Laboratory, Clinical-Related Processing and Time-Related Factors’ Effect on Properties of High Translucent Zirconium Dioxide Ceramics Intended for Monolithic Restorations a Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Definitions
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Search Strategy and Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.6. Data Synthesis
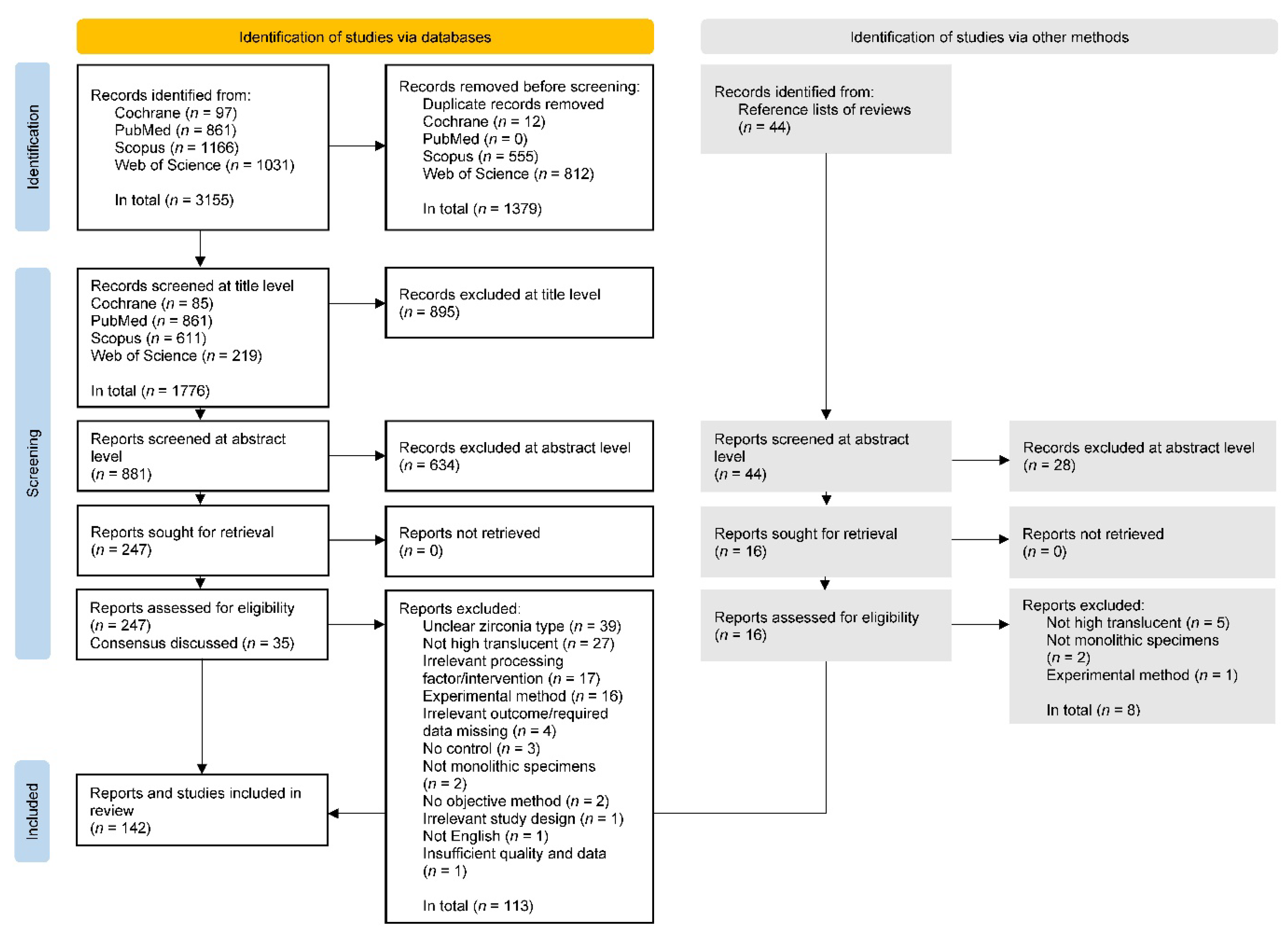
3. Results
3.1. Search Strategy
3.2. Study Characteristics
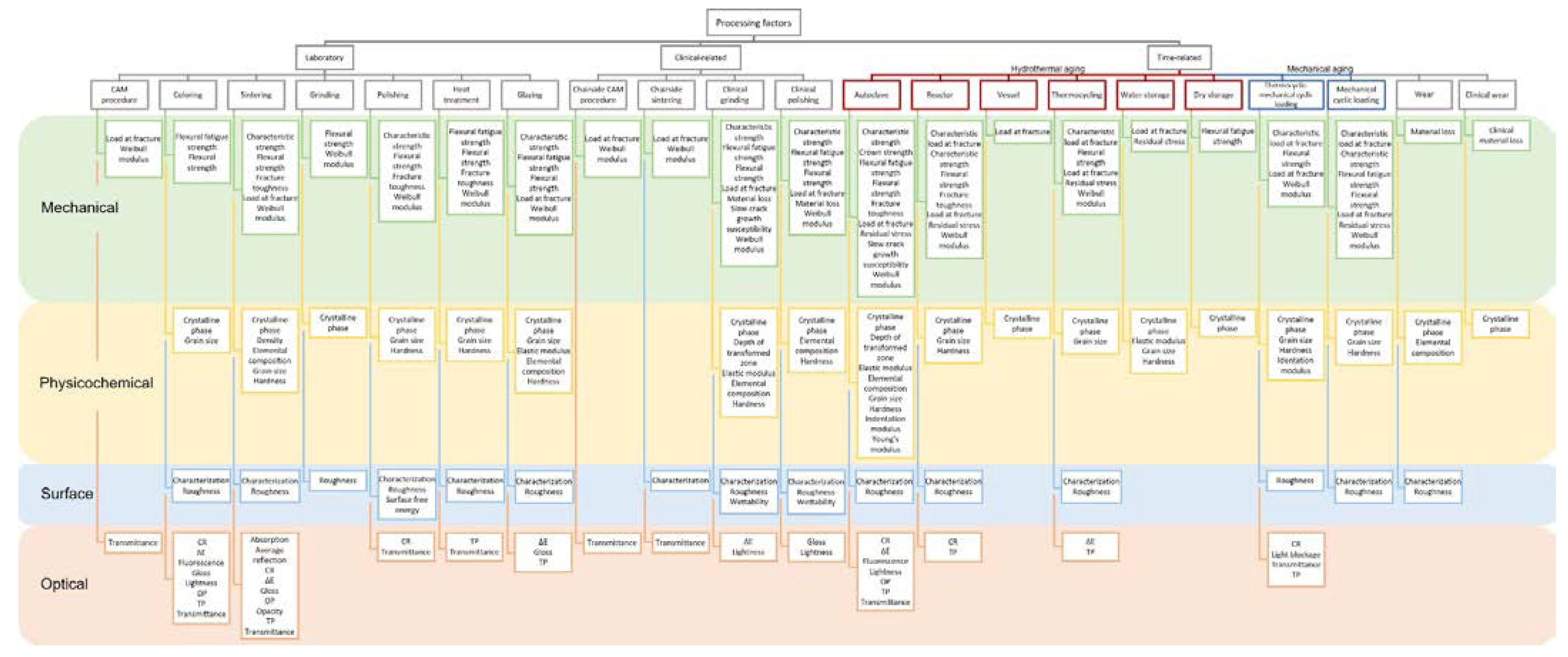
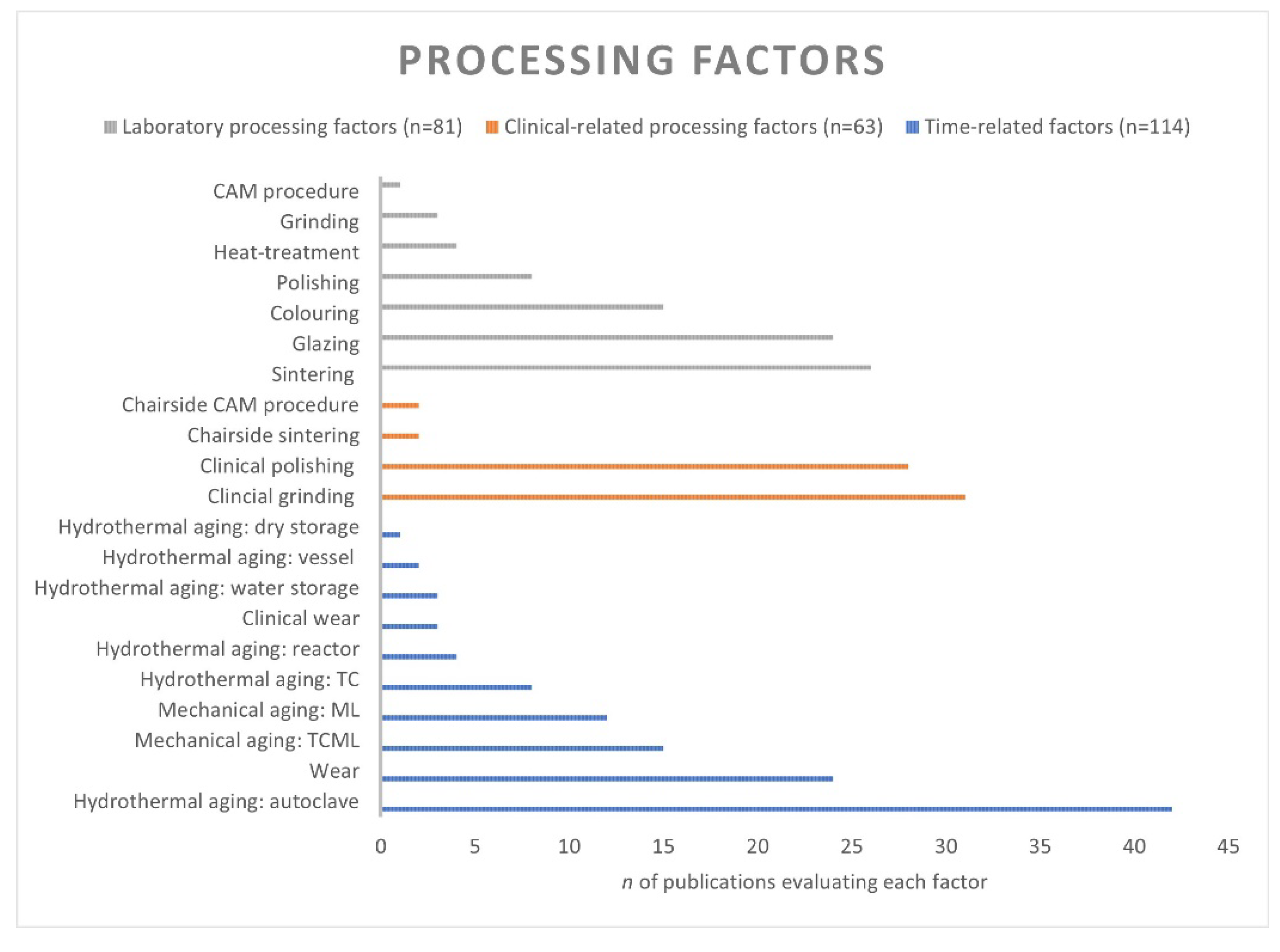
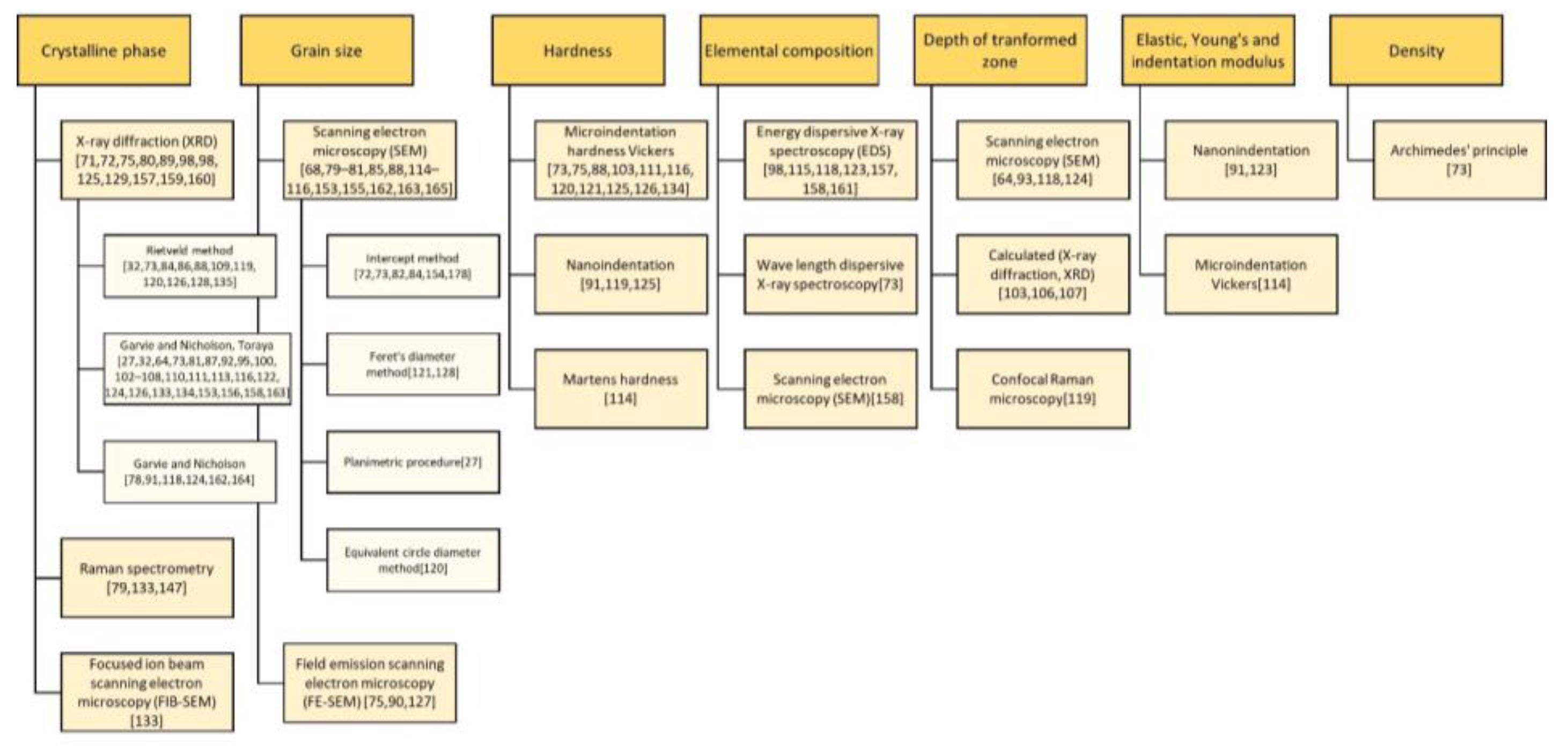
3.3. Zirconia Types, Processing Factors, Properties, and Methods
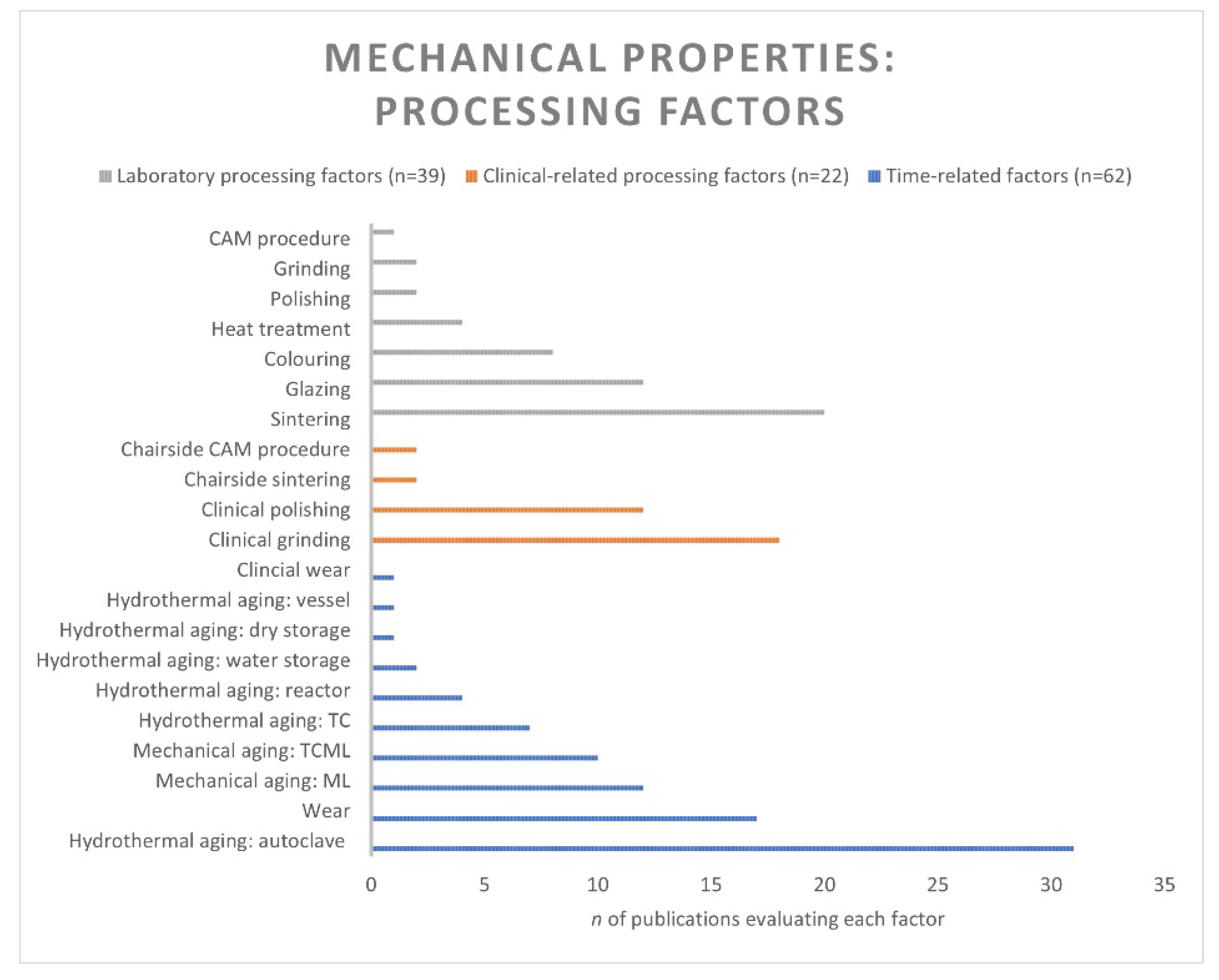
3.4. Mechanical Properties
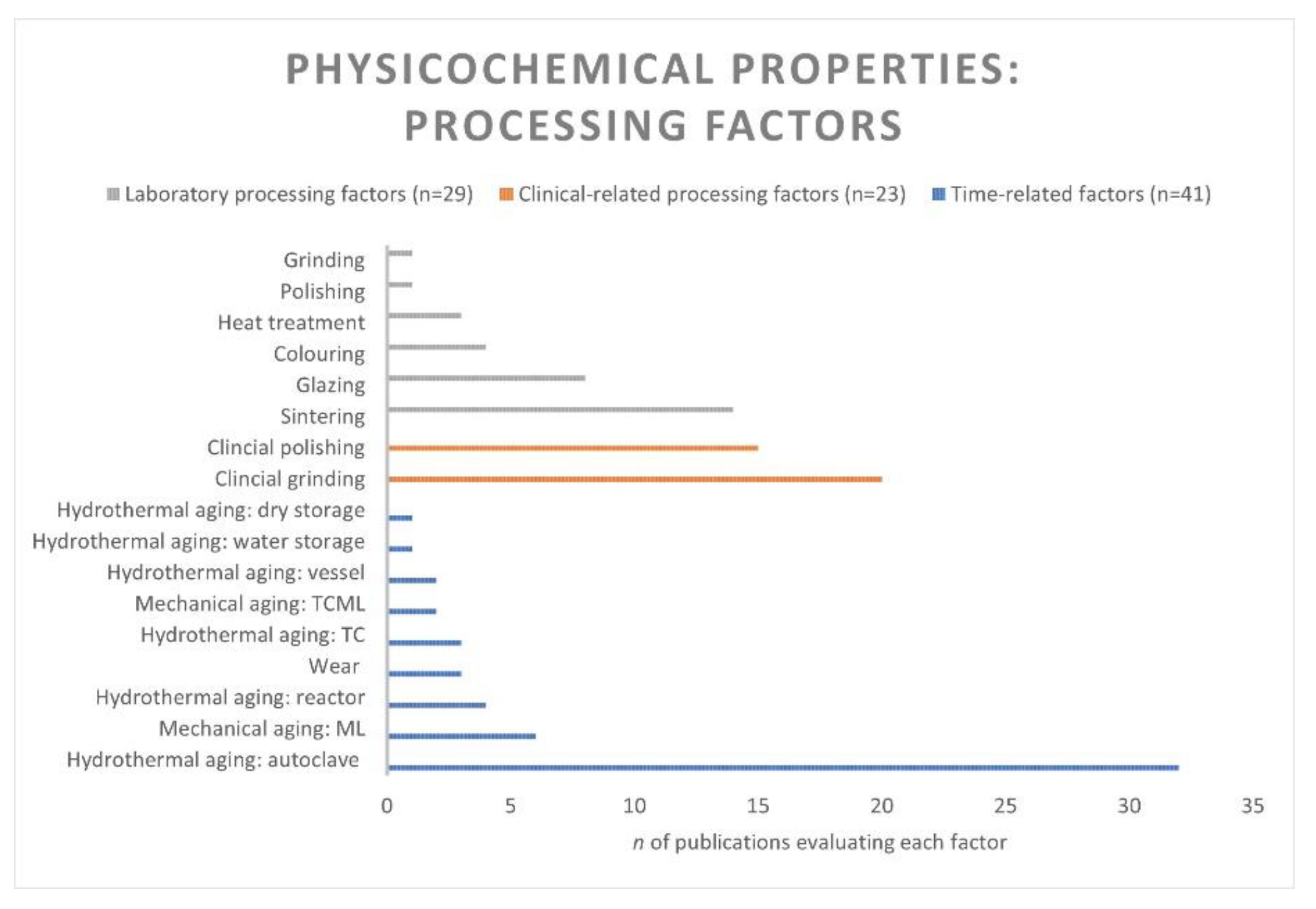
3.4.1. Laboratory Processing Factors
Factor: CAM Procedure. Properties: Load at Fracture and Weibull Modulus
- 4YSZ and Multilayer 3Y-TZP/5YSZ
Factor: Colouring. Properties: Flexural Strength and Flexural Fatigue Strength
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ
Factor: Sintering. Properties: Flexural Strength, Weibull Modulus, Characteristic Strength, Load at Fracture, and Fracture Toughness
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ, Multilayer 3Y-TZP/5YSZ, and 4YSZ/5YSZ
Factors: Grinding, Polishing, Heat Treatment, and Glazing. Properties: Flexural Strength, Weibull Modulus, Characteristic Strength, Flexural Fatigue Strength, and Fracture Toughness
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ and Multilayer 4YSZ/5YSZ
3.4.2. Clinical-Related Processing Factors
Factors: Chairside CAM Procedure and Sintering. Properties: Load at Fracture and Weibull Modulus
- HT 3Y-TZP
Factors: Clinical Grinding and Polishing. Properties: Flexural Strength, Weibull Modulus, Characteristic Strength, Flexural Fatigue Strength, Slow Crack Growth Susceptibility, and Material Loss
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 5YSZ and Multilayer 4YSZ/5YSZ
3.4.3. Time-Related Factors
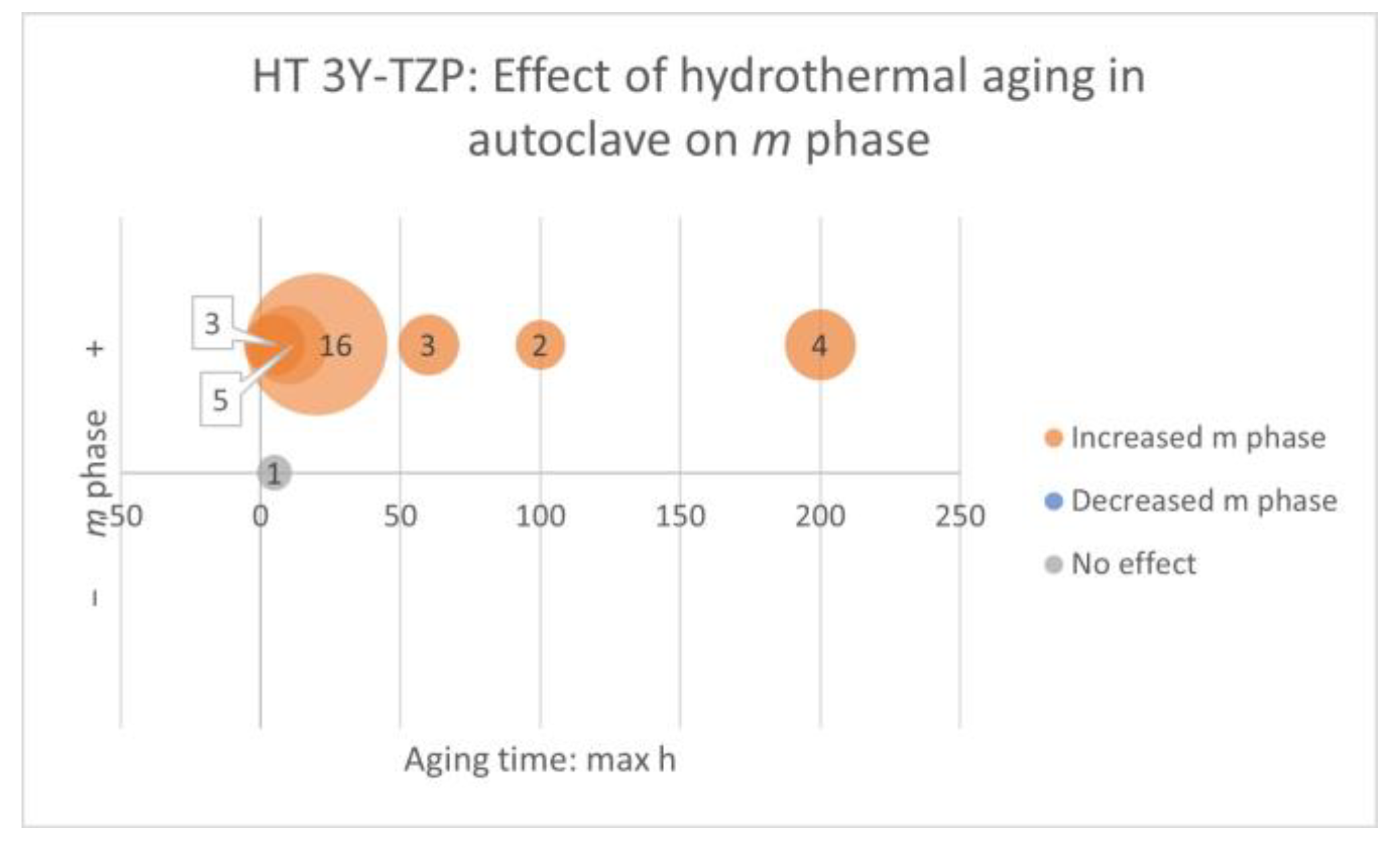
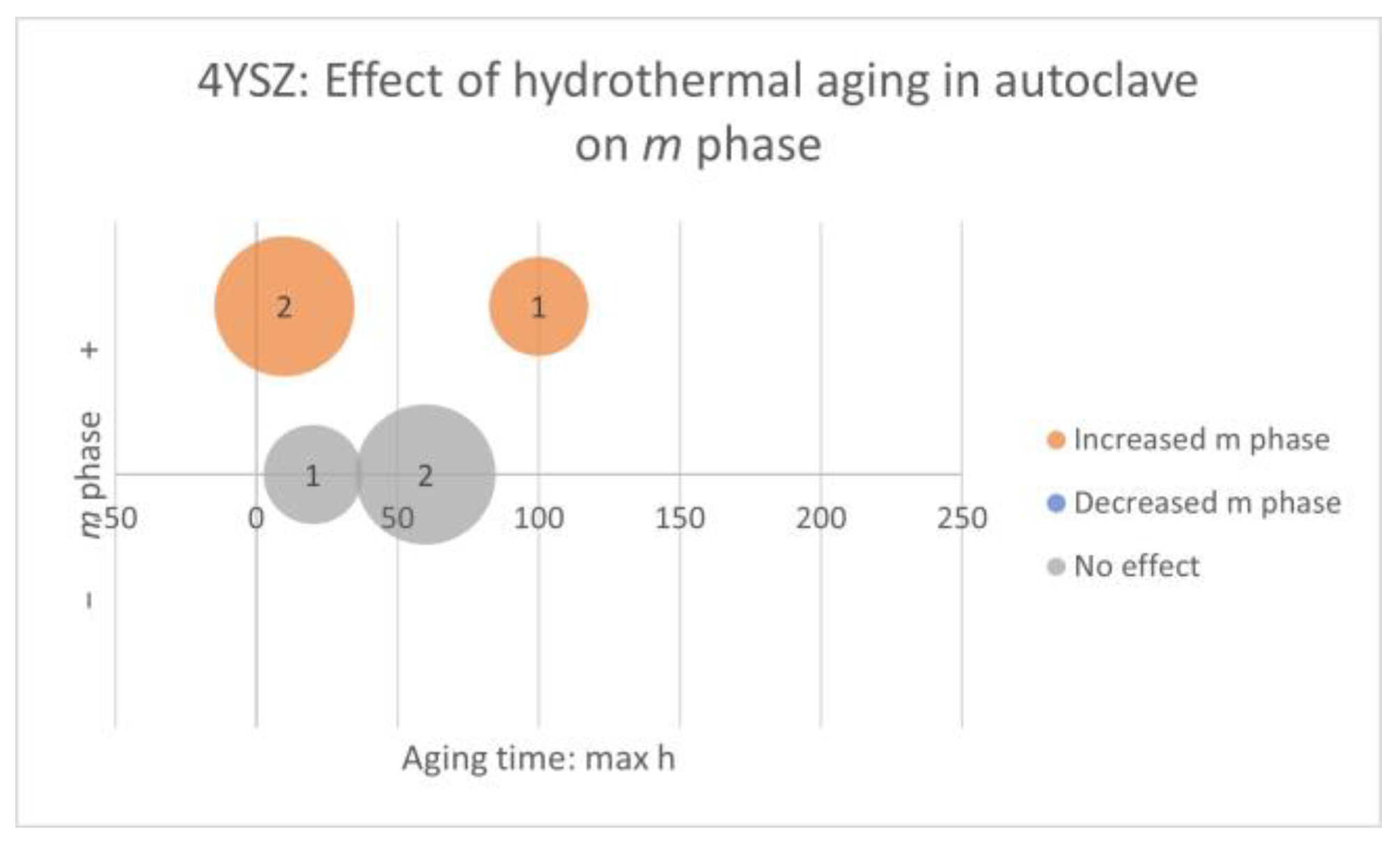
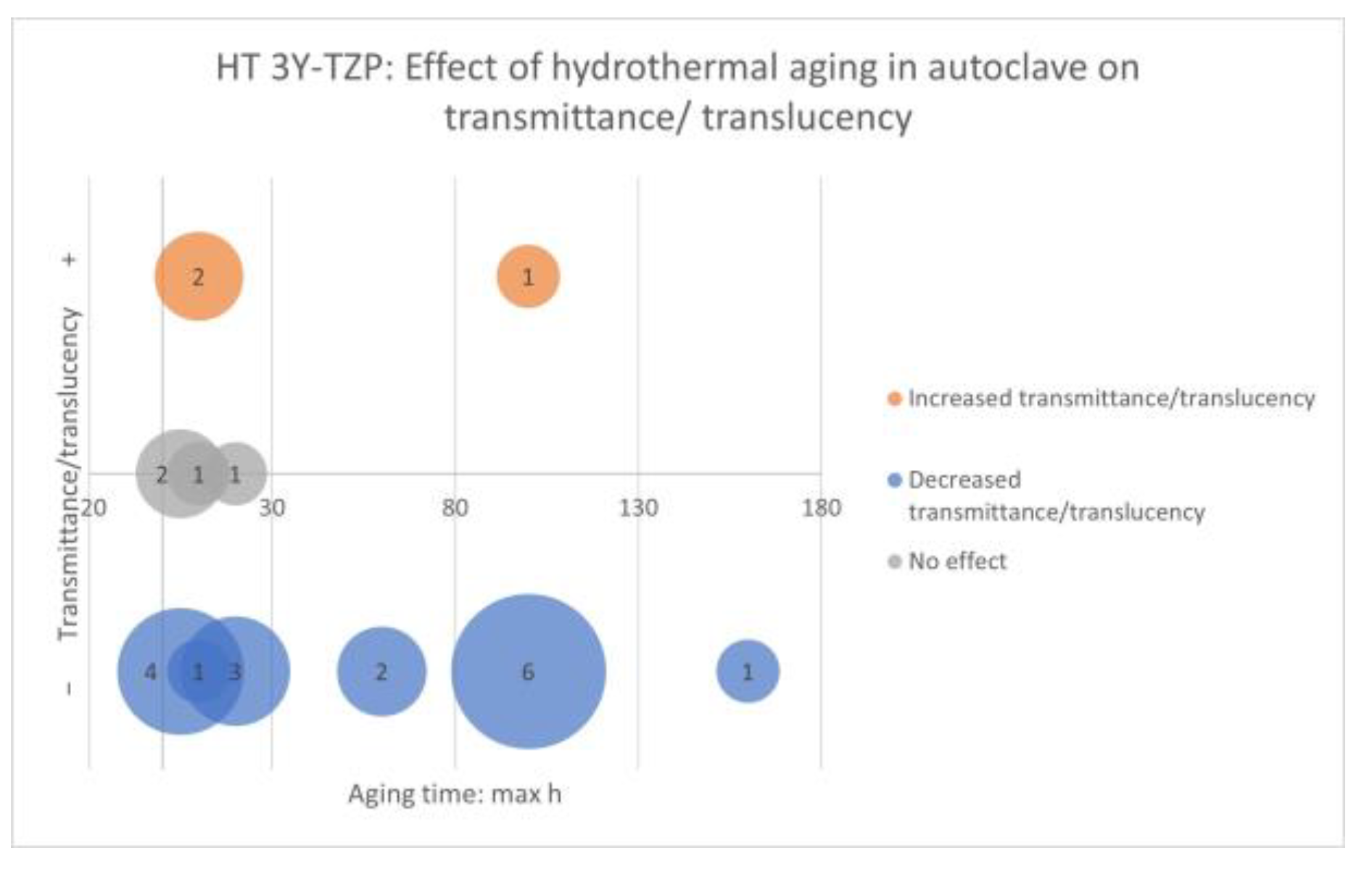
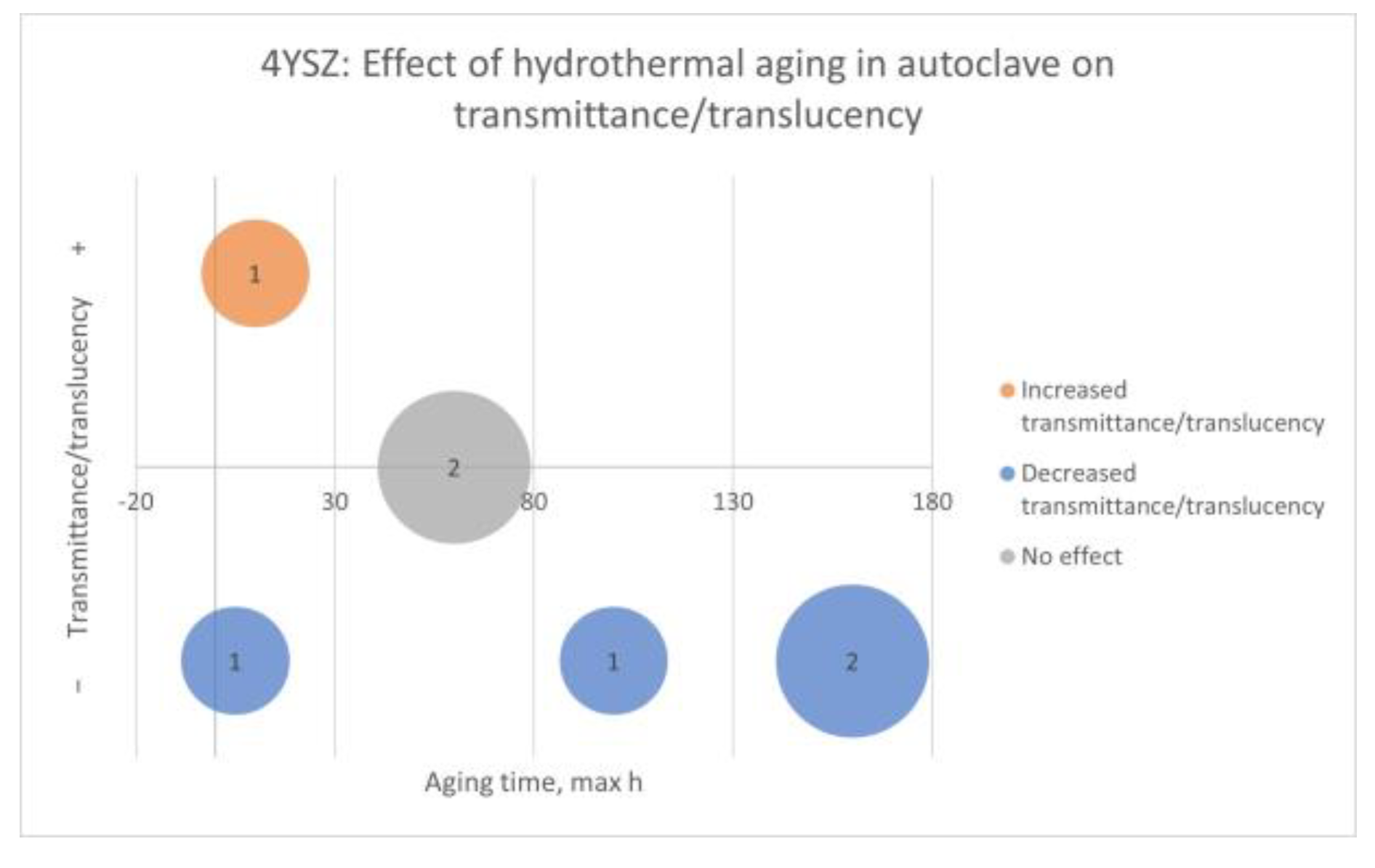
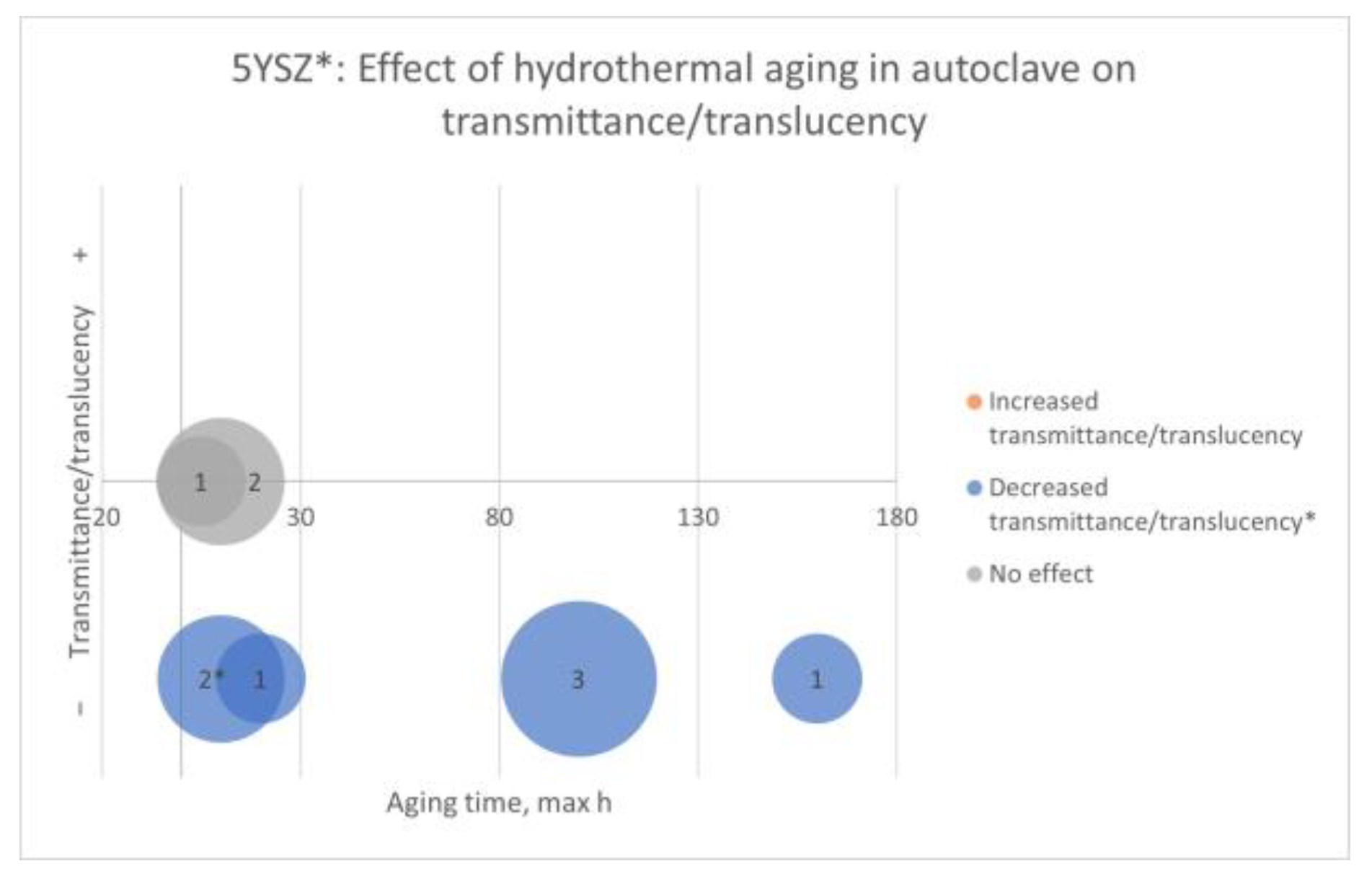
Factors: Hydrothermal Aging. Properties: Flexural Strength, Weibull Modulus, Characteristic Strength, Load at Fracture, Characteristic Load at Fracture, Crown Strength, Flexural Fatigue Strength, Fracture Toughness, Slow Crack Growth Susceptibility, and Residual Stress
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ
Factors: Mechanical Aging. Properties: Flexural Strength, Weibull Modulus, Characteristic Strength, Load at Fracture, Characteristic Load at Fracture, Flexural Fatigue Strength, and Residual Stress
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ, Multilayer 3Y-TZP/5YSZ, and 4YSZ/5YSZ
Factors: Two-Body, Three-Body, and Clinical Wear. Properties: Material Loss and Clinical Material Loss
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ
3.5. Physicochemical Properties and Structures
3.5.1. Laboratory Processing Factors
Factor: Colouring. Properties: Grain Size and Crystalline Phase
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ and Multilayer 3Y-TZP/5YSZ
Factor: Sintering. Properties: Grain Size, Crystalline Phase, Hardness, Elemental Composition, and Density
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ and Multilayer 3Y-TZP/5YSZ
Factors: Grinding, Polishing, Heat Treatment, and Glazing. Properties: Grain Size, Crystalline Phase, Hardness, Elemental Composition, and Elastic Modulus
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ and Multilayer 4YSZ/5YSZ
3.5.2. Clinical-Related Processing Factors
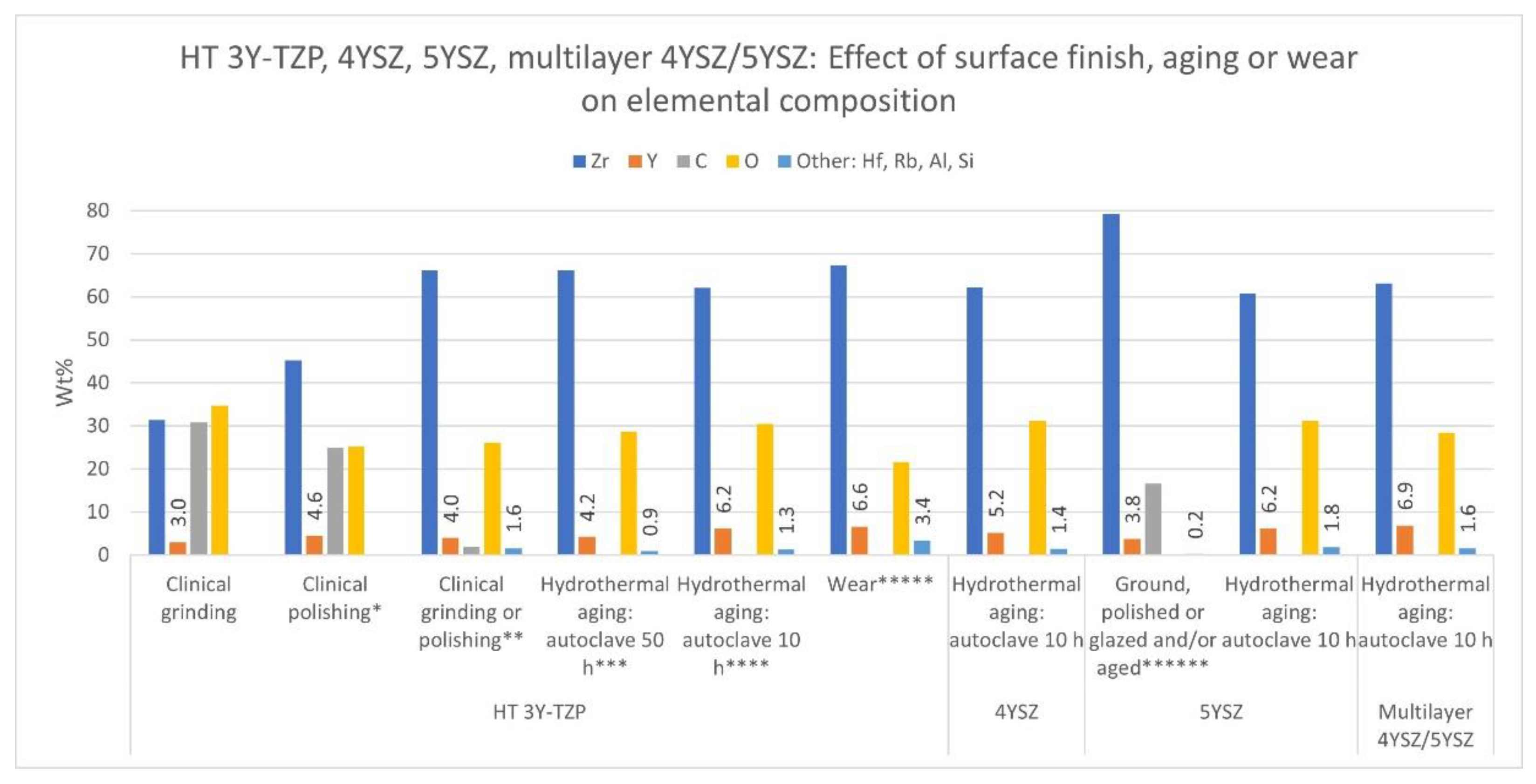
Factors: Clinical Grinding and Polishing. Properties: Crystalline Phase, Depth of Transformed Zone (TZD), Elemental Composition, Hardness, and Elastic Modulus
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 5YSZ and Multilayer 4YSZ/5YSZ
3.5.3. Time-Related Factors
Factors: Hydrothermal Aging and Mechanical Aging. Properties: Crystalline Phase, TZD, Elemental Composition, Hardness, Elastic Modulus, Grain Size, Young’s Modulus, and Indentation Modulus
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ and Multilayer 4YSZ/5YSZ
Factors: Two-Body and Clinical Wear. Properties: Crystalline Phase and Elemental Composition
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ
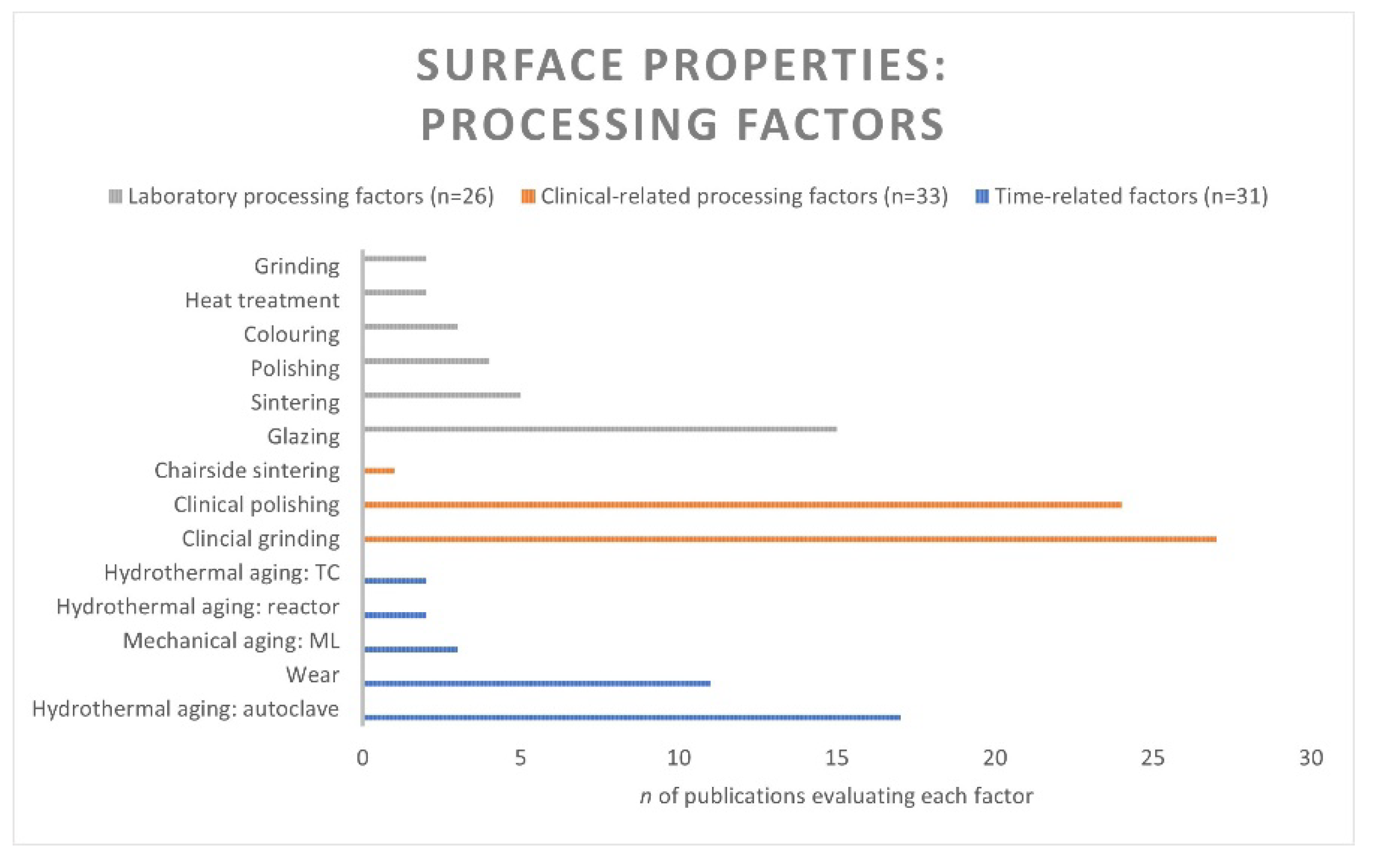
3.6. Surface Properties
3.6.1. Laboratory Processing Factors
Factor: Colouring. Properties: Surface Roughness and Surface Characterization
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ
Factor: Sintering. Properties: Surface Roughness and Surface Characterization
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 5YSZ
Factors: Grinding, Polishing, Heat Treatment, and Glazing. Properties: Surface Roughness, Surface Characterization, and Surface Free Energy
- HT 3Y-TZP
| Author, Year | Name of Material (Manufacturer) | Clinical Grinding Ra/Rz (µm) Mean (±SD) | Clinical Polishing Ra/Rz (µm) Mean (±SD) | Laboratory Grinding Ra/Rz (µm) Mean (±SD) | Laboratory Polishing Ra (µm) Mean (±SD) | Glazing Ra/Rz (µm) Mean (±SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-Haj Husain, 2016 [158] | Katana Zirconia HT (Kuraray Noritake) | 0.3 | Shofu 0.3 Ceragloss 0.4 Eve 1.1 Soflex 0.3 Diamond bur 0.1 | |||
| Al-Haj Husain, 2018 [112] | Katana Zirconia HT (Kuraray Noritake) | 0.27 | Shofu 0.27 Ceragloss 0.40 Eve 1.11 Soflex 0.29 Diamond bur 0.13 | |||
| Aliaga, 2020 [109] | Prettau Zirkon (Zirkonzahn) | Dry ground 1.53 (0.36) Wet ground 3.26 (0.43) | ||||
| Amer, 2015 [17] | Crystal diamond, Crystal Zirconia (Dental Laboratory Milling Supplies) | 0.45 * | 0.1 * | 0.25 * | ||
| Caglar, 2018 [159] | Katana Zirconia HT (Kuraray Noritake) | 1.77 (0.26) | Luster 0.28 (0.11) Eve Diacera 0.28 (0.07) Eve Diapol 0.78 (0.14) | |||
| Chavali, 2017 [171] | Zenostar Zr Translucent (Wieland) | CeraMaster 5000 rpm 4.0 (0.4) CeraMaster 15,000 rpm 3.8 (0.2) CeraMaster 40,000 rpm 4.0 (0.4) Dialite ZR 5000 rpm 4.0 (0.4) Dialite ZR 15,000 rpm 4.1 (0.3) Dialite ZR 40,000 rpm 3.8 (0.2) | CeraMaster 5000 rpm: Medium polished 30 s 2.7 (0.1)/60 s 2.8 (0.2)/Fine polished 2.3 (0.2) CeraMaster 15,000 rpm: Medium 30 s 3.0 (0.8)/ 0 s 2.4 (0.2)/Fine 1.0 (0.3) CeraMaster 40,000 rpm: Medium 30 s 2.5 (0.1)/60 s 2.1 (0.1)/Fine 1.6 (0.1) Dialite ZR 5000 rpm: Medium 30 s 2.4 (0.3)/60 s 2.3 (0.3)/Fine 2.0 (0.2) Dialite ZR 15,000 rpm: Medium 30 s 2.3 (0.4)/60 s 1.5 (0.4)/Fine 0.6 (0.2) Dialite ZR 40,000 rpm: Medium 30 s 1.8 (0.5)/ 60 s 1.4 (0.2)/Fine 1.3 (0.3) | CeraMaster 15,000/40,000/Dialite ZR 5000 rpm: Glazed lower than fine polished 1.0/1.6 /2.0 CeraMaster 5000 rpm: Glazed similar as fine polished 2.3 Dialite ZR 15,000/40,000 rpm: Glazed higher than fine polished 0.6/1.3 | ||
| Chun, 2017 [96] | Vita YZ HT (Vita Zahnfabrik) | Glazed, ground 0.61 (0.47) | Glazed, ground, polished 0.21 (0.11) | Glazed 1.12 (0.18) Ground, glazed 1.32 (0.33) Ground, polished, glazed 1.45 (0.42) | ||
| De Souza, 2020 [102] | Vipi Block Zirconn Translucent (Vipi) | 0.87 (0.16) | Ground, polished 0.55 (0.12) | |||
| Fratucelli, 2021 [86] | Prettau zirconia (Zirkonzahn) | Ra: 2.47 (0.91) Rz: 15.95 (4.62) | ||||
| Goo, 2016 [174] | Lava Plus High Translucency (3M ESPE) | White stone, Shofu 0.34 Shofu 0.39 Ceramisté 0.51 Ceramaster 0.42 Komet 0.25 * | ||||
| Hatanaka, 2020 [93] | Prettau (Zirkonzahn) | 4.30 (3.50, 5.05) ** | Ground, polished 2.12 (1.66, 2.41) ** | Glazed 0.45 (0.35, 0.52) Ground, glazed 0.97 (0.75, 1.04) Ground, polished, glazed 0.50 (0.40, 0.67) ** | ||
| Huh, 2016 [160] | Rainbow Trans (Genoss) | 0.93 (0.17) | D&Z 60 s 0.15 (0.03)/120 s 0.14 (0.02) EVE Diacera 60 s 0.16 (0.02)/120 s 0.17 (0.05) CeraGloss 60 s 0.19 (0.03)/120 s 0.21 (0.06) StarGloss 60 s 0.14 (0.03)/120 s 0.12 (0.02) Luster 60 s 0.16 (0.03)/120 s 0.16 (0.03) DFS 60 s 0.24 (0.08)/120 s 0.23 (0.04) | |||
| Huh, 2018 [161] | Zenostar T0 Zenostar sun Zenostar sun chroma (Ivoclar Vivadent) | 3.00 * (independent of material) | T0 0.17, Sun 0.19, Sun chroma 0.15 * 0.10 * (independent of material) | |||
| Incesu, 2020 [173] | Lava Plus Zirconia (3M ESPE) | Ra: Komet 0.24 (0.07) Luster 0.17 (0.03) Ceramisté 0.25 (0.06) OptraFine 0.10 (0.02) Rz: Komet 1.46 (0.42) Luster 0.96 (0.19) Ceramisté 1.52 (0.48) OptraFine 0.55 (0.14) | ||||
| Jum’ah, 2020 [168] | DD Bio ZX (DentalDirekt) | 1.82 (0.33) | Identoflex 1.03 (0.24) Diacera Twist 1.44 (0.38) DiaShine 0.41 (0.10) | 0.21 (0.05) | ||
| Khayat, 2018 [94] | Tizian Blank Translucent (Schütz) | 1.70 (0.44) | Brasseler 1.00 (0.31) Komet 0.81 (0.26) | Glazed (to be ground) 0.80 (0.16) Glazed (to be polished Brasseler) 0.67 (0.06) Glazed (to be polished Komet) 0.70 (0.12) Glazed (control) 0.79 (0.20) | ||
| Lee, 2019 [172] | Prettau (Zirkonzahn) | Ground 1.07 | Diamond, polishing 0.87 (0.11) Diamond, stone grinding, polishing 0.64 (0.10) Polishing 0.32 (0.06) Stone grinding, polishing 0.29 (0.07) | |||
| Mai, 2019 [156] | Prettau (Zirkonzahn) | Jota Coarse 0.32 (0.02) Meisinger Coarse 0.74 (0.11) Edenta Coarse 0.50 (0.06) | Jota: Coarse, medium polished 0.16 (0.07)/Coarse, fine polished 0.24 (0.03)/Coarse, medium, fine polished 0.05 (0.07) Meisinger: Coarse, medium 0.09 (0.08)/Coarse, fine 0.41 (0.07)/Coarse, medium, fine 0.08 (0.03) Edenta: Coarse, medium 0.29 (0.03)/Coarse, fine 0.44 (0.07)/Coarse, medium, fine 0.09 (0.04) | |||
| Manziuc, 2019 [169] | Katana HT (Kuraray Noritake) Vita YZ HT (VITA Zahnfabrik) Cercon HT (Dentsply Sirona) | Katana HT 0.09 Vita YZ HT 0.06 Cercon HT 0.12 *** (0.8, 1.5, 2.0 mm) | ||||
| Moqbel, 2019 [111] | Katana HT10 (Kuraray Noritake) | Ra: 0.01 (0.00) Rz: 0.03 (0.01) | ||||
| Pereira, 2016 [106] | Zirlux FC (Ivoclar Vivadent) | Ra: Coarse ground 1.32 (0.24) Extra-fine ground 0.64 (0.16) Rz: Coarse ground 6.74 (1.20) Extra-fine ground 4.29 (1.00) | ||||
| Pereira, 2016 [104] | Zirlux FC (Ivoclar Vivadent) | Ra: 1.04 (0.27) Rz: 6.51 (1.49) | ||||
| Prado, 2017 [107] | Zirlux FC (Ardent Dental) | Ra: 0.60 *** (0.5, 1.0 mm) Rz: 4.00 *** (0.5, 1.0 mm) | ||||
| Preis, 2015 [157] | Cercon HT (DeguDent) | 1.23 * | 0.20 * | |||
| Schatz, 2016 [95] | Ceramill Zolid (AmannGirrbach) Zenostar Zr Translucent (Wieland + Dental) DD Bio zx2 (Dental Direkt) | Dry polished 0.31–0.41 Wet polished 0.01–0.01 **** | ||||
| Tachibana, 2021 [167] | inCoris TZI (Sirona) | Experiment 1–3 3.16/3.18/3.17 | Experiment 1–3 0.02/0.02/0.03 | |||
| Zucuni, 2019 [105] | Zenostar T (Ivoclar Vivadent) | Ra: 1.21 Rz: 7.42 | Ra: Ground coarse, Eve Diacera 0.33/Ground coarse, fine, extrafine, Eve Diacera 0.33 Ground coarse, Kg Viking 0.84 Ground coarse, fine, extrafine, Kg Viking 0.57 Ground coarse, Optrafine 0.63 Ground coarse, fine, extrafine, Optrafine 0.47 Rz: Ground coarse, Eve Diacera 2.33/Ground coarse, fine, extrafine, Eve Diacera 2.07 Ground coarse, Kg Viking 5.38 Ground coarse, fine, extrafine, Kg Viking 3.85 Ground coarse, Optrafine 4.16 Ground coarse, fine, extrafine, Optrafine 3.27 | |||
| Zucuni, 2017 [87] | Zenostar T (Ivoclar Vivadent) | Ra: 1.10 (0.16) Rz: 4.97 (0.86) | Ra: Ground, polished 0.29 (0.05) Rz: Ground, polished 1.80 (0.32) | Ra: Ground, glazed 0.24 (0.11) Ground, polished, glazed 0.17 (0.05) Rz: Ground, glazed 1.24 (0.60) Ground, polished, glazed 0.93 (0.37) | ||
| Zucuni, 2019 [92] | Vita YZ-HT (Vita Zahnfabrik) | Ra: 1.03 (0.18) Rz: 6.47 (1.21) | Ra: Brush-glazed 0.54 (0.07) Spray-glazed 0.83 (0.29) Ground, brush-glazed 0.62 (0.17) Ground, spray-glazed 1.16 (0.42) Rz: Brush-glazed 3.61 (0.68) Spray-glazed 5.39 (1.90) Ground, brush-glazed 3.81 (1.06) Ground, spray-glazed 7.46 (2.51) |
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ and Multilayer 4YSZ/5YSZ
3.6.2. Clinical-Related Processing Factors
Factor: Chairside Sintering. Property: Surface Characterization
- HT 3Y-TZP
Factors: Clinical Grinding and Polishing. Properties: Surface Roughness, Characterization, and Surface Wettability
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ and Multilayer 4YSZ/5YSZ
3.6.3. Time-Related Factors
Factors: Hydrothermal Aging and Mechanical Aging. Properties: Surface Roughness and Surface Characterization
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ and Multilayer 4YSZ/5YSZ
Factors: Three-Body and Two-Body Wear. Properties: Surface Roughness and Surface Characterization
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ and Multilayer 4YSZ/5YSZ
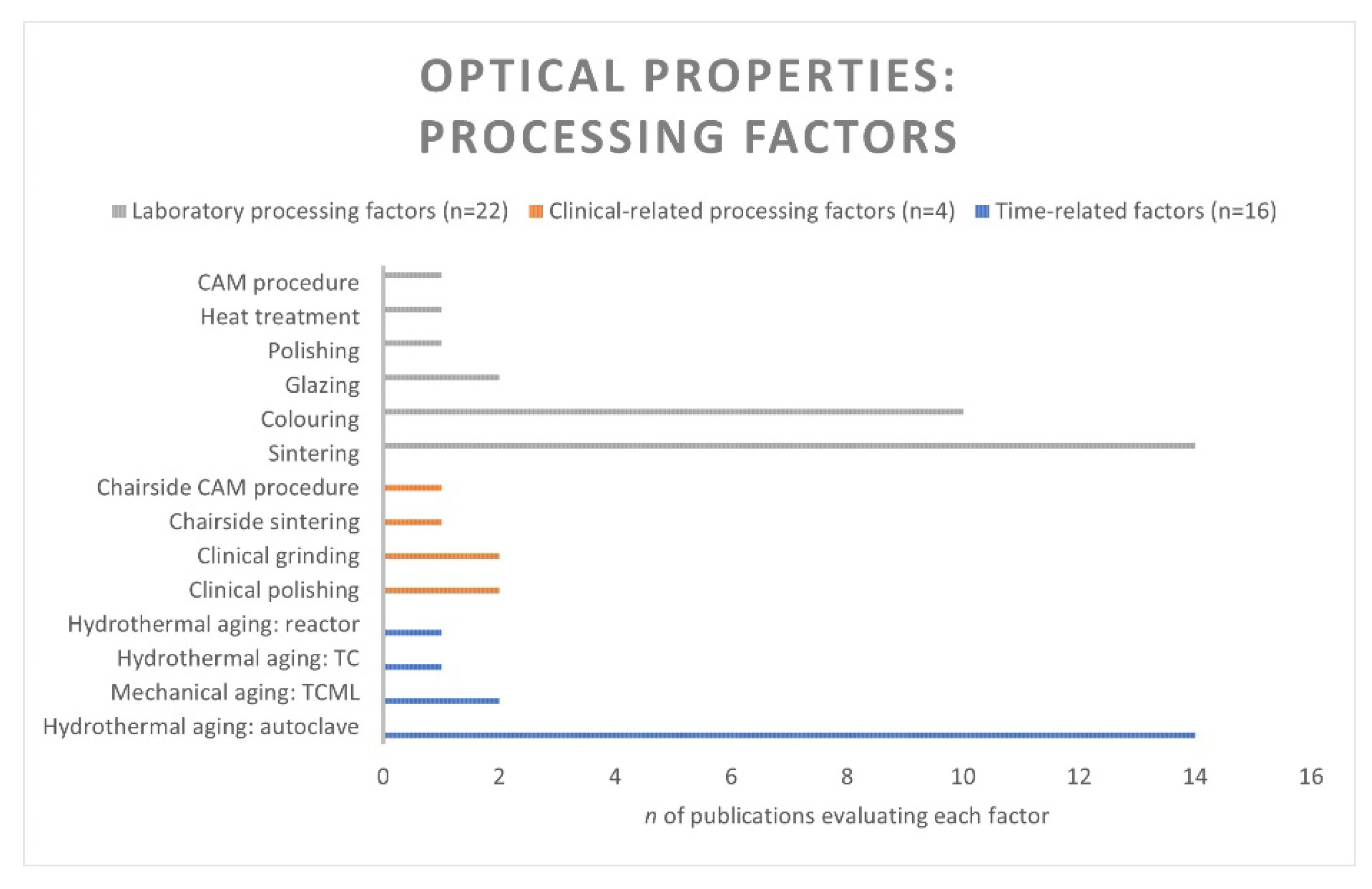
3.7. Optical Properties
3.7.1. Laboratory Processing Factors
Factor: CAM Procedure. Property: Transmittance
- 4YSZ and Multilayer 3Y-TZP/5YSZ
Factor: Colouring. Properties: Transmittance, TP, CR, ∆E, Gloss, Lightness, Opalescence Parameter (OP), and Fluorescence
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ
Factor: Sintering. Properties: Transmittance, TP, CR, ∆E, Gloss, OP, Reflectance, Opacity, and Absorption
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ
Factors: Polishing, Heat Treatment, and Glazing. Properties: Transmittance, TP, ∆E, and Gloss
- HT 3Y-TZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ
3.7.2. Clinical-Related Processing Factors
Factors: Clinical Grinding and Polishing. Properties: ∆E, Lightness, and Gloss
- HT 3Y-TZP
3.7.3. Time-Related Factors
Factors: Hydrothermal Aging and Mechanical Aging. Properties: Transmittance, TP, CR, ∆E, Lightness, OP, Fluorescence, and Light Blockage
- HT 3-YTZP
- 4YSZ
- 5YSZ
4. Discussion
4.1. Available Data for Each Zirconia Type
4.2. Processing Factors and Methods
4.3. Properties
4.4. Effect of Laboratory and Clinical-Related Processing and Time-Related Factors
4.4.1. Laboratory Processing Factor: Sintering
4.4.2. Laboratory and Clinical-Related Processing Factors: Grinding, Polishing, and Glazing
4.4.3. Time-Related Factors: Hydrothermal and Mechanical Aging and Wear
4.5. Comments on Methodology and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piconi, C.; Maccauro, G. Zirconia as a ceramic biomaterial. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lawn, B.R. Novel Zirconia Materials in Dentistry. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzaga, C.C.; Garcia, P.P.; Wambier, L.M.; Prochnow, F.H.O.; Madeira, L.; Cesar, P.F. Do tooth-supported zirconia restorations present more technical failures related to fracture or loss of retention? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 5129–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.; Papia, E.; Larsson, C. The clinical success of tooth- and implant-supported zirconia-based fixed dental prostheses. A systematic review. J. Oral Rehabil. 2015, 42, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, C.; Wennerberg, A. The clinical success of zirconia-based crowns: A systematic review. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2014, 27, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintze, S.D.; Rousson, V. Survival of zirconia- and metal-supported fixed dental prostheses: A systematic review. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2010, 23, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stawarczyk, B.; Keul, C.; Eichberger, M.; Figge, D.; Edelhoff, D.; Lümkemann, N. Three generations of zirconia: From veneered to monolithic. Part I. Quintessence Int. 2017, 48, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuer, F.; Stimmelmayr, M.; Gueth, J.F.; Edelhoff, D.; Naumann, M. In vitro performance of full-contour zirconia single crowns. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C.; Kmet, G.; Rivera, J.; Larsson, C.; Vult Von Steyern, P. Fracture strength of monolithic all-ceramic crowns made of high translucent yttrium oxide-stabilized zirconium dioxide compared to porcelain-veneered crowns and lithium disilicate crowns. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2014, 72, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontonasaki, E.; Rigos, A.E.; Ilia, C.; Istantsos, T. Monolithic Zirconia: An Update to Current Knowledge. Optical Properties, Wear, and Clinical Performance. Dent. J. 2019, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, S. Chemical durability of high translucent dental zirconia. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 39, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denry, I.; Kelly, J.R. State of the art of zirconia for dental applications. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.R.; Denry, I. Stabilized zirconia as a structural ceramic: An overview. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawarczyk, B.; Keul, C.; Eichberger, M.; Figge, D.; Edelhoff, D.; Lümkemann, N. Three generations of zirconia: From veneered to monolithic. Part II. Quintessence Int. 2017, 48, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, J.; Gremillard, L.; Virkar, A.V.; Clarke, D.R. The Tetragonal-Monoclinic Transformation in Zirconia: Lessons Learned and Future Trends. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, 1901–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Tabares, J.A.; Jiménez-Piqué, E.; Anglada, M. Subsurface evaluation of hydrothermal degradation of zirconia. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.K.R.; Venturini, A.B.; Silvestri, T.; Dapieve, K.S.; Montagner, A.F.; Soares, F.Z.M.; Valandro, L.F. Low-temperature degradation of Y-TZP ceramics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 55, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Making yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia translucent. Dent. Mater. 2014, 30, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Inokoshi, M.; Batuk, M.; Hadermann, J.; Naert, I.; Van Meerbeek, B.; Vleugels, J. Strength, toughness and aging stability of highly-translucent Y-TZP ceramics for dental restorations. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, e327–e337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaian, F. Color Aspect of Monolithic Zirconia Restorations: A Review of the Literature. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimke, J.; Trunec, M.; Krell, A. Transparent Tetragonal Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia Ceramics: Influence of Scattering Caused by Birefringence. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, Y.R.; Elias, C.N.; Monteiro, S.N.; Santos, H.; Santos, C.D. Modeling of the Influence of Chemical Composition, Sintering Temperature, Density, and Thickness in the Light Transmittance of Four Zirconia Dental Prostheses. Materials 2019, 12, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Reveron, H.; Spies, B.C.; Van Meerbeek, B.; Chevalier, J. Trade-off between fracture resistance and translucency of zirconia and lithium-disilicate glass ceramics for monolithic restorations. Acta Biomater. 2019, 91, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Van Meerbeek, B.; Vleugels, J. Importance of tetragonal phase in high-translucent partially stabilized zirconia for dental restorations. Dent. Mater. 2020, 36, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo-Júnior, E.N.S.; Bergamo, E.T.P.; Bastos, T.M.C.; Benalcázar Jalkh, E.B.; Lopes, A.C.O.; Monteiro, K.N.; Cesar, P.F.; Tognolo, F.C.; Migliati, R.; Tanaka, R.; et al. Ultra-translucent zirconia processing and aging effect on microstructural, optical, and mechanical properties. Dent. Mater. 2022, 38, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auzani, M.L.; Dapieve, K.S.; Zucuni, C.P.; Rocha Pereira, G.K.; Valandro, L.F. Influence of shading technique on mechanical fatigue performance and optical properties of a 4Y-TZP ceramic for monolithic restorations. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 102, 103457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, E.M.; Longhini, D.; Antonio, S.G.; Adabo, G.L. The effects of mechanical and hydrothermal aging on microstructure and biaxial flexural strength of an anterior and a posterior monolithic zirconia. J. Dent. 2017, 63, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, C.D.; Lien, W.; Gallardo, F.F.; Vandewalle, K.S. Assessing Flexural Strength Degradation of New Cubic Containing Zirconia Materials. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract 2020, 21, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontonasaki, E.; Giasimakopoulos, P.; Rigos, A.E. Strength and aging resistance of monolithic zirconia: An update to current knowledge. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2020, 56, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöppel, M.L.; Rosentritt, M.; Sturm, R.; Beuer, F.; Hey, J.; Schmid, A.; Schmidt, F. Fracture Load and Fracture Patterns of Monolithic Three-Unit Anterior Fixed Dental Prostheses after In Vitro Artificial Aging-A Comparison between Color-Gradient and Strength-Gradient Multilayer Zirconia Materials with Varying Yttria Content. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.K.; Park, M.G. Effect of different coloring liquids on the flexural strength of multilayered zirconia. J. Adv. Prosthodont 2019, 11, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolakarnprasert, N.; Kaizer, M.R.; Kim, D.K.; Zhang, Y. New multi-layered zirconias: Composition, microstructure and translucency. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michailova, M.; Elsayed, A.; Fabel, G.; Edelhoff, D.; Zylla, I.M.; Stawarczyk, B. Comparison between novel strength-gradient and color-gradient multilayered zirconia using conventional and high-speed sintering. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 111, 103977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardhaman, S.; Borba, M.; Kaizer, M.R.; Kim, D.; Zhang, Y. Wear behavior and microstructural characterization of translucent multilayer zirconia. Dent. Mater. 2020, 36, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekow, E.D.; Silva, N.R.; Coelho, P.G.; Zhang, Y.; Guess, P.; Thompson, V.P. Performance of dental ceramics: Challenges for improvements. J. Dent. Res. 2011, 90, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurélio, I.L.; Marchionatti, A.M.; Montagner, A.F.; May, L.G.; Soares, F.Z. Does air particle abrasion affect the flexural strength and phase transformation of Y-TZP? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, 827–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Holloway, J.A.; Denry, I.L. Effect of coloring with various metal oxides on the microstructure, color, and flexural strength of 3Y-TZP. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 87, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, J. What future for zirconia as a biomaterial? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lughi, V.; Sergo, V. Low temperature degradation -aging- of zirconia: A critical review of the relevant aspects in dentistry. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, C.; Franco-Tabares, S.; Larsson, C.; Papia, E. Laboratory, clinical-related processing and time-related factors’ effect on properties of high translucent zirconium dioxide ceramics intended for monolithic restorations. A systematic review. PROSPERO Int. Prospect. Regist. Syst. Rev. 2021, CRD42021232711. [Google Scholar]
- Bramer, W.M.; Giustini, D.; de Jonge, G.B.; Holland, L.; Bekhuis, T. De-duplication of database search results for systematic reviews in EndNote. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2016, 104, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swedish Agency for Health Technology Assessment and Assessment of Social Services. Assessment of Methods in Health Care and Social Services: A Handbook. Appendix 2. Tool to Assess Risk of Bias in Randomized Trials, 2nd ed.; Swedish Agency for Health Technology Assessment and Assessment of Social Services (SBU): Stockholm, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Faggion, C.M., Jr. Guidelines for reporting pre-clinical in vitro studies on dental materials. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2012, 12, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, S.; Tatt, I.D.; Higgins, J.P. Tools for assessing quality and susceptibility to bias in observational studies in epidemiology: A systematic review and annotated bibliography. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 36, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.M.A.; Mandour, M.H.; El-Sharkawy, Z.R. Optical Properties and Flexural Strength of Artificially Aged Tetragonal/Cubic Ultra-Translucent Zirconia. Al-Azhar Dent. J. Girls 2020, 7, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alraheam, I.A.; Donovan, T.; Boushell, L.; Cook, R.; Ritter, A.V.; Sulaiman, T.A. Fracture load of two thicknesses of different zirconia types after fatiguing and thermocycling. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 123, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, S.; Suzuki, T.; Yoshihara, K.; Sasaki, K.; Kawai, T.; Kono, H. Effect of coloring on mechanical properties of dental zirconia. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2014, 34, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camposilvan, E.; Leone, R.; Gremillard, L.; Sorrentino, R.; Zarone, F.; Ferrari, M.; Chevalier, J. Aging resistance, mechanical properties and translucency of different yttria-stabilized zirconia ceramics for monolithic dental crown applications. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattani-Lorente, M.; Durual, S.; Amez-Droz, M.; Wiskott, H.W.; Scherrer, S.S. Hydrothermal degradation of a 3Y-TZP translucent dental ceramic: A comparison of numerical predictions with experimental data after 2 years of aging. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, A.; Meyer, G.; Wille, S.; Kern, M. Influence of the yttrium content on the fracture strength of monolithic zirconia crowns after artificial aging. Quintessence Int. 2019, 50, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fontolliet, A.; Al-Haj Husain, N.; Özcan, M. Wear analysis and topographical properties of monolithic zirconia and CoCr against human enamel after polishing and glazing procedures. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 105, 103712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaonkar, S.H.; Aras, M.A.; Chitre, V. An in vitro study to compare the surface roughness of glazed and chairside polished dental monolithic zirconia using two polishing systems. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2020, 20, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, S.R.; Alotaibi, A.; Al Hazza, N.; Allam, Y.; AlGhazi, M. Two-body wear behavior of human enamel versus monolithic zirconia, lithium disilicate, ceramometal and composite resin. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2019, 11, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaizer, M.R.; Gierthmuehlen, P.C.; Dos Santos, M.B.; Cava, S.S.; Zhang, Y. Speed sintering translucent zirconia for chairside one-visit dental restorations: Optical, mechanical, and wear characteristics. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 10999–11005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.A.; Sampathkumar, J.; Ramakrishnan, H.; Mahadevan, V. Comparative evaluation of wear resistance of CAD-CAM zirconia and cast cobalt chromium alloy for indirect restorations against human enamel—An In Vitro study. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2020, 31, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Park, S.; Lee, K.; Yun, K.-D.; Lim, H.-P. Antagonist wear of three CAD/CAM anatomic contour zirconia ceramics. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 111, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preis, V.; Behr, M.; Hahnel, S.; Handel, G.; Rosentritt, M. In vitro failure and fracture resistance of veneered and full-contour zirconia restorations. J. Dent. 2012, 40, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stober, T.; Bermejo, J.L.; Schwindling, F.S.; Schmitter, M. Clinical assessment of enamel wear caused by monolithic zirconia crowns. J. Oral Rehabil. 2016, 43, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenmann, F.; Böhm, D.; Eichberger, M.; Edelhoff, D.; Stawarczyk, B. Influence of different surface treatments on two-body wear and fracture load of monolithic CAD/CAM ceramics. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 3049–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.W.; Kim, J.E.; Shin, Y.; Shim, J.S.; Kim, J.H. Enamel wear and aging of translucent zirconias: In vitro and clinical studies. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agingu, C.; Jiang, N.W.; Cheng, H.; Yu, H. Effect of Different Coloring Procedures on the Aging Behavior of Dental Monolithic Zirconia. J. Spectrosc. 2018, 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nossair, S.; Salah, T.; Ebeid, K. Biaxial flexural strength of different types of monolithic zirconia. Braz Dent. Sci. 2019, 22, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, N.; Sermet, I.B.; Cinar, S. Effect of coloring and sintering on the translucency and biaxial strength of monolithic zirconia. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 308.e1–308.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, T.A.; Abdulmajeed, A.A.; Donovan, T.E.; Vallittu, P.K.; Närhi, T.O.; Lassila, L.V. The effect of staining and vacuum sintering on optical and mechanical properties of partially and fully stabilized monolithic zirconia. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, T.A.; Abdulmajeed, A.A.; Shahramian, K.; Lassila, L. Effect of different treatments on the flexural strength of fully versus partially stabilized monolithic zirconia. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 118, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lümkemann, N.; Stawarczyk, B. Impact of hydrothermal aging on the light transmittance and flexural strength of colored yttria-stabilized zirconia materials of different formulations. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 125, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyar, P.; Durkan, R.; Deste, G. Effects of sintering time and hydrothermal aging on the mechanical properties of monolithic zirconia ceramic systems. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 126, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, C.; Can, G. Effect of sintering parameters on the mechanical properties of monolithic zirconia. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2019, 13, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, C.; Çelik, E. Influence of heating rate on the flexural strength of monolithic zirconia. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2019, 11, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cokic, S.M.; Vleugels, J.; Van Meerbeek, B.; Camargo, B.; Willems, E.; Li, M.; Zhang, F. Mechanical properties, aging stability and translucency of speed-sintered zirconia for chairside restorations. Dent. Mater. 2020, 36, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerman, E.; Wiedenmann, F.; Eichberger, M.; Reichert, A.; Stawarczyk, B. Effect of high-speed sintering on the flexural strength of hydrothermal and thermo-mechanically aged zirconia materials. Dent. Mater. 2020, 36, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Ding, S.J.; Lin, T.H.; Yan, M. Mechanical and optical properties evaluation of rapid sintered dental zirconia. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 26668–26674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juntavee, N.; Attashu, S. Effect of different sintering process on flexural strength of translucency monolithic zirconia. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2018, 10, e821–e830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juntavee, N.; Uasuwan, P. Influence of thermal tempering processes on color characteristics of different monolithic computer-assisted design and computer-assisted manufacturing ceramic materials. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2019, 11, e614–e624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Nakano, Y.; Usami, H.; Okamura, S.; Wakabayashi, K.; Yatani, H. In vitro investigation of fracture load and aging resistance of high-speed sintered monolithic tooth-borne zirconia crowns. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2020, 64, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.U.; Lümkemann, N.; Letz, I.; Pfefferle, R.; Sener, B.; Stawarczyk, B. Impact of high-speed sintering on translucency, phase content, grain sizes, and flexural strength of 3Y-TZP and 4Y-TZP zirconia materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 122, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersoy, N.M.; Aydogdu, H.M.; Degirmenci, B.U.; Cokuk, N.; Sevimay, M. The effects of sintering temperature and duration on the flexural strength and grain size of zirconia. Acta Biomater. Odontol. Scand. 2015, 1, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juntavee, N.; Uasuwan, P. Flexural Strength of Different Monolithic Computer-Assisted Design and Computer-Assisted Manufacturing Ceramic Materials upon Different Thermal Tempering Processes. Eur. J. Dent. 2020, 14, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, N.C.; Maharishi, A. Strength and translucency of zirconia after high-speed sintering. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2020, 32, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedenmann, F.; Pfefferle, R.; Reichert, A.; Jerman, E.; Stawarczyk, B. Impact of high-speed sintering, layer thickness and artificial aging on the fracture load and two-body wear of zirconia crowns. Dent. Mater. 2020, 36, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, K.V.; Adabo, G.L.; Mariscal-Muñoz, E.; Antonio, S.G.; Arioli Filho, J.N. Effect of sintering temperature on microstructure, flexural strength, and optical properties of a fully stabilized monolithic zirconia. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 124, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosentritt, M.; Preis, V.; Schmid, A.; Strasser, T. Multilayer zirconia: Influence of positioning within blank and sintering conditions on the in vitro performance of 3-unit fixed partial dentures. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 127, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratucelli, É.D.D.O.; Candido, L.M.; Pinelli, L.A.P. Surface properties and flexural strength of a monolithic zirconia submitted to grinding and regenerative heat treatment. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2021, 18, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucuni, C.P.; Guilardi, L.F.; Rippe, M.P.; Pereira, G.K.R.; Valandro, L.F. Fatigue strength of yttria-stabilized zirconia polycrystals: Effects of grinding, polishing, glazing, and heat treatment. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 75, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K. Effect of A Rapid-Cooling Protocol on the Optical and Mechanical Properties of Dental Monolithic Zirconia Containing 3–5 mol% Y2O3. Materials 2020, 13, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, M.G.; Park, M.G. Changes in the flexural strength of translucent zirconia due to glazing and low-temperature degradation. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 120, 969.e1–969.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumchai, H.; Juntavee, P.; Sun, A.F.; Nathanson, D. Effect of Glazing on Flexural Strength of Full-Contour Zirconia. Int. J. Dent. 2018, 2018, 8793481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Si, W.; Jiang, D.; Sun, T.; Shao, L.; Deng, B. Effects of small-grit grinding and glazing on mechanical behaviors and ageing resistance of a super-translucent dental zirconia. J. Dent. 2017, 66, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucuni, C.P.; Pereira, G.K.R.; Dapieve, K.S.; Rippe, M.P.; Bottino, M.C.; Valandro, L.F. Low-fusing porcelain glaze application does not damage the fatigue strength of Y-TZP. J. Mech. Behav. Mater. 2019, 99, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatanaka, G.R.; Polli, G.S.; Adabo, G.L. The mechanical behavior of high-translucent monolithic zirconia after adjustment and finishing procedures and artificial aging. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 123, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayat, W.; Chebib, N.; Finkelman, M.; Khayat, S.; Ali, A. Effect of grinding and polishing on roughness and strength of zirconia. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, C.; Strickstrock, M.; Roos, M.; Edelhoff, D.; Eichberger, M.; Zylla, I.M.; Stawarczyk, B. Influence of Specimen Preparation and Test Methods on the Flexural Strength Results of Monolithic Zirconia Materials. Materials 2016, 9, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, E.P.; Anami, L.C.; Bonfante, E.A.; Bottino, M.A. Microstructural analysis and reliability of monolithic zirconia after simulated adjustment protocols. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfefferle, R.; Lümkemann, N.; Wiedenmann, F.; Stawarczyk, B. Different polishing methods for zirconia: Impact on surface, optical, and mechanical properties. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila-Nova, T.E.L.; Gurgel de Carvalho, I.H.; Moura, D.M.D.; Batista, A.U.D.; Zhang, Y.; Paskocimas, C.A.; Bottino, M.A.; de Assunção, E.S.R.O. Effect of finishing/polishing techniques and low temperature degradation on the surface topography, phase transformation and flexural strength of ultra-translucent ZrO(2) ceramic. Dent. Mater. 2020, 36, e126–e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asli, H.N.; Rahimabadi, S.; Falahchai, M. Flexural strength of monolithic zirconia after different surface treatments. World J. Dent. 2019, 10, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucuni, C.P.; Pereira, G.K.R.; Valandro, L.F. Grinding, polishing and glazing of the occlusal surface do not affect the load-bearing capacity under fatigue and survival rates of bonded monolithic fully-stabilized zirconia simplified restorations. J. Mech Behav Biomed. Mater. 2020, 103, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Ender, A.; Mehl, A. Influence of CAD/CAM Fabrication and Sintering Procedures on the Fracture Load of Full-Contour Monolithic Zirconia Crowns as a Function of Material Thickness. Oper. Dent. 2020, 45, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, R.H.; Kaizer, M.R.; Borges, C.E.P.; Fernandes, A.B.F.; Correr, G.M.; Diógenes, A.N.; Zhang, Y.; Gonzaga, C.C. Flexural strength and crystalline stability of a monolithic translucent zirconia subjected to grinding, polishing and thermal challenges. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 26168–26175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, M.; Weitzel, I.; Silvestri, T.; Guilardi, L.F.; Pereira, G.K.R.; Valandro, L.F. Effect of grinding and aging on subcritical crack growth of a Y-TZP ceramic. Braz Oral Res. 2018, 32, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.K.R.; Silvestri, T.; Amaral, M.; Rippe, M.P.; Kleverlaan, C.J.; Valandro, L.F. Fatigue limit of polycrystalline zirconium oxide ceramics: Effect of grinding and low-temperature aging. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 61, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucuni, C.P.; Dapieve, K.S.; Rippe, M.P.; Pereira, G.K.R.; Bottino, M.C.; Valandro, L.F. Influence of finishing/polishing on the fatigue strength, surface topography, and roughness of an yttrium-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystals subjected to grinding. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 93, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.K.D.R.; Silvestri, T.; Camargo, R.; Rippe, M.P.; Amaral, M.; Kleverlaan, C.J.; Valandro, L.F. Mechanical behavior of a Y-TZP ceramic for monolithic restorations: Effect of grinding and low-temperature aging. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 63, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, R.D.; Pereira, G.K.R.; Bottino, M.A.; Melo, R.M.; Valandro, L.F. Effect of ceramic thickness, grinding, and aging on the mechanical behavior of a polycrystalline zirconia. Braz Oral Res. 2017, 31, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozer, F.; Naden, A.; Turp, V.; Mante, F.; Sen, D.; Blatz, M.B. Effect of thickness and surface modifications on flexural strength of monolithic zirconia. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliaga, R.; Miotto, L.N.; Candido, L.M.; Fais, L.; Pinelli, L. Does Diamond Stone Grinding Change the Surface Characteristics and Flexural Strength of Monolithic Zirconia? Oper. Dent. 2020, 45, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dapieve, K.S.; Silvestri, T.; Rippe, M.P.; Pereira, G.K.R.; Valandro, L.F. Mechanical performance of Y-TZP monolithic ceramic after grinding and aging: Survival estimates and fatigue strength. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 87, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moqbel, N.M.; Al-Akhali, M.; Wille, S.; Kern, M. Influence of Aging on Biaxial Flexural Strength and Hardness of Translucent 3Y-TZP. Materials 2019, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haj Husain, N.; Özcan, M. A Study on Topographical Properties and Surface Wettability of Monolithic Zirconia after Use of Diverse Polishing Instruments with Different Surface Coatings. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 27, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, S.; Zumstrull, P.; Kaidas, V.; Jessen, L.K.; Kern, M. Low temperature degradation of single layers of multilayered zirconia in comparison to conventional unshaded zirconia: Phase transformation and flexural strength. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 77, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerman, E.; Lümkemann, N.; Eichberger, M.; Zoller, C.; Nothelfer, S.; Kienle, A.; Stawarczyk, B. Evaluation of translucency, Marten’s hardness, biaxial flexural strength and fracture toughness of 3Y-TZP, 4Y-TZP and 5Y-TZP materials. Dent. Mater. 2021, 37, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghazzawi, T.F.; Janowski, G.M. Correlation of flexural strength of coupons versus strength of crowns fabricated with different zirconia materials with and without aging. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2015, 146, 904–912.e901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.D.; Xie, H.F.; Wu, X.Y.; Yang, J.X.; Liao, M.Y.; Chen, C. Evaluation of the effect of low-temperature degradation on the translucency and mechanical properties of ultra-transparent 5Y-TZP ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawarczyk, B.; Frevert, K.; Ender, A.; Roos, M.; Sener, B.; Wimmer, T. Comparison of four monolithic zirconia materials with conventional ones: Contrast ratio, grain size, four-point flexural strength and two-body wear. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 59, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flinn, B.D.; Raigrodski, A.J.; Mancl, L.A.; Toivola, R.; Kuykendall, T. Influence of aging on flexural strength of translucent zirconia for monolithic restorations. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, A.; Shishido, S.; Barkarmo, S.; Inagaki, R.; Kanno, T.; Örtengren, U.; Egusa, H.; Nakamura, K. Mechanical and microstructural properties of ultra-translucent dental zirconia ceramic stabilized with 5 mol% yttria. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 111, 103974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo-Júnior, E.N.S.; Bergamo, E.T.P.; Campos, T.M.B.; Benalcázar Jalkh, E.B.; Lopes, A.C.O.; Monteiro, K.N.; Cesar, P.F.; Tognolo, F.C.; Tanaka, R.; Bonfante, E.A. Hydrothermal degradation methods affect the properties and phase transformation depth of translucent zirconia. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 112, 104021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjold, A.; Schriwer, C.; Gjerdet, N.R.; Øilo, M. Effect of artificial aging on high translucent dental zirconia: Simulation of early failure. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 128, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.K.; Guilardi, L.F.; Dapieve, K.S.; Kleverlaan, C.J.; Rippe, M.P.; Valandro, L.F. Mechanical reliability, fatigue strength and survival analysis of new polycrystalline translucent zirconia ceramics for monolithic restorations. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 85, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Kang, K.H.; Att, W. Effect of aging process on some properties of conventional and multilayered translucent zirconia for monolithic restorations. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 1854–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Harada, A.; Kanno, T.; Inagaki, R.; Niwano, Y.; Milleding, P.; Ortengren, U. The influence of low-temperature degradation and cyclic loading on the fracture resistance of monolithic zirconia molar crowns. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 47, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, S.F.; Pereira, G.K.R.; Moris, I.C.M.; Marques, A.G.; Ribeiro, R.F.; Gomes, E.A. Physical properties of conventional and monolithic yttria-zirconia materials after low-temperature degradation. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 21038–21043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, P.; Monteiro, J.B.; Campos, T.M.B.; Thim, G.P.; de Melo, R.M. Degradation kinetics of high-translucency dental zirconias: Mechanical properties and in-depth analysis of phase transformation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 102, 103482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Ankyu, S.; Nilsson, F.; Kanno, T.; Niwano, Y.; Vult von Steyern, P.; Ortengren, U. Critical considerations on load-to-failure test for monolithic zirconia molar crowns. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 87, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarante, J.E.V.; Soares Pereira, M.V.; De Souza, G.M.; Pais Alves, M.F.R.; Simba, B.G.; Santos, C.D. Effect of hydrothermal aging on the properties of zirconia with different levels of translucency. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 109, 103847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamo, E.; da Silva, W.J.; Cesar, P.F.; Del Bel Cury, A.A. Fracture Load and Phase Transformation of Monolithic Zirconia Crowns Submitted to Different Aging Protocols. Oper. Dent. 2016, 41, e118–e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansour, H.M.; Alqahtani, F. The Effect of in vitro Aging and Fatigue on the Flexural Strength of Monolithic High-translucency Zirconia Restorations. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2018, 19, 867–873. [Google Scholar]
- Sarıkaya, I.; Hayran, Y. Effects of dynamic aging on the wear and fracture strength of monolithic zirconia restorations. BMC Oral Health 2018, 18, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bömicke, W.; Rues, S.; Hlavacek, V.; Rammelsberg, P.; Schmitter, M. Fracture Behavior of Minimally Invasive, Posterior, and Fixed Dental Prostheses Manufactured from Monolithic Zirconia. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2016, 28, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, B.C.; Zhang, F.; Wesemann, C.; Li, M.; Rosentritt, M. Reliability and aging behavior of three different zirconia grades used for monolithic four-unit fixed dental prostheses. Dent. Mater. 2020, 36, E329–E339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kengtanyakich, S.; Peampring, C. An experimental study on hydrothermal degradation of cubic-containing translucent zirconia. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2020, 12, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, W.; Garbrielsson, K.; Borhani, A.; Carlborg, M.; Molin Thorén, M. The effects of artificial aging on high translucent zirconia. Biomater. Investig. Dent. 2019, 6, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oblak, C.; Kocjan, A.; Jevnikar, P.; Kosmac, T. The effect of mechanical fatigue and accelerated ageing on fracture resistance of glazed monolithic zirconia dental bridges. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 4415–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashkari, A.; Yilmaz, B.; Brantley, W.A.; Schricker, S.R.; Johnston, W.M. Fracture analysis of monolithic CAD-CAM crowns. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2019, 31, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borba, M.; Okamoto, T.K.; Zou, M.; Kaizer, M.R.; Zhang, Y. Damage sensitivity of dental zirconias to simulated occlusal contact. Dent. Mater. 2021, 37, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishioka, G.; Prochnow, C.; Firmino, A.; Amaral, M.; Bottino, M.A.; Valandro, L.F.; Renata Marques de, M. Fatigue strength of several dental ceramics indicated for CAD-CAM monolithic restorations. Braz Oral Res. 2018, 32, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güngör, M.B.; Nemli, S.K.; Bal, B.T.; Tamam, E.; Yılmaz, H.; Aydın, C. Fracture resistance of monolithic and veneered all-ceramic four-unit posterior fixed dental prostheses after artificial aging. J. Oral Sci. 2019, 61, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulmajeed, A.; Sulaiman, T.; Abdulmajeed, A.; Bencharit, S.; Närhi, T. Fracture Load of Different Zirconia Types: A Mastication Simulation Study. J. Prosthodont. 2020, 29, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosentritt, M.; Preis, V.; Behr, M.; Strasser, T. Fatigue and wear behaviour of zirconia materials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 110, 103970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Suarez, C.; Tobar, C.; Sola-Ruiz, M.F.; Pelaez, J.; Suarez, M.J. Effect of Thermomechanical and Static Loading on the Load to Fracture of Metal-Ceramic, Monolithic, and Veneered Zirconia Posterior Fixed Partial Dentures. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouelenien, D.K.; Nasr, H.H.; Zaghloul, H. Wear behavior of monolithic zirconia against natural teeth in comparison to two glass ceramics with two surface finishing protocols: An in-vitro study. Braz Dent. Sci. 2020, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcangelo, C.; Vanini, L.; Rondoni, G.D.; Vadini, M.; De Angelis, F. Wear Evaluation of Prosthetic Materials Opposing Themselves. Oper. Dent. 2018, 43, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawarczyk, B.; Özcan, M.; Schmutz, F.; Trottmann, A.; Roos, M.; Hämmerle, C.H. Two-body wear of monolithic, veneered and glazed zirconia and their corresponding enamel antagonists. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2013, 71, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldegheishem, A.; Alfaer, A.; Brezavscek, M.; Vach, K.; Eliades, G.; Att, W. Wear behavior of zirconia substrates against different antagonist materials. Int. J. Esthet. Dent. 2015, 10, 468–485. [Google Scholar]
- Ludovichetti, F.S.; Trindade, F.Z.; Werner, A.; Kleverlaan, C.J.; Fonseca, R.G. Wear resistance and abrasiveness of CAD-CAM monolithic materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 120, 318.e1–318.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.J.; Lawson, N.C.; McLaren, E.E.; Nejat, A.H.; Burgess, J.O. Comparison of the mechanical properties of translucent zirconia and lithium disilicate. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 120, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlenz, M.A.; Skroch, M.; Schmidt, A.; Rehmann, P.; Wöstmann, B. Monitoring fatigue damage in different CAD/CAM materials: A new approach with optical coherence tomography. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2021, 65, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Piva, A.M.O.; Tribst, J.P.M.; Werner, A.; Anami, L.C.; Bottino, M.A.; Kleverlaan, C.J. Three-body wear effect on different CAD/CAM ceramics staining durability. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 103, 103579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, V.; Wulfman, C.; Bekaert, S.; Dupont, N.; Le Goff, S.; Eldafrawy, M.; Vanheusden, A.; Mainjot, A. Clinical behavior of second-generation zirconia monolithic posterior restorations: Two-year results of a prospective study with Ex vivo analyses including patients with clinical signs of bruxism. J. Dent. 2019, 91, 103229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juntavee, N.; Attashu, S. Effect of sintering process on color parameters of nano-sized yttria partially stabilized tetragonal monolithic zirconia. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2018, 10, e794–e804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, I.; Lopes, L.P.; Fonseca, M.; Portugal, J. Effect of Zirconia Pigmentation on Translucency. Eur. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 2018, 26, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sabet, H.; Wahsh, M.; Sherif, A.; Salah, T. Effect of different immersion times and sintering temperatures on translucency of monolithic nanocrystalline zirconia. Futur. Dent. J. 2018, 4, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, H.N.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, D.H. Effects of different finishing/polishing protocols and systems for monolithic zirconia on surface topography, phase transformation, and biofilm formation. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2019, 11, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preis, V.; Schmalzbauer, M.; Bougeard, D.; Schneider-Feyrer, S.; Rosentritt, M. Surface properties of monolithic zirconia after dental adjustment treatments and in vitro wear simulation. J. Dent. 2015, 43, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Haj Husain, N.; Camilleri, J.; Özcan, M. Effect of polishing instruments and polishing regimens on surface topography and phase transformation of monolithic zirconia: An evaluation with XPS and XRD analysis. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 64, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglar, I.; Ates, S.M.; Yesil Duymus, Z. The effect of various polishing systems on surface roughness and phase transformation of monolithic zirconia. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2018, 10, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, Y.H.; Park, C.J.; Cho, L.R. Evaluation of various polishing systems and the phase transformation of monolithic zirconia. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 116, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, Y.H.; Yang, E.C.; Park, C.J.; Cho, L.R. In vitro evaluation of the polishing effect and optical properties of monolithic zirconia. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, S.M.; El-Fallal, A.A.; El-Negoly, S.A.; El Bedawy, A.B. Translucency of monolithic and core zirconia after hydrothermal aging. Acta Biomater. Odontol. Scand. 2015, 1, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Kim, S.H. Effect of hydrothermal aging on the optical properties of precolored dental monolithic zirconia ceramics. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, A.; Chung, K.H.; Flinn, B.D.; Kuykendall, T.; Zheng, C.; Harada, K.; Raigrodski, A.J. Effect of hydrothermal treatment on light transmission of translucent zirconias. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 118, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljanobi, G.; Al-Sowygh, Z.H. The Effect of Thermocycling on the Translucency and Color Stability of Modified Glass Ceramic and Multilayer Zirconia Materials. Cureus 2020, 12, e6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, M.E.; Sari, F. Effects of speed sintering on multilayered monolithic zirconia. Cumhur. Dent. J. 2019, 22, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, K.; Atsuta, I.; Tsukiyama, Y.; Kuwatsuru, R.; Morita, T.; Yoshimatsu, H.; Matsushita, Y.; Narimatsu, I.; Ayukawa, Y.; Sawae, Y.; et al. The need for polishing and occlusal adjustment of zirconia prostheses for wear on antagonist teeth. Dent. Mater. J. 2021, 40, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jum’ah, A.A.; Brunton, P.A.; Li, K.C.; Waddell, J.N. Simulated clinical adjustment and intra-oral polishing of two translucent, monolithic zirconia dental ceramics: An in vitro investigation of surface roughness. J. Dent. 2020, 101, 103447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manziuc, M.M.; Gasparik, C.; Burde, A.V.; Colosi, H.A.; Negucioiu, M.; Dudea, D. Effect of glazing on translucency, color, and surface roughness of monolithic zirconia materials. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2019, 31, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, R.; Kürklü, D.; Johnston, W. Effect of simulated mastication on the surface roughness of three ceramic systems. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 114, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavali, R.; Lin, C.P.; Lawson, N.C. Evaluation of Different Polishing Systems and Speeds for Dental Zirconia. J. Prosthodont. 2017, 26, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Mai, H.N.; Thant, P.P.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, J.; Jeong, S.M.; Lee, K.W. Effects of different surface finishing protocols for zirconia on surface roughness and bacterial biofilm formation. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2019, 11, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incesu, E.; Yanikoglu, N. Evaluation of the effect of different polishing systems on the surface roughness of dental ceramics. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 124, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goo, C.L.; Yap, A.; Tan, K.; Fawzy, A.S. Effect of Polishing Systems on Surface Roughness and Topography of Monolithic Zirconia. Oper. Dent. 2016, 41, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Hamad, K.Q.; Abu Al-Addous, A.M.; Al-Wahadni, A.M.; Baba, N.Z.; Goodacre, B.J. Surface Roughness of Monolithic and Layered Zirconia Restorations at Different Stages of Finishing and Polishing: An In Vitro Study. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafael, C.F.; Cesar, P.F.; Fredel, M.; Magini, R.d.S.; Liebermann, A.; Maziero Volpato, C.A. Impact of laboratory treatment with coloring and fluorescent liquids on the optical properties of zirconia before and after accelerated aging. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 120, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpel, C.; Rammelsberg, P.; Rues, S.; Zenthöfer, A.; Seceleanu, I.; Corcodel, N. Color stability of individually stained monolithic zirconia following occlusal adjustment. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2021, 33, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanal, F.A.; Kilinc, H. Effect of shade and sintering temperature on the translucency parameter of a novel multi-layered monolithic zirconia in different thicknesses. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2020, 32, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbary, O.; Wahsh, M.; Sherif, A.; Salah, T. Effect of accelerated aging on translucency of monolithic zirconia. Futur. Dent. J. 2016, 2, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, K.; Meißner, H.; Range, U.; Sakkas, A.; Boening, K.; Wieckiewicz, M.; Konstantinidis, I. Translucency of Zirconia Ceramics before and after Artificial Aging. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, e319–e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghazzawi, T.F. The effect of extended aging on the optical properties of different zirconia materials. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2017, 61, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alraheam, I.A.; Donovan, T.E.; Rodgers, B.; Boushell, L.; Sulaiman, T.A. Effect of masticatory simulation on the translucency of different types of dental zirconia. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 122, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnassar, T.M. Influence of Different Treatments and Conditions on Optical Properties of Monolithic Zirconia: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqutaibi, A.Y.; Ghulam, O.; Krsoum, M.; Binmahmoud, S.; Taher, H.; Elmalky, W.; Zafar, M.S. Revolution of Current Dental Zirconia: A Comprehensive Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, J.; Cales, B.; Drouin, J.M. Low-Temperature Aging of Y-TZP Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 2150–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, J.; Gremillard, L.; Deville, S. Low-Temperature Degradation of Zirconia and Implications for Biomedical Implants. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2007, 37, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deville, S.; Gremillard, L.; Chevalier, J.; Fantozzi, G. A critical comparison of methods for the determination of the aging sensitivity in biomedical grade yttria-stabilized zirconia. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2005, 72, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocjan, A.; Cotič, J.; Kosmač, T.; Jevnikar, P. In vivo aging of zirconia dental ceramics—Part I: Biomedical grade 3Y-TZP. Dent. Mater. 2021, 37, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, M.S.; Darvell, B.W. Thermal cycling procedures for laboratory testing of dental restorations. J. Dent. 1999, 27, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshiyab, S.H.; Nawafleh, N.; George, R. Survival and testing parameters of zirconia-based crowns under cyclic loading in an aqueous environment: A systematic review. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2017, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohbauer, U.; Scherrer, S.S.; Della Bona, A.; Tholey, M.; van Noort, R.; Vichi, A.; Kelly, J.R.; Cesar, P.F. ADM guidance-Ceramics: All-ceramic multilayer interfaces in dentistry. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6872:2015; Dentistry—Ceramic Materials. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- ISO 15732:2003; Fine Ceramics (Advanced Ceramics, Advanced Technical Ceramics)—Test Method for Fracture Toughness of Monolithic Ceramics at Room Temperature by Single Edge Precracked Beam (SEPB) Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- ISO 18756:2003; Fine Ceramics (Advanced Ceramics, Advanced Technical Ceramics)—Determination of Fracture Toughness of Monolithic Ceramics at Room Temperature by the Surface Crack in Flexure (SCF) Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- ISO 24370:2005; Fine Ceramics (Advanced Ceramics, Advanced Technical Ceramics)—Test Method for Fracture Toughness of Monolithic Ceramics at Room Temperature by Chevron-Notched Beam (CNB) Method. International Organization for standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- Pekkan, G.; Pekkan, K.; Bayindir, B.; Özcan, M.; Karasu, B. Factors affecting the translucency of monolithic zirconia ceramics: A review from materials science perspective. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahmiri, R.; Standard, O.C.; Hart, J.N.; Sorrell, C.C. Optical properties of zirconia ceramics for esthetic dental restorations: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tholey, M.J.; Swain, M.V.; Thiel, N. SEM observations of porcelain Y-TZP interface. Dent. Mater. 2009, 25, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunt, A.; Salvati, E.; Baimpas, N.; Dolbnya, I.; Neo, T.K.; Korsunsky, A.M. Investigations into the interface failure of yttria partially stabilised zirconia—Porcelain dental prostheses through microscale residual stress and phase quantification. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, 1576–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainjot, A.K.; Douillard, T.; Gremillard, L.; Sadoun, M.J.; Chevalier, J. 3D-characterization of the veneer-zirconia interface using FIB nano-tomography. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutra, D.; Pereira, G.; Kantorski, K.Z.; Valandro, L.F.; Zanatta, F.B. Does Finishing and Polishing of Restorative Materials Affect Bacterial Adhesion and Biofilm Formation? A Systematic Review. Oper. Dent. 2018, 43, E37–E52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.S.; Billington, R.W.; Pearson, G.J. The in vivo perception of roughness of restorations. Br. Dent. J. 2004, 196, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denry, I.; Kelly, J.R. Emerging ceramic-based materials for dentistry. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etman, M.K. Confocal examination of subsurface cracking in ceramic materials. J. Prosthodont. 2009, 18, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etman, M.K.; Woolford, M.; Dunne, S. Quantitative measurement of tooth and ceramic wear: In vivo study. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2008, 21, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Solá-Ruíz, M.F.; Baima-Moscardó, A.; Selva-Otaolaurruchi, E.; Montiel-Company, J.M.; Agustín-Panadero, R.; Fons-Badal, C.; Fernández-Estevan, L. Wear in Antagonist Teeth Produced by Monolithic Zirconia Crowns: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, M.; Chen, H.; Kang, J.; Wang, H. Antagonist enamel wear of tooth-supported monolithic zirconia posterior crowns in vivo: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrechts, P.; Braem, M.; Vuylsteke-Wauters, M.; Vanherle, G. Quantitative in vivo wear of human enamel. J. Dent. Res. 1989, 68, 1752–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.K.R.; Fraga, S.; Montagner, A.F.; Soares, F.Z.M.; Kleverlaan, C.J.; Valandro, L.F. The effect of grinding on the mechanical behavior of Y-TZP ceramics: A systematic review and meta-analyses. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 63, 417–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Tabares, J.A.; Jiménez-Piqué, E.; Reyes-Gasga, J.; Anglada, M. Microstructural changes in ground 3Y-TZP and their effect on mechanical properties. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 6670–6683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotič, J.; Jevnikar, P.; Kocjan, A. Ageing kinetics and strength of airborne-particle abraded 3Y-TZP ceramics. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denry, I.L.; Holloway, J.A. Microstructural and crystallographic surface changes after grinding zirconia-based dental ceramics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 76, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, Y.; Mori, Y.; Ishitani, A.; Masaki, T. Rhombohedral Phase in Y2O3-Partially-Stabilized ZrO2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1988, 71, C-34–C-36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Tabares, S.; Wardecki, D.; Nakamura, K.; Ardalani, S.; Hjalmarsson, L.; Franke Stenport, V.; Johansson, C.B. Effect of airborne-particle abrasion and polishing on novel translucent zirconias: Surface morphology, phase transformation and insights into bonding. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2021, 65, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Gremillard, L. The influence of stresses on ageing kinetics of 3Y-and 4Y-stabilized zirconia. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Hioki, T.; Kamigaito, O. Cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transformation in zirconia by ion implantation. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1985, 4, 1092–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 13356:2015; Implants for Surgery—Ceramic Materials Based on Yttria-Stabilized Tetragonal Zirconia (Y-TZP). International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Kim, H.T.; Han, J.S.; Yang, J.H.; Lee, J.B.; Kim, S.H. The effect of low temperature aging on the mechanical property & phase stability of Y-TZP ceramics. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2009, 1, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvie, R.C.; Nicholson, P.S. Phase Analysis in Zirconia Systems. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1972, 55, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toraya, H.; Yoshimura, M.; Somiya, S. Calibration Curve for Quantitative Analysis of the Monoclinic-Tetragonal ZrO2 System by X-Ray Diffraction. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1984, 67, C-119–C-121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arata, A.; Campos, T.M.; Machado, J.P.; Lazar, D.R.; Ussui, V.; Lima, N.B.; Tango, R.N. Quantitative phase analysis from X-ray diffraction in Y-TZP dental ceramics: A critical evaluation. J. Dent. 2014, 42, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.A. The Rietveld Method; International Union of Crystallography: Chester, UK, 1993; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- French, R.H.; Glass, S.J.; Ohuchi, F.S.; Xu, Y.; Ching, W.Y. Experimental and theoretical determination of the electronic structure and optical properties of three phases of ZrO2. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter. 1994, 49, 5133–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deville, S.; Chevalier, J. Martensitic Relief Observation by Atomic Force Microscopy in Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 86, 2225–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, J.; Deville, S.; Münch, E.; Jullian, R.; Lair, F. Critical effect of cubic phase on aging in 3mol% yttria-stabilized zirconia ceramics for hip replacement prosthesis. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5539–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Ohmichi, N.; Ohgai, M.; Yoshida, H.; Ikuhara, Y. Grain Boundary Segregation-Induced Phase Transformation in Yttria-Stabilized Tetragonal Zirconia Polycrystal. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 114, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib, M.H.M.; Gonçalves, A.M.; Jasinevicius, R.G.; Duduch, J.G. Diamond Wheel Grinding Performance Evaluation of Yttria Stabilized Zirconia—Cubic and Tetragonal Phases. In Proceedings of the Euspen’s 15th International Conference & Exhibition, Leuven, Belgium, 1–5 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alao, A.R.; Stoll, R.; Song, X.F.; Miyazaki, T.; Hotta, Y.; Shibata, Y.; Yin, L. Surface quality of yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal in CAD/CAM milling, sintering, polishing and sandblasting processes. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 65, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Low Risk of Bias | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author, Year | Country of Origin | Name of Material | Manufacturer | Type of Zirconia | Laboratory Processing Factors | Clinical-Related Processing Factors | Time-Related Factors | Mechanical Properties | Physicochemical Properties | Surface Properties | Optical Properties |
| Al Hamad, 2019 [175] | Jordan | Zolid Fx | Amann Girrbach | 5YSZ | Clinical grinding Clinical polishing | Characterization Roughness: Ra, Rz | |||||
| Alghazzawi, 2017 [181] | Saudi Arabia | Bruxzir DD-BioZX2 Katana HT NexxZr T Zenostar Zr translucent Zirlux FC2 DD-cubeX2 | Glidewell Laboratories Dental Direkt GmbH Kuraray Noritake Dental Inc. Sagemax Bioceramics Inc. Ivoclar Vivadent Inc. Henry Schein Dental Direkt GmbH | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Colour difference ∆E CR OP TP | |||||
| Aliaga, 2020 [109] | Brazil | Prettau Zirkon | Zirkonzahn GmbH | HT 3Y-TZP | Clinical grinding | Flexural strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase | Characterization Roughness: Ra | |||
| Auzani, 2020 [26] | Brazil | IPS e.max ZirCAD MT BL | Ivoclar Vivadent | 4YSZ | Colouring: staining using brush, immersion technique | Flexural fatigue strength | Crystalline phase Grain size | Characterization Roughness: Ra Rz | Colour difference ΔE00 OP TP | ||
| Bömicke, 2016 [132] | Germany | Cercon ht | DeguDent GmbH | HT 3Y-TZP | Hydrothermal aging: thermocycling Mechanical aging: ML in water | Load at fracture | |||||
| Caglar, 2018 [159] | Turkey | Katana Zirconia HT | Kuraray-Noritake | HT 3Y-TZP | Clinical grinding Clinical polishing | Crystalline phase | Characterization Roughness: Ra | ||||
| Cardoso, 2020 [84] | Brazil | Prettau Anterior | Zirkonzahn | 5YSZ | Sintering: final temperature | Flexural strength | Crystalline phase Grain size | Characterization | Absorption-scattering sum of light (S/A) Average reflectance Colour difference ∆E00 Opacity percentage TP | ||
| Choi, 2020 [123] | Republic of Korea | KATANA Zirconia HT KATANA Zirconia ML Lava Plus High Translucency Zirconia IPS e.max ZirCAD MT Lava Esthetic Fluorescent Full-Contour Zirconia IPS e.max ZirCAD MT Multi | Kuraray Noritake Dental Inc. Kuraray Noritake Dental Inc 3M ESPE Ivoclar Vivadent AG 3M ESPE Ivoclar Vivadent AG | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP multilayer shade 4YSZ 5YSZ multilayer shade Multilayer 4YSZ/5YSZ | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Characteristic strength Flexural strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase Elemental composition Hardness Young’s modulus | Characterization Roughness: Ra | CR Transmittance | ||
| Chun, 2017 [96] | Brazil | Vita YZ HT | Vita Zahnfabrik | HT 3Y-TZP | Glazing | Clinical grinding Clinical polishing | Flexural fatigue strength | Crystalline phase | Roughness: Ra | ||
| Dal Piva, 2020 [151] | the Netherlands | Vita YZ HT | Vita Zahnfabrik | HT 3Y-TZP | Colouring: external staining technique using brush Glazing | Wear: three-body wear, wear simulator | Material loss: vertical loss of extrinsic characterization | Characterization Roughness: Ra | |||
| Dapieve, 2018 [110] | Brazil | Zirlux FC2 - Full-Contour zirconia | Ardent, INC, Ivoclar Vivadent | HT 3Y-TZP | Clinical grinding | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave, dry storage | Flexural fatigue strength | Crystalline phase | Characterization | ||
| Ersoy, 2015 [80] | Turkey | InCoris TZI | SironaDental Systems GmbH | HT 3Y-TZP | Sintering: conventional, speed, super-speed | Flexural strength | Crystalline phase Grain size | ||||
| Fratucelli, 2021 [86] | Brazil | Prettau zirconia | Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP | Grinding Heat treatment: regenerative | Flexural strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase | Roughness: Ra, Rz | |||
| Herpel, 2021 [177] | Germany | Cercon ht white | Dentsply Sirona | HT 3Y-TZP | Colouring: staining technique using brush | Clinical grinding | Colour difference ΔE00 | ||||
| Huh, 2018 [161] | Korea | Zenostar sun Zenostar sun chroma Zenostar T0 | Ivoclar Vivadent Ivoclar Vivadent Ivoclar Vivadent | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP | Clincial grinding Clincial polishing | Elemental composition | Characterization Roughness: Ra | Lightness CIE L * | |||
| Jerman, 2021 [114] | Germany | Translucent T Extra Translucent ET High Translucent HT | Pritidenta GmbH Pritidenta GmbH Pritidenta GmbH | HT 3Y-TZP 4YSZ 5YSZ | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave Mechanical aging: TCML | Flexural strength Fracture toughness Weibull modulus | Grain size Hardness Indentation modulus | Transmittance | |||
| Juntavee, 2018 [76] | Thailand | VITA YZ HT colour | Vita Zahnfabrik | HT 3YTZP | Sintering: final temperature, short, regular, prolonged holding time | Flexural strength Weibull modulus Characteristic strength | Crystalline phase Grain size * | ||||
| Juntavee, 2018 [153] | Thailand | VITA YZ HT colour | Vita Zahnfabrik | HT 3Y-TZP | Sintering: final temperature, short, regular, prolonged holding time | Crystalline phase Grain size | Colour difference ∆E CR OP TP | ||||
| Juntavee, 2020 [81] | Thailand | inCoris TZI | Sirona | HT 3Y-TZP | Sintering: slow, normal, fast cooling rate | Characteristic strength Flexural strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase Grain size | ||||
| Juntavee, 2019 [77] | Thailand | inCoris TZI | Sirona | HT 3Y-TZP | Sintering: slow, normal, fast cooling rate | Crystalline phase Grain size * | Colour difference ∆Ew CR OP TP | ||||
| Khayat, 2018 [94] | USA | Tizian Blank Translucent | Schütz | HT 3Y-TZP | Glazing | Clincial grinding Clinical polishing | Flexural strength | Characterization Roughness: Ra | |||
| Kim, 2020 [88] | Korea | Luxen Zr Luxen Enamel Luxen Smile | Dentalmax Dentalmax Dentalmax | HT 3Y-TZP 4YSZ 5YSZ | Heat treatment: rapid cooling | Flexural strength Fracture toughness | Crystalline phase Grain size Hardness | Transmittance TP | |||
| Kou, 2019 [135] | Sweden | DD cubeX2 Prettau Anterior | DentalDirekt Zirkonzahn | 5YSZ 5YSZ | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Flexural strength | Crystalline phase | Roughness: Ra | Transmittance | ||
| Nishioka, 2018 [139] | Brazil | Zirconia YZ HT | Vita Zahnfabrik | HT 3Y-TZP | Mechanical aging: ML | Flexural fatigue strength Flexural strength | |||||
| Oyar, 2020 [70] | Turkey | Upcera YZ HT Zircon X ST | Upcera DentalTechnology President Dental GmbH | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP | Sintering: heating rate, holding time | Hydrothermal aging: thermocycling | Flexural strength | ||||
| Pereira, 2016 [106] | Brazil | Zirlux FC | Ivoclar Vivadent, Amherst | HT 3Y-TZP | Clinical grinding | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Characteristic strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase Depth of transformed zone | Characterization Roughness: Ra, Rz | ||
| Prado, 2020 [126] | Brazil | inCoris TZI Vita YZ HT | Dentsply Sirona Vita Zahnfabrik | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP | Hydrothermal aging: isothermal reactor | Characteristics strength Flexural strength Weibull modulus Residual stress | Crystalline phase Grain size Hardness | ||||
| Putra, 2017 [164] | USA | Lava Plus High Translucency Katana Zirconia Super Translucent BruxZir Anterior Solid Zirconia Katana Zirconia Ultra Translucent | 3M Oral Care Glidewell Laboratories Kuraray Noritake Kuraray Noritake | HT 3Y-TZP 4YSZ 5YSZ 5YSZ | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Crystalline phase Elemental composition Grain size | Transmittance | ||||
| Sen, 2018 [66] | Turkey | Prettau Zirkonzahn Vita YZ HT Colour A2 Vita YZ HT White Prettau Anterior | Zirkonzahn Vita Zahnfabrik Vita Zahnfabrik Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ | Colouring: immersion technique. Sintering: final temperature | Flexural strength | TP | ||||
| Skjold, 2020 [121] | Norway | DD Bio ZX2 DD cube X2 | Dental Direkt Dental Direkt | HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ | Mechanical aging: ML in water Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Load at fracture | Grain size Hardness | ||||
| Walczak, 2019 [180] | Germany | BruxZir Solid Zirconia Cercon ht white LavaPlus Zenostar T0 | Prismatic Dentalcraft, Inc Glidewell Laboratories DeguDent GmbH 3M Deutschland GmbH Wieland Dental+Technik GmbH & Co. | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | CR TP | |||||
| Wiedenmann, 2020 [83] | Germany | Ceramill Zolid HT+ | Amann Girrbach AG | 4YSZ | Sintering: control, high-speed | Mechanical aging: TCML Wear: two-body wear, TCML | Load at fracture Material loss: volume loss | ||||
| Zimmermann, 2020 [101] | Switzerland | InCoris TZI | Dentsply Sirona | HT 3Y-TZP | Chairside CAM procedure: milling, grinding. Sintering: conventional, speed-fire, super-speed | Load at fracture | Characterization | ||||
| Zucuni, 2019 [105] | Brazil | Zenostar T | Ivoclar Vivadent | HT 3Y-TZP | Clincial grinding Clincial polishing | Flexural fatigue strength | Crystalline phase | Characterization Roughness: Ra, Rz | |||
| Zucuni, 2017 [87] | Brazil | Zenostar T | Ivoclar Vivadent | HT 3Y-TZP | Heat treatment: regenerative Glazing | Clinical grinding Clinical polishing | Flexural fatigue strength Flexural strength | Crystalline phase | Characterization Roughness: Ra, Rz | ||
| Moderate risk of bias | |||||||||||
| Abdelbary, 2016 [179] | Egypt | InCoris TZI | Sirona | HT 3Y-TZP | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | TP | |||||
| Abdulmajeed, 2020 [141] | Finland | Katana High Translucent Katana Super Translucent Multi Layered Katana Ultra Translucent Multi Layered | Kuraray Noritake Inc Kuraray Noritake Inc Kuraray Noritake Inc | HT 3Y-TZP 4YSZ 5YSZ | Mechanical aging: TCML | Load at fracture | |||||
| Abouelenien, 2020 [144] | Egypt | Prettau Zirconia | Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP | Polishing Glazing | Wear: two-body wear, ML | Material loss: weight loss | Characterization | |||
| Agingu, 2018 [64] | China | Katana HT SuperfectZir HTS | Kuraray Aidite | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP | Colouring: immersion technique | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Flexural strength | Crystalline phase Depth of transformed zone | |||
| Al-Haj Husain, 2016 [158] | Switzerland | Katana Zirconia HT | Kuraray-Noritake | HT 3Y-TZP | Clincial grinding Clinical polishing | Crystalline phase Elemental composition | Characterization Roughness: Ra | ||||
| Al-Haj Husain, 2018 [112] | Switzerland | Katana Zirconia HT | Kuraray-Noritake | HT 3Y-TZP | Clincial grinding Clinical polishing | Material loss: weight loss, volume loss, vertical loss after polishing | Characterization Roughness: Ra Wettability | ||||
| Aldegheishem, 2015 [147] | Germany | Zenostar Cercon HT | Wieland DeguDent | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP | Wear: two-body wear, TCML | Material loss: volumetric loss | Crystalline phase | Characterization | |||
| Alghazzawi, 2015 [115] | Saudi Arabia | Argen HT BruxZir DD BioZX2 Lava Plus High Translucency ZenoStar Zirlux | Argen Corp. Glidewell Laboratories Dental Direkt 3M ESPE Wieland Dental Ardent | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Crown strength Flexural strength | Grain size Elemental composition | ||||
| Aljanobi, 2020 [165] | Saudi Arabia | Prettau 2 Dispersive Prettau 4 Anterior Dispersive | Zirkonzahn GmbH Zirkonzahn GmbH | HT 3Y-TZP Multilayer shade 5YSZ multilayer shade | Hydrothermal aging: thermocycling | Grain size | Colour difference ΔE TP | ||||
| Almansour, 2018 [130] | Saudi Arabia | Ceramill Zolid White HT Copran Zr-i Monolith HT Lava Plus HT | Amann Girrbach White Peaks 3M ESPE | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZ HT 3Y-TZP | Hydrothermal aging: thermocycling Mechanical aging: ML in water | Flexural strength | |||||
| Alraheam, 2019 [182] | USA | BruxZir Shaded Zirconia BruxZir Anterior Solid Zirconia | Glidewell Laboratories Glidewell Laboratories | HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ | Mechanical aging: TCML | CR Light blockage TP | |||||
| Amaral, 2018 [103] | Brazil | Zirlux FC | Amherst | HT 3Y-TZP | Clincial grinding | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Flexural fatigue strength Slow crack growth susceptibility | Crystalline phase Depth of the transformed zone Hardness | Characterization Roughness: Ra, Rz | ||
| Amarante, 2020 [128] | Brazil | VIPI Block Zirconn Translucent VIPI Block Zirconn High-translucent | VIPI VIPI | HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ | Hydrothermal aging: reactor | Flexural strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase Grain size | Roughness: Ra, Rz | CR | ||
| Amer, 2015 [170] | USA | Crystal diamond, Crystal Zirconia | Dental Laboratory Milling Supplies | HT 3Y-TZP | Glazing | Clinical grinding Clinical polishing | Wear: three-body wear, wear simulator | Roughness: Ra | |||
| Asli, 2019 [99] | Iran | Ceramill Zolid Fx multilayer | Amann Girrbach | 5YSZ | Grinding Glazing | Clinical grinding Clinical polishing | Flexural strength | ||||
| Bergamo, 2016 [129] | Brazil | Ceramill Zolid | Amann Girrbach | HT 3Y-TZP | Hydrothermal aging: reactor, thermocycling Mechanical aging: ML in water | Characteristic load at fracture Load at fracture Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase | Characterization | |||
| Borba, 2021 [138] | USA | Zpex Zpex Smile | Tosoh Corporation Tosoh Corporation | HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ | Mechanical aging: ML in water | Flexural strength | Characterization | ||||
| Chavali, 2017 [171] | USA | Zenostar Zr Translucent | Wieland | HT 3Y-TZP | Glazing | Clinical polishing | Characterization Roughness: Ra | Gloss | |||
| Cokic, 2020 [73] | Belgium | CEREC Zirconia medi S inCoris TZI Katana STML Katana STML, 12Z | Dentsply Sirona Dentsply Sirona Kuraray Noritake Kuraray Noritake | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP 4YSZ 4YSZ | Sintering: conventional, speed | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Characteristic strength Flexural strength Fracture toughness Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase Density Elemental composition Grain size Hardness | CR TP | ||
| Coskun, 2019 [166] | Turkey | Katana ML | Noritake | HT 3Y-TZP multilayer shade | Sintering: speed, high-speed | Roughness: Ra | CR TP | ||||
| D’Arcangelo, 2018 [145] | Italy | Katana Zirconia ML | Kuraray Noritake Dental Inc | HT 3Y-TZP Multilayer shade | Wear: two-body wear, ML | Material loss: vertical loss, volumetric loss | Characterization | ||||
| de Araújo-Júnior, 2020 [120] | Brazil | Zirconn translucent | VIPI | HT 3Y-TZP | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave, reactor | Residual stress: compressive stress Fracture toughness Characteristic strength Flexural strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase Grain size Hardness | CR TP | |||
| De Souza, 2020 [102] | Brazil | Vipi Block Zirconn Translucent | Vipi | HT 3Y-TZP | Clinical grinding Clinical polishing | Hydrothemral aging: autoclave, thermocycling | Flexural strength | Crystalline phase | Characterization Roughness: Ra | ||
| Fathy, 2015 [162] | Egypt | Zirkonzahn Prettau | Zirkonzahn | HT 3YTZP | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Crystalline phase Grain size | TP | ||||
| Flinn, 2017 [118] | USA | Prettau BruxZir Katana HT13 Katana ML | Zirkonzahn Glidewell Laboratories Kuraray Noritake Kuraray Noritake | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP multilayer shade | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Flexural strength | Crystalline phase Depth of transformed zone Elemental composition | ||||
| Gomes, 2018 [154] | Portugal | Prettau Zirkon | Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP | Colouring: immersion technique | Grain size | Transmittance | ||||
| Goo, 2016 [174] | Malaysia | LAVA PLUS High Translucency | 3M ESPE | HT 3Y-TZP | Clinical polishing | Characterization Roughness: Ra | |||||
| Güngör, 2019 [140] | Turkey | Incoris TZI | Sirona Dental Systems | HT 3YTZP | Mechanical aging: TCML | Load at fracture | |||||
| Harada, 2020 [119] | Japan | Lava Plus Zirconia Lava Esthetic Zirconia | 3M ESPE 3M ESPE | HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ multilayer shade | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Characteristic strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase Depth of transformed zone Hardness | ||||
| Hatanaka, 2020 [93] | Brazil | Prettau. Prettau Anterior | Zirkonzahn Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ | Glazing | Clinical grinding Clinical polishing | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Characteristic strength Flexural strength Weibull modulus | Depth of transformed zone | Roughness: Ra | |
| Holman, 2020 [28] | USA | Katana ML Lava Plus Katana STML Katana UTML Lava Esthetic | Kuraray Noritake Dental 3M ESPE Kuraray Noritake Dental Kuraray Noritake Dental 3M ESPE | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP multilayer shade 4YSZ multilayer shade 5YSZ multilayer shade 5YSZ multilayer shade | Mechanical aging: ML | Flexural fatigue strength Flexural strength | |||||
| Huh, 2016 [160] | Korea | Rainbow Trans | Genoss | HT 3Y-TZP | Clinical polishing | Crystalline phase Grain size | Characterization Roughness: Ra | ||||
| Incesu, 2020 [173] | Turkey | Lava Plus Zirconia | 3M ESPE | HT 3Y-TZP | Clinical polishing | Characterization Roughness: Ra, Rz | |||||
| Jansen, 2019 [79] | Germany | Zolid Zolid HT+ | Amann Girrbach AG Amann Girrbach AG | HT 3Y-TZP 4YSZ | Sintering: final temperature, control, high-speed | Flexural strength | Crystalline phase Grain size | Transmittance | |||
| Jerman, 2020 [74] | Germany | Ceramill Zolid Ceramill Zolid HT+ | Amann Girrbach AG Amann Girrbach AG | HT 3Y-TZP 4YSZ | Sintering: conventional, high-speed | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave Mechanical aging: TCML | Flexural strength Weibull modulus | ||||
| Jum’ah, 2020 [168] | Jordan | DD Bio ZX DD cube ONE DD cubeX2 | DentalDirekt GmbH | HT 3Y-TZP 4YSZ 5YSZ | Glazing | Clinical grinding Clinical polishing | Characterization Roughness: Ra | ||||
| Kashkari, 2019 [137] | USA | Prettau Zirconia | Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP | Mechanical aging: ML in water | Load at fracture | |||||
| Kengtanyakich, 2020 [134] | Thailand | Vita YZ ST Vita YZ XT Prettau Anterior | VITA Zahnfabrik VITA Zahnfabrik Zirkonzahn GmbH | 4YSZ 5YSZ 5YSZ | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Flexural strength Fracture toughness | Crystalline phase Hardness | ||||
| Kim, 2019 [163] | Korea | Katana ML | Kuraray Noritake | HT 3Y-TZP Multilayer shade | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Crystalline phase | Characterization Roughness: Ra | Colour differences ΔE00 TP | |||
| Koenig, 2019 [152] (Clinical study) | Belgium | Lava Plus High Translucency Zirconia | 3M ESPE | HT 3Y-TZP | Clinical wear | Clinical material loss: vertical loss | |||||
| Kolakarnprasert, 2019 [32] | USA | Katana ML Katana STML Katana UTML | Kuraray Noritake Kuraray Noritake Kuraray Noritake | HT 3Y-TZP multilayer shade 4YSZ multilayer shade 5YSZ multilayer shade | Hydrothermal aging: hydrothermal vessel | Crystalline phase | |||||
| Kumchai, 2018 [90] | USA | InCoris TZI Prettau Zirconia Zirlux FC | Sirona Zirkonzahn Pentron Ceramics | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP | Heat-treatment: glaze firing cycle. Glazing | Flexural strength | |||||
| Kwon, 2018 [149] | USA | Katana HT Katana UTML | Kuraray Noritake Dental Kuraray Noritake Dental | HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ multilayer shade | Wear: two-body wear, wear simulator | Material loss: volumetric material loss | |||||
| Lai, 2017 [91] | China | ST (super-translucent) | UPCERA | HT 3Y-TZP | Glazing | Clinical grinding | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Characteristic strength Flexural strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase Elastic modulus Hardness | Characterization | |
| Lawson, 2020 [82] | USA | Katana STML Prettau Anterior | Kuraray Noritake Zirkonzahn | 4YSZ multilayer shade 5YSZ multilayer shade | Sintering: conventional, high-speed, custom high-speed | Flexural strength | Grain size | TP | |||
| Lee, 2019 [172] | Korea | Prettau | Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP | Clinical grinding Clincial polishing | Characterization Roughness: Ra | |||||
| Lopez-Suarez, 2019 [143] | Spain | Lava Plus | 3M ESPE | HT 3Y-TZP | Mechanical aging: TCML | Characteristic load at fracture Load at fracture Weibull modulus | |||||
| Ludovichetti, 2018 [148] | Brazil | Lava Plus | 3M ESPE | HT 3Y-TZP | Wear: two-body wear, wear simulator | Material loss: material loss | |||||
| Lümkemann, 2021 [69] | Germany | CeramillZolid. Ceramill Zolid fx. Ceramill Zolid ht+ Ceramill zolid ht+ Preshades | Amann Girrbach AG Amann Girrbach AG Amann Girrbach AG Amann Girrbach AG | HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ 4YSZ 4YSZ | Colouring: immersion technique Sintering: conventional, high-speed (4YSZ) | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Flexural strength | Transmittance | |||
| Mai, 2019 [156] | Korea | Prettau | Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP | Clinical grinding Clinical polishing | Crystalline phase | Roughness: Ra | ||||
| Manziuc, 2019 [169] | Romania | IPS e. max ZirCAD MT Katana HT Vita YZ HT Cercon HT | Ivoclar Vivadent Kuraray Noritake Dental Inc. VITA Zahnfabrik Dentsply Sirona | 4YSZ HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP | Glazing | Roughness: Ra | Colour difference ΔE00 TP | ||||
| Michailova, 2020 [33] | Germany | Katana Zirconia STML Block Katana Zirconia STML Disc IPS e. max ZirCAD Prime | Kuraray Noritake Dental Kuraray Noritake Dental Ivoclar Vivadent | 4YSZ multilayer shade 4YSZ multilayer shade Multilayer 3Y-TZP/5YSZ | CAM procedure Sintering: conventional | Chairside CAM procedure. Sintering: high-speed (4YSZ) | Mechanical aging: TCML Wear: two-body wear, TCML | Load at fracture Material loss: volumetric loss, vertical loss Weibull modulus | Transmittance | ||
| Moqbel, 2019 [111] | Germany | Katana HT10 | Kuraray | HT 3Y-TZP | Clinical polishing | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Flexural strength | Crystalline phase Hardness | Roughness: Ra, Rz | ||
| Muñoz, 2017 [27] | Brazil | Prettau Prettau Anterior | Zirkonzahn Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave Mechanical aging: ML in water | Characteristic strength Flexural strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase Grain size | Characterization | |||
| Nakamura, 2018 [127] | Japan | Lava Plus High Translucency Zirconia | 3M ESPE | HT 3Y-TZP | Hydrothermal aging: water storage, thermocycling Mechanical aging: ML in water | Load at fracture Residual stress: von Mises stress | |||||
| Nakamura, 2015 [124] | Japan | Lava Plus High Translucency Zirconia | 3M ESPE | HT 3Y-TZP | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave Mechanical aging: ML in water | Load at fracture | Crystalline phase Depth of transformed zone | ||||
| Nakamura, 2020 [78] | Japan | inCoris TZI | Dentsply Sirona | HT 3Y-TZP | Sintering: conventional, high-speed | Hydrothermal aging: decomposition vessel | Load at fracture | Crystalline phase | |||
| Nam, 2018 [89] | Korea | Lava plus | 3M ESPE | HT 3Y-TZP | Glazing | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Flexural strength | Crystalline phase Grain size | Characterization | ||
| Nossair, 2019 [65] | Egypt | Bruxzir shaded A2 Bruxzir unshaded Katana HT shade A2 Katana HT white Prettau unshaded Katana ST shade A2 Katana ST white Bruxzir anterior white Bruxzir anterior shade A2 Prettau anterior white | Glidewell Glidewell Kuraray Kuraray Zirkonzahn Kuraray Kuraray Glidewell Glidewell Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP 4YSZ 4YSZ 5YSZ 5YSZ 5YSZ | Colouring: immersion technique | Flexural strength | |||||
| Oblak, 2017 [136] | Slovenia | inCoris TZI | Sirona | HT 3Y-TZP | Mechanical aging: ML in water | Characteristic load at fracture Load at fracture Weibull modulus | |||||
| Ozer, 2018 [108] | Turkey | Prettau | Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP | Clinical polishing | Flexural strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase | Characterization | |||
| Pereira, 2018 [122] | Brazil | Katana ML/HT Katana STML Katana UTML | Kuraray Noritake Dental Inc Kuraray Noritake Dental Inc Kuraray Noritake Dental Inc | HT 3Y-TZP multilayer shade 4YSZ multilayer shade 5YSZ multilayer shade | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Characteristic strength Flexural fatigue strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase | Characterization | |||
| Pereira, 2016 [104] | Brazil | Zirlux FC | Ivoclar Vivadent | HT 3Y-TZP | Clinical grinding | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Flexural fatigue strength Flexural strength | Crystalline phase | Characterization Roughness: Ra, Rz | ||
| Pfefferle, 2020 [97] | Germany | Ceramill Zolid HT+ | Amann Girrbach | 4YSZ | Polishing: pre-sintered, fully sintered stage | Flexural strength | Free energy SFE Roughness: Ra | Transmittance | |||
| Poole, 2019 [125] | Brazil | ZirkOM SI | Qinhuangdao Aidite High-Technical Ceramics Co. Ltd | HT 3Y-TZP | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Flexural strength Fracture toughness | Crystalline phase Hardness | Roughness: Ra | |||
| Prado, 2017 [107] | Brazil | Zirlux FC | Ardent Dental Inc | HT 3Y-TZP | Clincial grinding | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Characteristics strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase Depth of transformed zone | Characterization Roughness: Ra, Rz | ||
| Preis, 2015 [157] | Germany | Cercon HT | DeguDent | HT 3Y-TZP | Clincial grinding Clincial polishing | Wear: two-body wear, wear simulator | Crystalline phase Elemental composition | Characterization Roughness: Ra | |||
| Rafael, 2018 [176] | Brazil | Prettau | Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP | Colouring: immersion technique | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Colour difference ΔE00 Fluorescence Lightness, chroma, hue | ||||
| Rosentritt, 2020 [142] | Germany | DD Bio ZX2 DD cube ONE DD cube ONE Multilayer ML DD cubeX2 | Dental Direkt Dental Direkt Dental Direkt Dental Direkt | HT 3Y-TZP 4YSZ 4YSZ multilayer shade 5YSZ | Mechanical aging: TCML Wear: two body wear, pin-on-block in water | Load at fracture Material loss: wear depth | Roughness: Ra, Rz | ||||
| Rosentritt, 2020 [85] | Germany | IPS e.max ZirCAD Prime | Ivoclar Vivadent | Multilayer 3Y-TZP/5YSZ | Sintering: fast, normal, long | Load at fracture | Grain size | ||||
| Sabet, 2018 [155] | Egypt | inCoris TZI | Dentsply Sirona ** | HT 3Y-TZP | Colouring: immersion technique. Sintering: final temperature | Grain size | TP | ||||
| Sanal, 2020 [178] | Turkey | Katana 12Z/STML A2 zirconia block Katana 12Z/STML A3 zirconia block | Kuraray Noritake Kuraray Noritake | 4YSZ multilayer shade 4YSZ multilayer shade | Sintering: final temperature | Grain size | TP | ||||
| Sarıkaya, 2018 [131] | Turkey | Incoris TZI | Sirona Dental Systems | HT 3Y-TZP | Hydrothermal aging: thermocycling Wear: two-body wear, ML in water | Load at fracture Material loss: volumetric loss | Characterization | ||||
| Schatz, 2016 [95] | Germany | Ceramill Zolid. DD Bio zx2 Zenostar Zr Translucent. | AmannGirrbach Wieland+Dental Dental Direkt | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP | Polishing: pre-sintered manually dry, fully sintered stage machine wet | Characteristic strength Flexural strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase | Characterization Roughness: Ra | |||
| Schlenz, 2021 [150] | Germany | Lava Plus Priti multidisc ZrO2 extra translucent Prettau anterior | 3M ESPE Pritidenta Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP 4YSZ 5YSZ | Wear: two-body wear, ML in water | Material loss: vertical, horizontal damage | |||||
| Shen, 2019 [116] | China | Ceramill Zolid White Lava Plus Katana UTML | AmannGirrbach 3M ESPE Kuraray Noritake | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Flexural strength | Crystalline phase Grain size Hardness | TP | |||
| Spies, 2020 [133] | Germany/Belgium | Priti multidisc ZrO2 translucent Priti multidisc ZrO2 extra translucent Priti multidisc ZrO2 high translucent | Pritidenta Pritidenta Pritidenta | HT 3Y-TZP 4YSZ 5YSZ | Hydrothermal aging: water storage Mechanical aging: TCML Wear: two-body wear, TCML | Load at fracture Material loss: intrusion depth, surface area, worn volume | Crystalline phase | ||||
| Stawarczyk, 2016 [117] | Germany | Ceramill Zolid DD Bio ZX2 InCoris TZI Zenostar | Amann Girrbach Dental Direkt Sirona Wieland+Dental | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave Mechanical aging: TCML Wear: two-body wear, TCML | Flexural strength Material loss: volume loss Weibull modulus | |||||
| Stawarczyk, 2013 [146] | Switzerland | ZENOTEC Zr Bridge transluzent | Wieland Dental + Technik | HT 3Y-TZP | Polishing: manually, mechanically Glazing | Wear: two-body wear, TCML | Material loss: vertical loss | Characterization | |||
| Sulaiman, 2015 [67] | Finland | Prettau Zirconia Prettau Anterior | Zirkonzahn Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ | Colouring: staining technique using brush. Sintering: non-vacuum, vacuum | Flexural strength | Characterization | CR Gloss TP | |||
| Sulaiman, 2017 [68] | USA | Prettau zirconia Prettau anterior | Zirkonzahn Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ | Colouring: staining technique using brush, immersion technique. Sintering: regular, vacuum | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Flexural strength | Grain size | |||
| Tachibana, 2021 [167] | Japan | inCoris TZI | Sirona | HT 3Y-TZP | Polishing Grinding | Wear: two-body wear, ML in water | Roughness: Ra | ||||
| Vardhaman, 2020 [34] | USA | IPS e.max ZirCAD LT IPS e.max ZirCAD Multi | Ivoclar Vivadent Ivoclar Vivadent | HT 3Y-TZP Multilayer 4YSZ/5YSZ | Wear: two-body wear, wear simulator | Material loss: volume loss, wear depth | Characterization | ||||
| Vila-Nova, 2020 [98] | Brazil | Prettau Anterior | Zirkonzahn | 5YSZ | Glazing | Clinical grinding Clinical polishing | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Characteristic strength Flexural strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase Elemental composition | Characterization Roughness: Ra | |
| Wille, 2018 [113] | Germany | IPS e.max ZirCAD Katana Zirconia ML Lava Plus | Ivoclar Vivadent Kuraray 3M ESPE | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP multilayer shade HT 3Y-TZP | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Flexural strength | Crystalline phase | ||||
| Yang, 2020 [75] | Taiwan | Copran Zr-i Ultra-T A2 Copran Zr-i Ultra-T white Cercon HT Cercon XT | Whitepeaks dental Whitepeaks dental Dentsply Sirona Dentsply Sirona | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ | Sintering: conventional, rapid | Characteristic strength Flexural strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase Grain size Hardness | Characterization | Colour difference ΔE TP | ||
| Yu, 2019 [31] | Korea | 3M Lava Esthetic | 3M | 5YSZ | Colouring: immersion technique, acid-based, aqueous colouring liquids | Flexural strength | Characterization | ||||
| Zucuni, 2019 [92] | Brazil | Vita YZ-HT | Vita Zahnfabrik | HT3-YTZP | Glazing: powder/liquid by brush, spray | Clinical grinding | Flexural strenght Flexural fatigue strenght | Crystalline phase | Characterization Roughness: Ra, Rz | ||
| Zucuni, 2020 [100] | Brazil | ZirCAD MT Multi | Ivoclar Vivadent | Multilayer 4YSZ 5YSZ | Glazing | Clinical grinding Clinical polishing | Flexural fatigue strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase | Characterization Roughness: Ra, Rz | ||
| Öztürk, 2019 [71] | Turkey | Incoris TZI C Upcera *** | Sirona Dental Systems GmbH Shenzhen Upcera Co. Ltd. | HT 3Y-TZP | Sintering: final temperature, holding time | Flexural strength | Crystalline phase | Roughness: Ra | |||
| Öztürk, 2019 [72] | Turkey | Upcera ST-Colour | Shenzhen Upcera Dental Technology Co., Ltd | HT 3Y-TZP | Sintering: heating rate | Characteristics strength Flexural strength Weibull modulus | Crystalline phase Grain size | ||||
| High risk of bias **** | |||||||||||
| Ahmed, 2020 [48] | Egypt | DD cube X2 | Dental Direkt ** | 5YSZ | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Flexural strength | Colour difference ΔE CR TP | ||||
| Alraheam, 2020 [49] | USA | BruxZir Shaded Zirconia BruxZir Anterior Solid Zirconia | Glidewell Laboratories Glidewell Laboratories | HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ | Mechanical aging: TCML | Load at fracture | |||||
| Ban, 2013 [50] | Japan | Zenostar pure Zirkonzahn Prettau | Wieland Zirkonzahn | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP | Colouring: immersion technique | Flexural strength | Colour difference ΔE | ||||
| Camposilvan, 2018 [51] | France | Aadva EI Aadva NT Katana UTML | Aadva, GC Tech Aadva, GC Tech Kuraray Noritake Dental Inc. | HT 3Y-TZP 5YSZ 5YSZ multilayer shade | Polishing Glazing | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave | Flexural strength Fracture toughness | Crystalline phase Grain size Hardness | CR Transmittance | ||
| Cattani-Lorente, 2016 [52] | Switzerland | Lava Plus | 3M ESPE | HT 3Y-TZP | Clincial grinding | Hydrothermal aging: autoclave, water storage | Crystalline phase Depth of transformed zone Elastic modulus Hardness | Characterization Roughness: Ra | |||
| Elsayed, 2019 [53] | Germany | DD Bio ZX2 DD cubeX2 HS DD cubeX2 | Dental Direkt Dental Direkt Dental Direkt | HT 3Y-TZP 4YSZ 5YSZ | Mechanical aging: TCML | Load at fracture | |||||
| Fontolliet, 2020 [54] | Switzerland | Zenostar Zr Translucent | Wieland Dental | HT 3Y-TZP | Glazing | Clinical polishing | Wear: two-body wear, ML | Material loss: weight loss, volume loss, vertical loss | Roughness: ΔRz, ΔRa | ||
| Gaonkar, 2020 [55] | India | Ceramill Zolid HT | Amann Girrbach | HT 3Y-TZP | Glazing | Clinical polishing | Characterization Roughness: Ra | ||||
| Habib, 2019 [56] | Saudi Arabia | Zolid fx preshade | Amann Girrbach | 5YSZ | Wear: two-body wear, TCML | Material loss: vertical loss, weight loss | Characterization Roughness ***** | ||||
| Kaizer, 2017 [57] | USA | inCoris TZI | Sirona | HT 3Y-TZP | Sintering: long-term, speed, super-speed | Wear: two-body wear, TCML | Material loss: wear depth, volume loss | Crystalline phase Grain size Hardness | TP | ||
| Kumar, 2020 [58] | India | Ceramill Zolid | Amann Girrbach | HT 3Y-TZP | Wear: three-body wear, pin-on-disc | Material loss: weight loss | Roughness: Ra | ||||
| Park, 2014 [59] | Korea | Prettau ZirBlank *** Zeno Zr *** | Zirkonzahn GmbH Acucera Inc. Wieland Dental | HT 3Y-TZP | Colouring: external staining technique using brush. Polishing Glazing | Wear: two-body wear, ML in water | Characterization Roughness ***** | ||||
| Preis, 2012 [60] | Germany | Cercon HT | DeguDent | HT 3Y-TZP | Glazing | Clincial grinding Clincial polishing | Mechanical aging: TCML | Load at fracture | Roughness: Ra | ||
| Stober, 2016 [61] (Clinical study) | Germany | Zenostar Zr Translucent | Wieland Dental | HT 3Y-TZP | Clincial wear | Clinical material loss: vertical loss | |||||
| Wiedenmann, 2020 [62] | Germany | Zenostar ZR Translucent | Wieland Dental | HT 3Y-TZP | Glazing | Clinical grinding Clinical polishing | Mechanical aging: TCML Wear: two-body wear, TCML | Load at fracture Material loss: volume loss | Characterization | ||
| Yang, 2019 [63] (Clinical part) | Korea | Katana ML Block Rainbow Shade Block | Genoss Kuraray Noritake | HT 3Y-TZP HT 3Y-TZP | Clincial wear Wear: two-body wear, TCML. | Clinical material loss: vertical loss Material loss: vertical wear | Crystalline phase (clinical) Crystalline phase | Roughness: Ra | |||
| CAM Procedure | |
|---|---|
| Type of milling unit | Milling/grinding: tools |
| Ceramill Motion [33] | Milling: NA [33] |
| Colouring | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technique | Colouring Liquid | Shade | Time (s/min)/Strokes (No) | Drying Condition (min, Temperature °C) |
| External staining using brush | Vita Akzent® Plus Effect Stains [151] | ES14 [151] | NA [151] | NA [151] |
| Immersion (pre-sintered) | TZI Sirona coloring liquid [155], Zirconia coloring liquid (Aidite) [64], IPS e.max ZirCAD MT Colouring Liquid (Ivoclar Vivadent) [26], Aquarell (Zirkonzahn)/SF1/SF4 (3M ESPE) [154], Ceramill Liquid (Amann Girrbach) [69], Zirkonzahn coloring liquid (Zirkonzahn) [65], Vita YZ HT shade liquid/Prettau Aquarell coloring liquid (Zirkonzahn) [66], Ko’s Liquid (Kuwotech)/Colour Liquid for Prettau Aquarell (Zirkonzahn) [31], Color Liquid Prettau/Liquid Fluoreszenz/Liquid Fluoreszenz, Color Liquid Prettau (Zirkonzahn) [176] | A1/A4/A1/A4 [154], A2 [26,64,65,66], A2/NA/NA, A2 [176], A3 [31,155], A4 [69] | 15/1 [66], 5 s × 2 [31], 10 [154] 30 [65] s 2 [64], 2/4 [26] 3/5/7 [69,155], 10/5/5, 10 [176] min | Bench dry 1440 min [155], 120 min, 37° [64] Drying lamp 3 min [65] Infrared drying lamp 1 min [176], NA/20 min [66], 45 min/Drying NA [154] Furnace 15 min, 70° [26], 60 min, 80° [69], 15 min, 150° [31] |
| Staining using brush (pre-sintered) | IPS e.max ZirCAD MT Colouring Liquid (Ivoclar Vivadent) [26] Color Liquid Prettau Watercolor (Zirkonzahn) [177], Color Liquid Prettau Anterior Aquarell (Zirkonzahn) [67,68] | A2 [26,67], A2/A3.5/A4 [177], A3.5 [68] | 1/3 [26], 2 [67,68], 4 × 6 applications [177] | Infrared drying lamp 20 min [67,68] Furnace 15 min, 70° [26], 20 min, 150° [177] |
| Sintering | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sintering Variable * | Starting Temperature (°C) | Heating Rate (°C/min) to Temperature (°C) | Heating Rate (°C/min) to Final Temperature | Final Sintering Temperature, FT (°C) | Holding Time, HT (min) | Cooling Rate (°C/min) to Temperature (°C) | Total Time (min) |
| Conventional [33], Conventional/High-speed [69,74,78], Control/High-speed [83], Speed/High-speed [166], Conventional/Speed/Super-speed [80], Control/High-speed/High-speed [79], Conventional/High-speed/Custom high-speed [82], Conventional/Conventional /Speed/Speed [73], Conventional/Conventional/ Rapid/Rapid [75], Fast/Normal/Long [85] | 20 [83], RT/Placed in final temp [166], NA/NA/ Placed in FT [80], NA [33,69,73,74,75,78,79,82,85] | NA/NA/350 to 1300, 150 to 1500/330 to 1050 [73], 10 to 950/22 to 880/50 to 1100/NA [75], NA [33,69,74,78,79,80,82,83,85,166] | 8/NA [69], 8/300 [83], NA/NA/10/150 [73], 6/11/20/69 [75], NA [33,74,78,79,80,82,85,166] | 1450/1580 [69,74], 1450/1570/1590 [79,83], 1500 [85], 1500/1550 [33], 1500/1520/1500/1540 [75], 1510/1580 [78,166], 1510/1540/1580 [80], 1550/NA/NA [82], 1550/1510/1560/ 1580 [73] | 30/10 [166], 120/10 [74,83], 120/NA [69], 120/10/10 [79], 120/25/10 [80], 120/120/16/3 [73], 120/NA/NA [82], 90/130/30/35 [75], NA [33,78,85] | 15 to 25/NA [69], 80 min to 20/10 min to 950 [83], Cooled to 600/Removed from FT [166], NA/NA/Removed from FT [80], NA/170 to 1200°, 480 to RT/175 to 1200°, 400 to RT [73], 30 to 750/30 to 750, 31 to 300/30 to 750/70 to 750 [75], NA [33,74,78,79,82,85] | NA/10 [166], 220/15 [78], 480/120/10 [80], 420/30/18 [82], 408/240/28/NA [73], 146/265/590 [85], NA [33,69,74,75,79,83,85] |
| FT [66,84,155,178], FT/Short/Regular/Prolonged HT ** [76,153], FT/HT ** [71] | RT [84], NA [66,71,76,153,155,178] | 8 [84], 25 to 800 [155], NA [66,71,76,153,178] | 10 [66,71,178], 15 [155], 17 [76,153], NA [84] | 1350/1450/1550 ** [76,153], 1350/1450/1600 [66,178], 1400/1500/1600 [155], 1450/1600 [84], NA/1400/1450/1500/1600 ** [71] | NA/30/60/120/240 ** [71], 60/120/180 ** [76,153], 120 [66,84,155,178] | 8 [84], 10 to RT [178], 10 [66,71], 17 [76,153], 30 to 200° [155] | NA [66,71,76,84,153,155,178] |
| Heating rate [72] Heating rate/HT *** [70], Slow/Normal/Fast cooling rate [77,81], Non-vacuum/Vacuum [67] Regular/Vacuum [68] | NA [67,68,72,77,81], *** [70] | 25 to 800 [66,71,77,81], NA [67,68,70,72] | 5/6 **** [67,68], 10/15/20/40 [72], 15 [77,81], *** [70] | 1450/1600 **** [67,68], 1500 [70,72], 1510 [77,81] | 30/60/90/60/90/120 [70], 90 [72], 120 [67,68], NA [77,81] | 5/6 **** [67,68], 5/25/50 [77,81], Natural cooling [72], *** [70] | 90/120/150/155/185/215 [70], 235/186/163/126 [72], NA [67,68,77,81] |
| Grinding | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Grinding Tool | Grit Size * | Hand Piece/Machine | Time (s) | Speed (rpm) | Water-Cooling |
| Diamond bur [167], Diamond stone [86,99] | Medium grit [86], NA [99,167] | Low-speed hand piece [86], Hand piece [99], NA [167] | 20 [99], N [86,167] | 20,000 [86], According to manufacturer [168], NA [99] | Y [167], NA [86,99] |
| Polishing | |||||
| Polishing system * | |||||
| Cerashain 112C (GC) [167], Silicon polishers [144], Manually goat hair brush (DT & Shop), diamond paste Dia-Glace (Yeti Dental)/Mechanically diamond suspensions (Struers) [146], | NA/diamond suspensions 3 μm [146], Medium and fine [167], NA [144] | Hand piece [144], NA/Polishing machine [146], NA [167] | 60/NA [146], 120 [167], NA [144] | According to manufacturer [144,167], NA [146] | Y [167], NA [144,146] |
| Pre-sintered: Felt wheel/Felt wheel polishing paste/Goat hair brush/Goat hair brush polishing paste (Komet, YETI dental)/Green-state finishing kit/Universal polisher (Amann Girrbach)/SiC polishing paper Buehler/Fully sintered: Polishing lab kit Post Wheel fine/Post Wheel medium, fine (Amann Girrbach) [97], Pre-sintered: manually dry SiC discs (Struers)/Fully sintered: machine wet diamond pads Code Granu, polishing plates MD-Largo, MD-Chem, diamond suspensions Dia Pro Allegro/Largo, Largo, colloidal silica suspension OP-S (Struers) [95] | SiC paper: #2000, #4000 granularity/ Polishing lab kit: fine, medium [97], P400, P500, P1000/Coarse 40, 20 μm, fine polishing plate, diamond suspensions 9, 3 μm, high polishing plate, colloidal silica suspension [95] | Hand piece [97], Manually/Polishing machine [95] | Pre-sintered: 180/Fully sintered: 240/Polishing lab kit: 900 [97], 5/disc/360 360, 30 [95] | Pre-sintered: 5000/Fully sintered: 10,000 min−1 [97] NA/150, NA, 150 [95] | N/Y [95], NA [97] |
| Heat Treatment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Treatment | Start Temperature | Drying Time (s) | Heating Rate (°C/min) | Final Temperature (°C) | Holding Time (min) | Cooling Rate (°C/min) | Environment |
| Rapid cooling [88], Regenerative [86,87], Simulated glaze firing [90] | 350/350/- [90], NA [86,87,88] | 5/5/360 [90], 18 [87], NA [86,88] | 65 [87], Placed in preheated furnace [86], 55 [91], NA [88] | 820/820/1000 [90], 900/1000 [86], 1050 [87], 1550 [88] | 2/2/0 [90], 15 [87], 60/30 [86], 60 [88] | 25 [87], Air-cooled within 1–2 min [88], -/-/Tray open at 480° [90], NA [86] | Air [88], Vacuum [90], NA [86,87] |
| Glazing | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glaze System | Predrying Standby Temp. (°C) Time (min) | Heating Rate (°C/min) | Firing Temperature (°C) | Holding Time (min) | |
| Glaze spray Zenostar Magic Glaze (Ivoclar Vivadent) [94], Glaze Zirox, Stain Liquid/Glaze spray ZenoStar Magic (Wieland Dental + Technik) * [146] Vita LT Glaze [171], Vita Akzent Glaze [151], Vita Akzent Plus Glaze powder [169], Vita Akzent powder/Vita Akzent Plus Spray [92], Glaze spray Vita Akzent Plus [100], Plus Glaze Body Spray [96] (Vita Zahnfabrik) Glaze Plus [93,144], Zirkonzahn glaze paste (Zirkonzahn)/Zirlux FC glaze paste (Pentron Ceramics) [90] Ivocolor fluor [98], IPS Ivocolor Glaze Paste [87], Glaze paste IPS e.max [91] (Ivoclar Vivadent) Cercon ceram kiss glasur * [89], Cercon glaze Glasur (DeguDent) [170], Ceramill Glaze (Amann Girrbach) [168], NA [99] | 350/NA [90], 403 [87], 500 [92,100,171], 575 [146], NA [89,91,93,94,96,98,99,144,151,168,169,170] | 2 [171], 4 [92,100], 5/2 [146], 5/6 [90], 6 [87], NA [89,91,93,94,96,98,99,144,151,168,169,170] | 45 [87,146], 50 [171], 55/55 [90], 80 [92,100], NA [89,91,93,94,96,98,99,144,151,168,169,170] | 500, 830 [91], 710 [87], 780–800 [144], 800 [169], 820/1000 [90], 880 [94,146], 900 [168,170], 900/950 [92], 950 [100], 960 [171], NA [89,93,96,98,99,151] | 1 [87,92,100,144,146,169], 2/0 [90], 3, 2 [91], NA [89,93,94,96,98,99,151,168,170,171] |
| Chairside CAM Procedure | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Milling Unit | Milling/Grinding: Tools | ||
| 3 + 1 axis, CEREC MCXL [33,101] | Milling: NA [33], Milling: carbide burs Shaper 25/RZ, Finisher 10. Grinding: diamond-coated burs, Step bur 20, Cylinder pointed bur 20) [101] | ||
| Chairside sintering | |||
| Sintering parameter * | Final sintering temperature (°C) | Holding time (min) | Total time (min) |
| Conventional/Speed-fire/Super-speed [101], High-speed [33] | 1510/1580/1580 [101], 1560 [33] | 120/2/10 [101], 19 ** [33] | 480/13.34/10 [101], 19 ** [33] |
| Clinical Grinding | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Grinding Tool | Grit Size | Hand Piece/Machine | Time (s) | Speed (rpm) | Water-Cooling |
| Diamond bur [87,92,93,98,99,100,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,110,112,157,158,159,161,168,172] | 25/181 [106], 27–76 [157], 30 [107], 46/30/181 [105], 90–120 [93,98], 96 [108], 181 [87,92,100,103,104,110], 220 µm [112,158], Medium grit [102,161], Coarse grit [159,172], NA [100,168] | High-speed hand piece [93,99,108,112,158,159,161,172], Low-speed hand piece [92,102,168], Contra-angle hand piece [87,92,100,103,104,105,106,107,110], High-speed [98], NA [157] | 10 [112,157,158,172], 10 × 2 [159], 20 [98,99], 30 [168], NA [87,92,93,100,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,110,161] | 8000–10,000 [102], 20,000 [93,108], 159,000 [112,157,158], 169,000 [87,92,100,103,104,105,106,110], 200,000 [172], 300,000 [168], 80% of max rpm recommended by manufacturer [159], NA [98,99,107,161] | Y [87,92,93,98,99,100,103,104,105,106,107,108,110,112,157,158,159,168,172], NA [102,161] |
| Diamond stone [109,156,172], Diamond tool of silicon carbide [156] | Medium grit [109], NA [156,172] | Low-speed hand piece [109,156,172] | 20 [156,172], NA [109] | 12,500 [172], 10,000–20,000 [156], 20,000 [109] | Y [172], Y/N [109], NA [156] |
| Abrasive papers [91], Diamond-impregnated lapidary wheel [170], Resin-bonded diamond disk [96], NA [94,177] | 120 grit [96], 320/2000 grit [91], 100 µm [170], NA [94,177] | Grinding/polishing machine [91,96,170,177], Hand piece [94] | 20 [96], 30 [94], 60 [170], 60 × 4 [91], NA [177] | 200 [91], 500 [96], NA [94,170,177] | Y [91,170], NA [94,96,177] |
| Clinical Polishing | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polishing System * | No. of Steps | Grit Size * | Hand Piece/Machine | Time (s) | Speed (rpm) | Water-Cooling |
| Luster for zirconia intra-oral adjustment kit [159], Luster for zirconia adjusting and polishing kit [156,160,161], Luster intraoral twist kit [173] (Hager & Meisinger) | 3 [159,160,161], NA [156,173] | Pregrinding, smoothing prepolishing, high gloss polishing [156,159,160,161], NA [173] | Low-speed hand piece [156,159], High-speed hand piece [161], NA [160,173] | 20/step [156], 20 × 2 [161], 30 × 2/step [159], 30 [173], 60/120 [160,161] | Step 1: 8000–12,000, 2–3: 7000–12,000 [159,160], 8500–20,000 [156], 10,000 [173], NA [161] | Y [159], NA [156,160,161,173] |
| Eve Diacera [100,105,159,160], Diacera Twist [168], Eve Diapol [159], Eve kit [112,158,168] (Eve Ernst Vetter) | 2 [100,105,160,168], 3 [112,158,159] | Fine, extra-fine [100], Medium, fine grit [105], Smoothing prepolishing, high gloss polishing [160,168], Pregrinding, smoothing prepolishing, high gloss polishing [159], NA [112,158] | Low-speed hand piece [112,158,159,160,168], Contra-angle hand piece [100,105] | 10/step [112,158], 25 [100,105], 30 × 2/step [159], 60/120 [160], 90 [168] | 7000 [168], 7000–12,000 [100,159,160], 17,000 [105], step 1: 7000, 2–3: 10,000 [112,158] | Y [100,105,112,158,159,168], NA [160] |
| CeraGloss [112,158], Cerapro CeraGloss/Cerapro StarGloss [160] Edenta Magic KIT Zir [156,172] (Edenta AG) | 3 [112,156,158,172], 4 [160] | Polisher standard, coarse, medium-coarse, super-fine grit/ Polisher standard, coarse, medium, super-fine [160], Diamond stone, silicone, fine silicone polishing bur [172], Coarse finishing, medium, fine polishing [156], NA [112,158] | Low-speed hand piece [112,156,158,160,172] | 10/step [112,158], 20/step [156,172], 60/120 [160] | Step 0,3: 10,000, 1–2: 20,000/Step 0: 10,000, 1–2: 15,000, 3: 7000 [160], Step 1: 10,000–20,000, 2: 8500–20,000 [156], 10,000 [112,158], Step 1: 12,500, 2: 20,000, 3: 10,000 [172] | Y [112,158,172], NA [156,160] |
| Dialite ZR polishing wheels [94,171], Komet ZR flash polisher [94], Komet ZR zirconia polishers [174], Keramikpolitur kit [173], (Gebr. Brasseler, Komet) | 2 [94,171,174], NA [173] | Medium, fine grit [171], Blue, light-grey polisher [174], NA [94,173] | Low-speed hand piece [171], Hand piece [94], NA [173,174] | 30/step [94,171,173], 90/step [173,174] | 5000/15,000/40,000 [171], 6000 [173], 8000 [174], According to manufacturers [94] | Wet slurry [174], N [171], NA [94,173] |
| Optrafine system (Ivoclar Vivadent) [87,105,173] | 3 [87,105,173] | 46, 30 μm, diamond paste 2–4 μm [87], Light-, dark-blue tips, nylon brush, diamond paste 2–4 μm [105], NA [173] | Contra-angle hand piece [87,105], NA [173] | 25/step [87,105], 30, diamond paste 60 [173] | 10,000 [173], 169,000 [87,105] | Y [87,105], NA [173] |
| CeraMaster [93,108,171], Brownie, Greenie, SuperGreenie [112,158], Ceramisté porcelain polishers [175], Shofu zirconia polishing kit/Ceramaster porcelain polishers/Dura White stone, Shofu zirconia polishing kit/Ceramisté porcelain polishers [174] (Shofu) | 2 [93,171], 3 [112,158], 2/2/3/3 [174], 4 [175], NA [108] | CeraMaster Coarse, CeraMaster [93,171], NA [108,112,158], Prepolisher, polisher/Coarse polisher, polisher/Stone, prepolisher, polisher/Prepolisher, yellow band polisher, white band polisher [174], Prepolishing regular, fine, ultra-fine grit, super polishing diamond paste [175] | Low-speed hand piece [112,158,171], High-speed hand piece [93,108], Hand piece [175], NA [174] | 10/step [112,158], 30/step [171], 60/step [175], 90/step/90/step/60/step/60/step [174], NA [93,108] | 5000 [112,158], 5000/15,000/40,000 [171], 10,000/10,000/Step 1: 200,000, 2–3: 10,000/10,000 [174], 20,000 [93,108], 80% of maximum rpm recommended by manufacturer [175] | Y [93,108,112,158,175], Stone: Y/Polishers: wet slurry [174], N [171] |
| Suprinity polishing set (Vita Zahnfabrik) [96], Zr polishing rubbers (Frank Dental) [102], D&Z Zirconia polishing set (D&Z)/DFS Diamond Zirconia Tools (DFS-Diamond) [160], Jota kit (Jota) [156], CeraGlaze (NTI) [157], Kg Viking (Kg Sorensen) [105], Identoflex (Kerr)/DiaShine dentist zirconia adjusting and polishing kit (VH Technologies) [168], 3 step zirconia RA (Prima Dental) [99], Premium Compact (Dhpro) [98] | 1/4 [168], 2 [96,105], 3 [98,99,102,156,157,160] | Prepolishing, high brightness [96], Fine, extra-fine grit [105], Coarse, intermediate finish, final finish [102], Grinding, polishing, glazing wheel [160], Coarse finishing, medium, fine polishing [156], NA/Diamond stone, medium prepolisher, fine polisher, horse hair brush diamond paste [168], Wear, prepolishing, high gloss [98], NA [99,105,157] | Low-speed hand piece [99,102,156,160,168], Contra-angle hand piece [105], Hand piece [96], High-speed [98], NA [157] | 15/step [96], 20/step [98,156], 25/step [105], 30 [157], 30 × 2 [99], 60/120 [160], NA [102], 180/Step 1–3: 60, 4: 30 [168] | Step 1: 7000–12,000, 2: 4000–8000 [96], Step 1: 15,000, 2: 10,000, 3: 5000 [157], 6000/Step 1: 1000, 2–3: 8000, 4: 9000 [168], 8000–10,000 [102], 8000–12,000/Step 1: 8000, 2–3: 10,000 [160], Step 1: 10,000–20,000, 2–3: 8500–20,000 [156], 12,000 [98], 170,000 [105], NA [99] | Y [99,105,157,168], NA [96,98,102,156,160] |
| Diamond bur (Intensiv)/Soflex Finishing and Polishing System Kit (3M ESPE) [112,158], Diamond grinding disc (Apex CGD), silicon carbide papers (CarbiMet), diamond suspensions MetaDi (Buehler) [111], Abrasive paper (NA), Axis High Shine (Axis Dental) [170] | 1/4 [112,158], NA [111,170] | 8 μm/NA [112,158], NA, 1200/2500 grit, 3/1 μm [111], 180, 600 grit, NA [170] | Low-speed hand piece [112,158], Polishing machine [111], Grinding/polishing machine, NA [170] | 10/step [112,158], 600, 8400–9000, 300 [111], NA [170] | 75,000/10,000 [112,158], NA [111,170] | Y [111,112,158], NA [170] |
| Hydrothermal Aging: Autoclave | ||
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | Pressure (Bars) | Duration (h) |
| 122 [134], 125 [68], 127 [98] | 1.7 [98], 2 [68,134] | 8 [68,134], 24 [98] |
| 134 | 2 | 1–3 [48], 5 [89,91,102,114,125,179,180], 8 [27] |
| 1–10 [163], 5–10 [123,135], 10 [74] | ||
| 15 [162], 5–20 [64,113], 20 [94,103,104,106,107,110,111,116,122] | ||
| 50 [115,119], 2–54 [51], 60 [73] | ||
| 5–100 [164], 10–100 [124] | ||
| 2–160 [69], 5–200 [118] | ||
| 134 | 2.1 [181], 2.2 [120], 2.3 [117], 3 [176], 3.2 [121] | 1 [121], 1–5 [176], 5 [12], 20 [120], 20–100 [181] |
| Hydrothermal aging: hydrothermal reactor | ||
| Temperature (°C) | Pressure (bars) | Duration (h) |
| 122 | 2 | 1 [129] |
| 134 | 2 [126,128] *, 2.2 [120] | 5 [128], 20 [120], 6–140 [126] |
| Hydrothermal aging: vessel in oven | ||
| Temperature (°C) | Pressure (bars) | Duration (h) |
| 120 [32] **, 134 [78] *** | 2.0265 [78], NA [32] | 10 [78], 12 [32] |
| Hydrothermal aging: thermocycling | ||
| Temperature (°C) | Dwell time (s) | N of cycles |
| 5, 55 | 10 [127], 15 [102], 20 [130], 30 [70,129,165], 60 [131] | 3500 [130], 10,000 [70,129,131], 10,000/30,000/50,000 [165], 100,000 [127] 200,000 [102] |
| 6.5, 60 | 45 [132] | 10,000 [132] |
| Hydrothermal aging: water/dry storage | ||
| Temperature (°C) | Storage environment | Duration (days) |
| 27 | Dry | 730 [110] |
| 37 | Pure water | 80 [127] |
| 80 | Water | 90 [133] |
| Mechanical Aging: Mechanical Cyclic Loading (ML) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen Design | Load (N) | Frequency (Hz) | N of Cycles | Environment, Temperature (°C) | Antagonist Material |
| Bars | Staircase method: initial 50% of maximum FS, step size 20% | 2 | 10,000 | Dry | NA [28] |
| Discs | 50/200 [138], 200 [130], 250/350 [27], Staircase method: initial 60% of mean FS, step size 5% [139] | 1.6 [130], 2 [138], 4 [27] 10 [139] | 250,000 [130], 100,000 [139], 2–1,000,000 [138], 1,000,000 [27] | Distilled water [138], Distilled water, 37 [27,130], Water [139] | 3Y-TZP [138], Stainless steel [27], NA [130,139] |
| Crowns | 70 [129], 60–200 [121], 250 [137], 50–300 [124,127] | 1 [121], 1.4 [129], 2 [137], 10 [124], 14.5 [127] | 30,000 [121], 10,000/50,000 [137], 1,000,000 [129], 2,400,000 [124,127] | Water [124], 37 [121], Pure water 37 [127], Distilled water, 37 [129,137] | Stainless steel [121,129], Steel [127,137], NA [124] |
| FDPs | 0–300 [136], 588–5104 [132] | 15 [136], NA [132] | 1,000,000 [136], 1,200,000 [132] | Deionized water [132], 37 [136] | Steel [132], Stainless steel [136] |
| Mechanical Aging: Thermocyclic-Mechanical Cyclic Loading (TCML, Chewing Simulator) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC | ML | ||||||
| Specimen Design | Temperature (°C) | Dwell Time (s) | N of Cycles | Load (N) | Frequency (Hz) | N Of Cycles | Antagonist Material |
| Bars | 5, 55 | 120 [117], NA [74] | 6000 [74], NA [117] | 10 [74], 100 [117] | 1.64 [117], NA [74] | 1,200,000 [74,117] | Steel [74], NA [117] |
| Discs | 5, 55 | 30 [141,182], NA [114] | 6000/12,000 [114], NA [141,182] | 10 [114], 110 [141,182] | 1.4 [141,182], NA [114] | 1,200,000 [141,182], 1,200,000/2,400,000 [114] | Steatite [141,182], Steel [114] |
| Crowns | 5, 55 | NA [33,83,142] | 6000 [33,83,142] | 50 [33,83,142] | 0.7 [33], 1.1 [83], NA [142] | 1,200,000 [33,83,142] | Enamel [33,83], Steatite [142] |
| FDPs | 5, 55 | 30 [133,143], NA [140] | 1032 [143], 2000 [140], 36,000 [133] | 50 [143], 98 [133], 200 [140] | 2 [133,140], NA [143] | 120,000 [143], 500,000 [140], 2,500,000 [133] | Steel [133,140], NA [143] |
| Wear | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two-Body | TC | ML | ||||||
| Specimen Design | Temperature (°C) | Dwell Time (s) | N of Cycles | Load (N) | Frequency (Hz) | N of Cycles | Environment, Temperature (°C) | Antagonist Material |
| Discs | 5, 50 [146] | 120 [146] | NA [146] | 49 [146] | 1.67 [146] | 120,000–1,200,000 [146] | Water [146] | Molar [146] |
| - | - | - | 25 [157], 49 [144,145], 50 [142] | 1.2 [142], 1.6 [145], 1.7 [144], 8 [157] | 120,000 [142,145,157], 2,400,000 [144] | Distilled water [142] 37 [144], Water [157], NA [145] | Incisors [144], HT 3Y-TZP [145], Steatite [142,157] | |
| Rectangular | 5, 55 [117,147] | NA [117,147] | NA [117,147] | 50 [117], 97 [147] | 1.6 [147], NA [117] | 120,000–1,200,000 [117], 1,200,000 [147] | Distilled water [117], NA [147] | Enamel [117], Enamel, lithium disilicate, feldspathic porcelain [147], |
| - | - | - | 15 [148], 20 [149], 30 [34] | 0.4 [149], 1 [148], 1.5 [34] | 200,000 [148], 300,000 [149], 500,000 [34] | Distilled water [34] room temperature [148], 33% glycerin lubricant [149] | Enamel [149], Composites, lithium disilicate, zirconia reinforced lithium silicate, HT 3Y-TZP, bovine enamel [148], Zirconia [34] | |
| Crowns | 5, 55 [33,83] | 30 [83], NA [33] | 6000 [33,83] | 50 [33,83] | 1.1 [83], NA [33] | 1,200,000 [33,83] | Distilled water [83], Water [33] | Enamel [33,83] |
| - | - | - | 49 [167], 50–500 [150] | 2 [150,167] | 300,000–900,000 [167], 1,000,000 [150] | Distilled water [167] 37 [150] | Enamel [167], Stainless steel [150] | |
| FDPs | 5, 55 [133] | 30 [133] | 36,000 [133] | 98 [133] | 2 [133] | 2,500,000 million [133] | Water [133] | Enamel [133] |
| - | - | - | 49 [131] | NA [131] | 1,200,000 [131] | NA [131] | Steatite [131] | |
| Three-body | ||||||||
| Rectangular | 15 [151], 20–70 [170] | 1 [170], NA [151] | 50,000 [170], 1,000,000 [151] | Food-like slurry [170], Rice grains, millet seed shells, bacteriostatic preservative, buffer solution [151] | Enamel [170], NA [151] | |||
| Clinical Wear | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N of Patients (N at Follow up) | Patient Gender m/f (%), Mean Age (Years) | Follow up Time (Months) | Restoration Type | Position | N of Restorations | Surface Treatment | Antagonist |
| 47 (45) [152] | 29.8/70.2, 54 [152] | 24 [152] | Tooth-, implant-supported crowns, implant-supported FDPs [152] | Premolars or molars [152] | 75 [152] | Glazed or unglazed [152] | Teeth or implants [152] |
| Author, Year | Name of Material (Manufacturer) | Clinical Grinding Ra (µm) Mean (±SD) | Clinical Polishing Ra (µm) Mean (±SD) | Laboratory Grinding Ra (µm) Mean (±SD) | Glazing Ra (µm) Mean (±SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jum’ah, 2020 [168] | DD cube ONE® (DentalDirekt) | 2.87 (0.62) | Identoflex 1.55 (0.37 Diacera Twist 1.95 (0.42) DiaShine 0.99 (0.15) | 0.45 (0.16) | |
| Manziuc, 2019 [169] | IPS e.max ZirCAD MT (Ivoclar Vivadent) | 0.07 * (0.8, 1.5, 2.0 mm) | |||
| Pfefferle, 2020 [97] | Ceramill Zolid HT+ (Amann Girrbach) | 1 step: Felt wheel/polishing paste 0.29/0.10 Goat hair brush/polishing paste 0.35/0.12 Green-state finishing kit 0.28 Universal polisher 0.18 SiC polishing paper 0.07 2 step: Felt wheel/polishing paste 0.07/0.07 Goat hair brush/polishing paste 0.09/0.08 Green-state finishing kit 0.12 Universal polisher 0.10 SiC polishing paper 0.05 Polishing lab kit 0.07 ** |
| Author, Year | Name of Material (Manufacturer) | Clinical Grinding Ra/Rz (µm) Mean (±SD) | Clinical Polishing Ra/Rz (µm) Mean (±SD) | Glazing Ra/Rz (µm) Mean (±SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al Hamad, 2019 [112] | Zolid Fx (Amann Girrbach) | Ra: Prepolished 0.17 (0.04) Polished 0.114 (0.02) Super-polished 0.111 (0.02) Diamond paste 0.11 (0.03) Rz: Prepolished 0.97 (0.25) Polished 0.65 (0.10) Super-polished 0.65 (0.11) Diamond paste 0.65 (0.20) | ||
| Hatanaka, 2020 [93] | Prettau Anterior (Zirkonzahn) | 5.10 (4.57, 5.83) * | Ground, polished 2.29 (1.95, 2.74) | Glazed 0.36 (0.32, 0.44) Ground, polished, glazed 0.62 (0.48, 0.77) Ground, glazed 1.21 (0.94, 1.56) * |
| Jum’ah, 2020 [168] | DD cubeX2 (DentalDirekt) | 3.57 (0.78) | Identoflex 1.54 (0.49) Diacera Twist 1.59 (0.39) DiaShine 1.46 (0.44) | 0.68 (0.16) |
| Vila-Nova, 2020 [98] | Prettau Anterior (Zirkonzahn) | 0.54 (0.15) | Ground, polished 0.05 (0.03) Polished 0.04 (0.03) | Ground, glazed 0.39 (0.30) |
| Zucuni, 2020 [100] | ZirCAD MT Multi (Ivoclar Vivadent) ** | Ra: 1.26 (0.28) Rz: 7.72 (1.52) | Ra: Ground, polished 0.70 (0.18) Rz: Ground polished 4.72 (1.15) | Ra: Ground, glazed 0.55 (0.28) Ground, polished, glazed 0.79 (0.26) Rz: Ground, glazed 3.05 (1.15) Ground, polished, glazed 5.44 (1.66) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Johansson, C.; Franco Tabares, S.; Larsson, C.; Papia, E. Laboratory, Clinical-Related Processing and Time-Related Factors’ Effect on Properties of High Translucent Zirconium Dioxide Ceramics Intended for Monolithic Restorations a Systematic Review. Ceramics 2023, 6, 734-797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics6010045
Johansson C, Franco Tabares S, Larsson C, Papia E. Laboratory, Clinical-Related Processing and Time-Related Factors’ Effect on Properties of High Translucent Zirconium Dioxide Ceramics Intended for Monolithic Restorations a Systematic Review. Ceramics. 2023; 6(1):734-797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics6010045
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohansson, Camilla, Sebastian Franco Tabares, Christel Larsson, and Evaggelia Papia. 2023. "Laboratory, Clinical-Related Processing and Time-Related Factors’ Effect on Properties of High Translucent Zirconium Dioxide Ceramics Intended for Monolithic Restorations a Systematic Review" Ceramics 6, no. 1: 734-797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics6010045
APA StyleJohansson, C., Franco Tabares, S., Larsson, C., & Papia, E. (2023). Laboratory, Clinical-Related Processing and Time-Related Factors’ Effect on Properties of High Translucent Zirconium Dioxide Ceramics Intended for Monolithic Restorations a Systematic Review. Ceramics, 6(1), 734-797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics6010045








