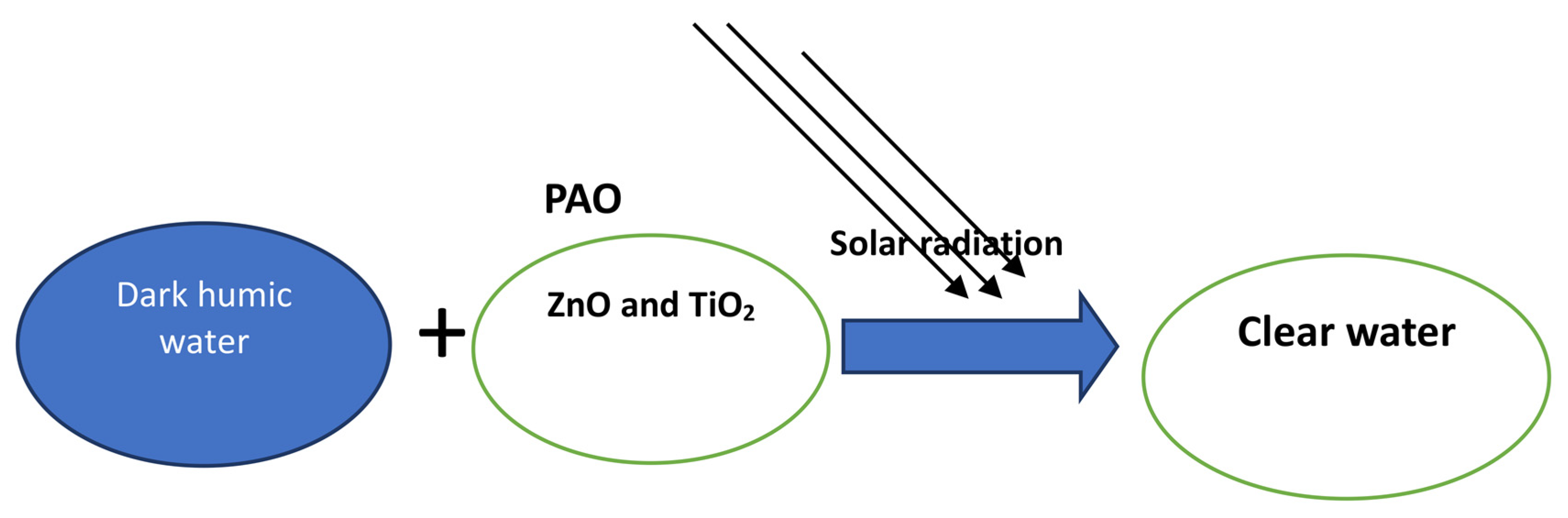
Treatment of Dark Humic Water Using Photocatalytic Advanced Oxidation (PAO) Processes under Visible and UV Light
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
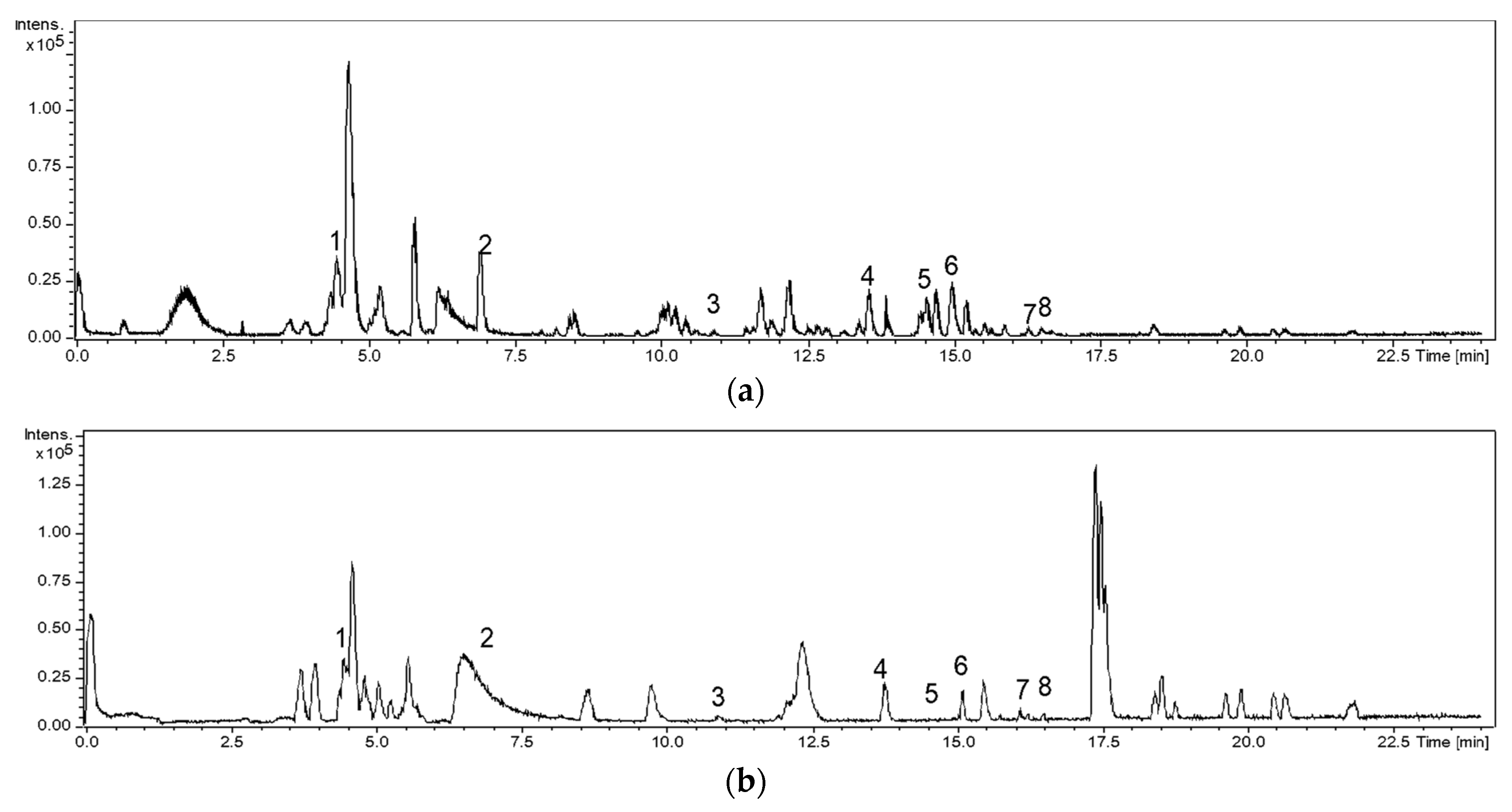
2.2. HPLC-MS Analysis of the Teas
2.3. Photocatalytic Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
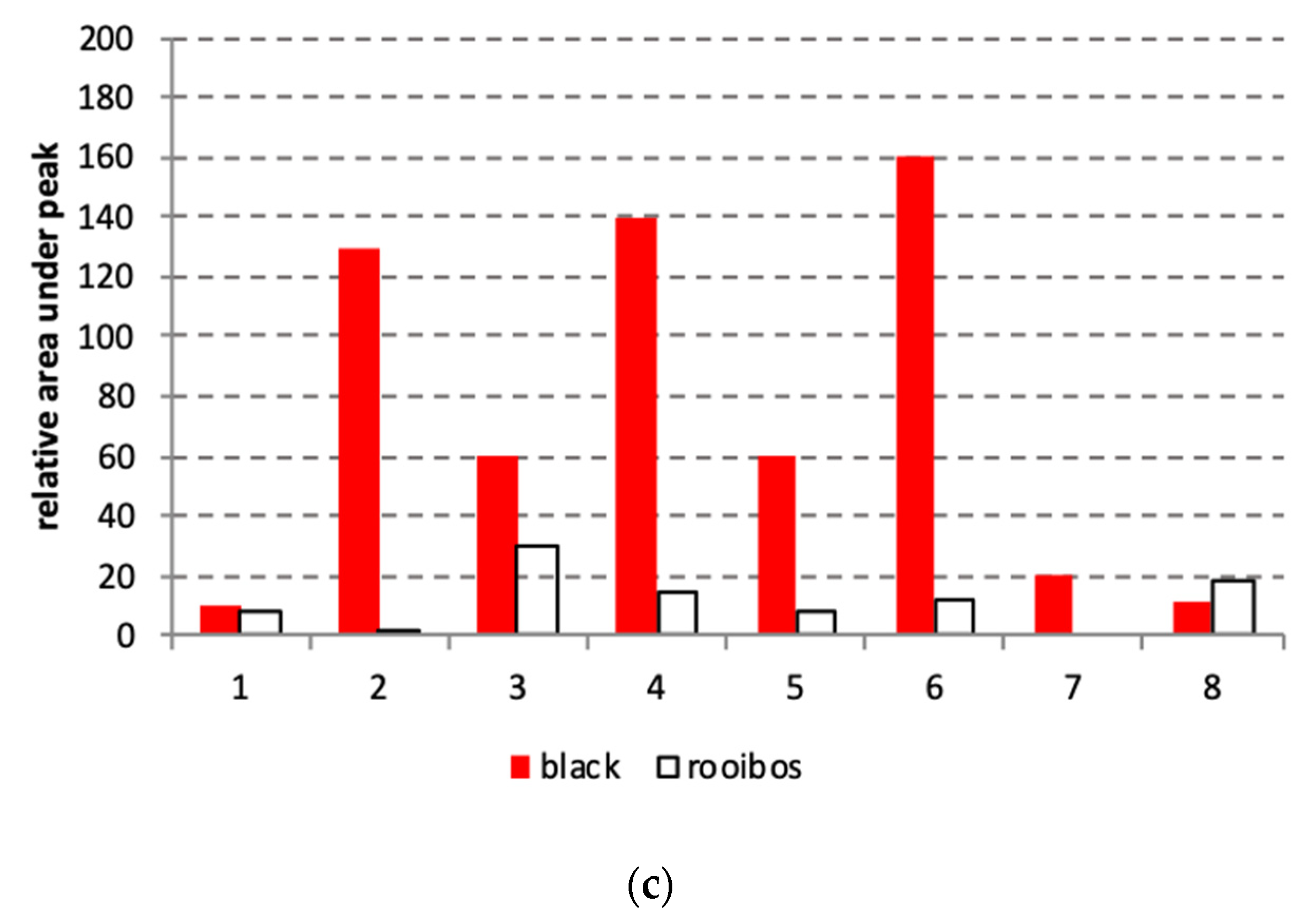
3.1. Characterization of Rooibos and Black Tea
3.2. Photocatalytic Degradation with Sunlight
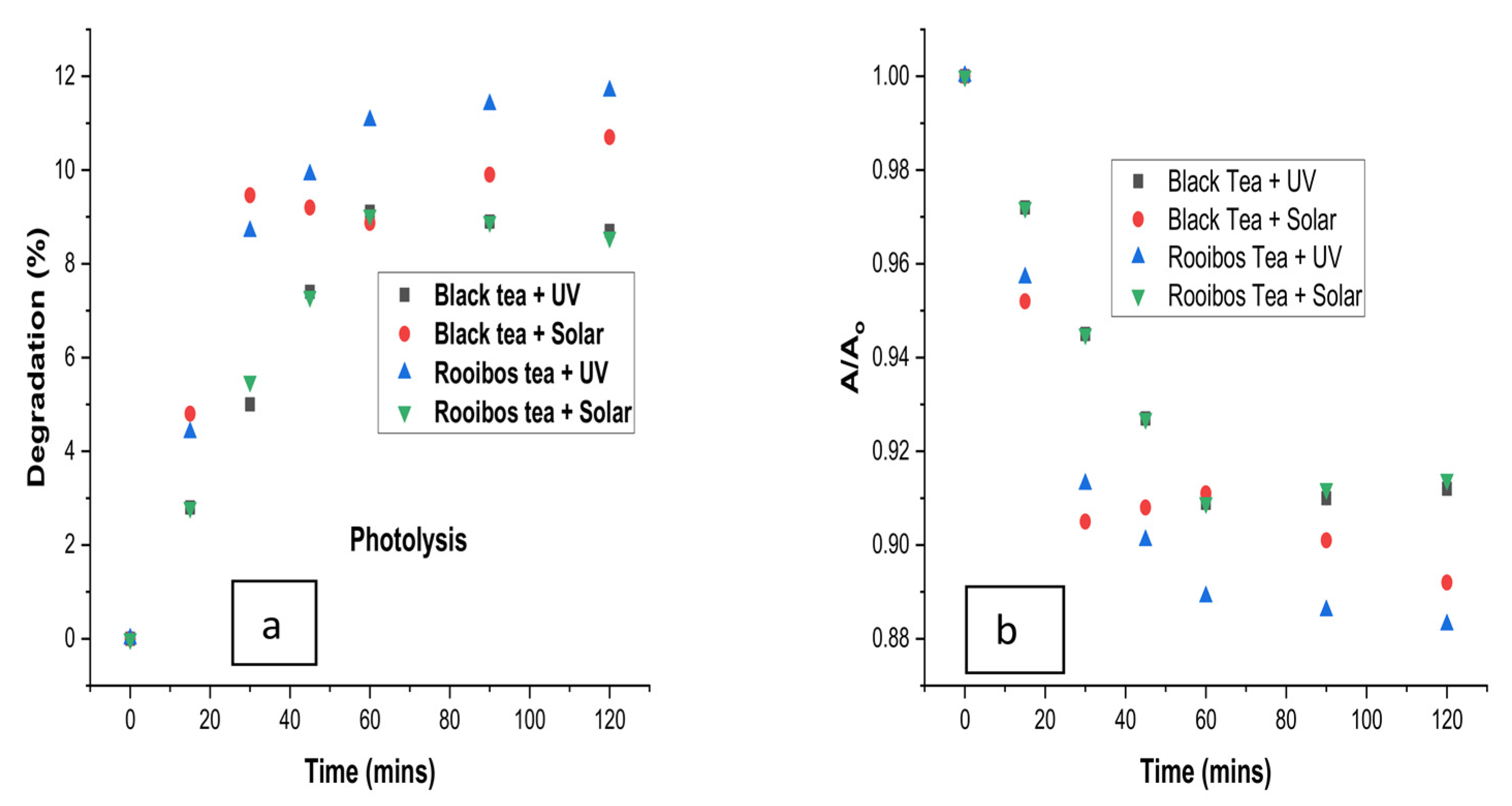
3.3. Photolysis with Halogen and UV Light without Catalysts
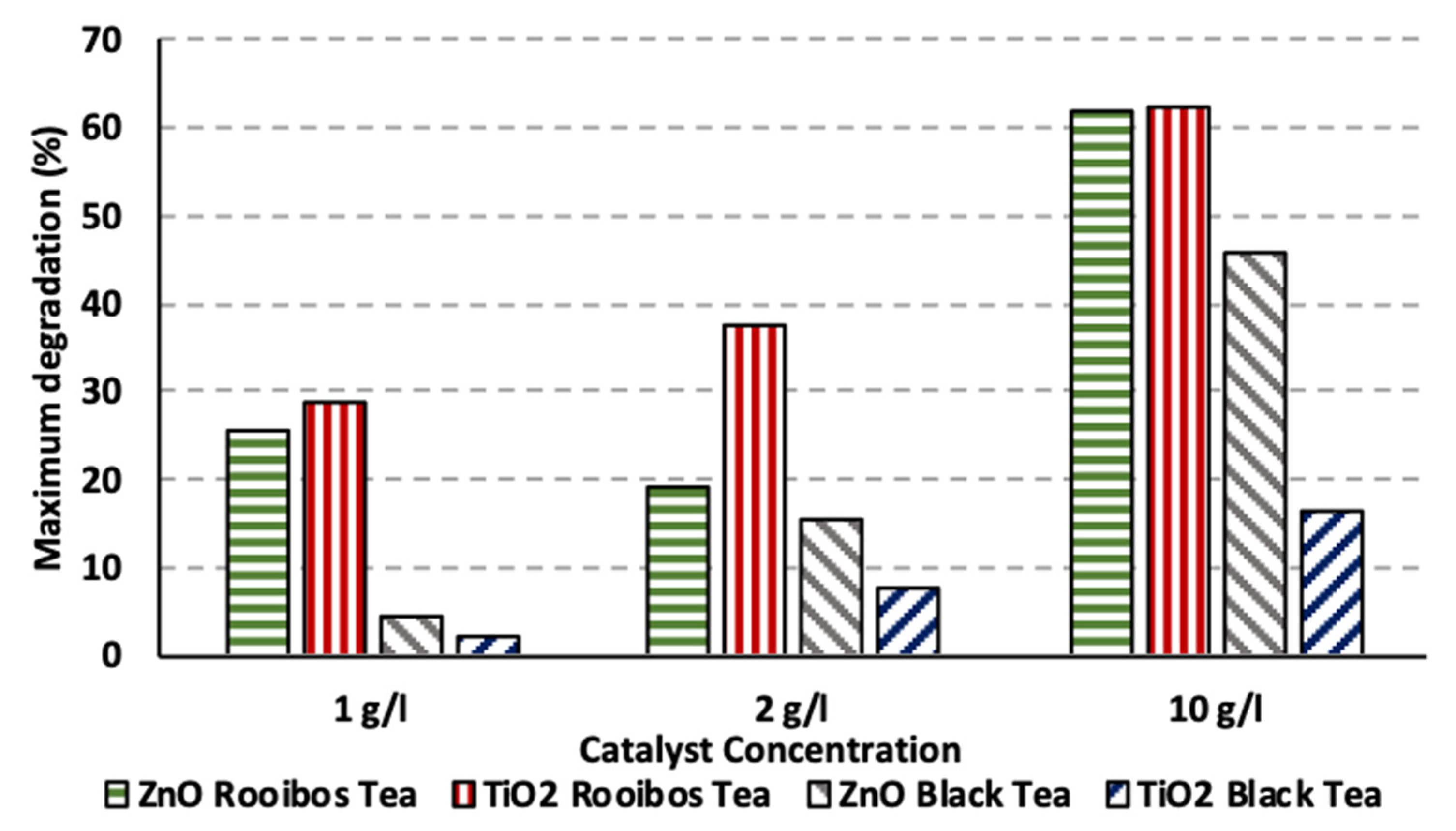
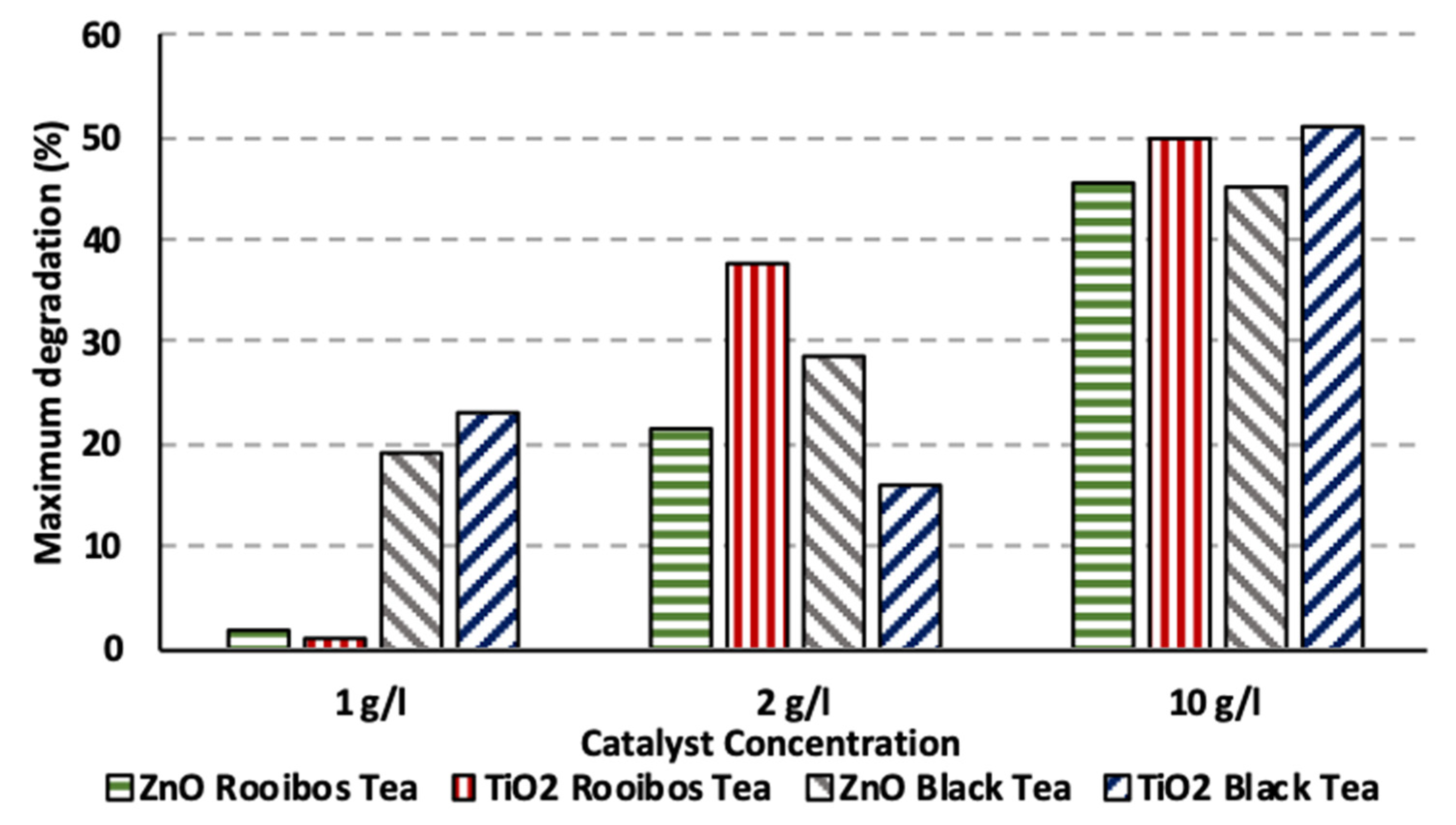
3.4. Impact of Catalyst Concentration under Artificial UV and Solar Irradiation
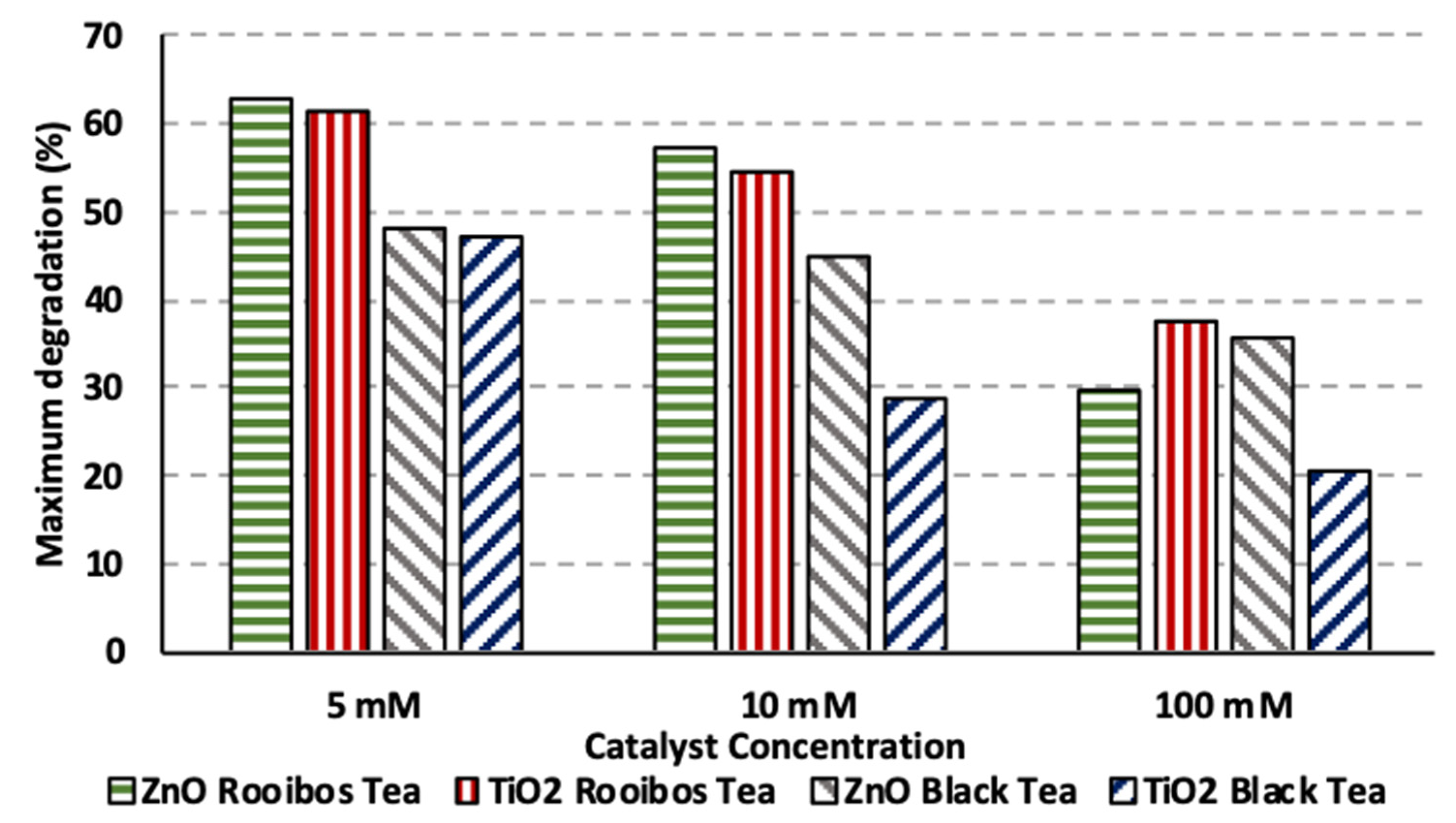
3.5. Impact of Hydrogen Peroxide Addition on Photocatalytic Degradation
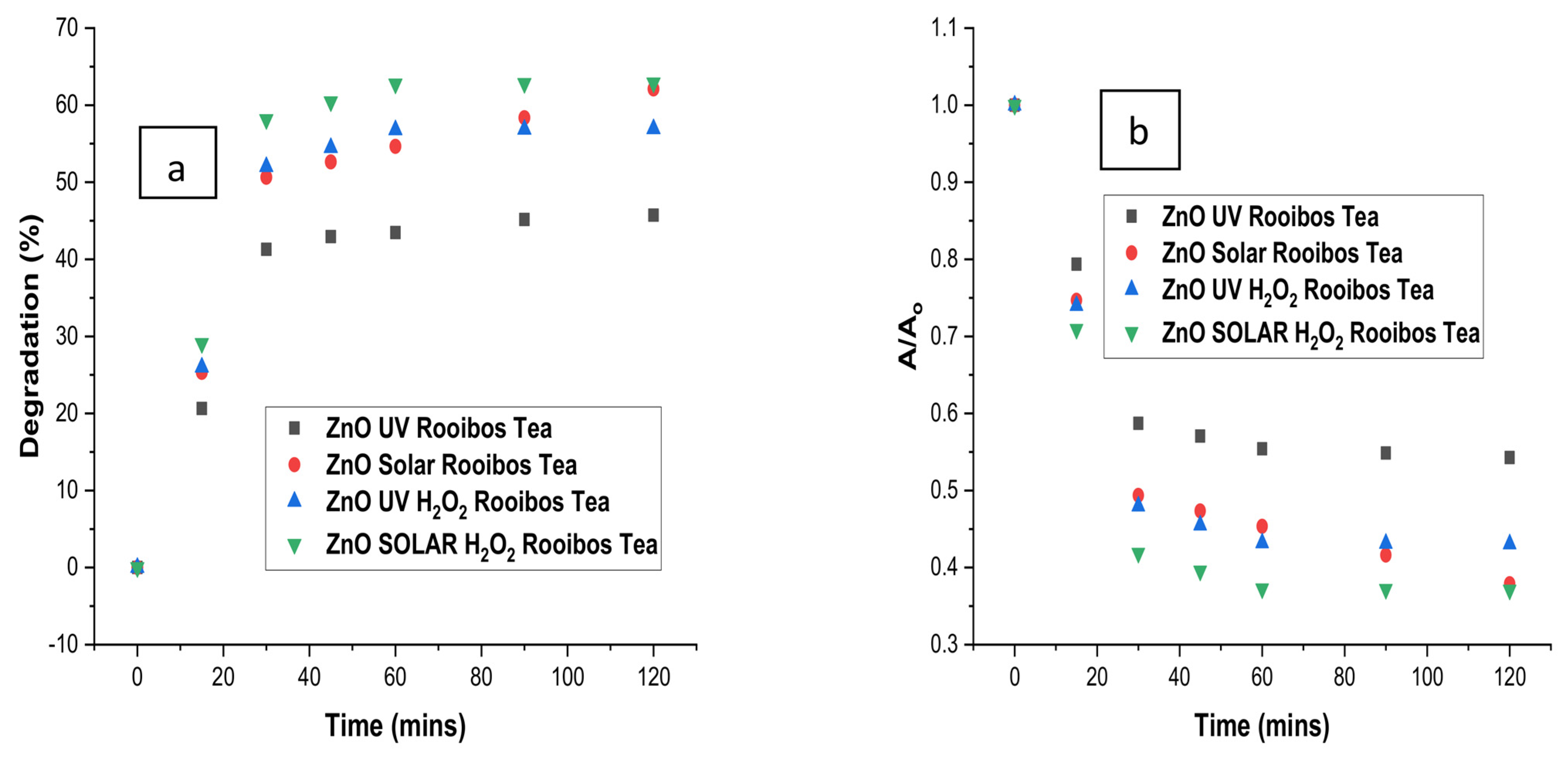
3.6. Comparison of Degradation with Time for Optimised Treatment of Rooibos Tea
3.7. Comparison of Degradation with Time for Optimised Treatment of Black Tea
3.8. Kinetic Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gardiner, A. A Study on the Water Chemistry and Plankton in Blackwater Lakelets of the South-Western Cape. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsuddin, N.; Das, D.B.; Starov, V.M. Filtration of natural organic matter using ultrafiltration membranes for drinking water purposes: Circular cross-flow compared with stirred dead end flow. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 276, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpää, M.; Ncibi, M.; Matilainen, A. Advanced oxidation processes for the removal of natural organic matter from drinking water sources: A comprehensive review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 2008, 56–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Boro, R.; Das, C. Treatment of tea industry wastewater using coagulation-spinning basket membrane ultrafiltration hybrid system. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamsal, R.; Walsh, M.; Gagnon, G. Comparison of advanced oxidation processes for the removal of natural organic matter. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3263–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. Removal of natural organic matter (NOM) and its constituents from water by adsorption—A review. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khettaf, S.; Bouramaf, R.; Benmahdi, F.; Bouhidel, K.-E.; Bouhelassa, M. Removal of the Neutral Dissolved Organic Matter (NDOM) from Surface Water by Coagulation/Flocculation and Nanofiltration. Anal. Lett. 2021, 54, 2713–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Rawindran, H.; Sinnathambi, C.; Lim, J. Comparison of various advanced oxidation processes used in remediation of industrial wastewater laden with recalcitrant pollutants. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 206, 012089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashiegbu, D.C.; Nosipho, M.; Potgieter, J.H. Improved photocatalytic activity of ZnO-[10%]BiOI and ZnO-[10%]WO3 heterostructure in the destruction of 2-chlorobiphenyl. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2023, 2, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, R. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Wastewater Treatment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosaka, Y.; Nosaka, A. Understanding Hydroxyl Radical (•OH) Generation Processes in Photocatalysis. ACS Energy Lett. 2016, 1, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirhashemi, M.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A.; Rahim Pouran, S. Review on the criteria anticipated for the fabrication of highly efficient ZnO-based visible-light-driven photocatalysts. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 62, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanavel, M.; Bankole, P.O.; Selvam, R.; Govindwa, S.P.; Sadasivam, S.K. Synergistic effect of biological and advanced oxidation process treatment in the biodegradation of Remazol yellow RR dye. Sci. Rep. 2020, 2020, 20234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amor, C.; Marchão, L.; Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Application of Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Treatment of Recalcitrant Agro-Industrial Wastewater: A Review. Water 2019, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.; Ng, L.; Mohammad, A. A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: Synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stander, M.A.; Van Wyk, B.E.; Taylor, M.J.C.; Long, H.S. Analysis of Phenolic Compounds in Rooibos Tea (Aspalathus linearis) with a Comparison of Flavonoid-Based Compounds in Natural Populations of Plants from Different Regions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10270–10281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabooter, D.; Broeckhoven, K.; Kalili, K.; Villers, A.; Desmet, G. Fast method development of rooibos tea phenolics using a variable column length strategy. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 7347–7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malongane, F.; McGaw, L.J.; Nyoni, H.; Mudau, F.N. Metabolic profiling of four South African herbal teas using high resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance. Food Chem. 2018, 257, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilainen, A.; Sillanpää, M. Removal of natural organic matter from drinking water by advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanshahi, N.; Karimi-Jashni, A. Comparison of photo-Fenton, O3/H2O2/UV and photocatalytic processes for the treatment of gray water. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štrbac, D.; Aggelopoulos, C.A.; Štrbac, G.; Dimitropoulos, M.; Novaković, M.; Ivetić, T.; and Yannopoulos, S.N. Photocatalytic degradation of Naproxen and methylene blue: Comparison between ZnO, TiO2 and their mixture. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 113, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Ahmad, Z.; Khan, A.U.; Mastoi, N.R.; Aslam, M.; Kim, J. Photocatalytic systems as an advanced environmental remediation: Recent developments, limitations and new avenues for applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4134–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.Q.; Mir, T.G.; Amin, O.; Sathish, M.; Kumar, D. Synthesis, characterization, photocatalytic effect of CuS-ZnO nanocomposite on photodegradation of Congo red and phenol pollutant. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 14, 109797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumam, T.V.A.; Panakkal, T.; Divya, T.; and Nikhila, M.P. Morphology controlled synthesis and photocatalytic activity of zinc oxide nanostructures. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 3769–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Segura, S.; Brillas, E. Applied photoelectrocatalysis on the degradation of organic pollutants in wastewaters. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2017, 31, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragavendran, C.; Kamaraj, C.; Jothimani, K.; Priyadharsan, A.; Kumar, D.A.; Natarajan, D.; Malafaia, G. Eco-friendly approach for ZnO nanoparticles synthesis and evaluation of its possible antimicrobial, larvicidal and photocatalytic applications. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2023, 36, e00597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Manoli, K.; Shen, X.; Wang, J.; Ray, A.K. Solar photocatalytic degradation of caffeine with titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 2019, 377, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tum, P.K.; Kariuki, D.K.; Oduor, F.D.O.; Wanyoko, J.K. Zinc oxide photocatalytic decolourization of black tea (Camellia Sinensis) wastewater from processing factories in Kenya. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 4, 2206–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ohland, C.; Jobin, C.; Sand, S. Degradation of black tea theaflavin through C-ring by gut microbiota. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2021, 11, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghanga, J.K.; Segor, F.K.; Etiégni, L.; Lusweti, J. Electrocoagulation method for colour removal in tea effluent: A case study of Chemomi Tea Factory in Rift Valley. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2009, 23, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaikai, W.; Sekine, M.; Tokumura, M.; Kawase, Y. UV light photo-Fenton degradation of polyphenols in oolong tea manufacturing wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2013, 49, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.; El-Amin, A. Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous TiO2 under different solar irradiation sources. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2007, 2, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Joubert, E.; De Beer, D. Rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) beyond the farm gate: From herbal tea to potential phytopharmaceutical. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2011, 77, 869–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beer, D.; Tobin, J.; Walczak, B.; van der Rijst, M.; Joubert, E. Phenolic composition of rooibos changes during simulated fermentation: Effect of endogenous enzymes and fermentation temperature on reaction kinetics. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krafczyk, N.; Glomb, M. Characterization of Phenolic Compounds in Rooibos Tea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 3368–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, D.H.; Juang, L.C.; Huang, H.H. Effect of Oxygen and Hydrogen Peroxide on the Photocatalytic Degradation of Monochlorobenzene in TiO2 Aqueous Suspension. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.L.; Xu, M. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment: Formation of Hydroxyl Radical and Application. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 251–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, N.; Salari, D.; Khatee, A. Photocatalytic degradation of azo dye acid red 14 in water on ZnO as an alternative catalyst to TiO2. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2004, 162, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, C.; Zhao, J. Mechanisms of photodecomposition of H2O2 and TiO2 surfaces under visible light irradiation. Langmuir 2001, 17, 4118–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.; Lant, P. Biodegradability of DOC and DON for UV/H2O2 pre-treated melanoidin-based wastewater. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 42, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; An, Y. Effects of zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on green algae under visible, UVA, and UVB irradiations: No evidence of enhanced algal toxicity under UV pre-irradiation. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

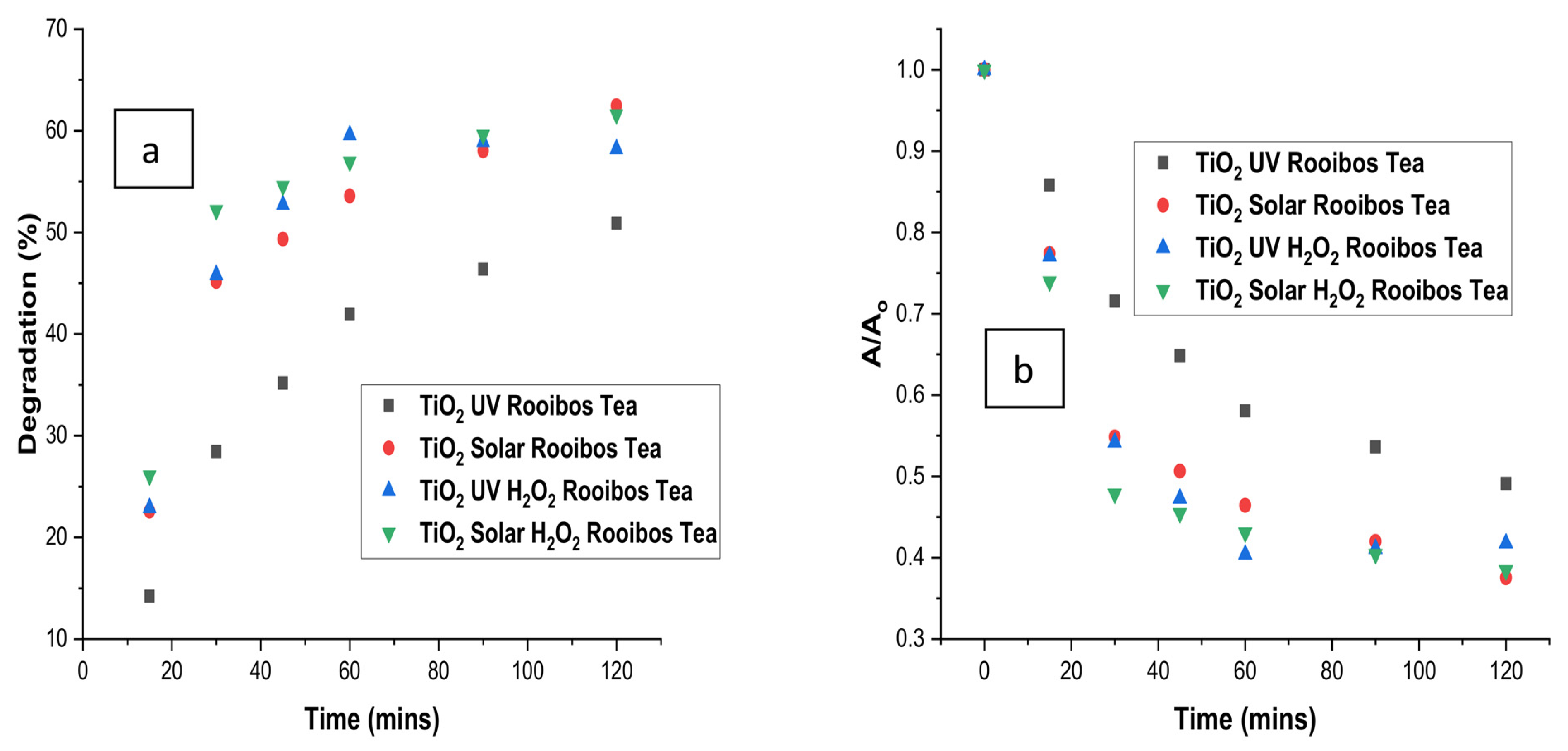
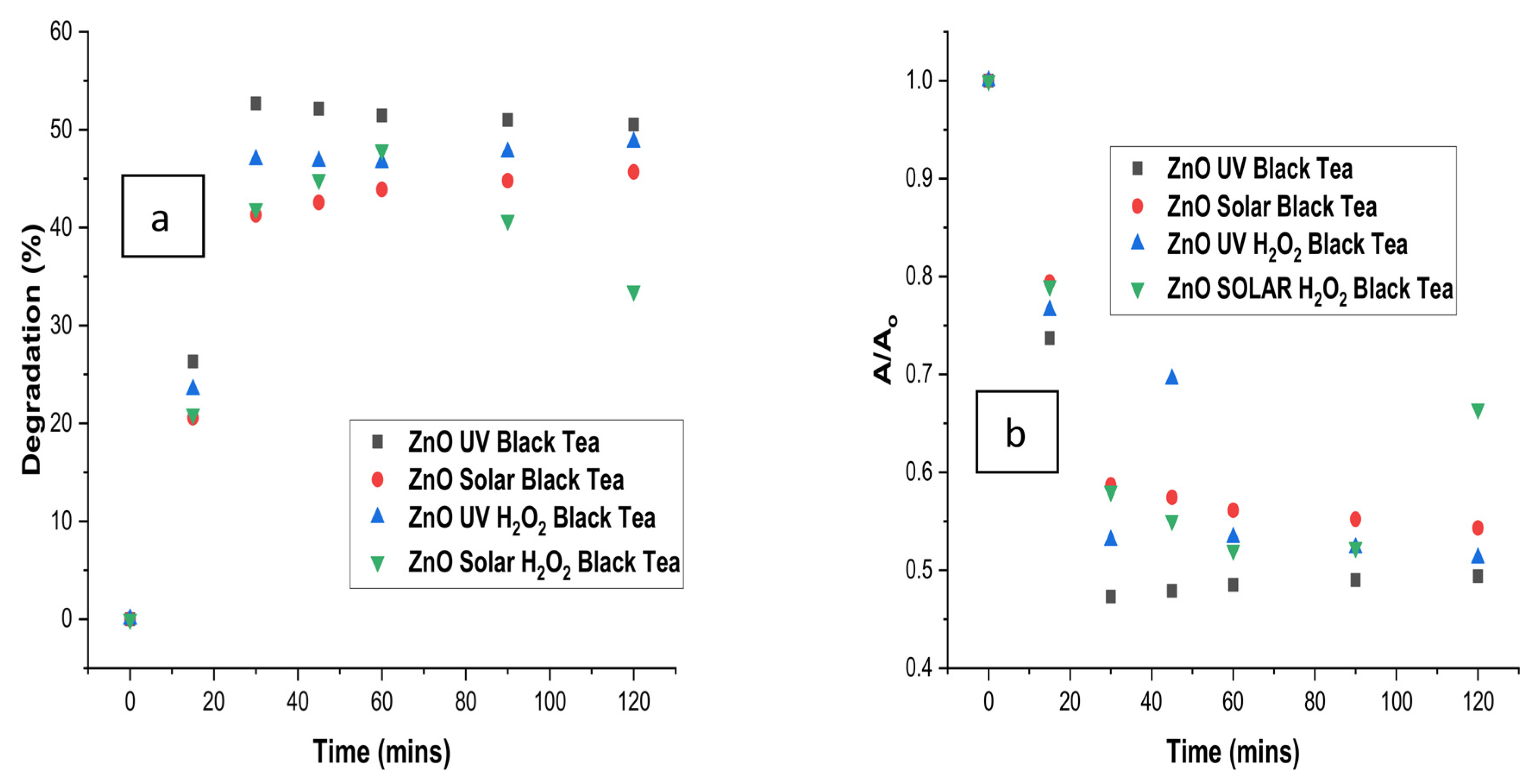
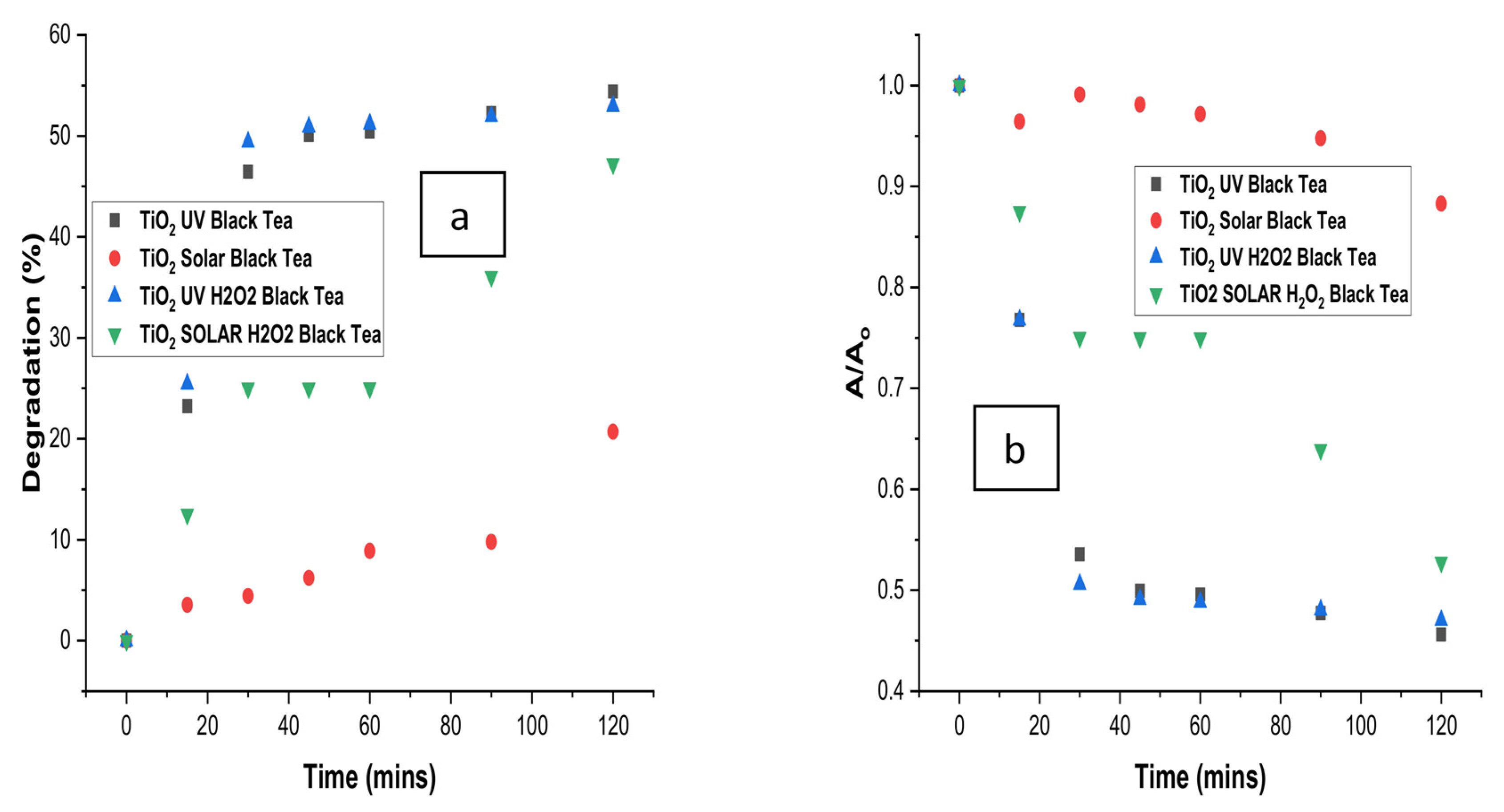
| Tea Type | Treatment Type | R2 (ln(A/Ao) | K (min−1) | R2 (1/A-1/Ao) | K2 (L mg−1 min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black | ZnO + UV | 0.349 | 0.107 | 0.931 | 0.0009 |
| Black | ZnO + Solar | 0.934 | 0.008 | 0.939 | 0.0016 |
| Black | ZnO + UV + H2O2 | 0.859 | 0.0017 | 0.235 | 0.0028 |
| Black | ZnO + SOLAR + H2O2 | 0.723 | 0.0018 | 0.499 | 0.0030 |
| Rooibos | ZnO + UV | 0.853 | 0.0070 | 0.841 | 0.0014 |
| Rooibos | ZnO + Solar | 0.899 | 0.0102 | 0.997 | 0.0068 |
| Rooibos | ZnO + UV + H2O2 | 0.849 | 0.0098 | 0.651 | 0.0024 |
| Rooibos | ZnO + SOLAR + H2O2 | 0.849 | 0.0116 | 0.659 | 0.0031 |
| Black | TiO2 + UV | 0.918 | 0.0016 | 0.929 | 0.0032 |
| Black | TiO2 + Solar | 0.915 | 0.0012 | 0.907 | 0.0013 |
| Black | TiO2 + UV + H2O2 | 0.929 | 0.0007 | 0.934 | 0.0015 |
| Black | TiO2 + SOLAR + H2O2 | 0.897 | 0.0041 | 0.885 | 0.0064 |
| Rooibos | TiO2 + UV | 0.948 | 0.0040 | 0.968 | 0.0069 |
| Rooibos | TiO2 + Solar | 0.988 | 0.0041 | 0.996 | 0.0092 |
| Rooibos | TiO2 + UV + H2O2 | 0.534 | 0.0025 | 0.629 | 0.0054 |
| Rooibos | TiO2 + SOLAR + H2O2 | 0.975 | 0.0024 | 0.984 | 0.0068 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gordon, A.; Leaper, M.C.; Potgieter, H.; Ashiegbu, D.; Sibanda, V. Treatment of Dark Humic Water Using Photocatalytic Advanced Oxidation (PAO) Processes under Visible and UV Light. Clean Technol. 2023, 5, 852-865. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5030042
Gordon A, Leaper MC, Potgieter H, Ashiegbu D, Sibanda V. Treatment of Dark Humic Water Using Photocatalytic Advanced Oxidation (PAO) Processes under Visible and UV Light. Clean Technologies. 2023; 5(3):852-865. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5030042
Chicago/Turabian StyleGordon, Alexandra, Mark C. Leaper, Herman Potgieter, Darlington Ashiegbu, and Vusumuzi Sibanda. 2023. "Treatment of Dark Humic Water Using Photocatalytic Advanced Oxidation (PAO) Processes under Visible and UV Light" Clean Technologies 5, no. 3: 852-865. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5030042
APA StyleGordon, A., Leaper, M. C., Potgieter, H., Ashiegbu, D., & Sibanda, V. (2023). Treatment of Dark Humic Water Using Photocatalytic Advanced Oxidation (PAO) Processes under Visible and UV Light. Clean Technologies, 5(3), 852-865. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5030042









