Effectiveness of Dynamic Vibration Absorber on Ground-Borne Vibration Induced by Metro
Abstract
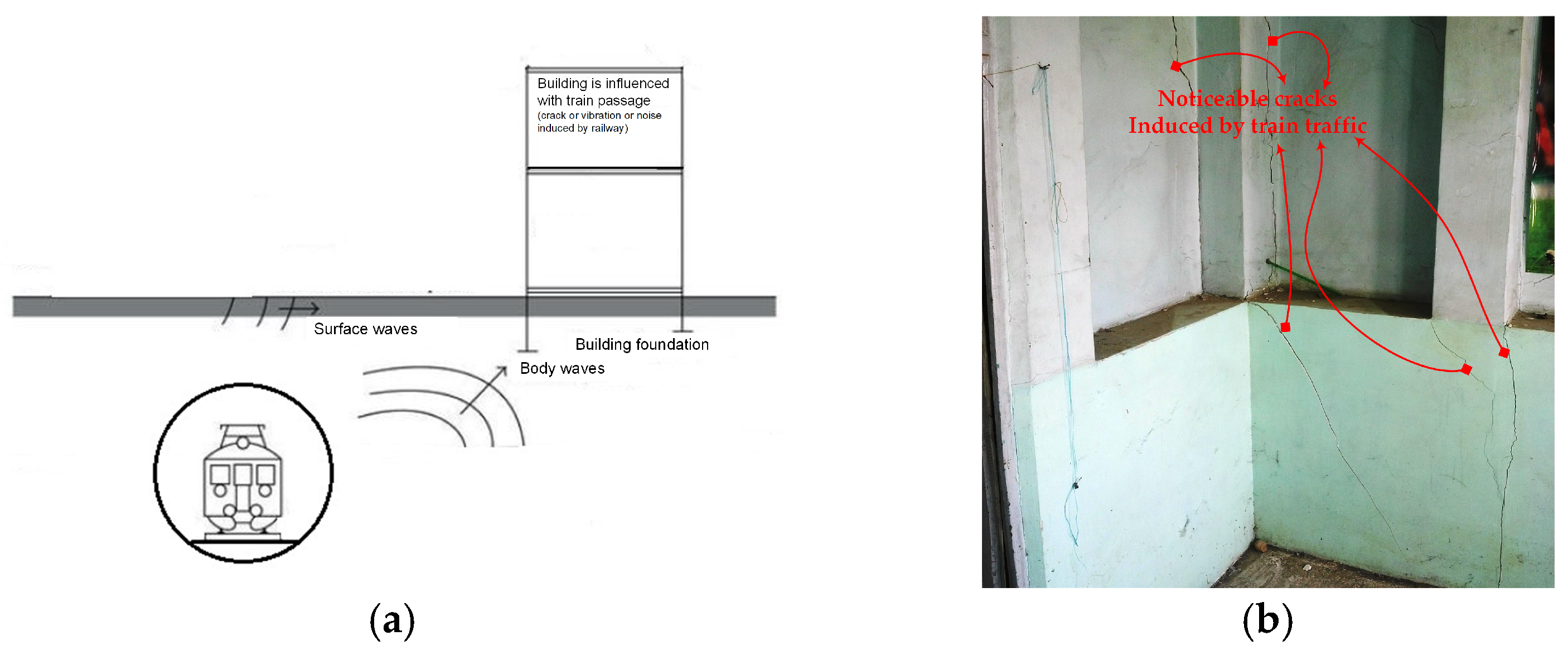
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Modeling
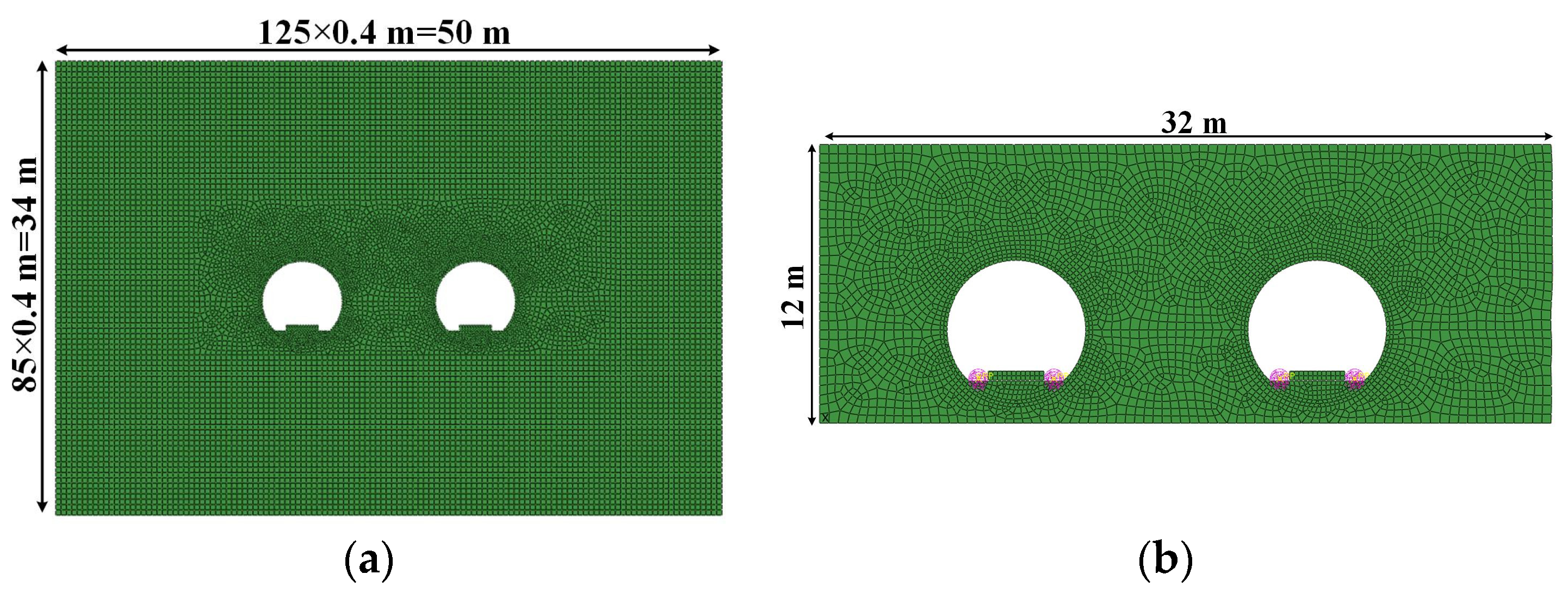
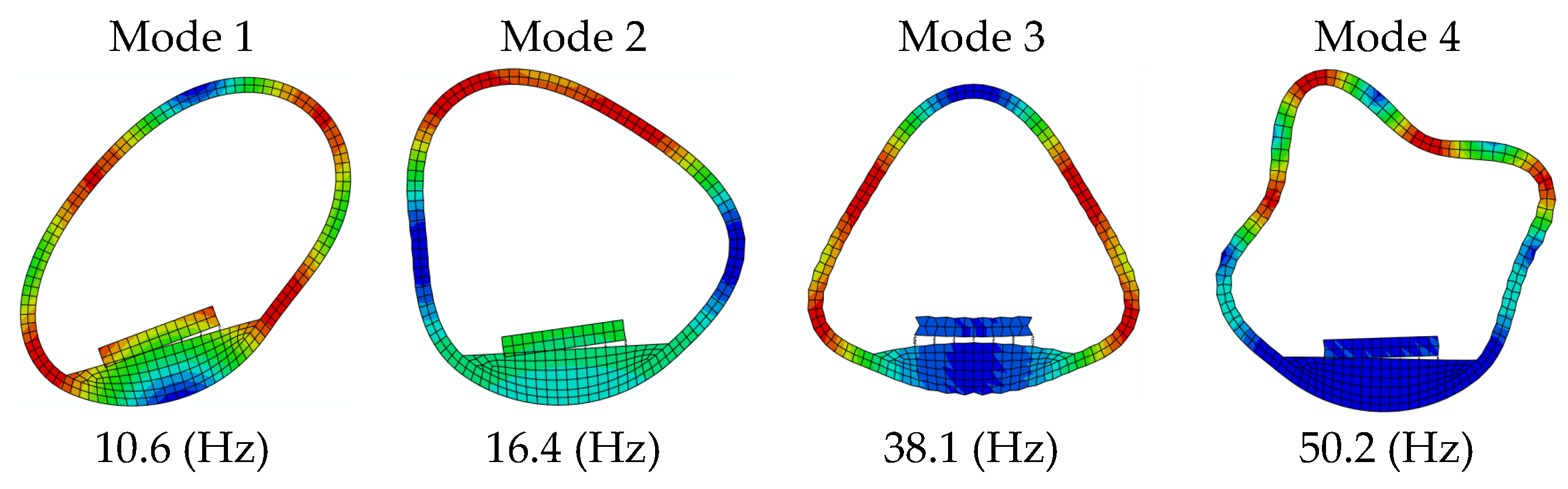
2.1. Finite Element Model
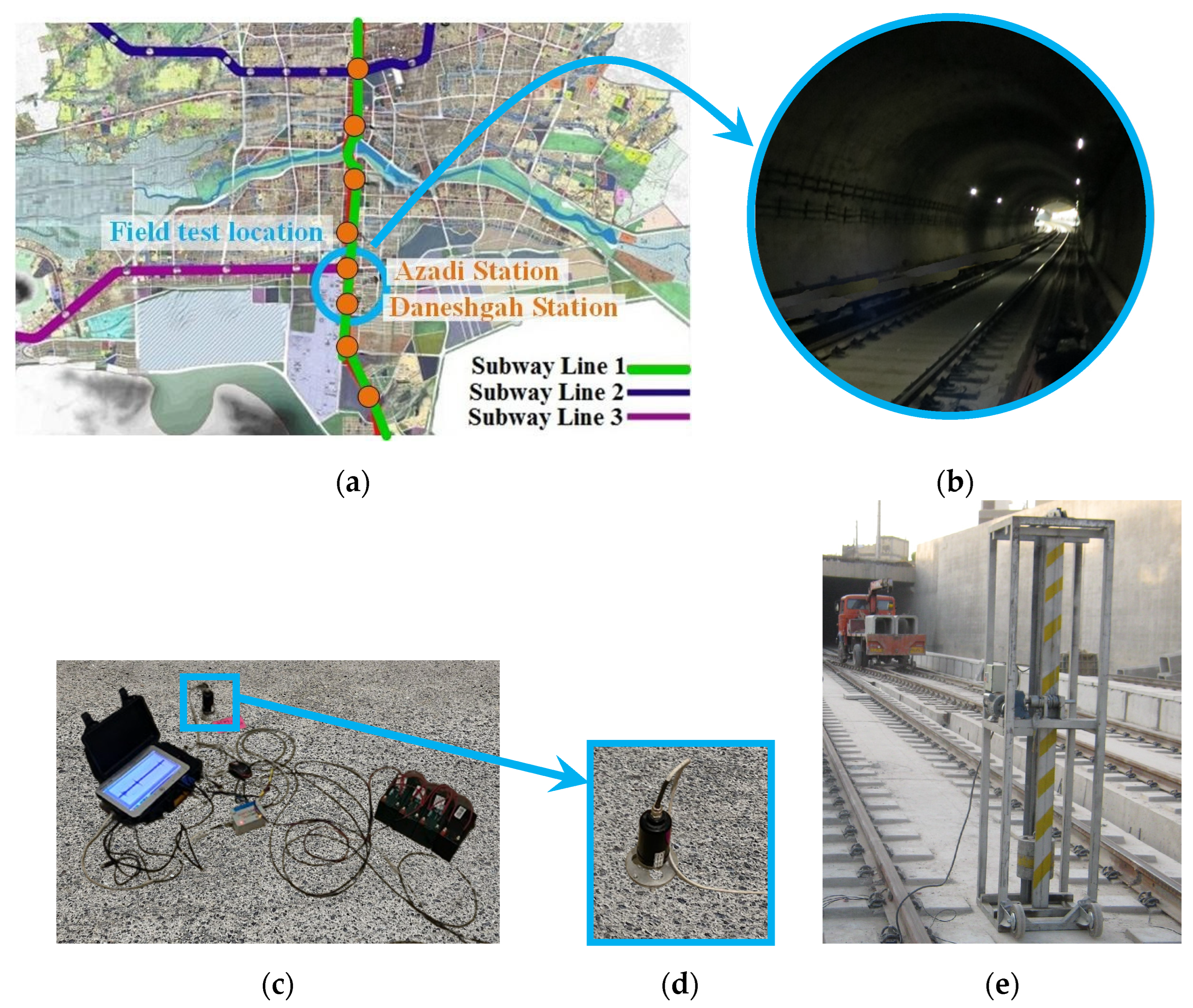
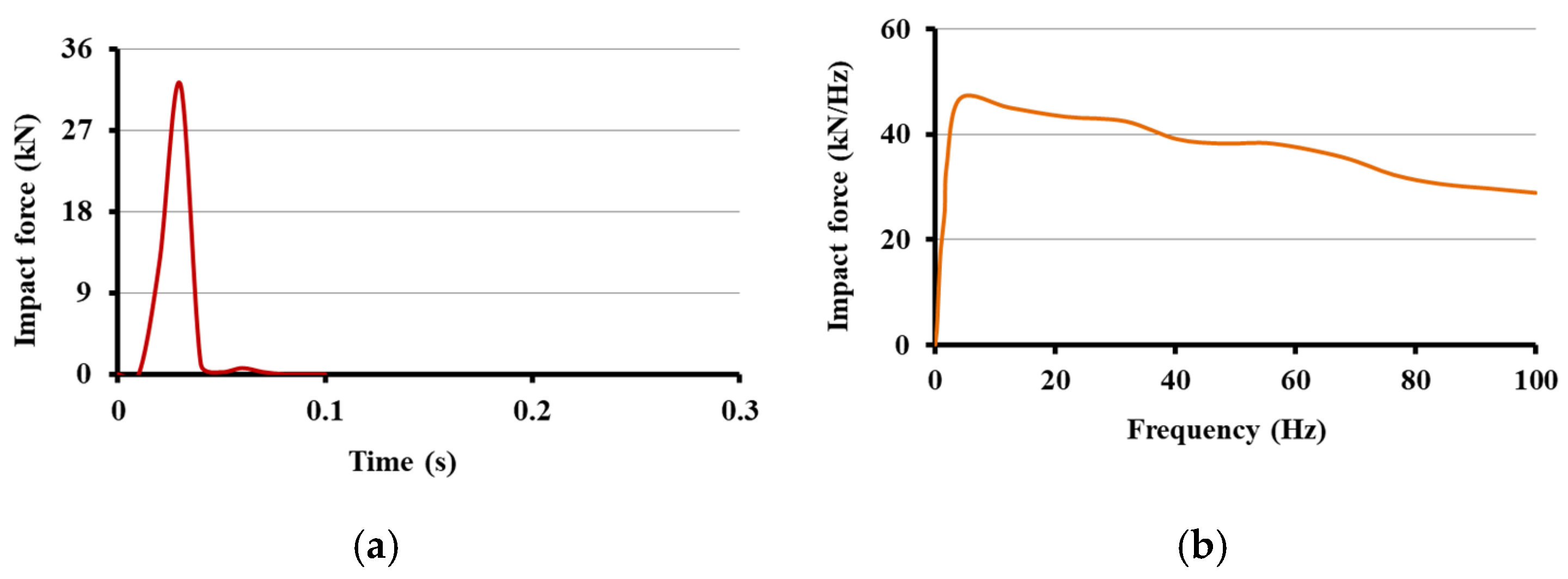
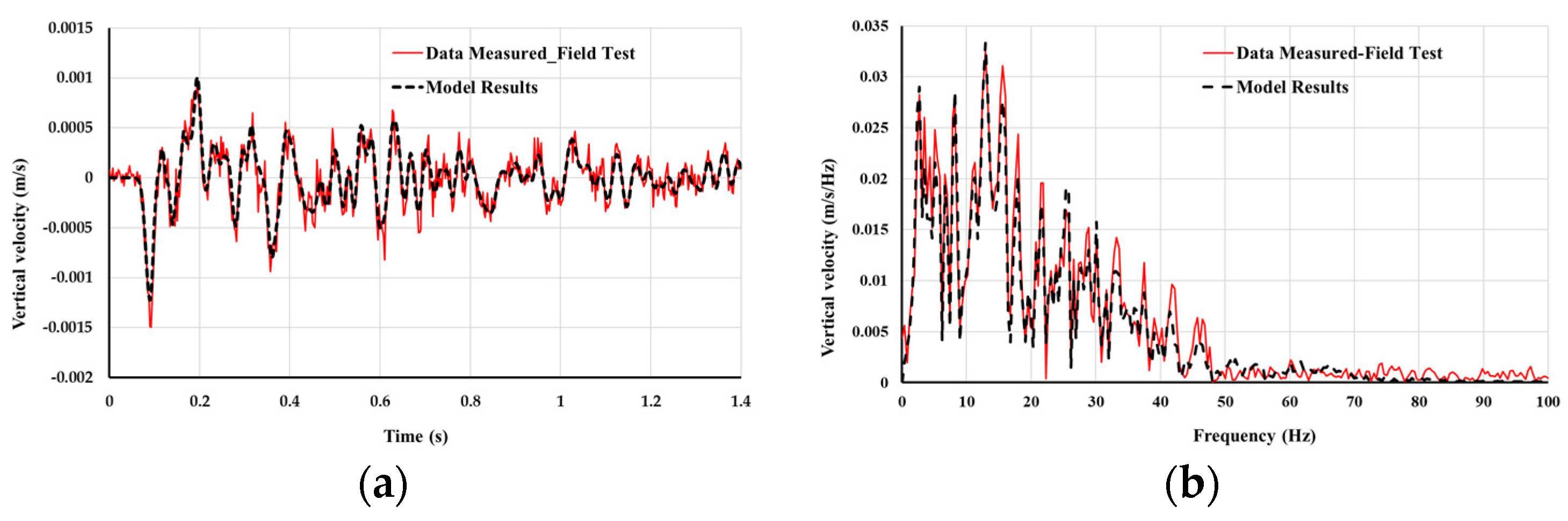
2.2. Field Test for Validation of Model Results
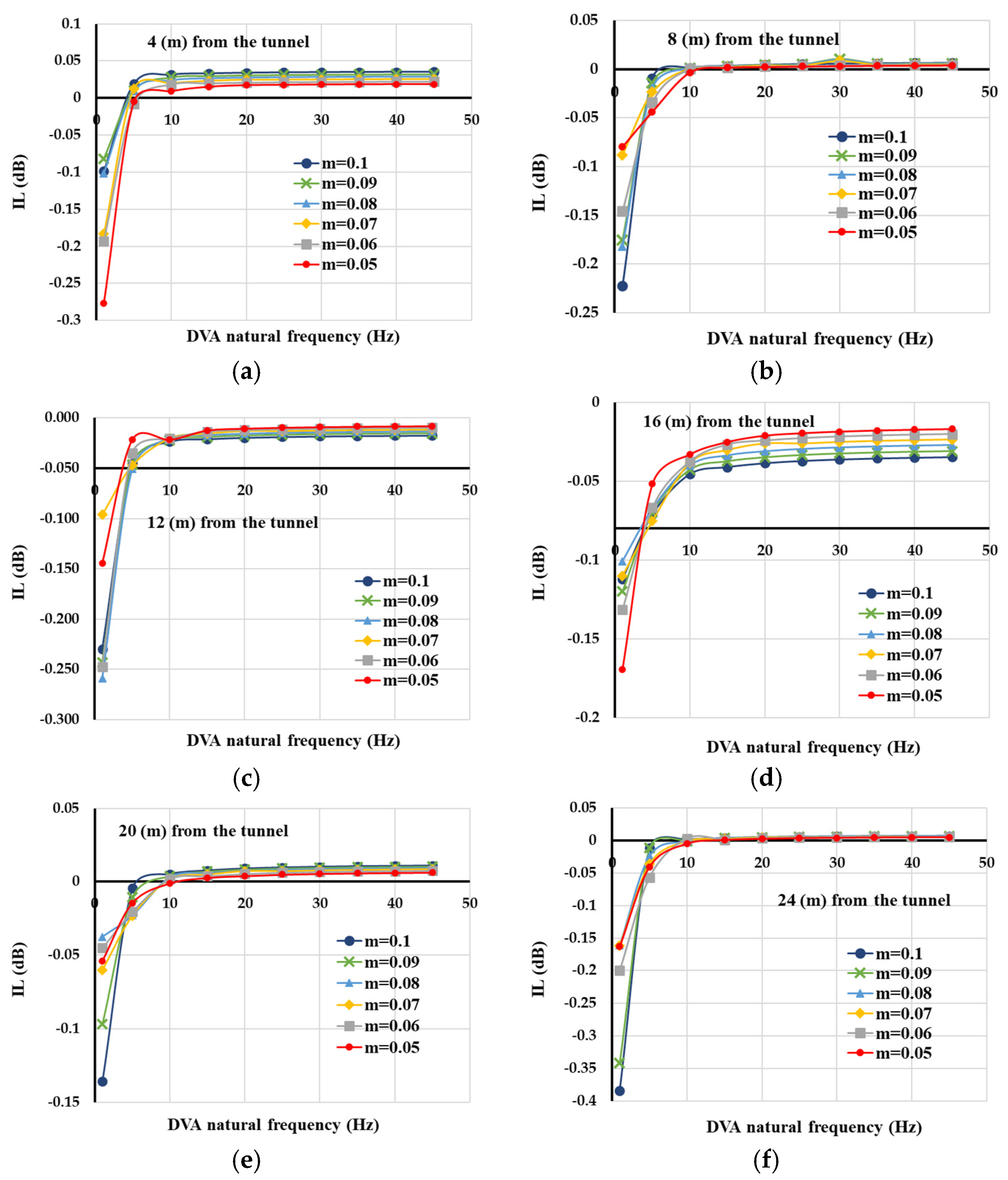
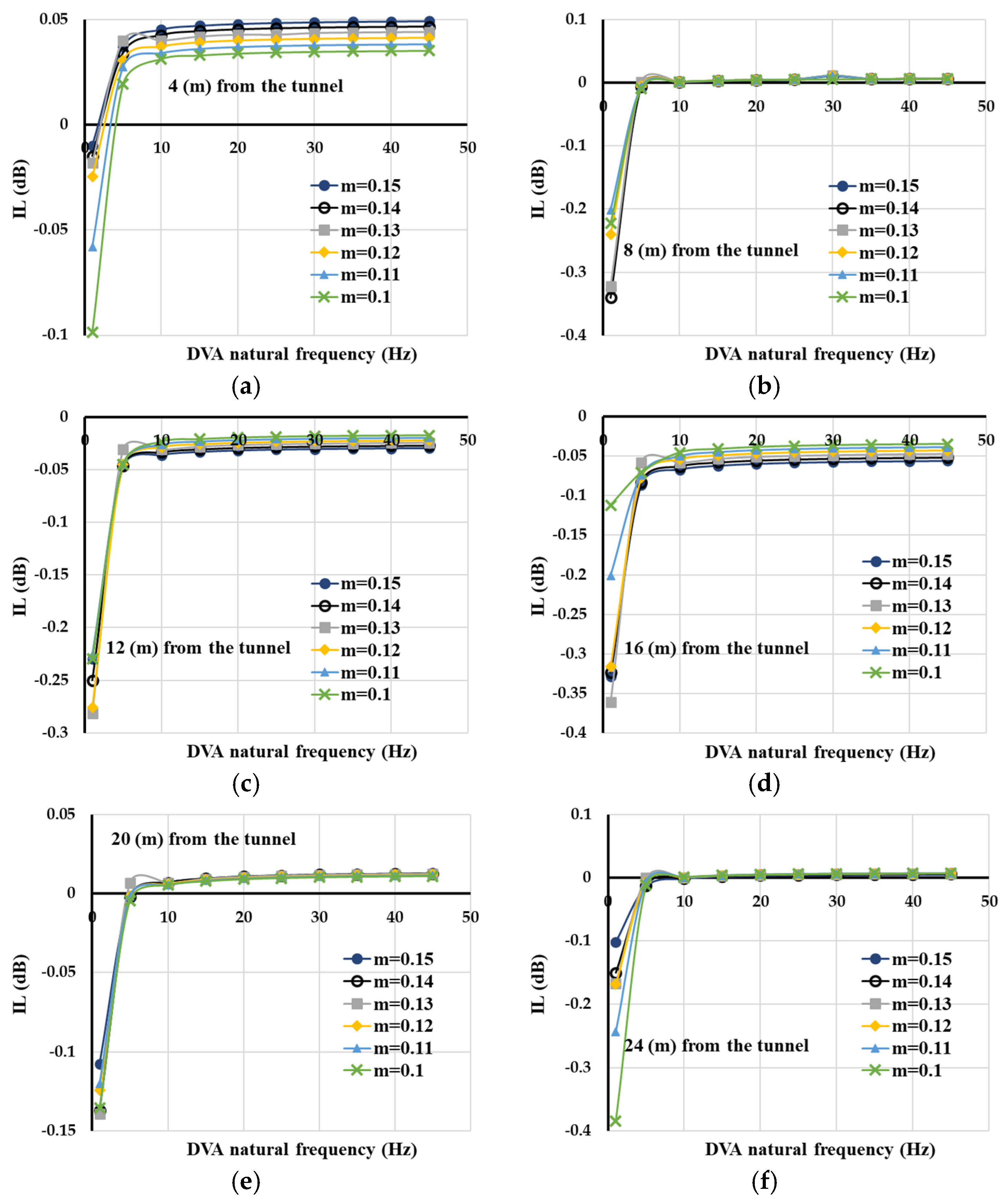
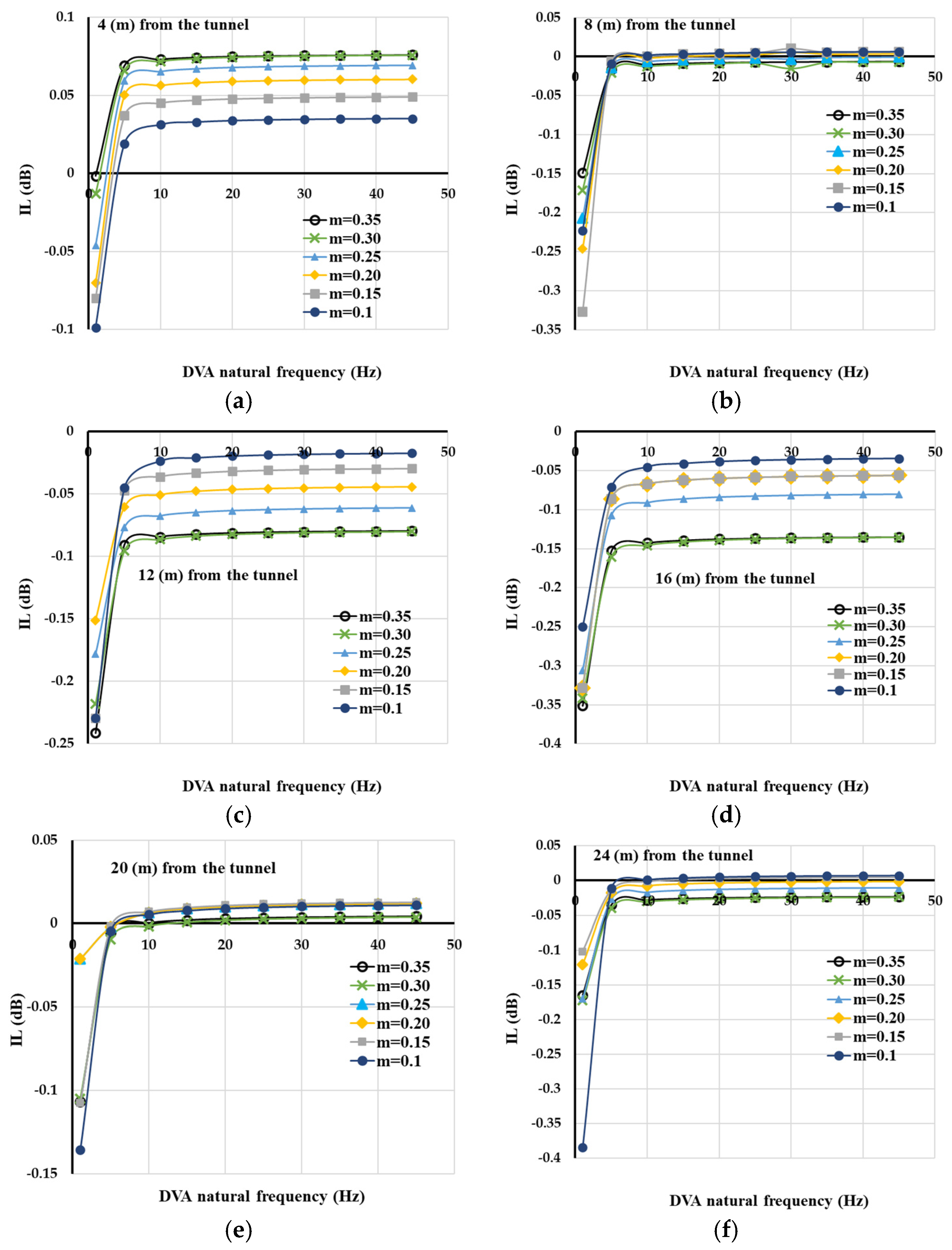
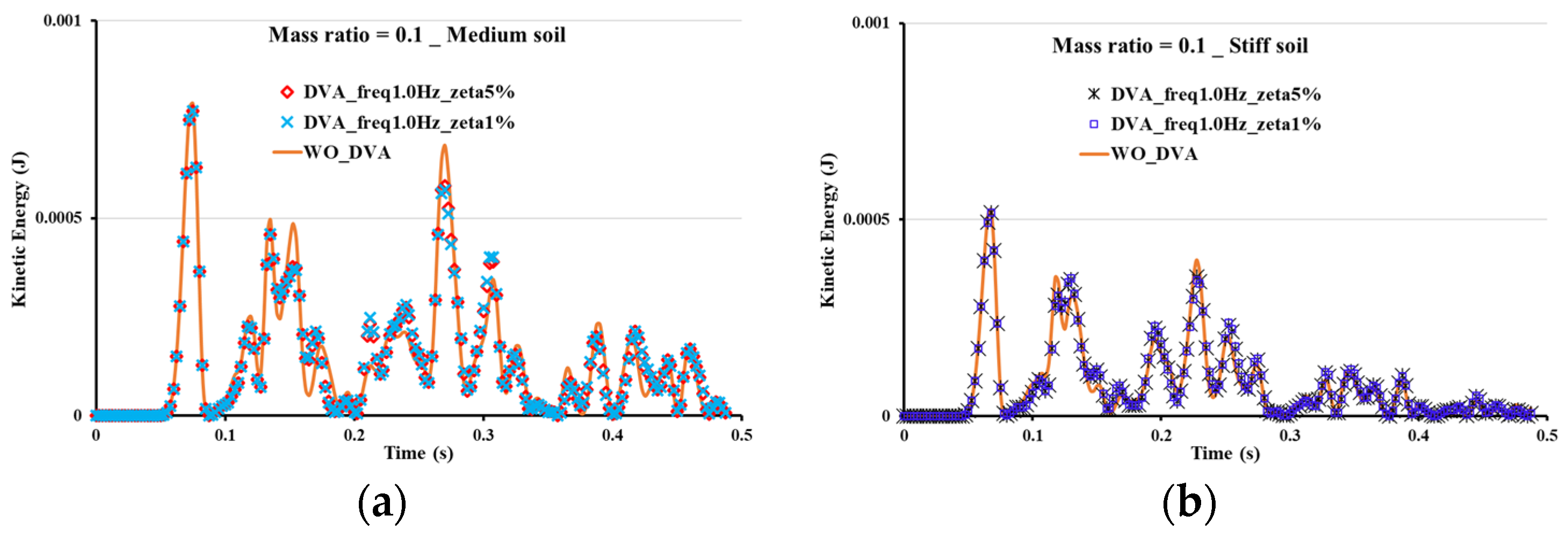
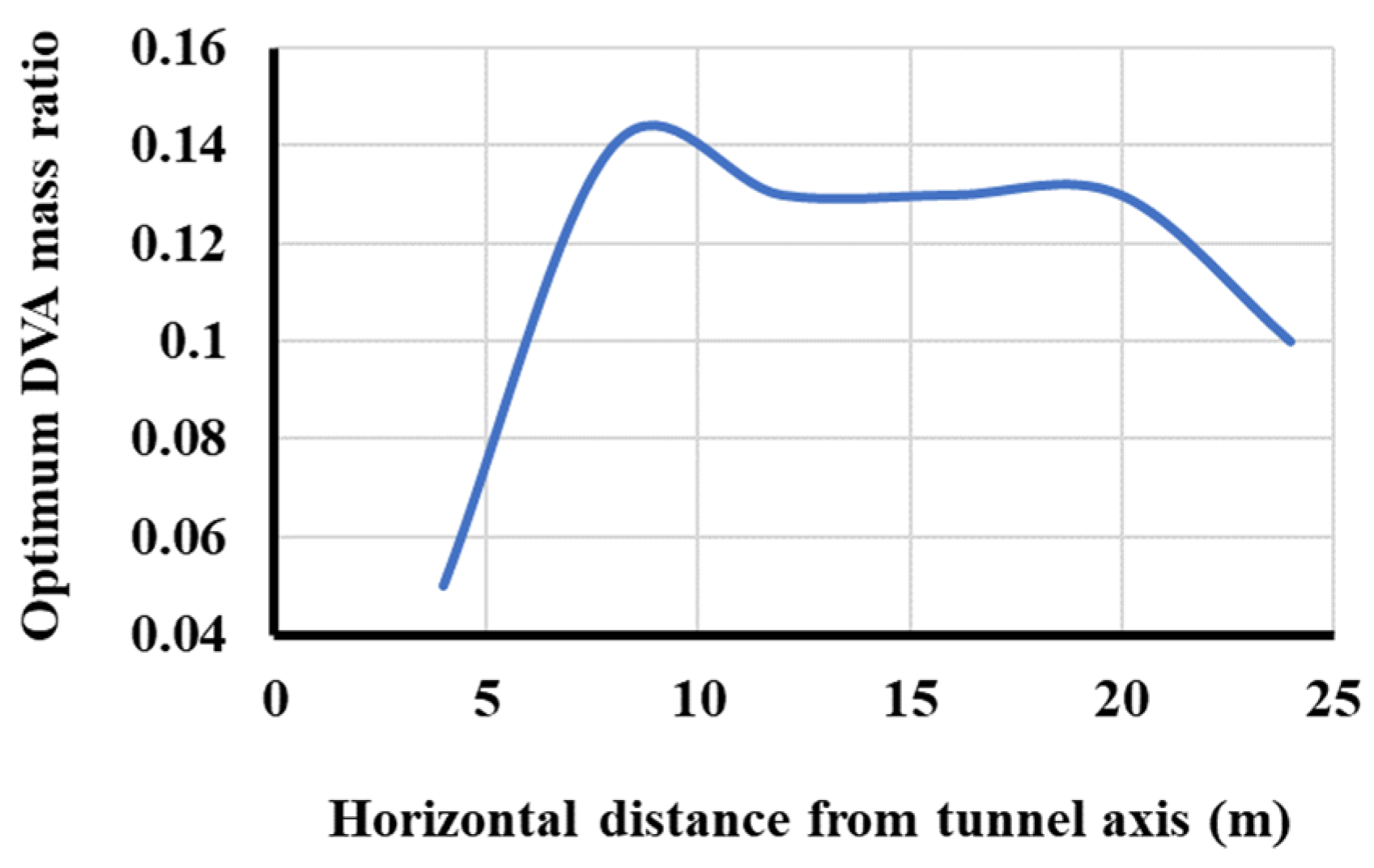
3. Parametric Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DVA | Dynamic vibration absorber |
| TMD | Tuned mass damper |
| FE | Finite element |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| SDOF | Single degree of freedom |
| 2D | Two-dimensional |
| PiP | Pipe-in-Pipe |
References
- Sadeghi, J.; Toloukian, A.; Shafieyoon, Y. Metro-induced vibration attenuation using rubberized concrete slab track. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 435, 136754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasheghani, M.; Sadeghi, J.; Khajehdezfuly, A. Legal consequences of train-induced structure borne noise and vibration in residential buildings. Noise Mapp. 2022, 9, 170–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yang, J.; Yan, H.; Zhang, L.; Cai, C. Low-frequency vibration control of floating slab tracks using dynamic vibration absorbers. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2015, 53, 1296–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, J.; Esmaeili, M.H. Safe distance of cultural and historical buildings from subway lines. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2017, 96, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.J.; Jiang, J.; Toward, M.G.R.; Hussein, M.F.M.; Dijckmans, A.; Coulier, P.; Degrande, G.; Lombaert, G. Mitigation of railway-induced vibration by using subgrade stiffening. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2015, 79, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toward, M.G.; Jiang, J.; Dijckmans, A.; Coulier, P.; Thompson, D.J.; Degrande, G.; Lombaert, G.; Hussein, M.F. Mitigation of railway induced vibrations by using subgrade stiffening and wave impeding blocks. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Structural Dynamics (EURODYN 2014), Porto, Portugal, 30 June–2 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ardian, A.R.R.; Handayani, D.; Marzuki, A. A Review: Vibration Caused by Transportation. Eng. Proc. 2025, 84, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Mendoza, D.; Romero, A.; Connolly, D.P.; Galvín, P. Scoping methodology to assess induced vibration by railway traffic in buildings. Procedia Eng. 2017, 199, 2717–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, W.; Shang, Y.; Su, N.; Feng, D. Field Test Study on the dynamic response of the cement-improved expansive soil subgrade of a heavy-haul railway. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 128, 105878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Kordestani, H.; Shadabfar, M. A combined review of vibration control strategies for high-speed trains and railway infrastructures: Challenges and solutions. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2023, 42, 272–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouroussis, G.; Connolly, D.P.; Verlinden, O. Railway-induced ground vibrations—A review of vehicle effects. Int. J. Rail Transp. 2014, 2, 69–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouroussis, G.; Mouzakis, H.P.; Vogiatzis, K.E. Structural impact response for assessing railway vibration induced on buildings. Mech. Ind. 2017, 18, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazi, M.K.A.M.; Adnan, M.A.; Sulaiman, N. The Impact of Train Operation Time with Ground Borne Vibration Induced by Railway Traffic. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2022; Volume 971, p. 012004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, H.; Tang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, R.; Lu, Y.; Aw, K.C. Vibration-based and computer vision-aided nondestructive health condition evaluation of rail track structures. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2023, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, B.; Cubría, V.; Arcos, R.; Clot, A.; Romeu, J. Optimization of Dynamic Vibration ABSORBERS placed on the Tunnel Interior Surface to Mitigate Underground Railway-Induced Vibration. In Proceedings of the 9th Iberian Acoustics Congress, 47th Spanish Congress on Acoustics, Porto, Portugal, 13–15 June 2016; Tecniacústica 2016; Sociedade Portuguesa de Acústica. EuroRegio: Gronau, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Noori, B.; Arcos, R.; Clot, A.; Romeu, J. Control of ground-borne underground railway-induced vibration from double-deck tunnel infrastructures by means of dynamic vibration absorbers. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 461, 114914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, D. Controlling the vibration and noise of a ballasted track using a dynamic vibration absorber with negative stiffness. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2020, 234, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yang, J.; Cai, C.; Pan, Z.; Zhai, W. Application of dynamic vibration absorbers in designing a vibration isolation track at low-frequency domain. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2017, 231, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouroussis, G.; Ainalis, D.; Zhu, S.; Zhai, W. Mitigation measures for urban railway induced ground vibrations using dynamic vibration absorbers. In Proceedings of the 25th International Congress on Sound and Vibration (ICSV25), Hiroshima, Japan, 8–12 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, N.; Fujino, Y.; Warnitchai, P. Optimal tuned mass damper for seismic applications and practical design formulas. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S. Mechanical Vibrations, 5th ed.; Chapter 9 Vibration Control; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fujino, Y.; Abé, M. Design formulas for tuned mass dampers based on a perturbation technique. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1993, 22, 833–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, J.J. Introduction to Structural Motion Control; Chapter 4 Tuned Mass Damper Systems; Prentice Hall Pearson Education, Incorporated: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, T.; Luo, Y. Parametric study of dynamic vibration absorber with negative stiffness applied to floating slab track. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 25, 3369–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, J.; Cai, C.; Wang, K.; Zhai, W.; Yang, J.; Yan, H. Development of a vibration attenuation track at low frequencies for urban rail transit. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2017, 32, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, B.; Arcos, R.; Clot, A.; Romeu, J. Assessment of Dynamic Vibration Absorbers Efficiency as a Counter-Measure for Ground-Borne Vibrations Induced by Train Traffic in Double-Deck Tunnels Using an Energy Flow Criterion. In Noise and Vibration Mitigation for Rail Transportation Systems, Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Railway Noise, Ghent, Belgium, 16–20 September 2019; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 454–461. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, L. Simulations and analyses of train-induced ground vibrations in finite element models. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2003, 23, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, H.R.; Degrande, G. Numerical modeling of free field vibrations due to pile driving using a dynamic soil-structure interaction formulation. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2008, 215, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysmer, J.; Kuhlemeyer, R.L. Finite dynamic model for infinite media. J. Eng. Mech. Div. 1969, 95, 859–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Du, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J. 3D viscous-spring artificial boundary in time domain. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2006, 5, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudreau, G.L.; Taylor, R.L. Evaluation of numerical integration methods in elastodynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1973, 2, 69–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.J.; Jiang, J.; Toward, M.G.R.; Hussein, M.F.M.; Ntotsios, E.; Dijckmans, A.; Coulier, P.; Lombaert, G.; Degrande, G. Reducing railway-induced ground-borne vibration by using open trenches and soft-filled barriers. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2016, 88, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajehdezfuly, A.; Shiraz, A.A.; Sadeghi, J. Assessment of vibrations caused by simultaneous passage of road and railway vehicles. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 211, 109510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.J.; Kouroussis, G.; Ntotsios, E. Modelling, simulation and evaluation of ground vibration caused by rail vehicles. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2019, 57, 936–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, S.P. Railway Induced Vibration-State of the Art Report; UIC-ETC (Railway Technical Publications): Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghi, J. Study, Experimental Analysis and Field Test on Isfahan Metro: Exploring Influence of Ground-Borne Vibration on Historical Buildings and Cultural Heritage; Technical Report conducted at IUST Led by J. Sadeghi, Research Report-2015-SRE; School of Railway Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology: Tehran, Iran, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hibbitt, Karlsson and Sorensen, Inc. ABAQUS User’s Manual, version 6.8-1; Hibbitt, Karlsson and Sorensen: Providence, RI, USA, 2008.
- Wair, B.R.; DeJong, J.T.; Shantz, T. Guidelines for Estimation of Shear Wave Velocity Profiles; PEER Report 2012-08; Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Talbot, J.P.; Hunt, H.E.M. Isolation of buildings from rail-tunnel vibration: A review. Build. Acoust. 2003, 10, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Soil Type | Modulus of Elasticity [MPa] | Density [kg/m3] | Poisson’s Ratio | Shear Wave Velocity [m/s] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soft | 150 | 2000 | 0.3 | 170 |
| Medium | 300 | 2000 | 0.3 | 240 |
| Stiff | 450 | 2000 | 0.3 | 294 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadeghi, J.; Toloukian, A.; Mehravar, S. Effectiveness of Dynamic Vibration Absorber on Ground-Borne Vibration Induced by Metro. Vibration 2025, 8, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration8040062
Sadeghi J, Toloukian A, Mehravar S. Effectiveness of Dynamic Vibration Absorber on Ground-Borne Vibration Induced by Metro. Vibration. 2025; 8(4):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration8040062
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadeghi, Javad, Alireza Toloukian, and Sogand Mehravar. 2025. "Effectiveness of Dynamic Vibration Absorber on Ground-Borne Vibration Induced by Metro" Vibration 8, no. 4: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration8040062
APA StyleSadeghi, J., Toloukian, A., & Mehravar, S. (2025). Effectiveness of Dynamic Vibration Absorber on Ground-Borne Vibration Induced by Metro. Vibration, 8(4), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration8040062








