Soil Erosion by Wind Storms in a Pampean Semi-Arid Region of Argentina: An Environmental Magnetism Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Experimental Techniques and Magnetic Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Magnetic Properties of Eolian Soil Particles
3.2. Soil Samples
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Properties
4.2. The Entic Haplustoll and Erosion Events
4.3. Eolian Soil Particles
4.4. Eolian Erosion Events over One Year
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lal, R. Soil erosion and the global carbon budget. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mendonça-Santos, M.L.; Comerma, J. Regional assessment of soil changes in Latin America and the Caribbean. In Status of the World’s Soil Resources (SWSR)—Main Report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and Intergovernmental Technical Panel on Soils (ITPS): Rome, Italy, 2016; Chapter 12; pp. 343–382. ISBN 978-92-5-109004-6. [Google Scholar]
- Casas, R.R.; Albarracín, G.F. El Deterioro Del Suelo Y Del Ambiente En La Argentina; Fundación Ciencia, Educación y Cultura. FECIC: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2015; Volume 2, ISBN 978-950-9149-40-3. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, S.; Cherlet, M.; Ivits, E. The Global Land Outlook, 1st ed.; UNCCD: Bonn, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Buschiazzo, D.E. Management Systems in Southern South America. In Agronomy Monographs; Peterson, G.A., Unger, P.W., Payne, W.A., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2006; pp. 395–425. ISBN 978-0-89118-265-8. [Google Scholar]
- Colazo, J.C.; Carfagno, P.; Gvozdenovich, J.; Buschiazzo, D. Soil Erosion. In The Soils of Argentina; Rubio, G., Lavado, R.S., Pereyra, F.X., Eds.; World Soils Book Series; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 239–250. ISBN 978-3-319-76853-3. [Google Scholar]
- Buschiazzo, D.E.; Zobeck, T.M.; Abascal, S.A. Wind erosion quantity and quality of an Entic Haplustoll of the semi-arid pampas of Argentina. J. Arid Environ. 2007, 69, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelena, R.O.; Irurtia, C.B. Susceptibility of soil to wind erosion in La Pampa province, Argentina. Arid Land Res. Manag. 1995, 9, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimar, S.B.; Mendez, M.J.; Buschiazzo, D.E. Predicción de la erosión eólica potencial con el modelo EWEQ en dos suelos loesicos: Efectos de las condiciones climáticas. Cienc. Suelo 2011, 29, 253–264. [Google Scholar]
- Buschiazzo, D.E.; Zobeck, T.M. Validation of WEQ, RWEQ and WEPS wind erosion for different arable land management systems in the Argentinean Pampas. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2008, 33, 1839–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panebianco, J.E.; Buschiazzo, D.E. Erosion predictions with the Wind Erosion Equation (WEQ) using different climatic factors. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2008, 19, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avecilla, F.; Panebianco, J.E.; Buschiazzo, D.E. Variable effects of saltation and soil properties on wind erosion of different textured soils. Aeolian Res. 2015, 18, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colazo, J.C.; Buschiazzo, D.E. Soil dry aggregate stability and wind erodible fraction in a semiarid environment of Argentina. Geoderma 2010, 159, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oro, L.A.; Colazo, J.C.; Avecilla, F.; Buschiazzo, D.E.; Asensio, C. Relative soil water content as a factor for wind erodibility in soils with different texture and aggregation. Aeolian Res. 2019, 37, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oro, L.A.; Buschiazzo, D.E. Threshold wind velocity as an index of soil susceptibility to wind erosion under variable climatic conditions. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2009, 20, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturri, L.A.; Avecilla, F.; Hevia, G.G.; Buschiazzo, D.E. Comparing adjacent cultivated and “virgin” soils in wind erosion affected environments can lead to errors in measuring soil degradation. Geoderma 2016, 264, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.J.; Buschiazzo, D.E. Wind erosion risk in agricultural soils under different tillage systems in the semiarid Pampas of Argentina. Soil Till. Res. 2010, 106, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B.A. The magnetic properties of Quaternary aeolian dusts and sediments, and their palaeoclimatic significance. Aeolian Res. 2011, 3, 87–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royall, D. Use of mineral magnetic measurements to investigate soil erosion and sediment delivery in a small agricultural catchment in limestone terrain. Catena 2001, 46, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, K. Characteristics of magnetic susceptibility on cropland and pastureland slopes in an area influenced by both wind and water erosion and implications for soil redistribution patterns. Soil Till. Res. 2020, 199, 104568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordanova, D.; Jordanova, N.; Petrov, P. Pattern of cumulative soil erosion and redistribution pinpointed through magnetic signature of Chernozem soils. Catena 2014, 120, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijano, L.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Marie, D.C.; Gaspar, L.; Navas, A. Relevant magnetic and soil parameters as potential indicators of soil conservation status of Mediterranean agroecosystems. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 198, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, Q. Identifying soil redistribution patterns by magnetic susceptibility on the black soil farmland in Northeast China. Catena 2015, 129, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakšík, O.; Kodešová, R.; Kapička, A.; Klement, A.; Fér, M.; Nikodem, A. Using magnetic susceptibility mapping for assessing soil degradation due to water erosion. Soil Water Res. 2016, 11, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menshov, O.; Kruglov, O.; Vyzhva, S.; Nazarok, P.; Pereira, P.; Pastushenko, T. Magnetic methods in tracing soil erosion, Kharkov Region, Ukraine. Stud. Geophys. Geod. 2018, 62, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarok, P.; Kruglov, O.; Menshov, O.; Kutsenko, M.; Sukhorada, A. Mapping soil erosion using magnetic susceptibility. A case study in Ukraine. Solid Earth Discuss. 2014, 6, 831–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ed-Dakiri, S.; Etebaai, I.; Moussaoui, S.E.; Tawfik, A.; Lamgharbaj, M.; Talibi, H.E.; Dekkaki, H.C.; Taher, M. Assessing soil erosion risk through geospatial analysis and magnetic susceptibility: A study in the Oued Ghiss dam watershed, Central Rif, Morocco. Sci. Afr. 2024, 26, e02401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattakhova, L.A.; Kuzina, D.M.; Antonenko, V.V. Identification of erosion processes in the soils of the coastal territory of lake Kandrykul (Republic of Bashkortostan). Izvestiya 2025, 336, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustakim, M.; Benmansour, M.; Bouarfa, R.; Amenzou, N.E.; Benkdad, A.; Damnati, B. Evaluation of the correlation between Caesium-137 inventory, magnetic susceptibility, and organic matter content to assess soil erosion status in two agricultural fields within El Hachef watershed of northwest Morocco. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Liu, H.; Fu, S. Magnetic susceptibility characteristics of surface soils in the Xilingele grassland and their implication for soil redistribution in wind-dominated landscapes: A preliminary study. Catena 2018, 163, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.; Gonzales, H.B.; Buynevich, I.V.; Li, J.; Sankey, J.B.; Dukes, D.; Wang, G. On the development of a magnetic susceptibility-based tracer for aeolian sediment transport research. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2019, 44, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordanova, D.; Jordanova, N.; Atanasova, A.; Tsacheva, T.; Petrov, P. Soil tillage erosion estimated by using magnetism of soils—A case study from Bulgaria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 183, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INTA; Gobierno de La Pampa; Universidad Nacional de La Pampa. Inventario Integrado De Los Recursos Naturales De La Provincia De La Pampa: Clima, Geomorfología, Suelo Y Vegetación; Instituto Nacional de Tecnología Agropecuaria: Buenos Aires, Argentina; Universidad Nacional de la Pampa: Santa Rosa, Argentina, 1980; 493p.
- SMN. Servicio Meteorológico Nacional. Available online: https://www.smn.gob.ar/estadisticas (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- USDA. Soil Taxonomy: A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making an Interpreting Soil Surveys; Soil Conservation Service Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1975. Available online: https://www.amazon.com/Soil-Taxonomy-Classification-Interpreting-Surveys/dp/B000K6Y8VG (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Bianchi, A.R.; Cravero, S.A.C. Atlas Climático Digital De La República Argentina; Instituto Nacional de Tecnología Agropecuaria (INTA): Salta, Argentina, 2010; ISBN 978-987-1623-95-2.
- Aimar, S.B. Estimaciones Cualitativas y Cuantitativas de Pérdidas Por Erosión Eólica en Suelos de la Región Semiárida Pampeana Central. Masther’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional del Sur, Bahia Blanca, Argentina, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fryrear, D.W. A field dust sampler. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1986, 41, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walden, J. Sample collection and preparation. In Environmental Magnetism: A Practical Guide Technical Guide Series; Walden, J., Oldfield, F., Smith, J., Eds.; Quaternary Research Association: London, UK, 1999; pp. 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Dearing, J.A.; Dann, R.J.L.; Hay, K.; Lees, J.A.; Loveland, P.J.; Maher, B.A.; O’Grady, K. Frequency-dependent susceptibility measurements of environmental materials. Geophys. J. Int. 1996, 124, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, M.A.E.; del Moralejo, M.P.; Böhnel, H.N.; Acebal, S.G. Iron oxide mineralogy in Mollisols, Aridisols and Entisols from southwestern Pampean region (Argentina) by environmental magnetism approach. Catena 2020, 190, 104534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, M.A.E.; Lirio, J.M.; Nuñez, H.; Gogorza, C.S.G.; Sinito, A.M. Preliminary magnetic studies of lagoon and stream sediments from Chascomús Area (Argentina)—Magnetic parameters as indicators of heavy metal pollution and some results of using an experimental method to separate magnetic phases. Environ. Geol. 2005, 49, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonhardt, R. Analyzing rock magnetic measurements: The RockMagAnalyzer 1.0 software. Comput. Geosci. 2006, 32, 1420–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conover, W.J. Practical Nonparametric Statistics, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999; ISBN 978-0-471-16068-7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Roberts, A.P.; Larrasoaña, J.C.; Banerjee, S.K.; Guyodo, Y.; Tauxe, L.; Oldfield, F. Environmental magnetism: Principles and applications. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties Reactions, Occurrences and Uses; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop, D.J.; Özdemir, Ö. Magnetizations in Rocks and Minerals. In Geomagnetism Treatise on Geophysices; Schubert, G., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 5, pp. 277–336. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, A.A.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Pires, M.; de Elorriaga, E.; Martinez Uncal, C. Influencia del hidromorfismo en la susceptibilidad magnética de suelos del departamento Trenel, La Pampa (Summary). In Proceedings of the Actas de Resúmenes del Decimoquinto Encuentro del Centro Internacional de Ciencias de la Tierra, Mendoza, Argentina, 23–25 November 2020; CNEA: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, A.A.; Bidegain, J.C.; Sinito, A.M. Magnetic parameter analysis of a climosequence of soils in the Southern Pampean Region, Argentina. Geof. Int. 2011, 50, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidegain, J.C.; Rico, Y.; Bartel, A.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Jurado, S. Magnetic parameters reflecting pedogenesis in Pleistocene loess deposits of Argentina. Quat. Int. 2009, 209, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samus, M.L.G.; Rico, Y.; Bidegain, J.C. Señal magnética en suelos del centro de la provincia de Buenos Aires, Argentina. Lat. Am. J. Sedimentol. Basin Anal. 2016, 23, 93–110. [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop, D.J.; Özdemir, Ö. Rock Magnetism: Fundamentals and Frontiers, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997; ISBN 978-0-521-00098-7. [Google Scholar]
- King, J.; Banerjee, S.K.; Marvin, J.; Özdemir, Ö. A comparison of different magnetic methods for determining the relative grain size of magnetite in natural materials: Some results from lake sediments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1982, 59, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschiazzo, D.E.; Taylor, V. Efectos de la erosión eólica sobre algunas propiedades de suelos de la Región Semiárida Pampeana Central. Cienc. Suelo 1993, 10, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Chepil, W.S. Soil Conditions That Influence Wind Erosion; United States Department of Agriculture’s Economic Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1958; p. 28.
- Kok, J.F.; Parteli, E.J.R.; Michaels, T.I.; Karam, D.B. The physics of wind-blown sand and dust. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

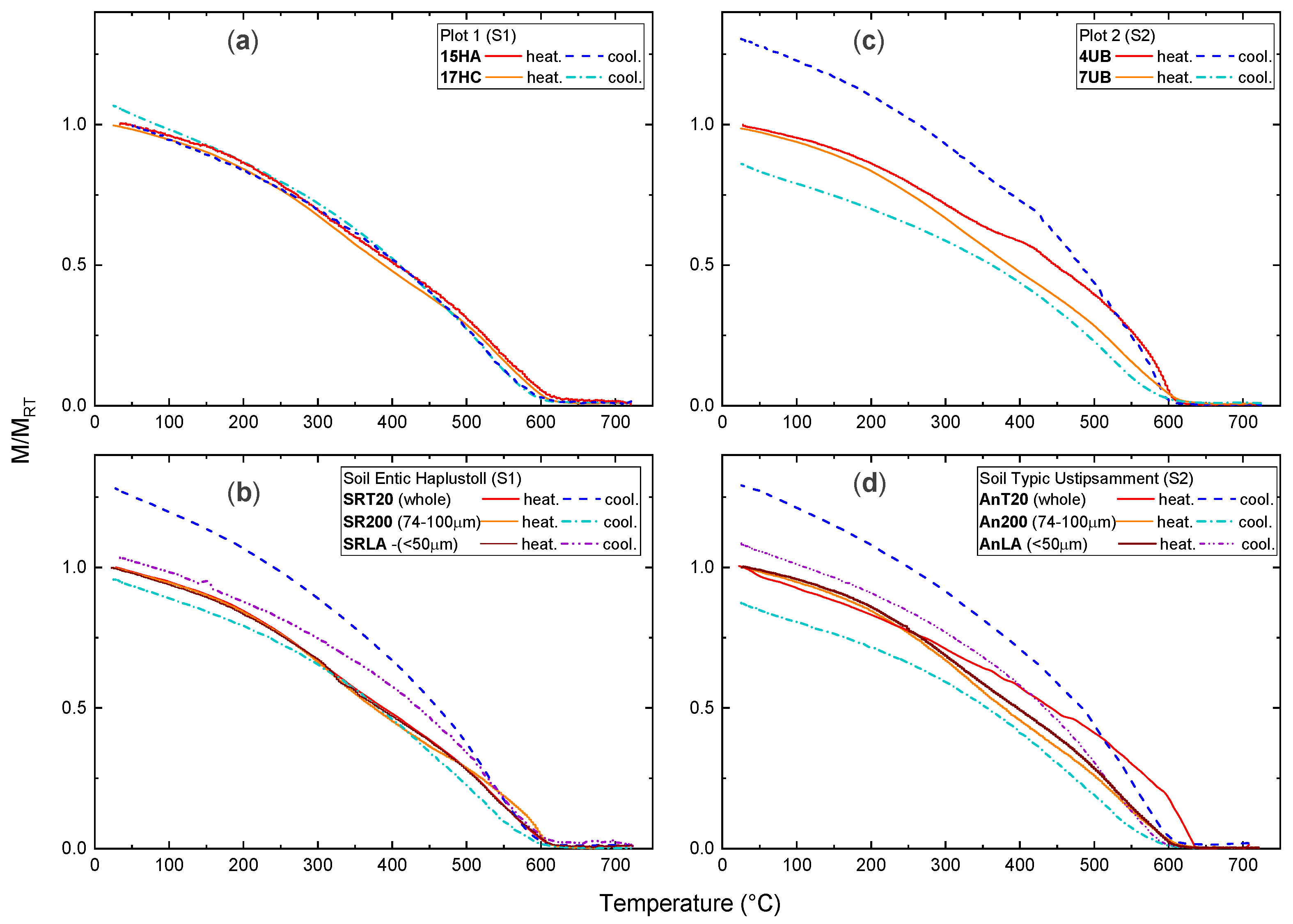
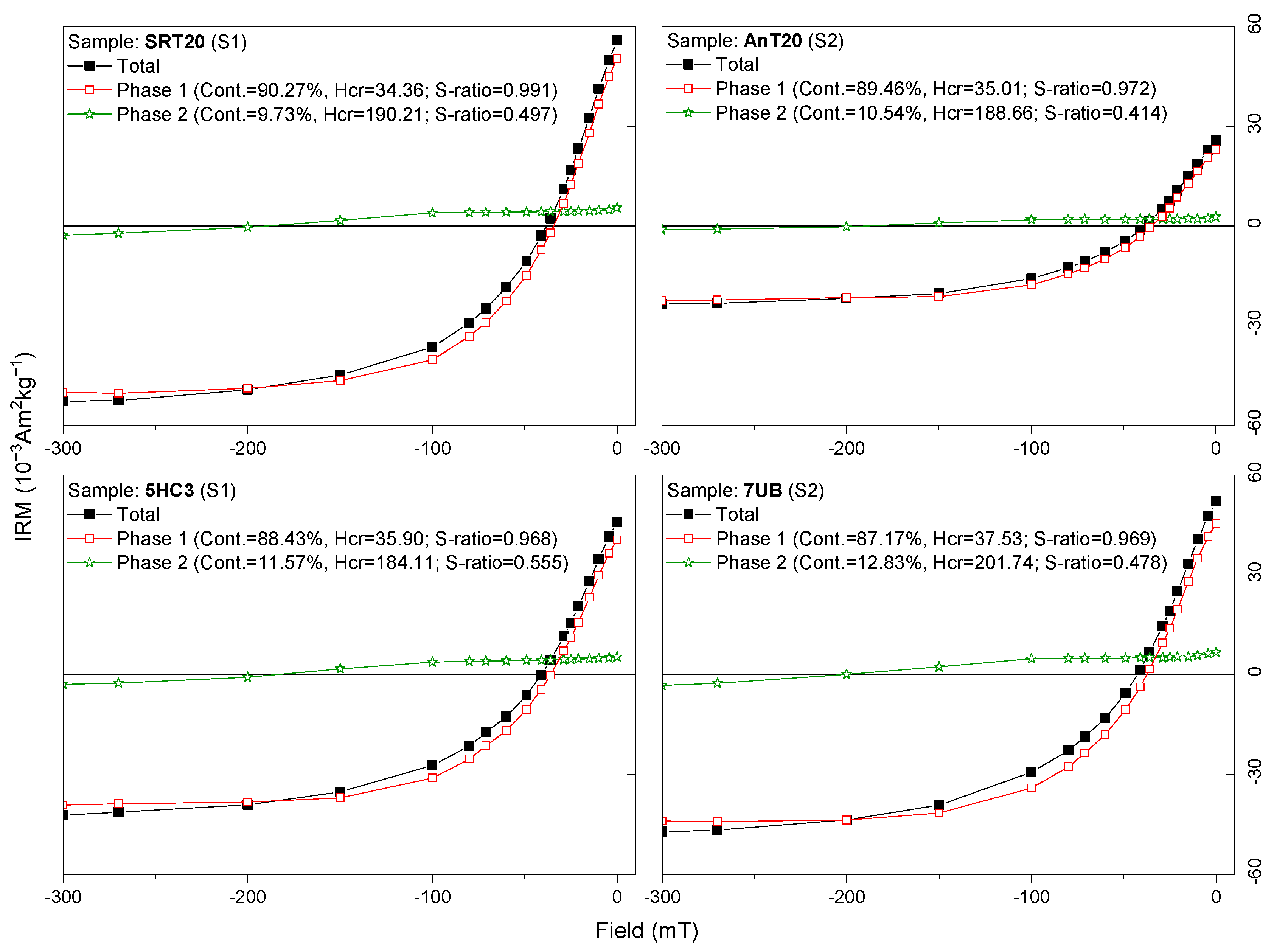
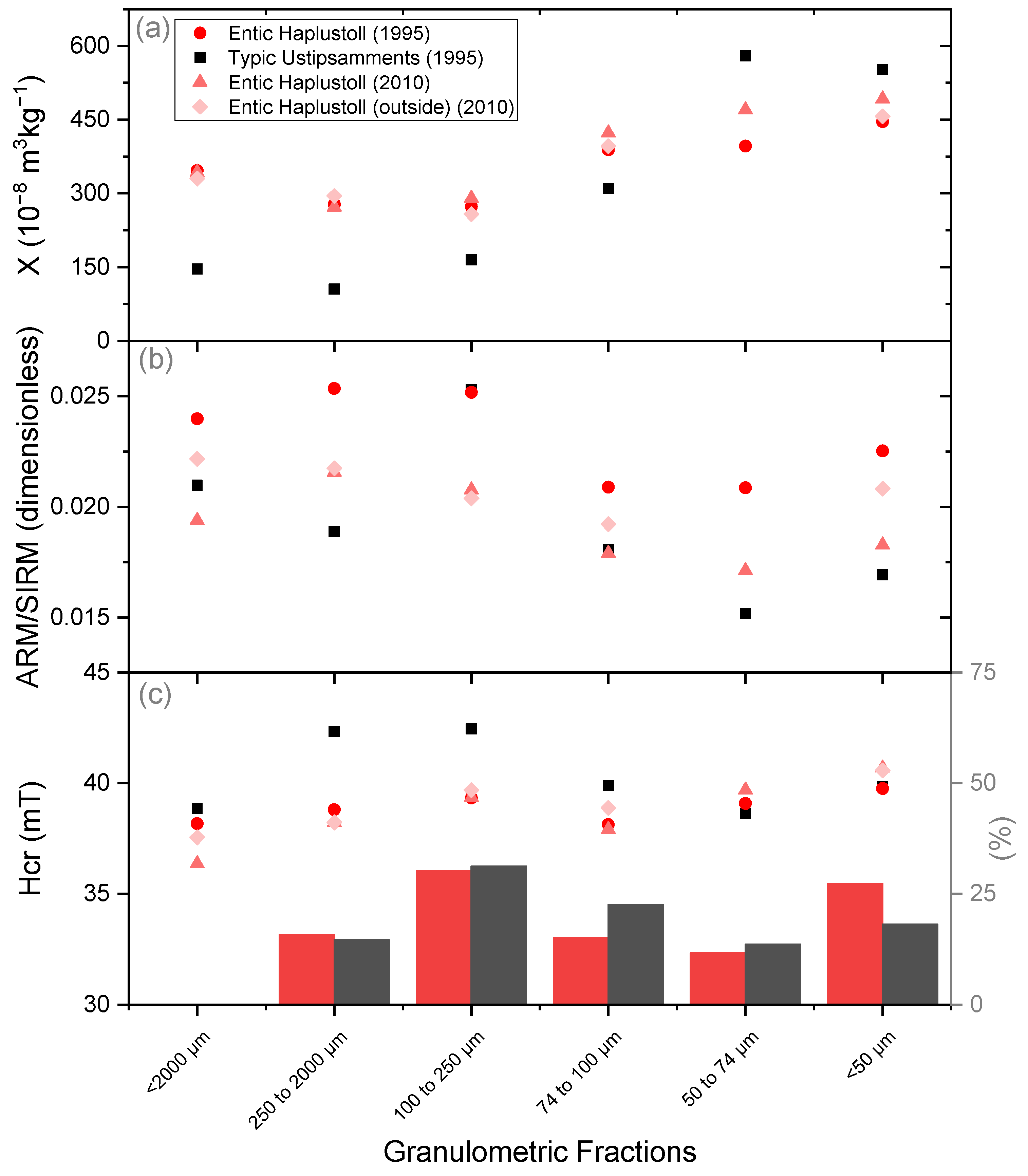
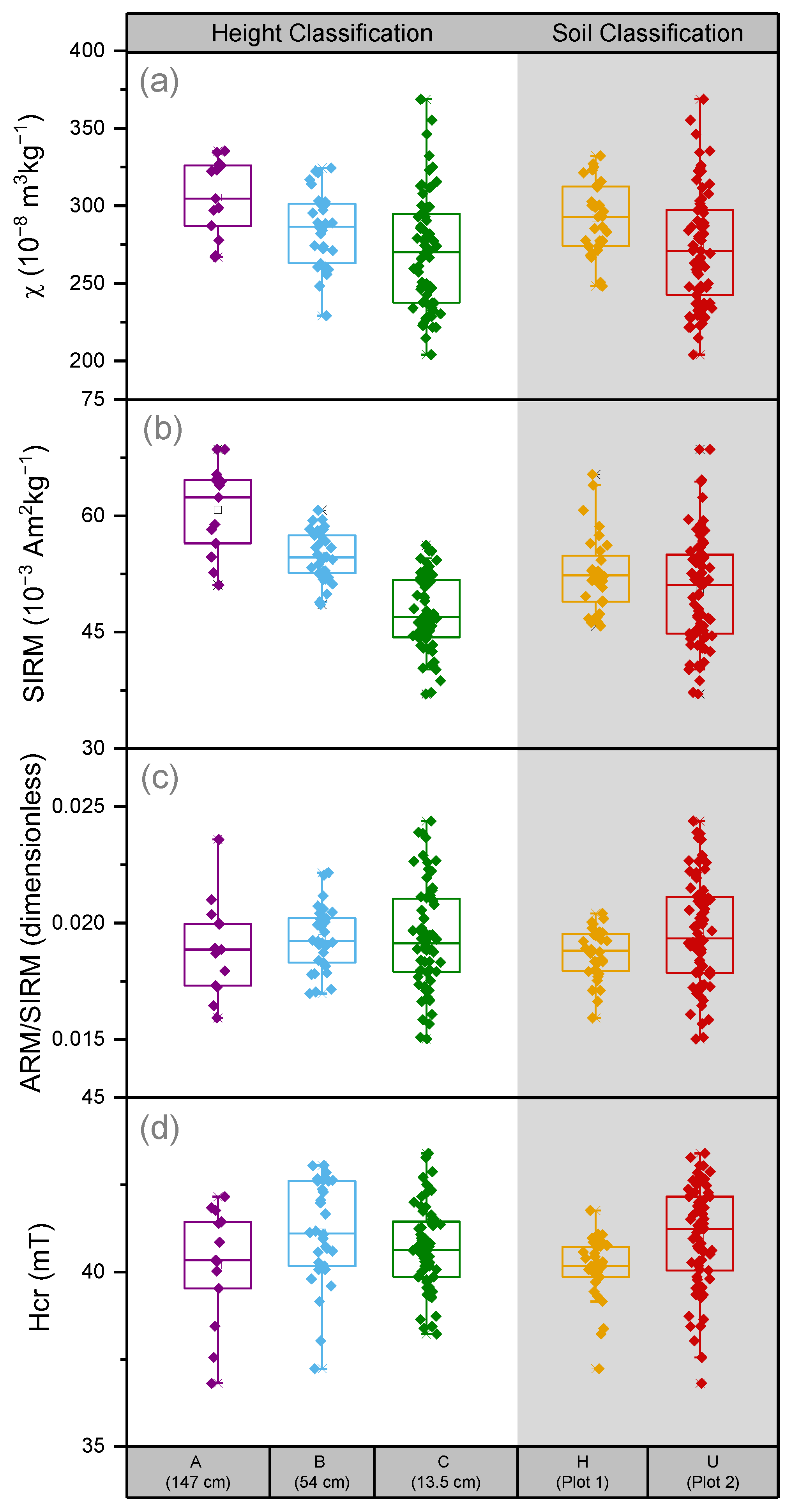


| Site | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entic Haplustoll (S1) | Typic Ustipsamment (S2) | ||||||
| Variable | Date | Storm Duration | Wind Speed | Total Eolian Erosion | Total Samples Studied (Present Work) | Total Eolian Erosion | Total Samples Studied (Present Work) |
| Units | dd-month | h | km h−1 | kg ha−1 | kg ha−1 | ||
| Year 1995 | 23-February | 13 | 17.1 | 547 | 6 | 2876 | 4 |
| 29-March | 13 | 19.5 | 641 | 24 | 6463 | 4 | |
| 16-June | 32 | 18.8 | 1498 | 7 | 8180 | 6 | |
| 30-June | 20 | 23.7 | 3734 | 3 | 4535 | 3 | |
| 10-July | 38 | 19.7 | 8754 | 3 | 5020 | 3 | |
| 25-July | 43 | 19 | 3214 | 16 | 224 | 4 | |
| 1-September | 48 | 18.4 | 632 | 10 | 16,681 | 3 | |
| 24-October | 38 | 21.5 | 5713 | 3 | 10,584 | 3 | |
| 21-November | 51 | 19.7 | 697 | 3 | 25,472 | 2 | |
| Entic Haplustoll (S1) | Typic Ustipsamment (S2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Analytic Soil Data | Units | Horizon A | |
| Organic matter | % | 1.6 | 1.1 |
| Moisture equivalent | 11.5 | 7.5 | |
| Clay, 0–2 μm | 10.2 | 7.3 | |
| Fine silt, 2–20 μm | 7.4 | 6.0 | |
| Coarse silt, 20–50 μm | 9.7 | 4.8 | |
| Very fine sand I, 50–74 μm | 11.7 | 13.6 | |
| Very fine sand II, 74–104 μm | 15.0 | 22.5 | |
| Fine sand, 104–246 μm | 30.2 | 31.2 | |
| Medium and coarse sand, 246–2000 μm | 15.7 | 14.6 | |
| Variable | Subset A (n = 13) | Subset B (n = 30) | Subset C (n = 64) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | SD | Min | Max | Mean | SD | Min | Max | Mean | SD | |
| χ (10−8 m3 kg−1) | 266.9 | 335.4 | 305.3 | 24.7 | 229.2 | 324.4 | 284.5 | 23.8 | 204.0 | 368.7 | 270.6 | 36.8 |
| χFD% (%) | 0.7 | 5.4 | 3.5 | 1.6 | −2.6 | 6.6 | 2.8 | 1.8 | 0.6 | 6.6 | 2.6 | 1.3 |
| ARM (10−6 A m2 kg−1) | 866.1 | 1276.3 | 1144.8 | 109.7 | 891.2 | 1196.7 | 1060.3 | 84.4 | 709.1 | 1087.6 | 911.0 | 80.9 |
| χARM (10−8 m3 kg−1) | 861.9 | 1690.1 | 1403.3 | 254.8 | 1051.7 | 1611.9 | 1365.5 | 144.7 | 823.7 | 1475.1 | 1179.7 | 134.8 |
| χARM/χ | 2.8 | 5.7 | 4.6 | 0.9 | 3.5 | 7.0 | 4.8 | 0.7 | 2.8 | 6.4 | 4.4 | 0.8 |
| SIRM (10−3A m2 kg−1) | 51.1 | 68.6 | 60.8 | 5.8 | 48.6 | 60.7 | 54.9 | 3.2 | 37.0 | 56.2 | 47.4 | 4.7 |
| ARM/SIRM | 0.016 | 0.024 | 0.019 | 0.002 | 0.017 | 0.022 | 0.019 | 0.001 | 0.015 | 0.024 | 0.019 | 0.002 |
| Hcr (mT) | 36.81 | 42.16 | 40.19 | 1.70 | 37.23 | 43.06 | 41.12 | 1.49 | 38.22 | 43.40 | 40.66 | 1.21 |
| S-ratio | 0.794 | 0.944 | -- | -- | 0.868 | 0.959 | -- | -- | 0.796 | 0.962 | -- | -- |
| Variable | Subset H (n = 32) | Subset U (n = 75) | ||||||||||
| χ (10−8 m3 kg−1) | 248.3 | 332.2 | 292.2 | 22.4 | 204.0 | 368.7 | 272.9 | 36.7 | ||||
| χFD% (%) | 0 | 6.6 | 2.5 | 1.7 | 0.6 | 6.6 | 2.9 | 1.4 | ||||
| ARM (10−6 A m2 kg−1) | 818.4 | 1276.3 | 980.1 | 100.2 | 709.1 | 1245.3 | 981.7 | 132.7 | ||||
| χARM (10−8 m3 kg−1) | 903.4 | 1541.5 | 1252.1 | 146.4 | 823.7 | 1690.1 | 1261.9 | 197.2 | ||||
| χARM/χ | 2.8 | 5.2 | 4.3 | 0.5 | 2.8 | 7.0 | 4.7 | 0.8 | ||||
| SIRM (10−3A m2 kg−1) | 45.8 | 65.3 | 52.5 | 4.9 | 37.0 | 68.6 | 50.5 | 7.2 | ||||
| ARM/SIRM | 0.016 | 0.020 | 0.019 | 0.001 | 0.015 | 0.024 | 0.020 | 0.002 | ||||
| Hcr (mT) | 37.2 | 41.8 | 40.1 | 0.9 | 36.8 | 43.4 | 41.0 | 1.5 | ||||
| S-ratio | 0.796 | 0.962 | -- | -- | 0.794 | 0.959 | -- | -- | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alba, B.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Bartel, A.A.; Böhnel, H.N.; Aimar, S.B. Soil Erosion by Wind Storms in a Pampean Semi-Arid Region of Argentina: An Environmental Magnetism Approach. Soil Syst. 2025, 9, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020060
Alba B, Chaparro MAE, Bartel AA, Böhnel HN, Aimar SB. Soil Erosion by Wind Storms in a Pampean Semi-Arid Region of Argentina: An Environmental Magnetism Approach. Soil Systems. 2025; 9(2):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020060
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlba, Brenda, Marcos A. E. Chaparro, Andrea A. Bartel, Harald N. Böhnel, and Silvia B. Aimar. 2025. "Soil Erosion by Wind Storms in a Pampean Semi-Arid Region of Argentina: An Environmental Magnetism Approach" Soil Systems 9, no. 2: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020060
APA StyleAlba, B., Chaparro, M. A. E., Bartel, A. A., Böhnel, H. N., & Aimar, S. B. (2025). Soil Erosion by Wind Storms in a Pampean Semi-Arid Region of Argentina: An Environmental Magnetism Approach. Soil Systems, 9(2), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020060









