Abstract
The high-elevation ecosystems of the Tibetan Plateau provide crucial ecosystem services including watershed protection and water provision for downstream human and wildlife communities. Thus, understanding the relationship between soil properties and vegetation under different management regimes is important as a warming climate alters these systems. This study assessed vegetation cover, quantified the distribution of soil nutrients, and examined the relationships among soil chemical properties and plant cover in the high-elevation shrublands (3300 to 3700 m) in the Qilian Mountains on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau of China. These vegetation surveys and soil sample collections were conducted on 15 shrubland plots at different soil depths and soil chemical properties were investigated at each elevation. The content of soil organic matter (SOM), total nitrogen (TN), available phosphorus (AP), and available potassium (AK) fluctuated along the elevational gradient, while soil pH was close to neutral (pH 7.4). At our sites, SOM and TN contents generally increased with elevation, and AK was positively correlated with Salix plant cover. Using PCA, we determined that PC1 captured 43% of the total variance, and SOM and TN were the top contributing features. As climate in the region warms and precipitation becomes more variable, understanding the current soil–vegetation equilibria and how vegetation may migrate in future years is important to predicting changes in this region, especially at high elevations. From a managerial perspective, our goal was to provide additional information for restoring and managing subalpine and alpine shrubland vegetation in the Qilian Mountains to ensure the future sustainable use of these systems.
1. Introduction
Soil physicochemical properties are key indicators for measuring the function and structure of terrestrial ecological systems and are closely linked to vegetation type with significant variation in nutrient stocks, nutrient cycling, and energy flux in the soil [1,2]. Accurately assessing the soil nutrient status under different vegetation types is of great significance for ecological restoration, vegetation protection, and the sustainable management of altered ecosystems [3]. For example, in the southern Alps, subalpine shrubs maintained higher concentrations of soil carbon than adjacent grasslands but were more susceptible to surface soil erosion and supported less biodiversity [4]. In the French and Austrian Alps, the succession of montane grassland to shrublands increased soil organic matter contents but decreased pH and phosphorus availability, demonstrating that shrub encroachment altered soil properties [5]. In the Spanish Pyrenees, subalpine shrub expansion into grasslands led to an increase in the C:N ratio and a decrease in soil N, P, and K contents, which may have been caused by (1) lowered nutrient inputs from domestic herbivore dung and (2) the transfer of nutrients from the soil to the shrub biomass [6].
In western China, the climatic and hydrological conditions of the Qilian Mountain region (16,133 km2) supports four forest types: deciduous broad-leaved shrublands, deciduous broad-leaved forests, evergreen coniferous forests, and mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forests. Among these, deciduous broad-leaved shrublands account for most of the total forested area of the Qilian Mountains, and they have a role in regional ecological environmental protection, particularly for water quality and quantity [7,8,9,10]. The Qilian Mountains are in the northeastern region of the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau, a vast high elevation region that is the headwaters to many of the major rivers in Asia. Thus, this region and the sustainable management of its ecosystems are of major importance.
Global climate models currently predict a warmer and wetter Tibetan Plateau in the future, and recent studies of the effects of climate change on vegetation on the Tibetan Plateau have demonstrated increases in grassland, forest, and shrubland cover while barren land is decreasing [11]. In addition, Wang et al. [11] reported increases in vegetation cover at higher elevations. In the northeastern region of the Plateau (our study region), significant vegetation greening trends were observed from 2000 to 2021 due to continuous increases in temperature and water availability [12]. In addition, from 1990 to 2019, Lu et al. [13] reported that increasing temperatures caused an upward movement of the greenness isoline at middle and high elevations (>4000 m) of the Plateau, indicating that vegetation was migrating due to changes in regional climate.
Currently, there is considerable research on the alpine shrublands of the Qilian Mountains, but it is mainly focused on stoichiometric characteristics [14,15], hydro-ecological functions [10,16], protection and management [17], and the influence of grazing on plant communities [18]. In addition, much research has focused on the invasion of shrubs into grassland communities at higher elevations on the Tibetan Plateau, and the effects of this succession on biodiversity and soil nutrients [19,20]. In the Qilian Mountains, patches of four different subalpine shrub species had soil organic matter (SOM) and macronutrient (N, P, and K) concentrations that varied according to patch species and soil depth [21]. In a watershed close to our research site, Ma et al. [22] indicated that soil fertility under Salix gilashanica C. Wang & P.Y. Fu was greater than under five other subalpine shrub types.
The present study examined the alpine shrublands of the Pailugou watershed in the Qilian Mountains, and the plant species and vegetation cover were documented for experimental plots located on an elevational gradient. A primary research objective was to estimate soil pH, soil organic matter (SOM), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), total potassium (TK), available phosphorus (AP), and available potassium (AK) at different depths and elevations to explore relationships among soil chemical factors and vegetative cover and compare our findings with prior studies in the region. A second research objective was to establish baseline data for these shrub communities so changes in species composition and soil physicochemical properties could be tracked in future years as the climate continues to change in this region. Our primary hypothesis was that SOM would increase with elevation and that changes in plant cover with elevation would be positively correlated with soil chemical properties. From a managerial perspective, our goal was to provide additional information for restoring and managing subalpine and alpine shrubland vegetation in the Qilian Mountains to ensure the future sustainable use of these systems.
2. Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
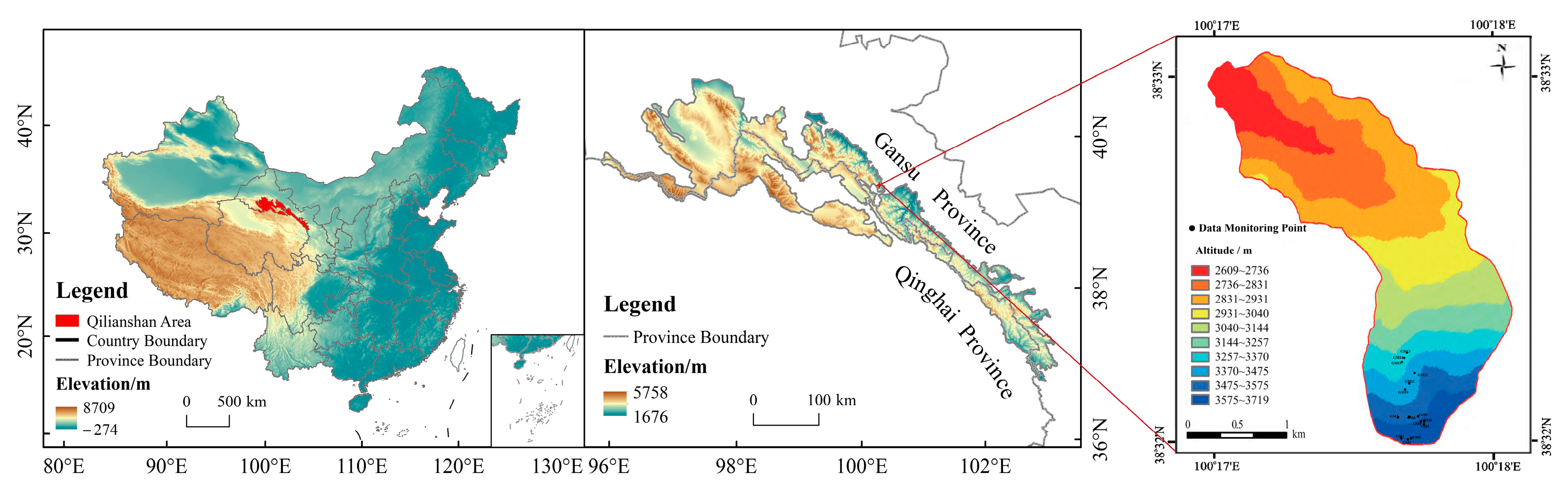
The study area was the Pailugou watershed on the northern section of the Qilian Mountains (38°24′ N, 100°17′ E). This watershed is the site of long-term ecological studies by the Gansu Qilian Mountain Water Conservation Forest Research Institute, headquartered in Zhangye, Gansu Province, China. The total area of the watershed is 2.85 km2, with a length of 4.25 km and an elevation range from 2600 to 3800 m. The average annual temperature ranges from −0.6 to 2.0 °C, with an average annual sunshine duration of 1893 h. The mean total solar radiation is 110 kW m−2. The area receives an average annual precipitation of 434 mm, with an average annual evaporation rate of 1081 mm, and has an average annual relative humidity of 60%. The climate is classified as montane, cold, and semi-arid [17].
Complex natural conditions and hydrothermal conditions within the watershed have given rise to vegetation and soil types that vary with elevation. Vegetation types are mountain grassland vegetation, mountain forest/grassland vegetation, subalpine shrub meadow vegetation, and alpine snow vegetation (Figure 1). The soils in the watershed are Entisols (Primosols) and Inceptisols (Cambisols) with Holocene loess (silty loam) predominant in the surface horizons. Locally, these soils are classified as mountain brown calcic soil, mountain gray-brown soil, subalpine shrub meadow soil, and alpine cold desert soil (from lower to higher elevation). Among these, mountain gray-brown soils and subalpine shrub meadow soils support forests. The mountain gray-brown soil between 2600–3300 m coincides with the distribution of spruce (Picea crassifolia Kom.) forests; the subalpine shrub meadow soil between 3300 to 3800 m coincides with moist hardwood shrub forests (Figure 1). Dominant shrub species include golden dewberry (Potentilla fruticosa L.), ghost arrow mallow (Caragana jubata (Pall.) Poir), Spiraea alpina Pall., and gila willow (Salix gilashanica C. Wang & P.Y. Fu).

Figure 1.
Location and elevational gradients of the Pailugou watershed in the Qilian Mountains [23].
The Pailugou Basin was declared on 14 May of 2019, by the China National Forestry and Grassland Administration, as a protected area, under the name Qilian Mountain National Park, supervised by the Zhangye Branch of Gansu Provincial Administration. Under this status, human activity, except for livestock grazing, was forbidden. Seasonal grazing of the subalpine shrublands by sheep and yak varies across the watershed.
2.2. Plot Layout
We selected the subalpine shrub community of the Pailugou experimental watershed (3300 to 3700 m) as the research site based on its representativeness for the area and linkage to other research efforts in the Pailugou research watershed. This is also the elevational band which currently supports the alpine shrub communities. Three 10 × 10 m plots were chosen at 100 m elevation intervals (15 plots total). In August 2020, we surveyed the distribution of shrub communities using a Global Positioning System (GPS) and recorded the latitude and longitude, elevation, aspect, and percent slope in the center of each sample plot. Then, each plot was divided into 5 × 5 m subplots using a grid method, and the average height, basal diameter, percent plant coverage (visual estimation of cover classes), and growth condition of the plants within the subplots were determined.
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
For each plot, triplicate soil samples were collected using a 2 cm diameter soil auger across five depth intervals: 0–10, 10–20, 20–30, and 30–40 cm. After separating plant residues, gravel, and other debris, soil samples were bagged, homogenized, and labeled for transport to the laboratory. Sample aliquots were air-dried, sieved through 1 mm and 0.149 mm mesh sieves, and ground. Soil analysis included the following: pH, soil organic matter (SOM), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), total potassium (TK), available phosphorus (AP), and available potassium (AK). Sample preparation and analysis were completed using standardized methods [24,25]. Soil pH was determined using potentiometry (Thermo Scientific Orion Star A211, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and soil organic matter (SOM) was determined using the potassium dichromate oxidation external heating method and analyzed with a spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UV-1800, Kyoto, Japan). Soil total nitrogen (TN) was determined using the semi-micro Kjeldahl method and analyzed with the FOSS Kjeltec™ 8400 (FOSS Analytical, Hillerod, Denmark). Total phosphorus (TP) and total potassium (TK) were determined using a sodium hydroxide decomposition technique [26]. After fusion, in nickel crucibles, phosphorus reacts with ammonium molybdate to form phosphomolybdenum blue for colorimetric measurement (Spectrophotometer Shimadzu UV-1800, Shimadzu, Japan). For TK, after fusion, K ions were measured by flame photometer (emission at 766.5 nm, Agilent 240FS AA, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Soil available phosphorus was determined using the Olsen method followed by spectrophotometry (700 nm). Soil available potassium was determined using the ammonium acetate extraction–flame photometry method. The potassium concentration in the filtrate was estimated using a flame photometer (766.5 nm emission, Sherwood Model 410, Sherwood Scientific, Cambridge, UK).
2.4. Data Analysis and a Comparison with Prior Studies
Statistical analyses, including the Pearson correlation analysis and one-way ANOVA (and ensuing Tukey’s HSD), were performed using SPSS 20.0. Because samples at each elevation were bulked, we performed a one-way ANOVA on each soil variable for elevation and a one-way ANOVA on each soil variable at depth. For the correlations between soil chemical properties and plant cover, we used a logit transformation on percent plant cover. To compare our results with prior studies at similar elevations in the Qilian Mountains, we developed predictive models for soil properties using a second-order polynomial regression. Principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted in R (R Core Team 2023).
3. Results
3.1. Soil Nutrients and pH at Different Elevations in Alpine Shrubland
The vegetation on all plots was composed of the four species: Potentilla fruticosa, Salix gilashanica, Caragana jubata, and Spiraea alpina. Shrub cover ranged from 91 to 99% with a mean of 95%. S. gilashanica covered the most area on average, followed by C. jubata, P. fruticosa, and S. alpina in declining order (Table 1).

Table 1.
Vegetation in the alpine shrubland sample plots of the Qilian Mountains.
There was significant variation in soil nutrients and pH at different elevations in our study plots (Table 2 and Table 3). Many variables were significantly different with elevation as an independent variable, while depth did not have much of an effect (Table 2 and Table 4). Soil pH was neutral and ranged from 7.13 to 7.83, with an average of 7.42 (Table 3). Soil pH generally decreased with increasing elevation. TN ranged from 5.60 to 7.21 g kg−1, found at 3300 m and 3500 m, respectively. There were no significant differences for TN at 3500 m, 3600 m, and 3700 m (p > 0.05).

Table 2.
One-way ANOVA p-values for soil variables with elevation and depth as independent variables.

Table 3.
Soil chemical properties (mean ± s.d.) at different elevations in alpine shrubland (0–40 cm).

Table 4.
Mean soil chemical properties (±SE) at depth intervals in alpine shrublands.
Total phosphorus generally increased with elevation, ranging from 0.53 to 0.66 g kg−1, with an average of 0.60 g kg−1. Between 3300 and 3700 m, available P in the soil represents only 1.8% to 2.2% of the TP content. This indicated that over 98% of the TP in the study area is not readily utilized or absorbed by the shrubs and other plants. Total soil potassium content was highest at 3600 m with 19.7 g kg−1, and lowest at 3700 m with 18.1 g kg−1. Soil available K in the soil was highest at 3500 m (98.6 g kg−1) and lowest at 3700 m (92.0 g kg−1). The Tukey HSD test identified significant differences between the 3300 m and 3500 m groups for SOM, pH, and TN (Table 3).
3.2. Variation in Soil Chemical Properties Across Depth Intervals Along an Elevational Gradient
There were few significant differences among soil depth intervals (Table 4). SOM and TN ranged from 175 to 182 g kg−1 and 6.03 to 7.10 g kg−1, respectively. In the 0–30 cm layer, SOM content was highest at 3500 m and was lowest at 3300 m. In the 30–40 cm layer, SOM content generally increased with elevation. Soil TN varied with increasing elevation, and soil pH increased with depth (Table 4). TP content ranged from 0.61 to 0.58 g kg−1, with an average of 0.60 g kg−1. In contrast, available P in the surface layer was 13.6 mg kg−1, which was significantly higher than the AP content in the 20–30 cm layer (p < 0.05). The Tukey HSD test for AK at different soil depths revealed significant differences between the 0–10 cm and 20–30 cm depths (p = 0.003) and the 0–10 cm and 30–40 cm depths (p = 0.002).
3.3. Correlation Among Soil Chemical Properties
Soil organic matter had a significant and positive correlation (r = Pearson correlation coefficient) with TN (p < 0.01) and a significant and positive correlation with AP (p < 0.05). Additionally, there was a significant negative correlation between SOM and pH (p < 0.01). Soil pH was negatively correlated with TN (p < 0.01), TP, AP, and AK (p < 0.05). Additionally, TN and AP were positively correlated (p < 0.05), but TP and AP were not (Table 5).

Table 5.
Correlation (r) among soil chemical properties in the subalpine shrub.
3.4. Principal Component Analysis
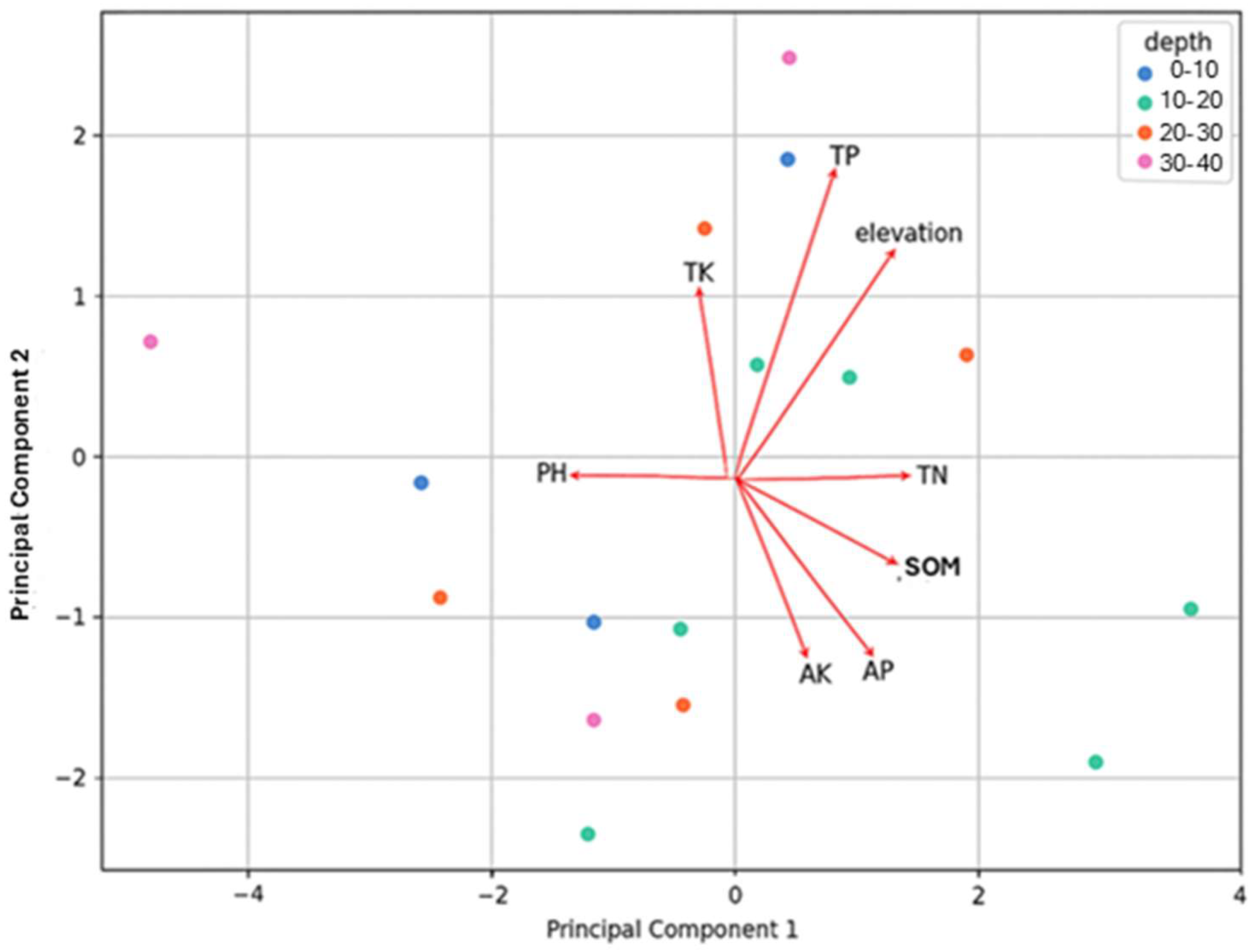
PC1 captured the largest amount of variance (43%) and the top contributing features for PC1 were TN, SOM, pH, and elevation. PC2 captured the second largest amount of variation (25%) and the top contributing features for PC2 were TP, elevation, AK, and AP (Figure 2).
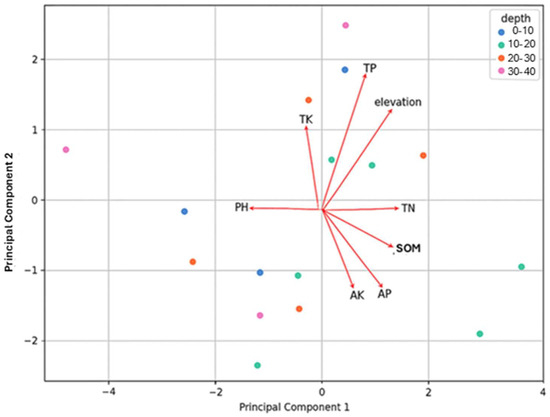
Figure 2.
PCA analysis for soils in alpine shrublands.
3.5. The Relationship Between Soil Chemical Properties and Vegetation Cover
We examined the relationships between soil properties (0–40 cm depth) and percent plant cover at all the experimental plots, and Salix had a positive correlation with AK (r = 0.8, p = 0.1). None of the other correlations had a p-value < 0.1. TN and Potentilla had a positive correlation (r = 0.75, p = 0.15), and AP had a positive correlation with Caragana (r = 0.75, p = 0.15). We also examined relationships between percent plant cover and soil properties for the surface horizon (0–10 cm depth) and pH was positively correlated with Spiraea (r = 0.69, p = 0.19), SOM was positively correlated with Potentilla (r = 0.72, p = 0.17), and AP was negatively correlated with Spiraea (r = −0.70, p-value = 0.18).
3.6. A Comparison with Prior Studies in the Qilian Mountains
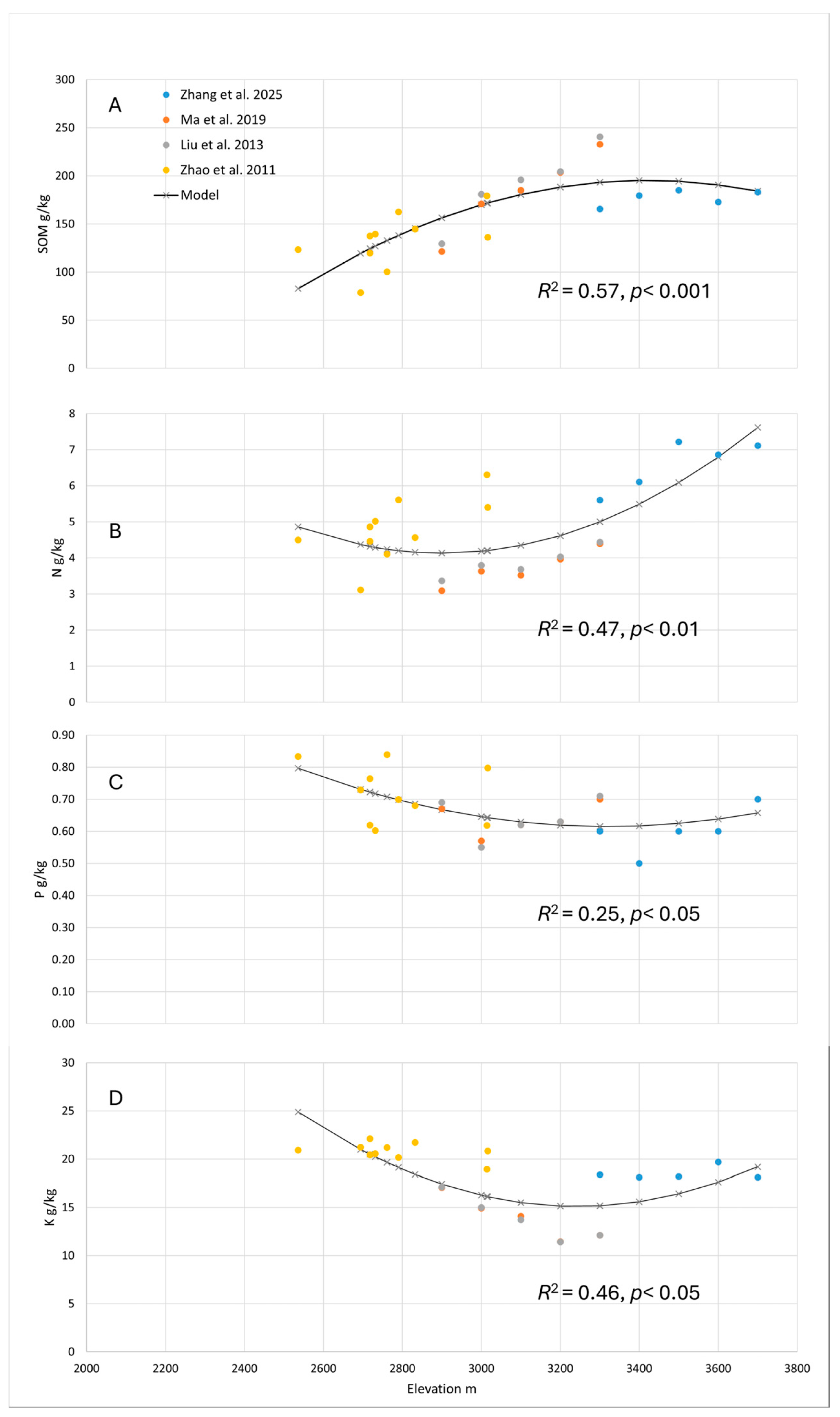
Second-order polynomial regression models were developed to predict how soil properties change with elevation. To develop the models, we used our data and data from other sites in the Qilian Mountains [27,28,29], and these models explained 57%, 47%, 25%, and 46% of the variation in SOM, TN, TP, and TK, respectively (Figure 3). The regression equations for each model were as follows: SOM = −0.000144(x2) + 0.984660(x) − 1488.506, TN = 0.000005(x2) − 0.03168(x) + 50.0945, TP = −0.001692(x) + 3.4332, TK = 0.00002(x2) − 0.12725(x) + 221.4312.

Figure 3.
Regression analysis of soil nutrients and SOM at elevational gradients in the Qilian Mountains including soil organic matter (A), total nitrogen (B), total phosphorus (C), and total potassium (D) as reported in [27,28,29] and this study.
4. Discussion
Soil Properties
Soil organic matter is critical in the development of soil structure which in turn influences soil water retention, erosion resistance, fertility, and bulk density [30]. Elevated levels of SOM, TN, and TK within the study area may be related to several factors. Subalpine shrublands are known to raise soil organic carbon and nutrient content by altering the microenvironment and increasing litter inputs to the soil [31]. Alpine shrubs in the Qilian Mountains are also known to alter soil physicochemical properties and microbial biochemical composition and activity [32]. A prior study also indicated that shrub species composition was significantly affected by elevation, slope, soil pH, and soil organic carbon, while species richness of these communities was related to slope and soil bulk density [33]. We note that our sampling took place during the month of August, which is one of the warmest months of the year at this elevation, and thus plant productivity, litterfall rates, and decomposition rates were likely elevated during our sampling period.
In other areas of the world, a changing and warming climate has shifted shrub species distribution in alpine environments and affected soil–vegetation dynamics. For example, in the Austrian Alps, earlier snowmelt in alpine shrub communities was related to shifts in bacterial and fungal community composition as well as ericaceous shrub expansion, and these changes in microbial populations were accompanied by altered soil functioning and decreased soil N availability [34]. In the Swiss Alps, the expansion of Alnus dominated shrublands in montane environments was found to convert N-poor grassland into N saturated shrubland which could potentially lead to a long-term reduction in soil C storage because the shrubs limit the re-establishment of natural montane forest [35]. In the Central Italian Alps, a survey of shrubs on a 1000 m elevational transect found that Salix shrubs, typically found in riparian forests, were encroaching into subalpine and alpine shrublands and grasslands as a result of climate change, thus changing plant species composition at higher elevations [36].
In the Qilian Mountains, the negative correlation between SOM and pH in our study was consistent with Zhang [37] who found similar trends in alpine grasslands. Low surface soil pH relative to the subsoil can be attributed to greater SOM content in surface horizons, which produces more intermediate products such as tannin and organic acids during decomposition [38]. In our study, average SOM along the elevation gradient was 177 g kg−1, which is lower than the 190 g kg−1 reported by prior research in the spruce forests of the Pailugou watershed in the Qilian Mountains [27,29]. Moreover, the “surface accumulation” effect of SOM in the spruce forests (0–10 cm depth) is stronger, with a content of 235 g kg−1, compared to the alpine shrublands, where SOM content was 182 g kg−1. This difference is attributed to the simpler vegetation structure and lower litter deposition in shrublands, which limits the “surface accumulation” effect of SOM compared to spruce forests. Jiang et al. [39] reported SOM content varied significantly under different vegetation types (p < 0.05), with SOM increasing progressively from grassland to shrubland to forest and with elevation. Finally, in a similar study of alpine shrubs in a nearby watershed, Ma et al. [22] also found that SOM and TN were the top contributing features to PC1 in their PCA.
At high elevation, soil phosphorus and nitrogen are important factors limiting vegetation growth and affecting the distribution of plant communities. Average TP for this and other studies in other regions of the Qilian Mountains were reported at less than 0.8 g kg−1, suggesting soils in the Qilian range are phosphorus deficient—irrespective of elevation [27,28,29]. Soils of the Picea crassifolia forest in the elevation band below this study (2500 to 3200 m) had an average of 0.761 g kg−1 of TP [28], which was similar to our study sites. At our sites, no significant correlation between TP and AP was observed, consistent with the findings of Song and colleagues [40] and Wang et al. [4]. In our sites, most of the TP was in plant-unavailable forms, which is ecologically significant because P limits plant productivity. Plant mycorrhizal associations may be critical for plant productivity in this environment because they aid plants in P uptake. The significant positive correlation between AP and SOM and TN (r = 0.46, r = 0.51, p < 0.05) indicated that higher levels of SOM and TN at our sites were associated with increased availability of phosphorus, perhaps via P mineralization during litter decomposition. The positive correlation between the presence of Salix and AK in our sites may be due to increased K release from growing season plant litter, as was reported in a Salix leaf decomposition experiment in India [41].
Soil chemical properties and their distribution can influence the direction of vegetation succession above ground. In turn, vegetation can affect soil nutrient properties; for example, Potentilla fruticosa can translocate P from lower depths to the soil surface [42]. Shrubs that have deeper rooting depths, wider root distributions, and mycorrhizal associations can move AP from deeper depths to the surface [42]. Caragana jubata is a nitrogen-fixing legume and likely has a positive effect on N across the sample area [43], and in general, alpine shrub patches act as aggregation centers for soil nutrients [21].
Although we did not quantify browsing damage in our plots (a limitation in this study), we noted that all the species in our experimental plots were moderately palatable to yak (Bos grunniens L.) and sheep (e.g., P. fruticosa is less palatable than S. alpina), and these shrubs are an indicator of overgrazing [44]. The Qilian Mountains have been grazed by wild and domestic yak for thousands of years [45] and many studies demonstrated that plant communities in the region are highly affected by livestock activity. Baranova et al. [46] indicated that the percentage of unpalatable and toxic plant species in the Qilian mountains is increasing, and Baranova and Schickhoff [18] reported that grazing in the Qilian Mountains by sheep, goats, and yak had a significant impact on the plant community composition. In addition, Li et al. [47] indicated that grazing intensity lowered soil organic carbon and total nitrogen stocks in numerous grasslands across the Tibetan Plateau, and grazing was reported to lower SOM, TN, and soil carbon, particularly on south-facing slopes at lower altitudes [46]. As noted, we did not quantify the extent of grazing and browsing on the vegetation in our plots, but the interaction between grazers and the vegetation that they alter as well as the influence of grazing on soil chemical properties in the alpine shrublands merits further attention.
5. Conclusions
Deciduous broad-leaved shrublands account for a large proportion of the total forested area of the Qilian Mountains in China; thus, it is important to understand soil and vegetation dynamics in these systems that will be highly affected by climate change. At our sites, SOM and TN contents generally increased with elevation, and pH decreased. Available K was positively correlated with Salix plant cover, and our sites had similar SOM, TN, TP, and TK contents compared to other sites in the Qilian Mountains. SOM, TN, and TP were also found to be the top contributing features in our PCA. Currently, the reduction in human and animal activities in the region may help minimize the destruction of alpine shrubland vegetation but may also contribute to shrub invasion of high elevation grasslands. Future research efforts should address the effects of a warmer and wetter climate at higher elevations in the Qilian Mountains, including (1) the potential migration of shrub species upwards in the Qilian Mountains and how climate alters vegetation–soil relationships in future years and (2) the effects of a decrease in livestock activity on alpine shrub and grassland communities including the effects on high-elevation biodiversity (including soil microbial communities).
Author Contributions
Project funding and supervision, J.Z., E.X. and X.R.; data collection, J.Z., W.J., R.W., X.J. and M.B.; data analysis, J.Z., M.B., X.R., A.M.E., I.D.A. and C.K.S.; writing and editing, J.Z., X.R., A.M.E., I.D.A., M.P., C.M. and C.K.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (U21A20468), Gansu Province Science and Technology Plan Project (25JRRG045, 24RCKG001, 25RCKG002, 24JRRG034), Gansu Province International Science and Technology Cooperation Project (25YFWG001), Gansu Sea Talent Project (GSHZJH 12-2025-01) and Gansu Forestry & Grassland Science and Technology Plan (2024kj104).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors have no financial or proprietary interest in any material discussed in this article.
References
- El-Ramady, H.R.; Alshaal, T.A.; Amer, M.; Domokos-Szabolcsy, É.; Elhawat, N.; Prokisch, J.; Fári, M. Soil quality and plant nutrition. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 14: Agroecology and Global Change; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 345–447. [Google Scholar]
- Puyang, X.H.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhao, Z.J.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y. Coupling relationships between vegetation and soil in different vegetation restoration models in the loess region of northern Shaanxi Province. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2021, 30, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, N.A.; Degen, A.A.; Deng, B.; Shi, F.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, T.; Long, R.; Shang, Z. Changes in vegetation parameters and soil nutrients along degradation and recovery successions on alpine grasslands of the Tibetan plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 284, 106593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornaro, C.; Schneider, M.K.; Leinauer, B.; Macolino, S. Above-and belowground patterns in a subalpine grassland-shrub mosaic. Plant Biosyst.-Int. J. Deal. All Asp. Plant Biol. 2017, 151, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laorden-Camacho, L.; Grigulis, K.; Tello-García, E.; Lyonnard, B.; Colace, M.P.; Gallet, C.; Tappeiner, U.; Leitinger, G.; Lavorel, S. Shrub encroachment modifies soil properties through plant resource economics traits. Plant Soil 2025, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, O.; Saravesi, K.; Ninot, J.M.; Geml, J.; Markkola, A.; Ahonen, S.H.; Penuelas, J. Encroachment of shrubs into subalpine grasslands in the Pyrenees modifies the structure of soil fungal communities and soil properties. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Shao, M. Patterns and driving factors of soil nutrient stoichiometry under three land use types in the alpine region of Tibet, China. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yuan, H. Disaster and prevention strategies of shrubbery in the Qilian Mountain Nature Reserve. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2005, 12, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. The role of shrubbery in the Qilian Mountain region and its development strategies. Gansu For. Sci. Technol. 2005, 30, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Study on the hydro-ecological function of shrubbery in the forest-grassland composite watershed of Qilian Mountains. Arid. Zone Geogr. 2013, 36, 922–929. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Niu, B.; He, Y.; Zu, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, X. Vegetation expansion on the Tibetan Plateau and its relationship with climate change. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anniwaer, N.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Xu, H.; Hong, S. Shifts in the trends of vegetation greenness and photosynthesis in different parts of Tibetan Plateau over the past two decades. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 345, 109851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Shen, X.; Cao, R. Elevational movement of vegetation greenness on the Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from the Landsat Satellite Observations during the Last Three Decades. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J. Study on the Ecological Stoichiometry Characteristics of Typical Shrub Communities in the Middle Section of the Northern Foothills of the Qilian Mountains; Gansu Agricultural University: Lanzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Jing, W.; Zhao, Y. Stoichiometric characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in plants and soils in typical shrubbery in the Dayankou watershed of the Qilian Mountains. Soils 2017, 49, 572–594. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W. Comprehensive evaluation of the hydrological function of subalpine shrubbery in the Xishui forest area of the Qilian Mountains. Arid. Zone Geogr. 2016, 39, 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, W.; He, Z. Characteristics of precipitation and its impact on runoff in a typical small watershed in the Qilian Mountains. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2008, 30, 776–777. [Google Scholar]
- Baranova, A.; Schickhoff, U. Mountain Pastures of Qilian Shan Under Continuous Grazing: Main Environmental Gradients, Vegetation Composition and Soil Properties. In Mountain Landscapes in Transition: Effects of Land Use and Climate Change; Sustainable Development Goals Series, Part F2672; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 555–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Sun, M.; Cao, Y.; Hu, J.; Yang, L.; Hu, J. Effects of shrub encroachment on grassland community and soil nutrients among three typical shrubby grasslands in the alpine subhumid region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 1068200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Wei, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, F. Shrub encroachment shapes soil nutrient concentration, stoichiometry and carbon storage in an abandoned subalpine grassland. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Adu, B.; Wang, J.; Fan, Y. Assessing Shrub Patch Characteristics and Soil Nutrient Distribution Patterns of Four Typical Alpine Shrub Plants in the Eastern Qilian Mountains. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Feng, Q.; Li, G.; Liu, W.; Chen, P.; Li, N.; Qian, W.; Teng, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J. Evaluation of Soil Fertility in Alpine Shrub Communities of the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China. Diversity 2025, 17, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Xu, E.; Smith, C.K.; Vrahnakis, M.; Jing, W.; Zhao, W.; Wang, R.; Jia, X.; Yan, C.; Liu, R. Changes in Surface Runoff and Temporal Dispersion in a Restored Montane Watershed on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Land 2024, 13, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Society of Soil Science. Soil Agricultural Chemistry Analysis Methods; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, B. Forest Soil Analysis Methods; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B.F.L.; Bain, D.C. A sodium hydroxide fusion method for the determination of total phosphate in soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1982, 13, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, X.; Li, G. Evaluation of soil fertility quality of Qinghai spruce forest in the middle section of Qilian Mountains. Arid. Zone Geogr. 2019, 42, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Lei, L.; Liu, X.; Jin, M.; Zhang, X.; Jing, W. Study on the physical and chemical properties of soil in Picea crassifolia forests in the eastern section of the Qilian Mountains. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 31, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, X.; Jing, W.; Fan, L. Characteristics of soil nutrient and pH changes in Qinghai spruce forest in the Pailugou watershed of Qilian Mountains. Arid. Zone Res. 2013, 30, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Bronick, C.J.; Lal, R. Soil structure and management: A review. Geoderma 2005, 124, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewnik, M.; Musielok, Ł.; Stolarczyk, M.; Mitka, J.; Gus, M. Effects of exposure and vegetation type on organic matter stock in the soils of subalpine meadows in the Eastern Carpathians. CATENA 2016, 147, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Yang, Y.; Geng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Niu, Z. Biochemical composition and function of subalpine shrubland and meadow soil microbiomes in the Qilian Mountains, Qinghai–Tibetan plateau, China. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.; Feng, Q.; Su, Y. Shrub communities and environmental variables responsible for species distribution patterns in an alpine zone of the Qilian Mountains, northwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 2015, 12, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, A.A.; Bahn, M.; Pritchard, W.J.; Newbold, L.K.; Goodall, T.; Guinta, A.; Snell, H.S.; Cordero, I.; Michas, A.; Grant, H.K.; et al. Shrub expansion modulates belowground impacts of changing snow conditions in alpine grasslands. Ecol. Lett. 2022, 25, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühlmann, T.; Körner, C.; Hiltbrunner, E. Shrub expansion of Alnus viridis drives former montane grassland into nitrogen saturation. Ecosystems 2016, 19, 968–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannone, N.; Guglielmin, M.; Casiraghi, C.; Malfasi, F. Salix shrub encroachment along a 1000 m elevation gradient triggers a major ecosystem change in the European Alps. Ecography 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D. Characteristics of soil fertility and the relationship between fertility factors in the alpine grassland of the Qilian Mountains. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2002, 11, 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, S.; Li, X.; Li, W. Analysis of soil nutrient characteristics at different elevations in the Niubeiliang Nature Reserve. J. Northwest AF Univ. 2013, 41, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Li, M.; Wang, Q. Study on soil nutrient status under different vegetation in the eastern section of the Qilian Mountains. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 18, 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Shang, Z.; Li, X. Characteristics of soil phosphorus and its influencing factors at different elevational gradients on the west slope of Helan Mountain. Pratacult. Sci. 2015, 32, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, M.A.; Zargar, M.Y.; Masoodi, N.A.; Khan, M.A. Leaf litter decomposition and nutrient release in Salix spp under temperate conditions of Kashmir valley (India). J. Hortic. For. Biotechnol. 2011, 15, 179–189. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.L.; Li, X.G. Potentilla fruticosa has a greater capacity to translocate phosphorus from the lower to upper soils than herbaceous grasses in an alpine meadow. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 228, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cheng, B.; Yang, Z.; Gao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. Nutritional characteristics of Caragana jubata shrub and distribution patterns of soil nutrients in Luya Mountain. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 17, 2287–2291. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Krüsi, B.; Li, S.; Cai, X.; Yu, F. Facilitation associated with three contrasting shrub species in heavily grazed pastures on the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Community Ecol. 2011, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhode, D.; Madsen, D.B.; Jeffrey Brantingham, P.; Dargye, T. Yaks, yak dung, and prehistoric human habitation of the Tibetan Plateau. Dev. Quat. Sci. 2007, 9, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, A.; Schickhoff, U.; Wang, S.; Jin, M. Mountain pastures of Qilian Shan: Plant communities, grazing impact and degradation status. Hacquetia 2016, 15, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Xue, Y.; Xu, J.; Xue, P.; Yan, H. Effects of Different Grazing Disturbances on the Plant Diversity and Ecological Functions of Alpine Grassland Ecosystem on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 765070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).