Offshore Electrical Grid Layout Optimization for Floating Wind—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bottom-Fixed Literature Approaches
2.1. Objectives and Common Constraints
2.2. Topologies
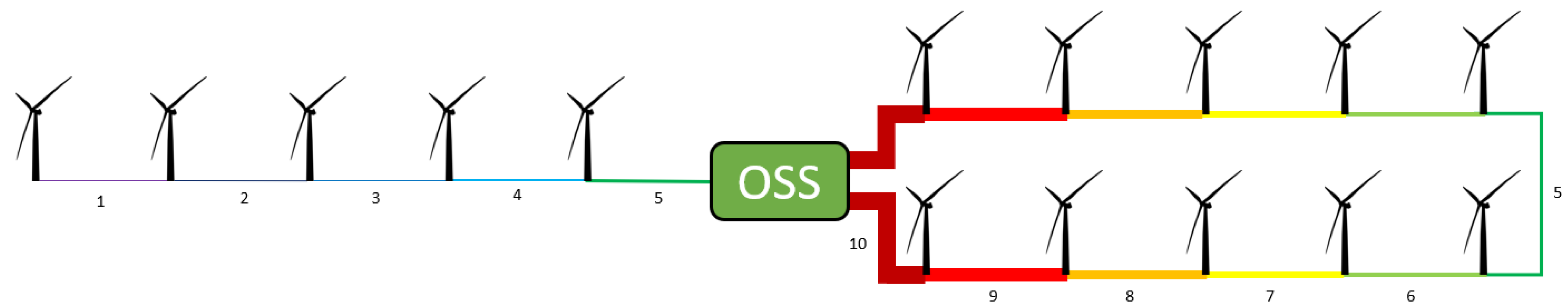
2.2.1. Branched Topology
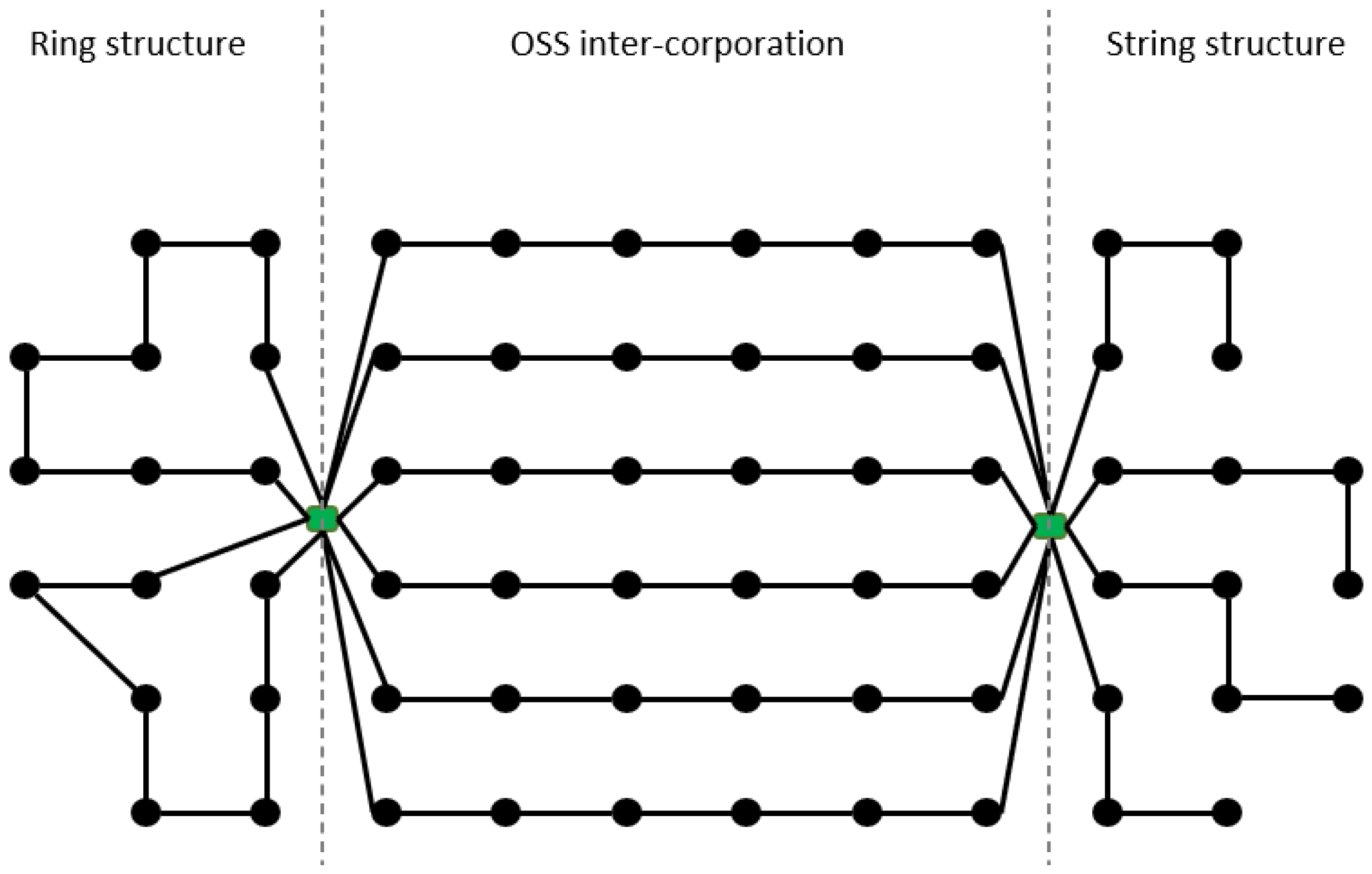
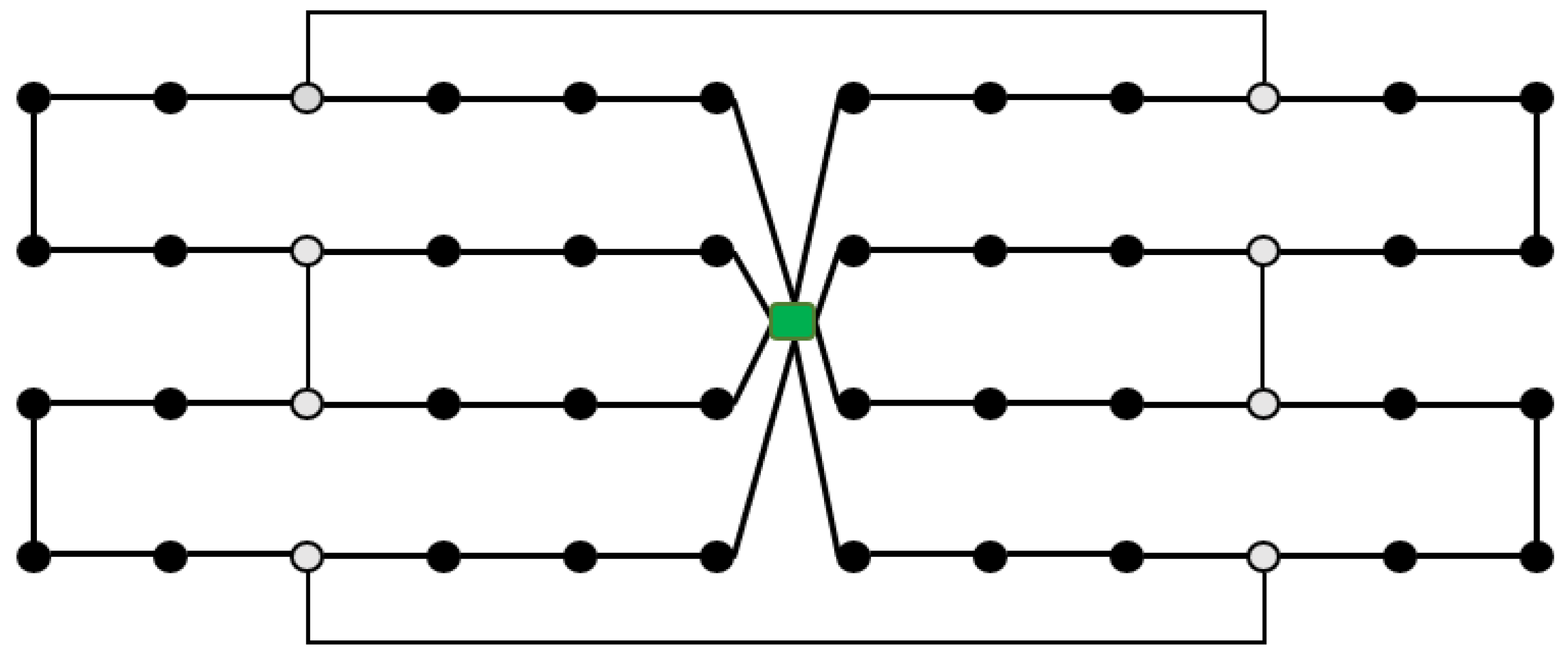
2.2.2. Ring Structure
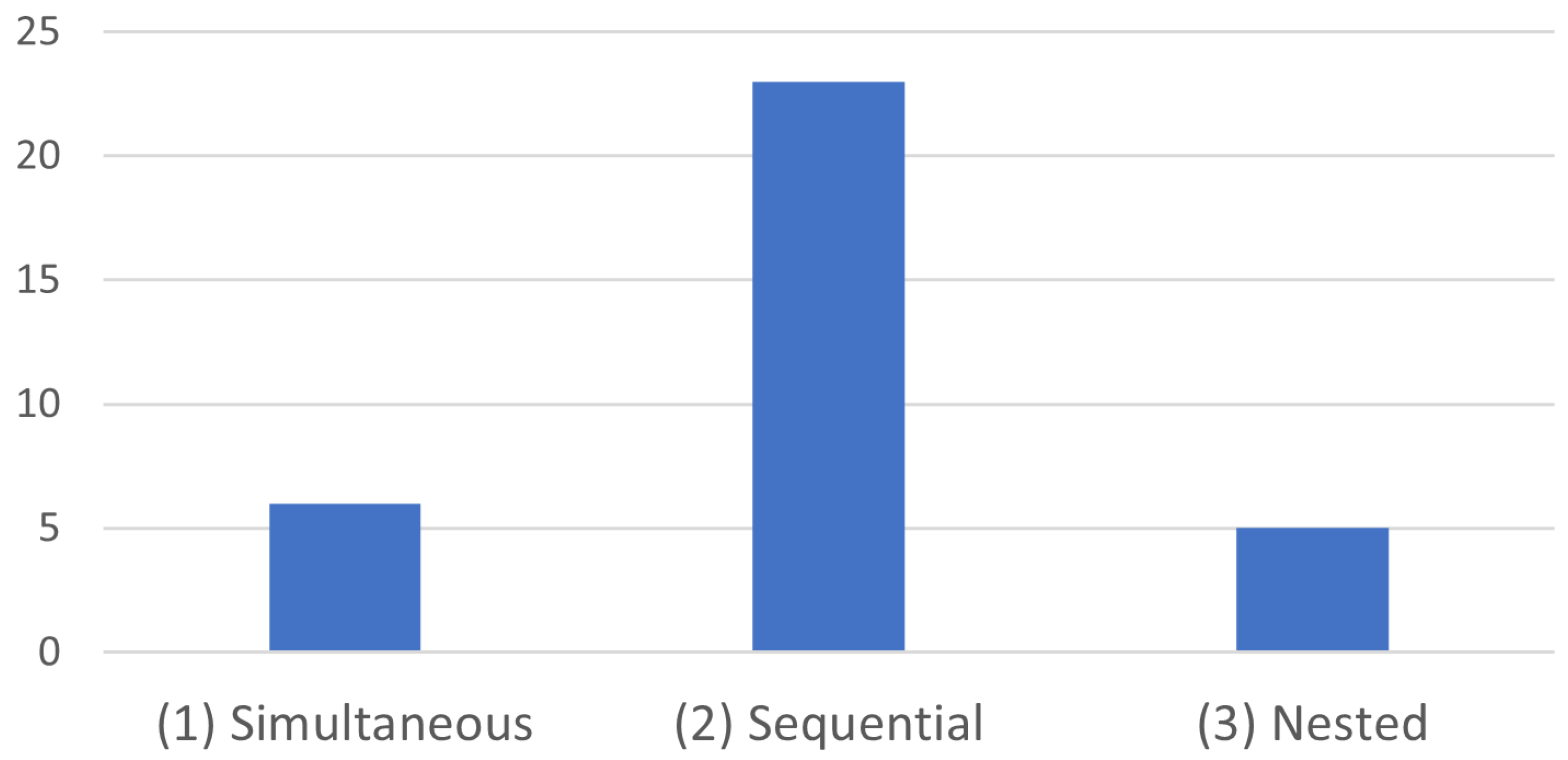
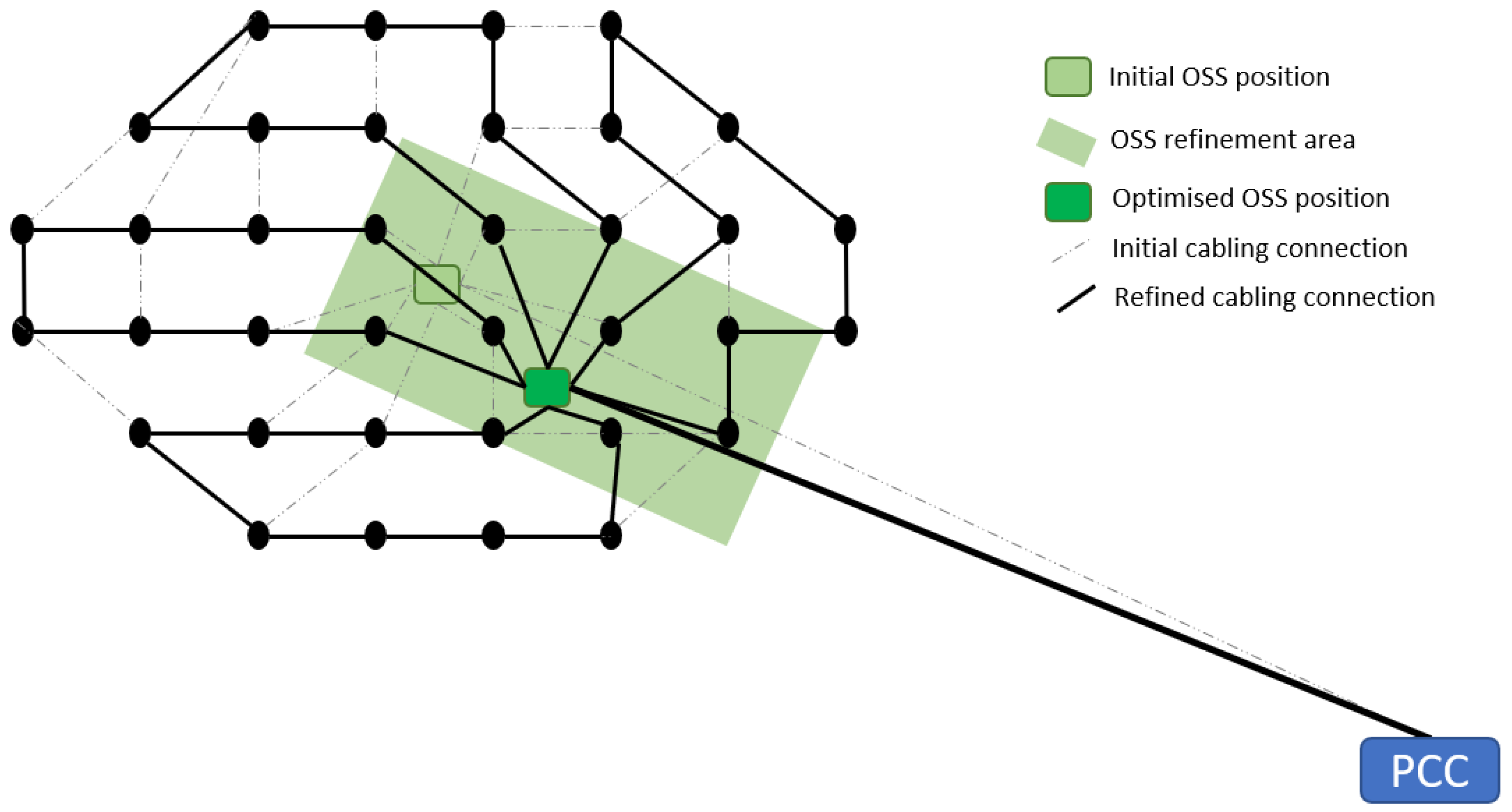
2.3. Clustering and OSS Positioning
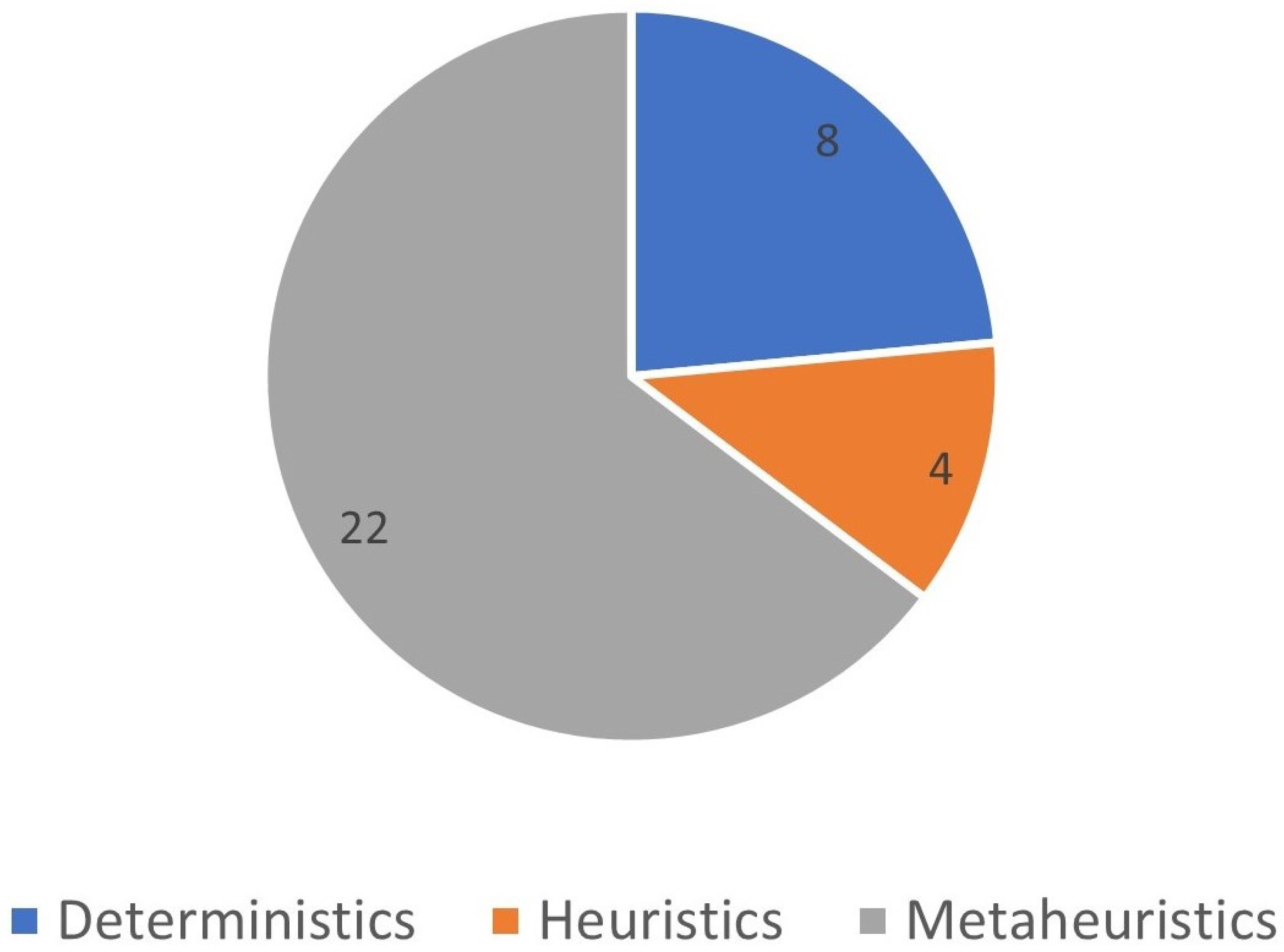
2.4. Optimization Techniques of the Inter-Array Cabling
2.4.1. Deterministics
2.4.2. Heuristics
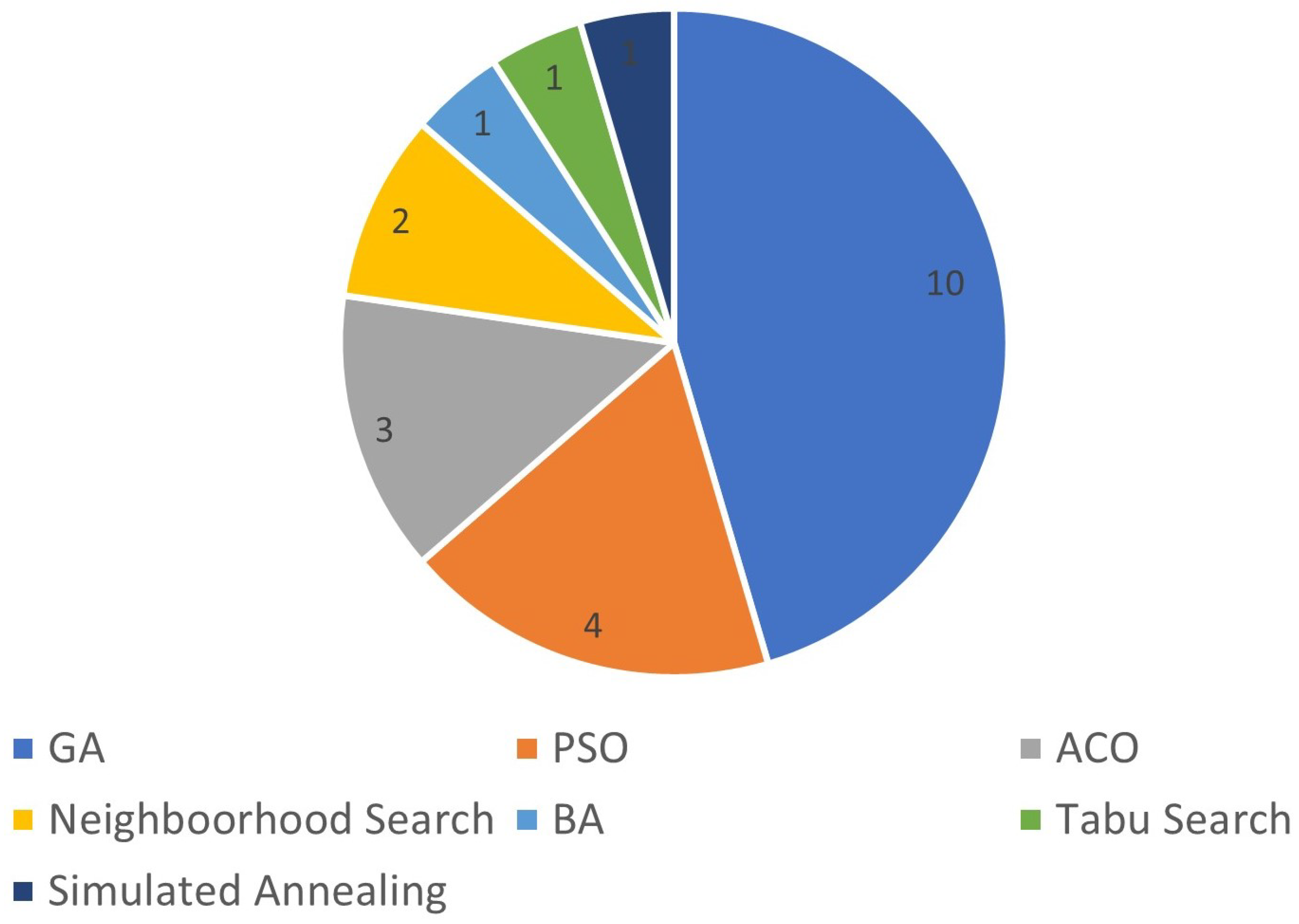
2.4.3. Metaheuristics
Genetic Algorithm
Particle Swarm Optimization
Ant Colony Optimization
Bat Algorithm
Neighborhood Search and Others
2.5. Comparison of Methodologies Used in the Literature
3. Floating Offshore Wind
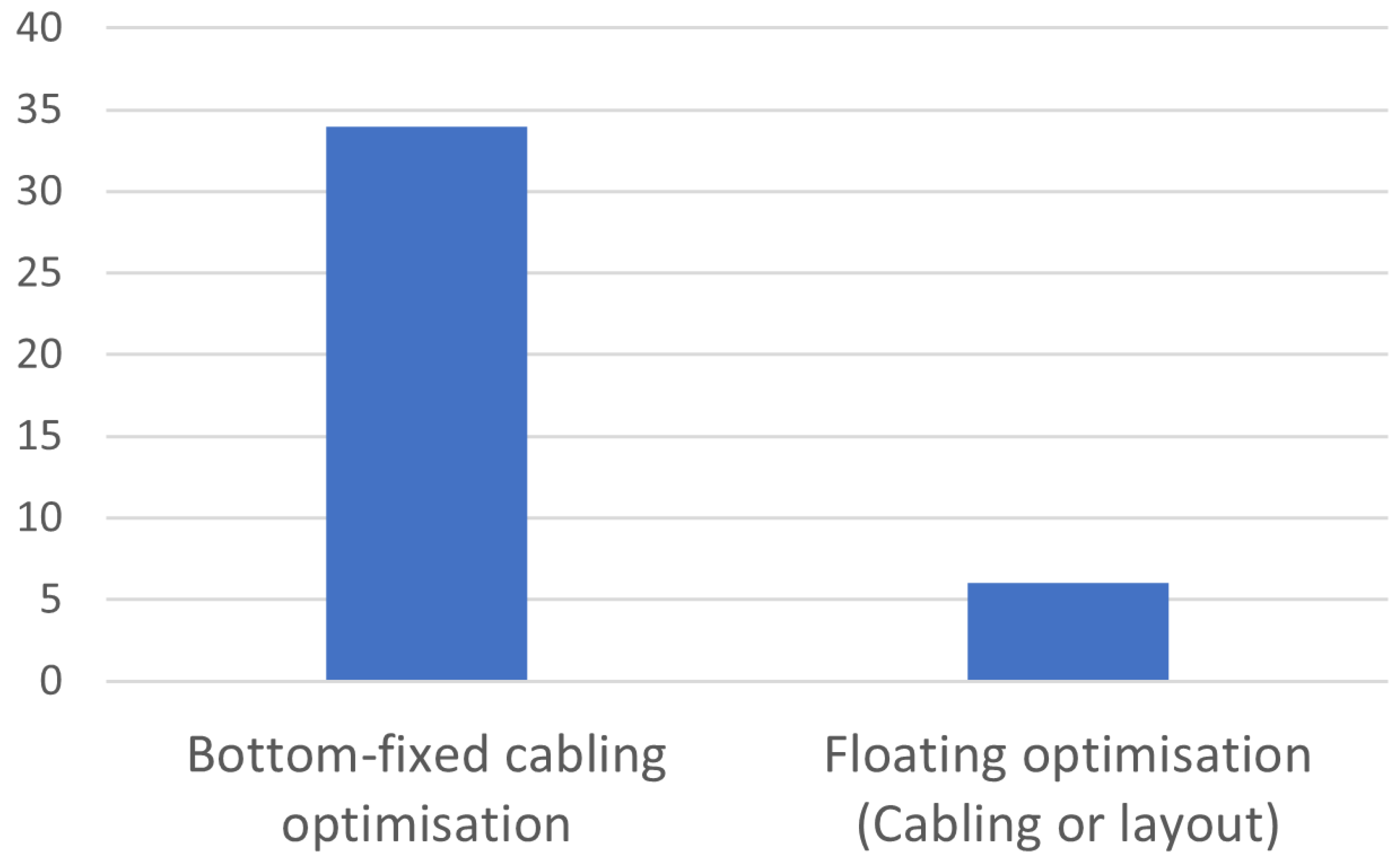
3.1. FOWF Inter-Array Cabling Optimization
3.2. FOWT Positioning
4. Discussion
4.1. Cabling Configuration
4.2. Station-Keeping System and Allowable Offsets
4.3. Bathymetry
4.4. Power Losses
4.5. OSS Positioning
4.6. Topology and Reliability
4.7. Incorporation of Multiple OWFs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AEP | Annual Energy Production |
| AC | Alternating Current |
| ACO | Ant Colony optimization |
| BA | Bat Algorithm |
| CAPEX | CAPital EXpenditure |
| DC | Direct Current |
| DECEX | DECommissioning EXpenditure |
| EENS | Expected Energy Not Supplied |
| FCM | Fuzzy C-Means (clustering) |
| FOWF | Floating Offshore Wind Farm |
| FOWT | Floating Offshore Wind Turbine |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| HOP | Hang-Off Point |
| HV | High Voltage |
| IA | Inter Array (cabling) |
| LCOE | Levelized Cost Of Energy |
| MTTR | Mean Time To Repair |
| MST | Minimum Spanning Tree |
| OPEX | OPerational EXpenditures |
| OSS | Offshore Substation |
| OTM | Offshore Transformer Module |
| OWF | Offshore Wind Farm |
| PCC | Point of Common Coupling |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| SA | Simulated Annealing |
| TDP | TouchDown Point |
| TLP | Tension-Leg Platform |
| TS | Tabu Search |
| VNS | Variable Neighborhood Search |
| WT | Wind Turbine |
References
- Lee, J.; Zhao, F.; Dutton, A.; Backwell, B.; Qiao, L.; Liang, W.; Clarke, E.; Lathigara, A.; Shardul, M.; Smith, M.; et al. Global Offshore Wind Report 2021; Technical Report; GWEC. 2021. Available online: https://gwec.net/global-offshore-wind-report-2021/ (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Pérez-Rúa, J.A.; Cutululis, N.A. A framework for simultaneous design of wind turbines and cable layout in offshore wind. Wind Energy Sci. 2022, 7, 925–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano González, J.; Burgos Payán, M.; Santos, J.M.R.; González-Longatt, F. A review and recent developments in the optimal wind-turbine micro-siting problem. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 30, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhennicheu, M.; Lynch, M.; Doole, S.; Borisade, F.; Wendt, F.; Schwarzkopf, M.A.; Matha, D.; Vicente, R.D.; Habekost, T.; Ramirez, L.; et al. D3.1 Review of the state of the art of dynamic cable system design. COREWIND. European Commission. 2020. Available online: https://corewind.eu/wp-content/uploads/files/publications/COREWIND-D3.1-Review-of-the-state-of-the-art-of-dynamic-cable-system-design.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Pérez-Rúa, J.A.; Cutululis, N. Electrical Cable Optimization in Offshore Wind Farms—A review. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 85796–85811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Zhu, J.; Ma, K.; Yang, G.; Hu, W.; Chen, Z. A review of offshore wind farm layout optimization and electrical system design methods. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2019, 7, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumbreras, S.; Ramos, A. Offshore wind farm electrical design: A review. Wind Energy 2013, 16, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemens Energy. New AC Grid Access Solution from Siemens: Lighter, Faster, Cheaper. 2015. Available online: https://press.siemens-energy.com/global/en/pressrelease/new-ac-grid-access-solution-siemens-lighter-faster-cheaper (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Cazzaro, D.; Pisinger, D. Balanced cable routing for offshore wind farms with obstacles. Networks 2022, 80, 386–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Abeynayake, G.; Liang, J.; Wang, K. Reliability and Economic Evaluation of Offshore Wind Power DC Collection Systems. Energies 2021, 14, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, A.; de Villiers, P.; Fitzgerald, B.; Matthiesen, J. Benefits in moving the intra-array voltage from 33 kV to 66 kV AC for large offshore wind farms. Carbon Trust 2012, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Young, D. Predicting Dynamic Subsea Cable Failure for Floating Offshore Wind; Technical Report; ORE Catapult. 2018. Available online: https://ore.catapult.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Predicting-Dynamic-Subsea-Cable-Failure-for-Floating-Wind-David-Young-AP-0016.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Wei, S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, F. Hierarchical Optimization for the Double-Sided Ring Structure of the Collector System Planning of Large Offshore Wind Farms. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2017, 8, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, K.; Tong, Z.; Dong, Z.Y.; Fu, Y. A Two-Layer Hybrid Optimization Approach for Large-Scale Offshore Wind Farm Collector System Planning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 7433–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmani, O.; Bourguet, S.; Machmoum, M.; Guerin, P.; Rhein, P.; Josse, L. Optimization and Reliability Evaluation of an Offshore Wind Farm Architecture. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2017, 8, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.C. GA based algorithms for offshore wind farm collector cable optimization. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2362, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.S.; Kim, J.O. Optimal Design for Offshore Wind Farm considering Inner Grid Layout and Offshore Substation Location. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, A.; Chick, J.; Johanning, L.; Khorasanchi, M. Offshore wind farm layout optimization using particle swarm optimization. J. Ocean Eng. Mar. Energy 2018, 4, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.W.; Wang, Y. Collection line optimization in wind farms using improved ant colony optimization. Wind Eng. 2020, 45, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Scutariu, M.; Smith, K. Optimization of offshore wind farm inter-array collection system. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2019, 13, 1990–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Li, S.; Li, H. Large-scale Offshore Wind Farm Electrical Collector System Planning: A Mixed-Integer Linear Programming Approach, 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.08569. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, K.; Tong, Z.; Dong, Z.Y.; Fu, Y. Collector System Topology Design for Offshore Wind Farm’s Repowering and Expansion. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2021, 12, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, K.; Dong, Z.Y. Collector System Topology for Large-Scale Offshore Wind Farms Considering Cross-Substation Incorporation. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2020, 11, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Meng, K.; Tong, Z.; Tang, Y.; Dong, Z.H. Offshore wind farm collector system layout optimization based on self-tracking minimum spanning tree. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2019, 29, e2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Overbye, T. A clustering based wind farm collector system cable layout design. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Power and Energy Conference, Urbana, IL, USA, 25–26 February 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Overbye, T.J. Optimal Wind Farm Collector System Topology Design Considering Total Trenching Length. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2012, 3, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzaro, D.; Fischetti, M.; Fischetti, M. Heuristic algorithms for the Wind Farm Cable Routing problem. Appl. Energy 2020, 278, 115617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, S.; Ergun, H.; Van Hertem, D. Application of Association Rule Mining in offshore HVAC transmission topology optimization. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 211, 108358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rúa, J.A.; Stolpe, M.; Das, K.; Cutululis, N. Global Optimization of Offshore Wind Farm Collection Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2020, 35, 2256–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rúa, J.A.; Lumbreras, S.; Ramos, A.; Cutululis, N.A. Reliability-based topology optimization for offshore wind farm collection system. Wind Energy 2022, 25, 52–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerveira, A.; Pires, E.J.S.; Baptista, J. Wind Farm Cable Connection Layout Optimization with Several Substations. Energies 2021, 14, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rúa, J.A.; Stolpe, M.; Cutululis, N.A. Integrated Global Optimization Model for Electrical Cables in Offshore Wind Farms. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2020, 11, 1965–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.; Haugland, D. Obstacle-aware optimization of offshore wind farm cable layouts. Ann. Oper. Res. 2019, 272, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulku, I.; Alabas-Uslu, C. Optimization of cable layout designs for large offshore wind farms. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 6297–6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marge, T.; Lumbreras, S.; Ramos, A.; Hobbs, B.F. Integrated offshore wind farm design: Optimizing micro-siting and cable layout simultaneously. Wind Energy 2019, 22, 1684–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulku, I.; Uslu, C. Optimization of offshore wind farm cable layouts. In Proceedings of the The Sixth European Conference on Renewable Energy Systems, Istanbul, Turkey, 25–27 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Rúa, J.A.; Lumbreras, S.; Ramos, A.; Cutululis, N. Closed-Loop Two-Stage Stochastic Optimization of Offshore Wind Farm Collection System. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1618, 042031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumbreras, S.; Ramos, A. Optimal design of the electrical layout of an offshore wind farm applying decomposition strategies. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 1434–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano González, J.; Trigo García, A.L.; Burgos Payán, M.; Riquelme Santos, J.; González Rodríguez, A.G. Optimal wind-turbine micro-siting of offshore wind farms: A grid-like layout approach. Appl. Energy 2017, 200, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Kuenzel, S.; Pal, B. Optimal Wind Farm Cabling. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2017, 9, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershenbaum, A. Computing capacitated minimal spanning trees efficiently. Networks 1974, 4, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.H. Genetic Algorithms. Sci. Am. 1992, 267, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Tang, Z.; Wang, T. An Integration Optimization Method for Power Collection Systems of Offshore Wind Farms. Energies 2019, 12, 3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, B.; Pereira, R.; Wade, C. Investigation of offshore wind farm layouts regarding wake effects and cable topology. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1222, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Feng, Y.; Liu, K.; Fu, Y. Optimization of Power Collector System for Large-scale Offshore Wind Farm Based on Topological Redundancy Assessment. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 194, 03025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Feng, X. A design methodology for wind farm layout considering cable routing and economic benefit based on genetic algorithm and GeoSteiner. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Lysgaard, J. The offshore wind farm array cable layout problem: A planar open vehicle routing problem. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2015, 66, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhl, D.; Warme, D.M.; Winter, P.; Zachariasen, M. The GeoSteiner software package for computing Steiner trees in the plane: An updated computational study. Math. Program. Comput. 2018, 10, 487–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roetert, T.; Raaijmakers, T.; Borsje, B. Cable route optimization for offshore wind farms in morphodynamic areas. In Proceedings of the 27th International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference, ISOPE 2017, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 June 2017; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA, 2017; pp. 595–606. [Google Scholar]
- Lerch, M.; De-Prada-Gil, M.; Molins, C. A metaheuristic optimization model for the inter-array layout planning of floating offshore wind farms. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 131, 107128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Hou, P.; Liu, G.; Jin, R.; Yang, Z.; Yang, G.; Dong, Z. Cable Connection Optimization for Heterogeneous Offshore Wind Farms via a Voronoi Diagram Based Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization with Local Search. Energies 2021, 14, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Xu, Q.; Feijóo, A.; Zheng, G. Joint Optimization of Wind Turbine Micrositing and Cabling in an Offshore Wind Farm. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mokhi, C.; Addaim, A. Optimization of Wind Turbine Interconnections in an Offshore Wind Farm Using Metaheuristic Algorithms. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Hou, P.; Yang, G.; Qi, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z. Cable routing optimization for offshore wind power plants via wind scenarios considering power loss cost model. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Yang, G.; Hu, W.; Chen, C.; Soltani, M.; Chen, Z. Cable Connection Scheme Optimization for Offshore Wind Farm Considering Wake Effect. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Hu, W.; Soltani, M.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z. Combined optimization for offshore wind turbine micro siting. Appl. Energy 2017, 189, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, A.; Chick, J.; Johanning, L.; Khorasanchi, M.; de Laleu, V. Offshore wind farm electrical cable layout optimization. Eng. Optim. 2015, 47, 1689–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Hu, W.; Chen, Z. Optimization for offshore wind farm cable connection layout using adaptive particle swarm optimization minimum spanning tree method. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2016, 10, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pookpunt, S.; Ongsakul, W. Optimal placement of wind turbines within wind farm using binary particle swarm optimization with time-varying acceleration coefficients. Renew. Energy 2013, 55, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.; Yue, H.; Campos-Gaona, D.; Anaya-Lara, O.; Jia, C. Wind farm array cable layout optimization for complex offshore sites - a decomposition based heuristic approach. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2023, 17, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischetti, M.; Pisinger, D. Optimizing wind farm cable routing considering power losses. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 270, 917–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischetti, M.; Pisinger, D. Optimal wind farm cable routing: Modeling branches and offshore transformer modules. Networks 2018, 72, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.S. A New Metaheuristic Bat-Inspired Algorithm. In Nature Inspired Cooperative Strategies for Optimization (NICSO 2010); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Hou, P.; Yang, L.; Yang, G. Simultaneous Optimization of Cable Connection Schemes and Capacity for Offshore Wind Farms via a Modified Bat Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, M.; Patnaik, L. Adaptive probabilities of crossover and mutation in genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1994, 24, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, A.C.; Chick, J.; Khorasanchi, M.; Barbouchi, S.; Johanning, L. Application of an offshore wind farm layout optimization methodology at Middelgrunden wind farm. Ocean Eng. 2017, 139, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Cohanim, B.; de Weck, O.; Venter, G. A Comparison of Particle Swarm Optimization and the Genetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 46th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 18–21 April 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhart, R.; Kennedy, J. A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In Proceedings of the MHS’95 Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science, Nagoya, Japan, 4–6 October 1995; pp. 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapha, J.I.; Domínguez, J.L. Suspended cable model for layout optimization purposes in floating offshore wind farms. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2018, 012033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.B.; Schnepf, A.; Ong, M.C. An optimization methodology for suspended inter-array power cable configurations between two floating offshore wind turbines. Ocean Eng. 2023, 278, 114406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerch, M.; De-Prada-Gil, M.; Molins, C. Collection Grid Optimization of a Floating Offshore Wind Farm Using Particle Swarm Theory. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1356, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banzo, M.; Ramos, A. Stochastic Optimization Model for Electric Power System Planning of Offshore Wind Farms. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 26, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.; Teixeira Pinto, R.; Soleimanzadeh, M.; Bosman, P.A.; Bauer, P. Wake losses optimization of offshore wind farms with moveable floating wind turbines. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 89, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annoni, J.; Seiler, P.; Johnson, K.; Fleming, P.; Gebraad, P. Evaluating wake models for wind farm control. In Proceedings of the 2014 American Control Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 4–6 June 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirabadi, A.C.; Nagamune, R. Real-time relocation of floating offshore wind turbine platforms for wind farm efficiency maximization: An assessment of feasibility and steady-state potential. Ocean Eng. 2020, 208, 107445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano González, J.; Burgos Payán, M.; Riquelme Santos, J.M.; González Rodríguez, A.G. Optimal Micro-Siting of Weathervaning Floating Wind Turbines. Energies 2021, 14, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfouz, M.Y.; Cheng, P.W. A passively self-adjusting floating wind farm layout to increase the annual energy production. Wind Energy 2023, 26, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanos, E.M.; Bottasso, C.L.; Tamaro, S.; Manolas, D.I.; Riziotis, V.A. Vertical wake deflection for floating wind turbines by differential ballast control. Wind Energy Sci. 2022, 7, 1641–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-García, N.; Kontos, S.; Pegalajar-Jurado, A.; Horcas, S.G.; Bredmose, H. Investigation of the floating IEA Wind 15 MW RWT using vortex methods Part I: Flow regimes and wake recovery. Wind Energy 2022, 25, 468–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bills, G. Offshore Wind’s Reactive Power. 2022. Available online: https://www.infrastructureinvestor.com/offshore-winds-reactive-power/ (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Schwarzkopf, M.A.; Borisade, F.; Matha, D.; Kallinger, M.D.; Mahfouz, M.Y.; Duran Vicente, R.; Munoz, S. D4.1 Identification of floating-wind-specific O&M requirements and monitoring technologies. COREWIND. European Commission. 2020. Available online: https://corewind.eu/wp-content/uploads/files/publications/COREWIND-D4.1-Identification-of-floating-wind-specific-O-and-M-requirements-and-monitoring-technologies.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Avanessova, N.; Gray, A.; Lazakis, I.; Thomson, R.C.; Rinaldi, G. Analysing the effectiveness of different offshore maintenance base options for floating wind farms. Wind Energy Sci. 2022, 7, 887–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, S.; Van Brusselen, K.; Van Hertem, D.; Ergun, H. A Techno-Economic MILP Optimization of Multiple Offshore Wind Concessions. In Proceedings of the Wind Energy Science Conference 2019 (WESC 2019), Cork, Ireland, 17–20 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, S.; Ergun, H.; Van Hertem, D. A Greedy Algorithm for Optimizing Offshore Wind Transmission Topologies. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2022, 37, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Huang, L.L.; Ren, Z.X.; Jia, F. Optimization of offshore grid planning considering onshore network expansions. Renew. Energy 2022, 181, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, P.; Verzijlbergh, R. The Impact of Wakes from Neighboring Wind Farms on the Production of the IJmuiden Ver Wind Farm Zone; Technical Report; Whiffle and TU Delft: Delft, The Netherlands, 2022; Available online: https://whiffle.nl/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/The-impact-of-wakes-from-neighboring-wind-farms-IJmuiden.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2023).




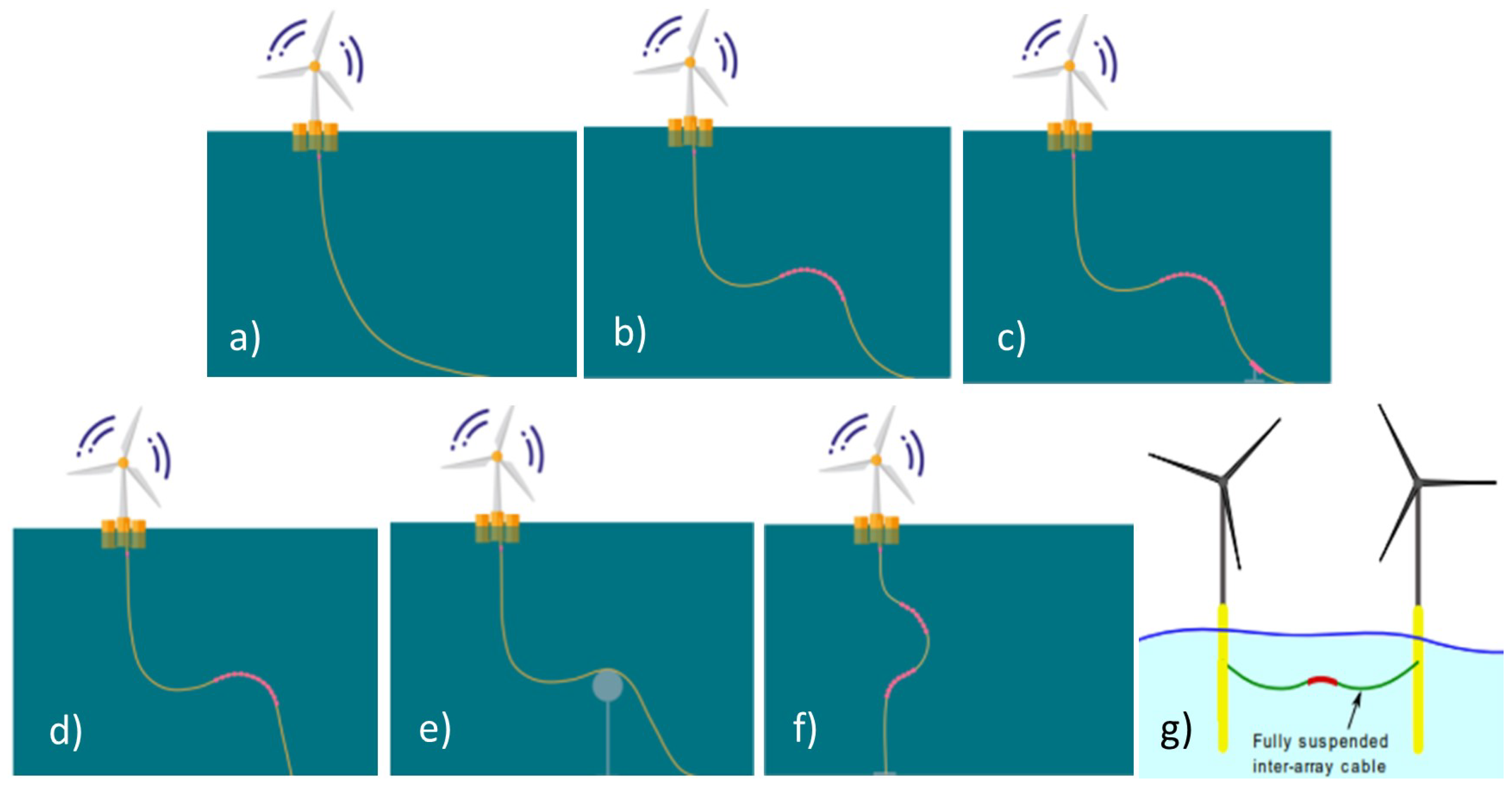

| Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) Catenary | Free hanging to seabed |
|
|
| (b) Lazy wave | Attached buoyancy modules provide lift at midwater cable section |
|
|
| (c) Tethered wave | Similar to lazy wave with additional tether restraining TDP |
|
|
| (d) Steep wave | Similar to lazy wave but connection to seabed junction is made vertically via bend stiffener |
|
|
| (e) Lazy S | Similar to lazy wave but with subsea buoy (fixed or floating) creating mid-water arch |
|
|
| (f) Chinese lantern | U-shaped slacked keeping tether vertically aligned with HOP |
|
|
| (g) w-shaped | Suspended between floaters without touching seabed and aided by buoyancy modules |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kallinger, M.D.; Rapha, J.I.; Trubat Casal, P.; Domínguez-García, J.L. Offshore Electrical Grid Layout Optimization for Floating Wind—A Review. Clean Technol. 2023, 5, 791-827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5030039
Kallinger MD, Rapha JI, Trubat Casal P, Domínguez-García JL. Offshore Electrical Grid Layout Optimization for Floating Wind—A Review. Clean Technologies. 2023; 5(3):791-827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5030039
Chicago/Turabian StyleKallinger, Magnus Daniel, José Ignacio Rapha, Pau Trubat Casal, and José Luis Domínguez-García. 2023. "Offshore Electrical Grid Layout Optimization for Floating Wind—A Review" Clean Technologies 5, no. 3: 791-827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5030039
APA StyleKallinger, M. D., Rapha, J. I., Trubat Casal, P., & Domínguez-García, J. L. (2023). Offshore Electrical Grid Layout Optimization for Floating Wind—A Review. Clean Technologies, 5(3), 791-827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5030039







