, W.J.; Menzie, C.A. Critical Review of Exposure and Effects: Implications for Setting Regulatory Health Criteria for Ingested Copper. Environ. Manag. 2020, 65, 131–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council, N.R. Drinking Water and Health: Volume 3; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1980; p. 415. [Google Scholar]
- Ferro-García, M.A.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Bautista-Toledo, I.; Mingorance, M.D. Removal of lead from water by activated carbons. Carbon 1990, 28, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, M. Lead in drinking water. CMAJ 2008, 179, 253–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UKTAG. UK Environmental Standards and Conditions (Phase 2). SR1–2007. 2008. Available online: https://www.wfduk.org/sites/default/files/Media/Environmental%20standards/Environmental%20standards%20phase%202_Final_110309.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2008).
- Hargreaves, A.J.; Vale, P.; Whelan, J.; Alibardi, L.; Constantino, C.; Dotro, G.; Cartmell, E.; Campo, P. Coagulation–flocculation process with metal salts, synthetic polymers and biopolymers for the removal of trace metals (Cu, Pb, Ni, Zn) from municipal wastewater. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuda, O.; Amoo, I.; Ipinmoroti, K.; Ajayi, O. Coagulation/flocculation process in the removal of trace metals present in industrial wastewater. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Mgt. 2006, 10, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, C.; Budiman, P.; Shak, K.; Wu, T. Recent Advancement of Coagulation-Flocculation and Its Application in Wastewater Treatment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charerntanyarak, L. Heavy metals removal by chemical coagulation and precipitation. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolthoff, I.M. Theory of Coprecipitation. The Formation and Properties of Crystalline Precipitates. J. Phys. Chem. 1932, 36, 860–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, S.; Chiang, P.-C.; Shah, K.J. Evaluation and optimization of enhanced coagulation process: Water and energy nexus. Water Energy Nexus 2019, 2, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Benedictis, C.A.; Vilella, A.; Grabrucker, A.M. The Role of Trace Metals in Alzheimer’s Disease. In Alzheimer’s Disease; Wisniewski, T., Ed.; Codon Publications Copyright: Brisbane, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gibril, M.; Tesfaye, T.; Sithole, B.; Lekha, P.; Ramjugernath, D. Optimisation and enhancement of crystalline nanocellulose production by ultrasonic pretreatment of dissolving wood pulp fibres. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2018, 52, 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Oyewo, O.A.; Mutesse, B.; Leswifi, T.Y.; Onyango, M.S. Highly efficient removal of nickel and cadmium from water using sawdust-derived cellulose nanocrystals. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.; Hrapovic, S.; Lam, E.; Liu, Y.; Male, K.; Mahmoud, K.; Luong, J. Characteristics and Properties of Carboxylated Cellulose Nanocrystals Prepared from a Novel One-Step Procedure. Small 2011, 7, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Tong, S.; Ge, M.-F.; Wu, L.; Zuo, J.; Cao, C.-Y.; Song, W. Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, M.A. A detailed IR study of the order–disorder phase transition of NaNO2. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 363, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.; Girinathannair, P.; Ohlinger, K.; Ritchie, S.; Teuber, L.; Kirby, J. Enhanced Removal of Heavy Metals in Primary Treatment Using Coagulation and Flocculation. Water Environ. Res. 2008, 80, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Vargas, S.; Huirache-Acuña, R.; Guadalupe Rutiaga-Quiñones, J.; Cortés-Martínez, R. Effective lead removal from aqueous solutions using cellulose nanofibers obtained from water hyacinth. Water Supply 2020, 20, 2715–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahankari, S.; George, T.; Subhedar, A.; Kar, K.K. Nanocellulose as a sustainable material for water purification. SPE Polym. 2020, 1, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkalane, A.; Oyewo, O.A.; Leswifi, T.; Onyango, M.S. Application of coagulant obtained through charge reversal of sawdust-derived cellulose nanocrystals in the enhancement of water turbidity removal. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 105060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyewo, O.A.; Adeniyi, A.; Sithole, B.B.; Onyango, M.S. Sawdust-Based Cellulose Nanocrystals Incorporated with ZnO Nanoparticles as Efficient Adsorption Media in the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 18798–18807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Xiang, Z.; Mo, L. Research on cellulose nanocrystals produced from cellulose sources with various polymorphs. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 33486–33493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh-Choobari, O. Impact of aerosol number concentration on precipitation under different precipitation rates. Meteorol. Appl. 2018, 25, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhadi, B.; Kot, P.; Hashim, K.; Shaw, A.; Muradov, M.; Al-Khaddar, R. Continuous-flow electrocoagulation (EC) process for iron removal from water: Experimental, statistical and economic study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.J.; Huang, Q.; Fu, S.; Zhang, X.J.; Shi, M.Y.; Liu, B. Removal of Molybdenum(VI) from Raw Water Using Nano Zero-Valent Iron Supported on Activated Carbon. Water 2020, 12, 3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, L.A.; Turner, A.; Thompson, R.C. Adsorption of trace metals to plastic resin pellets in the marine environment. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 160, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, R. Adsorption of Heavy Metals—A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 18, 4745–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantasha, I.; Hussain, S.; Ahmad, M.; Shahid, M. Two dimensional (2D) molecular frameworks for rapid and selective adsorption of hazardous aromatic dyes from aqueous phase. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 116413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, D.; Zhuo, Y.; Hu, L.; Zeng, Q.; Hu, Y.; He, Z. Research on the Adsorption Behavior of Heavy Metal Ions by Porous Material Prepared with Silicate Tailings. Minerals 2019, 9, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, E.; Jimoh, A. Adsorption of Pb, Fe, Cu, and Zn from industrial electroplating wastewater by orange peel activated carbon. Int. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2013, 4, 2305–8269. [Google Scholar]
- Agbozu, I.; Emoruwa, F. Batch adsorption of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Fe, Cr and Cd) from aqueous solutions using coconut husk. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 8, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Element wt.% | MCNC | Cu-flocs | Fe-flocs | Pb-flocs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 20.21 | 45.24 | 46.92 | 39.9 |
| O | 33.15 | 37.51 | 33.27 | 40.5 |
| Na | 24.25 | 2.1 | - | - |
| Mg | 0.04 | 0.03 | - | - |
| Al | 11.09 | 1.72 | 0.75 | 0.14 |
| Si | 3.06 | 0.03 | 0.69 | |
| S | 7.30 | 1.28 | 4.4 | 2.5 |
| Pb | - | - | - | 16.34 |
| Cl | 0.83 | - | - | |
| Fe | - | - | 13.92 | - |
| Cu | - | 12.09 | - | - |
| K | 0.03 | - | 0.02 | 0.62 |
| Ca | 0.04 | - | 0.03 | - |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Cu-Adsorption | Langmuir Isotherm Parameters | Freundlich Isotherm Parameters | ||||
| Temperature (°C) | qm (mg/g) | b (L/mg) | R2 | KF (L/g) | 1/n | R2 |
| 25 | 107.5 | 2.47 | 0.995 | 20.9 | 0.42 | 0.7287 |
| 35 | 111.1 | 2.09 | 0.999 | 22.5 | 0.41 | 0.7199 |
| 45 | 111.1 | 0.72 | 0.999 | 24.2 | 0.39 | 0.7365 |
| Pb-Adsorption | Langmuir Isotherm Parameters | Freundlich Isotherm Parameters | ||||
| Temperature (°C) | qm (mg/g) | b (L/mg) | R2 | KF (L/g) | 1/n | R2 |
| 25 | 2.55 | 1.56 | 0.998 | 0.58 | 0.35 | 0.6651 |
| 35 | 2.62 | 0.54 | 0.999 | 0.64 | 0.41 | 0.6371 |
| 45 | 2.82 | 0.47 | 0.999 | 1.75 | 0.34 | 0.5596 |
| Fe-Adsorption | Langmuir Isotherm Parameters | Freundlich Isotherm Parameters | ||||
| Temperature (°C) | qm (mg/g) | b (L/mg) | R2 | KF (L/g) | 1/n | R2 |
| 25 | 67.11 | 12.3 | 0.9404 | 7.85 | 0.49 | 0.998 |
| 35 | 79.37 | 22.8 | 0.7725 | 8.08 | 0.53 | 0.999 |
| 45 | 81.96 | 17.2 | 0.8825 | 8.94 | 0.55 | 0.999 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oyewo, O.A.; Ramaila, S.; Mavuru, L.; Leswifi, T.; Onyango, M.S. Adsorptive and Coagulative Removal of Trace Metals from Water Using Surface Modified Sawdust-Based Cellulose Nanocrystals. J 2021, 4, 193-205. https://doi.org/10.3390/j4020016
Oyewo OA, Ramaila S, Mavuru L, Leswifi T, Onyango MS. Adsorptive and Coagulative Removal of Trace Metals from Water Using Surface Modified Sawdust-Based Cellulose Nanocrystals. J. 2021; 4(2):193-205. https://doi.org/10.3390/j4020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleOyewo, Opeyemi A., Sam Ramaila, Lydia Mavuru, Taile Leswifi, and Maurice S. Onyango. 2021. "Adsorptive and Coagulative Removal of Trace Metals from Water Using Surface Modified Sawdust-Based Cellulose Nanocrystals" J 4, no. 2: 193-205. https://doi.org/10.3390/j4020016
APA StyleOyewo, O. A., Ramaila, S., Mavuru, L., Leswifi, T., & Onyango, M. S. (2021). Adsorptive and Coagulative Removal of Trace Metals from Water Using Surface Modified Sawdust-Based Cellulose Nanocrystals. J, 4(2), 193-205. https://doi.org/10.3390/j4020016






