Abstract
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising materials for drug delivery due to their structural tunability and high surface area. This work reports on the synthesis of ZIF-8 for the in situ encapsulation of hesperidin, a flavonoid with poor water solubility used in the treatment of circulatory system disorders, as a gastric-targeted drug delivery system (DDS). A 23 full factorial design was used to optimize drug loading, investigating the effects of DMSO concentration, 2-MIm/Zn2+ molar ratio, and final solution volume (water content). The materials were characterized by ATR-FT-IR, TG, XRD, and SEM analyses, confirming successful ZIF-8 synthesis and partial hesperidin encapsulation. Drug release kinetics were evaluated at pH 1.0 and 6.86. The system showed a faster and more pronounced release at pH 1.0, driven by MOF degradation, demonstrating its potential as a gastric-targeted DDS. This study confirms the feasibility of ZIF-8 to improve hesperidin solubility and bioavailability, highlighting a novel strategy for its therapeutic application.
1. Introduction
The oral route is considered the most preferred for drug administration, offering advantages such as ease of use, cost-effectiveness, and formulation flexibility [1]. However, for a drug to have a therapeutic effect, it must be absorbed into the systemic circulation, which fundamentally depends on its dissolution. Molecules with poor water solubility, like many natural compounds, often exhibit deficient absorption and, consequently, low bioavailability [2,3,4]. Hesperidin, a flavonoid already employed in the treatment of circulatory disorders is a notable example of this limitation.
To address the challenge of poor solubility, strategies such as particle size reduction and the use of solid dispersions are common [5]. Recently, research has turned to the development of materials capable of modulating drug dissolution and release. Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), composed of metal ions linked by organic ligands, are a class of hybrid materials with high structural versatility and surface area [6,7]. These properties make them ideal candidates for the development of drug delivery systems (DDS), capable of encapsulating and protecting molecules, while also controlling their release at the desired site [8].
Among MOFs, zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs) stand out in the biomedical context. ZIF-8, in particular, composed of 2-methylimidazole and zinc, exhibits stability at neutral and alkaline pH but degrades rapidly in acidic media [9]. This characteristic makes it a particularly promising DDS for gastric-targeted delivery, where a low-pH environment facilitates the release of the encapsulated drug [9,10].
In this study, ZIF-8 was synthesized for the in situ encapsulation of hesperidin. Our objective was to investigate the potential of ZIF-8 as a gastric DDS for hesperidin, evaluating its ability to improve the flavonoid’s dissolution and release, which could ultimately enhance its bioavailability and, consequently, its clinical efficacy. Previous studies have enhanced hesperidin solubility through polymeric carriers [11], nanostructured systems such as nanogels [12] and nanofibers [13], solvent engineering with deep eutectic solvents [14], or even ZIF-8 composites coated with hyaluronic acid for antibacterial purposes [15]. In contrast, the present work introduces the novelty of in situ encapsulating hesperidin within ZIF-8 and assessing its performance as a gastric-targeted DDS, focusing on dissolution and acid pH-triggered release to improve bioavailability.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
Hesperidin (C25H34O15), 2-methylimidazole (C4H6N2), and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO; C2H6SO) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO, USA). Zinc sulfate heptahydrate (ZnSO4∙7H2O) was purchased from Synth (São Paulo, SP, Brazil).
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Hesperidin Solubility Assay
Hesperidin solubility was determined by the shake flask method [16]. Excess hesperidin was dispersed in 5 mL of ultrapure water and stirred for 24 h at room temperature. The suspension was then centrifuged, and the supernatant was collected for spectrophotometric quantification at 283 nm. A calibration curve (1.83–36.63 µg∙mL−1) was prepared using hesperidin as the standard. The hesperidin concentration was expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3).
2.2.2. HPLC Quantification of Hesperidin
HPLC quantification of hesperidin was performed using a method adapted from Majumdar and Srirangam [11]. The mobile phase consisted of a 75:25 (v/v) mixture of solvent A (20 mM phosphate buffer, pH 2.5, Synth, São Paulo, SP, Brazil) and solvent B (acetonitrile, ACN, Tedia, Fairfield, OH, USA). Separation was achieved on an Agilent Poroshell 120 column (C18; 4.6 × 150 mm; 2.7 µm particle size, Santa Clara, CA, USA) at 30 °C. The flow rate was 1.0 mL∙min −1, and the injection volume was 10 µL. Detection was performed at 283 nm.
2.2.3. Synthesis of the ZIF-8 and Hesperidin-ZIF-8 System (H@ZIF-8)
ZIF-8 and H@ZIF-8 were synthesized using a modified in situ approach adapted from Kaur et al. [17]. For H@ZIF-8 synthesis, zinc sulfate heptahydrate (ZnSO4∙7H2O) and 2-methylimidazole (2-MIm) were separately dissolved in ultrapure water. A solution of hesperidin in DMSO was added to the 2-MIm solution, followed by the zinc sulfate solution, resulting in a white-yellowish suspension. After 24 h, the synthesis mixture was centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 15 min. The resulting solid was then washed with ultrapure water and absolute ethanol to remove unreacted species, filtered, and dried overnight at 45 °C. ZIF-8 was prepared under identical conditions, but without the addition of hesperidin.
Experimental Design
A 23 full factorial design was employed to investigate the effects of DMSO concentration (% v/v), Zn2+/2-MIm molar ratio, and final solution volume on drug loading. Table 1 and Table 2 present the levels of the independent variables and the design matrix, respectively. Three center points were included to assess experimental error and model curvature. Drug loading, the dependent variable, was quantified by decomposing an appropriate amount of H@ZIF-8 in 2 M HCl and analyzing the resulting solution by HPLC [18].

Table 1.
Levels of independent variables used in the 23 full factorial design for H@ZIF-8 synthesis.

Table 2.
Design matrix of the 23 factorial design experiment for evaluating the effects and interactions of synthesis variables on H@ZIF-8 drug loading.
2.2.4. Characterization
Attenuated Total Reflection Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FT-IR) Spectroscopy
Spectroscopic analyses were performed using a Shimadzu® IRTracer-100 (Kyoto, Japan) equipped with a zinc selenide (ZnSe) ATR accessory. Samples were placed on the crystal surface and scanned from 4000 to 600 cm−1. Results are expressed as percentage of transmittance (%T) versus wavenumber (cm−1).
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
Thermal stability was evaluated using a Shimadzu® TGA Q60 (Kyoto, Japan) thermobalance. Samples were heated in a platinum crucible under a nitrogen atmosphere (100 mL∙min−1) at a rate of 10 °C∙min−1. Hesperidin was heated from 25 °C to 600 °C, while ZIF-8 and H@ZIF-8 were heated from 25 °C to 900 °C.
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
XRD analysis was performed using a Shimadzu XRD-7000 (Kyoto, Japan) diffractometer with CuKα radiation (λ = 1.5418 Å), operated at 40 kV and 40 mA. Diffraction patterns were recorded from 5° to 50° (2θ) in step-scan mode with a step size of 0.01°.
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
Morphological analysis was using a Tescan® Vega3 microscope (Brno, Czech Republic). Samples were mounted on carbon tape on aluminum stubs and sputter-coated with gold (Au) at a rate of 5 nm∙min−1 for 5 min. Micrographs were acquired at an accelerating voltage of 10 kV.
2.2.5. Drug Release Profile
The release profiles of H@ZIF-8 were evaluated under non-sink conditions in 900 mL of either 1 M HCl (pH 1.0) or phosphate buffer (pH 6.86) at 37 °C and 232 rpm. At predetermined time intervals, 2 mL aliquots were collected, filtered, and analyzed by HPLC for hesperidin quantification. Results are expressed as the percentage of drug released over time.
2.2.6. Statistical Analyses
Results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Experimental design data were analyzed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) to determine the statistical significance of main effects and factor interactions. A curvature check was performed to assess the suitability of the linear model. Statistical significance was assumed at p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hesperidin Solubility
The solubility of a substance in an aqueous solvent is a critical parameter for drug bioavailability and efficacy, especially for the oral route, where dissolution is a prerequisite for absorption [19,20]. In the present study, hesperidin exhibited a solubility of 2.25 ± 0.09 µg∙mL−1 in water.
Table 3 summarizes the hesperidin solubility values in aqueous media found in the literature. Despite minor methodological variations, all studies, including the present one, confirm the poor aqueous solubility of hesperidin, a factor that limits its absorption and bioavailability after oral administration. This result reinforces the need for strategies, such as encapsulation in a delivery system, to improve the flavonoid’s dissolution properties and, consequently, its therapeutic potential.

Table 3.
Solubility of hesperidin in aqueous media as reported by different studies and experimental methods.
3.2. Synthesis of the ZIF-8 and H@ZIF-8
The 23 full factorial design was used to evaluate the influence of three independent variables on drug loading of hesperidin in ZIF-8. Table 4 presents the design matrix and the drug loading achieved for each synthesis condition. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) revealed that DMSO concentration (% v/v), the 2-MIm/Zn2+ ratio, and final solution volume, along with the interaction between the ratio and volume, and the three-factor interaction, all had a statistically significant (p < 0,05) effect on drug loading.

Table 4.
Design matrix and factor combinations used in the 23 factorial design for drug loading.
The linear model showed a high adjusted coefficient of determination (R2 = 0.9937), indicating that variables explained 99.37% of the variability of drug loading. The Pareto chart of the standardized effects (Figure 1) confirmed these findings, showing that the most influential factors were 2-MIm/Zn2+ ratio and the final solution volume.
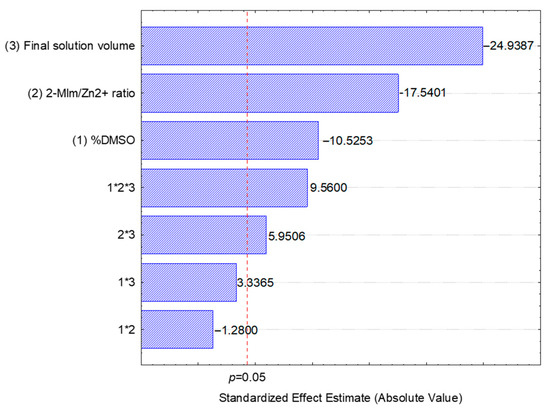
Figure 1.
Pareto chart of the standardized effects for the 23 full factorial design showing the influence of individual factors and their interactions on drug loading.
As shown in Figure 1, increasing the concentration of DMSO, the 2-MIm/Zn2+ ratio, and the final solution volume had a negative effect o drug loading. This can be attributed to the known effects of these variables on ZIF-8 synthesis. Previous reports indicate that a higher concentration of 2-MIm promotes nucleation, while a higher concentration of water (controlled by final volume) can shift the crystal morphology toward a two-dimensional multilayered structure [22,23]. Increasing DMSO concentration can delay nucleation and decrease the final yield, as it promotes charge separation and enhances solubility of polarizable molecules, thereby interfering with chemical equilibrium [24].
The significant curvature of the model (p = 0.003) indicates that the relationship between the independent variables and drug loading is not linear. Although the linear model identified the main effects, a first-order model is insufficient to fully describe the system’s behavior. This suggests that a more comprehensive optimization study is necessary to pinpoint the true optimal conditions for hesperidin encapsulation.
3.3. Material Characterization
A successful synthesis of ZIF-8 and the encapsulation of hesperidin were confirmed through multiple characterization techniques.
3.3.1. ATR-FT-IR Spectroscopy
The ATR-FT-IR spectra confirmed the presence of both the MOF and the encapsulated hesperidin (Figure 2). ZIF-8 exhibited characteristic bands for N–H bending (1581 cm−1), C–N stretching (1310, 1180, and 1146 cm−1), and C=C bending (760 and 694 cm−1). Hesperidin showed bands corresponding to O–H stretching (3475 cm−1), C–H stretching (2919 cm−1), C=C stretching (1647 and 1604 cm−1), and C–O stretching (1205 and 1276 cm−1). In the H@ZIF-8 spectrum, bands from both components were observed, though with reduced intensity, when compared to pure components, suggesting a reduced flexibility of both the framework and the flavonoid [12].
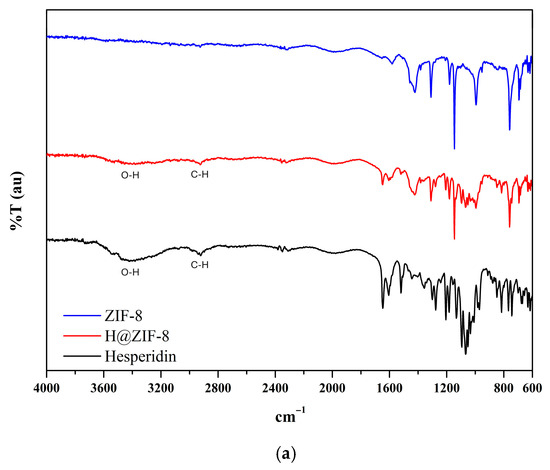
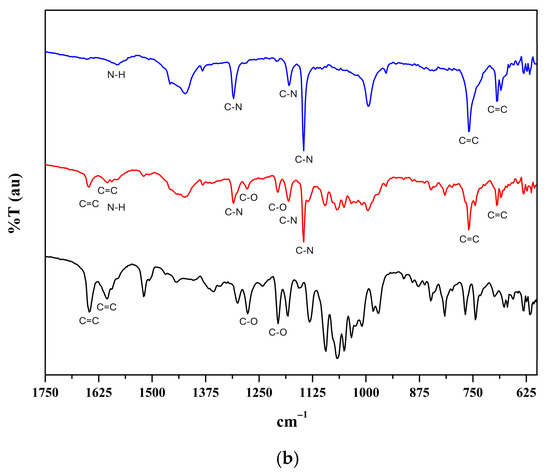
Figure 2.
ATR-FT-IR spectra of hesperidin (black line), ZIF-8 (blue line), and H@ZIF-8 (red line). (a) Spectra in the 4000 cm−1 to 600 cm−1 range. (b) Expanded view of the region between 1750 cm−1 and 600 cm−1.
3.3.2. Thermal Stability
TGA confirmed the thermal stability of the materials (Figure 3). Pure ZIF-8 showed high stability, with no significant mass loss until approximately 405 °C. Hesperidin’s thermogram showed a first mass loss of 3.37% (25–94 °C) due to adsorbed water, followed by decomposition at 276–306 °C (maximum rate at 284 °C), which is consistent with previous studies [11,25]. The H@ZIF-8 thermogram presented a mass loss of 13.03% (101–195 °C), indicating the removal of guest molecules, such as water or unreacted species [26,27,28]. The presence of a mass loss around 284 °C in the H@ZIF-8 thermogram, consistent with hesperidin’s decomposition, further supports its presence in the sample. The final mass loss occurs around 418 °C and corresponds to the degradation of the ZIF-8 framework.
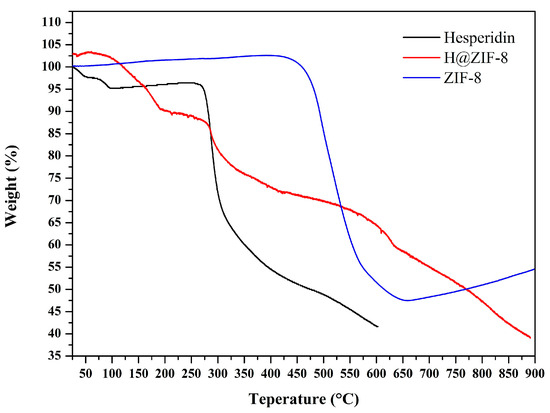
Figure 3.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) curves of hesperidin (black line), ZIF-8 (blue line), and H@ZIF-8 (red line), showing the thermal decomposition profile and evidence of partial flavonoid incorporation.
3.3.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
The XRD patterns confirmed the successful synthesis and structural integrity of the ZIF-8 framework during encapsulation (Figure 4). The H@ZIF-8 exhibited the characteristic reflections of ZIF-8 [28] at 10.3°, 12.6°, 14.6°, 16.4°, and 18.0°, indicating that hesperidin did not interfere with MOF formation. The presence of hesperidin was also confirmed by its characteristic reflections [29]. While the encapsulation process resulted in a decrease in crystallinity of ZIF-8, the preservation of the main reflections confirms that the MOF’s structural stability was maintained.
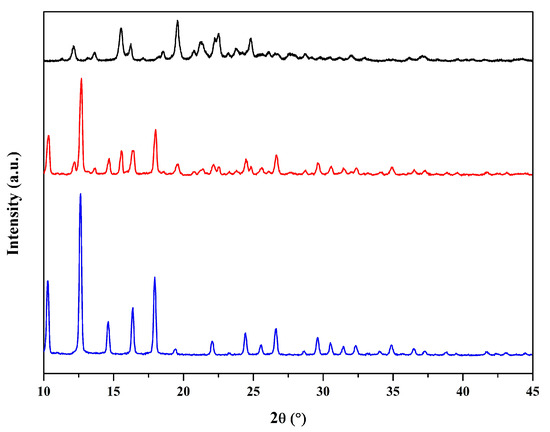
Figure 4.
XRD patterns of ZIF-8 (blue line), H@ZIF-8 (red line), and hesperidin (black line). The main reflections of ZIF-8 are preserved after hesperidin encapsulation, although their intensities are reduced, indicating decreased crystallinity.
3.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
SEM images revealed the morphology of the materials and provided insights into the encapsulation process (Figure 5). ZIF-8 exhibited its typical polyhedral morphology with an average particle size of 263.79 nm, consistent with previous reports for similar synthesis conditions [23]. Hesperidin bulk material did not exhibit a needle-like morphology. However, it is known that under certain conditions, its particles may agglomerate and assume a different shape during the crystallization process [30]. The H@ZIF-8 images showed a mix of ZIF-8 polyhedra and hesperidin crystals (needles), indicating that, despite successful encapsulation, a portion of the flavonoid was externally adsorbed onto the MOF surface. This observation corroborates the ATR-FT-IR and XRD data and is consistent with the results of the factorial design, which showed that the synthesis conditions were not fully optimized.
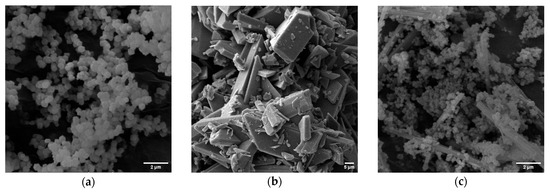
Figure 5.
SEM images showing the morphology of (a) pure ZIF-8 with polyhedral particles, (b) pure hesperidin, and (c) H@ZIF-8, revealing both MOF and flavonoid structures.
3.4. Drug Release Profile
The release profiles of hesperidin from H@ZIF-8 were evaluated at pH 1.0 (gastric environment) and pH 6.86 (intestinal environment) based on the standards stablished by the Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency (ANVISA) for comparative dissolution profiles [31]. The results, presented in Figure 6, show a distinct release pattern depending on the pH.
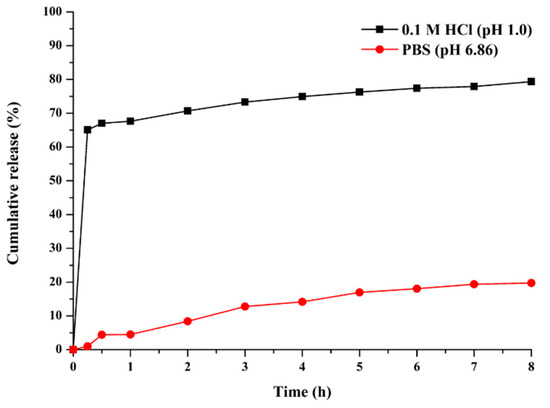
Figure 6.
In vitro release profile of hesperidin from H@ZIF-8 in 0.1 M HCl (pH 1.0, black line) and phosphate-buffered solution (PBS, pH 6.86, red line) under non-sink conditions.
At pH 1.0, the system displayed a biphasic release. A rapid burst effect occurred within the first 30 min, releasing 67.02% of hesperidin, followed by a plateau. After 8 h, the cumulative release reached 79.71%. This rapid release is a key feature of a ZIF-8 system in an acidic environment.
In contrast, at pH 6.86, the release was significantly more controlled, with no burst effect observed. The cumulative release was only 4.40% in the first 30 min, increasing gradually to 19.73% after 8 h. This difference highlights the pH-responsive nature of ZIF-8, which is stable in neutral media but degrades in acidic conditions.
The pronounced release at pH 1.0 confirms the potential of ZIF-8 as a gastric-targeted drug delivery system for poorly water-soluble drugs. For hesperidin, a class II molecule with low solubility and high permeability, the dissolution rate is the limiting factor for oral bioavailability [32]. The ZIF-8 system addresses this limitation by promoting supersaturation of the dissolution medium, which is crucial for enhancing the absorption of such compounds [33].
It is important to note the limitations of this in vitro study. As demonstrated by the characterization results, some hesperidin was adsorbed onto the external surface of the MOF. This external adsorption likely contributed to the burst release effect. Additionally, the dissolution media did not contain biological components, such as enzymes, which could influence the release kinetics in a real physiological environment. Future studies should focus on optimizing the encapsulation process, further characterizing the release kinetics, and conducting in vivo studies to confirm potential improvements in bioavailability.
4. Conclusions
The present study demonstrated the feasibility of ZIF-8 as a gastric delivery system for hesperidin. Characterization analyses by ATR-FT-IR, TGA, XRD, and SEM confirmed the formation of ZIF-8 with partial encapsulation of hesperidin. The drug release profile corroborated the hypothesis of a pH-responsive system, showing a significantly higher and faster release at pH 1.0 (gastric environment) than at pH 6.86 (intestinal environment). This is the first time that the degradation of ZIF-8 in acidic media has been confirmed as an effective mechanism to release encapsulated hesperidin, a poorly water-soluble drug, which can lead to improved oral bioavailability. Although it is necessary to optimize the synthesis conditions to improve encapsulation, our findings represent an important step toward overcoming hesperidin’s low oral bioavailability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.S. (Pedro Sá), J.S. and L.R.; formal analysis, P.S. (Pedro Sá); investigation, P.S. (Pedro Sá) and N.S.; resources, L.R.; data curation, P.S. (Pedro Sá); writing—original draft preparation, P.S. (Pedro Sá); writing—review and editing, N.S., P.S. (Pedrita Sampaio) and J.S.; visualization, P.S. (Pedro Sá); supervision, L.R.; project administration, L.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Ginetton Tavares for his technical support and valuable assistance during the SEM analyses. His contribution was essential to the execution and quality of the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| 2-MIm | 2-Methylimidazole |
| ATR-FT-IR | Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared |
| DDS | Drug Delivery System |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| H@ZIF-8 | Hesperidin-ZIF-8 System |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| MOF | Metal–Organic Framework |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analysis |
| XRD | X-Ray Diffraction |
| ZIF-8 | Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework |
References
- Savjani, K.T.; Gajjar, A.K.; Savjani, J.K. Drug Solubility: Importance and Enhancement Techniques. ISRN Pharm. 2012, 2012, 195727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, L.V., Jr.; Popovich, N.G.; Ansel, H.C. Formas Farmacêuticas e Sistema de Liberação de Fármacos, 9th ed.; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2013; ISBN 978-85-65852-84-5. [Google Scholar]
- Aulton, M.E.; Taylor, K.M.G. Aulton Delineamento de Formas Farmacêuticas, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2016; ISBN 978-85-352-8316-7. [Google Scholar]
- Coimbra, M.; Isacchi, B.; Van Bloois, L.; Torano, J.S.; Ket, A.; Wu, X.; Broere, F.; Metselaar, J.M.; Rijcken, C.J.F.; Storm, G.; et al. Improving Solubility and Chemical Stability of Natural Compounds for Medicinal Use by Incorporation into Liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 416, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.D.; Trevaskis, N.L.; Charman, S.A.; Shanker, R.M.; Charman, W.N.; Pouton, C.W.; Porter, C.J.H. Strategies to Address Low Drug Solubility in Discovery and Development. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 315–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxford, R.C.; Della Rocca, J.; Lin, W. Metal–Organic Frameworks as Potential Drug Carriers. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, A.J.; Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, T.C.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. Chemical, Thermal and Mechanical Stabilities of Metal–Organic Frameworks. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 15018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-Y.; Qin, C.; Wang, X.-L.; Su, Z.-M. Metal-Organic Frameworks as Potential Drug Delivery Systems. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venna, S.R.; Jasinski, J.B.; Carreon, M.A. Structural Evolution of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18030–18033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoop, M.; Walde, C.F.; Riccò, R.; Mushtaq, F.; Terzopoulou, A.; Chen, X.-Z.; deMello, A.J.; Doonan, C.J.; Falcaro, P.; Nelson, B.J.; et al. Biocompatibility Characteristics of the Metal Organic Framework ZIF-8 for Therapeutical Applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 11, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, X. Enhancement of the Water Solubility and Antioxidant Activity of Hesperidin by Chitooligosaccharide. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2422–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Jawaid, T.; Alsanad, S.M.; Kamal, M.; Rawat, P.; Singh, V.; Alam, P.; Alam, P. Solubility Enhancement, Formulation Development, and Antibacterial Activity of Xanthan-Gum-Stabilized Colloidal Gold Nanogel of Hesperidin against Proteus Vulgaris. Gels 2022, 8, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczkowska-Walendowska, M.; Miklaszewski, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Improving Solubility and Permeability of Hesperidin through Electrospun Orange-Peel-Extract-Loaded Nanofibers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekaari, H.; Zafarani-Moattar, M.T.; Mokhtarpour, M.; Faraji, S. Solubility of Hesperidin Drug in Aqueous Biodegradable Acidic Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yin, C.; Ding, X.; Yang, E.; Sun, D.; Wang, W.; Guo, F. Efficient Sterilization System Combining Flavonoids and Hyaluronic Acid with Metal Organic Frameworks as Carrier. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2022, 110, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S.; Srirangam, R. Solubility, Stability, Physicochemical Characteristics and in Vitro Ocular Tissue Permeability of Hesperidin: A Natural Bioflavonoid. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Mohanta, G.C.; Gupta, V.; Kukkar, D.; Tyagi, S. Synthesis and Characterization of ZIF-8 Nanoparticles for Controlled Release of 6-Mercaptopurine Drug. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 41, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Singh, A.; Garg, N.; Randhawa, J.K. Curcumin Encapsulated Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks as Stimuli Responsive Drug Delivery System and Their Interaction with Biomimetic Environment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storpirtis, S.; Gonçalves, J.E.; Chiann, C.; Gai, M.N. Ciências Farmacêuticas: Biofarmacotécnica, 1st ed.; Guanabara Koogan Ltda.: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2009; ISBN 978-85-277-1587-4. [Google Scholar]
- Guedes, N.M.; Silva, J.G.; Mesquita, L.L.G.D.M.; Castro, W.V.D.; Lima, E.D.S.P.; Santana, D.P.D.; Bedor, D.C.G. Review of the Dissolution Tests in the Brazilian Pharmacopeia. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 60, e23633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, M.K.; Al-Shdefat, R.; Jamil, S.; Alam, P.; Abdel-Kader, M.S.; Shakeel, F. Solubility of Bioactive Compound Hesperidin in Six Pure Solvents at (298.15 to 333.15) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2014, 59, 2065–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, L.; Hu, Q.; Dou, H. Mixed Solvent Method for Improving the Size Uniformity and Cargo-Loading Efficiency of ZIF-8 Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2021, 37, 10089–10099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, M.; Liu, B.; Liu, R.; Qu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. Water-Based Synthesis of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 with High Morphology Level at Room Temperature. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 48433–48441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wu, T.; Carreon, M.A. Synthesis of ZIF-67 and ZIF-8 Crystals Using DMSO (Dimethyl Sulfoxide) as Solvent and Kinetic Transformation Studies. J. Cryst. Growth 2016, 455, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, A.F.V.D.; Siqueira, S.M.C.; Ricardo, N.M.P.S.; Almeida Neto, F.W.D.Q.; Souza, C.A.G.D.; Costa, K.B.S.; Cunha, A.P.; Almeida, R.R.D.; Saraiva, G.D.; Marinho, E.S.; et al. Microencapsulation of Hesperidin with Galactomannan Biopolymer: Structural, Vibrational and Thermal Analysis. Mater. Lett. 2024, 357, 135784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Zhao, L.; Lai, Z. Rapid Synthesis of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 (ZIF-8) Nanocrystals in an Aqueous System. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Fang, X.; Wu, B.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, N. Facile Synthesis of Size-Tunable ZIF-8 Nanocrystals Using Reverse Micelles as Nanoreactors. Sci. China Chem. 2014, 57, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Yu, Y.; Fu, C.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Water-Based Synthesis of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 for CO2 Capture. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 29227–29232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Keck, C.M.; Müller, R.H. Oral Hesperidin-Amorphization and Improved Dissolution Properties by Controlled Loading onto Porous Silica. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 518, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Yoshinaga, A.; Takabe, K.; Yoshioka, T.; Ogawa, K.; Sakamoto, M.; Azuma, J.; Honda, Y. In Situ Detection and Identification of Hesperidin Crystals in Satsuma Mandarin (Citrus unshiu) Peel Cells. Phytochem. Anal. 2015, 26, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANVISA RDC 31/2010-Provides for Pharmaceutical Equivalence and Comparative Dissolution Profile Studies. 2010. Available online: https://anvisalegis.datalegis.net/action/ActionDatalegis.php?acao=abrirTextoAto&tipo=RDC&numeroAto=00000031&seqAto=000&valorAno=2010&orgao=RDC/DC/ANVISA/MS&codTipo=&desItem=&desItemFim=&cod_menu=1696&cod_modulo=134&pesquisa=true (accessed on 8 September 2025).
- Li, H.-F.; Zhang, D.; Qu, W.-J.; Wang, H.-L.; Liu, Y.; Borjigdai, A.; Cui, J.; Dong, Z.-Q. Biopharmaceutics classification and absorption mechanisms primary study on four kinds of flavonoids. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2016, 41, 1198–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.D.; Wen, H.; Taylor, L.S. Non-Sink Dissolution Conditions for Predicting Product Quality and In Vivo Performance of Supersaturating Drug Delivery Systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).