Abstract
Dementia prevention is a global public health priority, and lifestyle interventions, including nutrition, have gained interest for their potential to maintain cognitive health. Among nutritional interventions, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 FA), particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), have been widely studied for their potential to support cognitive health. This systematic review evaluated whether n-3 FA supplementation improves global cognition in cognitively unimpaired older adults. Nineteen randomized controlled trials (RCTs) met inclusion criteria, of which five reported significant improvements in global cognition. A random-effects meta-analysis of 11 placebo-controlled RCTs showed no significant effect (SMD = −0.02, 95% CI: −0.07 to 0.04). Heterogeneity in supplement type, dosage, duration, and outcome measures may have contributed to inconsistent findings and limited comparability. Furthermore, methodological quality of the trials was generally low. While current evidence does not demonstrate a significant effect of n-3 FA supplementation on global cognition, future research should prioritize well-powered, longer-duration RCTs that incorporate biomarker monitoring and more appropriate doses. Clarifying the role of n-3 FA in cognitive aging remains essential for informing nutrition-based dementia prevention strategies.
1. Introduction
Dementia is one of the largest public health challenges of our time, currently affecting over 55 million people worldwide, with cases projected to triple by 2050 [1]. This increase is largely driven by the global trend of population aging, particularly in high-income countries, where the proportion of individuals aged 65 and older is projected to rise from 20% in 2023 to 28% by 2050 [2]. The emotional, social, and economic burdens associated with cognitive decline are substantial, emphasizing the urgent need for scalable and effective preventive strategies.
A promising approach to significantly reduce this burden is the proactive monitoring and management of modifiable risk factors for dementia. The Lancet Commission on Dementia Prevention identified 14 modifiable risk factors, including hypertension, diabetes, and physical inactivity, that together account for approximately 45% of dementia cases globally [3]. Interventions aimed at improving cardiovascular health thus offer substantial potential for risk reduction, particularly when integrated into broader dementia prevention programs [4,5]. For instance, the Finnish Geriatric Intervention Study to Prevent Cognitive Impairment and Disability (FINGER), demonstrated that a multidomain intervention comprising diet, exercise, cognitive training, and vascular risk monitoring was more effective in improving global cognition than general health advice in at-risk older adults [6].
Building on evidence supporting lifestyle-based prevention, nutritional strategies have also gained attention for their potential role in cognitive and vascular health. Among these, omega-3 fatty acids (n-3 FA), essential polyunsaturated fats abundant in fish, nuts, and seeds, have gathered considerable attention for their potential role in preserving cognitive function and reducing the risk of cognitive decline [7]. These protective effects of n-3 FA extend to conditions that are known risk factors for cognitive decline, such as cardiovascular disease, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes [8]. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are among the most studied n-3 FA and have been proposed to improve cardiovascular and brain health. However, the randomized clinical trials (RCTs) investigating n-3 FA supplements have yielded mixed results. These inconsistencies are likely driven by the considerable variations in the supplement’s dose, source, and formulation used across the different studies [8]. Specifically, in dementia prevention, evidence addressing cognitively unimpaired older adults is limited, and the majority of RCTs do not incorporate a clinically meaningful outcome such as global cognition. Therefore, given the growing interest in the role of dietary and nutritional interventions for cognitive aging and dementia prevention, we conducted a systematic review to evaluate the effect of n-3 FA intake on global cognition in cognitively unimpaired older adults.
2. Materials and Methods
This systematic review constitutes a subgroup analysis focusing on omega-3 supplements and nutrients, derived from a broader project registered with the international prospective register of systematic reviews (PROSPERO; ID: CRD42024601975), which aims to assess single and multidomain interventions in global cognition among cognitively unimpaired older adults. Our study followed the recommendations outlined in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses [9].
2.1. Literature Search and Study Selection
The literature search was conducted in the PUBMED and EMBASE databases using terms related to randomized controlled trials, subjective cognitive decline, cognitively unimpaired subjects, and cognition and neuropsychological evaluation. The search strategy included combinations of keywords such as “subjective cognitive decline”, “memory complaints”, “cognitively unimpaired”, “older adults”, and “aging”, along with cognitive outcome terms like “cognition”, “cognitive performance”, “neuropsychological testing”, and specific cognitive scales. To identify relevant study designs, we included terms such as “randomized”, “RCT”, “clinical trial”, and “sham-controlled” and restricted the search to studies involving human participants. Initially, each abstract was screened in Rayyan [10] by two researchers independently. Subsequently, the full-text manuscripts were reviewed individually.
The inclusion criteria were the following: (i) RCTs; (ii) cognitively unimpaired older adults (>50 years old); (iii) global cognition as an outcome (e.g., Mini Mental State Examination [MMSE] or Montreal Cognitive Assessment [MoCA]); (iv) n-3 FA supplementation or intake of any nutrient containing high levels of n-3 FA. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (i) observational studies; (ii) patients with MCI or dementia, (iii) young adults (<50 years old); (iv) other outcomes (e.g., depression, biomarkers); (v) abstracts, posters; (vi) subjects with life threatening diseases or severe disability; (vii) subjects with severe/major psychiatric disorders; (viii) subjects with a diagnostic of neurological diseases associated with cognition.
2.2. Data Analysis and Risk of Bias
The following information was extracted from each study: study design, intervention, additional supplements, single/multidomain, period of intervention, sample size, age, baseline global cognition test (e.g., MMSE or MoCA). To calculate the standardized mean difference (SMD), we used the mean and standard deviation (SD) measured before and after the intervention, or the change scores between these time points. When means and SDs were not reported, we derived them from other available statistics (e.g., standard errors or confidence intervals [CI]). For RCTs that included multiple global cognition outcomes or multiple arms testing the same intervention, we averaged the effect estimates. We then performed random-effects meta-analyses restricted to studies comparing an n-3 FA supplement with a placebo, excluding studies that used alternative comparators (e.g., low-dose formulations or other supplements).
The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool version 2, which evaluated bias in five domains: (1) bias arising from the randomization process, (2) bias due to deviations from intended interventions, (3) bias due to missing outcome data, (4) bias in measurement of the outcome, and (5) bias in selection of the reported result [11]. Each domain was classified as “High risk”, “Some concerns”, or “Low risk” by two independent raters. A third researcher resolved the conflict in case of any mismatch between raters. The traffic light and summary plots were produced with the robvis package in R (Version 0.3.0, released on 22 November 2019) [12].
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Included Studies
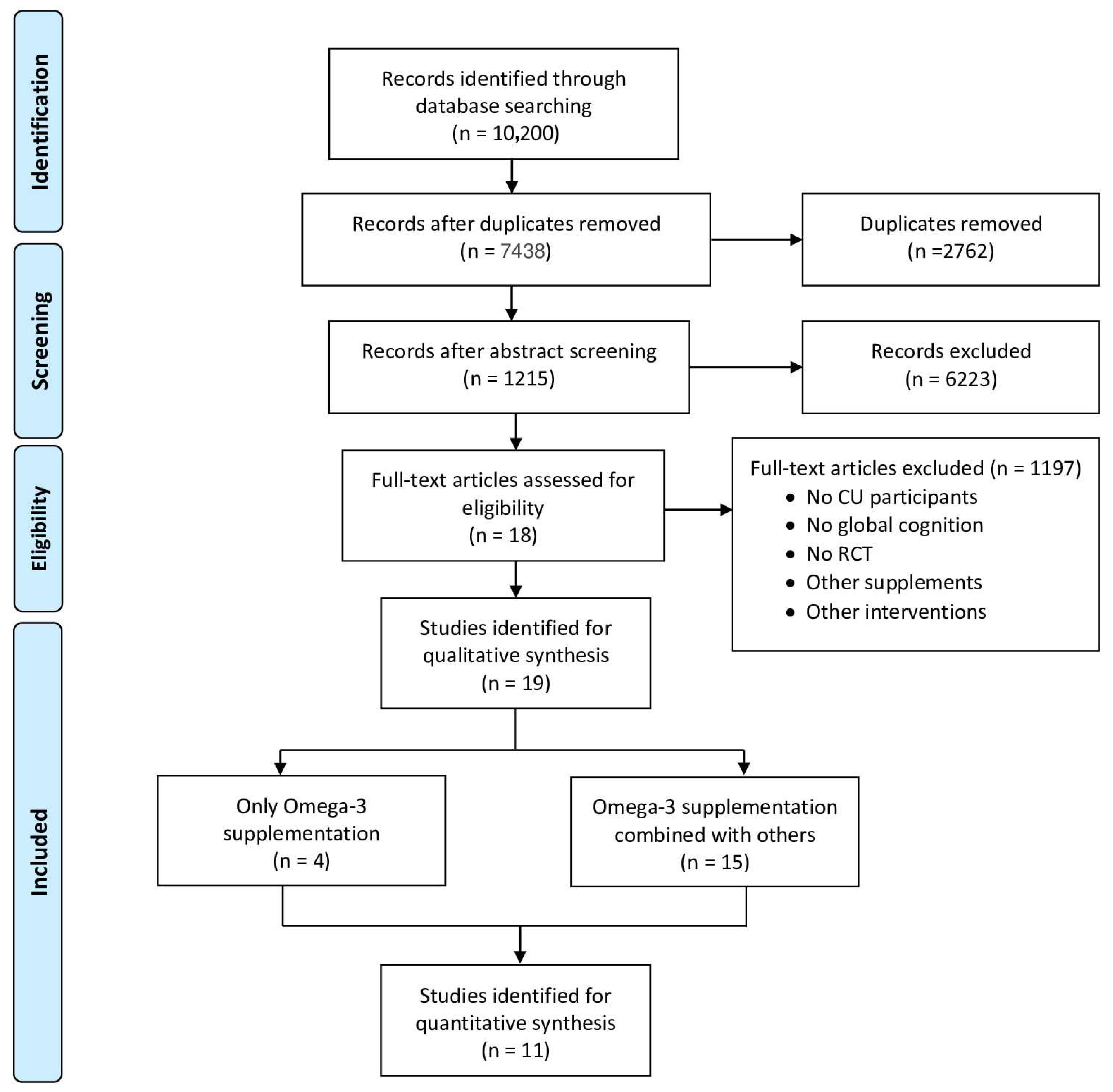
A total of nineteen studies were included, published between 2010 and 2024, with most of them testing n-3 FA in combination with other supplements/nutrients (n = 15), while just four studies examined isolated n3-FA (Figure 1). The study design of the included studies was mostly parallel with a total of sixteen studies [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]; only one had a crossover design [29], and two of them followed a factorial design [30,31]. The average age of the study populations ranged from 65.7 [18] to 78.4 years [17]. The duration of the n-3 FA intake ranged from 6 weeks [25] to 5 years [31], while the sample size varied between 10 [29] and 3024 participants [31].
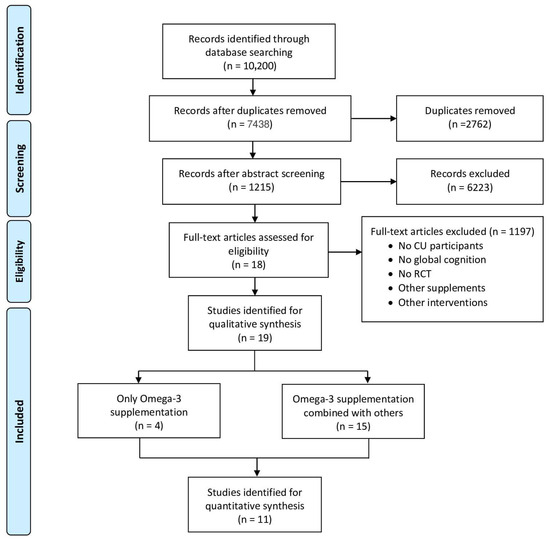
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram on the identification and selection of studies for the systematic review and meta-analysis.
The included studies comprised different n-3 FA supplements or nutrients; namely three studies used fish oil [18,21,29], one used flaxseed oil [13], two used perilla frutescens seed oil [14,19], six used capsules containing DHA and EPA [16,22,23,24,31], three used nuts [25,26,27], one used a nutritional blend containing DHA and EPA [17], one used canola oil, pilchards and fish paste [20], one used a DHA-enriched milk beverage [15,28], and one used DHA-only capsules [28].
Some studies used additional supplements either as an add-on to n-3 FA supplementation or as comparators in the control group. Specifically, participants received Cordifolia leaf powder [14], a mix of vitamins [17], curcumin [18], Ponkan powder [19], carotenoids and vitamin E [21,28], vitamin B complex [28], vitamin D3 [22], vitamin D3 combined with a training program [30], panax ginseng phospholipid complex and green tea catechin phospholipid complex [29], a multidomain intervention (i.e., cognitive training, physical activity, and nutrition) [23], ascorbyl palmitate, mixed tocopherols, and rosemary extract [24], lutein/zeaxanthin [31], strength and endurance training [25], and a Mediterranean diet [27]. Please see Table 1 for a summary of the study characteristics.

Table 1.
Table with characteristics of included studies in the qualitative synthesis.
3.2. Qualitative Synthesis of n-3 FA Supplementation in Global Cognition
Twelve studies used either the MMSE, MoCA, or both as global cognition tests [13,14,15,17,19,21,24,25,27,28,29,30] one used the Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination (ACE-III) [18], one used the Cognitive Abilities Screening Instrument (CASI) [20], and five used a global composite score [16,22,23,26,31]. Improvements in global cognition following n-3 FA supplementation were observed in five out of the nineteen studies.
In one study, both MoCA and MMSE were administered; however, only the MoCA score significantly improved in the intervention group, while no significant difference was observed in MMSE [14]. In another study, both tests were used, but the significant improvement was found only in the MMSE [15]. The remaining three studies reported significant improvements in their sole global cognition measure: CASI [20], MoCA [25], and MMSE [29]. The other 14 studies did not show statistically significant differences in global cognition after the intervention (Table 1).
The studies showing positive effects of n-3 FA supplements in global cognition had different methodological characteristics. For instance, we observed a positive effect on global cognition in the study by Kühn and colleagues, using the CASI test, in which 31 subjects received canola oil, canned pilchards, and fish paste as sources of EPA, DHA, and alpha-linolenic acid for 12 weeks, while 26 subjects received canned meatballs and texturized soya as a control group [20]. A positive effect on the MMSE was also found in the study by Carmichael and colleagues, in which, in a crossover design, 10 subjects alternately received, for 26 days, a liquid emulsion containing fish oil (a source of DHA and EPA), Panax ginseng phospholipid complex, and green tea catechin phospholipid complex, along with a placebo emulsion [29]. Another study with a positive effect on global cognition, using the MoCA, was that of Kamoun and colleagues [25], where 10 subjects consumed 15 g/day of walnuts (a source of alpha-linolenic acid) as an add-on to a training program for 6 weeks. In the study by Ichinose and colleagues [15], a significant improvement in MMSE scores was observed: participants received a DHA-enriched milk beverage containing 297 mg of DHA and 137 mg of EPA, while the control group received a placebo milk beverage. In two studies, participants received perilla seed oil as a source of alpha-linolenic acid either alone or with an add-on: in one study it was Ponkan powder and in another, Cordifolia leaf powder. Both studies showed positive effects on global cognition in the groups receiving the add-on [14,15].
3.3. Quantitative Synthesis of n-3 FA Supplementation in Global Cognition
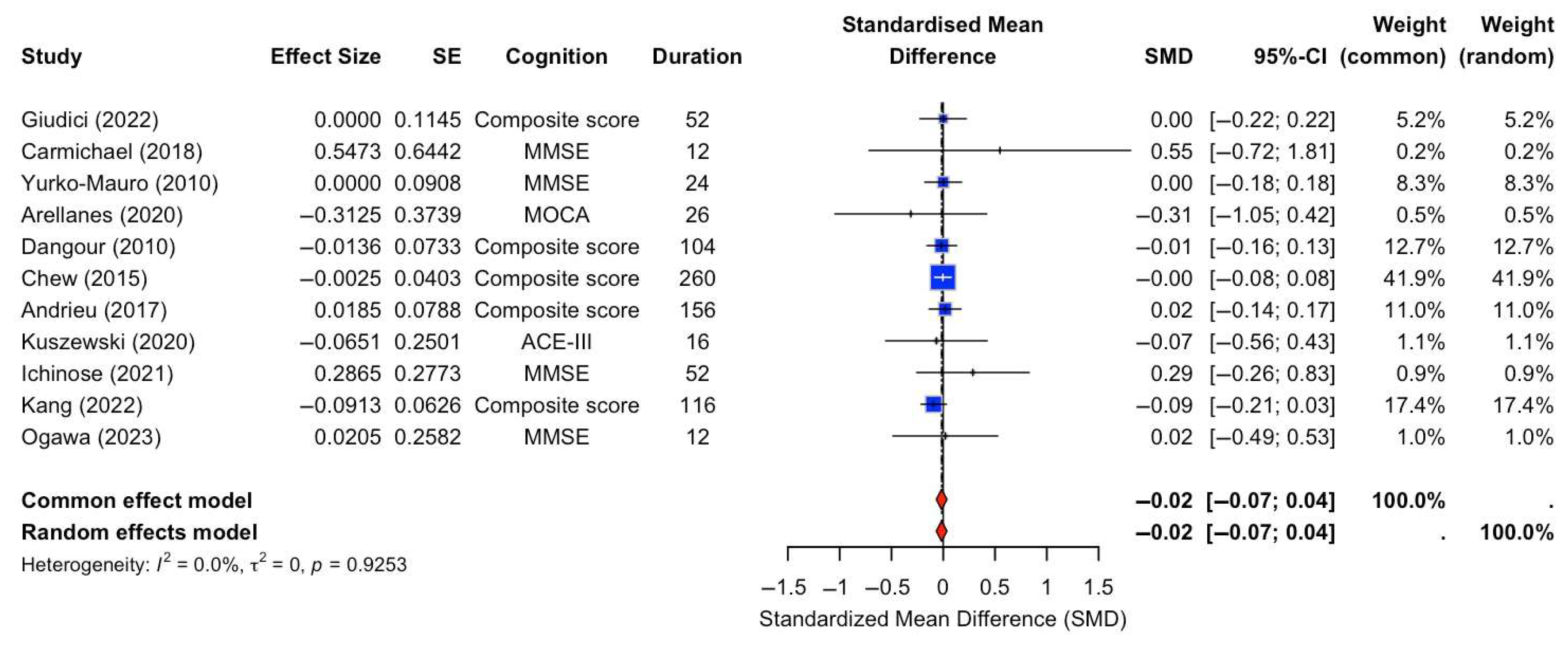
A random-effects meta-analysis was conducted to assess the effect of n-3 FA supplementation on global cognition. The analysis included 11 RCTs that specifically compared n-3 FA supplementation against placebo controls. Cognitive outcomes varied across studies and included measures such as the MMSE, composite scores, MoCA, ACE-III, and 3MS, with intervention durations ranging from 12 to 260 weeks. The pooled SMD was −0.02 with a 95% CI of [−0.07, 0.04], indicating no statistically significant effect of n-3 FA supplementation on global cognition compared to placebo (Figure 2). There was no evidence of heterogeneity across studies (I2 = 0.0%, τ2 = 0, p = 0.9253).
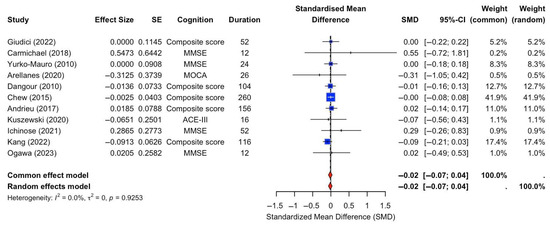
Figure 2.
Forest plot of SMDs in global cognition outcomes between n-3 FA supplements and placebo [13,15,16,17,18,22,23,24,28,29,31].
3.4. Risk of Bias
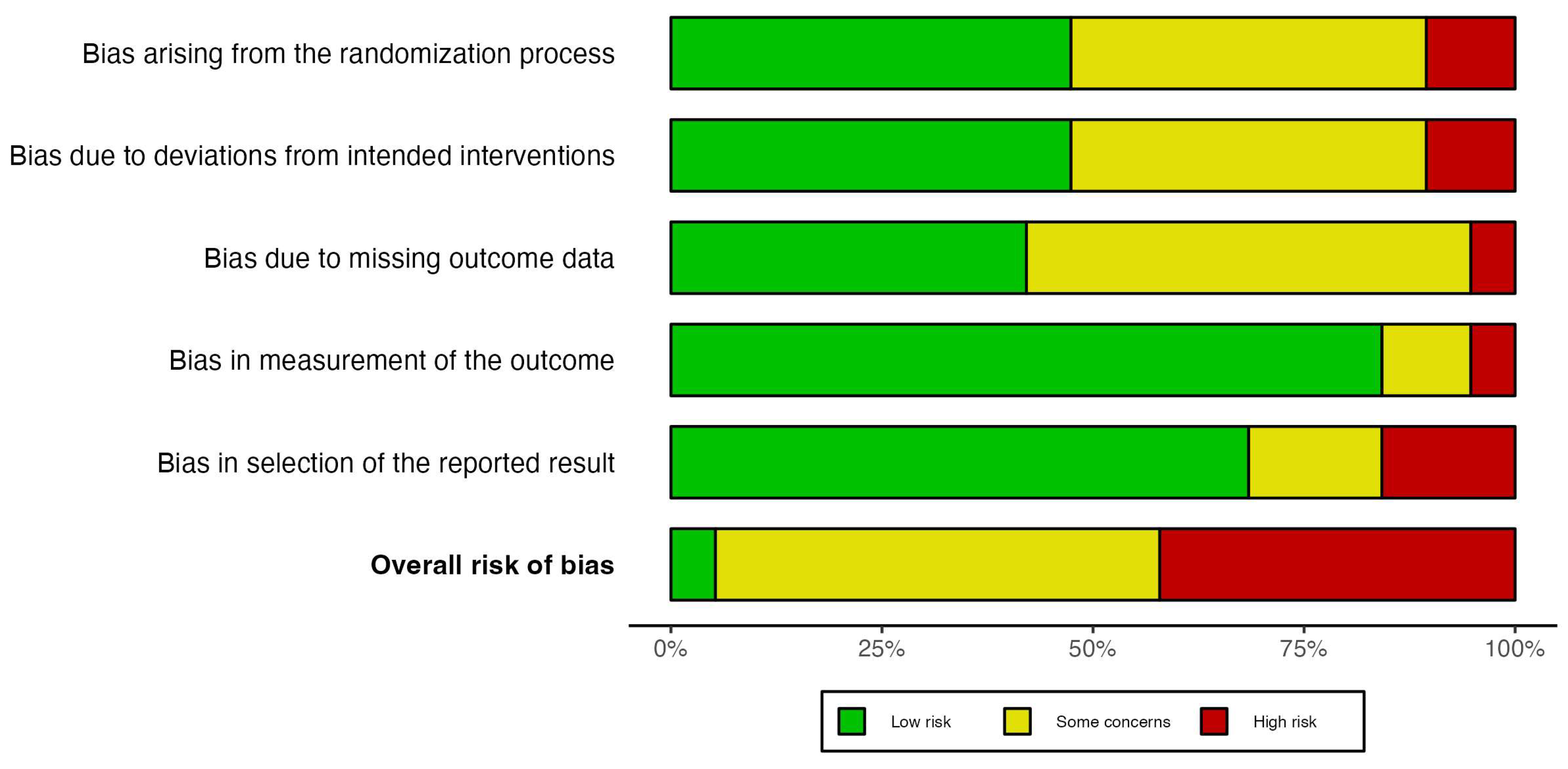
The overall risk of bias was mostly classified as “Some concerns” and “High risk” in 18 out of 19 studies, while only one study was labeled as “Low risk” following the criteria of the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool (Figure 3). In the bias arising from the randomization process, most of studies were labeled as “Low risk” (9 out of 19 studies), followed by “Some concerns” (8 out 19 studies) and “High risk” (2 out of 19 studies). The primary causes of randomization bias were insufficient information and poor allocation concealment practices. The bias due to deviations from intended intervention was classified in a similar way, namely “Low risk” (9 out of 19 studies), “Some concerns” (8 out of 19 studies), and “High risk” (2 out of 19 studies). The bias was mostly due to inappropriate analysis to estimate the effect of assignment to intervention such as the per-protocol analysis. On the other hand, most of the studies reported bias related to missing data; specifically ten studies were labeled as “Some concerns”, and one study classified as “High risk” (Figure 3). Moreover, the bias in measurement of the outcome was mostly evaluated as “Low risk” (16 out of 19 studies) because most of the studies followed a double-blind methodology. Lastly, the bias in selection of the reported result were classified as “Low risk” and as “High risk” or “Some concerns” in three studies each (Figure 3). The increased risk in this domain was mostly due to multiple analysis of the global cognition outcome.
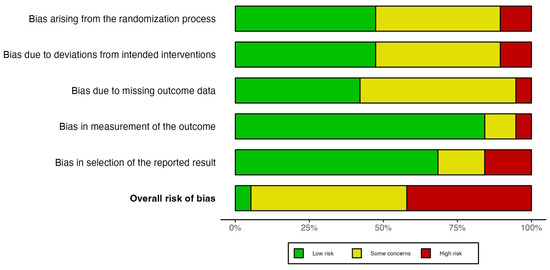
Figure 3.
Risk of bias assessment of the included randomized controlled trials using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2.0 tool.
4. Discussion
The objective of this review was to establish the impact of supplementation with n-3 FA sources on global cognition in cognitively unimpaired older adults. We identified 19 RCTs that tested n-3 FA supplementation on a global cognition outcome. While fourteen studies did not demonstrate any effect on global cognition, statistically significant improvements were observed in five out of nineteen trials. In addition, the meta-analysis of placebo-controlled trials does not support a significant benefit of n-3 FA supplementation on global cognitive function in cognitively unimpaired older adults.
We have observed substantial heterogeneity in the sources of supplementation across studies, including fish oil [18,21,29], flaxseed oil [13], perilla frutescens seed oil [14,19], canola oil, cans of pilchards, and fish paste [20], walnuts and other nuts [25,26,27], marine algae [30], DHA-enriched milk beverage [15], and capsules or nutritional blends containing DHA and EPA [16,17,22,23,24,31]. Notably, studies reporting significant improvements in global cognition have supplemented the participants in the intervention group with perilla frutescens seed oil and cordifolia leaf powder [14], a DHA-enriched milk beverage [15], canola oil, fish paste, and cans of pilchards [20], fish oil [29], and walnuts [25].
These effects might be explained by the distinct mechanisms of n-3 FA functions and their diverse effects on the human body. Specifically, the two most important types of n-3 long-chain (LC) polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in the human brain are EPA and DHA [32]. DHA is abundantly present in the mammalian brain, comprising up to 40% of the total brain fatty acids. In contrast, EPA accounts for less than 1% of the total fatty acids in the brain [33]. DHA and EPA can be obtained either directly from dietary sources, particularly fish oils (e.g., fatty fish), or synthesized enzymatically from alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), an n-3 FA found in vegetable sources, such as flax, soy, rapeseeds, and walnuts [34]. Both PUFAs are essential for proper healthy aging. Within cells, fatty acids exist either as components of membrane phospholipids or as free molecules. In both forms, PUFAs play a crucial role in shaping membrane properties, including organization, ion permeability, elasticity, and microdomain formation [33]. These structural effects also contribute to broader cellular functions. In addition to their structural role, PUFAs serve as precursors to several potent lipid mediators, which are considered beneficial in the prevention or treatment of various diseases [35]. The influence of PUFAs is particularly relevant in the context of brain health. Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain the potential neuroprotective effects of n-3 FA in dementia, including their anti-inflammatory properties, promotion of neurogenesis, and modulation of membrane fluidity [36]. In fact, the intake of n-3 fatty acids has been recently associated with slower cognitive decline, coupled with reduced progression in plasma amyloid biomarkers [37].
In our review, the studies with a significant difference in global cognition were those in which the supplementation was either a source of ALA or a source of EPA and DHA but, in these cases, combined with another supplement (except for one study which supplemented a milk beverage with only DHA [15]). Additionally, three out of the five studies that demonstrated improvements in global cognition used food sources for omega-3 fatty acid supplementation rather than formulated or isolated supplements, which may indicate that food sources result in higher plasma concentrations [38]. Another important factor is the dose of n-3 FA used in these studies. The highest dosage was found in the study where participants were supplemented with 30 to 60 g of walnuts per day [26], which translates to approximately 3 to 6 g of ALA daily. In contrast, the lowest dosage was found in the study that used a milk beverage containing 297 mg of DHA and 137 mg of EPA [15]. The doses used in all the trials are relatively low, considering that the European Food Safety Authority has established a safe upper intake limit for n-3 FA (DHA and EPA) at 5 g per day [39], implying that higher doses could potentially be used in RCTs. The studies also have different durations: two studies lasted 12 months [14,15], while the other three were shorter (i.e., 12 weeks [20], 26 days [29], and 6 weeks [25]), but in all of them the n-3 FA source was given with another supplement or with physical exercise. This suggests that the effect could be due to the other supplements, or due to a synergistic relationship between n-3 FA and other supplements/interventions.
Moreover, the heterogenous results in global cognition may also be explained by differences in individual absorption. Recent studies have shown that the presence of apolipoprotein ɛ̝4 (APOE4) influences the response to DHA intake. For instance, in the RCT conducted by Arellanes and colleagues, 33 individuals were provided with a vitamin B complex and randomized to 2152 mg of DHA per day or placebo over 6 months. Participants were then evaluated separately based on APOE4 genotype [28]. There was a trend for a greater increase in CSF DHA in APOE4 non-carriers compared to carriers, and the change in CSF EPA levels in both groups was significantly greater in APOE4 non-carriers compared to carriers. However, most studies in our review did not evaluate APOE4 status, and in those that did, no significant differences were observed. This limits the ability to assess genotype-specific effects of supplementation. Another point that should be taken into consideration for the interpretation of our results is the bioavailability of DHA and EPA. Most RCTs do not report the timing of supplements intake, which could be relevant, as the absorption of EPA and DHA depends on the presence of dietary fat to facilitate optimal digestion and enhance bioavailability [40].
Limitations
Our systematic review only considered studies that had global cognition as the outcome measure, excluding those that evaluated only specific cognitive domains that may be improved by n-3 FA supplementation. Likewise, most of the included trials used either the MMSE or MoCA as global cognition measures, which are brief screening tools and, hence, exhibit lower sensitivity and specificity compared to a global composite score derived from a comprehensive neuropsychological assessment. Regarding the potential effect of n-3 FA supplementation in biomarkers, we noted that, in most studies, the blood levels of EPA and DHA were not evaluated before and after the intervention. This omission prevents a full understanding of the appropriate dose of supplementation needed to affect cognition. In line with this, we included all sources of n-3 FA, which led to increased heterogeneity in the type of supplements analyzed in our review. Additionally, the specific effects of omega-3 supplementation are difficult to isolate, as many interventions combined n-3 FA with other components such as CL powder, multivitamins, or lifestyle modifications including physical exercise. Lastly, only one out of the nineteen studies included was rated as having overall “Low risk” of bias according to the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool version 2, indicating that the methodological rigor in the RCTs assessing n-3 FA supplementation in healthy aging was generally unsatisfactory.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, most studies included in our systematic review did not demonstrate significant effectiveness in enhancing global cognition among cognitively unimpaired older adults. However, several limitations may have influenced these findings. Future research should concentrate on interventions that combine higher doses of PUFAs with other supplements, while also monitoring baseline and post-intervention blood concentration of EPA and DHA, as well as extending the duration of these interventions to better capture potential long-term effects. Furthermore, it is crucial to improve the methodological quality of future intervention studies to ensure more robust and reliable findings. N-3 FA supplementation should continue to be investigated within the context of dementia prevention programs, supported by larger and more rigorous RCTs.
Author Contributions
A.J.M., F.R. and G.B.F. conceptualized the study. A.J.M., O.S., G.K., R.M., G.V., G.R., U.N. and S.G.-L. independently screened abstracts and full-text articles for eligibility, extracted the data from the included studies, and conducted the risk of bias assessment. A.J.M. analyzed the quantitative data and R.M. analyzed the qualitative data. A.J.M. and R.M. wrote the original draft of the manuscript. Writing—review and editing: S.M. and S.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset analyzed in this study is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
F.R. is supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (Projects No. 320030_182772 and 32003B_220269). G.B.F. has received funding through the Private Foundation of Geneva University Hospitals from: A.P.R.A.—Association Suisse pour la Recherche sur la Maladie d’Alzheimer, Genève; Fondation Segré, Genève; Ivan Pictet, Genève; Race Against Dementia Foundation, London, UK; Fondation Child Care, Genève; Fondation Edmond J. Safra, Genève; Fondation Minkoff, Genève; Fondazione Agusta, Lugano; McCall Macbain Foundation, Canada; Nicole et René Keller, Genève; Fondation AETAS, Genève. G.B.F. has received funding through the University of Geneva or Geneva University Hospitals: for IISSs from ROCHE Pharmaceuticals OM Pharma EISAI Pharmaceuticals Biogen Pharmaceuticals and Novo Nordisk; for competitive research projects from: H2020, Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI), IMI2, Swiss National Science Foundation, VELUX Foundation, and Schmidheiny Foundation. G.B.F. has received consulting fees through his institution from: Biogen, Diadem, Roche, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Ac Immune, Novo Nordisk, Schwabe, Bromatech, AtonRâ, World Clinical Trials, J&J Innovative Medicine. G.B.F. has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events through his institution from: Biogen, Roche, Novo Nordisk, GE HealthCare, Vifor Pharma.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| EPA | Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| n-3 FA | Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trials |
| ALA | Alpha-linolenic acid |
| PUFA | Polyunsaturated fatty acids |
References
- Nichols, E.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Vollset, S.E.; Fukutaki, K.; Chalek, J.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdoli, A.; Abualhasan, A.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Akram, T.T.; et al. Estimation of the Global Prevalence of Dementia in 2019 and Forecasted Prevalence in 2050: An Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e105–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division. World Population Ageing 2023: Challenges and Opportunities of Population Ageing in the Least Developed Countries|DESA Publications; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Liu, K.Y.; Costafreda, S.G.; Selbæk, G.; Alladi, S.; Ames, D.; Banerjee, S.; Burns, A.; Brayne, C.; et al. Dementia Prevention, Intervention, and Care: 2024 Report of the Lancet Standing Commission. Lancet 2024, 404, 572–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisoni, G.B.; Altomare, D.; Ribaldi, F.; Villain, N.; Brayne, C.; Mukadam, N.; Abramowicz, M.; Barkhof, F.; Berthier, M.; Bieler-Aeschlimann, M.; et al. Dementia Prevention in Memory Clinics: Recommendations from the European Task Force for Brain Health Services. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2023, 26, 100576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisoni, G.B.; Ribaldi, F.; Allali, G.; Bieth, T.; Brioschi Guevara, A.; Cappa, S.; Cipolotti, L.; Frederiksen, K.S.; Georges, J.; Jessen, F.; et al. Brain Health Services for the Secondary Prevention of Cognitive Impairment and Dementia: Opportunities, Challenges, and the Business Case for Existing and Future Facilities. J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 2025, 12, 100098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngandu, T.; Lehtisalo, J.; Solomon, A.; Levälahti, E.; Ahtiluoto, S.; Antikainen, R.; Bäckman, L.; Hänninen, T.; Jula, A.; Laatikainen, T.; et al. A 2 Year Multidomain Intervention of Diet, Exercise, Cognitive Training, and Vascular Risk Monitoring versus Control to Prevent Cognitive Decline in at-Risk Elderly People (FINGER): A Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 2255–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriambelo, B.; Stiffel, M.; Roke, K.; Plourde, M. New Perspectives on Randomized Controlled Trials with Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplements and Cognition: A Scoping Review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 85, 101835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Hussain, M.; Jiang, B.; Zheng, L.; Pan, Y.; Hu, J.; Khan, A.; Ashraf, A.; Zou, X. Omega-3 Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Metabolism and Health Implications. Prog. Lipid Res. 2023, 92, 101255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan-a Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, L.A.; Higgins, J.P.T. Risk-of-Bias VISualization (Robvis): An R Package and Shiny Web App for Visualizing Risk-of-Bias Assessments. Res. Synth. Methods 2021, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Sawane, K.; Ookoshi, K.; Kawashima, R. Supplementation with Flaxseed Oil Rich in Alpha-Linolenic Acid Improves Verbal Fluency in Healthy Older Adults. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, M.; Matsuzaki, K.; Maruyama, K.; Sumiyoshi, E.; Hossain, S.; Wakatsuki, H.; Kato, S.; Ohno, M.; Tanabe, Y.; Kuroda, Y.; et al. Perilla Frutescens Seed Oil Combined with Anredera Cordifolia Leaf Powder Attenuates Age-Related Cognitive Decline by Reducing Serum Triglyceride and Glucose Levels in Healthy Elderly Japanese Individuals: A Possible Supplement for Brain Health. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 7226–7239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichinose, T.; Matsuzaki, K.; Kato, M.; Tanabe, Y.; Tachibana, N.; Morikawa, M.; Kato, S.; Ohata, S.; Ohno, M.; Wakatsuki, H.; et al. Intake of Docosahexaenoic Acid-Enriched Milk Beverage Prevents Age-Related Cognitive Decline and Decreases Serum Bone Resorption Marker Levels. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 1829–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangour, A.D.; Allen, E.; Elbourne, D.; Fasey, N.; Fletcher, A.E.; Hardy, P.; Holder, G.E.; Knight, R.; Letley, L.; Richards, M.; et al. Effect of 2-y n-3 Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation on Cognitive Function in Older People: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1725–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudici, K.V.; Guyonnet, S.; Cantet, C.; de Souto Barreto, P.; Weiner, M.W.; Tosun, D.; Boschat, C.; Hudry, J.; Andrieu, S.; Vellas, B.; et al. A 1-Year Randomized Controlled Trial of a Nutritional Blend to Improve Nutritional Biomarkers and Prevent Cognitive Decline among Community-Dwelling Older Adults: The Nolan Study. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2022, 8, e12314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuszewski, J.C.; Howe, P.R.C.; Wong, R.H.X. Evaluation of Cognitive Performance Following Fish-Oil and Curcumin Supplementation in Middle-Aged and Older Adults with Overweight or Obesity. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 3190–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Matsuzaki, K.; Maruyama, K.; Hossain, S.; Sumiyoshi, E.; Wakatsuki, H.; Kato, S.; Ohno, M.; Tanabe, Y.; Kuroda, Y.; et al. Perilla Seed Oil in Combination with Nobiletin-Rich Ponkan Powder Enhances Cognitive Function in Healthy Elderly Japanese Individuals: A Possible Supplement for Brain Health in the Elderly. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2768–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, L.; MacIntyre, U.E.; Kotzé, C.; Becker, P.J.; Wenhold, F.A.M. Twelve Weeks of Additional Fish Intake Improves the Cognition of Cognitively Intact, Resource-Limited Elderly People: A Randomized Control Trial. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2022, 26, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, R.; Nolan, J.M.; Prado-Cabrero, A.; Roche, W.; Coen, R.; Power, T.; Mulcahy, R. Omega-3 Fatty Acid, Carotenoid and Vitamin E Supplementation Improves Working Memory in Older Adults: A Randomised Clinical Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Vyas, C.M.; Okereke, O.I.; Ogata, S.; Albert, M.; Lee, I.M.; D’Agostino, D.; Buring, J.E.; Cook, N.R.; Grodstein, F.; et al. Marine N-3 Fatty Acids and Cognitive Change among Older Adults in the VITAL Randomized Trial. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2022, 8, e12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrieu, S.; Guyonnet, S.; Coley, N.; Cantet, C.; Bonnefoy, M.; Bordes, S.; Bories, L.; Cufi, M.N.; Dantoine, T.; Dartigues, J.F.; et al. Effect of Long-Term Omega 3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation with or without Multidomain Intervention on Cognitive Function in Elderly Adults with Memory Complaints (MAPT): A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurko-Mauro, K.; McCarthy, D.; Rom, D.; Nelson, E.B.; Ryan, A.S.; Blackwell, A.; Salem, N.; Stedman, M. Beneficial Effects of Docosahexaenoic Acid on Cognition in Age-Related Cognitive Decline. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2010, 6, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamoun, A.; Yahia, A.; Farjallah, M.A.; Maaloul, R.; Marzougui, H.; Bouaziz, M.; Souissi, N.; Elleuch, M.H.; Hammouda, O. Concurrent Training Associated with Moderate Walnut Consumption Improved Isokinetic Strength, Subjective Sleep Quality, Cognitive Performance and Postural Balance in Elderly Active Men: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2024, 36, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala-Vila, A.; Valls-Pedret, C.; Rajaram, S.; Coll-Padros, N.; Cofan, M.; Serra-Mir, M.; Perez-Heras, A.M.; Roth, I.; Freitas-Simoes, T.M.; Domenech, M.; et al. Effect of a 2-Year Diet Intervention with Walnuts on Cognitive Decline. The Walnuts and Healthy Aging (WAHA) Study: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Biochem. 2020, 167, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valls-Pedret, C.; Sala-Vila, A.; Serra-Mir, M.; Corella, D.; De La Torre, R.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Martínez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Fitó, M.; Pérez-Heras, A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; et al. Mediterranean Diet and Age-Related Cognitive Decline: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellanes, I.C.; Choe, N.; Solomon, V.; He, X.; Kavin, B.; Martinez, A.E.; Kono, N.; Buennagel, D.P.; Hazra, N.; Kim, G.; et al. Brain Delivery of Supplemental Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA): A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, O.T.; Pillai, S.; Shankapal, P.; McLellan, A.; Kay, D.G.; Gold, B.T.; Keller, J.N. A Combination of Essential Fatty Acids, Panax Ginseng Extract, and Green Tea Catechins Modifies Brain FMRI Signals in Healthy Older Adults. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Vellas, B.; Rizzoli, R.; Kressig, R.W.; Da Silva, J.A.P.; Blauth, M.; Felson, D.T.; McCloskey, E.V.; Watzl, B.; Hofbauer, L.C.; et al. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation, Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation, or a Strength-Training Exercise Program on Clinical Outcomes in Older Adults: The DO-HEALTH Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 1855–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, E.Y.; Clemons, T.E.; Agrón, E.; Launer, L.J.; Grodstein, F.; Bernstein, P.S. Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Lutein/Zeaxanthin, or Other Nutrient Supplementation on Cognitive Function: The AREDS2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2015, 314, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, D.J.; van Montfort, S.J.T.; Oranje, B.; Durston, S.; Smeets, P.A.M. Effects of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Human Brain Morphology and Function: What Is the Evidence? Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 26, 546–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorjão, R.; Azevedo-Martins, A.K.; Rodrigues, H.G.; Abdulkader, F.; Arcisio-Miranda, M.; Procopio, J.; Curi, R. Comparative Effects of DHA and EPA on Cell Function. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 122, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchtman, D.W.; Song, C. Cognitive Enhancement by Omega-3 Fatty Acids from Child-Hood to Old Age: Findings from Animal and Clinical Studies. Neuropharmacology 2013, 64, 550–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, D.; Block, R.; Mousa, S.A. Omega-3 Fatty Acids EPA and DHA: Health Benefits Throughout Life. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, G.M.; Ma, Q.L.; Frautschy, S.A. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Dementia. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2009, 81, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoost, S.S.; Honig, L.S.; Kang, M.S.; Bahl, A.; Lee, A.J.; Sanchez, D.; Reyes-Dumeyer, D.; Lantigua, R.A.; Dage, J.L.; Brickman, A.M.; et al. Association of Dietary Fatty Acids with Longitudinal Change in Plasma-Based Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 2025, 12, 100117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visioli, F.; Risé, P.; Barassi, M.C.; Marangoni, F.; Galli, C. Dietary Intake of Fish vs. Formulations Leads to Higher Plasma Concentrations of n-3 Fatty Acids. Lipids 2003, 38, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostoni, C.; Bresson, J.-L.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Flynn, A.; Golly, I.; Korhonen, H.; Lagiou, P.; Løvik, M.; Marchelli, R.; Martin, A.; et al. Scientific Opinion on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA), Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) and Docosapentaenoic Acid (DPA). EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Schacky, C. Importance of EPA and DHA Blood Levels in Brain Structure and Function. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Swiss Federation of Clinical Neuro-Societies. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).