Mechanical Performance of Concrete with Graphene-Oxide-Treated Recycled Coarse Ceramic Aggregates: Effects on Aggregate Water Absorption and Workability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Concrete Mixes
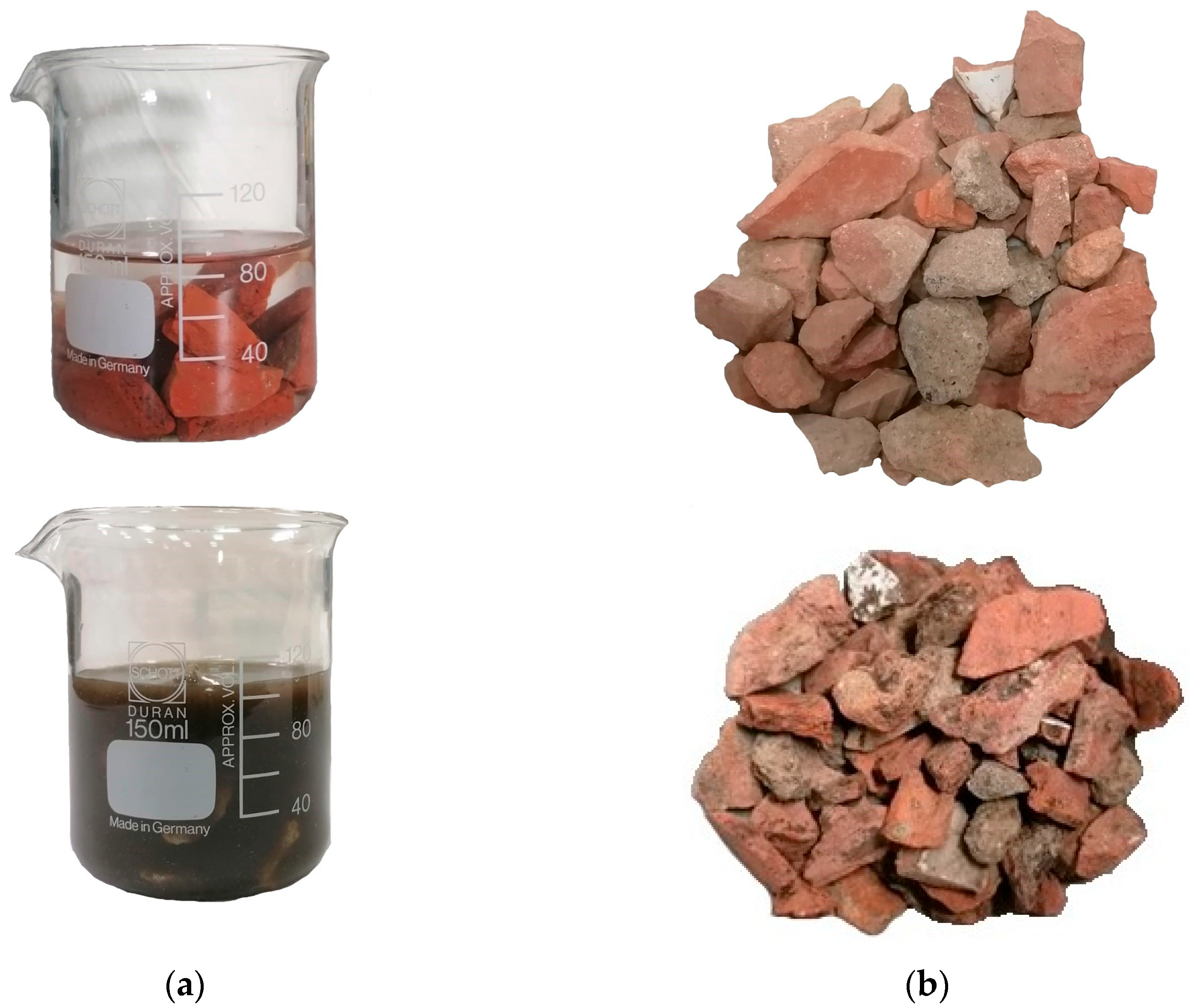
2.3. Treatment of Recycled Aggregates
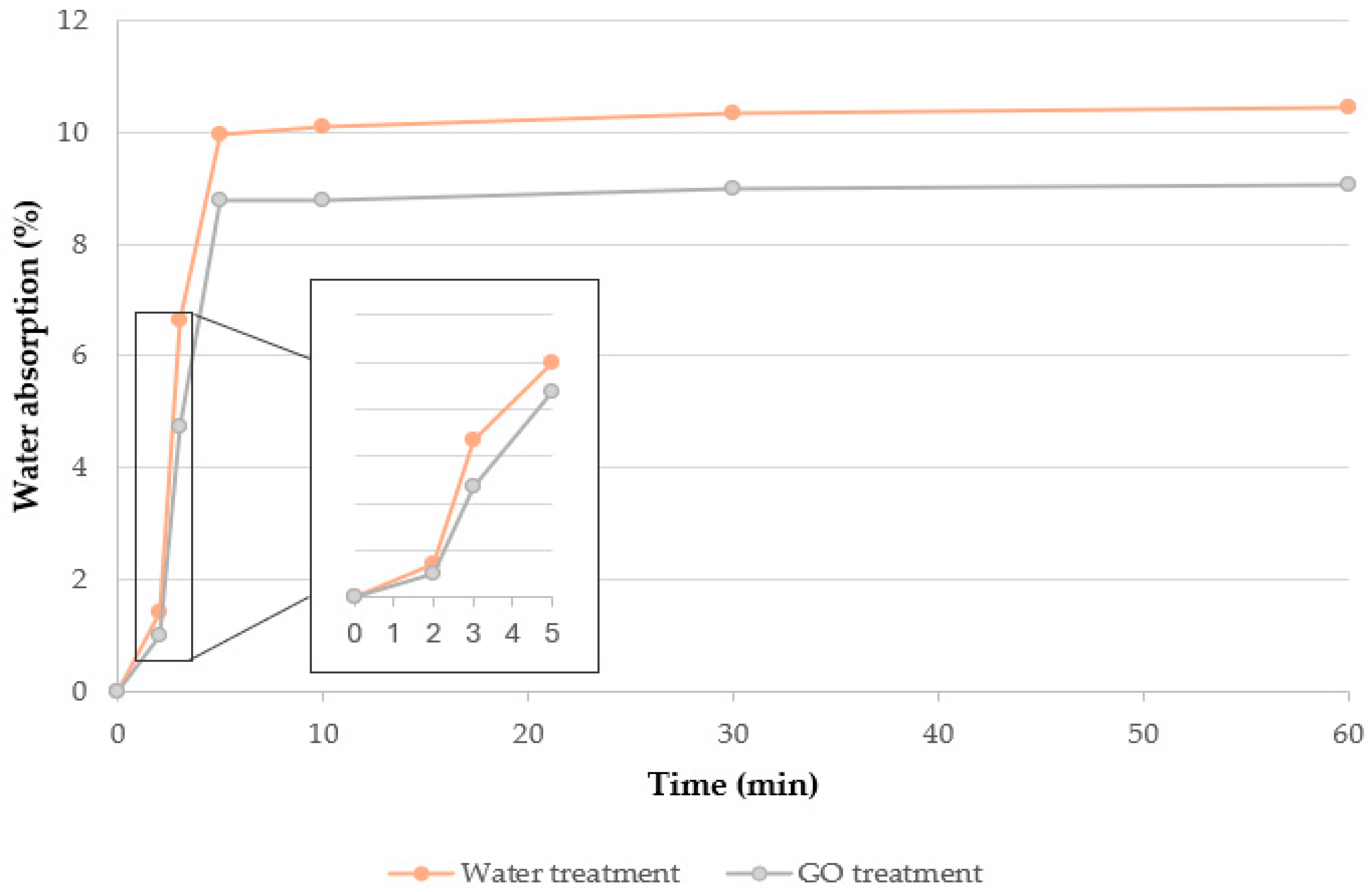
2.4. Water Absorption
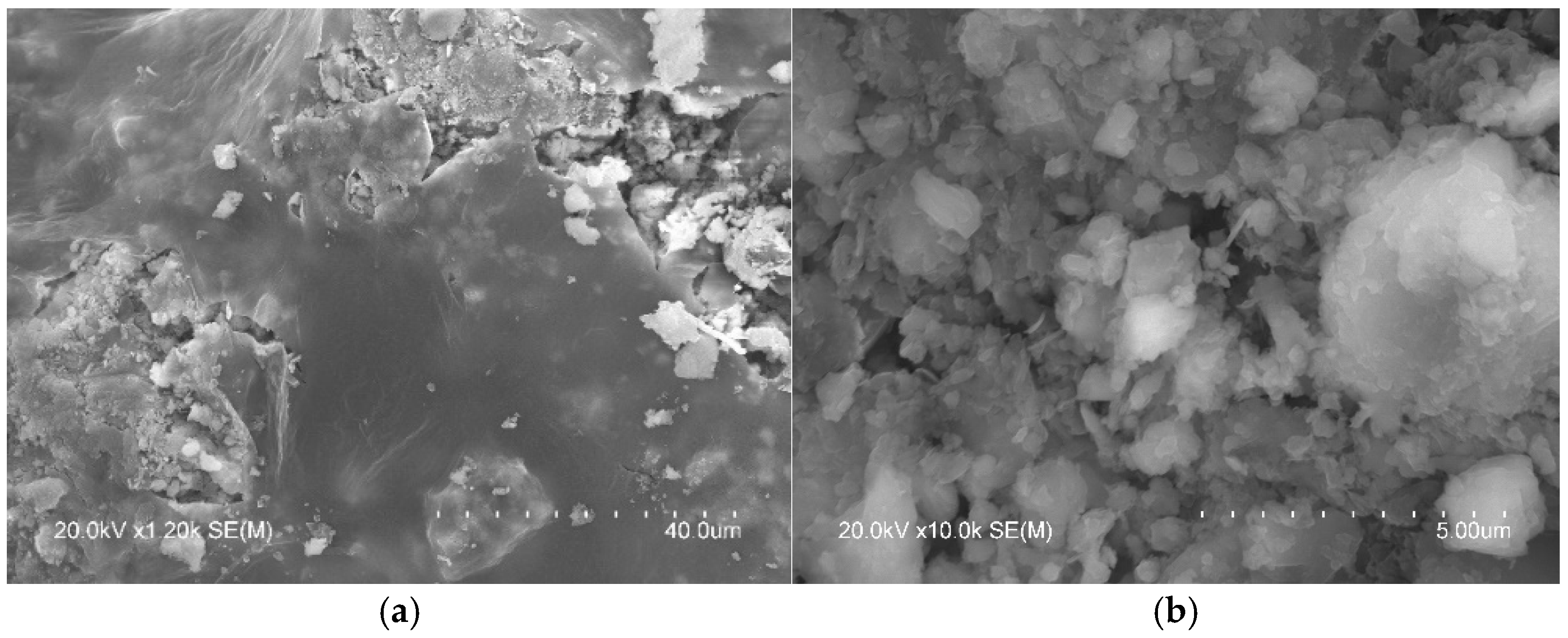
2.5. SEM Analysis
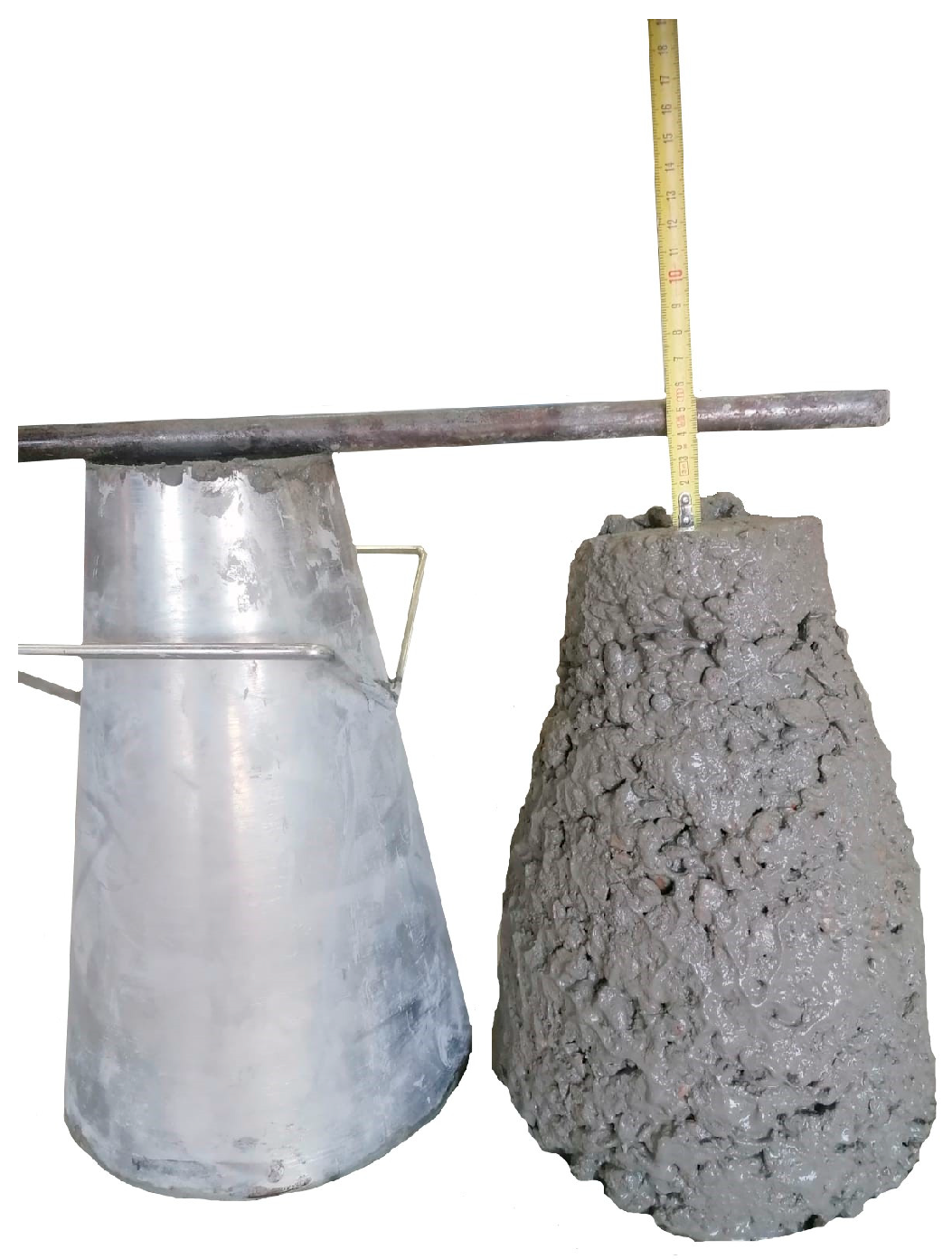
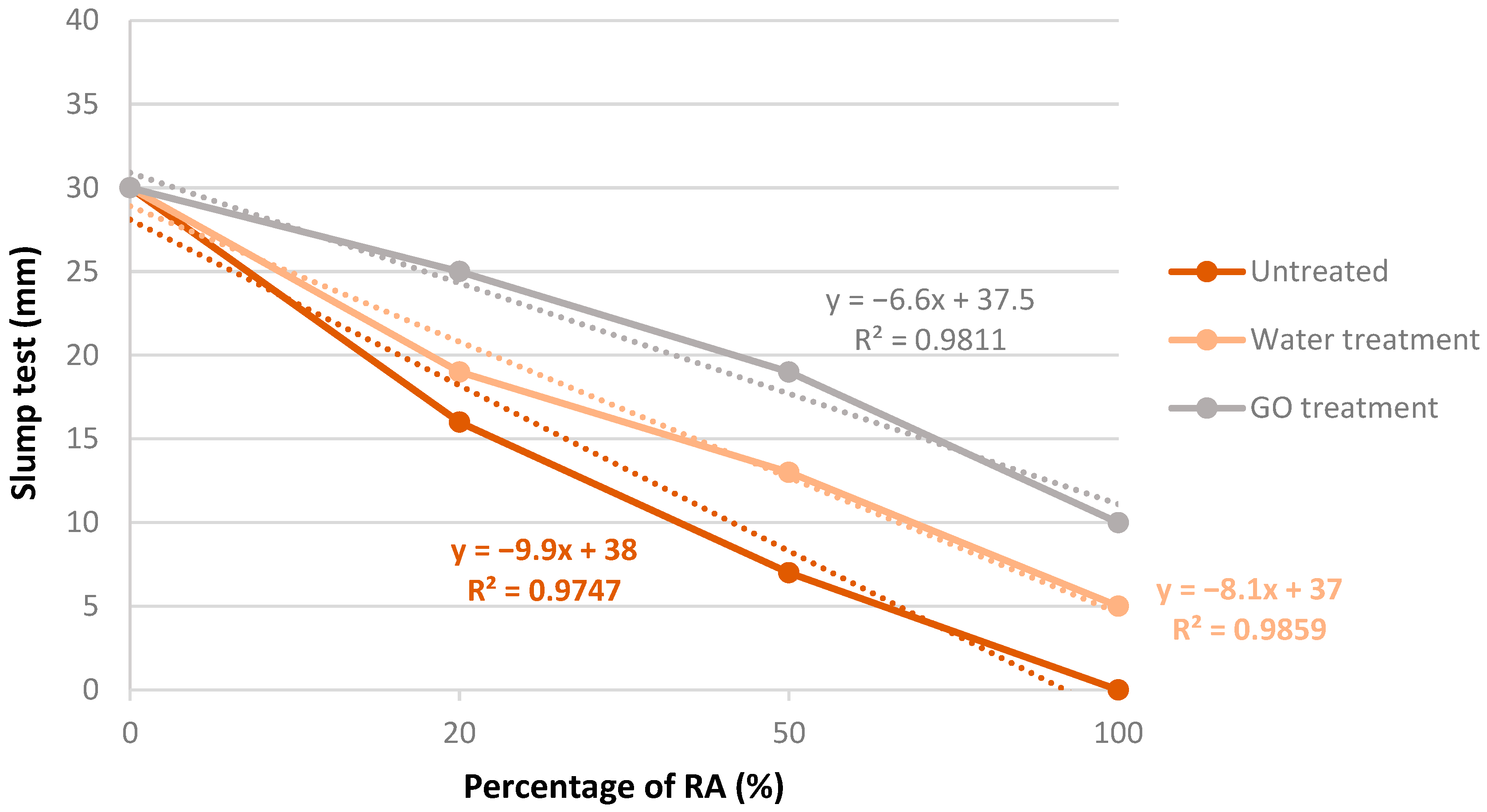
2.6. Consistency
2.7. Compressive Strength
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Absorption
3.2. SEM Analysis
3.3. Slump Test
3.4. Compressive Strength
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding

Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDW | Construction and demolition waste |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| HCl | Hydrochloric acid |
| NA | Natural aggregates |
| RA | Recycled aggregates |
| ITZ | Interfacial interaction zone |
| XRF | X-ray fluorescence |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
References
- Shajidha, H.; Mortula, M.M. Sustainable waste management in the construction industry. Front. Sustain. Cities 2025, 7, 1582239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, M.; Chen, Z.; Xie, Z.; Huang, L.; Osman, A.I.; Farghali, M.; Sandanayake, M.; Liu, E.; Ahn, Y.H.; et al. Conversion of waste into sustainable construction materials: A review of recent developments and prospects. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 27, 100930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifazi, G.; Grosso, C.; Palmieri, R.; Serranti, S. Current trends and challenges in construction and demolition waste recycling. Curr. Opin. Green. Sustain. Chem. 2025, 53, 101032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade Salgado, F.; de Andrade Silva, F. Recycled aggregates from construction and demolition waste towards an application on structural concrete: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 52, 104452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, G.S.D.; Quattrone, M.; Ambrós, W.M.; Cazacliu, B.G.; Sampaio, C.H. Current applications of recycled aggregates from construction and demolition: A review. Materials 2021, 14, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.V.; de Brito, J.; Dhir, R.K. Use of recycled aggregates arising from construction and demolition waste in new construction applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN 4226-100:2002; Aggregates for Mortar and Concrete—Part 100: Recycled Aggregates. Sai Global: Sydney, Australia, 2002.
- NEN 5905:2010; Dutch Supplement to NEN-EN 12620+A1 “Aggregates for Concrete”. The Netherlands Standardization Institute: Delft, The Netherlands, 2008.
- Turk, O.; Yehia, S.; Abdelfatah, A.; Elchalakani, M. Sustainable concrete production: The potential of utilizing recycled waste materials. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, S.M.; Helene, P. Durability of recycled aggregates concrete: A safe way to sustainable development. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1975–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.S.; Shui, Z.H.; Lam, L.; Fok, H.; Kou, S.C. Influence of moisture states of natural and recycled aggregates on the slump and compressive strength of concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Hwang, C.L. Properties of HPC with recycled aggregates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Morales, J.; Burciaga-Diaz, O.; Gomez-Zamorano, L.Y.; Escalante-Garcia, J.I. Transforming construction and demolition waste concrete as a precursor in sustainable cementitious materials: An innovative recycling approach. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 204, 107474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Structural Code; Royal Decree 470/2021; Spanish Ministry of the Presidency, Relations with the Courts and Democratic Memory: Madrid, Spain, 2021.
- Kumar, A.; Singh, G.J. Improving the physical and mechanical properties of recycled concrete aggregate: A state-of-the-art review. Eng. Res. Express 2023, 5, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, A.; Selvaranjan, K.; Srikanth, G.; Gamage, J.C.P.H. Development of high strength recycled aggregate concrete-composite effects of fly ash, silica fume and rice husk ash as pozzolans. Mater. Struct. Mater. Et. Constr. 2022, 55, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Shiuly, A. Exploring mechanical characteristics of recycled concrete aggregates from demolition waste: Advancements, challenges, and future directions for sustainable construction: A review. Discov. Civ. Eng. 2025, 2, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Zhao, W.; Ye, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C. Measurement of Water Absorption of Recycled Aggregate. Materials 2022, 15, 5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djerbi Tegguer, A. Determining the water absorption of recycled aggregates utilizing hydrostatic weighing approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 27, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.C.; Faruky, S.A.U.; Babafemi, A.J.; Miah, M.J. Eco-friendly concrete with waste ceramic tile as coarse aggregate: Mechanical strength, durability, and microstructural properties. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 2023, 24, 3363–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngayakamo, B.H. Sustainable concrete production: The role of ceramic waste as a partial coarse aggregate substitute. Discov. Civ. Eng. 2025, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, P.; Wu, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y. Mechanical Properties and Durability of Sustainable Concrete Manufactured Using Ceramic Waste: A Review. J. Renew. Mater. 2023, 11, 937–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Du, Q.; Bao, Y. Concrete with recycled concrete aggregate and crushed clay bricks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 1935–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roig-Flores, M.; Reig, L.; Albero, V.; Hernández-Figueirido, D.; Melchor-Eixea, A.; Pitarch, Á.M.; Piquer, A. Utilisation of Ceramic Stoneware Tile Waste as Recycled Aggregate in Concrete. Buildings 2023, 13, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, N.B.; Khalid, F.S.; Irwan, J.M.; Anting, N.; Mazenan, P.N. A study on the performance of concrete containing recycled aggregates and ceramic as materials replacement. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 271, 012081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Gan, W.; Yao, G.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, R. Effect of Permeable Crystalline Materials on the Mechanical and Porosity Property of Recycled Aggregate and Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Materials 2023, 16, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, F.d.A.; Silva, F.d.A. Properties of recycled aggregates from different composition and its influence on concrete strength. Rev. IBRACON De Estrut. E Mater. 2021, 14, 41952021000600005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, P.; Abhiram, K.; Manoj, B. Properties of treated recycled aggregates and its influence on concrete strength characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandurangan, K.; Dayanithy, A.; Om Prakash, S. Influence of treatment methods on the bond strength of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 120, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.J.; Kazmi, S.M.S.; Wu, Y.F.; Lin, X. Axial stress-strain performance of steel spiral confined acetic acid immersed and mechanically rubbed recycled aggregate concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 34, 101891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, W.F.; Quattrone, M.; John, V.M.; Angulo, S.C. Roughness, wettability and water absorption of water repellent treated recycled aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 146, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Singh, S.P. Carbonation and electrical resistance of self compacting concrete made with recycled concrete aggregates and metakaolin. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 121, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, D.; de Brito, J.; Evangelista, L. Evaluation of high-performance concrete with recycled aggregates: Use of densified silica fume as cement replacement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 147, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.; Christodoulou, C.; Goodier, C.; Austin, S.; Dunne, D. Durability performance of sustainable structural concrete: Effect of coarse crushed concrete aggregate on rapid chloride migration and accelerated corrosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, M.; Oliveira, M. Mitigation of the negative effects of recycled aggregate water absorption in concrete technology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 133, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhao, P.; Lu, L.; Cheng, X. Effect of the optimized triple mixing method on the ITZ microstructure and performance of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 203, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Vandevyvere, B.; Vanhessche, S.; Schoon, J.; Boon, N.; De Belie, N. Microbial carbonate precipitation for the improvement of quality of recycled aggregates. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 156, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, J.; Rodríguez-Robles, D.; Wang, J.; De Belie, N.; Morán-del Pozo, J.M.; Guerra-Romero, M.I.; Juan-Valdés, A. Quality improvement of mixed and ceramic recycled aggregates by biodeposition of calcium carbonate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.R.; Hong, Z.Q.; Zhang, J.L.; Kou, S.C. Pore size distribution and ITZ performance of mortars prepared with different bio-deposition approaches for the treatment of recycled concrete aggregate. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 111, 103631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, D.; Zhan, B.; Poon, C.S. Durability of recycled aggregate concrete prepared with carbonated recycled concrete aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 84, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Poon, C.S.; Xiao, J.; Xuan, D. Effect of carbonated recycled coarse aggregate on the dynamic compressive behavior of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayasundara, M.; Mendis, P.; Crawford, R.H. Methodology for the integrated assessment on the use of recycled concrete aggregate replacing natural aggregate in structural concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.; Zhou, B.; Xiao, J. Pore structure and chloride diffusivity of recycled aggregate concrete with nano-SiO2 and nano-TiO2. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 150, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.J.; Zheng, D.; Duan, H.B.; Han, N.; Xing, F. Performance enhancement and environmental impact of cement composites containing graphene oxide with recycled fine aggregates. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Xiang, P. High Temperature Exposure Assessment of Graphene Oxide Reinforced Cement. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 786260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, S.; Pan, Z.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Wang, C.M.; Duan, W.H. Nano reinforced cement and concrete composites and new perspective from graphene oxide. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 73, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsaei, E.; de Souza, F.B.; Yao, X.; Benhelal, E.; Akbari, A.; Duan, W. Graphene-based nanosheets for stronger and more durable concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 183, 642–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Gong, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhong, J. Effects of combined usage of supplementary cementitious materials on the thermal properties and microstructure of high-performance concrete at high temperatures. Materials 2020, 13, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Zhong, J. Carbon-based nanomaterials engineered cement composites: A review. J. Infrastruct. Preserv. Resil. 2022, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Dong, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Xu, Q. Steel corrosion and corrosion-induced cracking in recycled aggregate concrete. Corros. Sci. 2014, 85, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Shi, X.; Wong, H.S.; Jiang, Z.; Zhong, J. Graphene coated sand for smart cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 346, 128313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Shi, X.; Zhong, J. Interfacial nano-engineering by graphene oxide to enable better utilization of silica fume in cementitious composite. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 354, 131381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Zhang, Q.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K.; Duan, W. Graphene oxide-coated sand for improving performance of cement composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 124, 104279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNE-EN 12620:2003+A1:2009; Aggregates for Concrete. Asociación Española de Normalización y Certificación (AENOR): Madrid, Spain, 2009.
- UNE-EN 933-1:2012; Test for Geometrical Properties of Aggregates-Part 1: Determination of Particle Size Distribution-Sieving Method. Asociación Española de Normalización y Certificación (AENOR): Madrid, Spain, 2012.
- UNE-EN 933-2:2002; Test for Geometrical Properties of Aggregates-Part 2: Determination of Particle Size Distribution-Test Sieves, Nominal Size of Apertures. Asociación Española de Normalización y Certificación (AENOR): Madrid, Spain, 2002.
- UNE-EN 1097-6:2025; Test for Mechanical and Physical Properties of Aggregates-Part 6: Determination of Particle Density and Water Absorption. Asociación Española de Normalización y Certificación (AENOR): Madrid, Spain, 2025.
- UNE-EN 933-3:2012; Test for Geometrical Properties of Aggregates-Part 3: Determination of Particle Shape-Flakiness Index. Asociación Española de Normalización y Certificación (AENOR): Madrid, Spain, 2012.
- UNE-EN 1097-2:2021; Test for Mechanical and Physical Properties of Aggregates-Part 2: Methods for the Determination of Resistance to Fragmentation. Asociación Española de Normalización y Certificación (AENOR): Madrid, Spain, 2021.
- UNE-EN 933-11:2009; Test to Determine the Geometric Properties of Aggregates-Part 11: Classification Test of the Components of Recycled Coarse Aggregates. Asociación Española de Normalización y Certificación (AENOR): Madrid, Spain, 2009.
- García-González, J.; Rodríguez-Robles, D.; Juan-Valdés, A.; del Pozo, J.M.M.; Guerra-Romero, M.I. Pre-saturation technique of the recycled aggregates: Solution to the water absorption drawback in the recycled concrete manufacture. Materials 2014, 7, 6224–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNE-EN 12350-2:2020; Testing Fresh Concrete-Part 2: Slump-Test. Asociación Española de Normalización y Certificación (AENOR): Madrid, Spain, 2020.
- UNE-EN 12390-3:2020; Testing Hardened Concrete-Part 3: Compressive Strength of Test Specimens. Asociación Española de Normalización y Certificación (AENOR): Madrid, Spain, 2020.
- Nekahi, A.; Marashi, S.P.H.; Fatmesari, D.H. Modified structure of graphene oxide by investigation of structure evolution. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2015, 38, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Chung, J.H.Y.; Chiu, H.Y.; Yeh, N.L.; Chang, S.J.; Chan, C.H.; Shih, C.C.; Chen, G.Y. Enhancing Cementitious Composites with Functionalized Graphene Oxide-Based Materials: Surface Chemistry and Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, J. Nano-engineering the interfacial transition zone between recycled concrete aggregates and fresh paste with graphene oxide. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 384, 131244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Wirth, C. Pentzer, Efficient sizing of single layer graphene oxide with optical microscopy under ambient conditions. Carbon 2020, 157, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musielak, M.; Gagor, A.; Zawisza, B.; Talik, E.; Sitko, R. Graphene Oxide/Carbon Nanotube Membranes for Highly Efficient Removal of Metal Ions from Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 28582–28590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhu, M.; Wang, K.; Zhong, M.; Wei, J.; Wu, D.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, H. Selective Ion Penetration of Graphene Oxide Membranes. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devapura, P.; Ginigaddara, T.; Udumulla, D.; Mendis, P.; Booy, M.; Herath, N. Effect of graphene oxide on interfacial transition zone and strength enhancement of recycled aggregate concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 105, 112570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Chen, G.; Cai, Z.; Shao, J. Mechanical Properties, Impermeability, and Microstructure of Mortar Containing Recycled Fine Aggregates Modified by Graphene Oxide After High-Temperature Exposure. Buildings 2025, 15, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-Cuesta, V.; Skaf, M.; Faleschini, F.; Manso, J.M.; Ortega-López, V. Self-compacting concrete manufactured with recycled concrete aggregate: An overview. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P. Methods for improving the durability of recycled aggregate concrete: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 6367–6386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Lu, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S. Influence of the Graphene Oxide on the Pore-Throat Connection of Cement Waste Rock Backfill. Materials 2023, 16, 4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Jia, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, X. Hydroxylated Graphene: A Promising Reinforcing Nanofiller for Nanoengineered Cement Composites. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 30465–30477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lu, Z.; Chuah, S.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Duan, W.H.; Li, Z. Effects of graphene oxide aggregates on hydration degree, sorptivity, and tensile splitting strength of cement paste. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 100, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junak, J.; Sicakova, A. Effect of surface modifications of recycled concrete aggregate on concrete properties. Buildings 2017, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basquiroto de Souza, F.; Yao, X.; Lin, J.; Naseem, Z.; Tang, Z.Q.; Hu, Y.; Gao, W.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K.; Duan, W. Effective strategies to realize high-performance graphene-reinforced cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 324, 126636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, J.; Liu, W. Utilization of waste concrete recycling materials in self-compacting concrete. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 104930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabiri, H.; Kioumarsi, M.; Kheyroddin, A.; Kandiri, A.; Sartipi, F. Compressive strength of concrete with recycled aggregate; a machine learning-based evaluation. Clean. Mater. 2022, 3, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Shi, X.; Zhong, J. Nano-engineering the interfacial transition zone in cement composites with graphene oxide. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 356, 129284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, M.; De Brito, J.; Pontes, J.; Evangelista, L. Mechanical performance of concrete made with aggregates from construction and demolition waste recycling plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 99, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mufti, R.L.; Fried, A.N. Improving the strength properties of recycled asphalt aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxeberria, M.; Vázquez, E.; Marí, A.; Barra, M. Influence of amount of recycled coarse aggregates and production process on properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Standard | Test | Test and Result | Limit Value [14] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recycled Aggregates | Natural Aggregates | |||
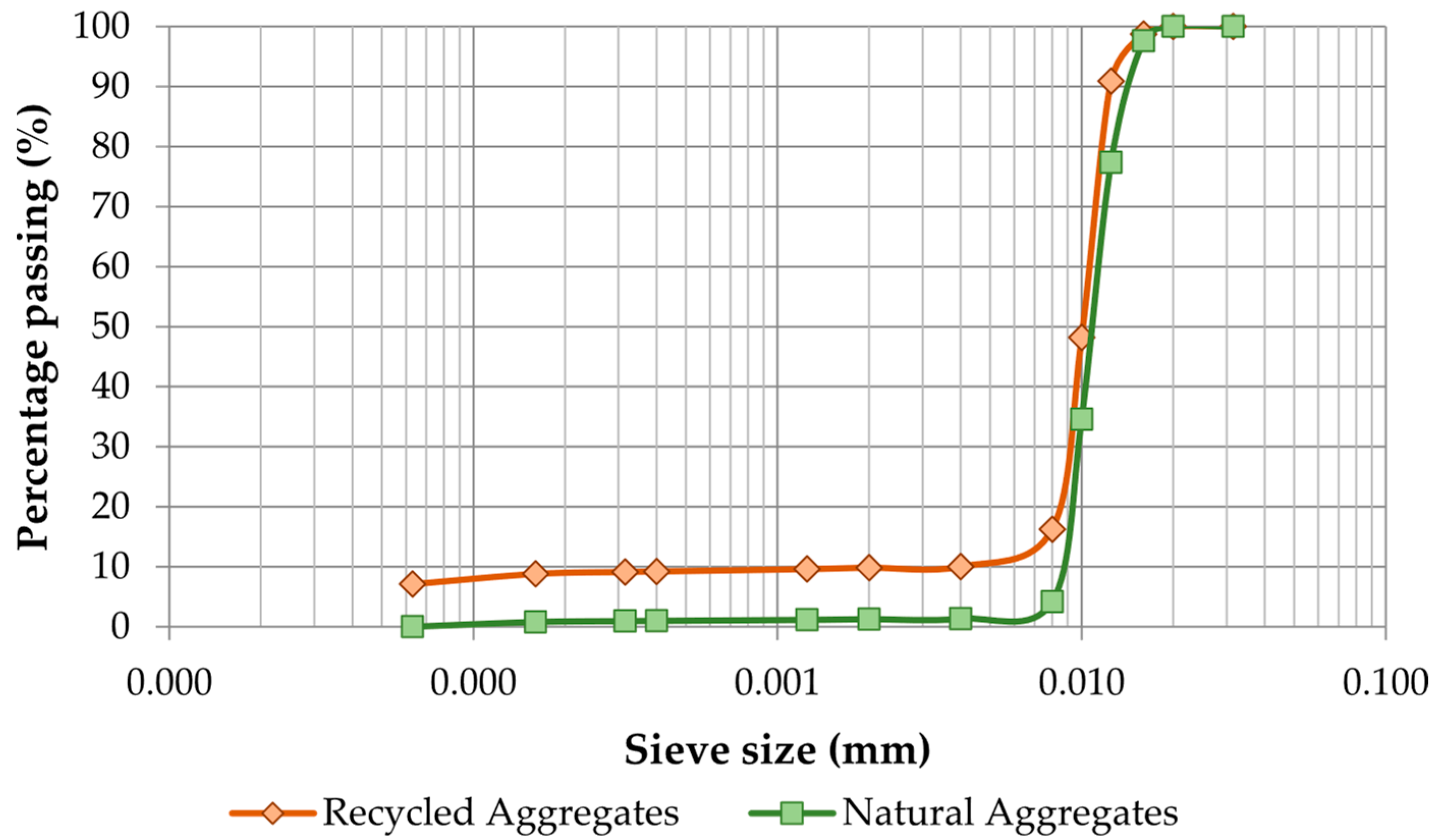
| UNE-EN 933-1:2012 [55] UNE-EN 933-2:2022 [56] | Particle size analysis | |||
| D/d ratio | 4 | 4 | ≥1.4 | |
| Fines content | 1.46% | 0.02% | ≤1.5% | |
| UNE-EN 1097-6:2025 [57] | Water absorption | 8.68% | 1.18% | ≤7.0% |
| Apparent density | 2.58 Mg/m3 | 2.63 Mg/m3 | - | |
| After oven-drying density | 1.91 Mg/m3 | 1.94 Mg/m3 | - | |
| Saturate surface density | 2.17 Mg/m3 | 2.58 Mg/m3 | - | |
| UNE-EN 933-3:2012 [58] | Flakiness index | 4.64% | 3.60% | ≤35% |
| UNE-EN 1097-2:2021 [59] | Los Angeles coefficient | 38.47% | 24.06% | ≤40% |
| Component | Recycled Aggregates (%) |
|---|---|
| Ru: Natural aggregates | 0.0 |
| Rb: Bricks and tiles | 98.6 |
| Rc: Concrete and mortar | 1.4 |
| Ra: Bituminous materials | 0.0 |
| Rg: Glass | 0.0 |
| X: Others | 0.0 |
| Elements (wt%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | SO3 | K2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | LOI |
| 42.04 | 11.54 | 4.28 | 0.07 | 2.51 | 20.66 | 0.76 | 2.71 | 1.99 | 0.54 | 0.14 | 12.67 |
| Mixtures | Amount of NA | Amount of RA |
|---|---|---|
| Mix 0 | 100% | 0% |
| Mix 20 | 80% | 20% |
| Mix 50 | 50% | 50% |
| Mix 100 | 0% | 100% |
| Components (kg/m3) | Quantity of RA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 20% | 50% | 100% | |
| Natural aggregates | 1060.9 | 790.0 | 442.6 | 0.0 |
| Recycled aggregates | 0.0 | 197.5 | 442.6 | 732.3 |
| Sand | 667.1 | 669.2 | 744.1 | 811.0 |
| Cement | 390.0 | 390.0 | 390.0 | 390.0 |
| Water | 215.0 | 215.0 | 215.0 | 215.0 |
| Water/cement ratio | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antolín-Rodríguez, A.; Juan-Valdés, A.; Guerra-Romero, M.I.; Morán-del Pozo, J.M.; Krzywon, R.; Maravelaki, P.-N.; García-González, J. Mechanical Performance of Concrete with Graphene-Oxide-Treated Recycled Coarse Ceramic Aggregates: Effects on Aggregate Water Absorption and Workability. Ceramics 2025, 8, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8030104
Antolín-Rodríguez A, Juan-Valdés A, Guerra-Romero MI, Morán-del Pozo JM, Krzywon R, Maravelaki P-N, García-González J. Mechanical Performance of Concrete with Graphene-Oxide-Treated Recycled Coarse Ceramic Aggregates: Effects on Aggregate Water Absorption and Workability. Ceramics. 2025; 8(3):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8030104
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntolín-Rodríguez, Andrea, Andrés Juan-Valdés, Manuel Ignacio Guerra-Romero, Julia María Morán-del Pozo, Rafal Krzywon, Pagona-Noni Maravelaki, and Julia García-González. 2025. "Mechanical Performance of Concrete with Graphene-Oxide-Treated Recycled Coarse Ceramic Aggregates: Effects on Aggregate Water Absorption and Workability" Ceramics 8, no. 3: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8030104
APA StyleAntolín-Rodríguez, A., Juan-Valdés, A., Guerra-Romero, M. I., Morán-del Pozo, J. M., Krzywon, R., Maravelaki, P.-N., & García-González, J. (2025). Mechanical Performance of Concrete with Graphene-Oxide-Treated Recycled Coarse Ceramic Aggregates: Effects on Aggregate Water Absorption and Workability. Ceramics, 8(3), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8030104








